Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
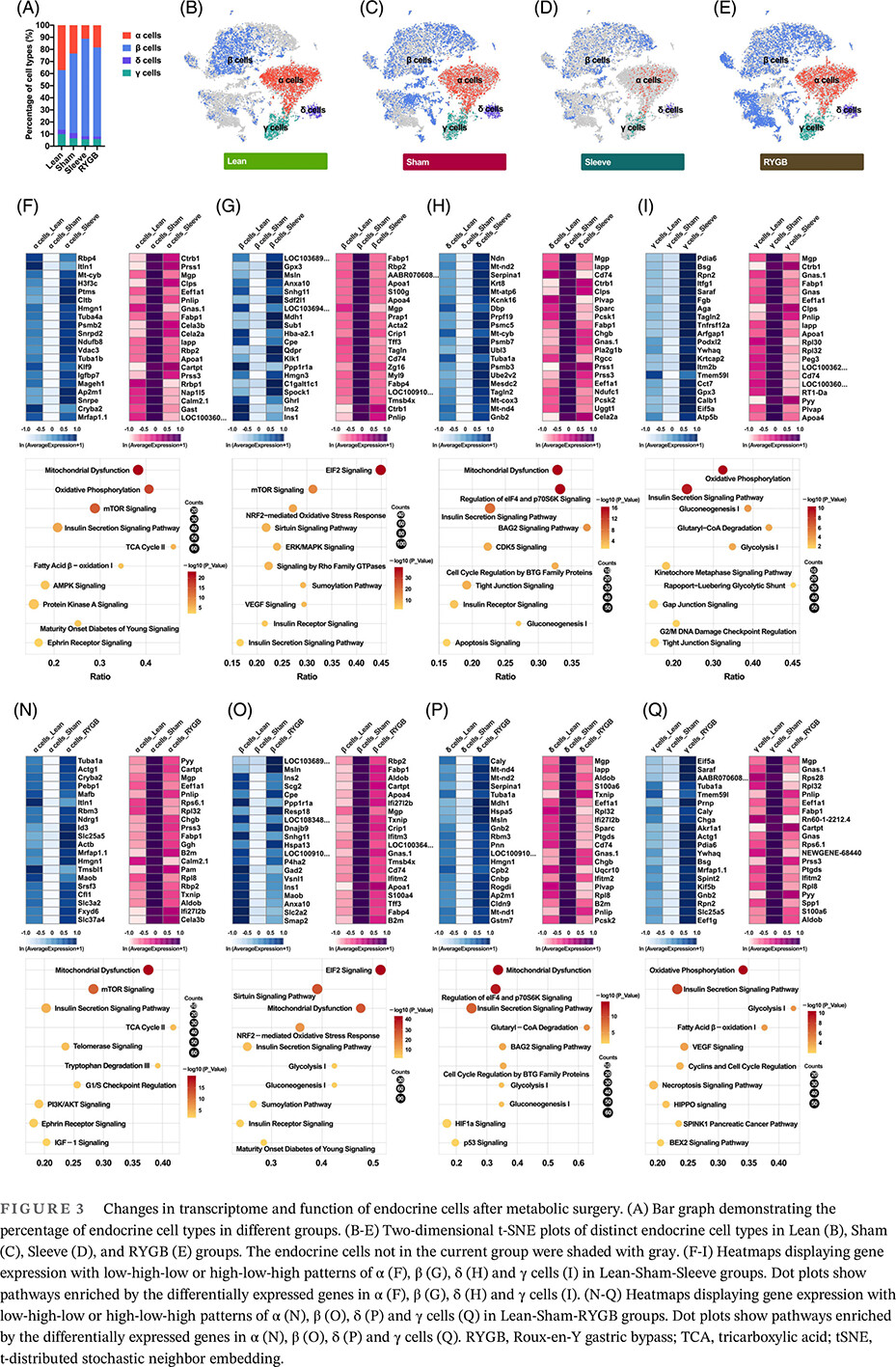
Bariatric surgery induces pancreatic cell transdifferentiation as indicated by single-cell transcriptomics in Zucker diabetic rats
- First Published: 27 December 2023
Highlights
- The single-cell transcriptome map of Zucker diabetic fatty rats' pancreatic endocrine cells after bariatric surgery were reported for the first time.
- An increased ratio of pancreatic β cells, which is associated with other pancreatic endocrine cell types transdifferentiated into β cells, was observed following bariatric surgery.
- For the first time, we identify the elevation of cells in the pancreas following bariatric surgery, which is indirect evidence to support the existence of transdifferentiation.
