Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
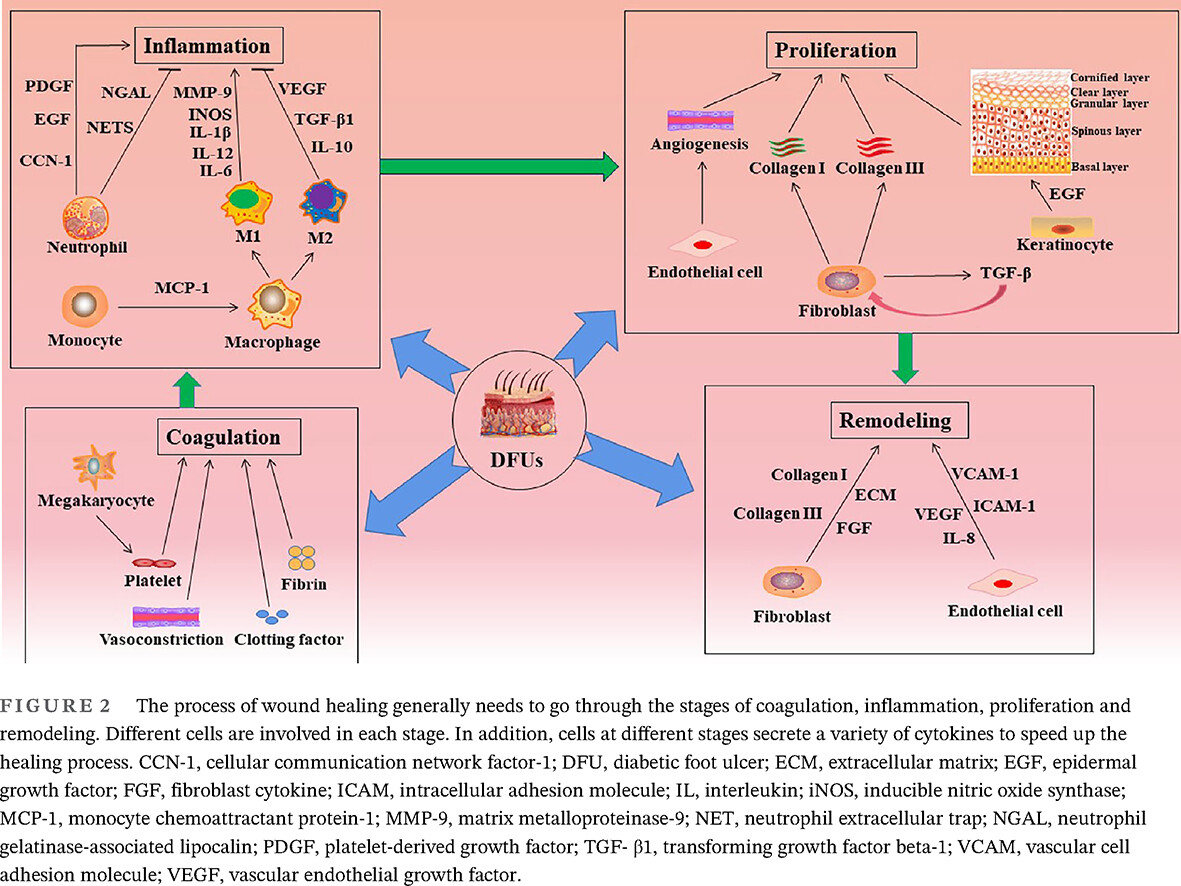
Mechanisms of diabetic foot ulceration: A review
糖尿病足溃疡发生机制综述
- First Published: 09 March 2023
Highlights
- With the increase in the elderly population, diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) severely affect human health and societies worldwide. They will pose significant medical, social, and socioeconomic challenges.
- Reviewing the existing studies on the pathogenesis of DFUs, most of them focus on clinical nursing and treatment. However, the molecular mechanisms of DFUs are poorly studied.
- The mechanisms of inflammatory response, signal pathway, and epigenetics in DFUs are highlighted.
