Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARIES
Commentary on the T1D exchange quality improvement collaborative learning session November 2023 abstracts
- First Published: 17 January 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
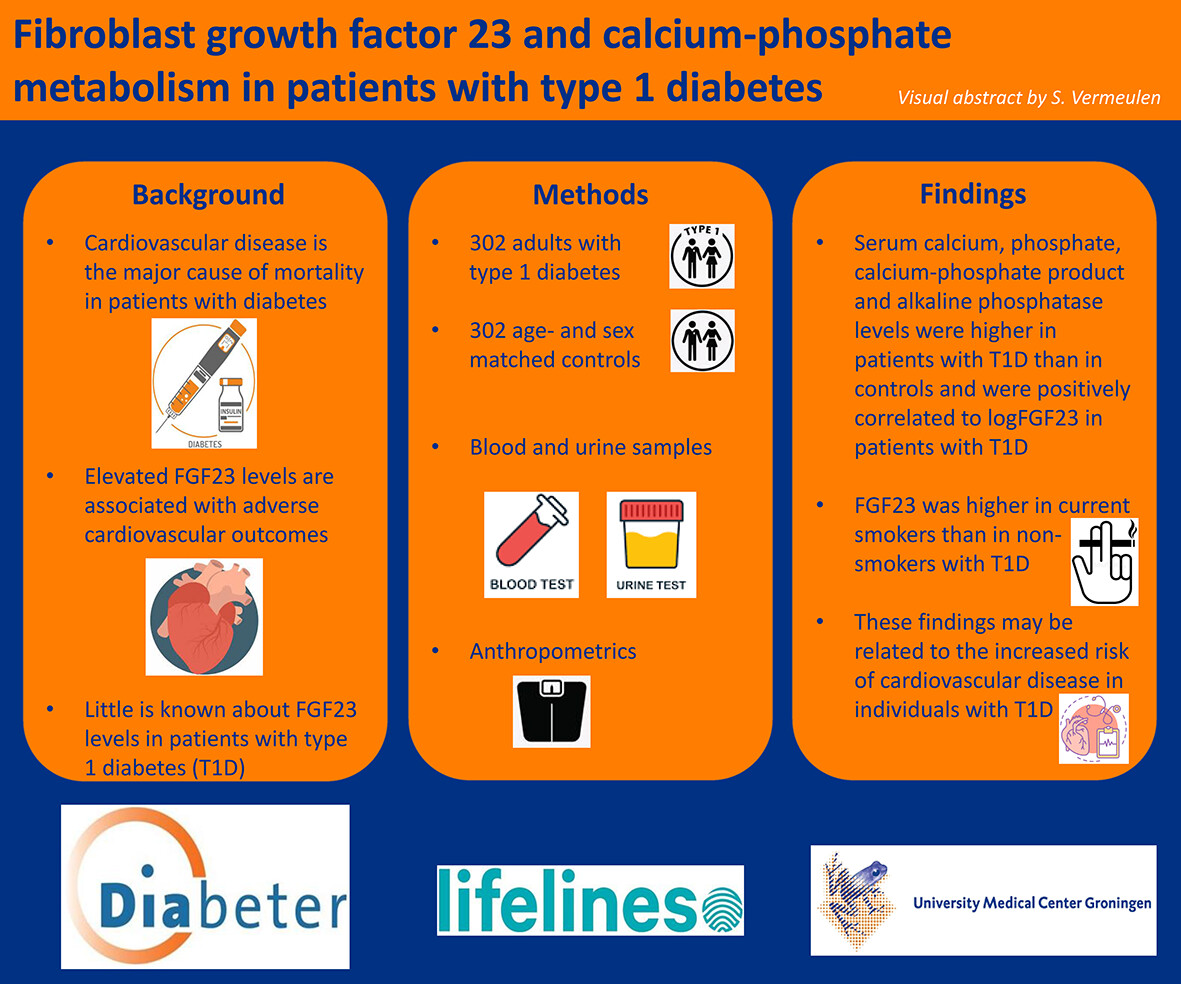
Fibroblast growth factor 23 and calcium-phosphate metabolism in relation to cardiovascular risk factors in patients with type 1 diabetes
- First Published: 20 December 2023
Highlights
- Serum calcium, phosphate, calcium-phosphate product and alkaline phosphatase levels were significantly higher in adult patients with type 1 diabetes (T1D) than in controls and were positively correlated to fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) in patients with T1D. FGF23 was higher in current smokers than in nonsmokers with T1D. These findings may be related to the increased risk of cardiovascular disease in individuals with T1D.
