Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
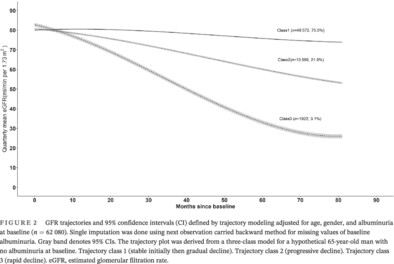
Kidney function trajectories, associated factors, and outcomes in multiethnic Asian patients with type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 02 January 2024
Highlights
- Three estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) trajectories were identified among Asian individuals with type 2 diabetes: stable initially then gradual decline (75%), progressive decline (21.9%), and rapid decline (3.1%)
- Multiple factors were associated with progressive or rapid eGFR decline (eg, women, low socioeconomic status, high hemoglobin A1c, and albuminuria)
- Progressive and rapid eGFR decline were associated with a higher risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD)
- Our results highlight the gender and social disparities in renal function decline and also underscore the potential benefit of multifactorial intervention targeting the modifiable risk factors to postpone ESKD.
REVIEW ARTICLE
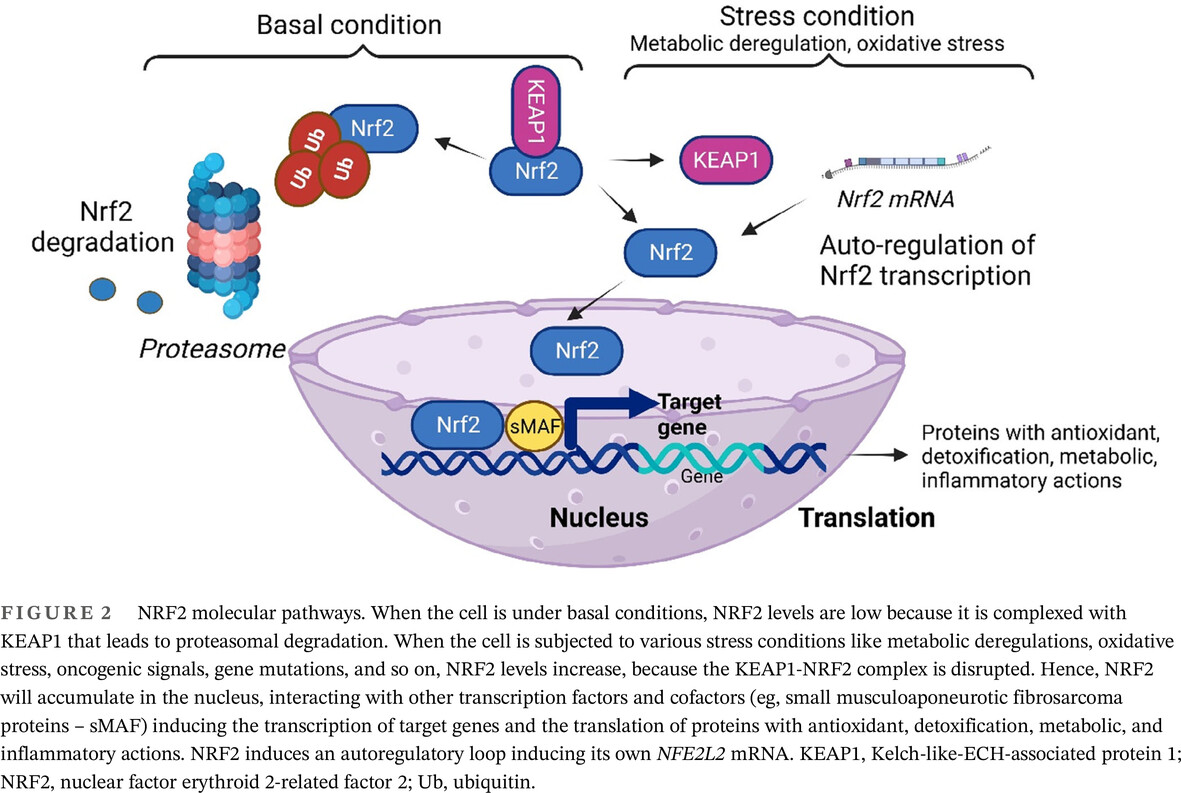
Diabetic neuropathy: A NRF2 disease?
