Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
A novel simple disposition index (SPINA-DI) from fasting insulin and glucose concentration as a robust measure of carbohydrate homeostasis
- First Published: 02 January 2024
Highlights
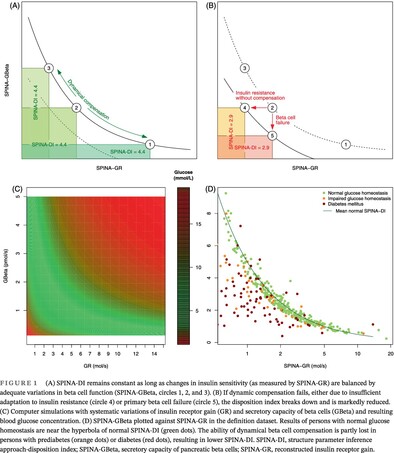
- We defined a fasting-based disposition index (structure parameter inference approach-disposition index [SPINA-DI]), calculated as the product of the secretory capacity of pancreatic beta cells (SPINA-GBeta) multiplied by estimated insulin receptor gain (SPINA-GR).
- SPINA-DI mirrors the recognized hyperbolic relationship between beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity.
- It significantly correlates with the dynamic disposition index based on frequently sampled oral glucose tolerance tests (Matsuda–DeFronzo method) and other important measures of insulin-glucose homeostasis.
- For the diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes, it has a higher discriminatory power than other static function tests (homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance, and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index) and dynamic, oral glucose tolerance testing-derived parameters (insulin sensitivity index, insulinogenic index and disposition index according to Matsuda and DeFronzo).
- SPINA-DI has high retest reliability compared to other markers of glucose homeostasis.
- This novel fasting-based disposition index (SPINA-DI) is defined as the product of insulin receptor gain (SPINA-GR) multiplied by beta-cell function (SPINA-GBeta). SPINA-DI may be reduced due to insulin resistance with insufficient dynamical compensation of beta-cell mass (red horizontal arrow) or due to primary beta-cell failure (red vertical arrow). SPINA-DI was validated in three cohorts. It had advantages in validity, reliability, and diagnostic power compared to established criteria.
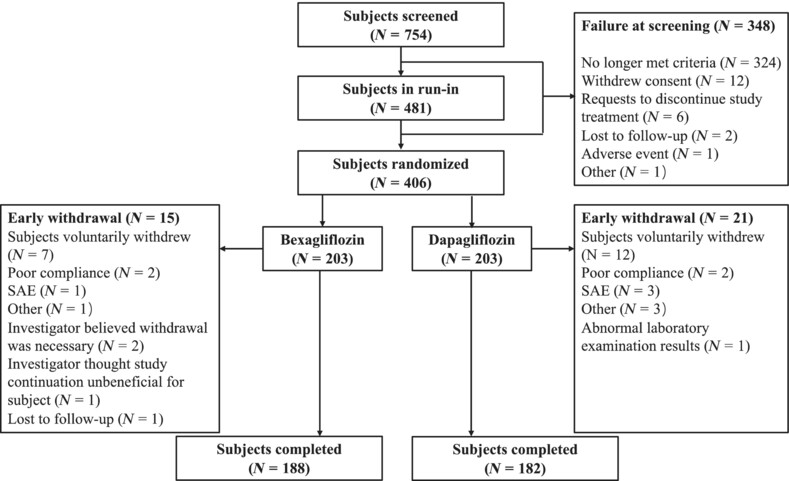
Efficacy and safety of bexagliflozin compared with dapagliflozin as an adjunct to metformin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 trial
- First Published: 07 April 2024
Highlights
- This is the first randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial collecting data on the efficacy and safety of bexagliflozin compared to that of dapagliflozin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Bexagliflozin provides identical efficacy in improving key efficacy parameters including glycated hemoglobin, fasting plasma glucose, 2-h postprandial blood glucose, and clinical response without an increase in adverse events compared with dapagliflozin.
The metabolic effects of habitual leg shaking: A randomized crossover trial
- First Published: 25 April 2024
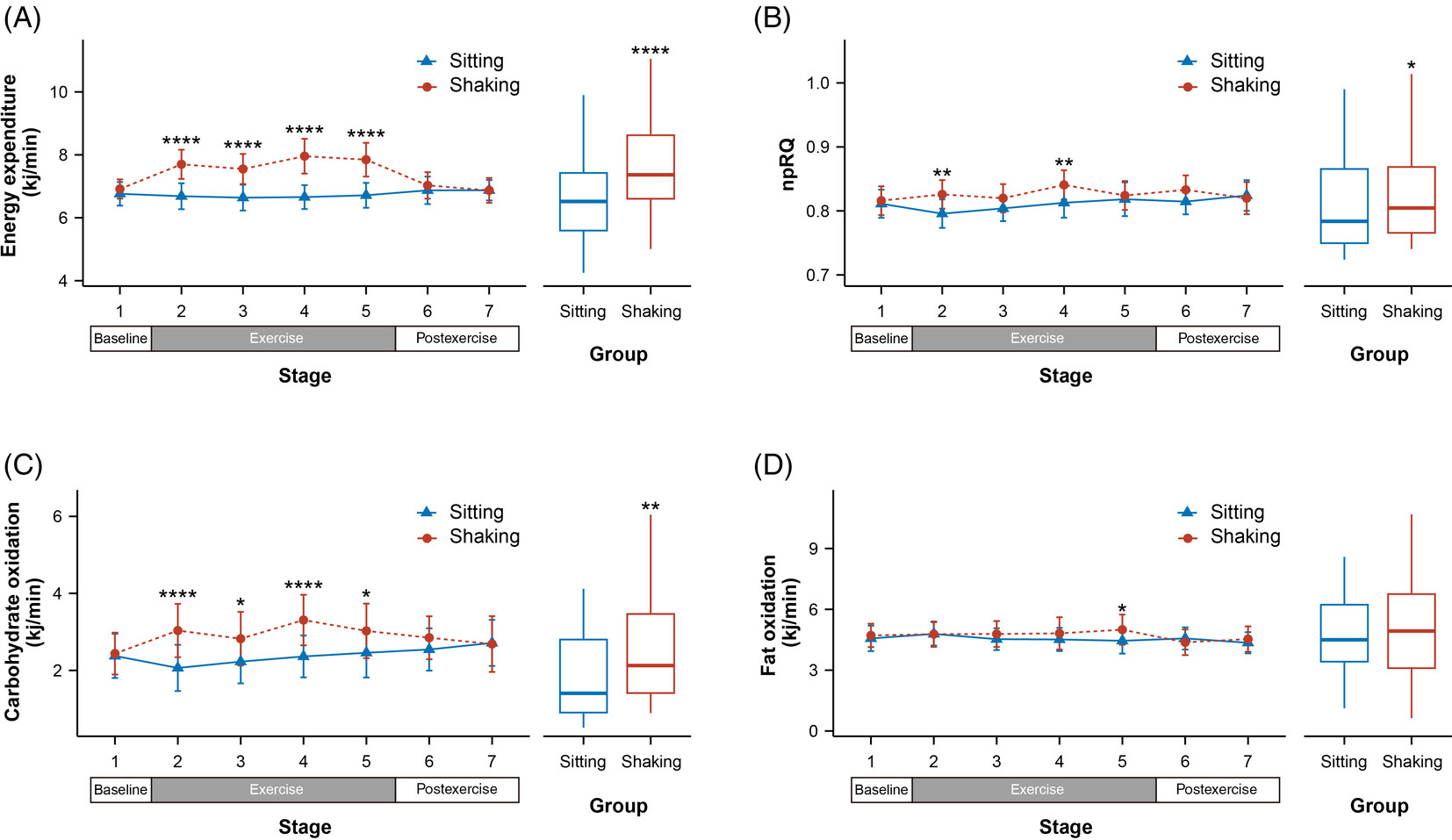
Highlights
- Previous research has established the detrimental effects of sedentary behavior on obesity and chronic diseases. Efforts to mitigate heightened sedentary behavior through measures such as promoting elevated physical activity or incorporating extended standing and exercise during sedentary intervals have faced challenges in implementation.
- Our study confirmed that habitual leg shaking effectively increased energy expenditure by approximately 16.3%, elevated the metabolic equivalent to a nonhealthy level, enhanced carbohydrate oxidation, improved blood oxygen saturation and minute ventilation, while avoiding additional cardiovascular burden.