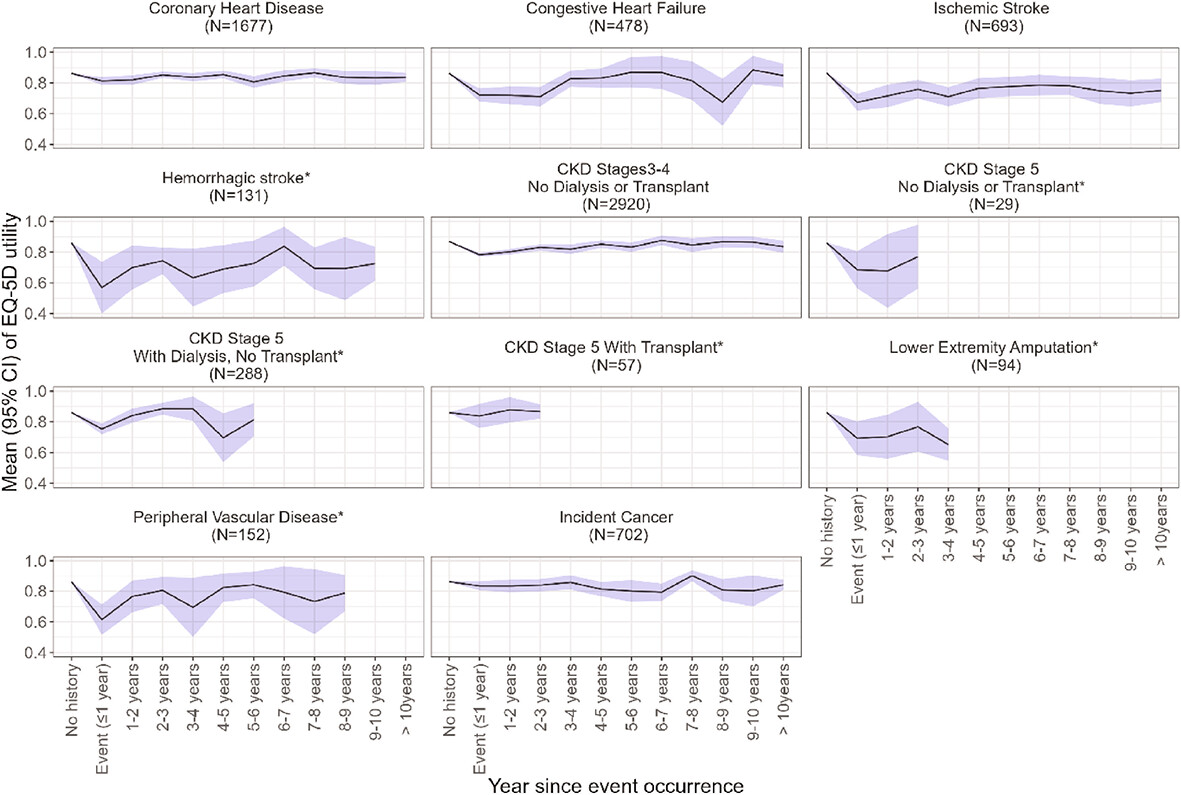
Temporal associations of diabetes-related complications with health-related quality of life decrements in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes: A prospective study among 19 322 adults—Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) register (2007–2018)
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Highlights
- This is the first report on health-related quality-of-life (HRQoL) decrements associated with subtypes of diabetes-related cardiovascular-renal complications in the year of occurrence and their residual impacts in subsequent years amongst 19 322 ambulatory Asian patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) enrolled in the clinic-based Joint Asia Diabetes Evaluation (JADE) Register (2007–2018)
- The largest HRQoL decrements expressed as EuroQol five-dimensional questionnaire utility scores were observed in the year of occurrence of hemorrhagic stroke (−0.230), followed by ischemic stroke (−0.165), peripheral vascular disease (−0.117), lower extremity amputation (−0.093), chronic kidney disease (CKD) G5 without renal replacement therapy (RRT) (−0.079), congestive heart failure (−0.061) and CKD G3–G4 without RRT (−0.042)
- Residual impacts on HRQoL persisted for 2 years after occurrence of CHF or ischemic stroke, and 1 year after hemorrhagic stroke or CKD G3–G4 without RRT
- HRQoL estimates considering residual impacts of diabetes complications would improve accuracy of evaluation of cost-effectiveness of novel diabetes interventions at an individual level in an Asian setting
RESEARCH LETTERS
Out of stock: A brief clinical reference for rough equivalency of glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) ± glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) receptor agonists for A1c and weight reduction in people with type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Highlights