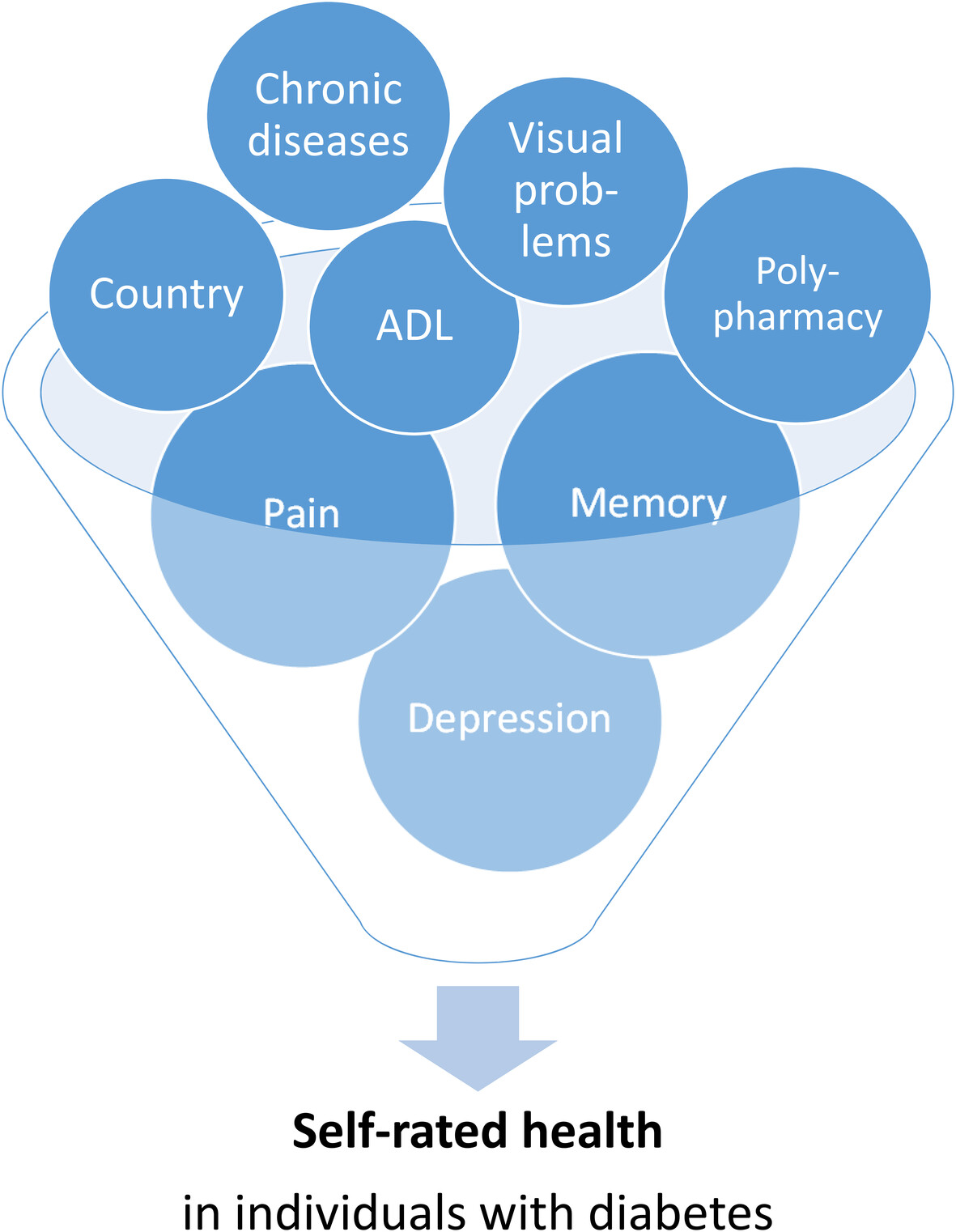
Exploring factors associated with self-rated health in individuals with diabetes and its impact on quality of life: Evidence from the Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement in Europe
- First Published: 02 January 2024
Highlights
- Individuals with diabetes tend to report their health as less than very good more frequently compared to individuals without diabetes
- We have identified several factors that influence self-rated health in individuals with diabetes. Depression, pain, and memory function emerged as the most influential factors.
- Self-rated health was determined to be an independent predictor of quality of life.
