Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 8/2014
- Pages: 1272-1278
- First Published: 24 July 2014
Editorial
Highlights
Research Articles
In Situ Growth Measurements of Sodium Sulfate during Cooling Crystallization
- Pages: 1283-1290
- First Published: 09 July 2014
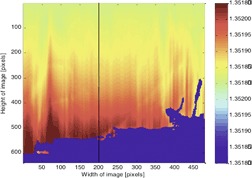
Cooling crystallization provides a potential treatment solution for salt recovery from hypersaline brine streams. Combined rainbow Schlieren deflectometry and liquid crystal thermography allowed the decoupling of concentration and temperature effects and were applied as in situ, non-intrusive techniques during crystallization of sodium sulfate from aqueous solution.
Designing Printable Medicinal Products: Solvent System and Carrier-Substrate Screening
- Pages: 1291-1296
- First Published: 09 July 2014
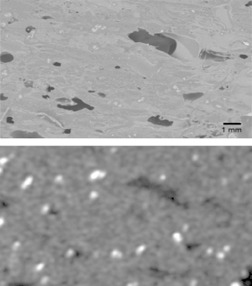
More flexible yet robust manufacturing solutions are needed in the pharmaceutical industry. Novel engineering solutions for continuous manufacturing of flexible pharmaceutical products are discussed. Critical factors affecting the printing process and quality of the printable medicinal products are studied with piroxicam as model compound. Future directions highlighting the potential are evaluated.
Crystallization of Piroxicam Solid Forms and the Effects of Additives
- Pages: 1297-1304
- First Published: 09 July 2014
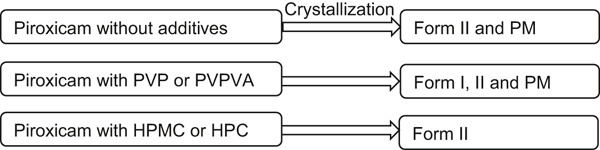
Solid form selection can help improve the solubility and dissolution rate of poorly water-soluble drug candidates. The relative stabilities of the anhydrous and monohydrate solid forms of piroxicam in ethanol/water mixtures were studied. The validity of the Hansen solubility parameter in the preliminary screening of additives for controlling the piroxicam solid form during crystallization is demonstrated.
Raman, UV, NIR, and Mid-IR Spectroscopy with Focused Beam Reflectance Measurement in Monitoring Polymorphic Transformations
- Pages: 1305-1313
- First Published: 24 July 2014
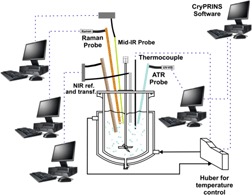
The most common techniques for in situ monitoring of polymorphic transformation are compared and evaluated. The proposed integrated approach which combines signals from two process analytical technology tools to include solid concentration in the calibration model of polymorphic composition can provide accurate calibration faster and with less material required.
Effect of Operating Conditions on Ice Characteristics in Continuous Eutectic Freeze Crystallization
- Pages: 1314-1320
- First Published: 09 July 2014

