Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Duodenal-jejunal bypass surgery activates eNOS and enhances antioxidant system by activating AMPK pathway to improve heart oxidative stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats
- First Published: 12 December 2023
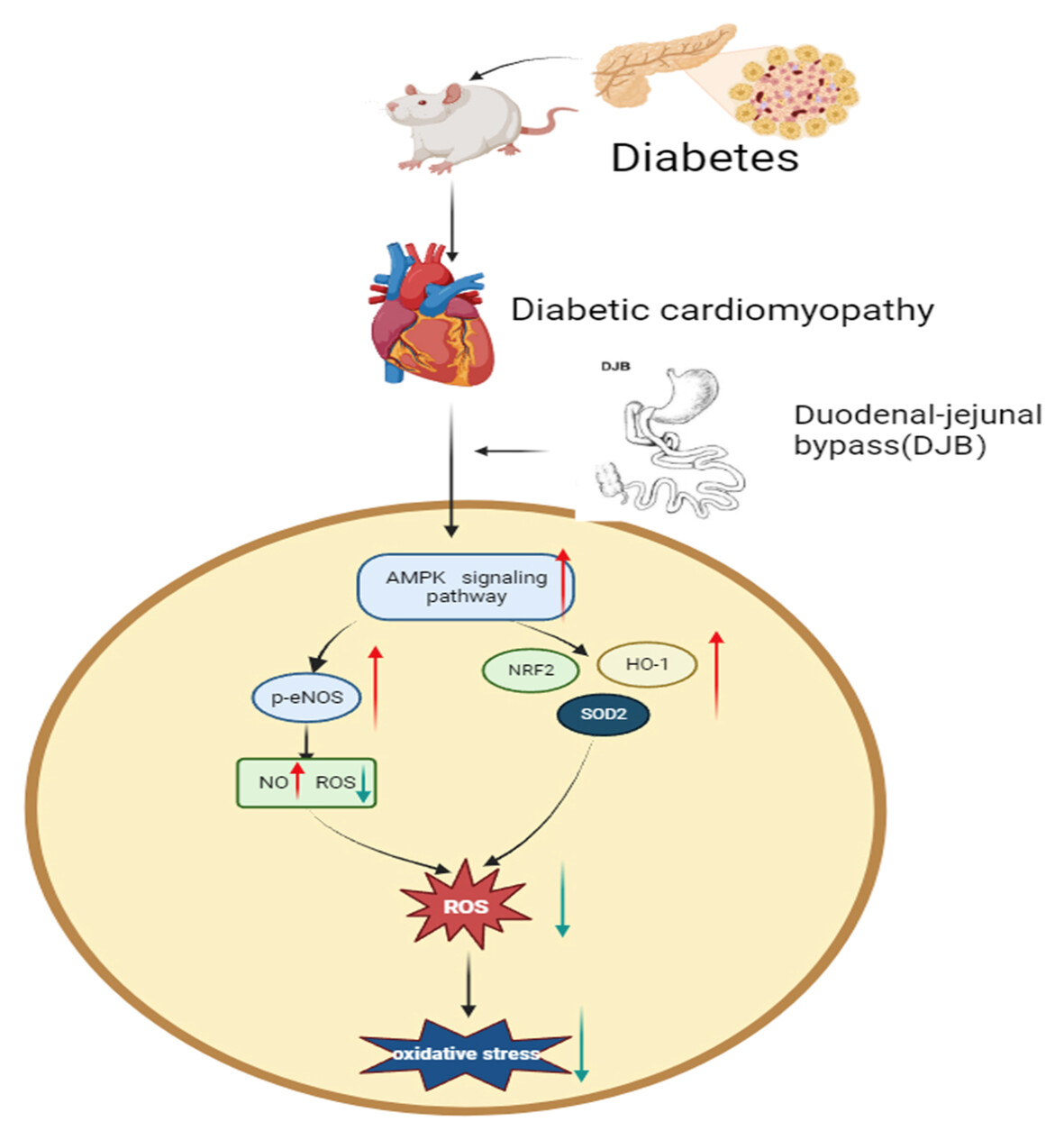
Highlights
- This study revealed that duodenal-jejunal bypass (DJB) attenuated oxidative stress in diabetic cardiomyopathy rats by activating the adenosine monophosphate (AMP)-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway, thereby augmenting the antioxidative system and elevating the phosphorylation level of nitric oxide synthase (eNOS).
