Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
More Milestones: 15 Years of physica status solidi (RRL) – Rapid Research Letters
- First Published: 06 January 2022
Reviews
Fabrication of Crystalline Si Thin Films for Photovoltaics
- First Published: 21 September 2022
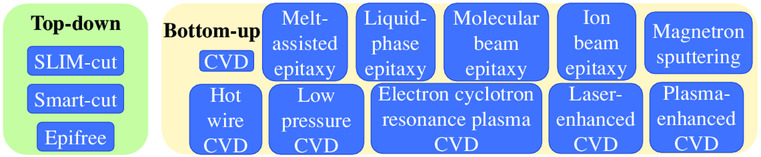
Crystalline Si thin films can be fabricated mainly via “top-down” and “bottom-up” approaches. The “top-down” approaches involve producing a fragile interfacial layer inside a crystalline Si substrate. In the “bottom-up” approaches, various epitaxial growth techniques allow to deposit thin crystalline Si films on a parent substrate. Both approaches require the transfer of the thin c-Si layer to a foreign substrate.
Review on the Microstructure of Ferroelectric Hafnium Oxides
- First Published: 22 July 2022
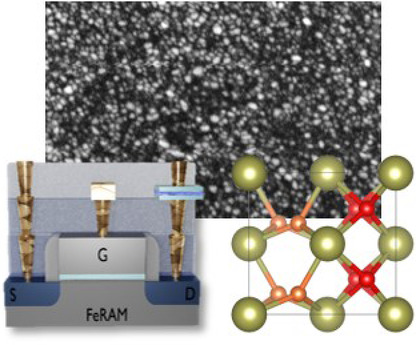
Ferroelectric hafnium oxide is of great interest for various applications in microelectronics like nonvolatile memories, neuromorphic computing, actuators, and sensors. In this review article, the influence of the microstructure on the ferroelectric and electric performance is discussed for the aforementioned applications and related device concepts, giving a coherent picture of the state-of-the-art knowledge.
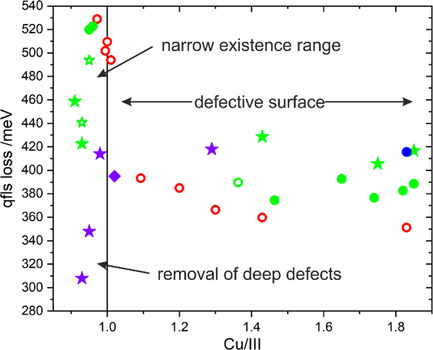
Sulfide Chalcopyrite Solar Cells––Are They the Same as Selenides with a Wider Bandgap?
- First Published: 20 May 2022
Domain Wall Formation and Magnon Localization in Twisted Chromium Trihalides
- First Published: 13 April 2022
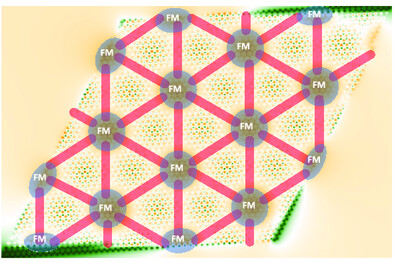
Herein, a brief overview of the theory and recent experimental advances of twisted 2D magnets are given, together with a description of the effect of stacking and twist angles on the magnon dispersion and localization. Interestingly, the magnon dispersion close to the Dirac point is stacking dependent. For small twist angles, 1D channels form connecting ferromagnetic centers along antiferromagnetic pathways.
Experimental Observations versus First-Principles Calculations for Ni–Mn–Ga Ferromagnetic Shape Memory Alloys: A Review
- First Published: 05 March 2022
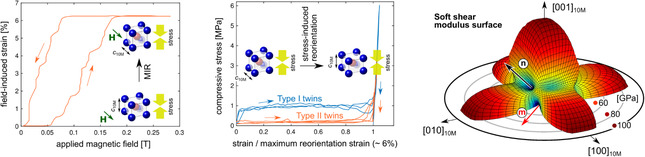
This review summarizes recent advances in first-principles simulations of the structural, mechanical, and magnetomechanical properties of Ni–Mn–Ga-based ferromagnetic shape memory alloys from the perspective of the experimentalist. When experiments and theory are discussed together, new challenges arise for both.
