Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Correlation of Structure and EBIC Contrast from Threading Dislocations in AlN/Si Films (Phys. Status Solidi B 11/2019)
- First Published: 08 November 2019
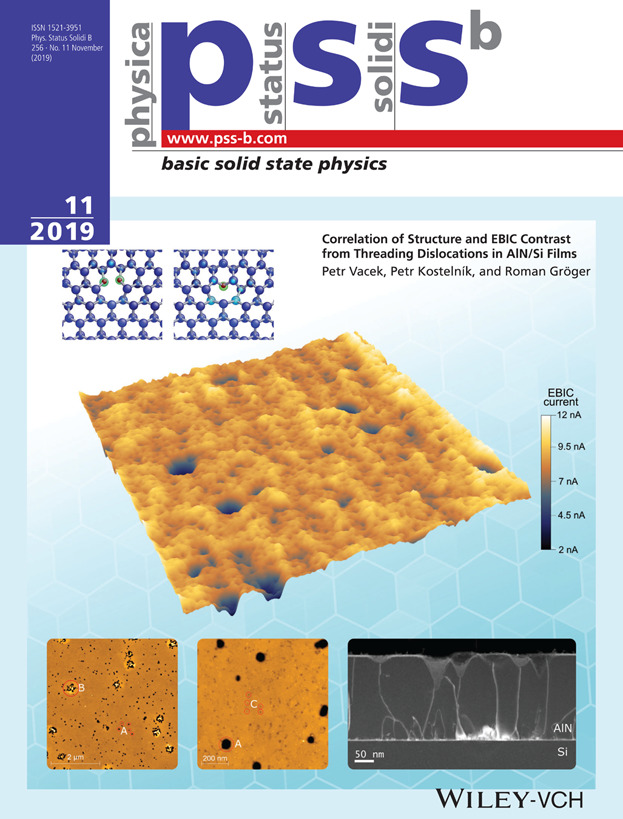
A combination of several microscopy methods, in this case electron beam induced current (EBIC), transmission electron microscopy (TEM) and atomic force microscopy (AFM), allows to correlate structural and electrical properties of AlN films as shown on the cover. AFM reveals the positions of surface terminations of threading dislocations and V-defects, and EBIC characterizes electrical activities of individual defects. The latter measurements allow to quantify the properties of AlN films and their changes around extended defects. For more information, see article no. 1900279 by Vacek et al.
Masthead
Back Cover
An Ultra-Broadband Metamaterial Absorber with High Absorption Rate Throughout the X-Band (Phys. Status Solidi B 11/2019)
- First Published: 08 November 2019
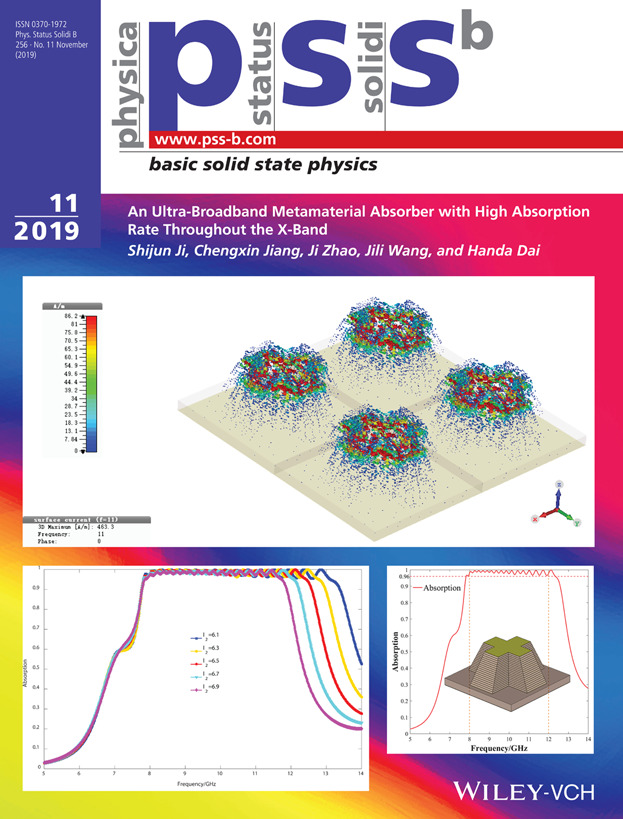
In article no. 1900069 by Shijun Ji et al., a polarizationinsensitive ultra-broadband metamaterial absorber (UMMA) is proposed. The UMMA's unit cell consists of a metal film and a multilayer-crosscone structure separated by a dielectric layer. Through a larger number of calculations, analysis and optimization from physical parameters of electromagnetic wave and structural parameters on the absorber, optimized parameters for the unit cell are obtained. The UMMA is polarization-insensitive for normal incident wave and its absorptivity is more than 96% in the entire X-band (8-12 GHz).
Original Papers
Weak Ferromagnetism
Enhanced Magnetic Component in Synthetic Goethite (α-FeOOH) and its Relation with Morphological and Structural Characteristics
- First Published: 13 June 2019
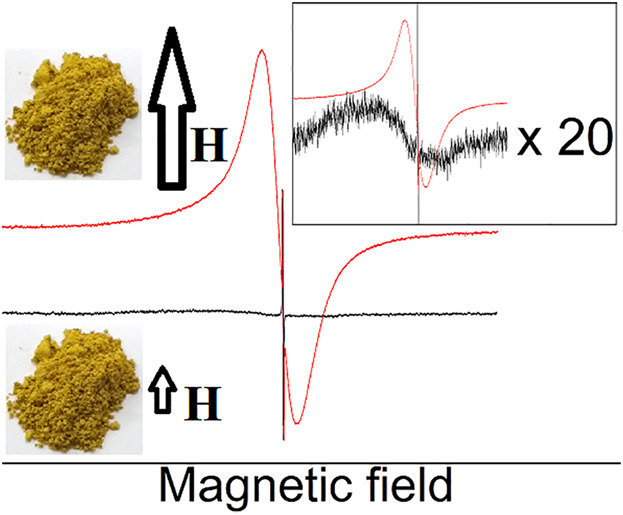
Goethite is an antiferromagnetic material but has a superimposed magnetic component, known as weak ferromagnetism. An investigation with different samples and technics is presented. It has been shown with ESR results that this component can be enhanced or suppressed when morphological and structural properties are changed by annealing or use of different synthesis route.