- The authors suggest reasonable choices of finding out important targets for treatment of disorders of DFUs and developing the effective products underlying the molecular pathogenesis of DFUs.
- Future insights into the use of motor molecules to carry drug molecules in combination with existing materials are briefly discussed.
Use of basal insulin in the management of adults with type 2 diabetes: An Asia-Pacific evidence-based clinical practice guideline
使用基础胰岛素治疗成人2型糖尿病:亚太地区循证临床实践指南
- First Published: 23 April 2023

Highlights
- This is a systematic review-based clinical practice guideline. After internal and external review, two strong recommendations, six conditional recommendations, and one qualifying statement were made for insulin-naive adult patients with type 2 diabetes. Although the guideline authors came from the Asia-Pacific region, the eligible evidence was based on recent English publications. The recommendations and the clinical thresholds set up in the guideline can be used as references for clinicians worldwide.
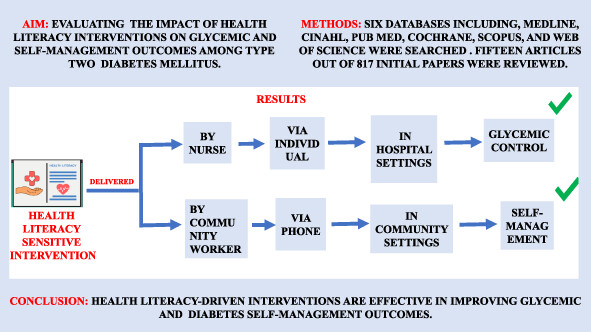
The impact of health literacy interventions on glycemic control and self-management outcomes among type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review
健康素养干预对2型糖尿病患者血糖控制和自我管理结果的影响:一项系统综述
- First Published: 05 July 2023
Highlights
- Health literacy (H)L-driven interventions were effective in controlling glycemic levels and improving diabetes self-management outcomes.
- The level of glycemic control and self-management skills were improved better through individual and telephone-based intervention, respectively, in comparing group intervention.
- Community worker led interventions were effective in improvements in diabetes knowledge and self-care behaviors; however, nurse-led interventions were more effective in glycemic control.
- Better glycemic control was achieved in hospital settings compared with outpatient settings.
- HL interventions yielded better improvement in self-management among people with a longer diabetes duration (more than 7 years) than those with short duration of diabetes.
- It was possible to achieve a significant reduction in HbA1c level after a 3-month intervention in hospital settings.
Mechanisms of bariatric surgery for weight loss and diabetes remission
减重手术减轻体重和缓解糖尿病的机制
- First Published: 13 July 2023
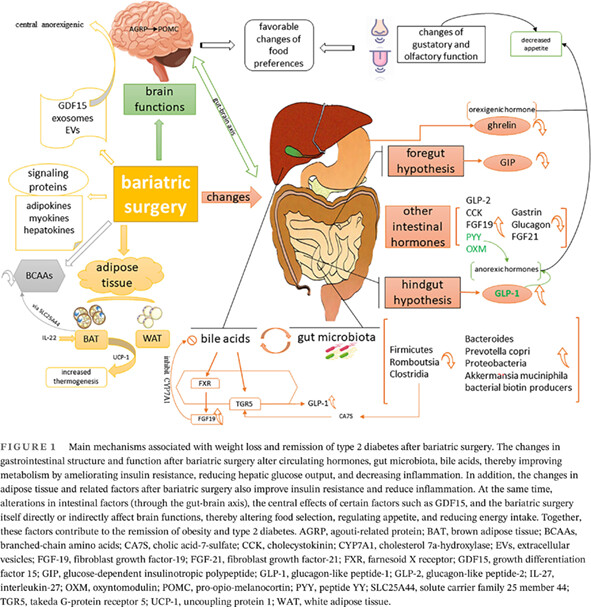
Highlights
- Controversial changes in intestinal hormones after bariatric surgery (BS) were summarized.