- Leg shaking offers a simple and feasible approach to enhance physical activity without disrupting daily routines.
Factors associated with diabetic foot ulcers and lower limb amputations in type 1 and type 2 diabetes supported by real-world data from the German/Austrian DPV registry
- First Published: 25 February 2024
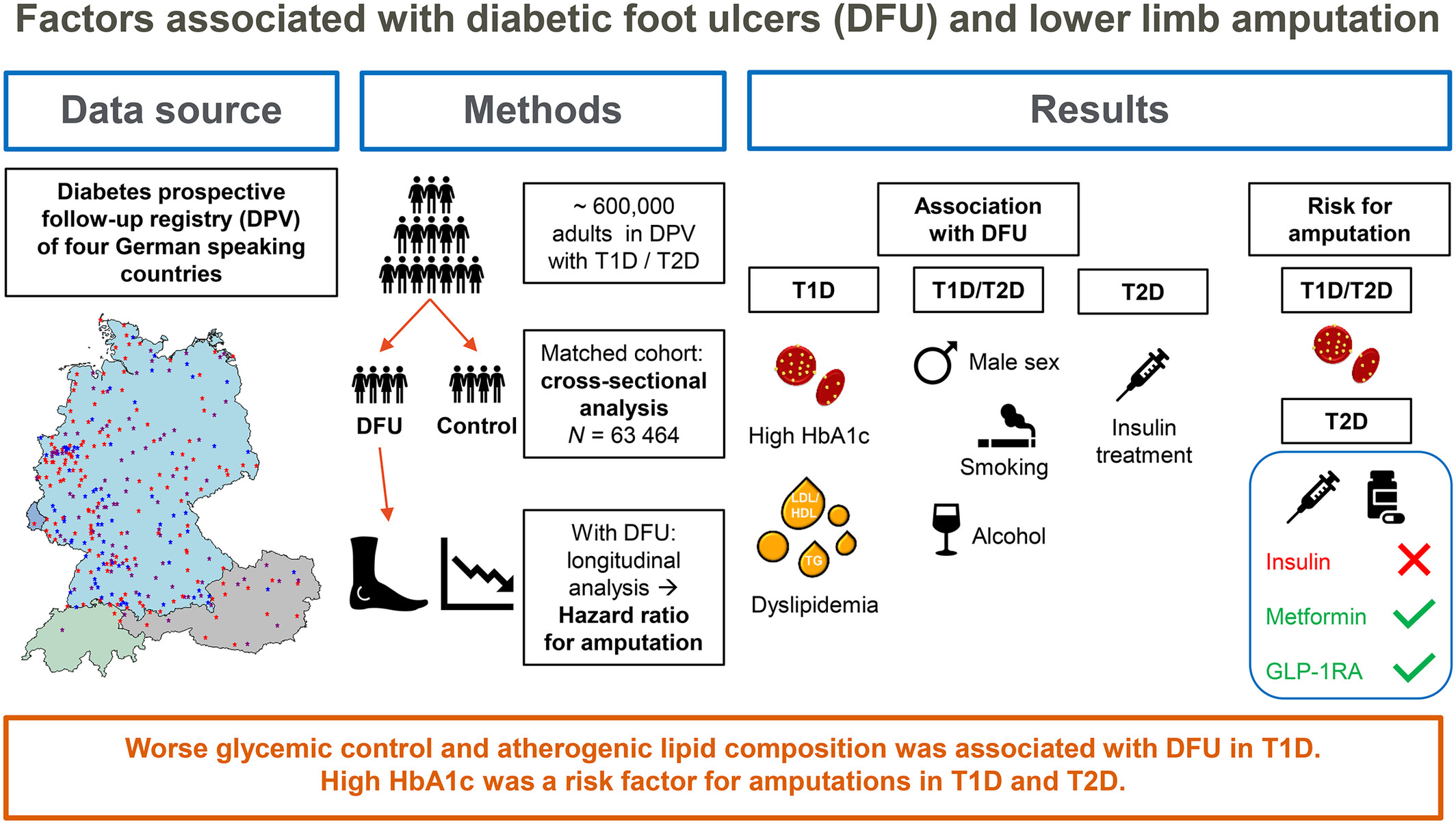
Highlights
- Poor glycemic control and high lipid levels were associated more closely with diabetic foot ulcers in type 1 compared to type 2 diabetes.
- Gender differences regarding the association of diabetic foot ulcers with metabolic outcomes were more pronounced in type 1 diabetes.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption might be important in developing foot ulcers but play a minor role in prevention of amputations.
- The role of oral hypoglycemic medication in development of diabetic foot ulcers should be further analyzed in type 2 diabetes.
Impact of treatment with GLP-1RAs on suicide attempts in adults persons with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective comparative effectiveness study based on a global TriNetX health research database
- First Published: 19 March 2024
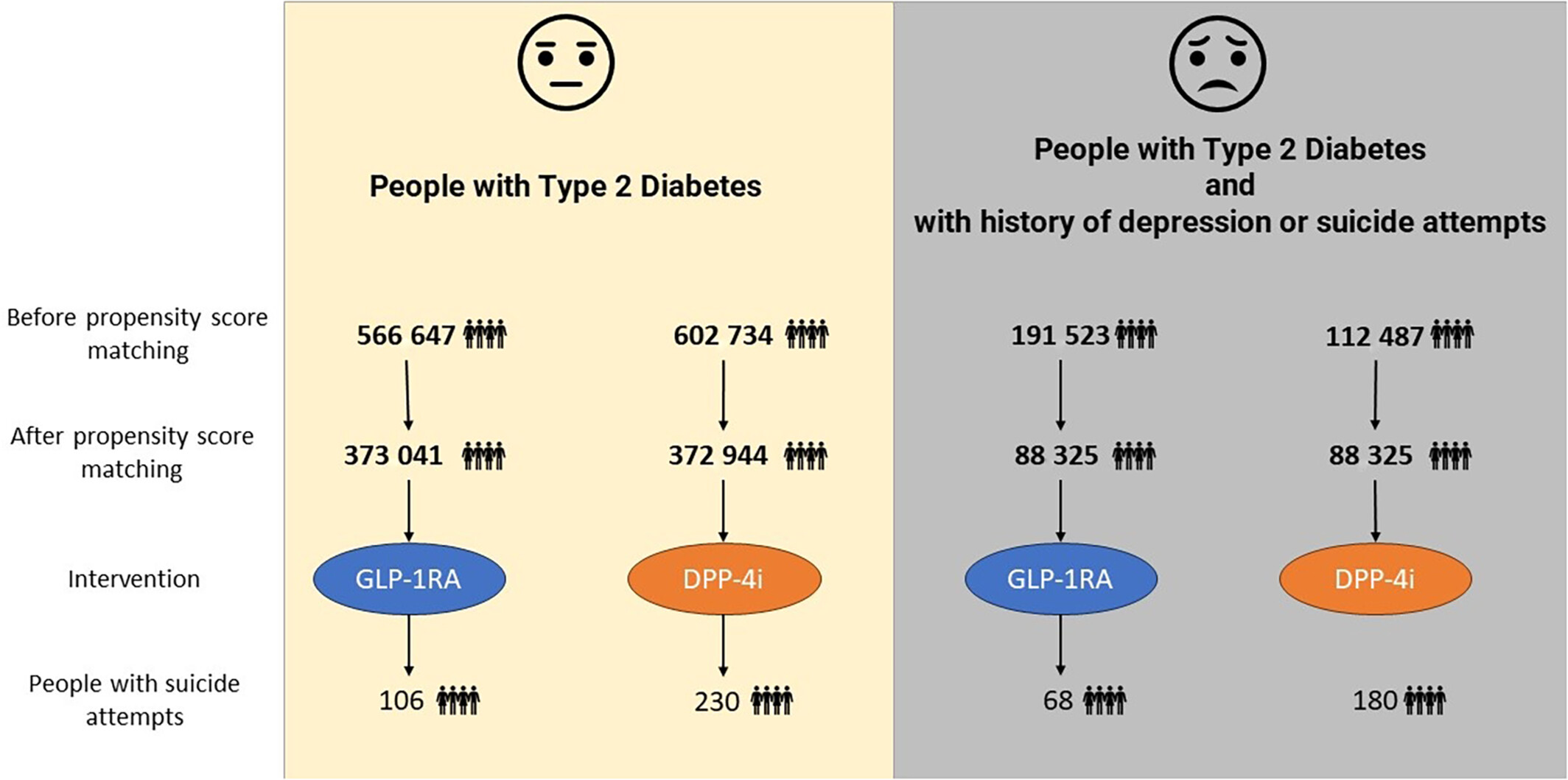
Highlights
- This retrospective cohort study utilized the TriNetX global database and showed that the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) is associated with lower suicide risk in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- Further, the use of GLP-1RA was particularly associated with lower suicide risk compared with the use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) in people with T2D with a history of depression or suicide attempts.
