Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Antiphase Domain Boundary Formation in 2D Ba–Ti–O on Pd(111): An Alternative to Phase Separation
- First Published: 13 January 2022

Surface science studies of two-dimensional Ba–Ti–O films on Pd(111) identify three different small unit cell structures (see article number 2100389 by Stefan Förster and co-workers). In scanning tunneling microscopy these structures exhibit an atomic base of four atoms of one species, decorating the vertices of two triangles. As depicted on the cover, this base rearranges upon atomic density variations. In a fully stretched-out fashion (left side), corresponding to the lowest density state, a square lattice is formed. In the high-density limit (right side) a rectangular structure forms, in which rhombuses fill the gaps. The medium density motif incorporates squares and rhombuses.
Masthead
Back Cover
Janus Monolayers of Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: A DFT Study
- First Published: 13 January 2022

MXY (M = W, Mo; X, Y = S, Se, Te) Janus monolayers are noncentrosymmetric systems with strong spin–orbit coupling effects, giving rise to interesting physical phenomena. By using the full-potential linearized augmented plane-wave method (FP-LAPW), Daniel Olguín and co-workers study the electronic properties of the MoXY (X, Y = S, Se, Te) Janus monolayers (see article number 2100248). These Janus monolayers are found to present a spin polarization near the high symmetry Γ, K–, and K+ points of the valence band. Among the studied systems, MoSeTe and MoSSe present spin–valley polarization, Rashba spin-splitting, and a direct bandgap, representing an interesting atomically thin material that can be exploited in different applications such as spintronics, spin-orbitronics, and nanoelectronics.
Editorials
More Milestones: 15 Years of physica status solidi (RRL) – Rapid Research Letters
- First Published: 13 January 2022
Reviews
60 years of pss
Research Articles
60 years of pss
Theoretical and Experimental Studies of Charge Ordering in CaFeO3 and SrFeO3 Crystals
- First Published: 06 November 2021
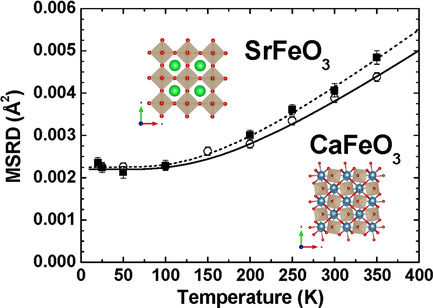
A comparative study of the isoelectronic and perovskites has been performed by means of ab initio quantum chemical calculations, and by EXAFS and XANES measurements for the first time. The results of simulations support a cubic perovskite structure of and transition from the room-temperature orthorhombic charge-delocalized state in to the low-temperature monoclinic charge-disproportionated state.
Janus Monolayers of Transition Metal Dichalcogenides: A DFT Study
- First Published: 02 November 2021
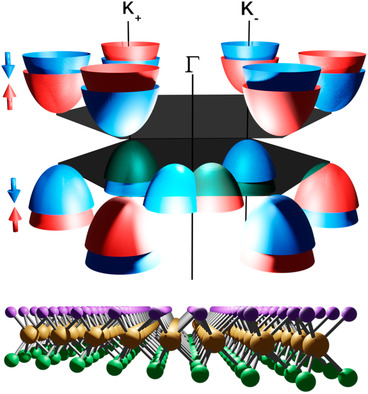
A computational study is presented using GGA and on-site hybrid approximations to determine the structural and electronic properties of different Janus transition metal dichalcogenides. The calculated electronic band structures show a Rashba splitting around the Γ point and the Zeeman spin-splitting at the K− and K+ points, suggesting that these 2D materials can be exploited to develop orbitronic applications.
Exploring Anomalies by Many-Body Correlations
- First Published: 14 October 2021
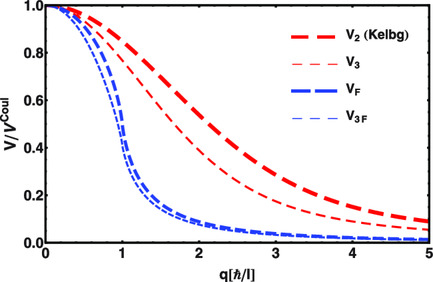
Reinterpreting the many-body averaging a connection to Pauli–Villars regularization is established, which gives the quantum trace anomaly a new interpretation as arising from quantum fluctuations by many-body correlations at short distances. Effective many-body quantum potentials avoid such anomaly but approach the same anomalous result. The derived quantum potentials can be used to describe quantum effects in classical simulations.
