Optogenetic therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus
Xin Deng
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorDandan Peng
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYuanfa Yao
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorKe Huang
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJinling Wang
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhihao Ma
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Junfen Fu
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Correspondence
Junfen Fu, Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 3333 Binsheng Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310051, China.
Email: [email protected]
Yingke Xu, Department of Biomedical Engineering, 38 Zheda Road, Yuquan Campus, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yingke Xu
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Binjiang Institute of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Correspondence
Junfen Fu, Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 3333 Binsheng Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310051, China.
Email: [email protected]
Yingke Xu, Department of Biomedical Engineering, 38 Zheda Road, Yuquan Campus, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorXin Deng
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorDandan Peng
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorYuanfa Yao
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorKe Huang
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorJinling Wang
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorZhihao Ma
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Junfen Fu
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Correspondence
Junfen Fu, Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 3333 Binsheng Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310051, China.
Email: [email protected]
Yingke Xu, Department of Biomedical Engineering, 38 Zheda Road, Yuquan Campus, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Yingke Xu
Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, National Clinical Research Center for Child Health, Hangzhou, China
Department of Biomedical Engineering, MOE Key Laboratory of Biomedical Engineering, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Cardio-Cerebral Vascular Detection Technology and Medicinal Effectiveness Appraisal, Zhejiang Provincial Key Laboratory of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Clinical Evaluation and Translational Research, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Binjiang Institute of Zhejiang University, Hangzhou, China
Correspondence
Junfen Fu, Department of Endocrinology, Children's Hospital of Zhejiang University School of Medicine, 3333 Binsheng Road, Hangzhou, Zhejiang Province 310051, China.
Email: [email protected]
Yingke Xu, Department of Biomedical Engineering, 38 Zheda Road, Yuquan Campus, Zhejiang University, Hangzhou 310027, China.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorXin Deng and Dandan Peng contributed equally to this work.
Abstract
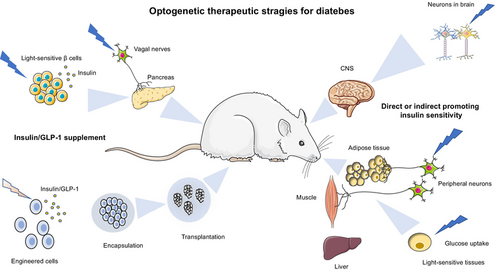
Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a common chronic disease affecting humans globally. It is characterized by abnormally elevated blood glucose levels due to the failure of insulin production or reduction of insulin sensitivity and functionality. Insulin and glucagon-like peptide (GLP)-1 replenishment or improvement of insulin resistance are the two major strategies to treat diabetes. Recently, optogenetics that uses genetically encoded light-sensitive proteins to precisely control cell functions has been regarded as a novel therapeutic strategy for diabetes. Here, we summarize the latest development of optogenetics and its integration with synthetic biology approaches to produce light-responsive cells for insulin/GLP-1 production, amelioration of insulin resistance and neuromodulation of insulin secretion. In addition, we introduce the development of cell encapsulation and delivery methods and smart bioelectronic devices for the in vivo application of optogenetics-based cell therapy in diabetes. The remaining challenges for optogenetics-based cell therapy in the clinical translational study are also discussed.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no competing interests. No human or animal studies involved or no ethical statement for the study.