- Overall, based on these data, GLP-1RA might provide more protection for the risk of suicide attempts compared to DPP-4i in people with T2D.
Association between the skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017–2018
- First Published: 16 May 2024
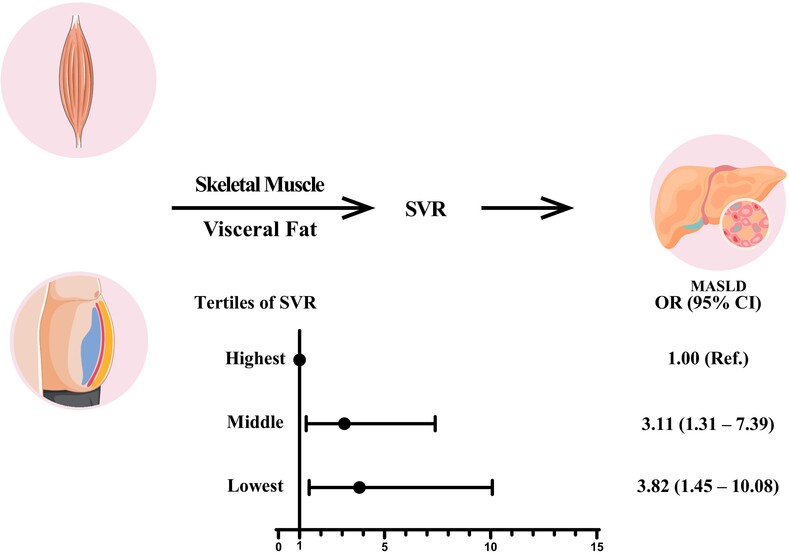
Highlights
- Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, our study is among the first to investigate the relationship between sarcopenic obesity, represented by the skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio (SVR), and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in the US population.
- Measurements for SVR were obtained using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, and MASLD was diagnosed with controlled attenuation parameter scores and cardiometabolic risk factors.
- The present study revealed that lower levels of SVR were strongly associated with an increased risk of MASLD.
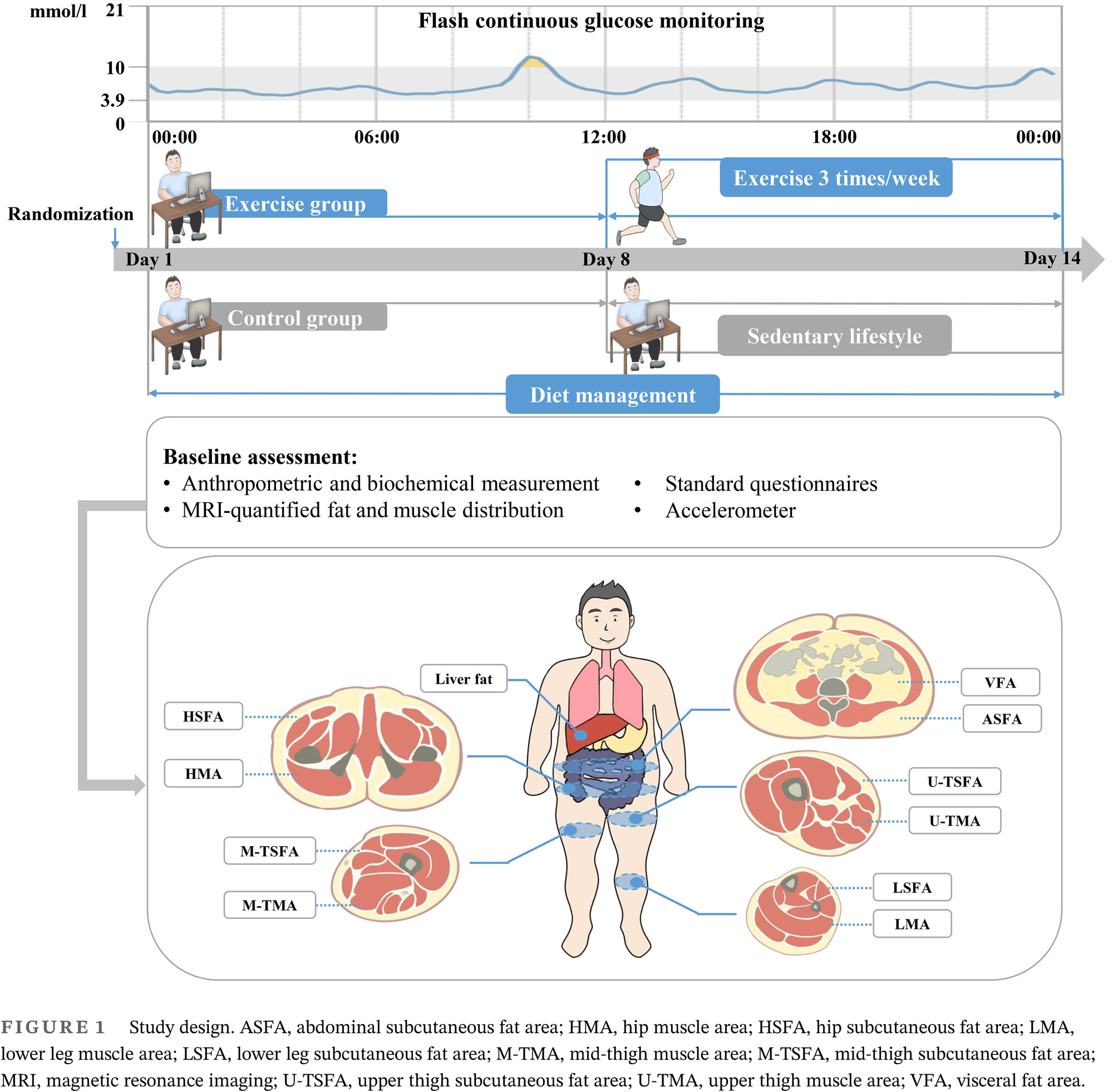
Exercise-induced improvement of glycemic fluctuation and its relationship with fat and muscle distribution in type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 07 April 2024
Acellular fish skin grafts in the treatment of diabetic wounds: Advantages and clinical translation
- First Published: 25 April 2024
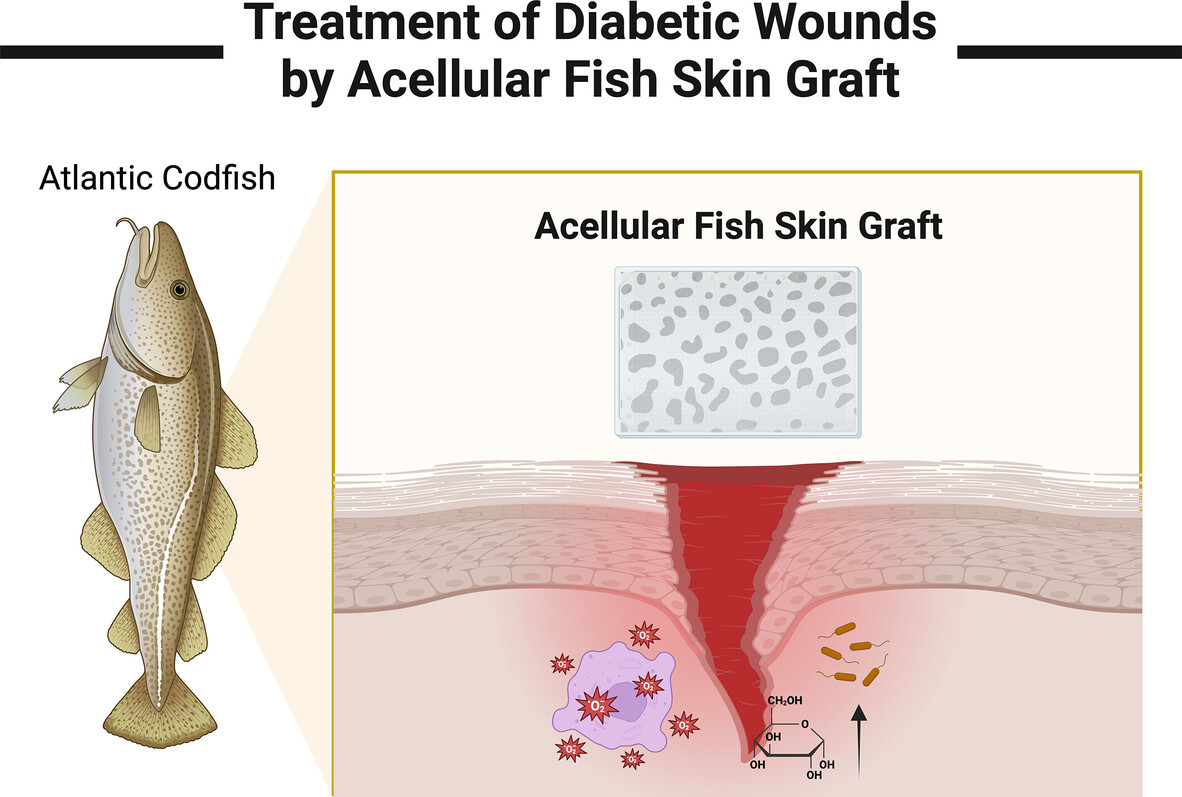
Highlights
- Concisely included the latest research on the role of acellular fish skin grafts (AFSGs) in treating diabetic wounds, providing readers with a basic framework,
- This review outlined the therapeutic advantages and prospects of AFSGs,
- This work emphasized the role of cost-effectiveness in the treatment of diabetic wound dressings.