Antiphase Domain Boundary Formation in 2D Ba–Ti–O on Pd(111): An Alternative to Phase Separation
- First Published: 16 October 2021
Small unit cell structures are reported for 2D layers of Ba–Ti–O on Pd(111). In scanning tunneling microscopy, three different unit cells are distinguished, sharing a base of four atoms. Due to a periodic repetition in quadratic, rectangular, or hexagonal fashion, different atomic densities are realized. The density is further tuned by an incorporation of 1D antiphase domain boundaries.
Topological Origin of the Super-Flexible Phase of Se and Se-Rich Glasses and Aging-Induced 5-fold Narrowing of Glass Transition Width
- First Published: 28 October 2021
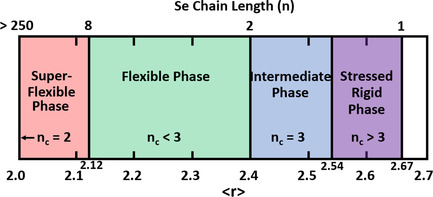
Pure Se and Se-rich glasses can exist in a new topological phase called the super-flexible phase. In this phase, polymeric Sen chains exist in the 250 > n > 8 length range. Glass transition widths of such glasses can narrow by a factor of 3–5 upon room temperature aging for 4 months as the long Sen chains reconstruct.
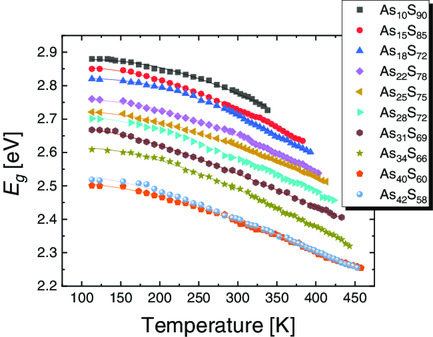
On the Temperature Behavior of Optical Gap in Arsenic Sulfide Glasses
- First Published: 28 October 2021
Critical Behavior of the (111)-Oriented LaCoO3/SrTiO3 Thin Film
- First Published: 09 November 2021
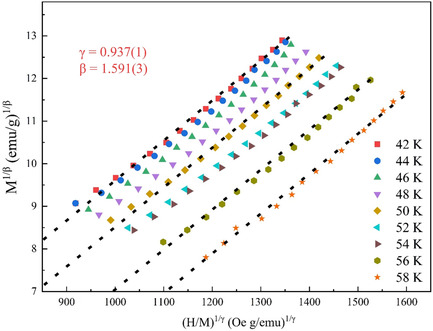
The critical behavior of (111)-oriented LaCoO3 (LCO) epitaxial films is studied by reconstructing a modified Arrott plot. The final critical exponents are determined to β = 1.591(3) and γ = 0.937(1). The film exhibits a space dimensionality d = 2 and spin dimensionality n = 1 long-range magnetic interaction, and the magnetic exchange interaction decays as J(r) ≈ r −2.4473.
Qualitative Analysis of the Valence and Conduction Band Offset Parameters in FeNiO/CuNiO Bilayer Film Using X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
- First Published: 02 November 2021
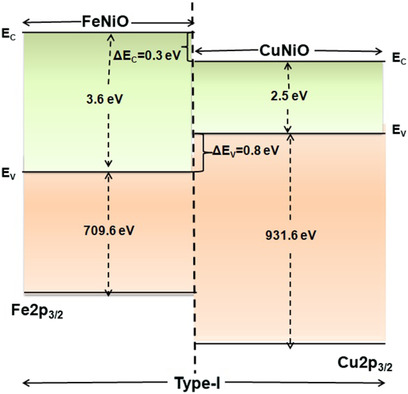
Band offset parameters in FeNiO/CuNiO bilayer film are obtained using X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy and ultraviolet–visible spectroscopy. From valence band maxima and core level energy positions, the valence band and conduction band offsets are estimated to be 0.8 eV and 0.3 eV, respectively. A type-I band alignment is identified at the interface of the grown bilayer film.