- Despite the common practice of switching patients from one medicine to another—to improve efficacy, safety, or tolerability—guidance on how to do so is uncommon. During this time of global shortage of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist (GLP-1 RA) ± glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) RA therapies, this research letter offers a quick clinical reference of rough equivalency between GLP-1 ± GIP RA for A1c and body weight reduction in people with type 2 diabetes.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
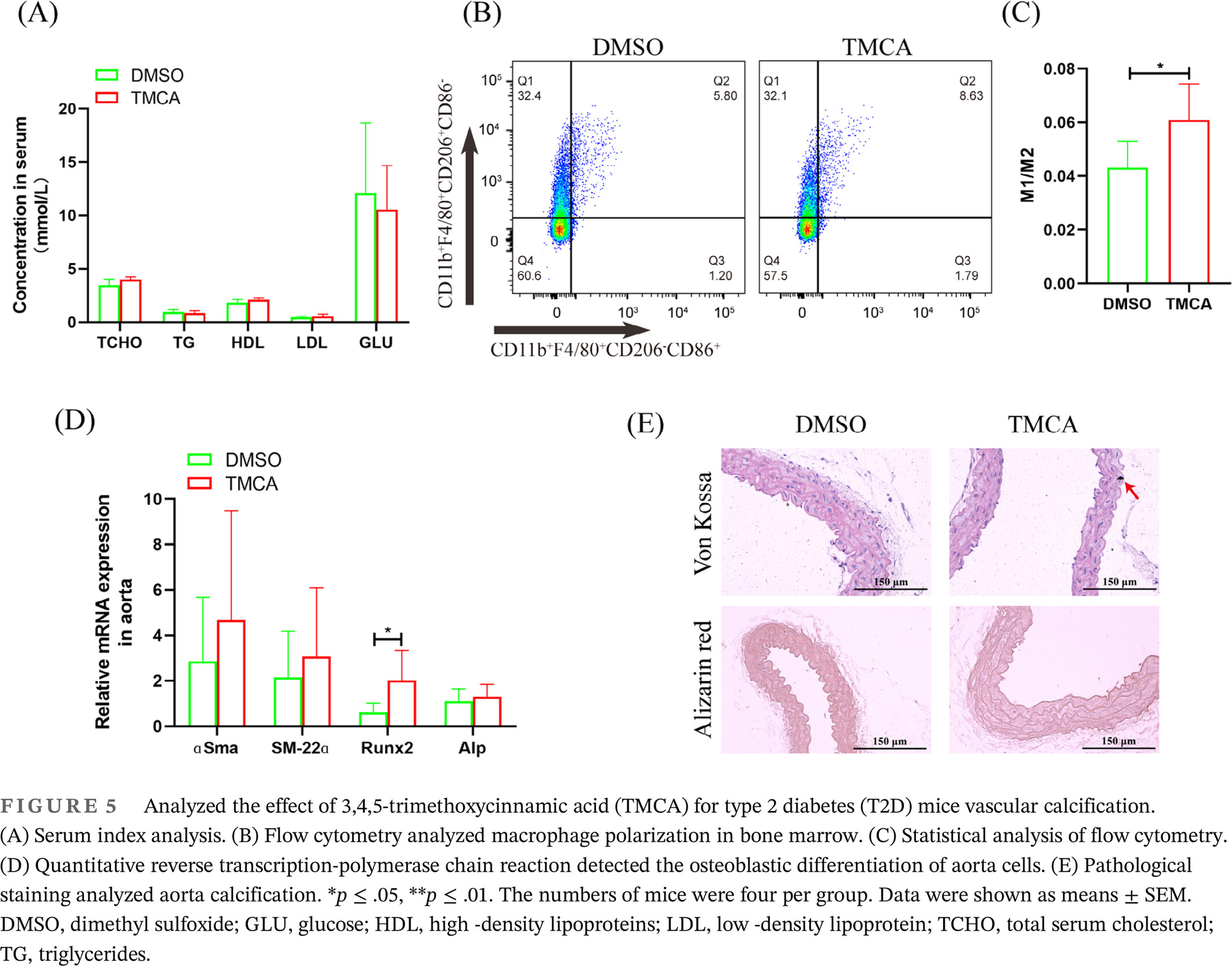
Pravastatin promotes type 2 diabetes vascular calcification through activating intestinal Bacteroides fragilis to induce macrophage M1 polarization
- First Published: 19 December 2023
Highlights
- It is first reported that pravastatin treatment induce Bacteroides fragilis activation.
- It is first reported that 3,4,5-trimethoxycinnamic acid (TMCA) is an important metabolite of Bacteroides fragilis after pravastatin treatment
- It is first reported that TMCA promotes type 2 diabetes vascular calcification via inducing macrophage M1 polarization.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Optogenetic therapeutic strategies for diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 16 May 2024
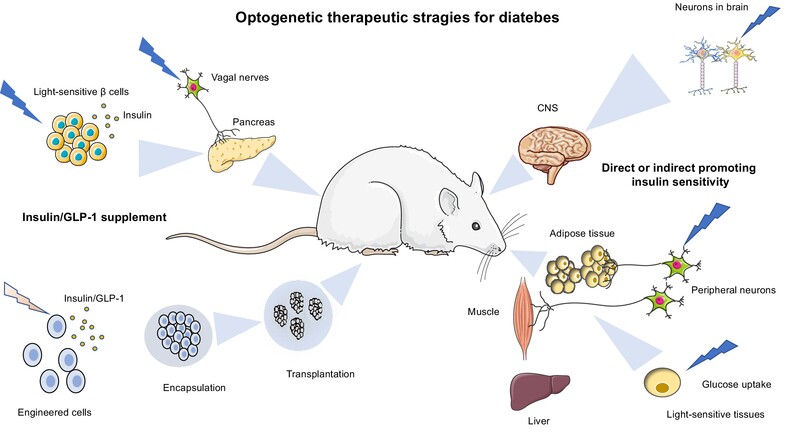
Highlights
- Optogenetics has become a new evolving therapeutic approach for diabetes.
- Synthetic cells with light-responsive modules for insulin/glucagon-like peptide-1 production have been developed to treat diabetes.
- Insulin-responsive tissues are targets of optogenetics, which works to lower blood glucose and alleviate insulin resistance.