- We summarized the shortcomings and corrective measures of current AFSGs clinical trials.
- We explored the resistance that may be encountered by AFSGs in various stages of clinical studies.
Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents: A 50-year, single-center experience
- First Published: 25 April 2024
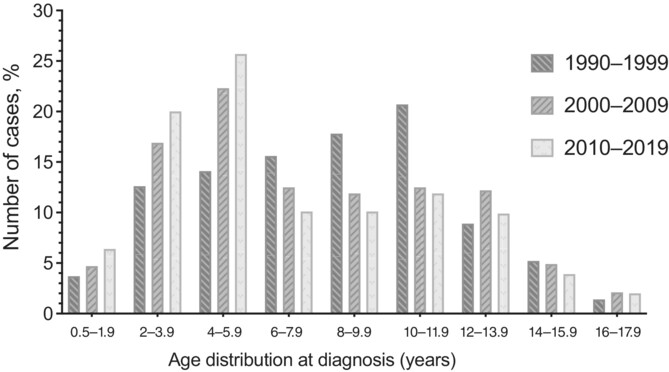
Highlights
- This study provides important data from a single quarternary reference center where cases with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) come from a wide range of geographical distribution over 50 years and may well reflect secular trends in T1DM in Turkey.
- The mean age at diagnosis was 9.5 ± 4.0 years from 1969 to 1990, and it significantly decreased to 7.1 ± 3.6 years over the subsequent 50 years. Similarly, age at diagnosis peaked at 12–14 years between 1969 and 1990, then fell to 10–11.9 years between 1990 and 1999, and to 4–5.9 years between 2000–2009 and 2010–2019.
- Although the percentage of patients diagnosed <6 years of age is gradually increasing, the percentage diagnosed between ages of 6 and 11.9 years is decreasing, and the percentage diagnosed ≥12 years remained stable.
- Approximately half of the patients had ketoacidosis at the time of diagnosis and the frequency of presentation with DKA did not decrease, but the severity decreased slightly.
- Although the frequency of patients with mild DKA increased over time, frequency of patients with moderate DKA decreased; however, no significant difference was observed among patients with severe ketoacidosis.
Optogenetic therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 16 May 2024
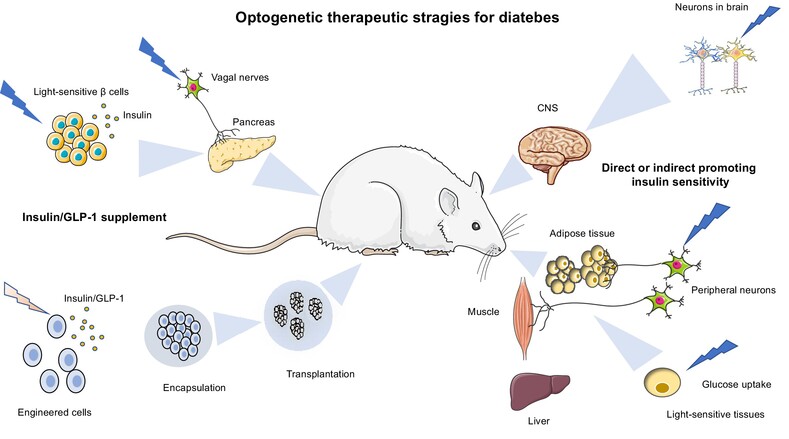
Highlights
- Optogenetics has become a new evolving therapeutic approach for diabetes.
- Synthetic cells with light-responsive modules for insulin/glucagon-like peptide-1 production have been developed to treat diabetes.
- Insulin-responsive tissues are targets of optogenetics, which works to lower blood glucose and alleviate insulin resistance.
- The latest development of optogenetics in diabetes treatment and the remaining challenges are summarized.
Recent drug development of dorzagliatin, a new glucokinase activator, with the potential to treat Type 2 diabetes: A review study
- First Published: 23 May 2024
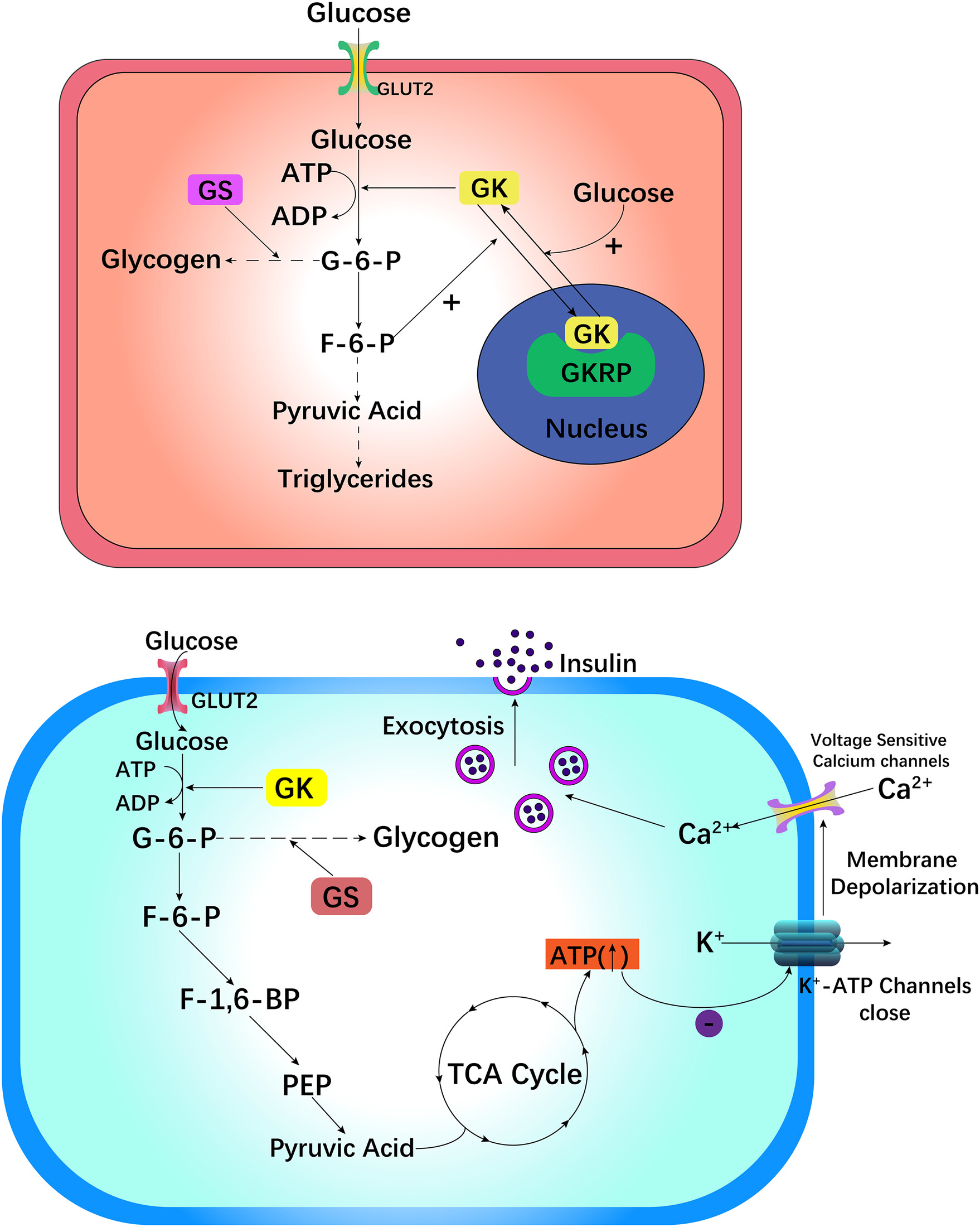
Highlights
- This article is a retrospective review article, aiming to briefly review the working principle of glucokinase (GK) and summarize the development of glucokinase activators (GKA), a new antidiabetes drug targeting GK. In this review, we focus on the development of the new GKA, dorzagliatin, and summarize the results of the latest controlled clinical trials of dorzagliatin. At the same time, we also point out the current limitations of dorzagliatin and the future development direction of dorzagliatin.
