Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW ARTICLE
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and kidney outcomes
- First Published: 04 October 2024
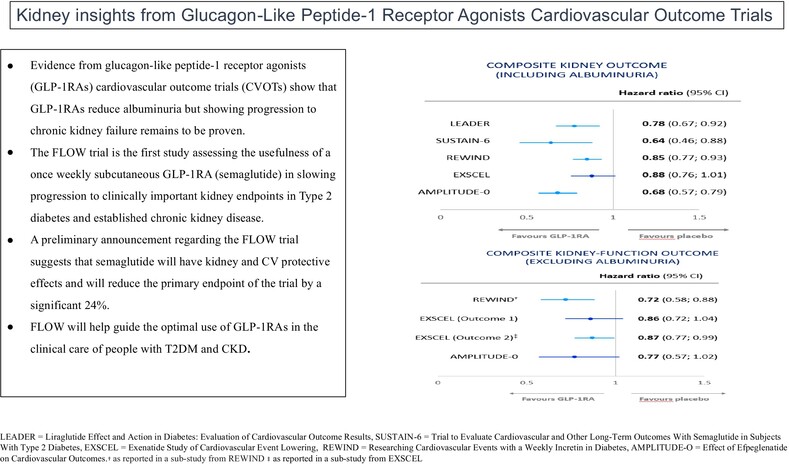
Highlights
- Evidence from GLP-1RAs CVOTs show that GLP-1RAs reduce albuminuria but slowing of progression to chronic kidney failure remains to be proven.
- The FLOW trial is the first study assessing the usefulness of a once-weekly subcutaneous GLP-1RA (semaglutide) in slowing progression to clinically important kidney end points and protection form cardiovascular disease people with T2DM and established CKD.
- FLOW will help guide the optimal use of GLP-1RAs in the clinical care of people with T2DM and CKD.