Organic Semiconductor–Insulator Blends for Organic Field-Effect Transistors
- First Published: 08 February 2022
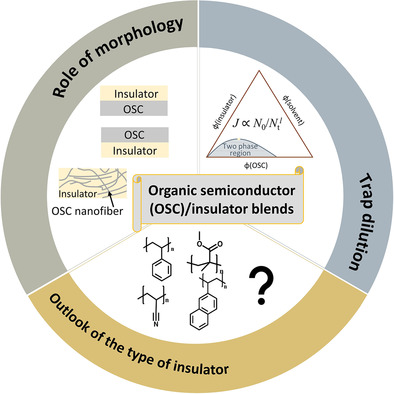
This review focuses on how to use organic semiconductor/insulator blends to achieve better organic field-effect transistors (OFETs). It covers the latest advances in blended OFETs. Then, several schemes, including morphology control, trap dilution, and various insulator types, are proposed to deepen the understanding of the intrinsic properties of insulator blends and provide clinical directions for device optimization.
Rational Control of GeSn Nanowires
- First Published: 31 December 2021
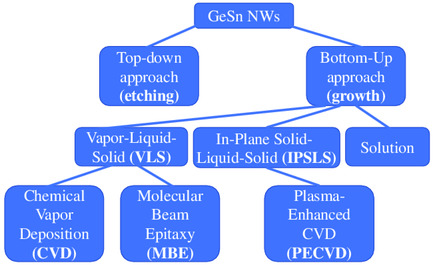
GeSn nanowires can be synthesized via top-down and bottom-up approaches. Top-down involves growing GeSn layers on a Ge buffer layer and combining wet etching with selective dry etching to achieve strain-free GeSn nanowires. Bottom-up methods include i) vapor–liquid–solid processes via chemical vapor deposition and molecular beam epitaxy, ii) plasma-assisted in-plane solid–liquid–solid growth, and iii) solution-based mechanisms.
Catastrophic Optical Damage in Semiconductor Lasers: Physics and New Results on InGaN High-Power Diode Lasers
- First Published: 17 November 2021
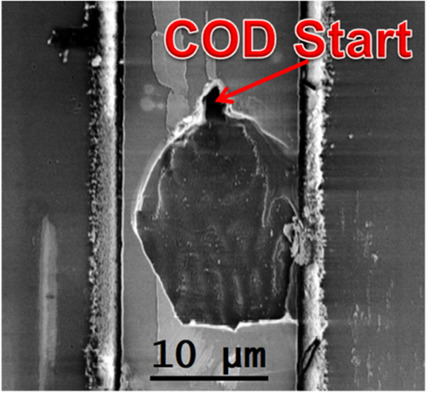
Catastrophic optical damage (COD) is an optical output-limiting destructive mechanism in semiconductor diode lasers. An overview of the mechanism and its causes is given, differences between COD in GaAs-based and GaN-based diode lasers are discussed, and recent findings on COD with starting points inside GaN-based devices are presented and analyzed.
Auxetic Behavior and Other Negative Thermomechanical Properties from Rotating Rigid Units
- First Published: 14 August 2021

The important role of rotating rigid units in the field of mechanical metamaterials and architected materials is explored. In particular, herein, various implementations of this mechanism are delved into, ranging from rotating squares to much more complex renditions, to generate negative Poisson's ratios (auxetic behavior), negative thermal expansion, and/or negative compressibility.
Recent Progress and Perspectives of Field-Effect Transistors Based on p-Type Oxide Semiconductors
- First Published: 21 September 2021
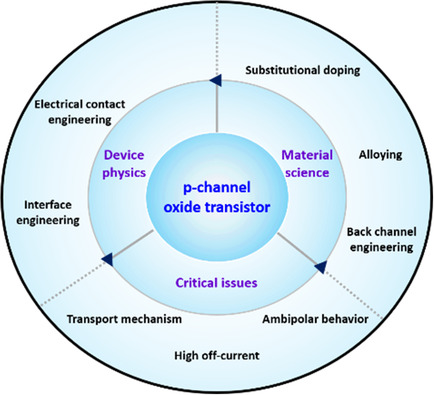
A brief history, recent achievements, and future directions for p-channel oxide field-effect transistors are addressed. The representative p-type oxide semiconductors based on copper and tin are reviewed. The studies reviewed adopted complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor (CMOS)-compatible fabrication methods, such as physical or chemical vapor deposition.