- The changes of signaling proteins involved in insulin resistance and the newly proposed changes in growth differentiation factor 15, exosomes, and extracellular vesicles after BS were elucidated.
- The interactions between bile acids and gut microbiota and the gut–brain axis play an indispensable role in BS.
Effectiveness, safety, initial optimal dose, and optimal maintenance dose range of basal insulin regimens for type 2 diabetes: A systematic review with meta-analysis
基础胰岛素治疗2型糖尿病的有效性、安全性、初始最佳剂量和最佳维持剂量范围:一项meta分析的系统综述
- First Published: 10 April 2023
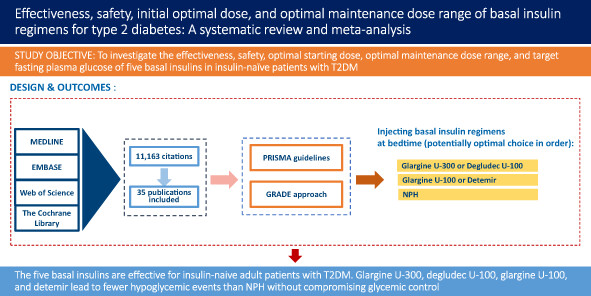
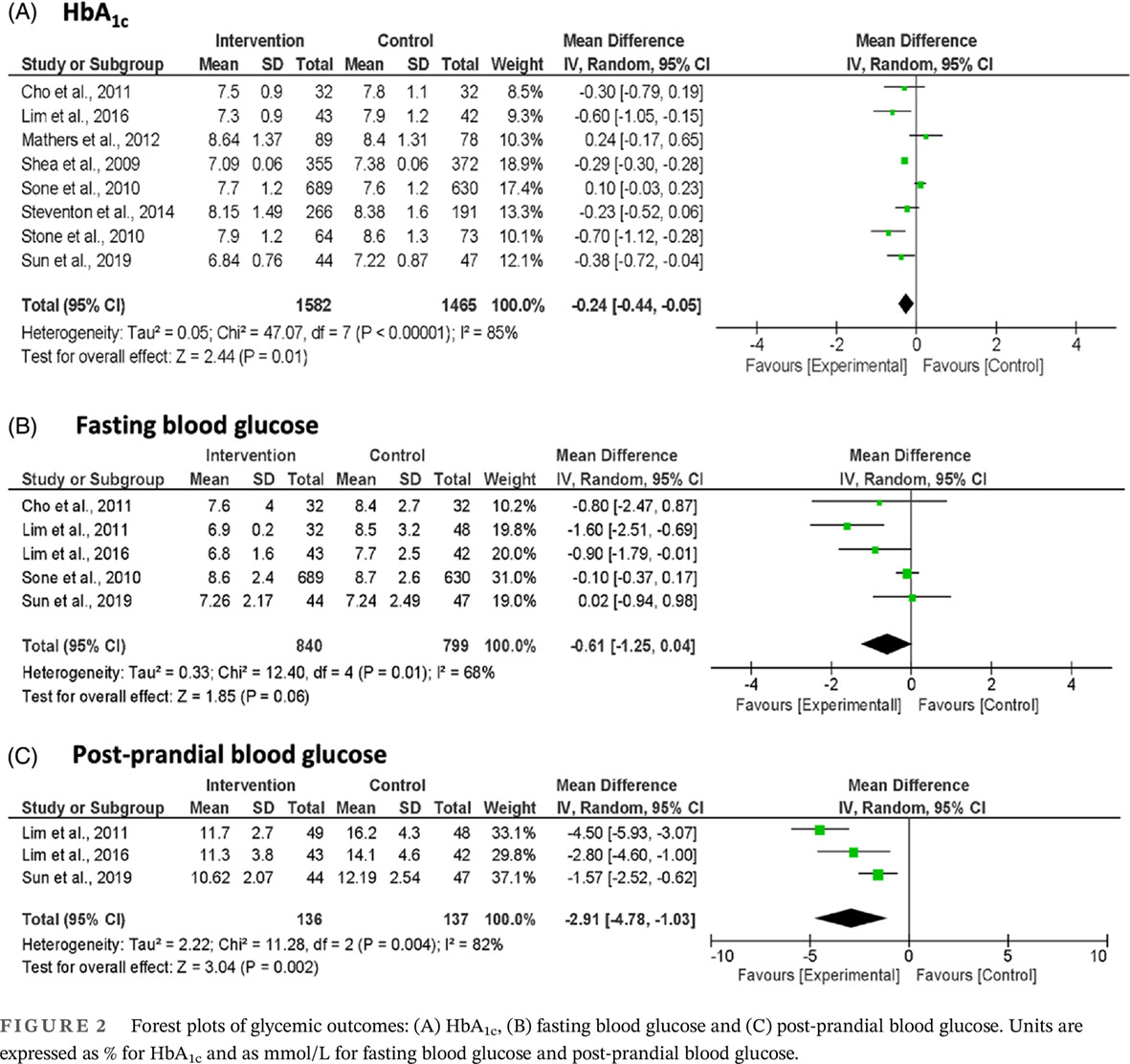
Highlights
This is a systematic review and meta-analysis. MEDLINE, EMBASE, Web of Science, and the Cochrane Library were searched