REFERENCES
- 1Saeedi P, Petersohn I, Salpea P, et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2019; 157:107843. doi:10.1016/j.diabres.2019.107843
- 2Harding JL, Pavkov ME, Magliano DJ, Shaw JE, Gregg EW. Global trends in diabetes complications: a review of current evidence. Diabetologia. 2019; 62(1): 3-16. doi:10.1007/s00125-018-4711-2
- 3Eizirik DL, Pasquali L, Cnop M. Pancreatic β-cells in type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus: different pathways to failure. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2020; 16(7): 349-362. doi:10.1038/s41574-020-0355-7
- 4Taylor R. Type 2 diabetes: etiology and reversibility. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36(4): 1047-1055. doi:10.2337/dc12-1805
- 5Yaribeygi H, Farrokhi FR, Butler AE, Sahebkar A. Insulin resistance: review of the underlying molecular mechanisms. J Cell Physiol. 2019; 234(6): 8152-8161. doi:10.1002/jcp.27603
- 6Petersen MC, Shulman GI. Mechanisms of insulin action and insulin resistance. Physiol Rev. 2018; 98(4): 2133-2223. doi:10.1152/physrev.00063.2017
- 7Li H, Yao Y, Li L. Coumarins as potential antidiabetic agents. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2017; 69(10): 1253-1264. doi:10.1111/jphp.12774
- 8Beck RW, Bergenstal RM, Laffel LM, Pickup JC. Advances in technology for management of type 1 diabetes. Lancet. 2019; 394(10205): 1265-1273. doi:10.1016/s0140-6736(19)31142-0
- 9Moroder L, Musiol HJ. Insulin-from its discovery to the industrial synthesis of modern insulin analogues. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017; 56(36): 10656-10669. doi:10.1002/anie.201702493
- 10Bally L, Thabit H, Hartnell S, et al. Closed-loop insulin delivery for glycemic control in noncritical care. N Engl J Med. 2018; 379(6): 547-556. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1805233
- 11Foster NC, Beck RW, Miller KM, et al. State of type 1 diabetes management and outcomes from the T1D exchange in 2016–2018. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2019; 21(2): 66-72. doi:10.1089/dia.2018.0384
- 12Latres E, Finan DA, Greenstein JL, Kowalski A, Kieffer TJ. Navigating two roads to glucose normalization in diabetes: automated insulin delivery devices and cell therapy. Cell Metab. 2019; 29(3): 545-563. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2019.02.007
- 13Sneddon JB, Tang Q, Stock P, et al. Stem cell therapies for treating diabetes: Progress and remaining challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2018; 22(6): 810-823. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2018.05.016
- 14Melton D. The promise of stem cell-derived islet replacement therapy. Diabetologia. 2021; 64(5): 1030-1036. doi:10.1007/s00125-020-05367-2
- 15Sun ZY, Yu TY, Jiang FX, Wang W. Functional maturation of immature β cells: a roadblock for stem cell therapy for type 1 diabetes. World J Stem Cells. 2021; 13(3): 193-207. doi:10.4252/wjsc.v13.i3.193
- 16Cameron DE, Bashor CJ, Collins JJ. A brief history of synthetic biology. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2014; 12(5): 381-390. doi:10.1038/nrmicro3239
- 17Kitada T, DiAndreth B, Teague B, Weiss R. Programming gene and engineered-cell therapies with synthetic biology. Science. 2018; 359(6376):eaad1067. doi:10.1126/science.aad1067
- 18Scheller L, Fussenegger M. From synthetic biology to human therapy: engineered mammalian cells. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019; 58: 108-116. doi:10.1016/j.copbio.2019.02.023
- 19Deisseroth K. Optogenetics. Nat Methods. 2011; 8(1): 26-29. doi:10.1038/nmeth.f.324
- 20Chen R, Gore F, Nguyen QA, et al. Deep brain optogenetics without intracranial surgery. Nat Biotechnol. 2021; 39(2): 161-164. doi:10.1038/s41587-020-0679-9