The combined effect of triglyceride–glucose index and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein on cardiovascular outcomes in patients with chronic coronary syndrome: A multicenter cohort study
- First Published: 13 August 2024
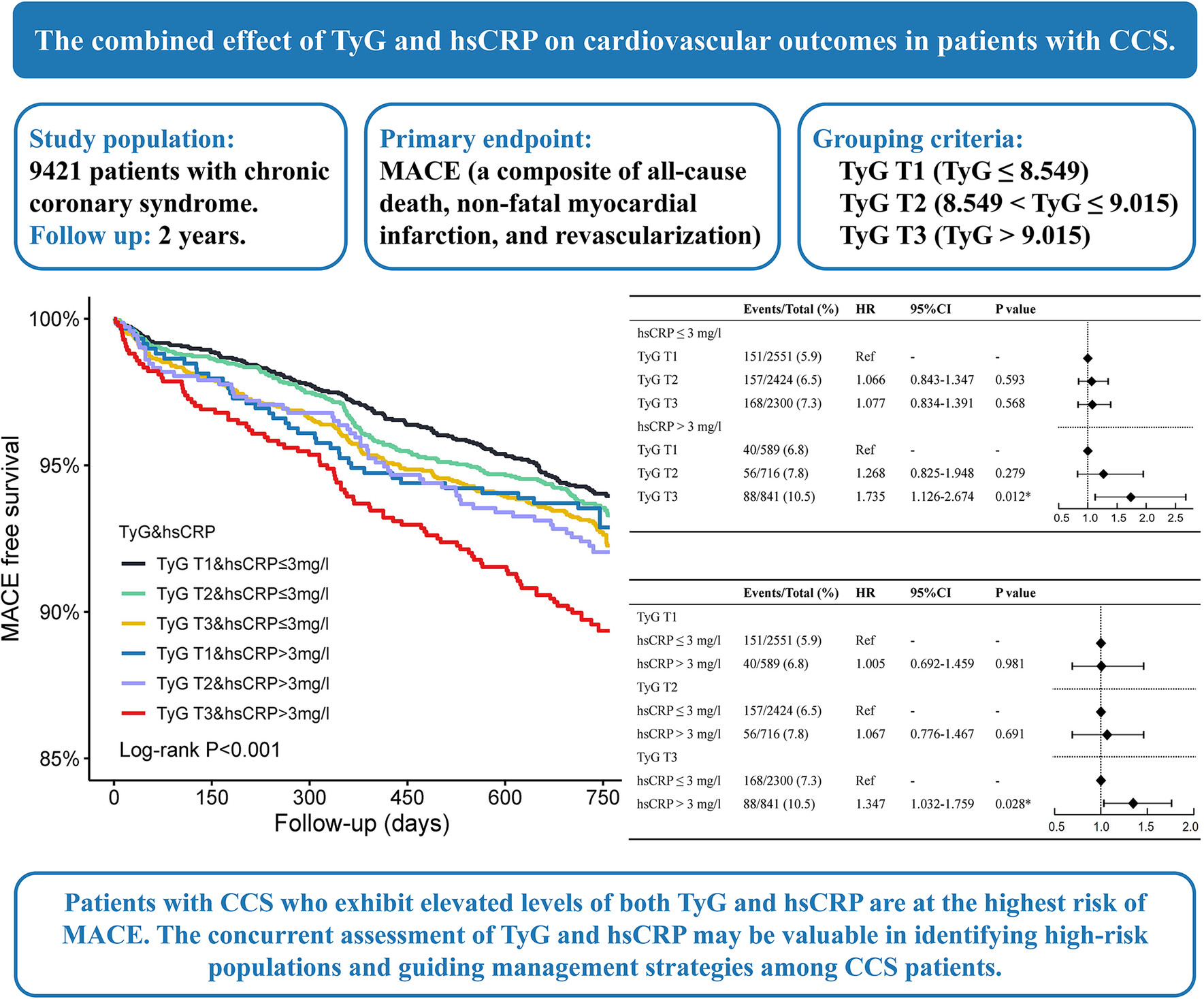
Highlights
- A large-scale study investigating the joint prognostic effect of TyG and hsCRP in patients with CCS.
- Patients with CCS who exhibit elevated levels of both TyG and hsCRP are at the highest risk of MACE.
- Simultaneous assessment of TyG and hsCRP may be valuable in identifying the high-risk populations and guiding management strategies among patients with CCS.
The efficacy of interventions to prevent type 2 diabetes among women with recent gestational diabetes mellitus—A living systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 13 August 2024
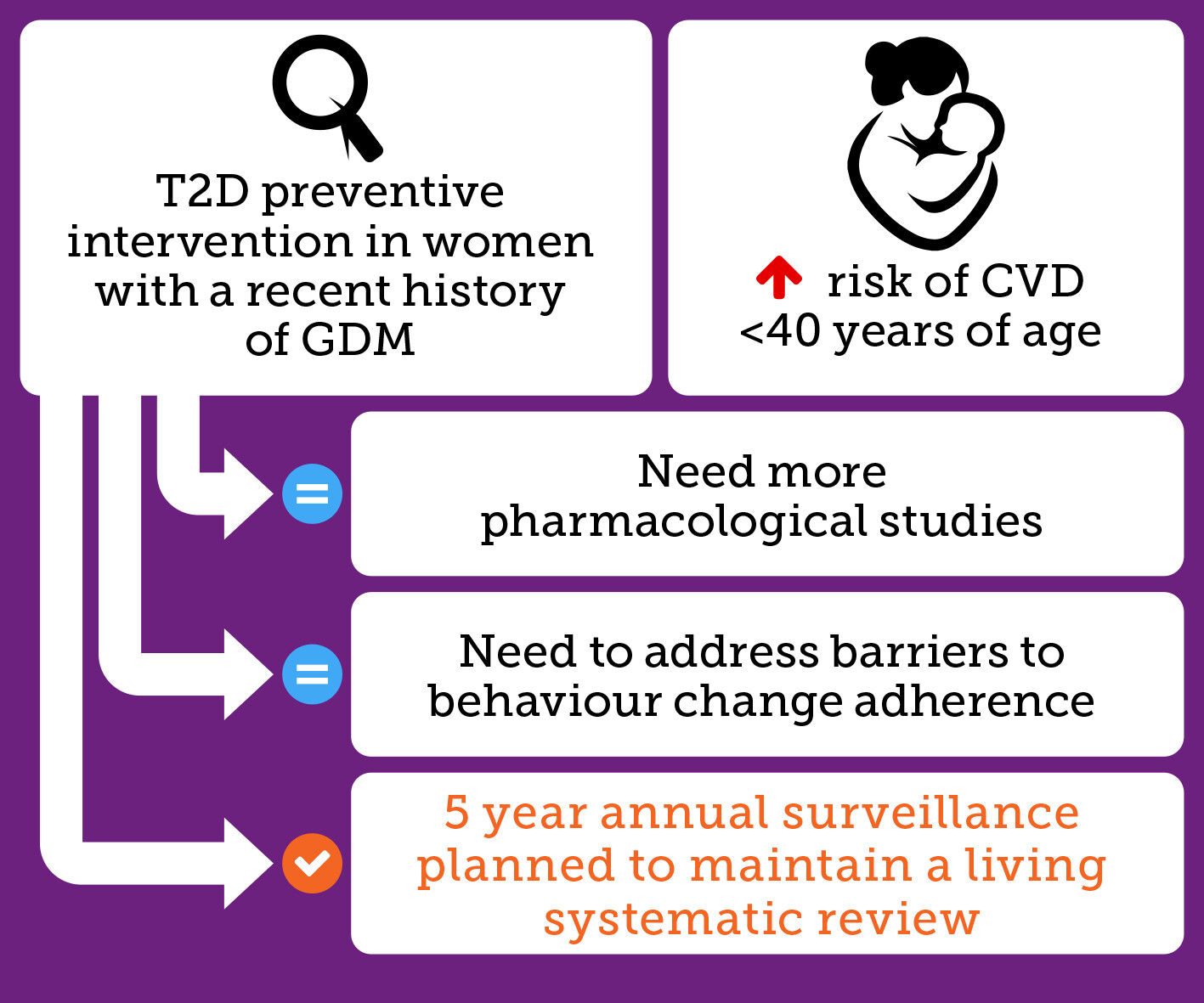