from January 2000 to February 2022. Among 11,163 citations retrieved, 35 publications met the pre-planned criteria. The five basal insulins are effective for insulin-naive adult patients with T2DM. Glargine U-300, degludec U-100, glargine U-100, and detemir lead to fewer hypoglycemic events than NPH without compromising glycemic control.
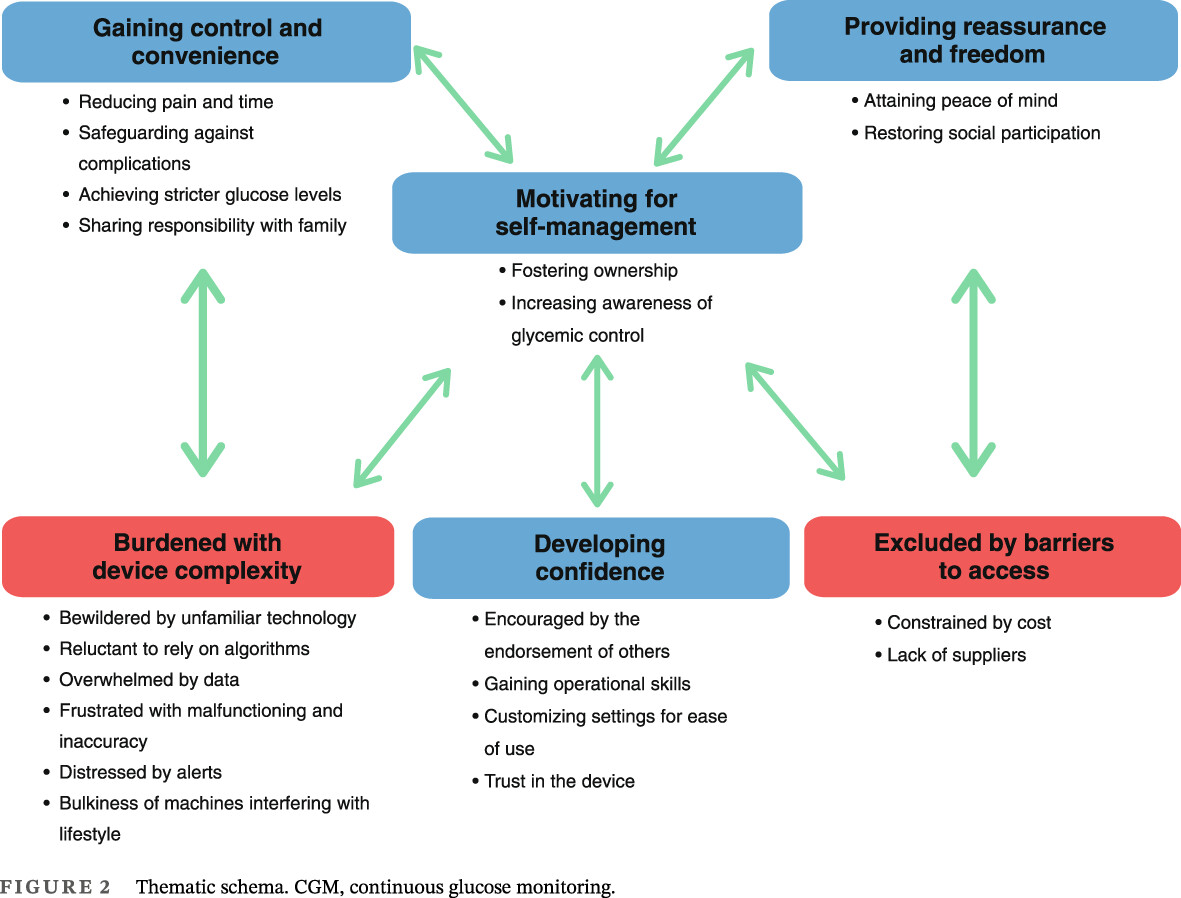
Patient experiences of continuous glucose monitoring and sensor-augmented insulin pump therapy for diabetes: A systematic review of qualitative studies
糖尿病患者接受连续血糖监测和传感器增强胰岛素泵治疗的体验:对定性研究的系统综述
- First Published: 08 August 2023
Effects of mobile health interventions on health-related outcomes in older adults with type 2 diabetes: A systematic review and meta-analysis
移动健康干预对老年2型糖尿病患者健康相关结果的影响: 系统综述和meta分析