- 21Mickle AD, Won SM, Noh KN, et al. A wireless closed-loop system for optogenetic peripheral neuromodulation. Nature. 2019; 565(7739): 361-365. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0823-6
- 22Kushibiki T. Current topics of Optogenetics for medical applications toward therapy. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021; 1293: 513-521. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_35
- 23Kleinlogel S, Vogl C, Jeschke M, Neef J, Moser T. Emerging approaches for restoration of hearing and vision. Physiol Rev. 2020; 100(4): 1467-1525. doi:10.1152/physrev.00035.2019
- 24Xu Y, Melia TJ, Toomre DK. Using light to see and control membrane traffic. Curr Opin Chem Biol. 2011; 15(6): 822-830. doi:10.1016/j.cbpa.2011.10.016
- 25Mansouri M, Strittmatter T, Fussenegger M. Light-controlled mammalian cells and their therapeutic applications in synthetic biology. Adv Sci. 2019; 6(1):1800952. doi:10.1002/advs.201800952
10.1002/advs.201800952 Google Scholar
- 26Leopold AV, Chernov KG, Verkhusha VV. Optogenetically controlled protein kinases for regulation of cellular signaling. Chem Soc Rev. 2018; 47(7): 2454-2484. doi:10.1039/c7cs00404d
- 27Häusser M. Optogenetics: the age of light. Nat Methods. 2014; 11(10): 1012-1014. doi:10.1038/nmeth.3111
- 28Repina NA, Rosenbloom A, Mukherjee A, Schaffer DV, Kane RS. At Light speed: advances in Optogenetic Systems for Regulating Cell Signaling and Behavior. Annu Rev Chem Biomol Eng. 2017; 8: 13-39. doi:10.1146/annurev-chembioeng-060816-101254
- 29Kato HE. Structure-function relationship of Channelrhodopsins. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021; 1293: 35-53. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_3
- 30Iwata T, Masuda S. Photoreaction mechanisms of Flavoprotein photoreceptors and their applications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021; 1293: 189-206. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_11
- 31Losi A, Gardner KH, Moglich A. Blue-Light receptors for Optogenetics. Chem Rev. 2018; 118(21): 10659-10709. doi:10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00163
- 32Padmanabhan S, Pérez-Castaño R, Elías-Arnanz M. B(12)-based photoreceptors: from structure and function to applications in optogenetics and synthetic biology. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2019; 57: 47-55. doi:10.1016/j.sbi.2019.01.020
- 33Wilson A, Punginelli C, Gall A, et al. A photoactive carotenoid protein acting as light intensity sensor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2008; 105(33): 12075-12080. doi:10.1073/pnas.0804636105
- 34Padmanabhan S, Jost M, Drennan CL, Elías-Arnanz M. A new facet of vitamin B(12): gene regulation by cobalamin-based photoreceptors. Annu Rev Biochem. 2017; 86: 485-514. doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-061516-044500
- 35Kramer MM, Lataster L, Weber W, Radziwill G. Optogenetic approaches for the spatiotemporal control of signal transduction pathways. Int J Mol Sci. 2021; 22(10): 5300. doi:10.3390/ijms22105300
- 36Kichuk TC, Carrasco-López C, Avalos JL. Lights up on organelles: Optogenetic tools to control subcellular structure and organization. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med. 2021; 13(1):e1500. doi:10.1002/wsbm.1500
- 37Guntas G, Hallett RA, Zimmerman SP, et al. Engineering an improved light-induced dimer (iLID) for controlling the localization and activity of signaling proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2015; 112(1): 112-117. doi:10.1073/pnas.1417910112
- 38Niopek D, Wehler P, Roensch J, Eils R, Di Ventura B. Optogenetic control of nuclear protein export. Nat Commun. 2016; 7: 10624. doi:10.1038/ncomms10624