Density Functional Theory-Based Prediction of the Pressure-Dependent Magnetic Properties of CaRuO3
- First Published: 12 October 2021
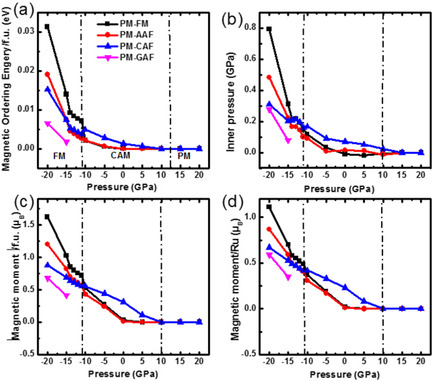
CaRuO3 with a perovskite ABO3 structure has attracted considerable interest due to the possible non-Fermi liquid behavior, a spin (or cluster) glass state, itinerant ferromagnetic states, its proximity to a magnetic quantum critical point, etc. Herein, the density functional theory is used to study the magnetic structure of CaRuO3 as a function of hydrostatic pressure.
DFT Calculations for Some Perovskites and Their Solid Solutions
- First Published: 12 October 2021
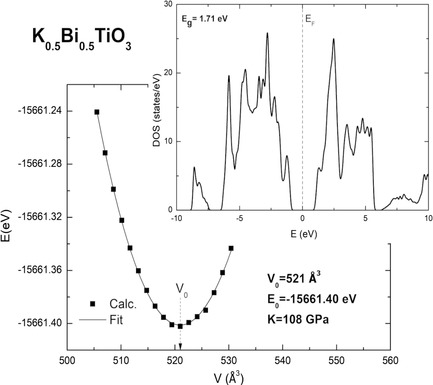
Sodium-bismuth titanate (NBT) and potassium-bismuth titanate (KBT) are lead-free materials, but their functional properties are weaker than observed in lead titanate (PT). Materials with low Pb content may replace the currently used lead materials. The calculations of some of their solid solutions show an increasing value of the bulk modulus when the PT content in KBT and NBT increases.
Substitution Site Selection and Thermoelectric Performance-Enhancing Mechanism of Cu12Sb4S13 Doped with Pb/Ge/Sn
- First Published: 22 October 2021
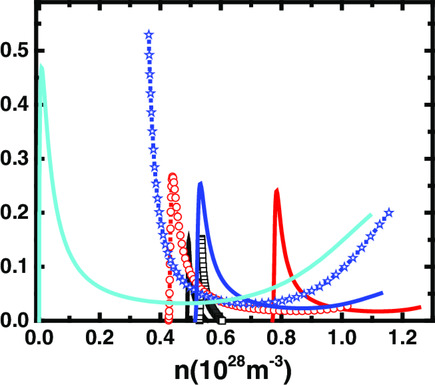
Element substitution mechanisms and the relations between element substitution sites and thermoelectric performances of Pb/Ge/Sn-doped Cu12Sb4S13 are investigated. It is found that the most energetically favorable sites and the sites corresponding to preferable optimizing thermoelectric performance are different. A 15-time improvement on ZT of the host by doping is obtained.
Impact of Thickness and Poling Condition on Dielectric and Piezoelectric Properties of Pb(In0.5Nb0.5)O3–PbTiO3 Ferroelectric Crystals
- First Published: 02 October 2021
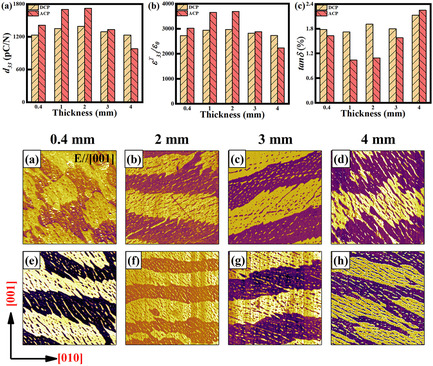
The effect of poling method (alternating or direct current poling, ACP or DCP) and thickness is studied for Pb(In0.5Nb0.5)O3–PbTiO3 (PIN–PT) crystals. The 2 mm ACP 0.655PIN–0.345PT crystals exhibit high piezoelectric coefficient and free permittivity, enhanced by 24% compared to DCP samples, which is attributed to the regular periodic domain structure and a smaller domain width. Decrease in coercive field is also beneficial for the improvement of piezoelectric performance.
Phonons in WSe2/MoSe2 van der Waals Heterobilayers
- First Published: 05 November 2021

Structural and vibrational properties of van der Waals heterobilayers (HBLs) WSe2/MoSe2 are studied using density-functional theory. The first-principles results reveal the existence of interlayer rigid-layer shear and breathing phonon modes in the HBLs. These special low-frequency optical modes exist only in bilayers and are paramount to understanding the different scattering mechanisms in layered 2D materials.