Chemical Vapor Deposition Single-Crystal Diamond: A Review
- First Published: 17 September 2021

Single-crystal diamond is the material of choice for future power electronics and quantum devices. The state of the art of single-crystal diamond growth by chemical vapor deposition, either starting with a diamond substrate (homoepitaxy) or controlling diamond nucleation on a foreign substrate (heteroepitaxy) is described. Future challenges and roles of both materials in the applications are discussed.
Research Articles
Atomistic Modeling of the Electrical Conductivity of Single-Walled Carbon Nanotube Junctions
- First Published: 08 June 2022
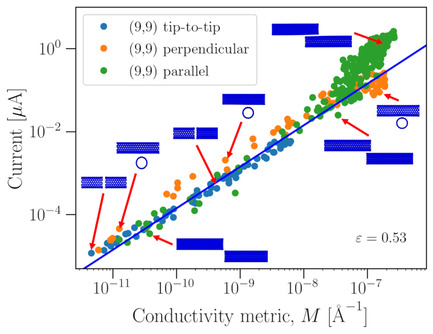
The electrical conductivity of single-walled carbon nanotubes (CNTs) is systematically investigated using density functional tight binding and the nonequilibrium Green's function formalism. The rate of electron tunneling at such structures is controlled by the local atomic structure at the contact point between CNTs. Simple models are constructed that enable the calculation of junction conductivities from molecular dynamics structures.
Factors Determining the Resistive Switching Behavior of Transparent InGaZnO-Based Memristors
- First Published: 26 April 2022
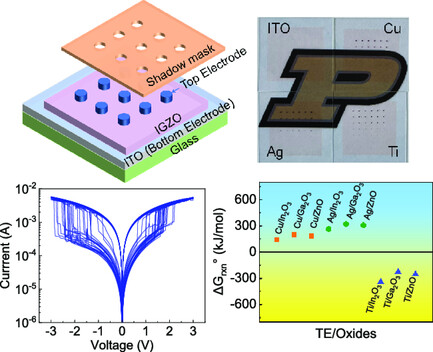
Transparent memristors are realized based on InGaZnO and ITO as switching layer and bottom electrode. Universal strategies regarding the oxygen vacancy concentration in the switching layer and thermodynamic-based metallization stability/instability are suggested to achieve high performance and reliable IGZO-based memristors. Herein, insightful design criteria for oxide memristors in artificial intelligence applications are provided.
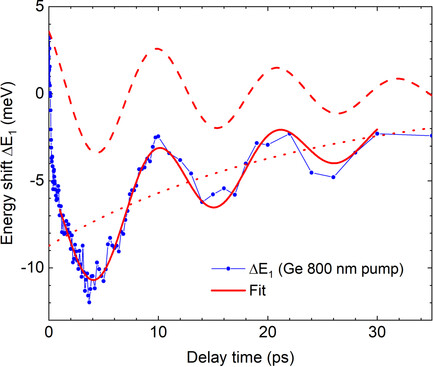
Coherent Acoustic Phonon Oscillations and Transient Critical Point Parameters of Ge from Femtosecond Pump–Probe Ellipsometry
- First Published: 23 April 2022
A Giant Dual-Resonant in Magnetoelectric Composite Based on Electrical and Electromechanical Coupling Towards Enhanced Working Bandwidth and Frequency Tuning
- First Published: 21 April 2022
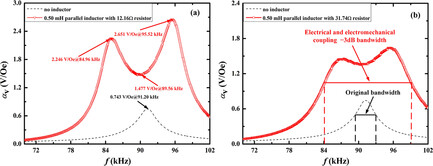
Herein, a novel dual-coupling method is proposed to realize wide bandwidth and frequency tuning in a magnetoelectric composite. The theoretical model based on the equivalent circuit method is also developed for this approach. Accordingly, an ultra-wide bandwidth was increased to 13.91 kHz, and a ME voltage coefficient was enhanced by 302.29% under the connection of different external inductors.