- 39Zhou XX, Fan LZ, Li P, Shen K, Lin MZ. Optical control of cell signaling by single-chain photoswitchable kinases. Science. 2017; 355(6327): 836-842. doi:10.1126/science.aah3605
- 40Kainrath S, Stadler M, Reichhart E, Distel M, Janovjak H. Green-Light-induced inactivation of receptor signaling using cobalamin-binding domains. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2017; 56(16): 4608-4611. doi:10.1002/anie.201611998
- 41Manoilov KY, Verkhusha VV, Shcherbakova DM. A guide to the optogenetic regulation of endogenous molecules. Nat Methods. 2021; 18: 1027-1037. doi:10.1038/s41592-021-01240-1
- 42Campbell JE, Newgard CB. Mechanisms controlling pancreatic islet cell function in insulin secretion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2021; 22(2): 142-158. doi:10.1038/s41580-020-00317-7
- 43Kalwat MA, Cobb MH. Mechanisms of the amplifying pathway of insulin secretion in the β cell. Pharmacol Ther. 2017; 179: 17-30. doi:10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.05.003
- 44Kushibiki T, Okawa S, Hirasawa T, Ishihara M. Optogenetic control of insulin secretion by pancreatic β-cells in vitro and in vivo. Gene Ther. 2015; 22(7): 553-559. doi:10.1038/gt.2015.23
- 45Zhang F, Tzanakakis ES. Amelioration of diabetes in a murine model upon transplantation of pancreatic β-cells with Optogenetic control of cyclic adenosine monophosphate. ACS Synth Biol. 2019; 8(10): 2248-2255. doi:10.1021/acssynbio.9b00262
- 46Shao J, Xue S, Yu G, et al. Smartphone-controlled optogenetically engineered cells enable semiautomatic glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice. Sci Transl Med. 2017; 9(387):eaal2298. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aal2298
- 47Reinbothe TM, Safi F, Axelsson AS, Mollet IG, Rosengren AH. Optogenetic control of insulin secretion in intact pancreatic islets with β-cell-specific expression of Channelrhodopsin-2. Islets. 2014; 6(1):e28095. doi:10.4161/isl.28095
- 48Broichhagen J, Schönberger M, Cork SC, et al. Optical control of insulin release using a photoswitchable sulfonylurea. Nat Commun. 2014; 5: 5116. doi:10.1038/ncomms6116
- 49Choi J, Shin E, Lee J, et al. Light-stimulated insulin secretion from pancreatic islet-like organoids derived from human pluripotent stem cells. Mol Ther. 2023; 31(5): 1480-1495. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2023.03.013
- 50Tengholm A, Gylfe E. cAMP signalling in insulin and glucagon secretion. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2017; 19(Suppl 1): 42-53. doi:10.1111/dom.12993
- 51Iseki M, Park SY. Photoactivated adenylyl Cyclases: fundamental properties and applications. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021; 1293: 129-139. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_7
- 52Zhang F, Tzanakakis ES. Optogenetic regulation of insulin secretion in pancreatic β-cells. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):9357. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-09937-0
- 53Ye H, Daoud-El Baba M, Peng RW, Fussenegger M. A synthetic optogenetic transcription device enhances blood-glucose homeostasis in mice. Science. 2011; 332(6037): 1565-1568. doi:10.1126/science.1203535
- 54Müller K, Naumann S, Weber W, Zurbriggen MD. Optogenetics for gene expression in mammalian cells. Biol Chem. 2015; 396(2): 145-152. doi:10.1515/hsz-2014-0199
- 55Zhou Y, Kong D, Wang X, et al. A small and highly sensitive red/far-red optogenetic switch for applications in mammals. Nat Biotechnol. 2021; 40: 262-272. doi:10.1038/s41587-021-01036-w
- 56Yu G, Zhang M, Gao L, et al. Far-red light-activated human islet-like designer cells enable sustained fine-tuned secretion of insulin for glucose control. Mol Ther. 2022; 30(1): 341-354. doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.09.004