Prevalence and influencing factors of malnutrition in diabetic patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 04 October 2024
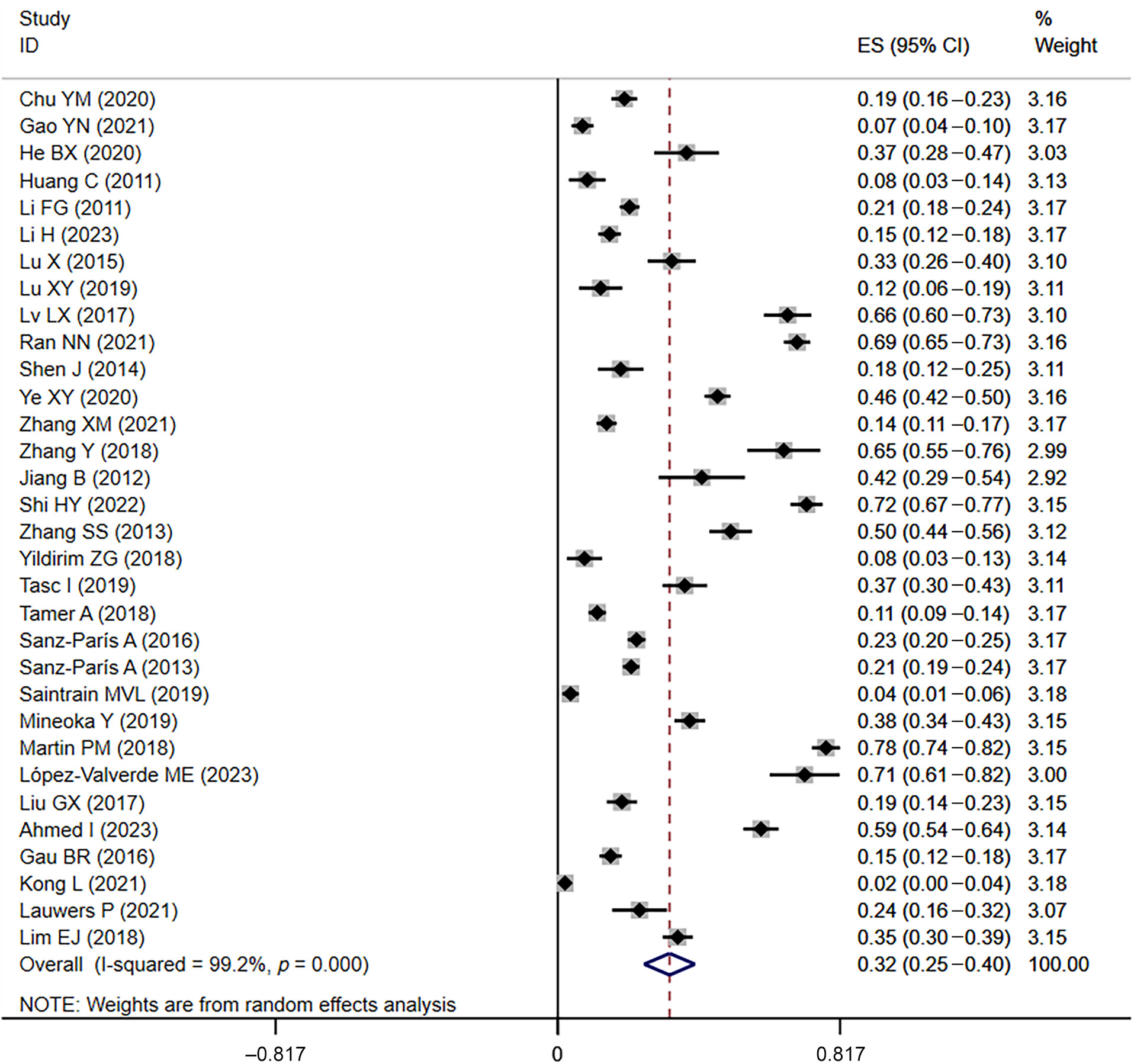
Highlights
- The overall prevalence of malnutrition in diabetic patients was 33% (95% CI: 0.25–0.40), and the at-risk prevalence of malnutrition was 44% (95% CI: 0.34–0.54).
- Diabetic patients with malnutrition had significantly lower levels of body mass index, albumin, hemoglobin, triglyceride, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, while showing an increase in glycosylated hemoglobin.
- C-reactive protein >10 mg/L, age, duration of diabetes, Wagner grades 3–5, with cardiovascular disease, and using insulin were identified as risk factors for malnutrition in diabetic patients.