High-Entropy Alloys
Thermodynamic Properties of Wx(TaTiVCr)1−x High-Entropy(-Like) Alloy and Influence of Tungsten Content
- First Published: 31 May 2019
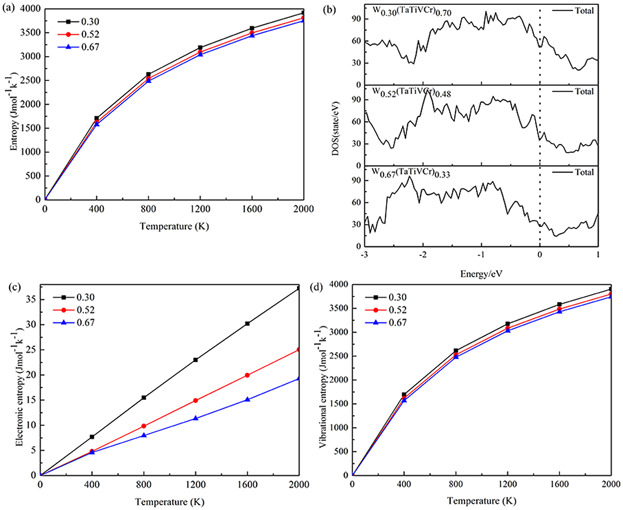
The softening of Wx(TaTiVCr)1−x is enhanced with higher temperature and lower W content. The influence of W content on both the heat capacity at constant volume (CV) and at constant pressure (Cp) is very small. Thermo-entropy of Wx(TaTiVCr)1−x rises with increasing temperature and lowering W content. The W–W bond of Wx(TaTiVCr)1−x is stronger than W–M and M–M bonds (M = Ta, Ti, V, Cr).
Double Perovskites
Influence of Cation Order and Valence States on Magnetic Ordering in La2Ni1−xMn1+xO6
- First Published: 11 June 2019
TiO2 Nanorods
Structural Properties and Wettability of TiO2 Nanorods
- First Published: 30 May 2019
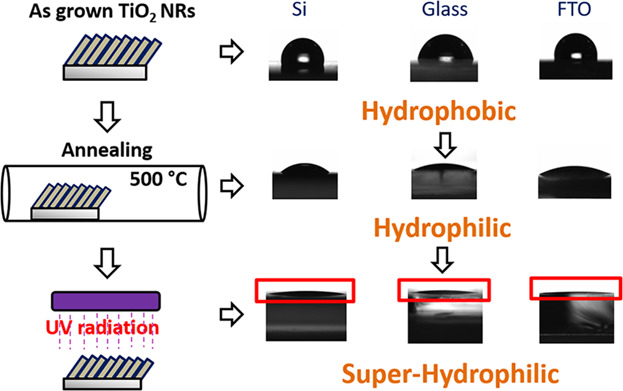
TiO2 slanted nanorods have been deposited by e-beam evaporation method utilizing glancing angle deposition technique on Si, glass, and FTO substrates. The structural evolution of nanorods is found to be controlled by the roughness of the substrates and nucleation centers present on the substrates. Annealing makes the TiO2-slanted nanorods hydrophilic and the further UV irradiation modifies them to super-hydrophilic.
2D Ferromagnetic Semiconductors
Magnetic Entropy Scaling in Ferromagnetic Semiconductor CrGeTe3
- First Published: 21 June 2019

The magnetocaloric effect and the magnetic entropy (ΔSM(T,H)) scaling around the magnetic transition temperature (TC) have been investigated in two-dimensional ferromagnetic semiconductor CrGeTe3 single crystal. The ΔSM(T,H) under different magnetic fields can be scaled into a single curve independent of external field and temperature. The critical parameters n, l, and m have been obtained based on ΔSM(T,H).
Metamaterial Absorbers
An Ultra-Broadband Metamaterial Absorber with High Absorption Rate Throughout the X-Band
- First Published: 21 June 2019
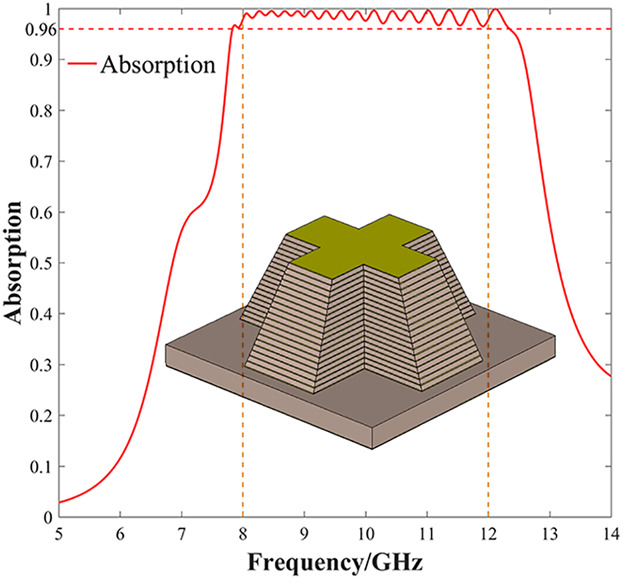
A polarization-insensitive and ultra-broadband metamaterial absorber (UMMA) is designed and demonstrated. The UMMA consists of alternately stacking Cu film and FR-4 dielectric layer. The calculation result shows that the UMMA's absorption rate is greater than 96% in the entire X-band (8–12 GHz). It can be applied in electromagnetic stealth, electromagnetic shielding and other fields.