- 57Wang X, Chen X, Yang Y. Spatiotemporal control of gene expression by a light-switchable transgene system. Nat. Methods. 2012; 9(3): 266-269. doi:10.1038/nmeth.1892
- 58Mansouri M, Hussherr MD, Strittmatter T, et al. Smart-watch-programmed green-light-operated percutaneous control of therapeutic transgenes. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1): 3388. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23572-4
- 59Li CY, Wu T, Zhao XJ, et al. A glucose-blue light AND gate-controlled chemi-optogenetic cell-implanted therapy for treating type-1 diabetes in mice. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023; 11:1052607. doi:10.3389/fbioe.2023.1052607
- 60Ash C, Dubec M, Donne K, Bashford T. Effect of wavelength and beam width on penetration in light-tissue interaction using computational methods. Lasers Med Sci. 2017; 32(8): 1909-1918. doi:10.1007/s10103-017-2317-4
- 61Xu Y, Xia N, Lim M, et al. Multichannel optrodes for photonic stimulation. Neurophotonics. 2018; 5(4):045002. doi:10.1117/1.NPh.5.4.045002
- 62Dieter A, Klein E, Keppeler D, et al. μLED-based optical cochlear implants for spectrally selective activation of the auditory nerve. EMBO Mol Med. 2020; 12(8):e12387. doi:10.15252/emmm.202012387
- 63Chen S, Weitemier AZ, Zeng X, et al. Near-infrared deep brain stimulation via upconversion nanoparticle-mediated optogenetics. Science. 2018; 359(6376): 679-684. doi:10.1126/science.aaq1144
- 64Lin Y, Yao Y, Zhang W, et al. Applications of upconversion nanoparticles in cellular optogenetics. Acta Biomater. 2021; 135: 1-12. doi:10.1016/j.actbio.2021.08.035
- 65All AH, Zeng X, Teh DBL, et al. Expanding the toolbox of Upconversion nanoparticles for in vivo Optogenetics and Neuromodulation. Advanced Materials (Deerfield Beach, Fla). 2019; 31(41):e1803474. doi:10.1002/adma.201803474
- 66Berglund K, Stern MA, Gross RE. Bioluminescence-Optogenetics. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021; 1293: 281-293. doi:10.1007/978-981-15-8763-4_17
- 67Love AC, Prescher JA. Seeing (and using) the Light: recent developments in bioluminescence technology. Cell Chemical Biology. 2020; 27(8): 904-920. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.07.022
- 68Li T, Chen X, Qian Y, et al. A synthetic BRET-based optogenetic device for pulsatile transgene expression enabling glucose homeostasis in mice. Nat Commun. 2021; 12(1): 615. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-20913-1
- 69Mansouri M, Xue S, Hussherr MD, Strittmatter T, Camenisch G, Fussenegger M. Smartphone-flashlight-mediated remote control of rapid insulin secretion restores glucose homeostasis in experimental type-1 diabetes. Small. 2021; 17: e2101939. doi:10.1002/smll.202101939
- 70Czech MP. Insulin action and resistance in obesity and type 2 diabetes. Nat Med. 2017; 23(7): 804-814. doi:10.1038/nm.4350
- 71Qi YK, Chen JY, Liu XC, et al. Development of a wireless-controlled LED Array for the tunable Optogenetic control of cellular activities. Engineering. 2018; 4(6): 745-747. doi:10.1016/j.eng.2018.08.005
- 72Yan J, Li CX, Liu J. Remotely ameliorating blood glucose levels in type 2 diabetes via a near-infrared laser. Adv Funct Mater. 2021; 31(8):2007215. doi:10.1002/adfm.202007215
- 73Xu Y, Nan D, Fan J, Bogan JS, Toomre D. Optogenetic activation reveals distinct roles of PIP3 and Akt in adipocyte insulin action. J Cell Sci. 2016; 129(10): 2085-2095. doi:10.1242/jcs.174805
- 74Czech MP. Mechanisms of insulin resistance related to white, beige, and brown adipocytes. Mol. Metab. 2020; 34: 27-42. doi:10.1016/j.molmet.2019.12.014
- 75Betz MJ, Enerbäck S. Targeting thermogenesis in brown fat and muscle to treat obesity and metabolic disease. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2018; 14(2): 77-87. doi:10.1038/nrendo.2017.132