- First Published: 29 December 2023
Highlights
- Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) is an oxidant stress response transcription factor, and is involved in metabolism, inflammation, autophagy, proteostasis, mitochondrial physiology, and immune responses.
- Chronic hyperglycemia in diabetes and prediabetes conditions induces a decrease in NRF2 that leads to an increase of oxidative stress and inflammation.
- NRF2 links neuroinflammation and apoptotic pathways and contributes to the development of diabetic neuropathy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
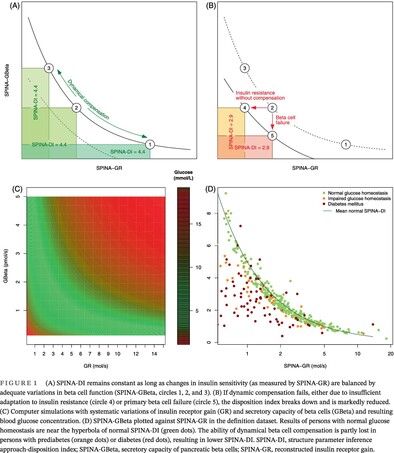
A novel simple disposition index (SPINA-DI) from fasting insulin and glucose concentration as a robust measure of carbohydrate homeostasis
- First Published: 02 January 2024
Highlights
- We defined a fasting-based disposition index (structure parameter inference approach-disposition index [SPINA-DI]), calculated as the product of the secretory capacity of pancreatic beta cells (SPINA-GBeta) multiplied by estimated insulin receptor gain (SPINA-GR).
- SPINA-DI mirrors the recognized hyperbolic relationship between beta-cell function and insulin sensitivity.
- It significantly correlates with the dynamic disposition index based on frequently sampled oral glucose tolerance tests (Matsuda–DeFronzo method) and other important measures of insulin-glucose homeostasis.
- For the diagnosis of diabetes and prediabetes, it has a higher discriminatory power than other static function tests (homeostatic model assessment of β-cell function, homeostatic model assessment of insulin resistance, and quantitative insulin sensitivity check index) and dynamic, oral glucose tolerance testing-derived parameters (insulin sensitivity index, insulinogenic index and disposition index according to Matsuda and DeFronzo).
- SPINA-DI has high retest reliability compared to other markers of glucose homeostasis.
- This novel fasting-based disposition index (SPINA-DI) is defined as the product of insulin receptor gain (SPINA-GR) multiplied by beta-cell function (SPINA-GBeta). SPINA-DI may be reduced due to insulin resistance with insufficient dynamical compensation of beta-cell mass (red horizontal arrow) or due to primary beta-cell failure (red vertical arrow). SPINA-DI was validated in three cohorts. It had advantages in validity, reliability, and diagnostic power compared to established criteria.