Highlights
- GDM is now a well-established risk factor for developing T2DM. This risk appears to be particularly high in the first few years after childbirth, providing a compelling case for early intervention.
- This review found equivocal evidence about the efficacy of preventive interventions on development of T2DM in women with a recent (within 5 years) history of GDM.
- Very few data evaluating pharmacotherapy were available, highlighting the need for further studies.
Trends in diabetic ketoacidosis- and hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state-related mortality during the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States: A population-based study
- First Published: 13 August 2024
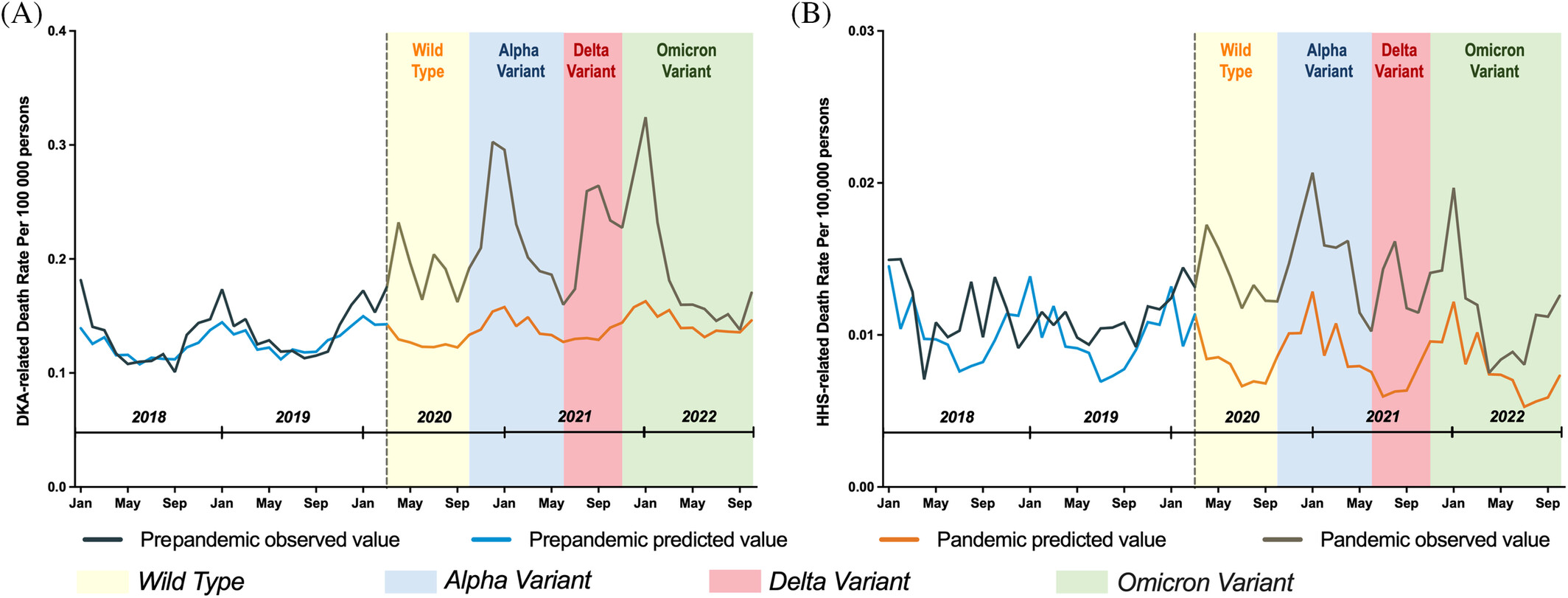
Highlights
- The incidence and management of DKA and HHS, emergent complications of diabetes mellitus, were affected during the pandemic.