Silicene Nanoribbons
Spin Transport in Armchair Silicene Nanoribbon on the Substrate: The Role of Charged Impurity
- First Published: 28 June 2019
Molecular Wires
Modified Superexchange Model for Electron Tunneling Across the Terminated Molecular Wire
- First Published: 23 June 2019
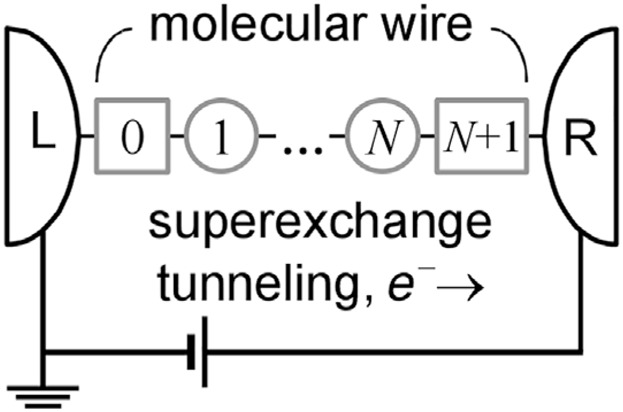
The modified superexchange model is used to obtain analytic expressions adapted to describe the nonresonance tunneling current across molecular wires, in which the current is mediated by terminal and interior repeating units of the wire. The analysis of the current–voltage characteristics of the alkane chain anchored to the electrodes by thiol groups shows a good agreement between the theory and the experiment.
Multiferroics
Predicting High Magneto-Electric Coupling in Gd Substituted BiFeO3
- First Published: 11 July 2019
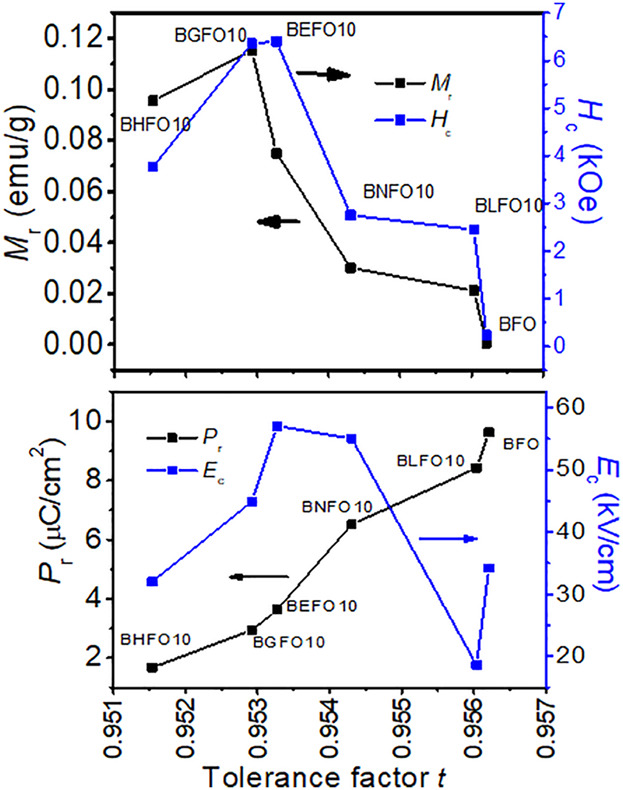
In the present manuscript, the influence of rare earth substitution on the multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 is investigated by preparing the compounds at the same level of substitution and under the similar synthesis conditions. This study is useful to estimate the potential of the substituent to tune the multiferroic properties of BiFeO3 among other rare earth elements.
Three-Level Jumping
A Simple Model for Stretched Exponential Relaxation in Three-Level Jumping Process
- First Published: 21 June 2019

The operator formalism is briefly introduced for the three-level discrete jumping processes. This formalism is generalized to the non-Markovian case to discuss relaxation and internal-friction peak. Stretched exponential relaxation, namely, Kohlrausch–Williams–Watts function and internal frictions are obtained for a three-level discrete process. Results are numerically obtained. Figures are represented.
Damage Recovery
Energetic Stability of Vacancy-Carbon Clusters in Solid Solution Alloys: The Fe-Cr-C Case
- First Published: 11 June 2019
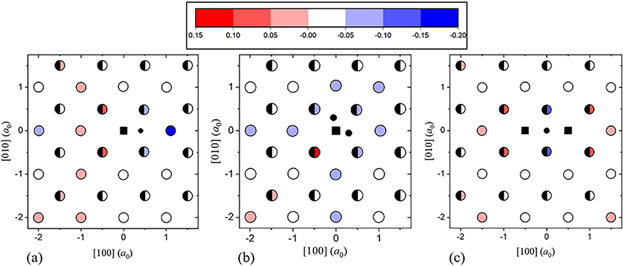
The stability of vacancy-carbon (v-C) clusters plays a key role in the post-irradiation damage recovery in steels. Therefore, the stability of v-C clusters in the presence of a solid solution background is essential. A model estimating the stability of v-C clusters in random solid solutions is presented. The model is parameterized for the Fe-Cr-C alloy using density functional theory.
Ternary Chalcogenides
First-Principles Calculations to Investigate the Refractive Index and Optical Dielectric Constant of Na3SbX4 (X = S, Se) Ternary Chalcogenides
- First Published: 04 June 2019
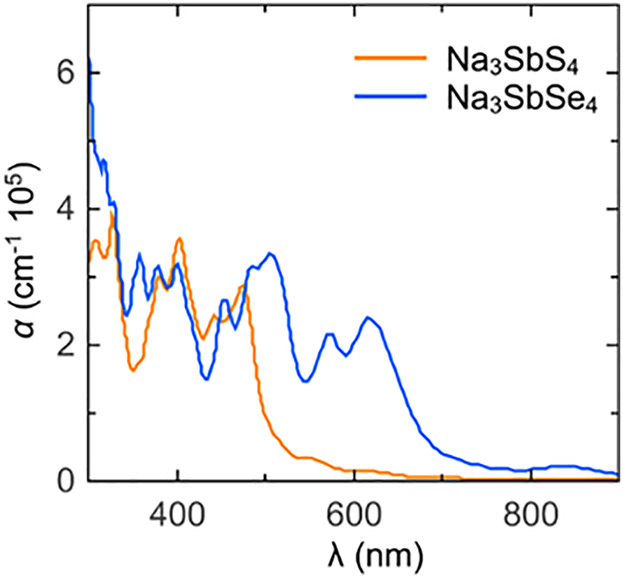
Ternary chalcogenides Na3SbX4 (X = S, Se) are investigated by first-principles calculations based on density functional theory. The electronic and optical properties are computed to assess the superionic conductors and energy storage applications for development of visible-light harvesting materials. These chalcogenides have direct bandgap. The optical absorption is investigated by calculating dielectric functions, refractive index, and optical dielectric constant.