The effectiveness of eutectic freeze crystallization (EFC) is directly dependent on size and morphology of the crystalline products. Supersaturation and residence time influence these product characteristics and were investigated in a continuous EFC process. Crystal size distribution and morphology during the crystallization process were evaluated by digital image processing.
Scaling of Calcium Carbonate on the Exterior of Heated Surfaces in a Flow-Through Setup
- Pages: 1321-1328
- First Published: 09 July 2014
Scaling is a complicated interplay where heat and mass transfer influence the crystallization process. Morphology and polymorphism of the scale structure was related to the scaling parameters supersaturation and temperature. Scale growth rates of aragonite were determined and the growth-front temperature estimated, relating the growth front kinetics to observed growth behavior.
Mathematical Modeling of Chiral Symmetry Breaking due to Differences in Crystal Growth Kinetics
- Pages: 1329-1339
- First Published: 09 July 2014
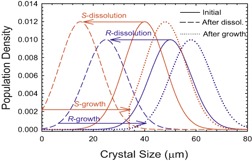
Deracemization using temperature cycles with fast racemization in the liquid phase of a suspension is a new process to convert a racemic suspension into an enantiopure suspension. The current work proposes and checks two models relating to growth and dissolution of the suspension, to confirm that these processes may be responsible for the deracemization.
Determination of Pitzer Parameters for 1-1 Nitrate and 1-2 Sulfate Solutions from Freezing Point Data
- Pages: 1340-1346
- First Published: 24 July 2014
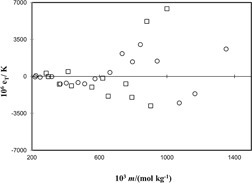
Thermodynamics models help in designing separation and purification processes such as eutectic freeze concentration. New values of Pitzer interaction parameters at 273.15 K derived from freezing point data are presented for nitrate and sulfate solutions. For some of the studied salt solutions, these parameters appear to interpret freezing point data more accurately than the thermodynamic models given in the literature.
Mechanism of Process-Induced Salt-to-Free Base Transformation of Pharmaceutical Products
- Pages: 1347-1352
- First Published: 24 July 2014
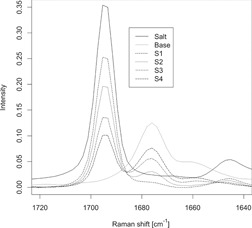
The application of Raman spectroscopy to monitor procaine concentration with a very large concentration span was proven to be possible. In experiments with additives in wet massing, only MgO influenced the drug stability. Simply determining pHmax is not sufficient in order to determine the excipients that may be used without adverse effects in drug manufacturing.
Purification of Lysozyme from Protein Mixtures by Solvent-Freeze-Out Technology
- Pages: 1353-1357
- First Published: 30 June 2014
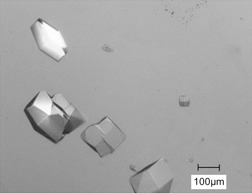
The new solvent-freeze-out (SFO) technology is an innovative, effective, and very promising method in protein crystallization. Purification of hen egg white lysozyme from a lysozyme/crude extract mixture was carried out by the SFO technology on laboratory scale. Tetragonal lysozyme crystals were obtained during the process, which were then verified by X-ray powder diffraction.
Prevention of Solvent-Mediated Isomer Transfer of Carotenoids
- Pages: 1358-1362
- First Published: 03 July 2014
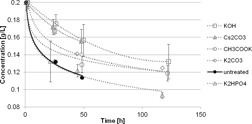
Astaxanthin is an important feed supplement. The molecule itself is susceptible to various factors and/or substances resulting in isomerization and/or degradation. The production of AXT-containing products would be more economical if a higher stability could be ensured. Consequently, stability-enhancing additives were applied.
Mass Transfer and Kinetics Study of Heterogeneous Semi-Batch Precipitation of Magnesium Carbonate
- Pages: 1363-1368
- First Published: 03 July 2014

Solid samples from reaction crystallization of Mg(OH)2 and CO2 were characterized by Raman spectroscopy. The univariate method based on the peak height ratio proved a suitable quantitative criterion for monitoring precipitation kinetics. The method reflects not only the dissolution rate of Mg(OH)2 but also the precipitation rate of MgCO3.
Optimized Coating through Phase Separation in Tablets by Melt Crystallization
- Pages: 1369-1375
- First Published: 03 July 2014
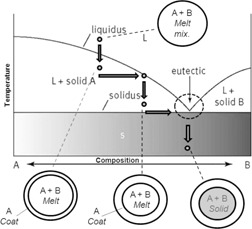
Applying melt crystallization in tableting simplifies the complex manufacturing procedure, resulting in power savings and less quality control requirements. The drop forming method is the direct laboratory-scale simulation process of the real tableting device. By cooling a molten-mixture drop, a full tablet is produced in just one thermodynamically controlled production step.
Fast Dispersible Cocoa Tablets: A Case Study of Freeze-Casting Applied to Foods
- Pages: 1376-1382
- First Published: 03 July 2014
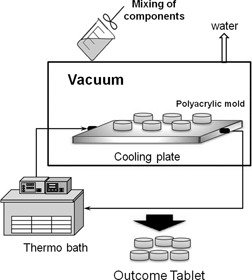
Substances in fine powder form face agglomeration phenomena when they are to be dissolved or dispersed in a liquid. A tablet fulfilling the dissolution time and mechanical strength requirements for fast-dispersal tablets is achieved by controlling the temperature gradient and the freezing modes, and especially by adding a binder.
Crystallization Kinetics within a Generic Modeling Framework
- Pages: 1383-1392
- First Published: 24 July 2014
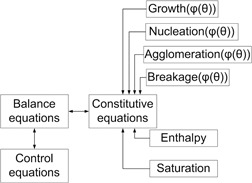
A generic modeling framework with kinetic model identification tools for crystallization modeling is presented to study crystallization kinetics of various systems. The advantages of systematically exploring the kinetics of multiple systems and employing a model library are highlighted. Morris screening is applied for model analysis and a possible reduction is discussed.
Effect of Co-Grinding on Crystallinity of Clopidogrel Bisulfate
- Pages: 1393-1398
- First Published: 24 July 2014
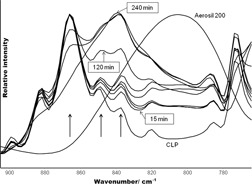
Major alterations can occur in the crystal structure of materials during co-grinding and the presence of the amorphous form may cause serious problems. Changes of crystallinity of a model powder mixture during a long-time co-grinding process were determined. Secondary H-bonds are formed between the molecules which can stabilize the molecularly disperse system in the amorphous phase.
Spherulitic Growth of Gold Particles Precipitated from Aqueous Solution
- Pages: 1399-1407
- First Published: 09 July 2014