- In this study, we showed that DKA- and HHS-related mortality increased dramatically during the pandemic, with widening age, sex, and racial/ethnic disparities.
- Our findings have implications for public health strategies to improve diabetes care and suggest a greater focus on these populations during future public health crises.
Remnant cholesterol is more positively related to diabetes, prediabetes, and insulin resistance than conventional lipid parameters and lipid ratios: A multicenter, large sample survey
- First Published: 13 August 2024
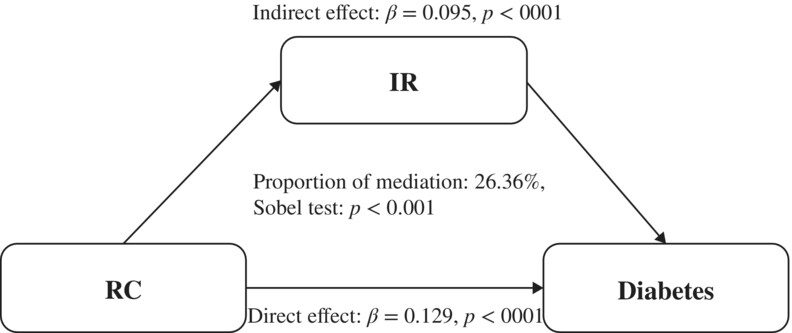
Highlights
- This is the first investigation comparing remnant cholesterol (RC) and traditional lipids and lipid ratios with diabetes, prediabetes, and insulin resistance (IR) among a large, multicenter Chinese general population.
- RC is more positively related to diabetes, prediabetes, and IR than other conventional lipids and lipid ratios.
- The relationship between RC and diabetes, prediabetes, and IR are stable, even if conventional lipids are at appropriate levels.
- There is a significant indirect effect of IR between RC and diabetes and prediabetes with mediation.
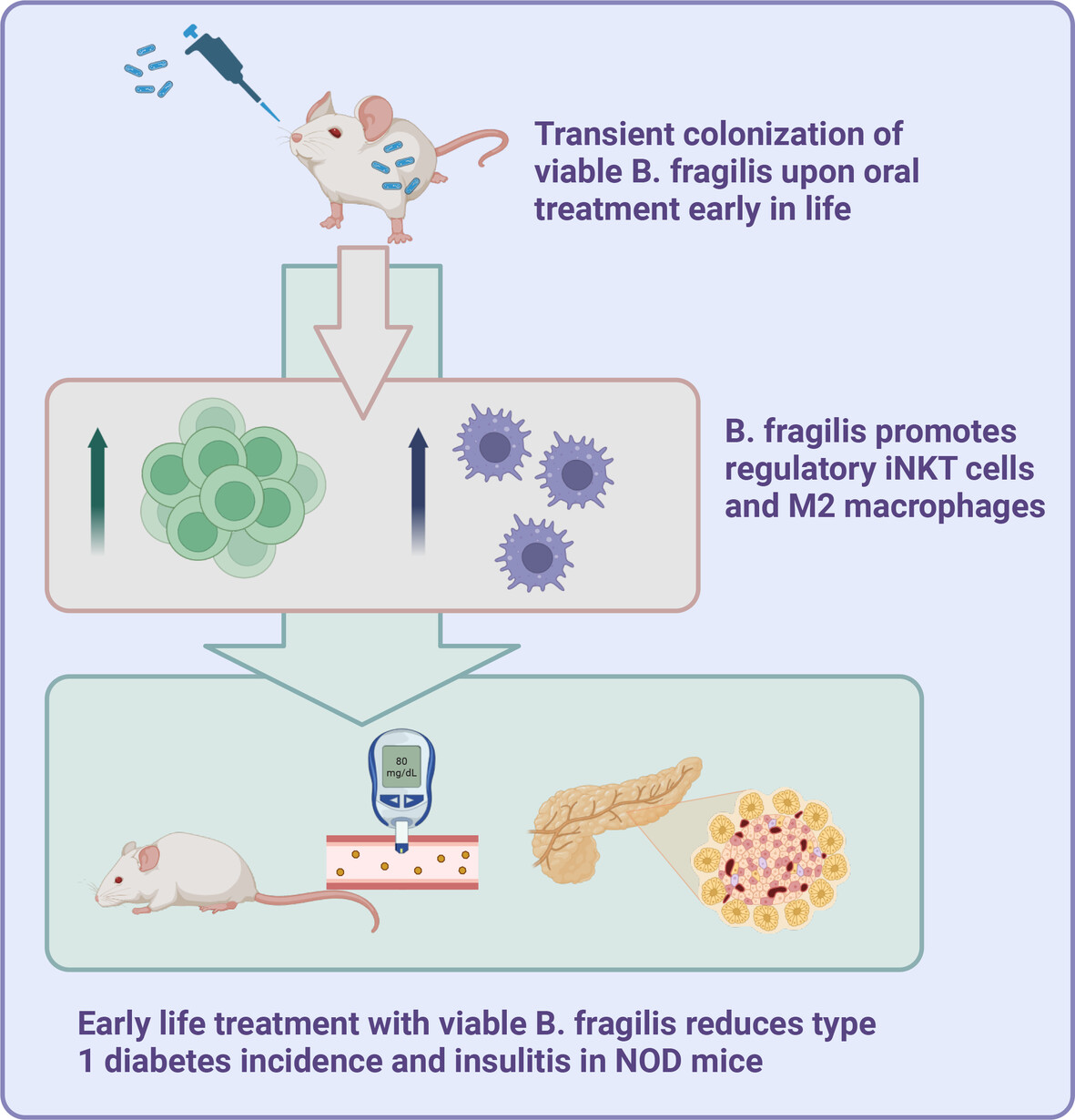
Probiotic treatment with viable α-galactosylceramide-producing Bacteroides fragilis reduces diabetes incidence in female nonobese diabetic mice
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Highlights
- Transient colonization by viable B. fragilis reduces type 1 diabetes incidence in NOD mice.