- The application of sera obtained from distinct groups and the agonist of AMPK pathway to stimulate H9C2 cells revealed that DJB intervention partially alleviated heart oxidative stress by activating the AMPK pathway, rather than solely by improving blood glucose levels.
Clinical outcomes of obese and nonobese patients with atrial fibrillation according to associated metabolic abnormalities: A report from the COOL-AF registry
- First Published: 14 December 2023
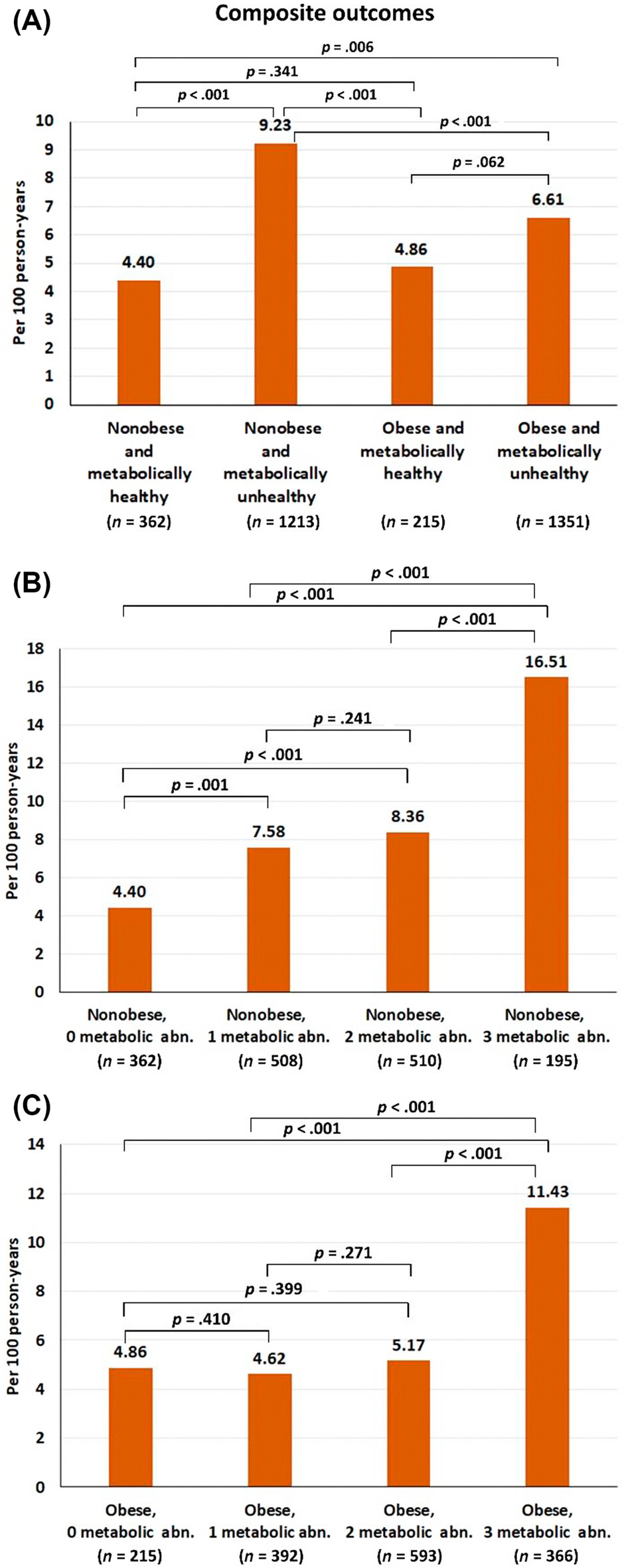
Highlights
- The results of this prospective multicenter nationwide study showed that among patients with atrial fibrillation (AF), metabolic unhealthy obese subjects were associated with an increased risk of adverse outcomes in patients with AF.