Ternary Sulfides
Electronic Structure, Elastic and Optical Properties of AEuS2 (A = Na, K, Rb, and Cs) Ternary Sulfides: First-Principles Study
- First Published: 02 July 2019
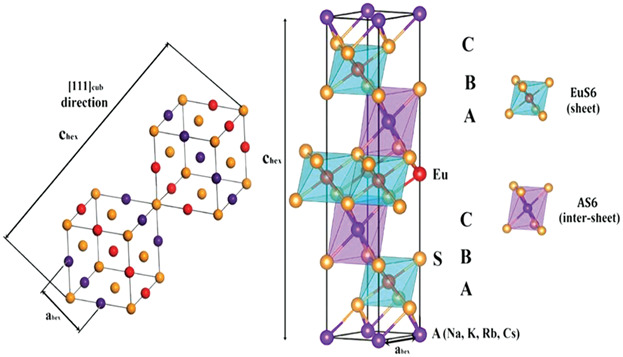
The structural parameters, elastic moduli, electronic structure, and optical properties of the ternary rhombohedral AEuS2 (A = Na, K, Rb, and Cs) are reported. The mechanical stability of the AEuS2 compounds is investigated, and the macroscopic elastic parameters are determined. It is shown that these crystals are indirect band gap semiconductors. The optical properties of the studied compounds are found to be anisotropic.
Quantum-Dot Heterostructures
Enhanced Performance of In(Ga)As QD Based Optoelectronic Devices through Improved Interface Quality between QD and Matrix Material
- First Published: 21 June 2019
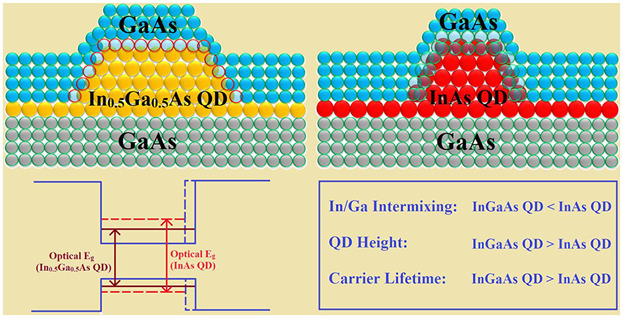
A detailed investigation regarding Stranski–Krastanov grown InAs and In0.5Ga0.5As quantum dots (QDs) is carried out. This study ascertains the cause of larger QD formation and better interface quality in case of In0.5Ga0.5As QD compared to the InAs QD. Hence, heterostructures with In0.5Ga0.5As QDs are useful for light-emitting diode and laser applications.
Magnetic Nanocomposites
Electronic Transport and Magnetic Properties of Co/SiO2 Magnetic Nanocomposites
- First Published: 18 June 2019
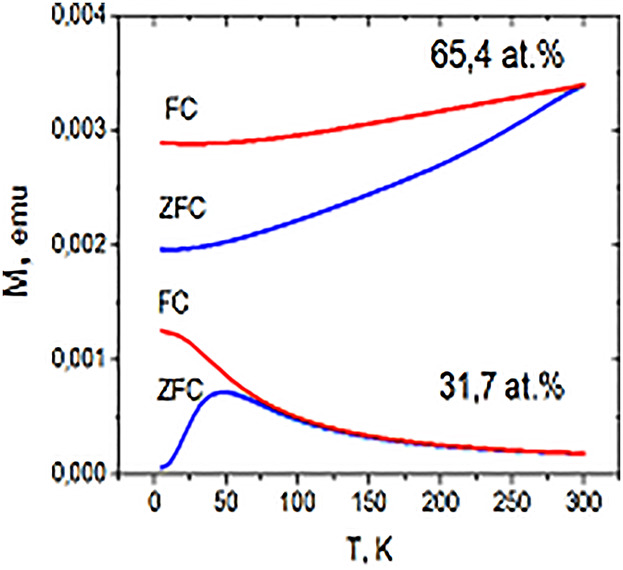
The structure and the electric, magnetic and thermoelectric properties of the magnetic nanocomposite Co/SiO2 have been studied. Negative magnetothermoelectric power has been discovered. The explanation is related to the conductivity mechanism in the magnetic nanocomposite and its structure. It is shown that structural imperfections (such as defects in the Co nanocrystals, magnetic size distribution, phase intermixing) have additional impact on the magnetic properties.
Single-Layer CrS2
First-Principles Prediction of the Structural, Electronic, and Magnetic Properties of Nonmetal Atoms Doped Single-Layer CrS2
- First Published: 02 July 2019
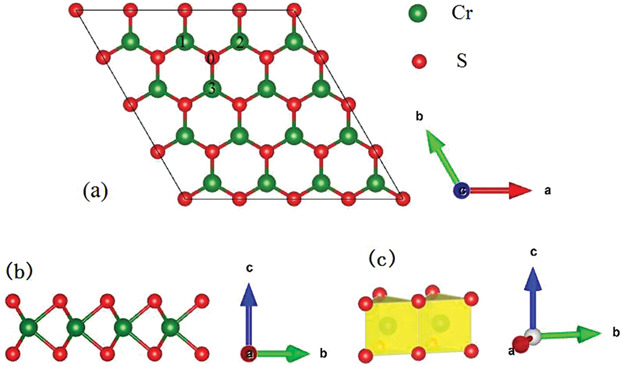
Substitutional doping of H-phase single-layer CrS2 at S-site with a nonmetal atom, such as B, C, N, P, As, O, or F, is investigated through first-principles calculations within the framework of spin-polarized density functional theory. The results reveal that the electronic and magnetic properties of single-layer CrS2 can be effectively modulated via nonmetal atoms.