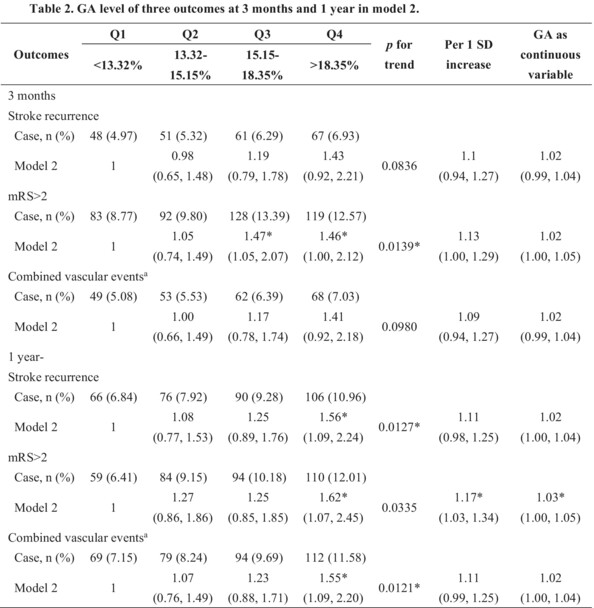
Glycated albumin levels are associated with adverse stroke outcomes in patients with acute ischemic stroke in China
- First Published: 12 September 2024
Fasting blood glucose level and risk of all-cause and cause-specific mortality in peritoneal dialysis patients
- First Published: 12 September 2024
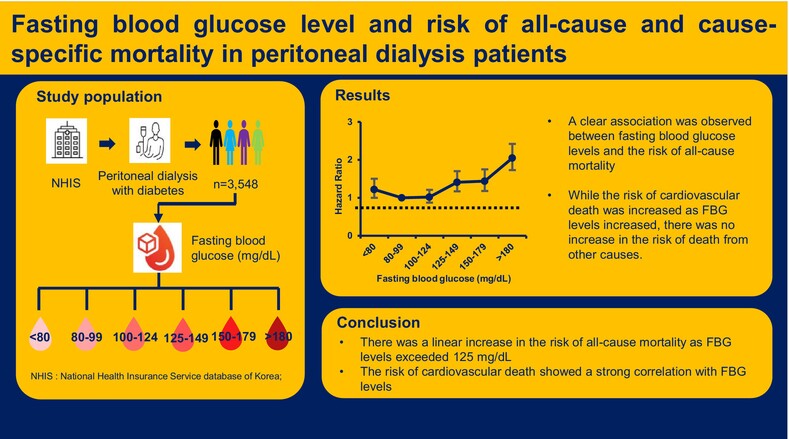
Highlights
- A clear association was observed between FBG levels and the risk of all-cause mortality in PD patients, indicating that FBG is a significant indicator for quantifying the risk of all-cause mortality in these patients.
- Although a higher FBG level was significantly associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular-related death, there was no notable increase in the risk of death from cancer or infections as the FBG levels increased.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Continuous glucose monitor metrics and hemoglobin A1c correlation in youth with diabetes: A retrospective analysis of real-world correlations
- First Published: 12 September 2024
Type B insulin resistance syndrome induced by anti-PD-1 therapy
- First Published: 12 September 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Diabetes mellitus in stable chronic heart failure and the combination with humoral activation, their association, and prediction of 2-year adverse outcomes. Data from the FAR NHL registry
- First Published: 12 September 2024
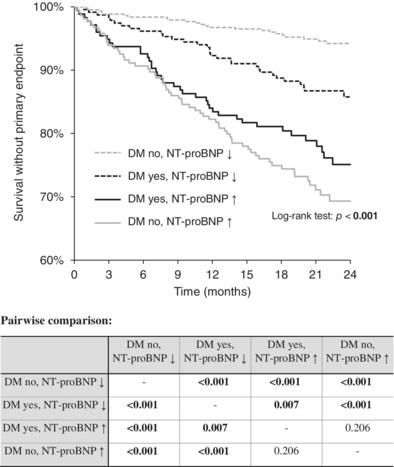
Highlights
- Diabetic patients more often has comorbidities such as ischemic heart disease, hypertension, dyslipidemia, or renal impairment, higher uric acid, lower hemoglobin, and lower eGFR.
- Based on a large prospective multicenter registry, we found that the combination of diabetes and NT-proBNP levels may help stratify the prognosis of patients with chronic heart failure when the NT-proBNP level is low.
- High NT-proBNP is in itself a strong predictor of events (all-cause death, left ventricle assist device implantation, and orthotopic heart transplantation), that the addition of diabetes mellitus will no longer improve the stratification of patient prognosis in this group.