- Obese patients with AF and good metabolic control or metabolically healthy obesity were not associated with an increased risk.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
The impact of a diabetes diagnosis on health and well-being: Findings from the English Longitudinal Study of Ageing
- First Published: 19 December 2023
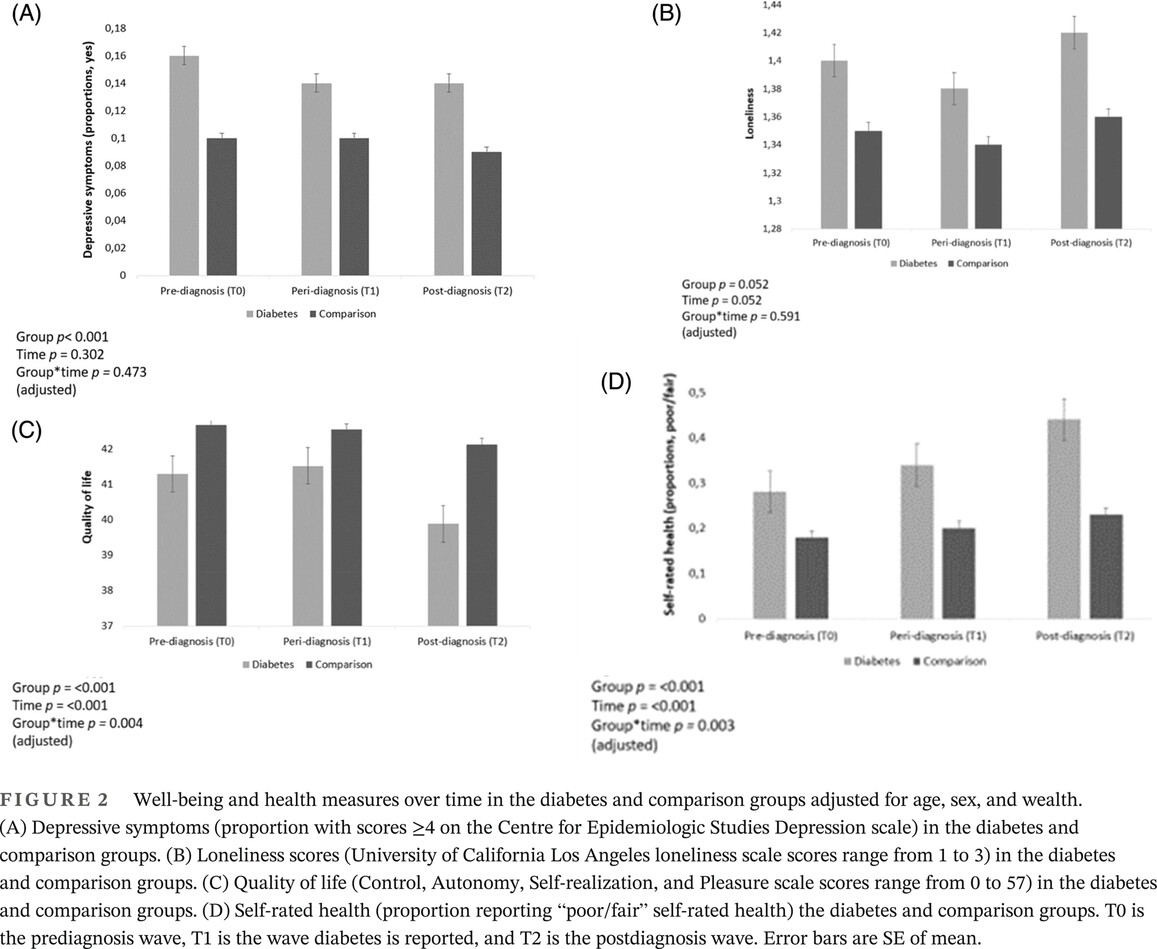
Highlights
- People who develop diabetes report greater depressive symptoms and lower quality of life and rate their health as poorer than those who do not develop diabetes.
- Around the time of diagnosis, people with diabetes experience a greater decline in quality of life and self-rated health than adults who do not develop the condition.