- Alpha-galactosylceramide-producing B. fragilis induces anti-inflammatory immunity.
- Protection against diabetes by B. fragilis is not based on systemic immune cells.
- B. fragilis may become a next-generation probiotic for prevention of type 1 diabetes.
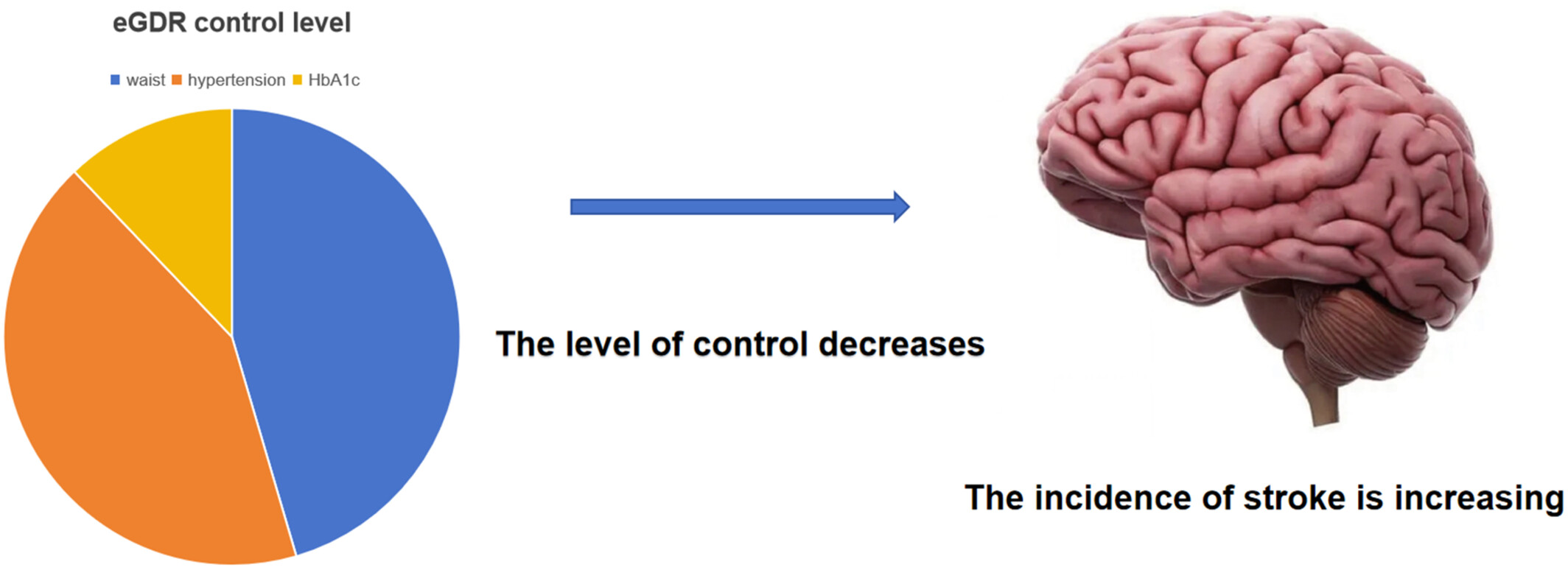
Association between estimated glucose disposal rate control level and stroke incidence in middle-aged and elderly adults
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Highlights
- In middle-aged and elderly adults, poorly managed estimate glucose disposal rate (eGDR) levels are linked to an increased risk of stroke.
- As a result, controlling eGDR levels in stroke prevention measures needs additional focus.
- Furthermore, dynamic tracking of long-term eGDR changes may be able to identify those who are more likely to have a stroke early on, which could make it easier to put more focused preventive measures in place.