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Comparing Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists versus metformin in drug-naive patients: A nationwide cohort study
- First Published: 04 October 2024
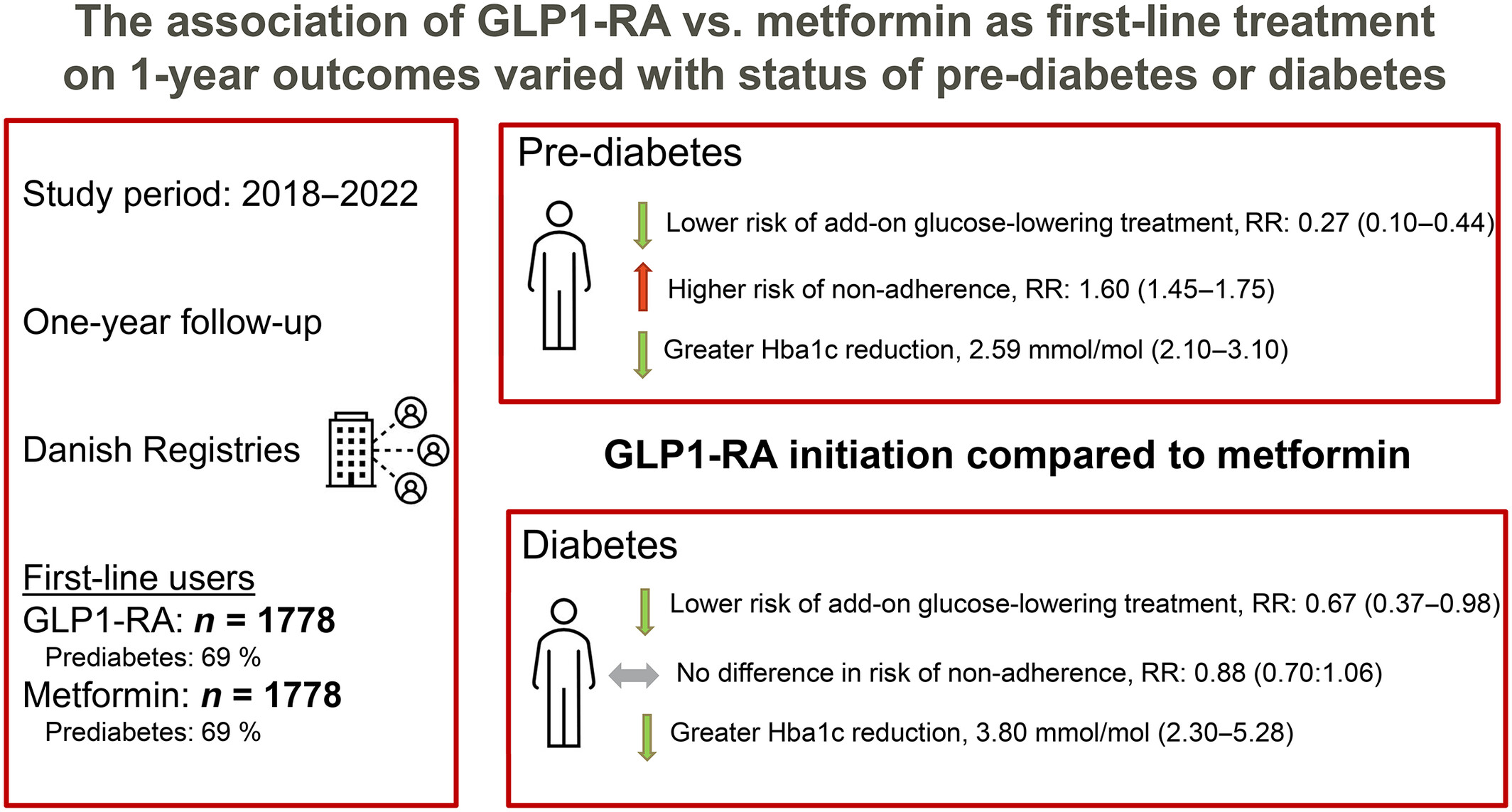
Highlights
- In this nationwide cohort study, initiating GLP-1 RA as the first-line treatment was associated with improved 1-year HbA1c levels compared with metformin.
- GLP-1 RA initiation was also associated with a lower risk of requiring additional glucose-lowering therapy; however, initial treatment adherence varied depending on the prediabetes or diabetes status.