Liraglutide does not increase heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction
- First Published: 03 January 2024
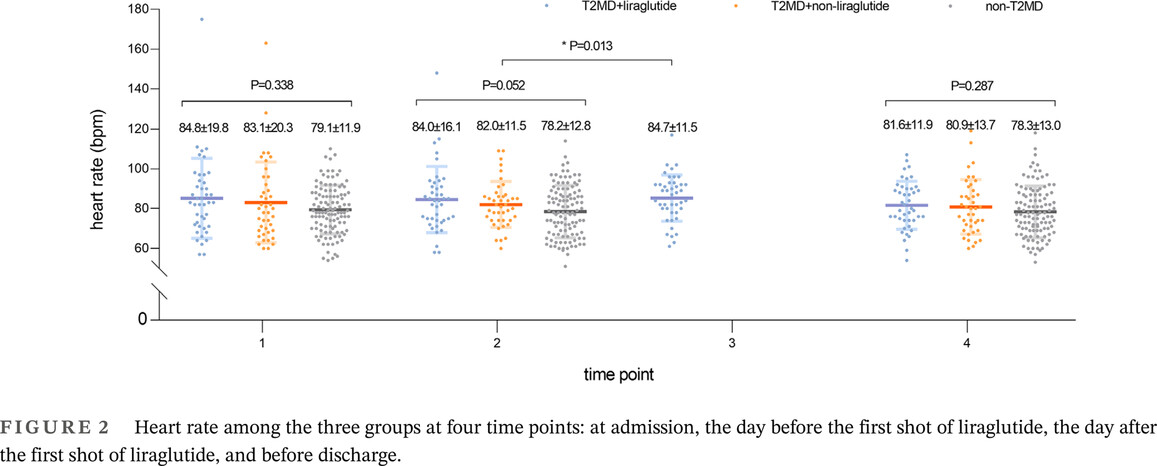
Highlights
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists have been shown to reduce all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Previous studies have found that liraglutide can increase the heart rate in patients, so the use of liraglutide should be controlled in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
- We found that liraglutide did not increase the heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction and it had no effect on blood pressure.
- Therefore, liraglutide is safe for use in the early stages of acute myocardial infarction.
RESEARCH LETTERS
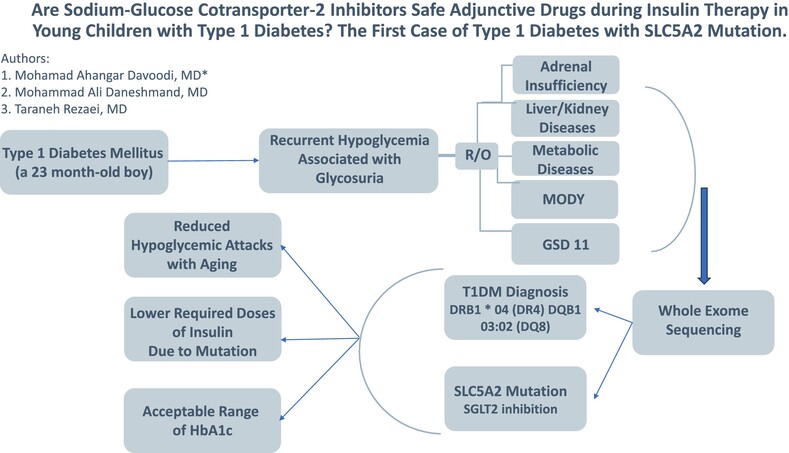
Are sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors safe adjunctive drugs during insulin therapy in young children with type 1 diabetes? The first case of type 1 diabetes with SLC5A2 mutation
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Highlights
- A persistent glycosuria alongside hypoglycemia in pediatric type 1 diabetes mellitus needs further evaluation.
- Morning hypoglycemia is a limiting side effect of sodium glucose transporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors in children younger than 5 years old.
- SLC5A2 mutation functioning as a SGLT2 inhibitor can result in acceptable range of glycated hemoglobin in younger children and lower required doses of insulin.