Association of obstructive sleep apnea symptoms with all-cause mortality and cause-specific mortality in adults with or without diabetes: A cohort study based on the NHANES
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
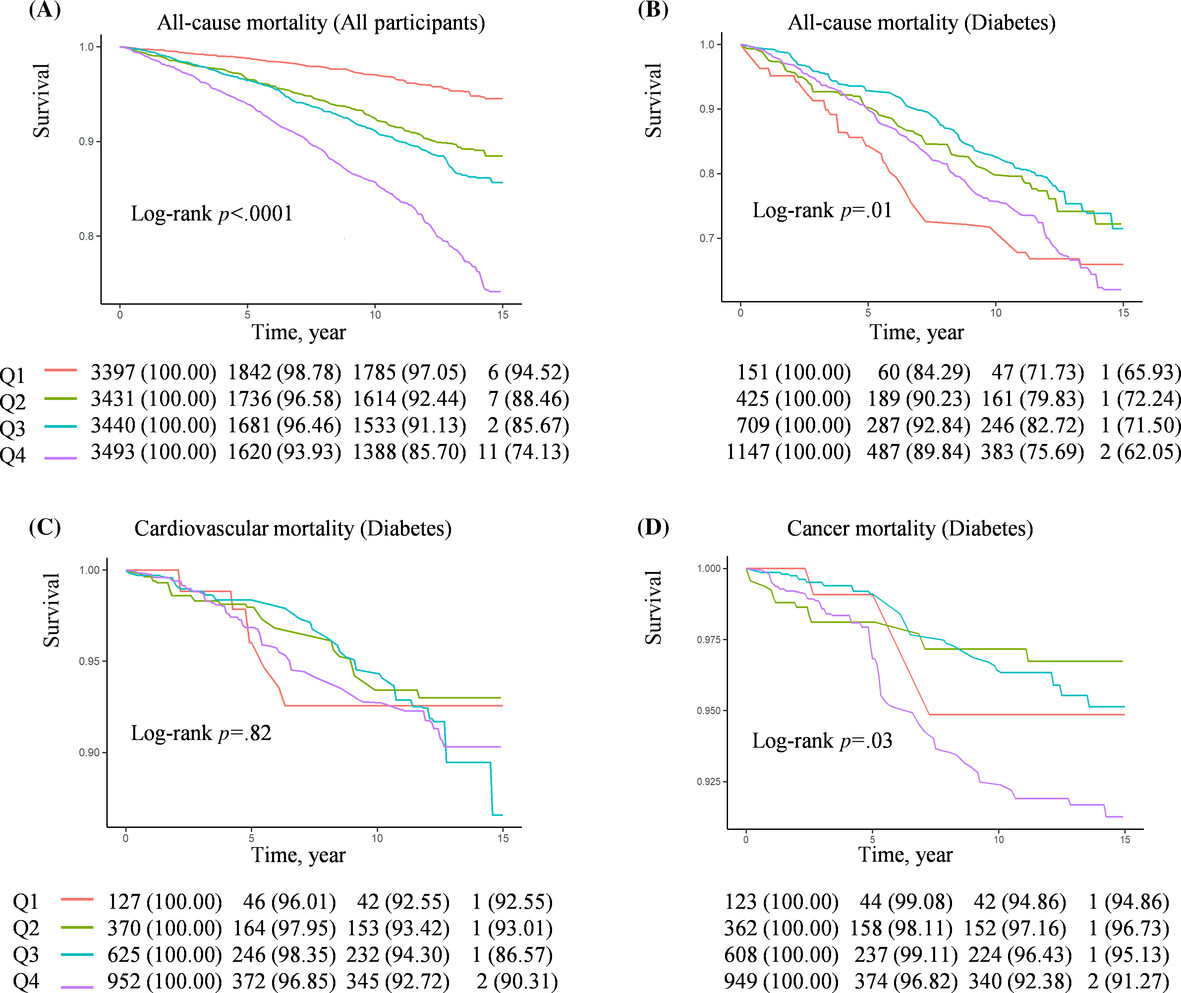
- The study examined the association between obstructive sleep apnea symptoms (OSAS) and all-cause as well as cause-specific mortality in US individuals with and without diabetes, utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
- Among patients without diabetes, OSAS was positively associated with all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality.
- For diabetes patients, the relationship between OSAS and the risk of all-cause mortality and cancer mortality exhibited L-shaped curves.
National burden and risk factors of diabetes mellitus in China from 1990 to 2021: Results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2021
- First Published: 07 October 2024
Highlights
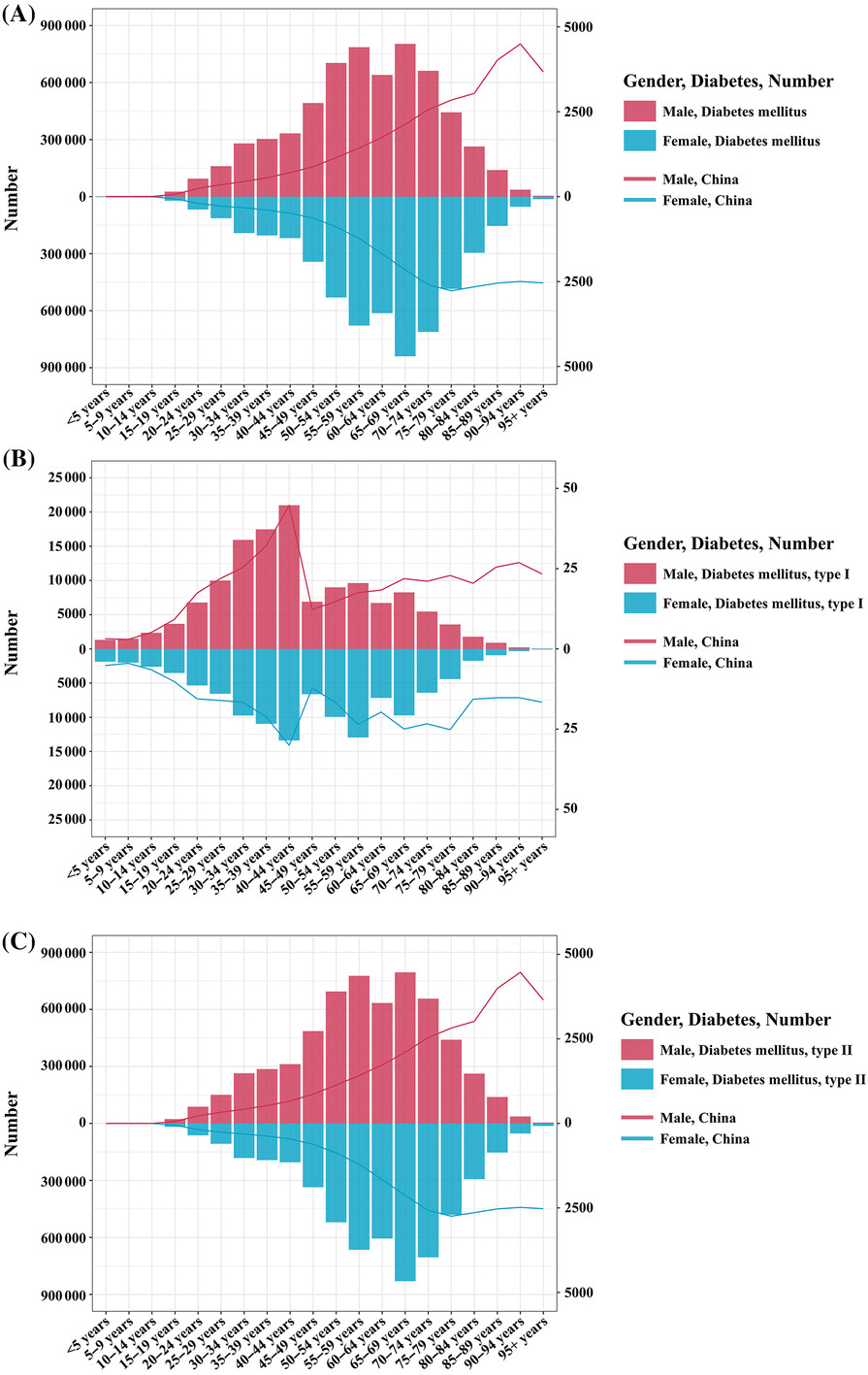
- The incidence, prevalence, and DALYs rate of diabetes in China are at relatively high levels, with a severe and rapidly growing burden of disability, particularly prominent among males.