A Novel BN Polymorph in P4/mbm Phase with a (4,4) Nanotube
- First Published: 08 October 2021
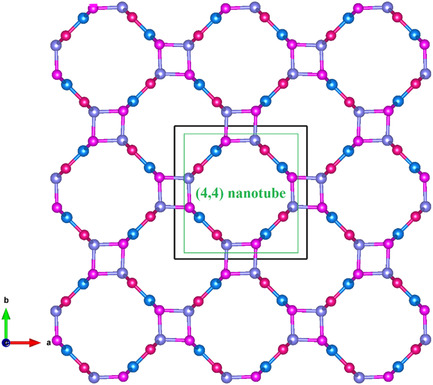
The shear modulus and Young's modulus of the P4/mbm BN, proposed herein, are larger than those of P-4m2 B7N7, B11N11, and B15N15. Compared with SiC and GaN, P4/mbm BN has a wider bandgap of 4.8 eV, it might be more suitable for making high temperature, high frequency, radiation resistance, and high-power devices.
Energy Gap Decrease in Cation Multidoped Aluminum Oxide
- First Published: 14 October 2021
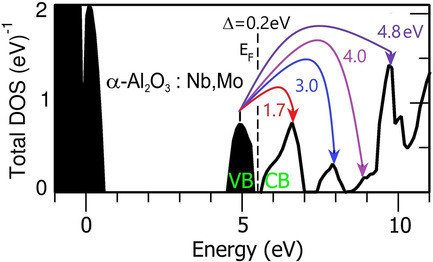
Corundum energy gap narrowing by cation d (Zr, Nb, Mo)- and s (Mg)-impurities multidoping due to the formation of new partially filled 4d bands inside the undoped α-Al2O3 energy gap is calculated within the coherent potential approximation. New insulator and semiconductor corundum-based compounds with strictly defined mutual concentrations of disordered impurities are proposed for novel optoelectronic devices creation.
Polarization Spectroscopy of Anisotropic Plasmons in Self-Oriented Nanoclusters of Gold on Monolayer of Nitrogen Atoms Chemisorbed at GaAs(001) Surface
- First Published: 11 November 2021
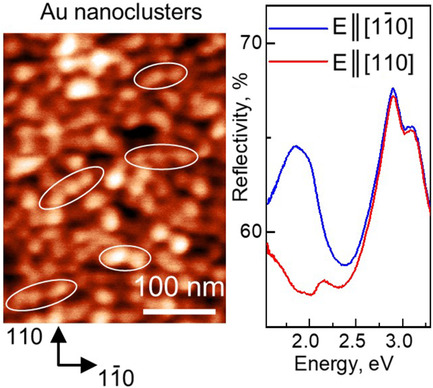
Chemically clean gold nanoclusters are fabricated on GaAs(001) surface covered by a monolayer of chemisorbed nitrogen atoms. The on-surface Au clusters possess a pronounced anisotropy of both shape and orientation in crystallographic [] direction on GaAs surface. Localized plasmons of the clusters also reveal rather strong in-surface anisotropy detected by polarized reflection spectroscopy.
A Study of Thermoelectric Performance of TlGaSe2 Layered Dichalcogenides from First-Principles Calculations: Vacancy Defects Modeling and Engineering
- First Published: 09 November 2021
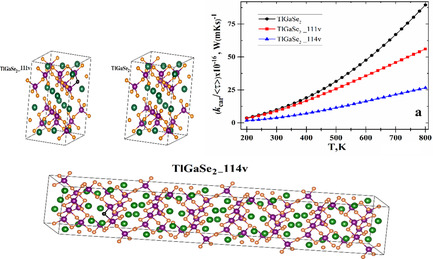
Herein, the effects of Se vacancies on the electronic thermal conductance, electrical conductance, Seebeck coefficient, figure of merit and electronic fitness function of TlGaSe2 layered semiconductor are theoretically studied. The findings indicate that Se-vacancies can improve the thermoelectric performance of TlGaSe2. This work provides concrete ways to enhance the thermoelectric performance of TlGaSe2 by defect engineering and modeling.
Luminescence Characteristics in Hexagonal and Cubic-Phase GaN on Micropatterned Si(100) Substrate
- First Published: 05 November 2021
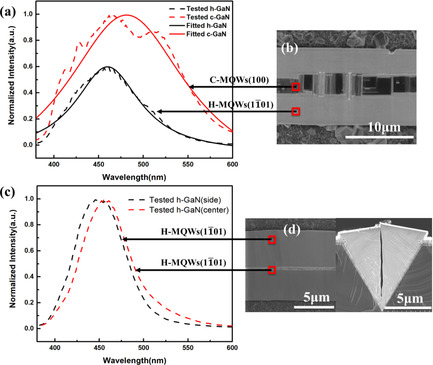
The luminescence characteristics of the hexagonal GaN and cubic GaN on micropatterned Si(100) substrates are explored. Photoluminescence and cathodoluminescence measurements reveal that a cubic InGaN/GaN quantum well has produced longer wavelengths. The cubic multiple quantum wells could incorporate higher indium content and realize longer wavelength emissions, which has great potential to realize red light emitting diode.