- First Published: 17 January 2023
Highlights
- Mobile health (mHealth) is an emerging forefront in patient-centric care.
- Efficacy of mHealth interventions on health outcomes among older adults with type 2 diabetes is limited.
- Modest benefits on cardiometabolic outcomes with mHealth interventions have uncovered critical gaps in the field and offered insights to address barriers at hand.
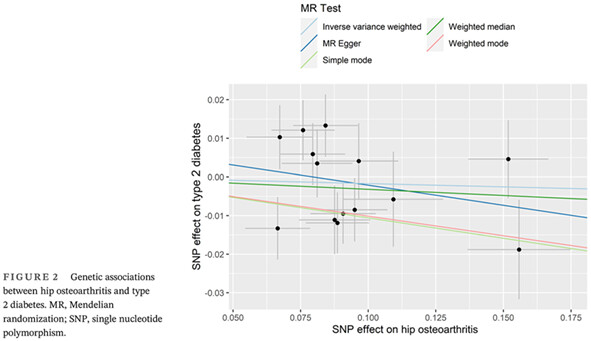
Osteoarthritis and risk of type 2 diabetes: A two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis
骨关节炎与2型糖尿病的风险:一项双样本孟德尔随机化分析
- First Published: 31 July 2023
Noninsulin-based antihyperglycemic medications in patients with diabetes and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis
糖尿病合并COVID-19患者的非胰岛素类降糖药物治疗:一项系统综述和荟萃分析