Kesterite Alloys
EXAFS Study of the Local Order in Cu2ZnSn(SxSe1–x)4 Alloys
- First Published: 14 June 2019
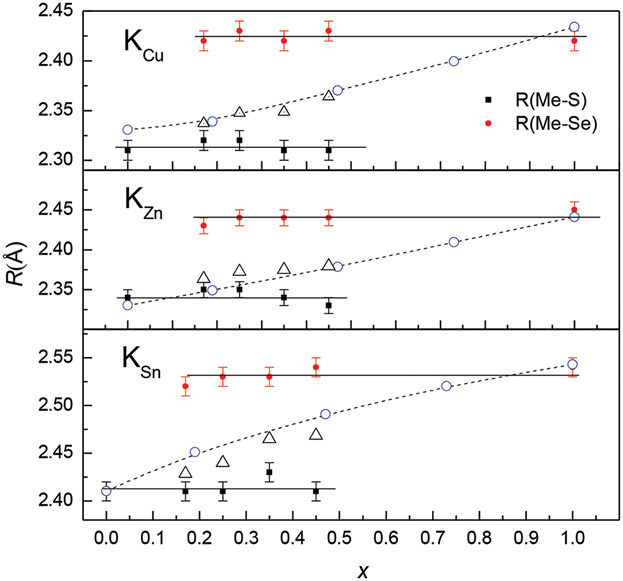
Extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis of the nearest neighbor environment in kesterite Cu2ZnSn(SxSe1–x)4 alloys is presented. Bimodal behavior of the cation–anion distances is observed for the metal–sulfur and metal–selenium bonds. Differences in the static disorder around the metal atoms are noted.
Heusler Alloys
Electronic Structure, Optical, and Magnetic Properties of Mn100−xGex (x = 20, 25, and 30) Alloys Near Tetragonal–Orthorhombic Structural Phase Transition
- First Published: 28 July 2019
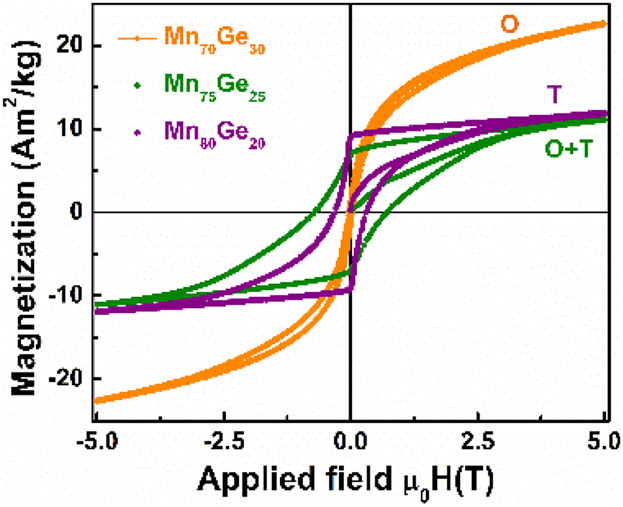
The effect of Mn100−xGex composition (for x = 20, 25, 30) on phase formation, electronic structure, and magnetic properties of polycrystalline Mn–Ge alloys is investigated. The structural analysis in agreement with electronic structure calculations and optical data suggests that Mn–Ge undergoes a tetragonal (T) to orthorhombic (O) transition in this composition range, which significantly alters the magnetic properties of these alloys.
Magnetic Bubbles
Formation of Zero-Field Magnetic Bubbles and Magnetic Phase Transitions in PbFe12O19 via In Situ Lorentz Microscopy
- First Published: 01 July 2019
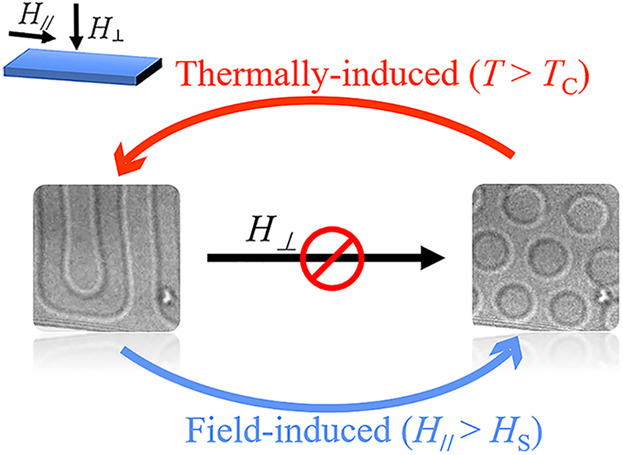
Lorentz microscopy experiments reveal the suppression of the stripe-to-bubble transition through application of magnetic fields perpendicular to hexaferrite PbFe12O19 thin plates. By contrast, zero-field stabilized magnetic bubbles can be generated after in-plane field treatment. In situ heating experiments reveal the metastable nature of zero-field bubbles and the facilitating role of Bloch lines in stripes for forming magnetic bubbles.
Cubic Boron Nitride
Anharmonic Quantum Effects in Cubic Boron Nitride Crystal by Path Integral Monte Carlo Simulations
- First Published: 04 July 2019
Li-Ion Battery Electrodes
Oxygen Doping Enhanced Lithiation in MgCl2 for Battery Applications
- First Published: 25 June 2019

Oxygen doping makes MgCl2 electrochemically active because of strong interaction with Li. The bulk and monolayer deliver high Li specific capacities of 941 and 1098 mAh g−1, respectively. The diffusion barrier for the bulk is calculated to be 0.6 eV. O doping may be achieved by O annealing because of a low reaction enthalpy.