CASE REPORT
A novel nonsense mutation c.747C>G in the NEUROD1 gene detected within a Chinese family affected by maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 6
- First Published: 12 September 2024
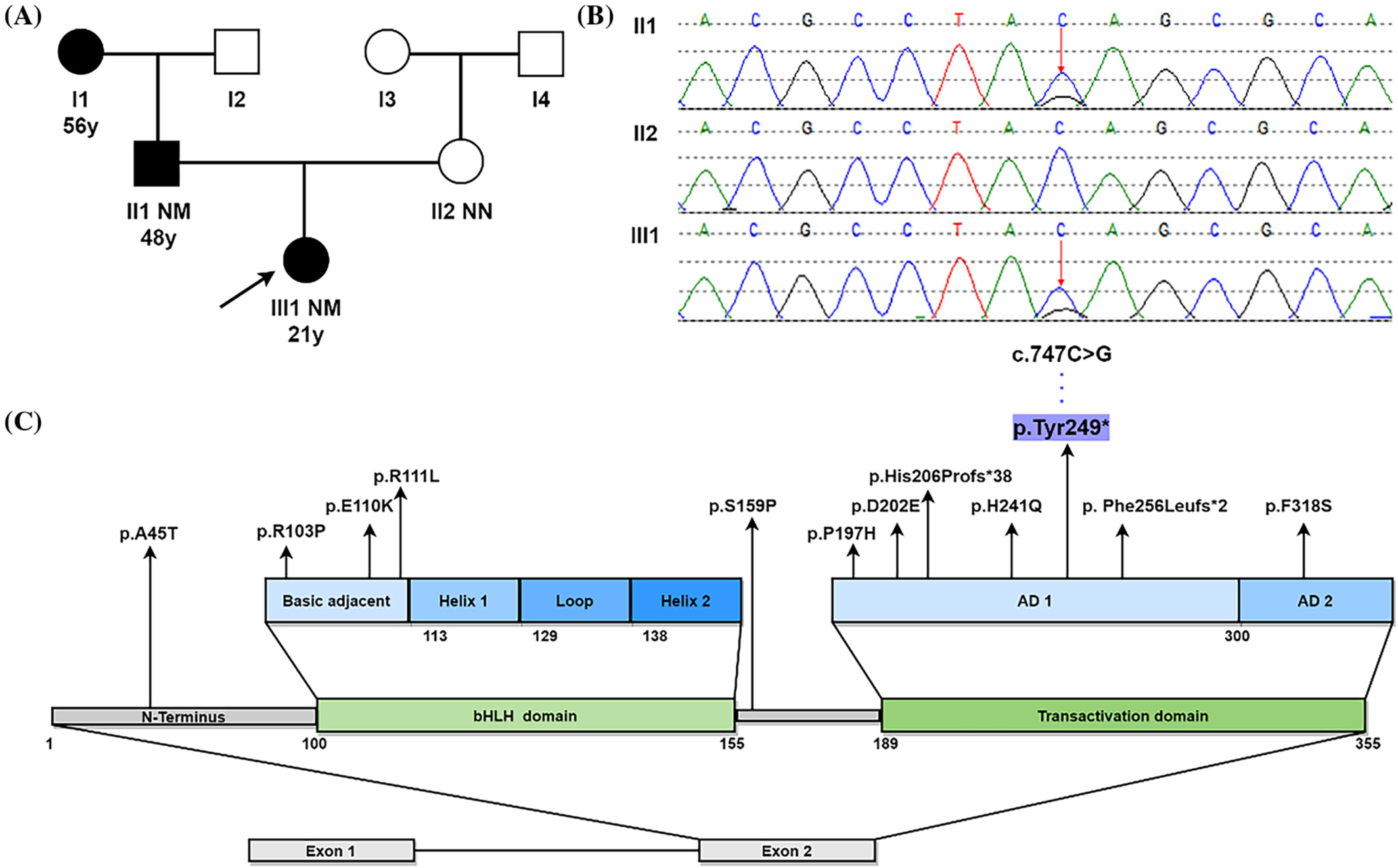
Highlights
- Maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 6 (MODY6) is a rare form of monogenic diabetes mellitus due to NEUROD1 gene mutation on chromosome 2q32.
- A 21-year-old woman exhibiting weight loss, polyuria, and hyperglycemia was initially misdiagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Considering the early-onset age, a three-generation family history of diabetes, and negative autoimmune antibodies, a MODY diagnosis was suspected.
- Genetic analysis revealed that she inherited a novel heterozygous nonsense NEUROD1 mutation c.747C>G (p.Tyr249*) from her father.