- The latest development of optogenetics in diabetes treatment and the remaining challenges are summarized.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes in diabetes in relation to achieved glycemic control. A Danish nationwide study
- First Published: 16 May 2024
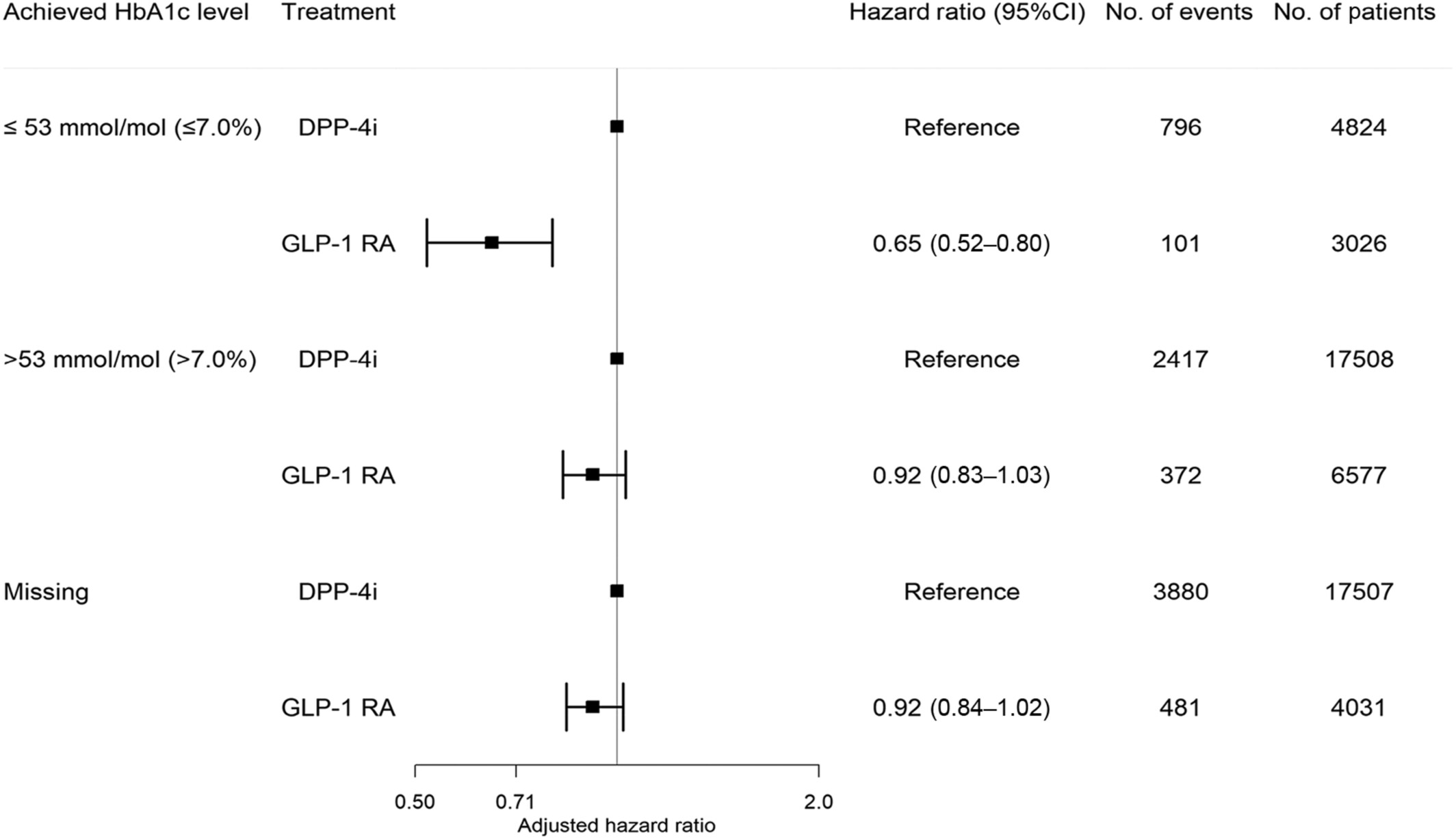
Highlights
- Question: Does achieving the target glycemic level while on treatment with glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i) reduce the rate of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes (MACE)?
- Findings: The rate of MACE among GLP-1 RA versus DPP-4i users was significantly reduced when achieving lower HbA1c levels: HbA1c ≤ 53 mmol/mol: 0.65 (0.52–0.80); HbA1c > 53 mmol/mol: 0.92 (0.83–1.03); missing HbA1c: 0.92 (0.83–1.03).
- Meaning: GLP-1 RA use was associated with a lower rate of MACE. The association was stronger in patients achieving the target glycemic level and weaker in patients not achieving the target glycemic level, suggestive of an interaction between achieved HbA1c level and GLP-1 RA.
Diabetes and gastric cancer incidence and mortality in the Asia Cohort Consortium: A pooled analysis of more than a half million participants
- First Published: 16 May 2024
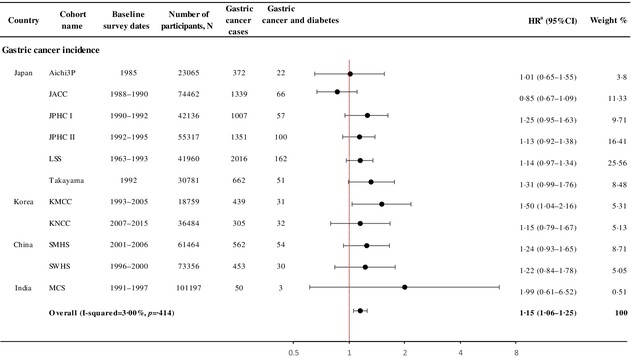
Highlights
- Having diabetes increased gastric cancer risk by 15%, and the risk increased during the first decade following diabetes diagnosis.
- Diabetes increases the risk of gastric cancer regardless of sex, anatomical subsite, or histological subtype.
- Given the substantial diabetes burden in Asia and other regions, our findings underline the importance of diabetes diagnosis and diabetes duration for gastric cancer prevention.