- Overall, GLP-1 RAs as the first-line choice for 1-year outcomes may exhibit variability regarding treatment management based on prediabetes or diabetes status, but they generally result in improved glycemic control.
Assessing and predicting type 2 diabetes risk with triglyceride glucose-body mass index in the Chinese nondiabetic population—Data from long-term follow-up of Da Qing IGT and Diabetes Study
- First Published: 04 October 2024
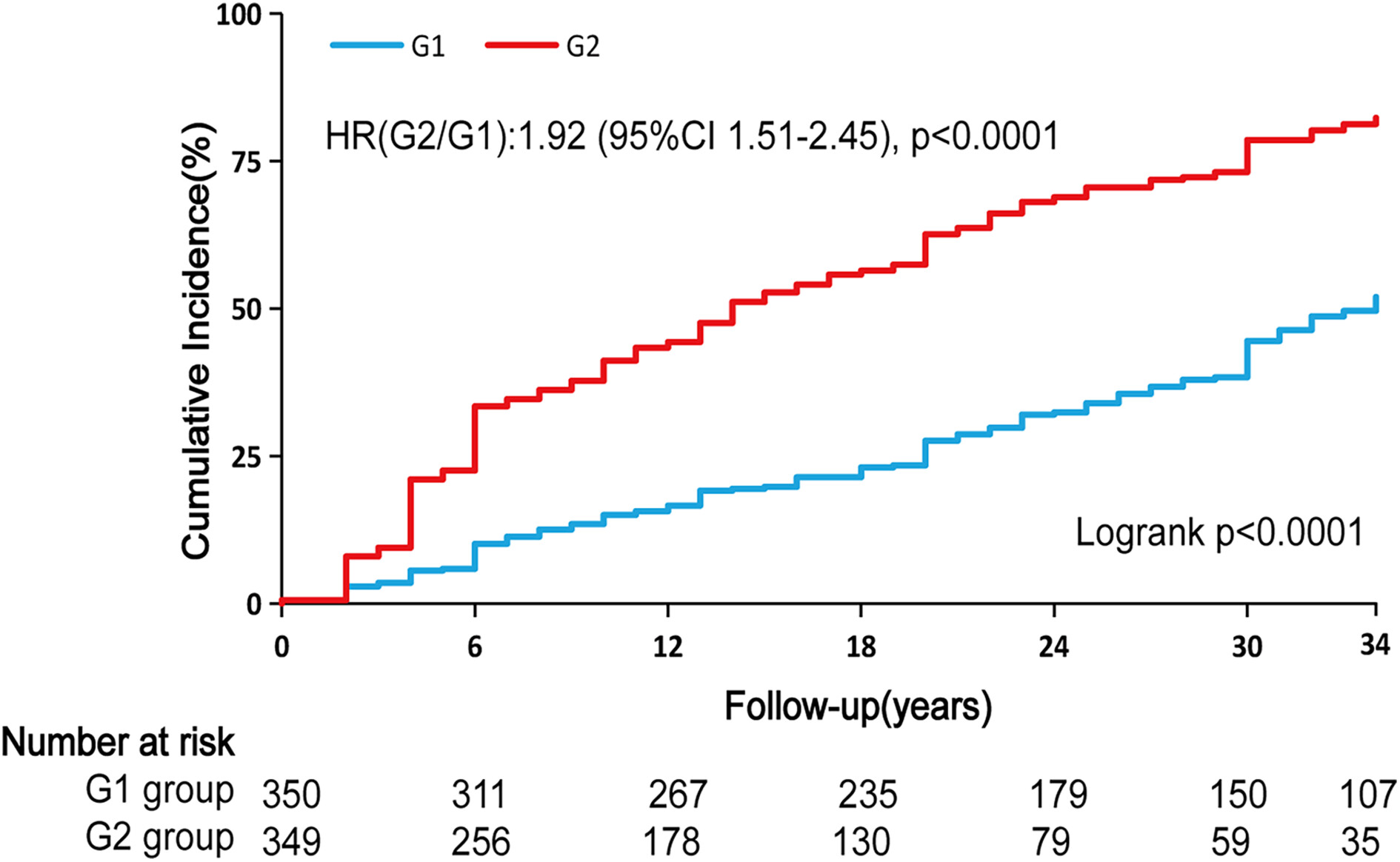
Highlights
- After the 34-year follow-up, increased TyG-BMI was independently associated with a higher risk of type 2 diabetes.
- TyG-BMI exhibited higher predictive ability than TyG or HOMA-IR in both short (6-year) and long terms (34-year). The best thresholds of TyG-BMI to predict diabetes were relatively stable (195.24–208.41).