Nanodiamonds
Structural and Electronic Properties of Oxidized and Amorphous Nanodiamond Surfaces with Covalently Grafted Polypyrrole
- First Published: 18 June 2019
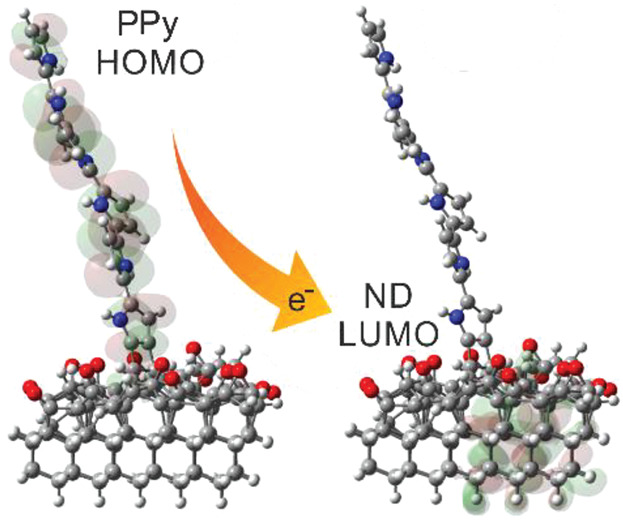
Density functional theory calculations are applied to study covalent interactions between inorganic diamond nanoparticles (nanodiamonds, ND) and organic-conjugated polymer polypyrrole (PPy) for photovoltaic applications. Spatially separated highest occupied molecular orbitals (HOMO) and lowest unoccupied molecular orbitals (LUMO) obtained for a considerable number of the PPy–ND structures are favorable for exciton dissociation. The figure is the example of spatially separated HOMO and LUMO in physisorbed structure with indicated electron excitation from PPy to ND.
Copper Zinc Tin Selenide
Majority Carrier Properties of Single Crystal Cu2−xZnSnSe4 with Varying Copper Composition
- First Published: 16 July 2019
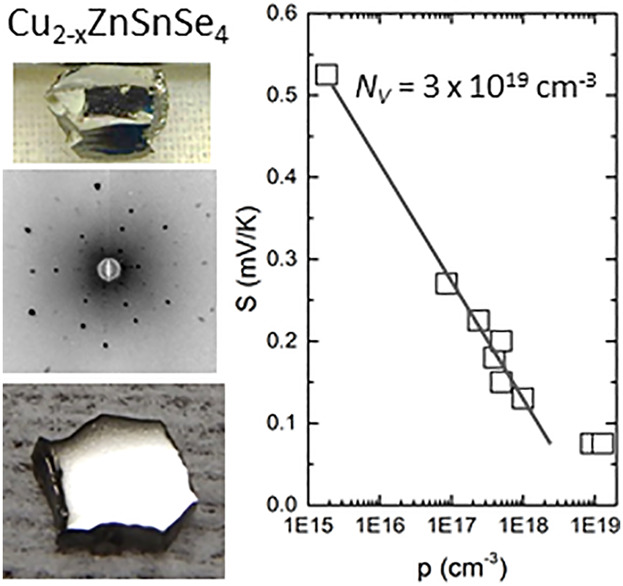
Single crystal kesterite Cu2−xZnSnSe4 are grown over a wide range of Cu/(Zn + Sn) compositions in quasi-equilibrium without fluxing agents. Van der Pauw resistivity provides majority carrier concentration and mobility. Hot probe voltage provides the Seebeck coefficient used to determine the valence band density of states. Optical band gap and temperature-dependent conductivity are determined for a crystal subset.
Magnetic Properties
First-Principles Study on the Electronic, Magnetic, and Optical Properties in TM Atom Doped Cadmium Sulfide Nanosheets
- First Published: 07 July 2019
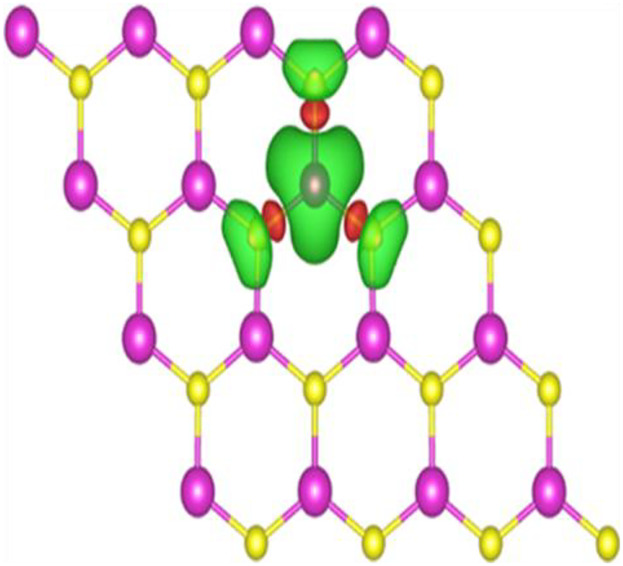
The TM atom (Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, or Ni) doped CdSNSs results in spin-polarized states with the preservation of its direct band gap character. The magnetism of doped CdSNSs is mainly attributed to the TM atom with a strong localized magnetic moment. The red-shift phenomenon is found in low-energy region.