- Correct MODY6 diagnosis facilitates appropriate interventions.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
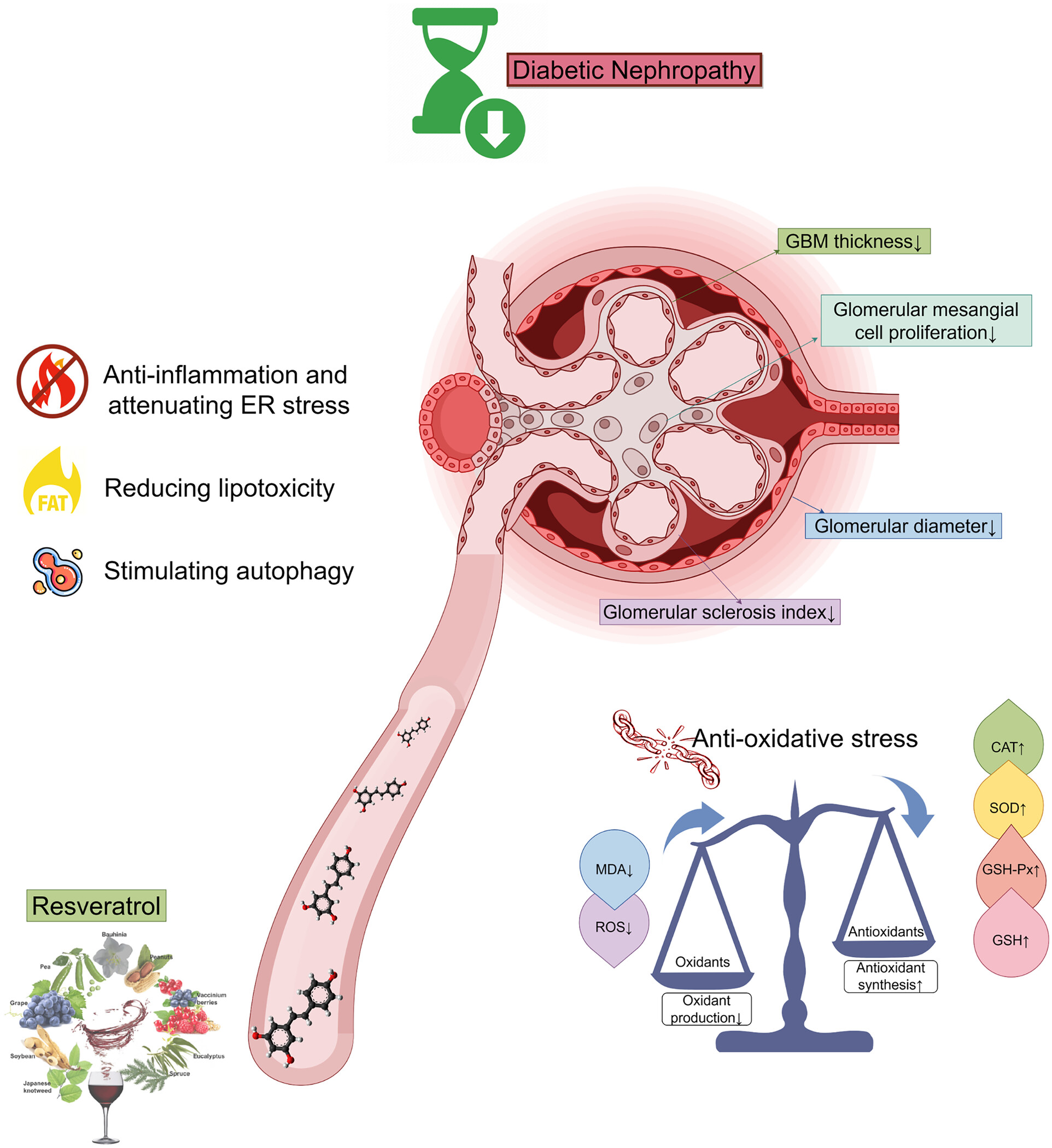
Resveratrol delays the progression of diabetic nephropathy through multiple pathways: A dose–response meta-analysis based on animal models
- First Published: 12 September 2024
Effect of patient-centered self-management intervention on glycemic control, self-efficacy, and self-care behaviors in South Asian adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter randomized controlled trial
- First Published: 12 September 2024
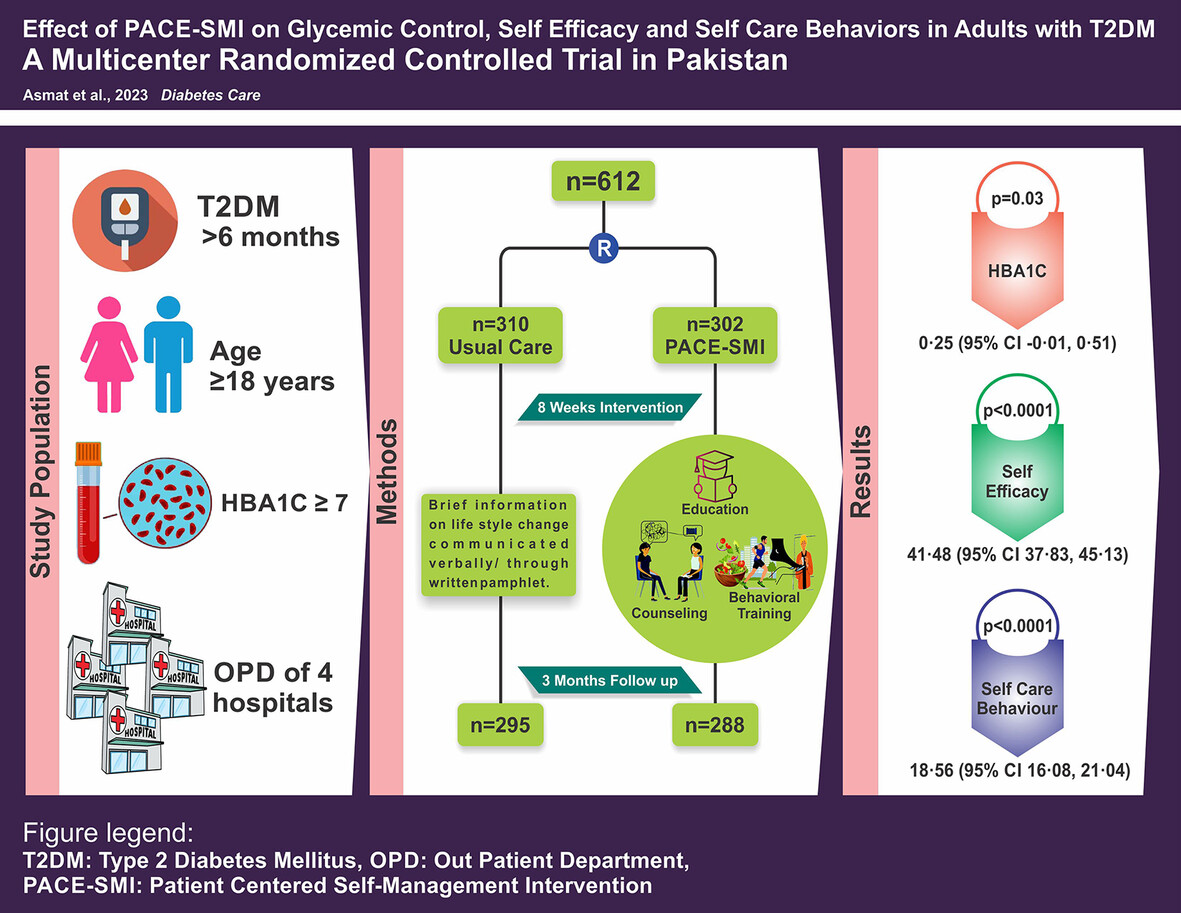
Highlights
- T2DM dominates worldwide, especially in the low middle income countries (LMICs) of South Asia.
- Despite acknowledging self-management as the corner stone in T2DM, LMICs face an implementation gap due to lacking policies and the fragmented care systems, neglecting crucial personal, behavioral, and social factors.
- In this first large-scale multicenter randomized controlled trial conducted in Pakistan, a LMIC, the nurse-led PACE-SMI demonstrated significant improvement in HbA1c, self-efficacy, and self-care behaviors in adults with T2DM at 3 months.
- Considering the substantial health and economic impact of T2DM in LMICs, evidence presented in this study holds implications for the healthcare policies, advocating for integration of PACE-SMI into standard practice.