- Our results provide the possibility to utilize TyG-BMI for predicting diabetes risk in clinical practice.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Effectiveness of wearable technology-based physical activity interventions for adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-regression
- First Published: 04 October 2024
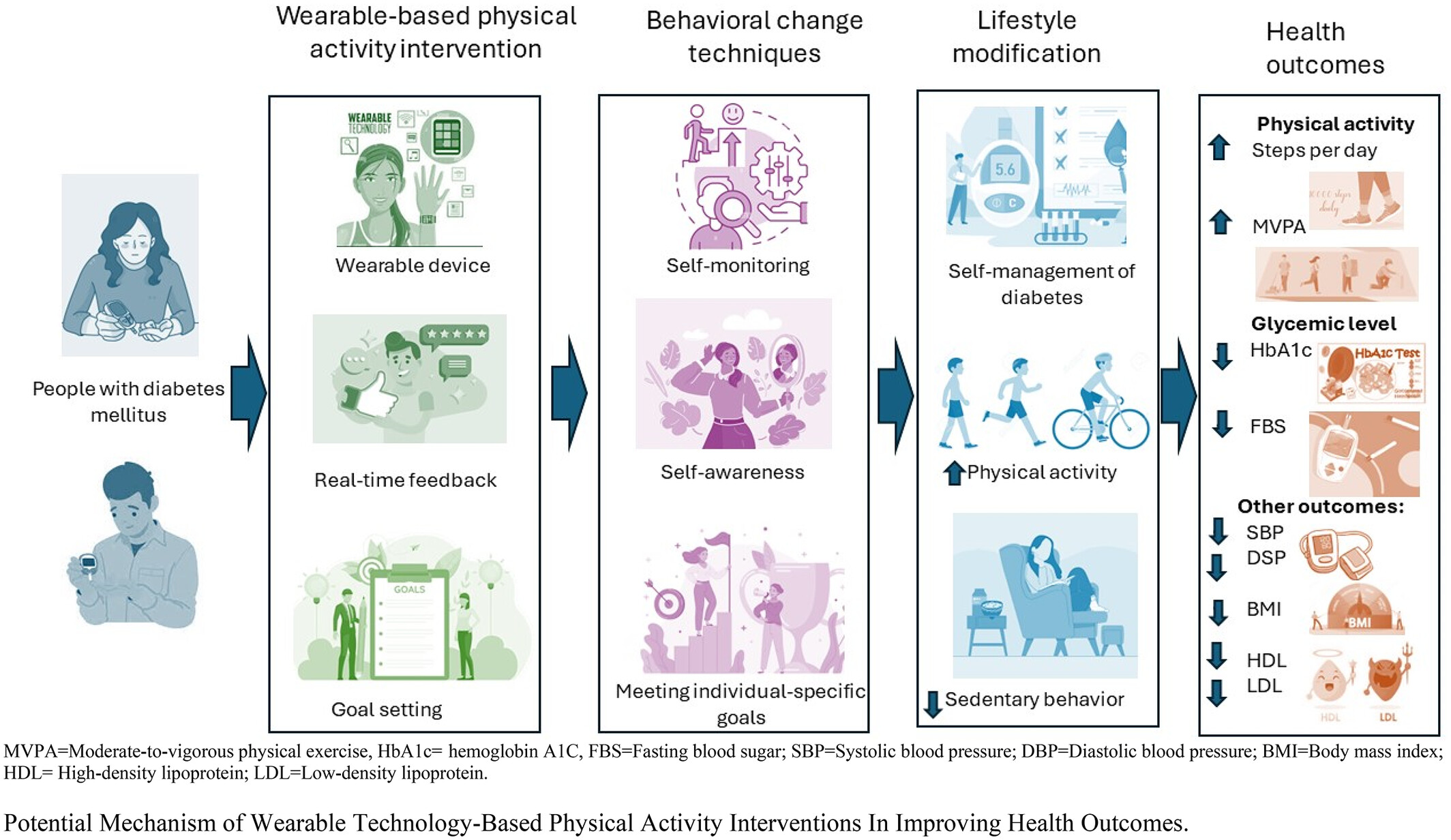
Highlights
- In people with diabetes mellitus, wearable technology-based physical activity interventions significantly increased daily steps and reduced systolic blood pressure.
- Intervention had a goal-setting component among T2DM patients, which had a greater effect on lowering BMI than their counterparts.