Over One Watt Output Power Terahertz Quantum Cascade Lasers by Using High Doping Concentration and Variable Barrier-Well Height
- First Published: 21 April 2022
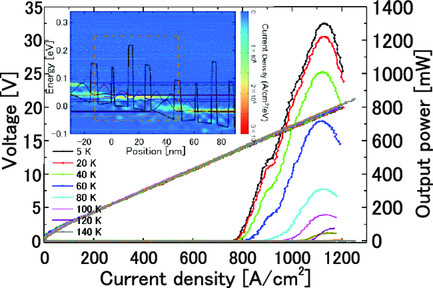
Terahertz (THz) quantum cascade lasers (QCLS) with a peak power of 1.31 W and an average power of 52 mW are demonstrated. Variable amounts of Al are used with higher design freedom, making it able to work at a heavy doping level. Optimization is carried out, including the realignment of resonant tunneling and suppression of leakages via high-energy confined levels.
Adsorbate-Induced Modifications in the Optical Response of the Si(553)–Au Surface
- First Published: 17 March 2022
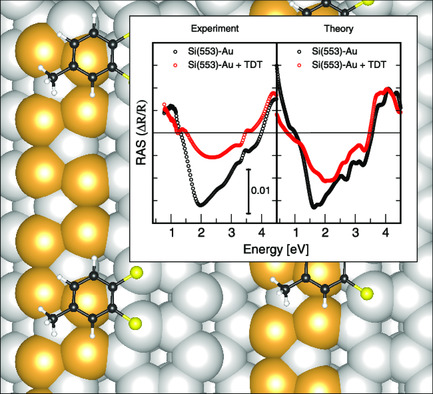
Reflectance anisotropy spectroscopy (RAS) and infrared ellipsometry are particularly suited to identify the spectral features related to atomic-scale structural motifs at surfaces or interfaces. Here, adsorbates on Au–Si(553) are studied by experiment and atomistic calculations. The adsorption occurs at the step edge and thereafter on the terrace. An adsorbate-to-substrate charge transfer modifies the chain structure. Accordingly, optical signatures are identified.
Molecular-Beam Epitaxy Growth and Properties of AlGaAs Nanowires with InGaAs Nanostructures
- First Published: 08 April 2022
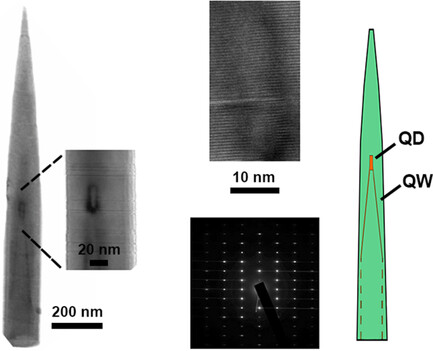
Herein, the results of growing AlGaAs nanowires with InGaAs quantum dots by molecular-beam epitaxy on a silicon substrate are shown. The optimal growth temperature is determined and the physical properties of the grown nanostructures are studied. It is shown that the grown nanostructures exhibit photoluminescence (PL) signal up to room temperature in a wide wavelengths range, including 1.3 μm emission.
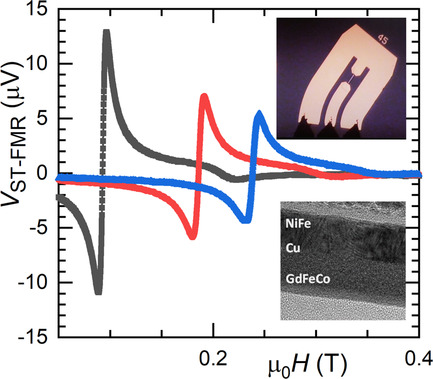
Ferrimagnet GdFeCo Characterization for Spin-Orbitronics: Large Field-Like and Damping-Like Torques
- First Published: 12 March 2022