- 76Sato M, Tsuji T, Yang K, et al. Cell-autonomous light sensitivity via Opsin3 regulates fuel utilization in brown adipocytes. PLoS Biol. 2020; 18(2):e3000630. doi:10.1371/journal.pbio.3000630
- 77Zhang KX, D'Souza S, Upton BA, et al. Violet-light suppression of thermogenesis by opsin 5 hypothalamic neurons. Nature. 2020; 585(7825): 420-425. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2683-0
- 78Tajima K, Ikeda K, Tanabe Y, et al. Wireless optogenetics protects against obesity via stimulation of non-canonical fat thermogenesis. Nat Commun. 2020; 11(1): 1730. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-15589-y
- 79Ondrusova K, Fatehi M, Barr A, et al. Subcutaneous white adipocytes express a light sensitive signaling pathway mediated via a melanopsin/TRPC channel axis. Sci Rep. 2017; 7(1):16332. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-16689-4
- 80Steinbusch L, Labouèbe G, Thorens B. Brain glucose sensing in homeostatic and hedonic regulation. Trends Endocrinol Metab. 2015; 26(9): 455-466. doi:10.1016/j.tem.2015.06.005
- 81Schwartz MW, Seeley RJ, Tschöp MH, et al. Cooperation between brain and islet in glucose homeostasis and diabetes. Nature. 2013; 503(7474): 59-66. doi:10.1038/nature12709
- 82Timper K, Brüning JC. Hypothalamic circuits regulating appetite and energy homeostasis: pathways to obesity. Dis Model Mech. 2017; 10(6): 679-689. doi:10.1242/dmm.026609
- 83Dodd GT, Kim SJ, Méquinion M, et al. Insulin signaling in AgRP neurons regulates meal size to limit glucose excursions and insulin resistance. Sci. Adv. 2021; 7(9):eabf4100. doi:10.1126/sciadv.abf4100
- 84Deem JD, Muta K, Scarlett JM, Morton GJ, Schwartz MW. How should we think about the role of the brain in glucose homeostasis and diabetes? Diabetes. 2017; 66(7): 1758-1765. doi:10.2337/dbi16-0067
- 85Meek TH, Nelson JT, Matsen ME, et al. Functional identification of a neurocircuit regulating blood glucose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016; 113(14): E2073-E2082. doi:10.1073/pnas.1521160113
- 86Ter Horst KW, Lammers NM, Trinko R, et al. Striatal dopamine regulates systemic glucose metabolism in humans and mice. Sci Transl Med. 2018; 10(442):eaar3752. doi:10.1126/scitranslmed.aar3752
- 87Steculorum SM, Ruud J, Karakasilioti I, et al. AgRP neurons control systemic insulin sensitivity via Myostatin expression in Brown adipose tissue. Cell. 2016; 165(1): 125-138. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.044
- 88Fontaine AK, Ramirez DG, Littich SF, et al. Optogenetic stimulation of cholinergic fibers for the modulation of insulin and glycemia. Sci Rep. 2021; 11(1): 3670. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-83361-3
- 89Kawana Y, Imai J, Morizawa YM, et al. Optogenetic stimulation of vagal nerves for enhanced glucose-stimulated insulin secretion and β cell proliferation. Nat Biomed Eng. 2023. doi:10.1038/s41551-023-01113-2
- 90Lyons CE, Razzoli M, Larson E, et al. Optogenetic-induced sympathetic neuromodulation of brown adipose tissue thermogenesis. FASEB J. 2020; 34(2): 2765-2773. doi:10.1096/fj.201901361RR
- 91Jeong JH, Chang JS, Jo YH. Intracellular glycolysis in brown adipose tissue is essential for optogenetically induced nonshivering thermogenesis in mice. Sci Rep. 2018; 8(1): 6672. doi:10.1038/s41598-018-25265-3
- 92Tamayo A, Gonçalves LM, Rodriguez-Diaz R, et al. Pericyte control of blood flow in intraocular islet grafts impacts glucose homeostasis in mice. Diabetes. 2022; 71(8): 1679-1693. doi:10.2337/db21-1104
- 93Michau A, Lafont C, Bargi-Souza P, et al. Metabolic stress impairs Pericyte response to Optogenetic stimulation in pancreatic islets. Front Endocrinol. 2022; 13:918733. doi:10.3389/fendo.2022.918733