Semiconductor Photocatalysts
The Electronic Structure and Optical Properties of Two-Dimensional BiOX–YO3 (X = Cl, Br, and I; Y = Mo, W) Heterostructures
- First Published: 03 July 2019
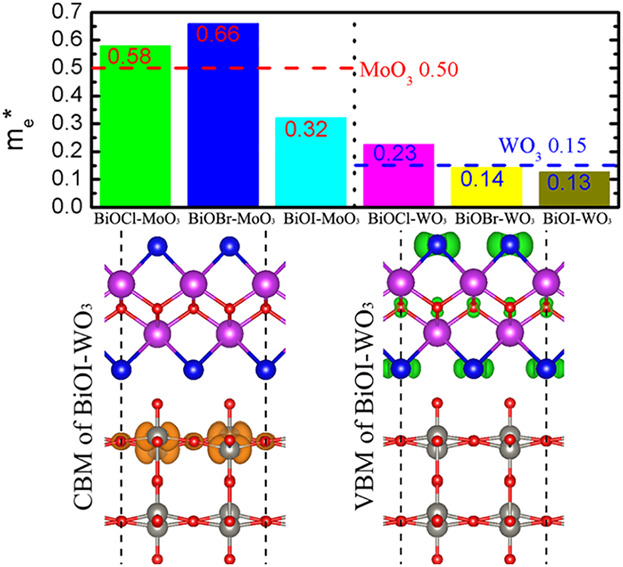
BiOX–YO3 (X = Cl, Br, I; Y = Mo, W) heterostructures exhibit good absorption in the visible light region. The electron effective masses of the BiOI–YO3 heterostructures, especially BiOI–WO3, are lower than those of the YO3 monolayer components. Besides, the valence band maximum (VBM) and conduction band minimum (CBM) of BiOX–YO3 are separate and reside in the BiOX and YO3 layers, respectively.
2D Heterostructures
Tunable Electronic Properties and Giant Spontaneous Polarization in Graphene/Monolayer GeS van der Waals Heterostructure
- First Published: 19 June 2019
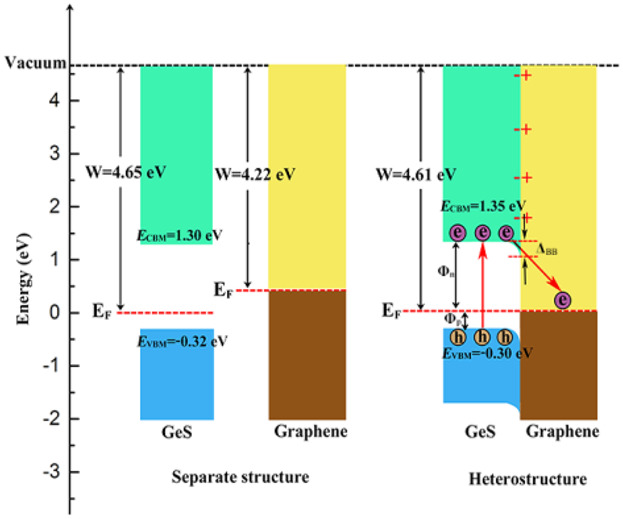
The properties of both graphene and GeS are preserved in the van der Waals (vdW) heterostructure, which is advantageous for improving photocatalytic efficiency. Additionally, the vdW heterostructure shows increased spontaneous polarization and controllable Schottky barrier height. The compressive strain can have a significant impact on both the spontaneous polarization and the energy barrier height of the vdW heterostructure.
Tensile Deformation
Molecular Dynamics Simulations of Structural and Mechanical Properties in MgSiO3 Glass
- First Published: 19 July 2019
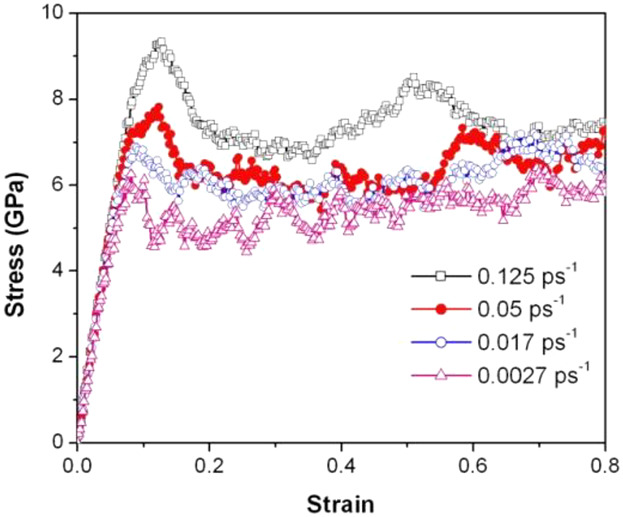
The network structure of MgSiO3 glass consists of SiOx and MgOy units. These units link to others by corner-, edge- and face-sharing bonds. Tension tests are performed on this glass. The stress–strain curves exhibit the elastic and plastic characteristics. The formation of shear transformation zones occurs in the plastic region. Shear band is observed at the strain of 0.82.
Photonic Crystal Cavities
Theoretical Design and Simulation Optimization of Photonic Crystal Cavity for Tetrahydrofuran Vapor Sensing
- First Published: 15 July 2019
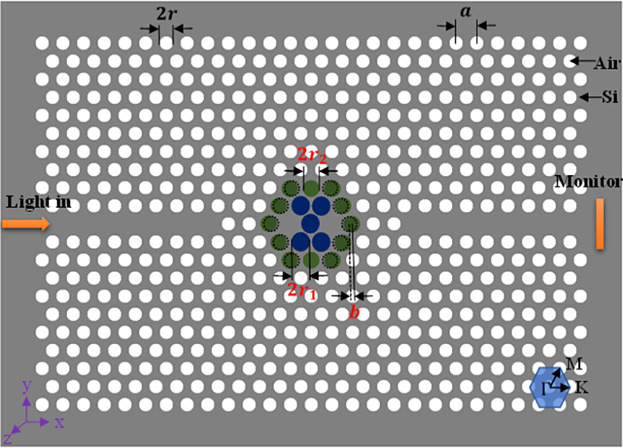
A photonic crystal (PC) cavity with high quality factor, wide measurement range, and high refractive index sensitivity is proposed. Combined with the gas sensitive characteristics of cholesteric liquid crystal (CLC) and the resonance characteristics of the PC cavity, this proposed PC cavity can be theoretically used for tetrahydrofuran vapor sensing.