- First Published: 23 January 2023
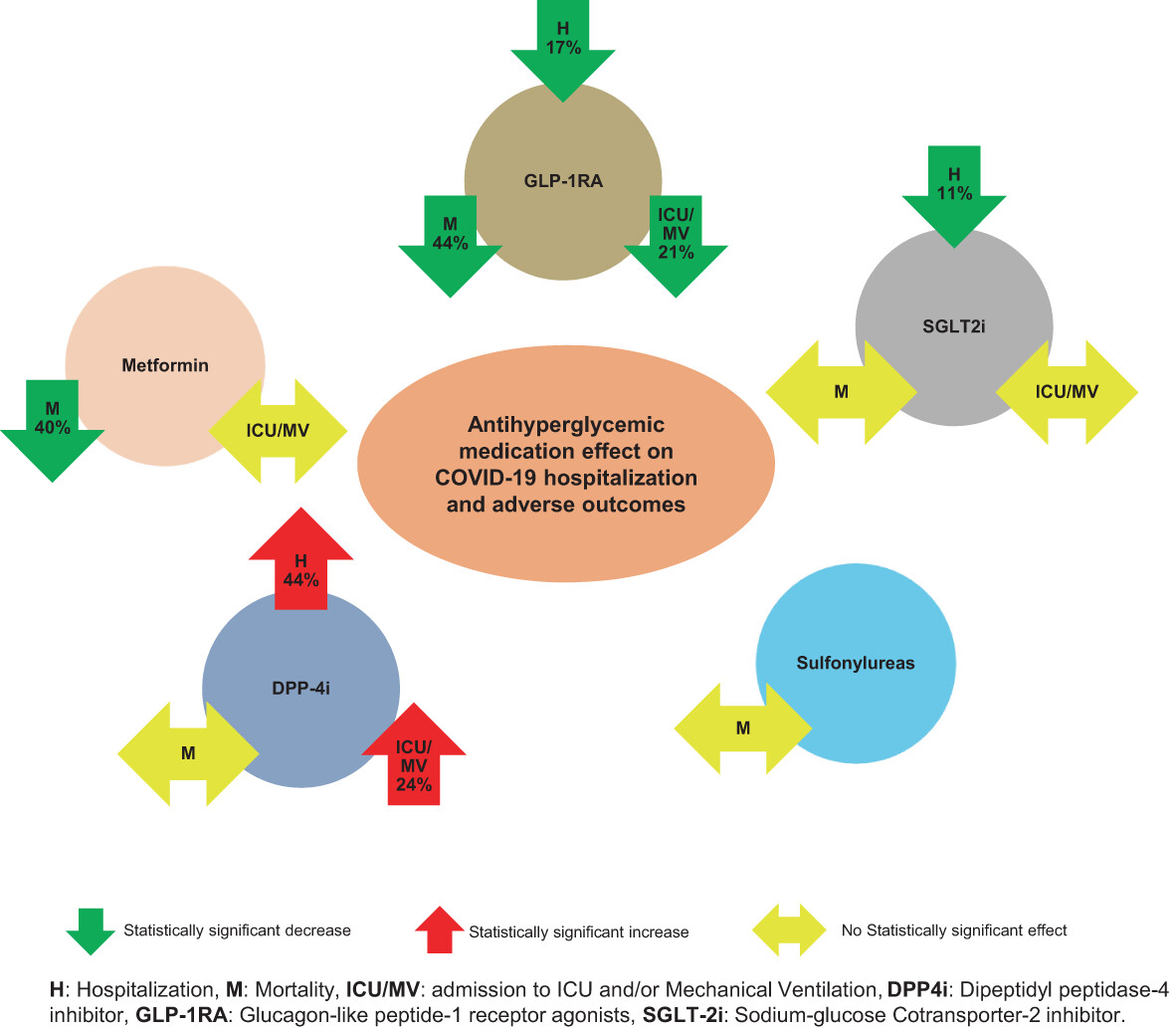
Highlights
- Metformin was associated with statistically significantly lower overall mortality for inpatients and outpatients.
- Dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor use was associated with statistically significant higher hospitalization risk and higher risk of intensive care unit (ICU) admissions and/or mechanical ventilation.
- There was a statistically significant decrease in hospitalization for sodium glucose transporter 2 inhibitor) users vs. nonusers.
- Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist use was associated with a statistically significant decrease in mortality, ICU admission and/or mechanical ventilation, and hospitalization.