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Assessment of community-managed blood glucose control in patients with diabetes mellitus in Shenzhen, China
- First Published: 26 June 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
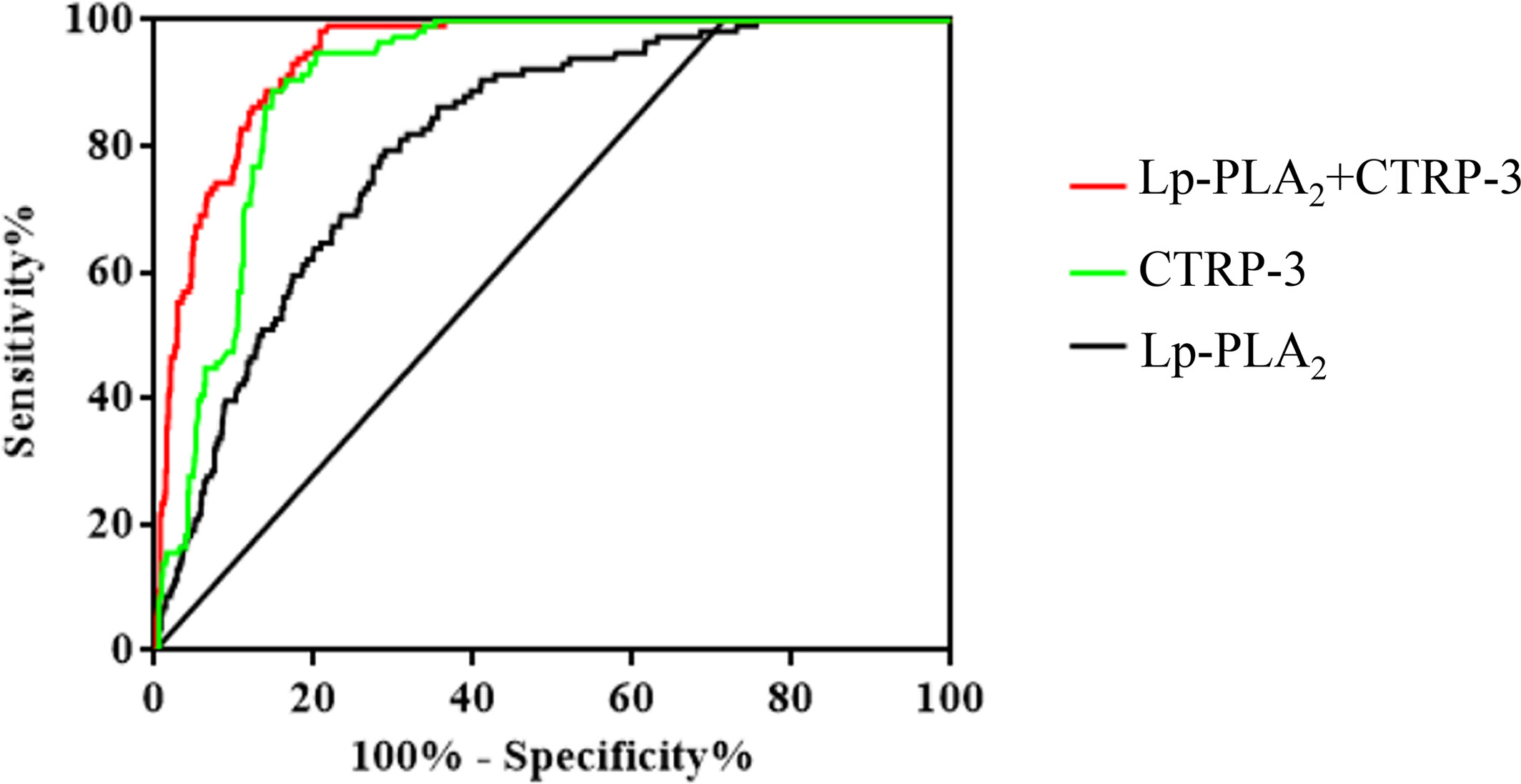
The relationships between biological novel biomarkers Lp-PLA2 and CTRP-3 and CVD in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Highlights
- In this study, the positive group of CVD in T2DM showed higher Lp-PLA2 activity and lower CTRP-3 levels for a 7-year median follow-up compared with the negative group.
- The results of this study suggest Lp-PLA2, CTRP3, and their combination detection can effectively increase the diagnostic efficacy of CVD in patients with T2DM, and it will be conducive to further risk assessment of patients with T2DM and predict the high-risk population of CVD.