The control of size and morphology of crystalline materials requires understanding of the underlying growth mechanism. Spontaneous and seeded experiments were performed to investigate if the formation mechanism of gold polycrystalline particles precipitated from aqueous solution at room temperature is an assembly of nanoparticles or crystal growth.
Communications
Application of In Situ Coating on a Two-Compound System
- Pages: 1408-1412
- First Published: 30 June 2014
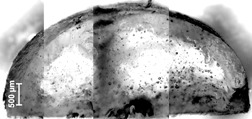
In situ coating as alternative coating technology combines shaping and coating in only one process step. The classical nucleation techniques, ultrasound and seeding, were applied separately and in combination to initiate a controlled nucleation in drop-forming of xylitol-isomalt pastilles. A separation of both compounds by crystallization in the pastilles was achieved.
Influence of Caffeine on the Crystallization Behavior of Sugar
- Pages: 1413-1416
- First Published: 03 July 2014

To create new products for the food industry it is necessary to know the effect new additives can have on the product. As caffeine can be used in beverages as well as in candies, it was chosen as additive in a sugar solution. The influence of caffeine on crystallization of sugar in terms of metastable zone, crystal growth rate, and crystal shape is examined.
Crystallization and Resolution of cis-Permethric Acid with Carbon Dioxide Antisolvent
- Pages: 1417-1421
- First Published: 09 July 2014
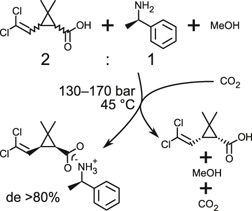
The rising demand for chiral molecules requires an economically viable and environmentally safe production. Resolution of cis-permethric acid is realized by diastereomer salt precipitation using the gas antisolvent or supercritical antisolvent process. Diastereomeric excesses in one step exceed those reported in literature. Both methods yielded diastereomeric salts with excellent diastereoselectivity.
Polyacrylic Acid-Assisted Crystallization Phenomena of Carbonate Crystals
- Pages: 1422-1426
- First Published: 09 July 2014

The application of carbonate crystals in the industry requires the precise control of their quality. The effects of polyacrylic acid (PAA) on lithium and calcium carbonate crystals were investigated during reaction crystallization in a single-jet system. PAA, in dependence on its molecular weight, strongly influences the shape, size and polymorph type of the carbonate crystals.
Effect of Specific Amino Acids on Controlling Crystal Pseudopolymorphism of L-Arginine Hydrochloride
- Pages: 1427-1430
- First Published: 24 July 2014
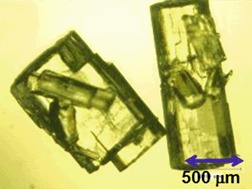
Precise control of polymorphs and pseudopolymorphs is important to obtain highly functional crystals in industry. The effect of a defined amount of amino acid additives on the pseudopolymorphism of L-arginine hydrochloride (LAHCL) is evaluated. A very small amount of specific amino acids is sufficient to stabilize the anhydrate form of LAHCL crystals at low temperature.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 8/2014
- Page: 1431
- First Published: 24 July 2014