- 94Morrish NJ, Wang SL, Stevens LK, Fuller JH, Keen H. Mortality and causes of death in the WHO multinational study of vascular disease in diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001; 44(Suppl 2): S14-S21. doi:10.1007/pl00002934
- 95Forbes JM, Cooper ME. Mechanisms of diabetic complications. Physiol Rev. 2013; 93(1): 137-188. doi:10.1152/physrev.00045.2011
- 96Ivanova E, Bianchimano P, Corona C, Eleftheriou CG, Sagdullaev BT. Optogenetic stimulation of cholinergic Amacrine cells improves capillary blood flow in diabetic retinopathy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2020; 61(10): 44. doi:10.1167/iovs.61.10.44
- 97Samsu N. Diabetic nephropathy: challenges in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and treatment. Biomed Res Int. 2021; 2021:1497449. doi:10.1155/2021/1497449
- 98Kimbrel EA, Lanza R. Next-generation stem cells - ushering in a new era of cell-based therapies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2020; 19(7): 463-479. doi:10.1038/s41573-020-0064-x
- 99Yamanaka S. Pluripotent stem cell-based cell therapy-promise and challenges. Cell Stem Cell. 2020; 27(4): 523-531. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2020.09.014
- 100Cubillos-Ruiz A, Guo T, Sokolovska A, et al. Engineering living therapeutics with synthetic biology. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2021; 20(12): 941-960. doi:10.1038/s41573-021-00285-3
- 101Desai T, Shea LD. Advances in islet encapsulation technologies. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017; 16(5): 338-350. doi:10.1038/nrd.2016.232
- 102Orive G, Santos E, Poncelet D, et al. Cell encapsulation: technical and clinical advances. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 36(8): 537-546. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2015.05.003
- 103Farina M, Alexander JF, Thekkedath U, Ferrari M, Grattoni A. Cell encapsulation: overcoming barriers in cell transplantation in diabetes and beyond. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2019; 139: 92-115. doi:10.1016/j.addr.2018.04.018
- 104Orive G, Hernández RM, Gascón AR, et al. Cell encapsulation: promise and progress. Nat Med. 2003; 9(1): 104-107. doi:10.1038/nm0103-104
- 105Fang Y, Meng L, Prominski A, Schaumann EN, Seebald M, Tian B. Recent advances in bioelectronics chemistry. Chem Soc Rev. 2020; 49(22): 7978-8035. doi:10.1039/d0cs00333f
- 106Yu G, Yu Y, Ye H. Constructing a smartphone-controlled semiautomatic Theranostic system for glucose homeostasis in diabetic mice. Methods Mol Biol. 2021; 2312: 141-158. doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-1441-9_9
- 107Folcher M, Oesterle S, Zwicky K, et al. Mind-controlled transgene expression by a wireless-powered optogenetic designer cell implant. Nat Commun. 2014; 5: 5392. doi:10.1038/ncomms6392
- 108Liu Z, Zhou Y, Qu X, et al. A self-powered Optogenetic system for implantable blood glucose control. Research. 2022; 2022:9864734. doi:10.34133/2022/9864734
- 109Ye H, Fussenegger M. Optogenetic medicine: synthetic therapeutic solutions precision-guided by light. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2019; 9(9):a034371. doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a034371
- 110Bansal A, Shikha S, Zhang Y. Towards translational optogenetics. Nat Biomed Eng. 2023; 7(4): 349-369. doi:10.1038/s41551-021-00829-3
- 111Ceriello A, Prattichizzo F, Phillip M, Hirsch IB, Mathieu C, Battelino T. Glycaemic management in diabetes: old and new approaches. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022; 10(1): 75-84. doi:10.1016/s2213-8587(21)00245-x
- 112Tan P, He L, Huang Y, Zhou Y. Optophysiology: illuminating cell physiology with optogenetics. Physiol Rev. 2022; 102(3): 1263-1325. doi:10.1152/physrev.00021.2021