Measuring Energy Gaps of Organic Semiconductors by Electron Energy Loss Spectroscopies
- First Published: 09 November 2021
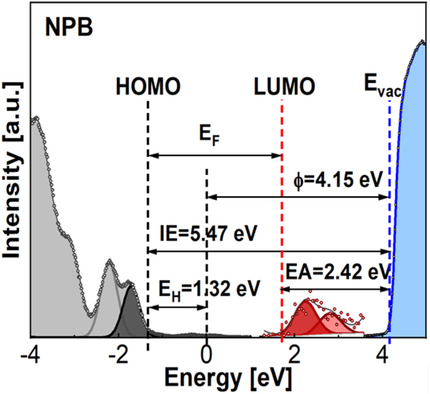
The authors show that reflection electron energy loss spectroscopy (REELS) can be used to measure the bandgaps of organic semiconductors. By combining REELS and ultra-violet photoemission spectroscopy (UPS), it is further shown that all key energy structures such as bandgap, ionization energy, Fermi energy level, work function, electron affinity, HOMO and LUMO can be concurrently measured from the same sample.
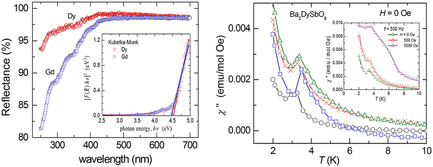
Optical and Magnetic Properties of Cubic Double Perovskites Ba2RSbO6 (R= Dy, Gd) Coordinated to Lattice Dynamical and Crystal-Field Computations
- First Published: 28 October 2021
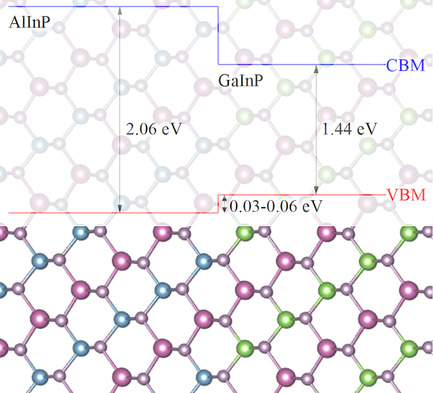
GaInP/AlInP(001) Interfaces from Density Functional Theory
- First Published: 09 November 2021
Effect of Intrinsic Nb5+ Vacancy on Dielectric and Polarization Behaviors of KSr2Nb5O15: First-Principles Investigation
- First Published: 30 October 2021
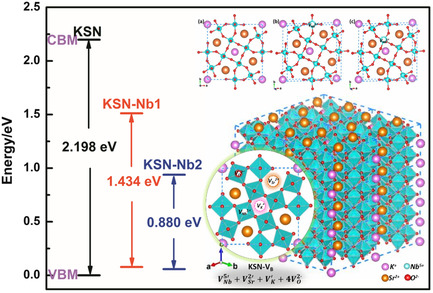
The dielectric constants and polarization responses of ferroelectric KSr2Nb5O15 are different when vacancy is formed at the two types of Nb sites (Nb1 or Nb2), respectively. Furthermore, the experimental results support the effects of different Nb5+ vacancies on the polarization behavior of the material. This study provides a theoretical foundation for improving the polarization behavior of tungsten bronze structure ferroelectrics.
Structure, Stability, Properties, and Application of Atomically Thin Coinage Metal Flatland in Graphene Pore: A Density Functional Theory Calculation
- First Published: 20 October 2021
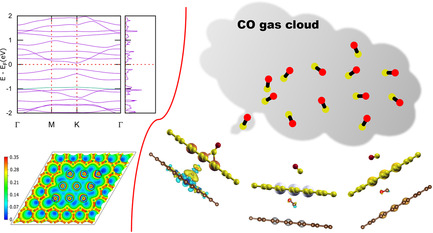
2D metals are emerging materials in the field of materials science. Herein, attention is paid to investigate the energetic stability and electronic properties of coinage-metal-patched graphene to probe its applications. All the systems are metallic except eight-Au-patched graphene. Cu-patched graphene is more selective for CO adsorption compared to Ag- and Au-patched graphene surfaces.