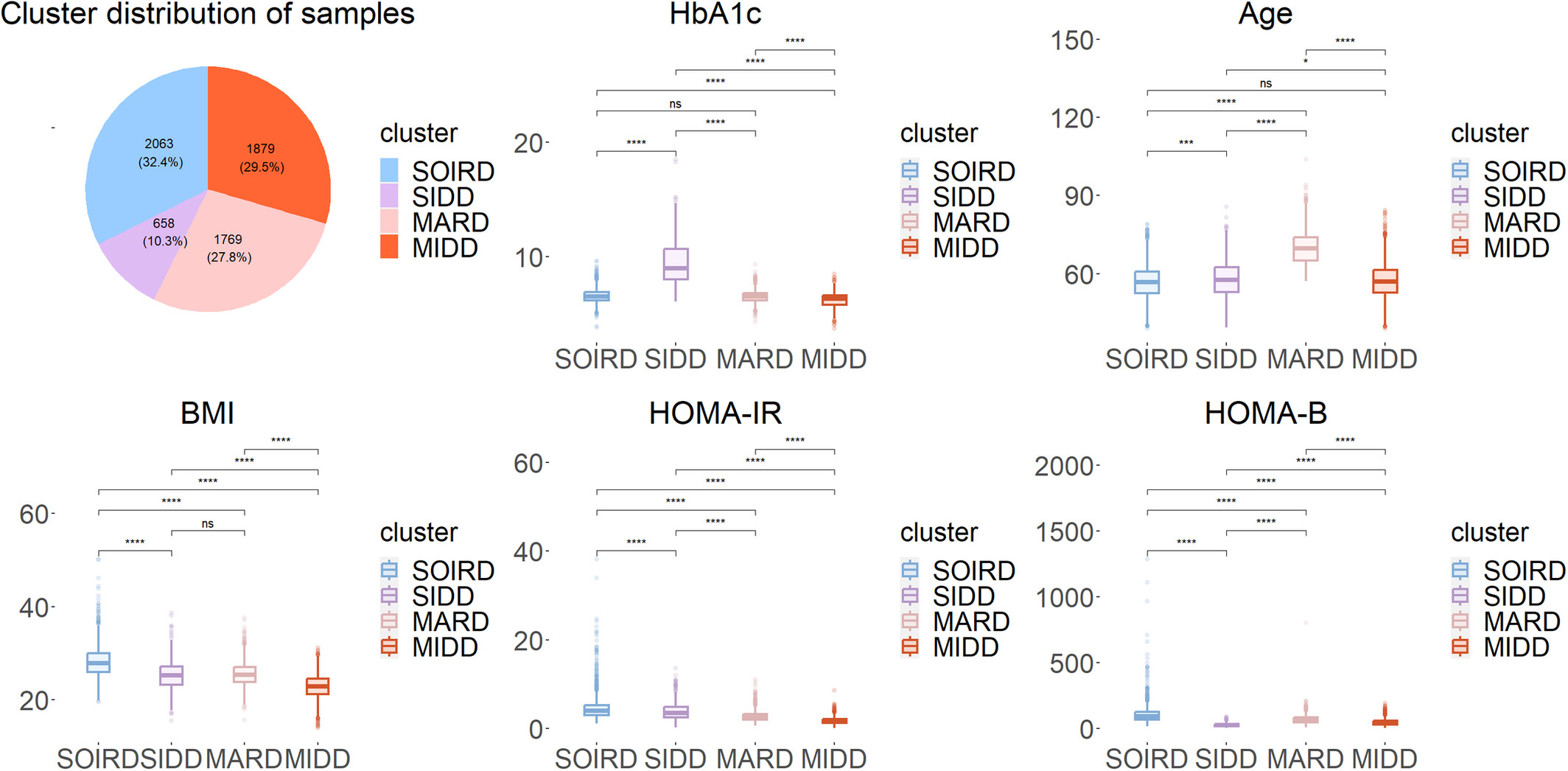
Clinical characteristics and complication risks in data-driven clusters among Chinese community diabetes populations
- First Published: 13 August 2024
Highlights
- The current study is the first one, to our knowledge, that clustered and typed a large sample, multicenter Chinese community-based diabetic populations.
- This is also the first study, to our knowledge, that reported the MIDD cluster, which had a low risk burden equivalent to prediabetes, but with reduced insulin secretion.
- We explored differences in lifestyle habits and family history of disease among the various clusters of patients, which has rarely been studied previously.
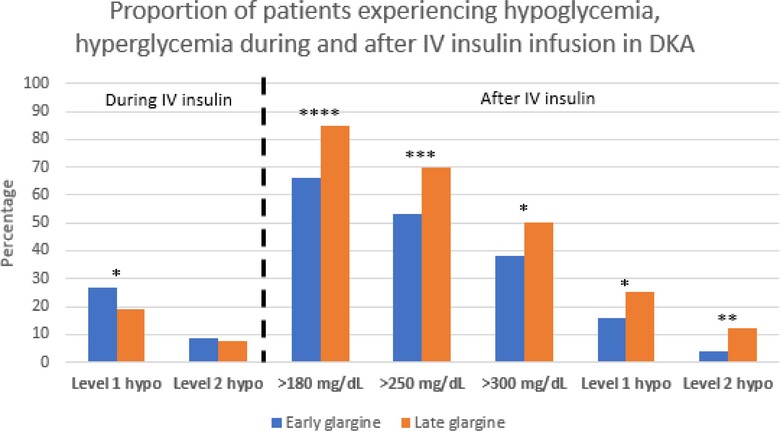
Management of diabetic ketoacidosis in children: Does early insulin glargine help improve outcomes?