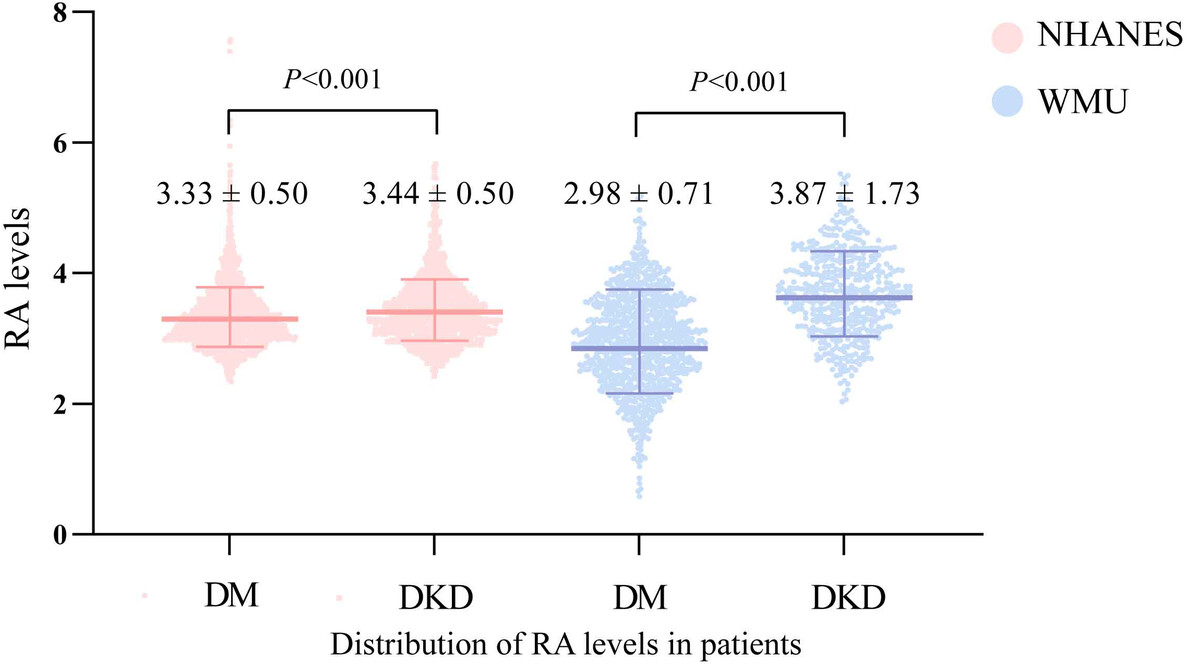
Association between red cell distribution width/serum albumin ratio and diabetic kidney disease
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Highlights
- RA levels differ between DM and DKD patients in both the NHANES databases and WMU data.
- After accounting for confounders and using propensity score-matched analysis, both RA levels were found to be independently associated with DKD.
- The RA, a cost-effective and easily accessible biomarker, could be useful for risk stratification of DKD.
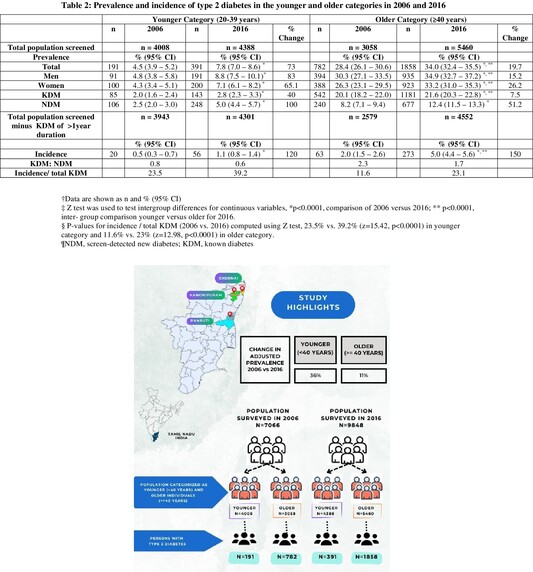
The rising prevalence of type 2 diabetes among the youth in southern India—An ancillary analysis of the Secular TRends in DiabEtes in India (STRiDE-I) study
- First Published: 26 June 2024
Highlights
- The study reports a comparative profile on prevalence and incidence of T2DM and its associated risk factors in the younger and the older individuals in 2006 and 2016.
- Prevalence of T2DM increased both in the younger (36%) and older individuals (11%) in a decade's time.
- Incidence rose by 120% in the younger individuals and 150% in the older group.
- Percentage increase in cardiometabolic risk was higher among the younger than in the older individuals.
- Obesity and family history of diabetes were the primary contributing factors for the rising prevalence in both groups.