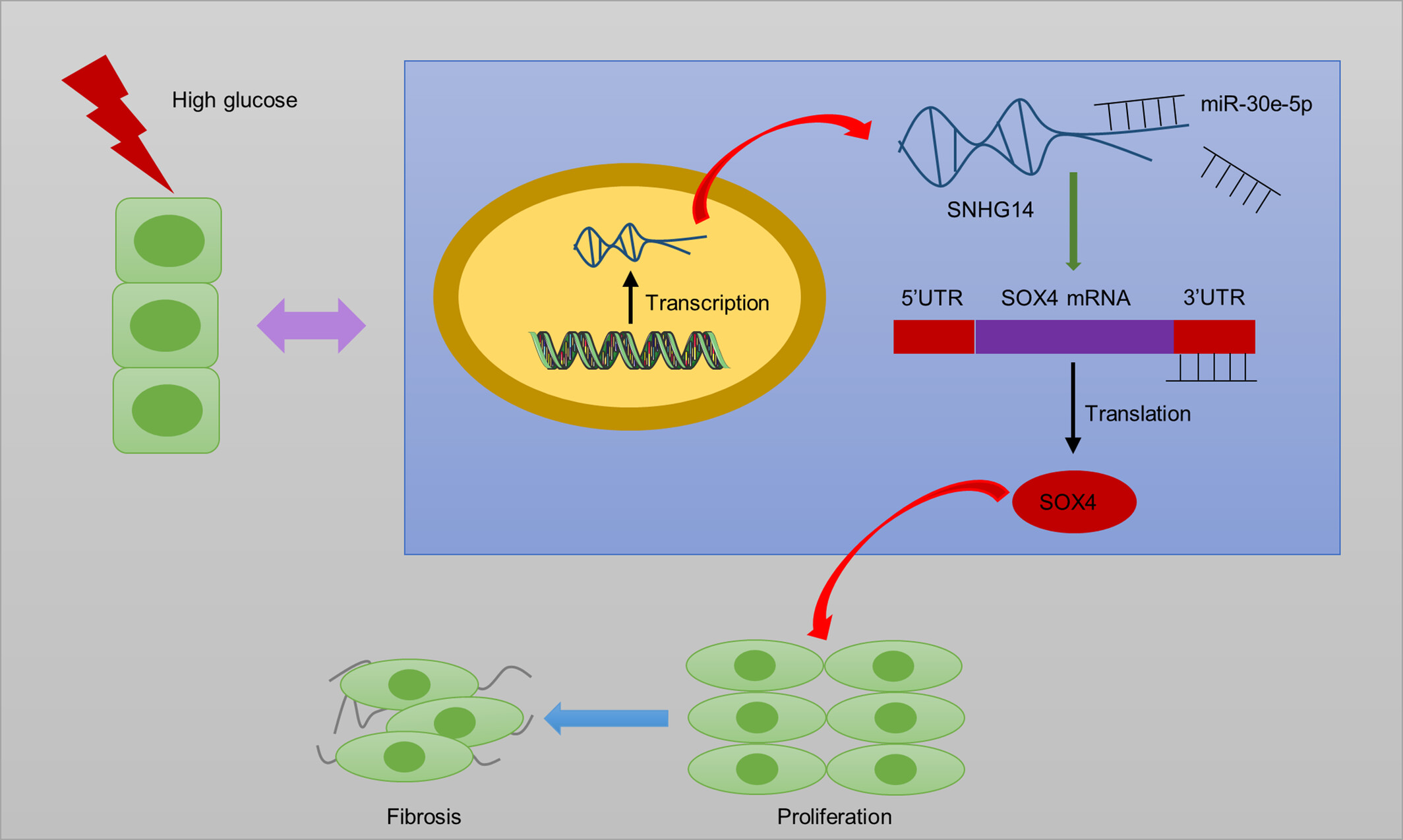
LncRNA SNHG14 silencing attenuates the progression of diabetic nephropathy via the miR-30e-5p/SOX4 axis
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Renal effects and safety between Asian and non-Asian chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes treated with nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid antagonists
- First Published: 16 May 2024
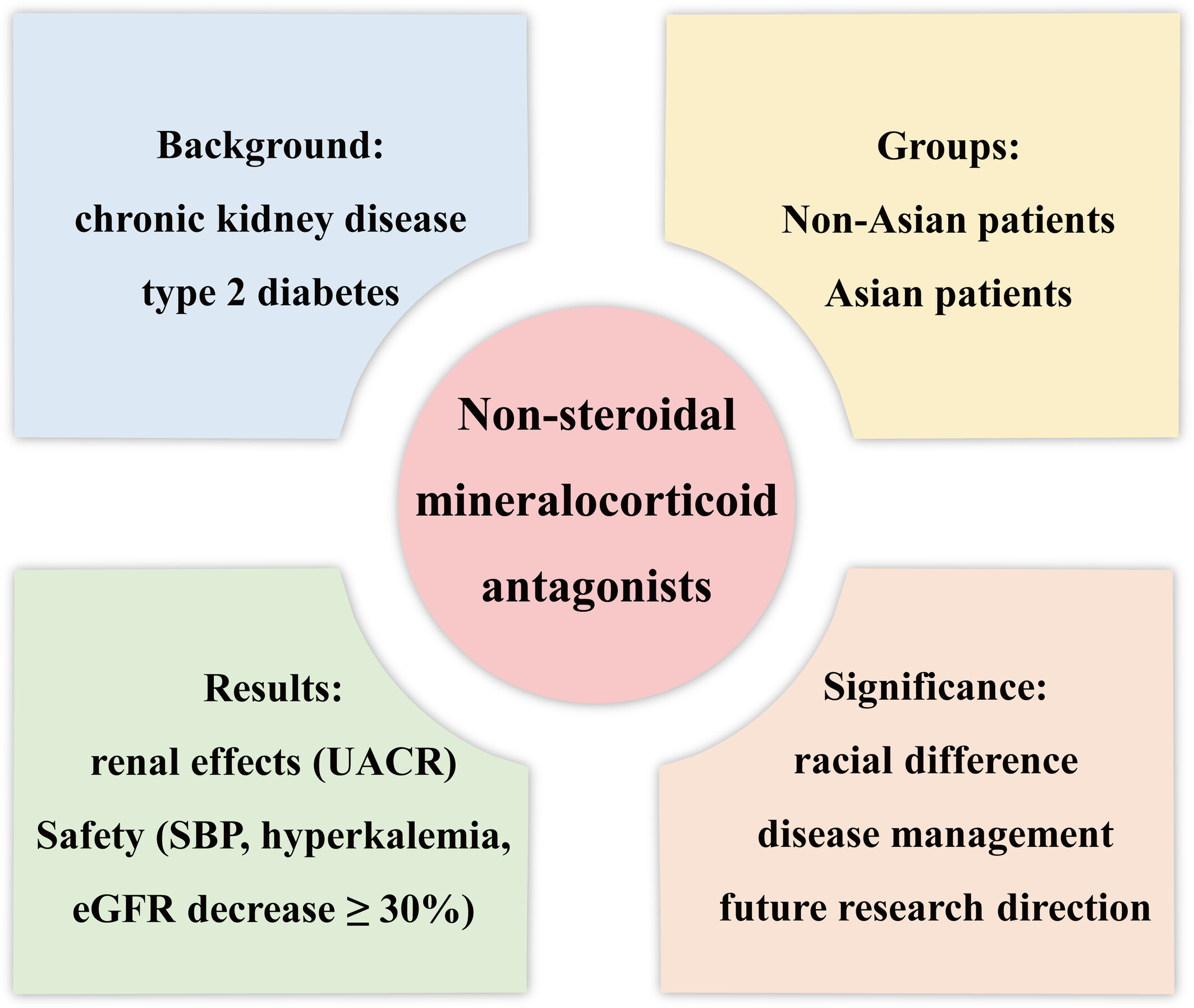
Highlights
Our study indicated that nonsteroidal mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists decreased urinary albumin to creatinine ratio and systolic blood pressure significantly greater in Asian chronic kidney disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus patients than non-Asian patients. The average decline in estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) did not show racial preference. However, hyperkalemia and eGFR decrease ≥ 30% occurred more frequently in Asians, which was acceptable without renal failure or death.