- First Published: 13 August 2024
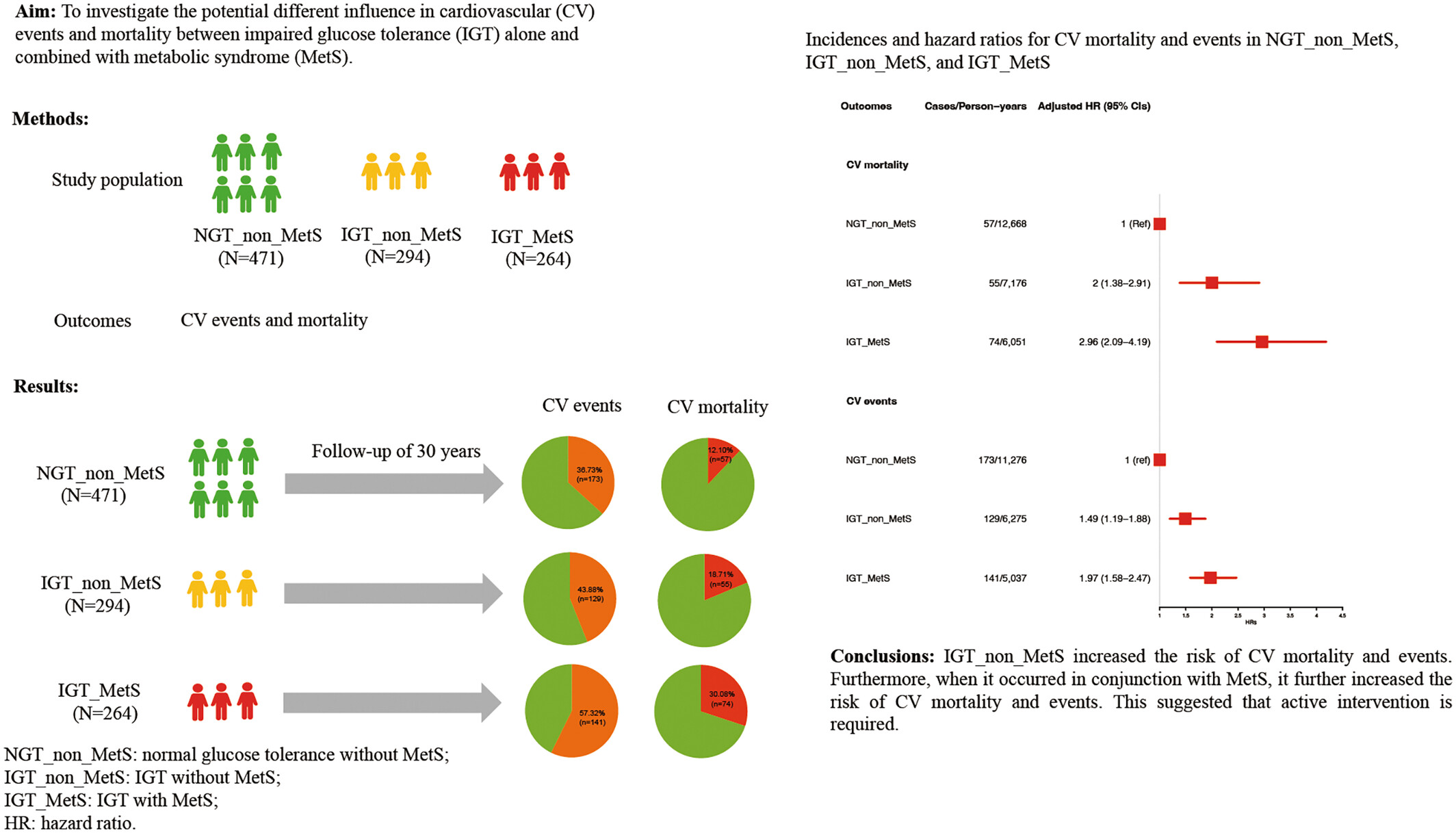
Influence of impaired glucose tolerance alone and combined with metabolic syndrome on long-term risk of cardiovascular events and mortality
- First Published: 19 August 2024
Highlights
- The IGT_non_MetS or IGT_MetS increased the risk of CV mortality and events.
- We found that the IGT_non_MetS and IGT_MetS groups had higher risk of all-cause mortality, MI events or MI mortality, and stroke events or stroke mortality compared with the NGT_non_MetS group.
- Tailoring interventions according to whether IGT was accompanied by MetS can potentially maximize cost-effectiveness, especially within the constraints of limited medical resources.
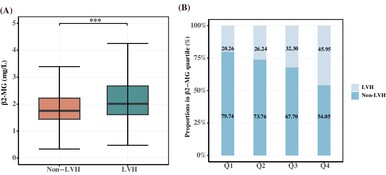
Association between serum β2-microglobulin and left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 19 August 2024