- Interventions should be strengthened for major factors contributing to the diabetes burden, including high fasting plasma glucose, high body mass index, air pollution, and dietary risks.
Advanced multifunctional hydrogels for diabetic foot ulcer healing: Active substances and biological functions
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
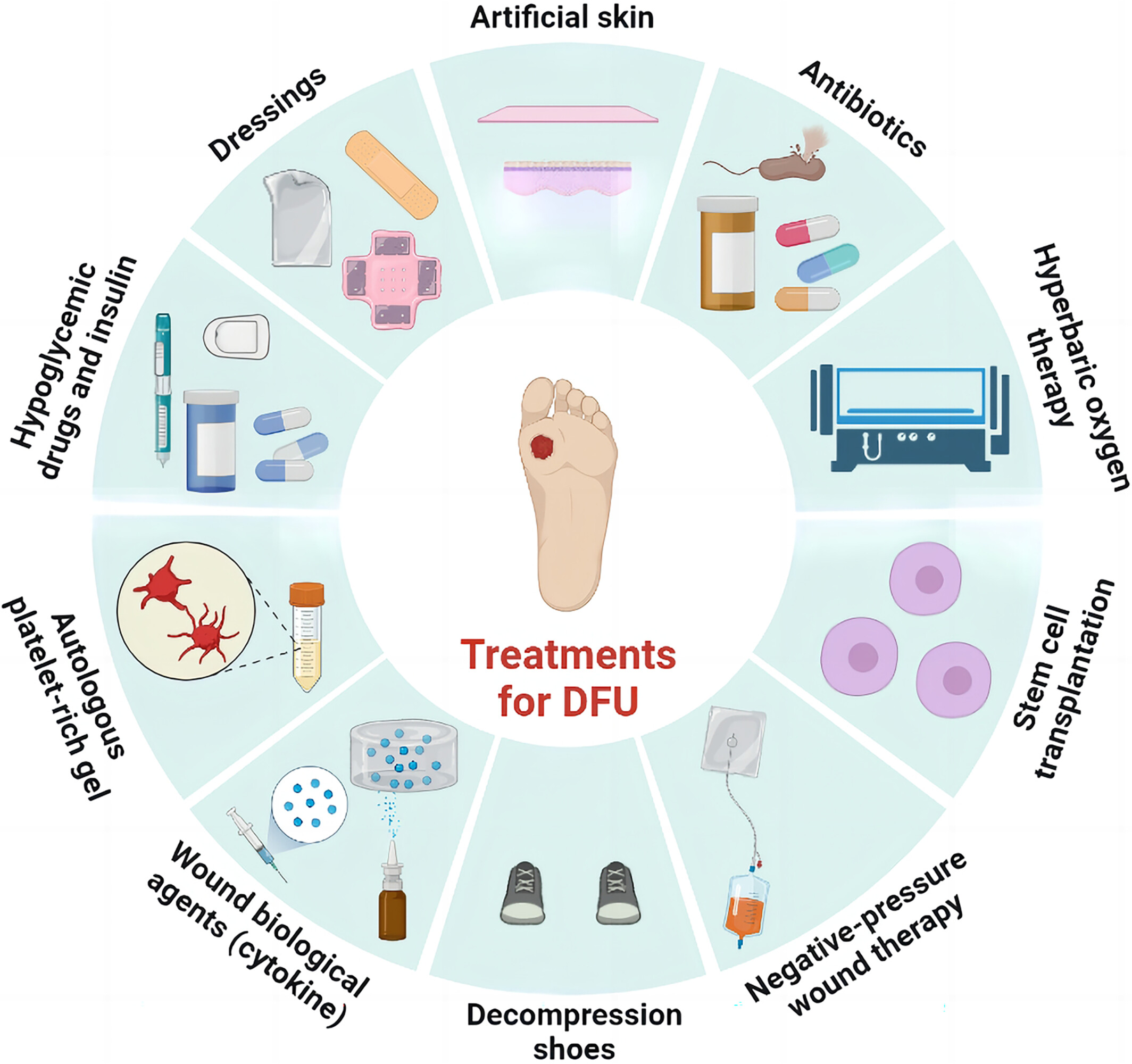
- A review was conducted of studies on the combination of hydrogels and diabetic foot ulcer pathogenesis.
- Various hydrogels were classified and elaborated based on their biological functions.
- The summary of biological functions provides guidance for future research and clinical application.
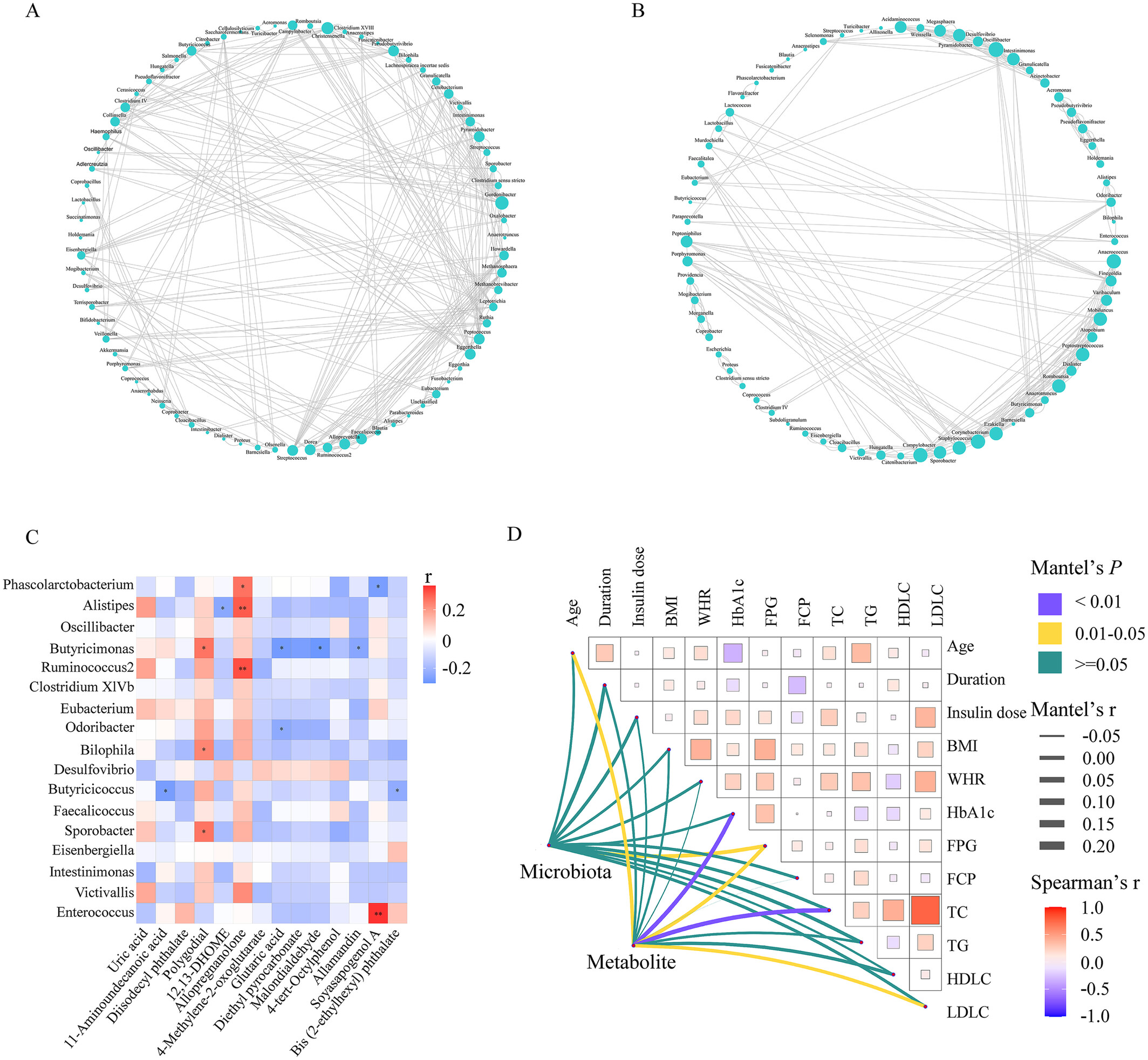
Microbial and metabolomic profiles of type 1 diabetes with depression: A case–control study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Estimated glucose disposal rate predicts the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: A 5-year follow-up study
- First Published: 15 January 2024
Highlights
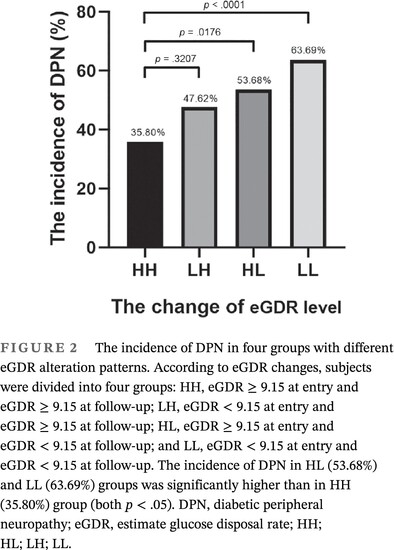
- After 5.91 years, 198 of 366 (54.1%) participants with type 2 diabetes progressed to diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
- Subjects with low baseline estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR < 9.15) had significantly higher risk of DPN at the end of follow-up (odds ratio = 1.75), even after adjusting for other known DPN risk factors.