2D Materials
Near Band-Edge Optical Excitation Leading to Catastrophic Ionization and Electron–Hole Liquid in Room-Temperature Monolayer MoS2
- First Published: 14 June 2019
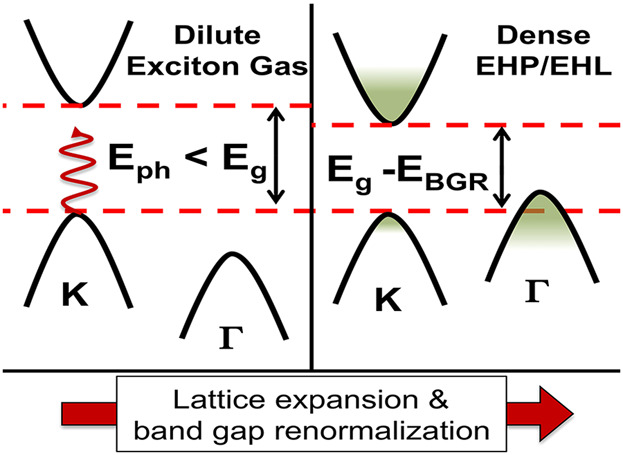
Below-band-edge excitation leads to thermal expansion, followed by electron–hole liquid (EHL) formation in monolayer MoS2. The initial excitation is to the near edge defect states. As the material heats, the band gap tunes and excitation photons become resonant, creating enough density of excitons for ionization and EHL condensation.
Van der Waals Heterostructures
Strain Engineering and Electric Field Tunable Electronic Properties of Janus MoSSe/WX2 (X = S, Se) van der Waals Heterostructures
- First Published: 15 July 2019
Surface Reconstructions
Surface Reconstructions of SrTiO3(110) Calibrated with STM and LEED
- First Published: 25 June 2019
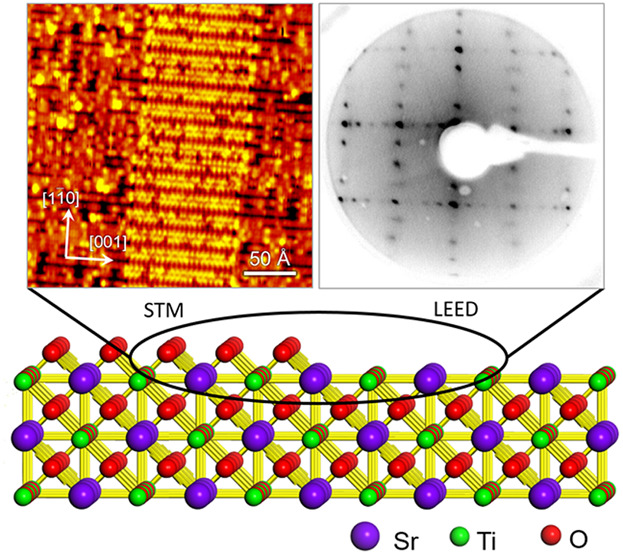
On the SrTiO3(110) surface, a series of reconstructions are created via repeated cycles of argon ion sputtering and annealing. These reconstructions are studied with scanning tunneling microscopy (STM) and low energy electron diffraction (LEED). Typical structural units in the reconstructed surface are identified. Meanwhile, the combination of STM and LEED eliminates the interference from the coexisting multiple structures.
AlN/Si Substrates
Correlation of Structure and EBIC Contrast from Threading Dislocations in AlN/Si Films
- First Published: 03 July 2019
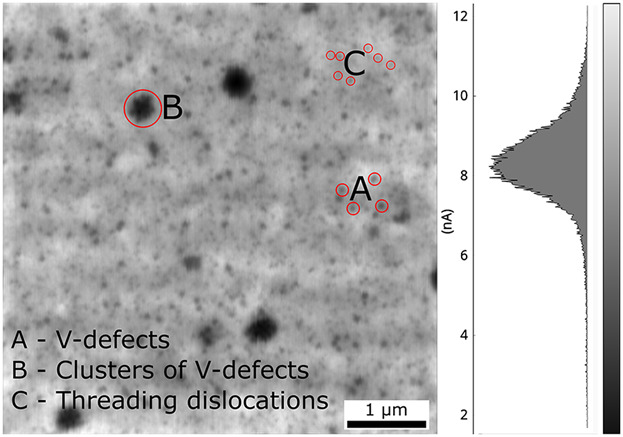
The effect of threading dislocations, V-defects and clusters of V-defects on the electrical properties of AlN on Si {111} was studied. Threading dislocations have the largest impact on electrical properties of AlN due to their high density and uniform distribution. The impact of V-defects and their clusters is lower because of localized nature of these defects.
Superhard Materials
Elastic and Bandgap Modulations of Hexagonal BC2N From First-Principles Calculations
- First Published: 16 July 2019
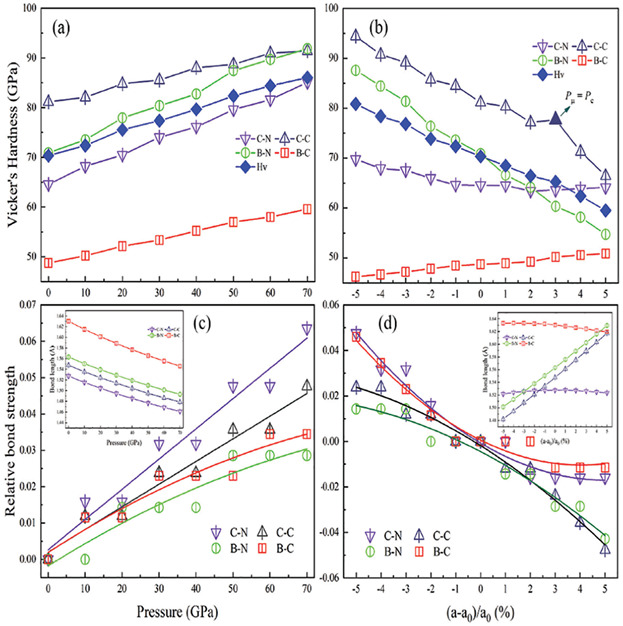
Hexagonal boron carbon nitride (BC2N), an indirect bandgap semiconductor with brittle manner, has a hardness of 70 GPa. All elastic constants and elastic modulus are positively correlated with the modulation of the external forces, while the situations in Vicker's hardness are much more complicated. Moreover, anisotropic properties, as well as the Debye temperature are also discussed.