Association between the skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio and metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: A cross-sectional study of NHANES 2017–2018
- First Published: 16 May 2024
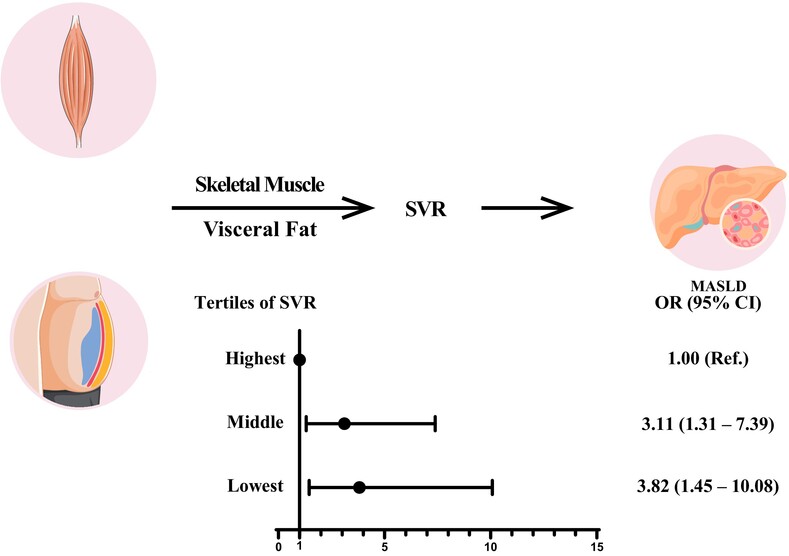
Highlights
- Using data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, our study is among the first to investigate the relationship between sarcopenic obesity, represented by the skeletal muscle mass to visceral fat area ratio (SVR), and metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD) in the US population.
- Measurements for SVR were obtained using dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry, and MASLD was diagnosed with controlled attenuation parameter scores and cardiometabolic risk factors.
- The present study revealed that lower levels of SVR were strongly associated with an increased risk of MASLD.
Comparing long-term outcomes of children treated with new-onset type 2 diabetes in an outpatient versus inpatient setting: A retrospective chart review
- First Published: 16 May 2024
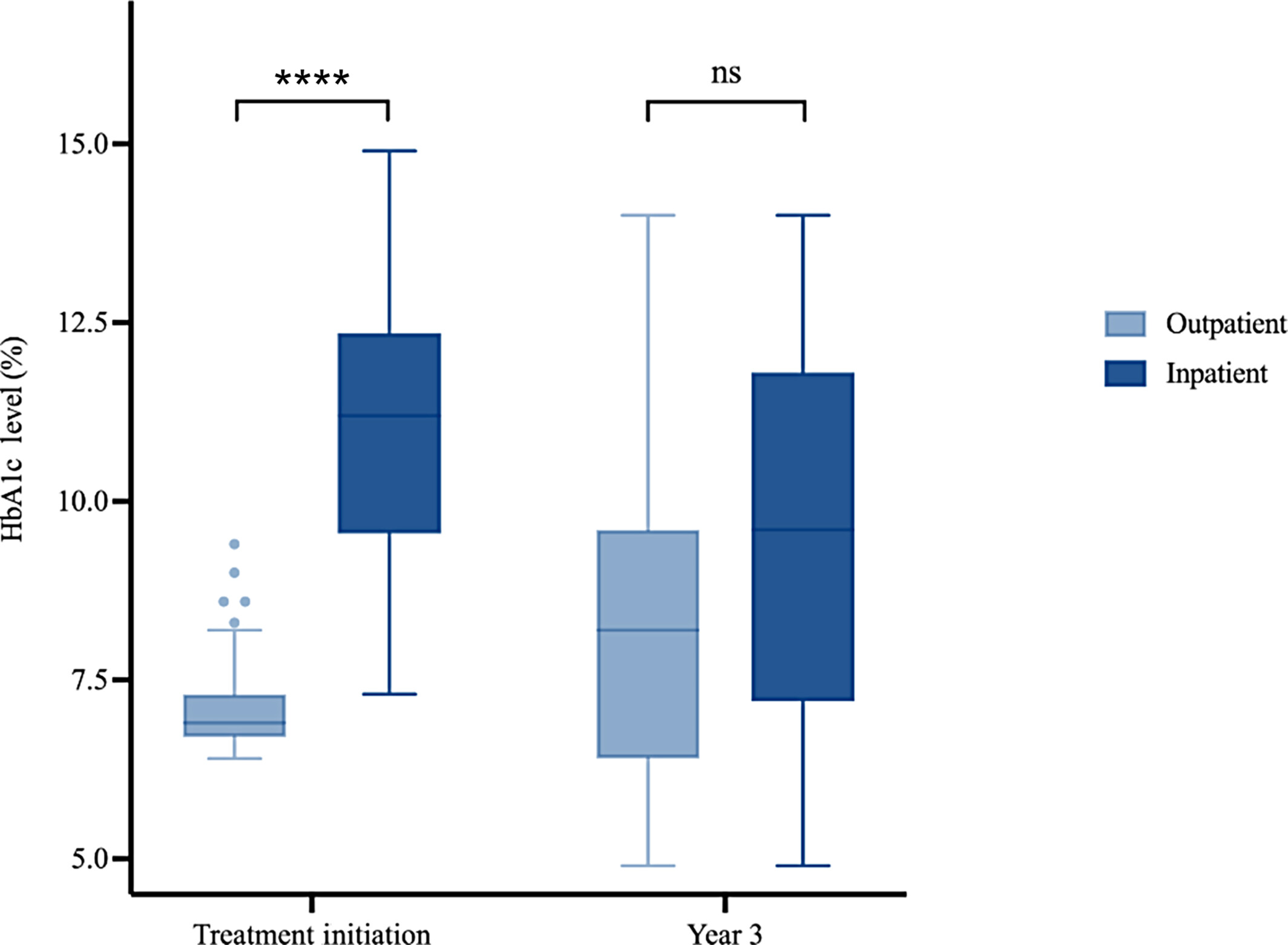