- Diabetic patients with low eGDR are more prone to DPN and, therefore, require more intensive screening and more attention.
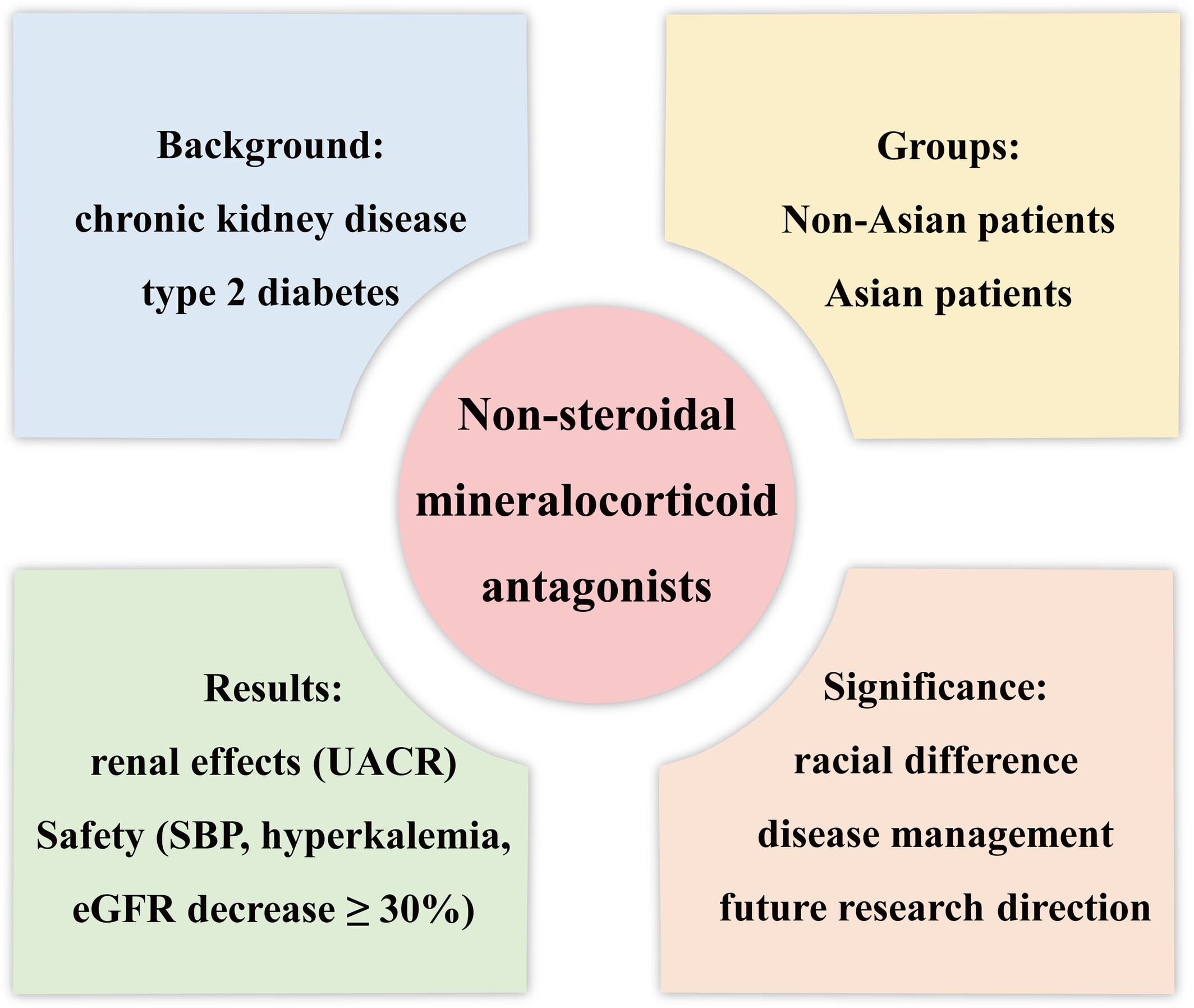
Renal effects and safety between Asian and non-Asian chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes treated with nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonists
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Highlights
Our study indicated that nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists decreased urinary albumin to creatinine ratio and systolic blood pressure significantly greater in Asian chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients than non-Asian patients. The average decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) did not show racial preference. However, hyperkalemia and eGFR decrease ≥ 30% occurred more frequently in Asians, which was acceptable without renal failure or death.
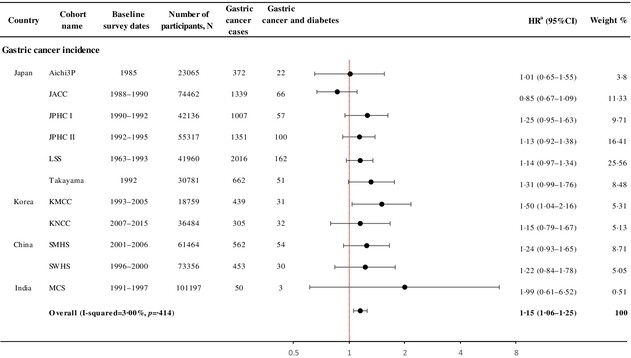
Diabetes and gastric cancer incidence and mortality in the Asia Cohort Consortium: A pooled analysis of more than a half million participants
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Highlights
- Having diabetes increased gastric cancer risk by 15%, and the risk increased during the first decade following diabetes diagnosis.
- Diabetes increases the risk of gastric cancer regardless of sex, anatomical subsite, or histological subtype.
- Given the substantial diabetes burden in Asia and other regions, our findings underline the importance of diabetes diagnosis and diabetes duration for gastric cancer prevention.