Protective effects of nattokinase against microvasculopathy and neuroinflammation in diabetic retinopathy
纳豆激酶对糖尿病视网膜病变微血管病变和神经炎症的保护作用
- First Published: 04 July 2023
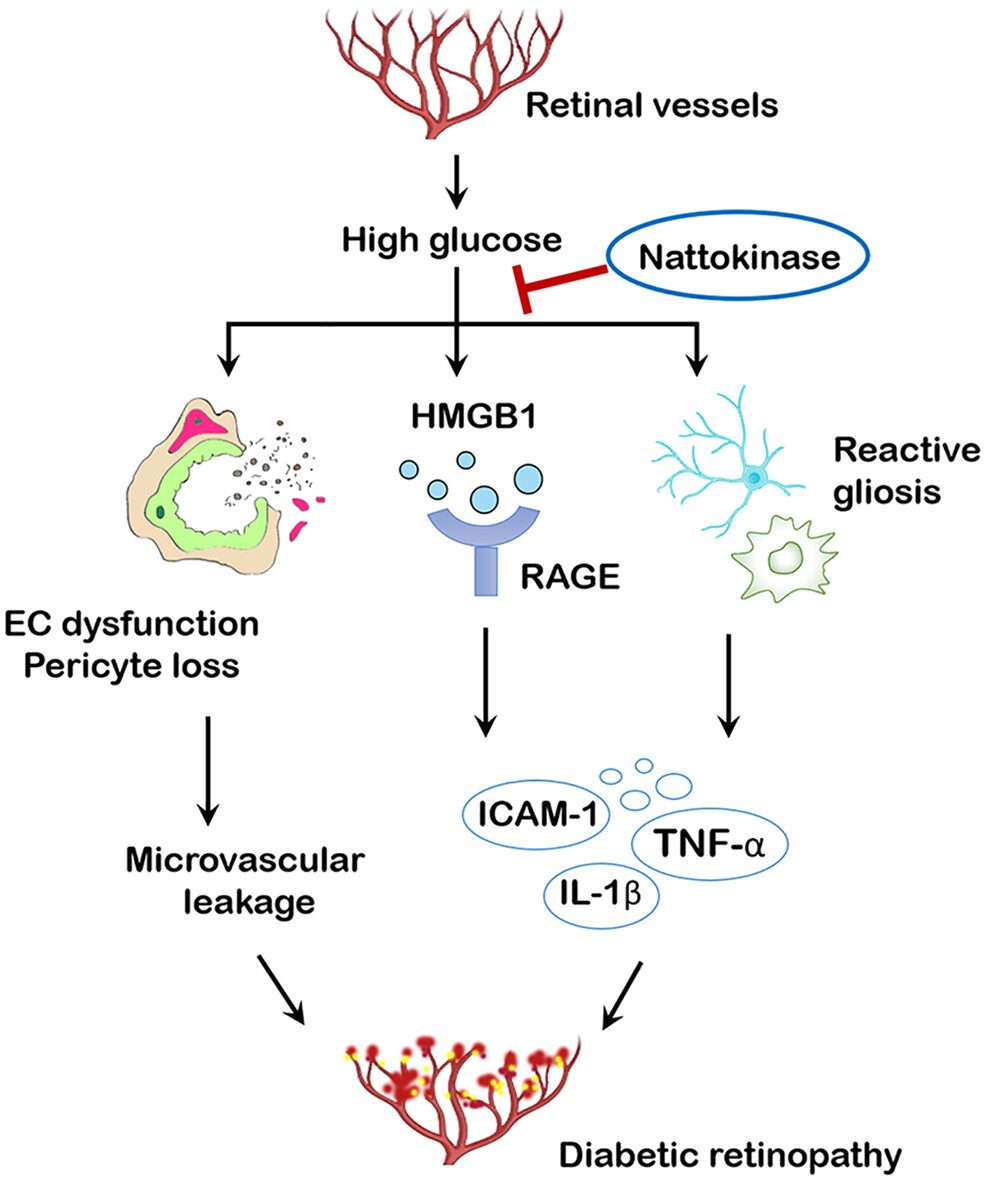
Highlights
- Nattokinase rescued endothelial dysfunction and pericyte loss in the diabetic retina.
- Nattokinase attenuated diabetes-induced retinal inflammation and neurodegeneration.
- High mobility group box 1 signaling was involved in nattokinase-mediated retinal protection.
- Nattokinase might be developed as a pharmaceutical product for early diabetic retinopathy.