Highlights
- This study assesses if the severity of type 2 diabetes in children at presentation, inferred by the location of treatment initiation (inpatient vs outpatient) influences long-term clinical outcomes.
- Children with new-onset type 2 diabetes treated in an inpatient setting presented with higher glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels at initiation and were treated with higher doses of insulin.
- After 3 years, there was no significant difference in HbA1c levels between inpatient and outpatient groups.
- However, patients initially treated inpatient continued to have higher prescribed insulin dosages after 3 years of diagnosis.
Association between the stress–hyperglycemia ratio and all-cause mortality in community-dwelling populations: An analysis of the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 1999–2014
- First Published: 20 May 2024
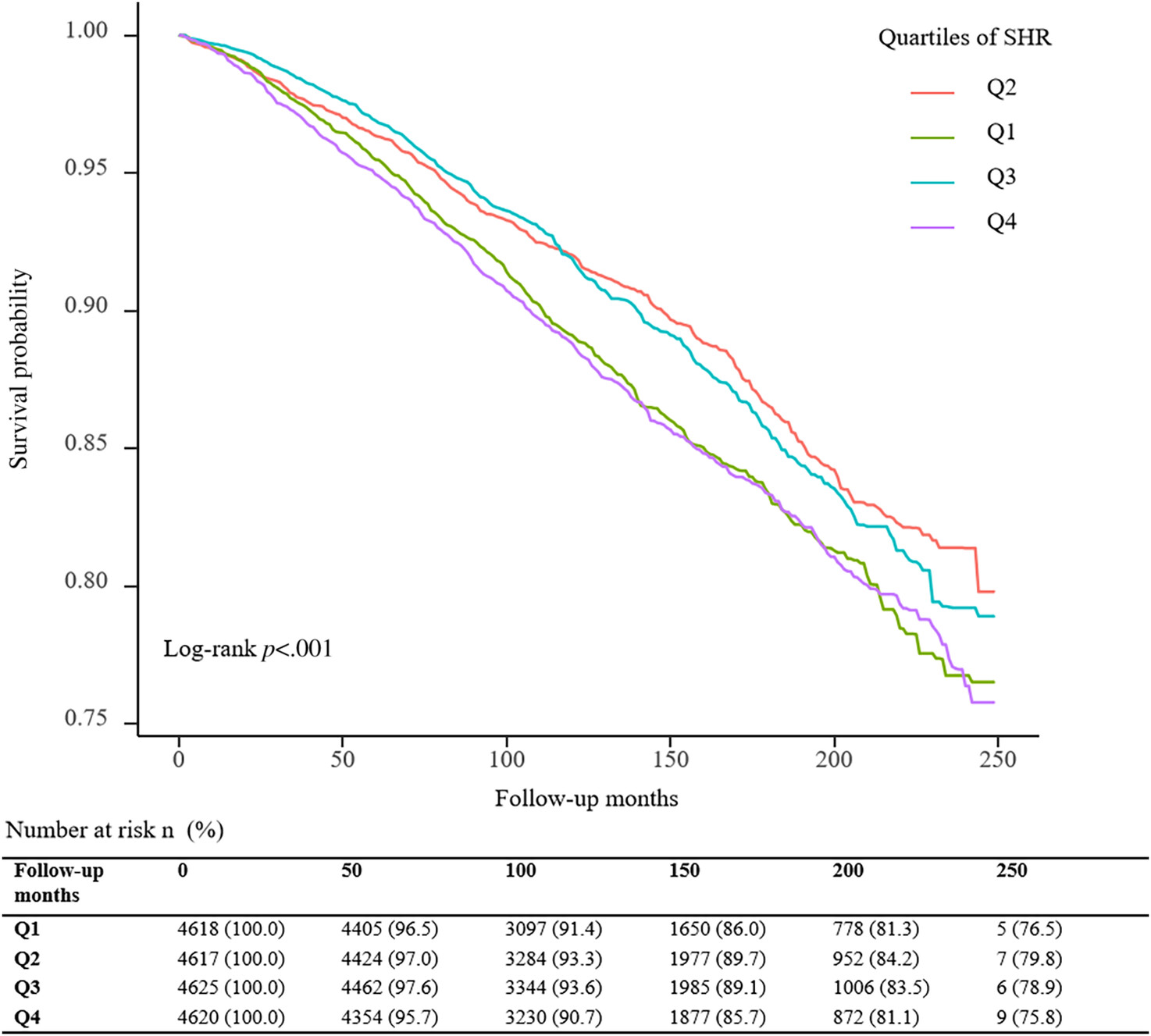
Highlights
- Based on 18 480 residents, our study found for the first time that the stress–hyperglycemia ratio (SHR) is significantly associated with all-cause mortality in community dwellers.