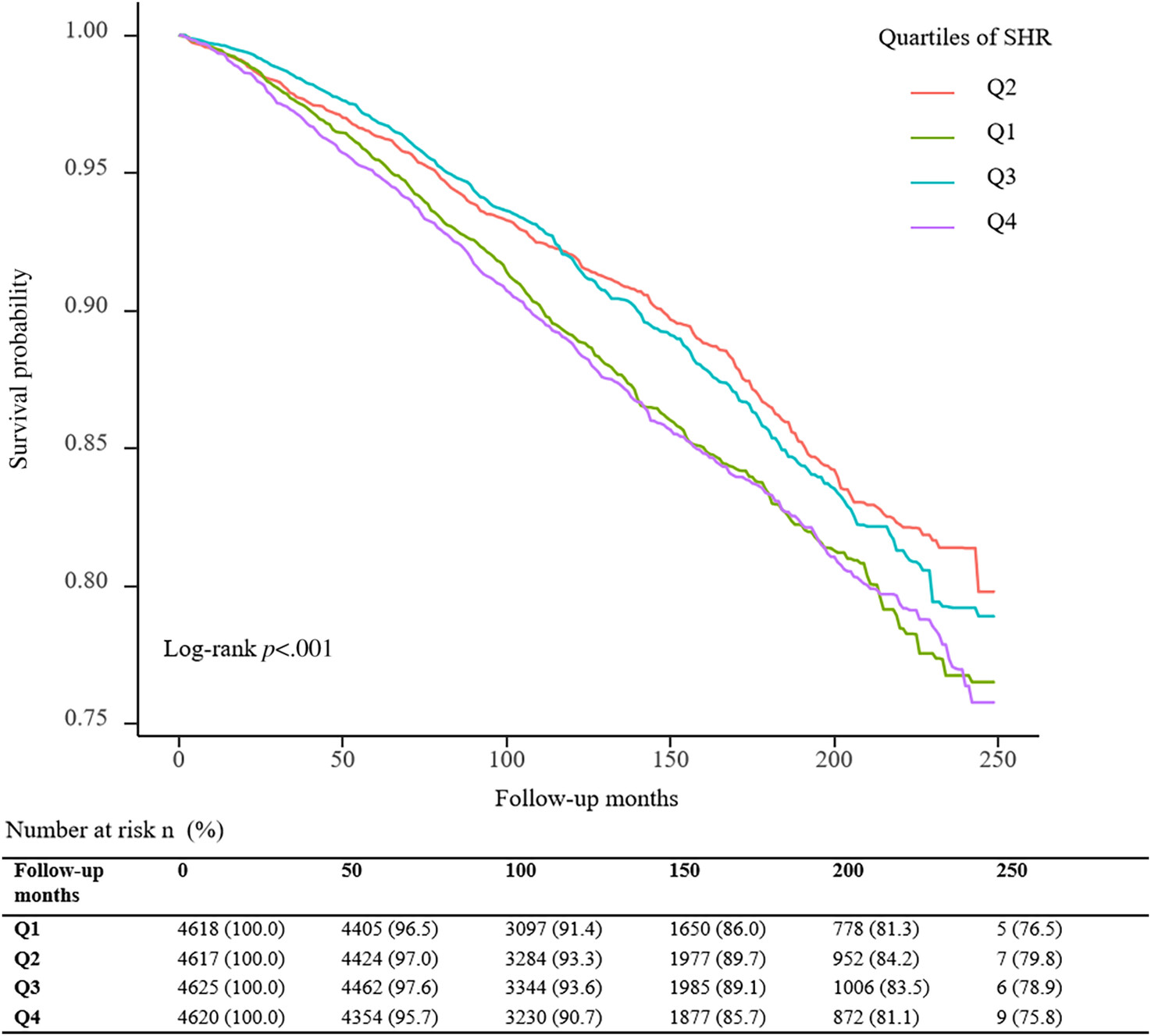
Association between the stress–hyperglycemia ratio and all-cause mortality in community-dwelling populations: An analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2014
- First Published: 20 May 2024
Highlights
- Based on 18 480 residents, our study found for the first time that the stress–hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) is significantly associated with all-cause mortality in community dwellers.
- SHR and all-cause mortality had a dose–response relationship, and the relationship was U shaped.
- After adjusting for the confounding factors, compared with subjects in the second SHR quartile (Q2), participants in the highest (Q4, adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.49, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.28–1.73) and lowest quartiles (Q1, adjusted HR 1.37, 95% CI 1.16–1.60) have a higher probability of all-cause death.
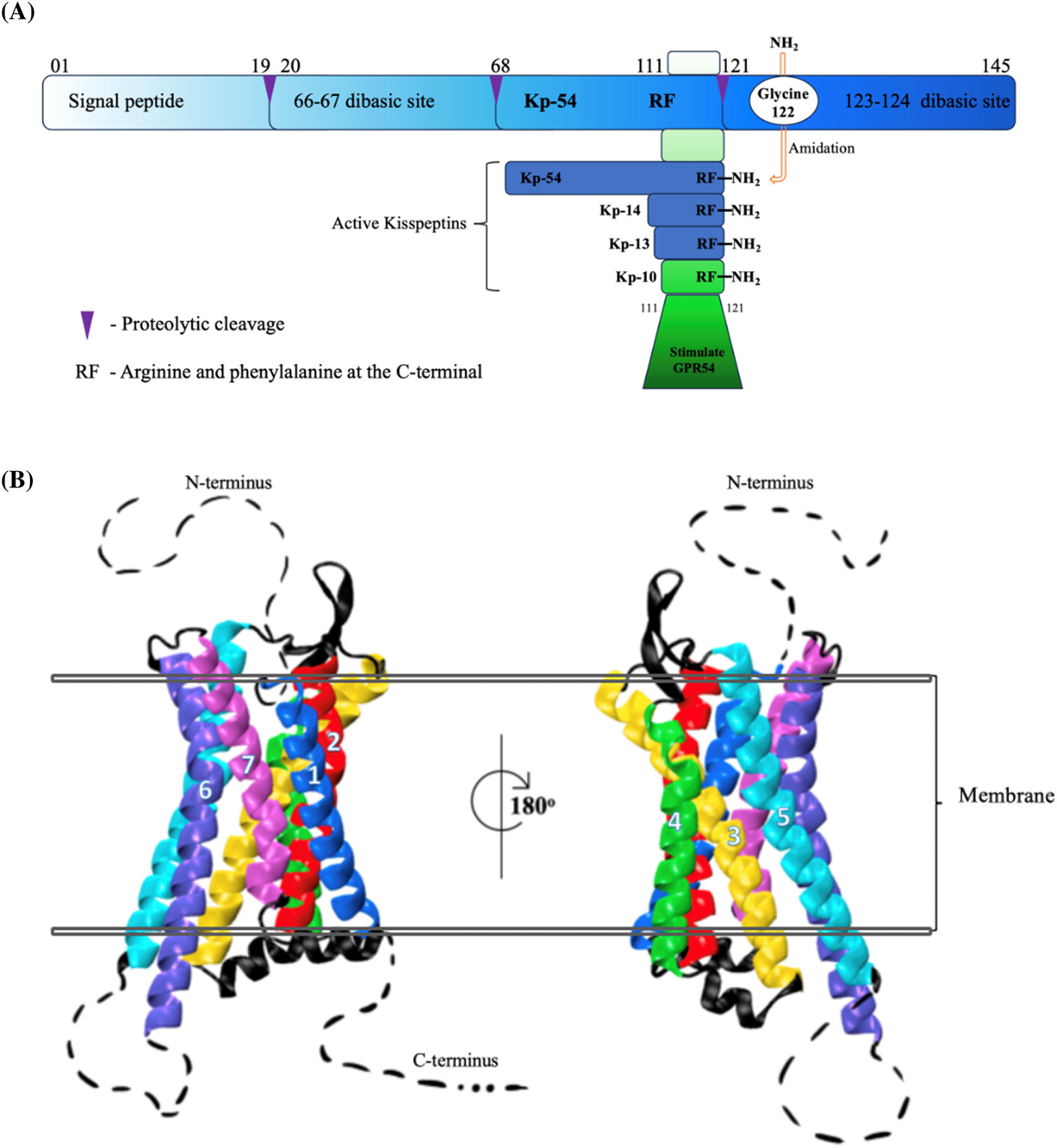
Kisspeptin a potential therapeutic target in treatment of both metabolic and reproductive dysfunction
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
- Kisspeptins (KPs) were first discovered to have antimetastatic action. Historically, a role in reproduction was demonstrated. Today, there is growing experimental and clinical evidence that KPs and their receptors regulate metabolism.
- Disruption of KP and receptor interaction provides an interesting approach to treating metabolic conditions, as well as reproductive disorders.
- Clinical trials have focused mainly on treating reproductive dysfunctions; however, greater understanding of the biology and mechanisms of action of KPs is being used in the therapeutic armory against insulin-related dysfunctions.
- Linkage between reproduction and metabolism via the KP system also allows for therapeutic targeting.