- SHR and all-cause mortality had a dose–response relationship, and the relationship was U shaped.
- After adjusting for the confounding factors, compared with subjects in the second SHR quartile (Q2), participants in the highest (Q4, adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 1.49, 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.28–1.73) and lowest quartiles (Q1, adjusted HR 1.37, 95% CI 1.16–1.60) have a higher probability of all-cause death.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Recent drug development of dorzagliatin, a new glucokinase activator, with the potential to treat Type 2 diabetes: A review study
- First Published: 23 May 2024
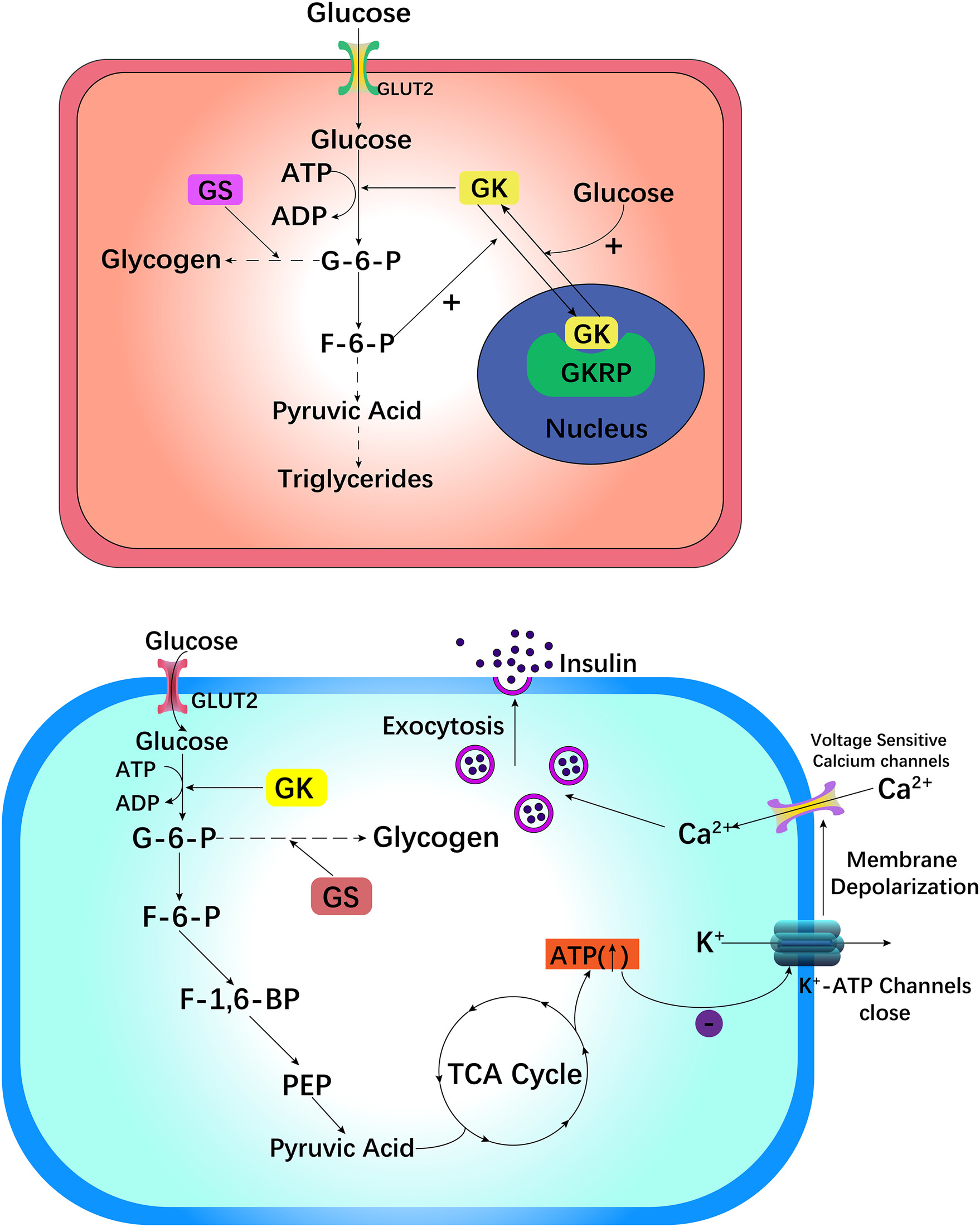
Highlights
- This article is a retrospective review article, aiming to briefly review the working principle of glucokinase (GK) and summarize the development of glucokinase activators (GKA), a new antidiabetes drug targeting GK. In this review, we focus on the development of the new GKA, dorzagliatin, and summarize the results of the latest controlled clinical trials of dorzagliatin. At the same time, we also point out the current limitations of dorzagliatin and the future development direction of dorzagliatin.