- In terms of BMI reduction, the year of publication was a significant covariate.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Increased prevalence of diabetes mellitus and its metabolic risk factors from 2002 to 2017 in Shanghai, China
- First Published: 07 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
National burden and risk factors of diabetes mellitus in China from 1990 to 2021: Results from the Global Burden of Disease study 2021
- First Published: 07 October 2024
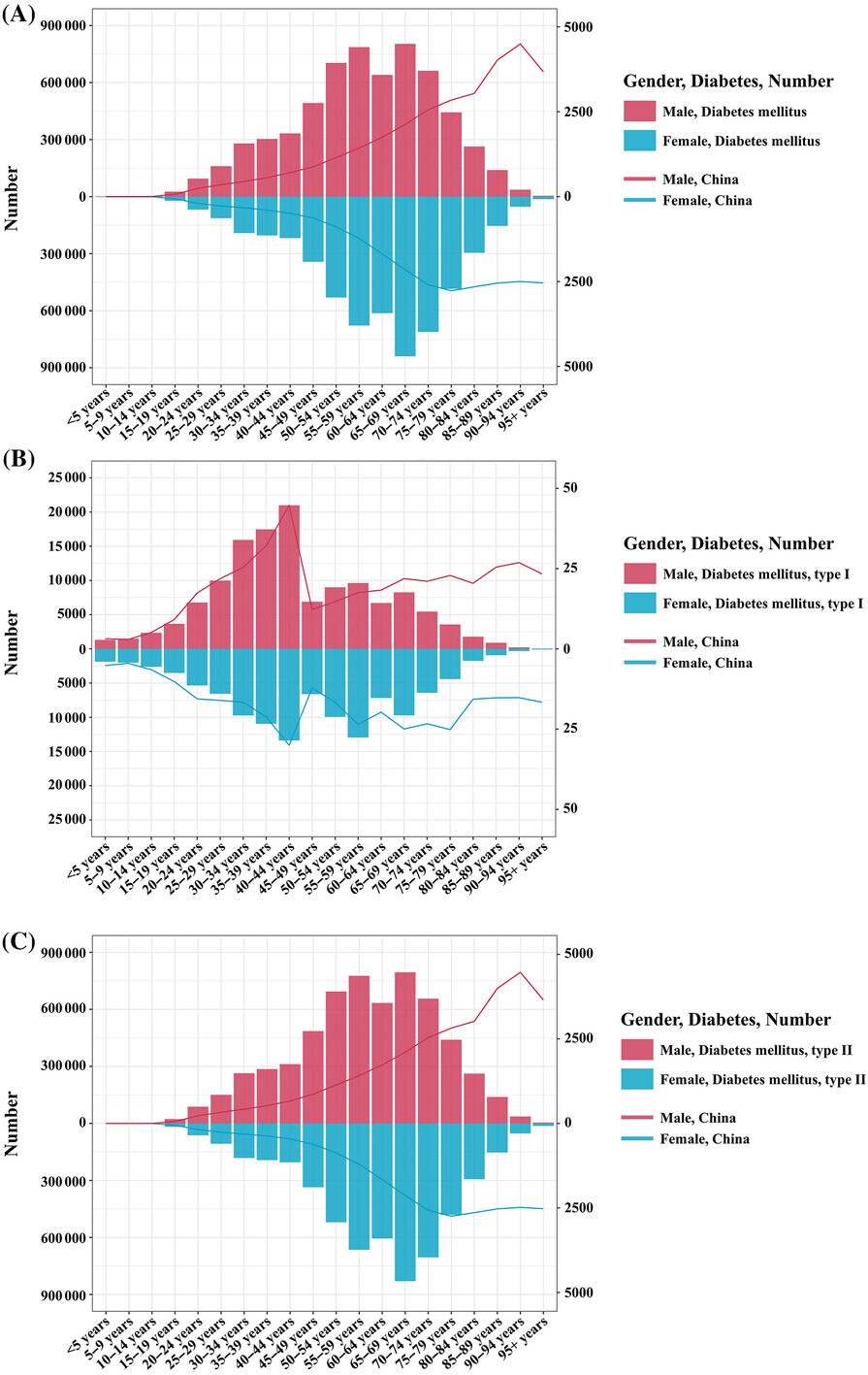
Highlights
- The incidence, prevalence, and DALYs rate of diabetes in China are at relatively high levels, with a severe and rapidly growing burden of disability, particularly prominent among males.
- Interventions should be strengthened for major factors contributing to the diabetes burden, including high fasting plasma glucose, high body mass index, air pollution, and dietary risks.
The association of ideal cardiovascular health and its change with subclinical atherosclerosis according to glucose status: A prospective cohort study
- First Published: 10 October 2024
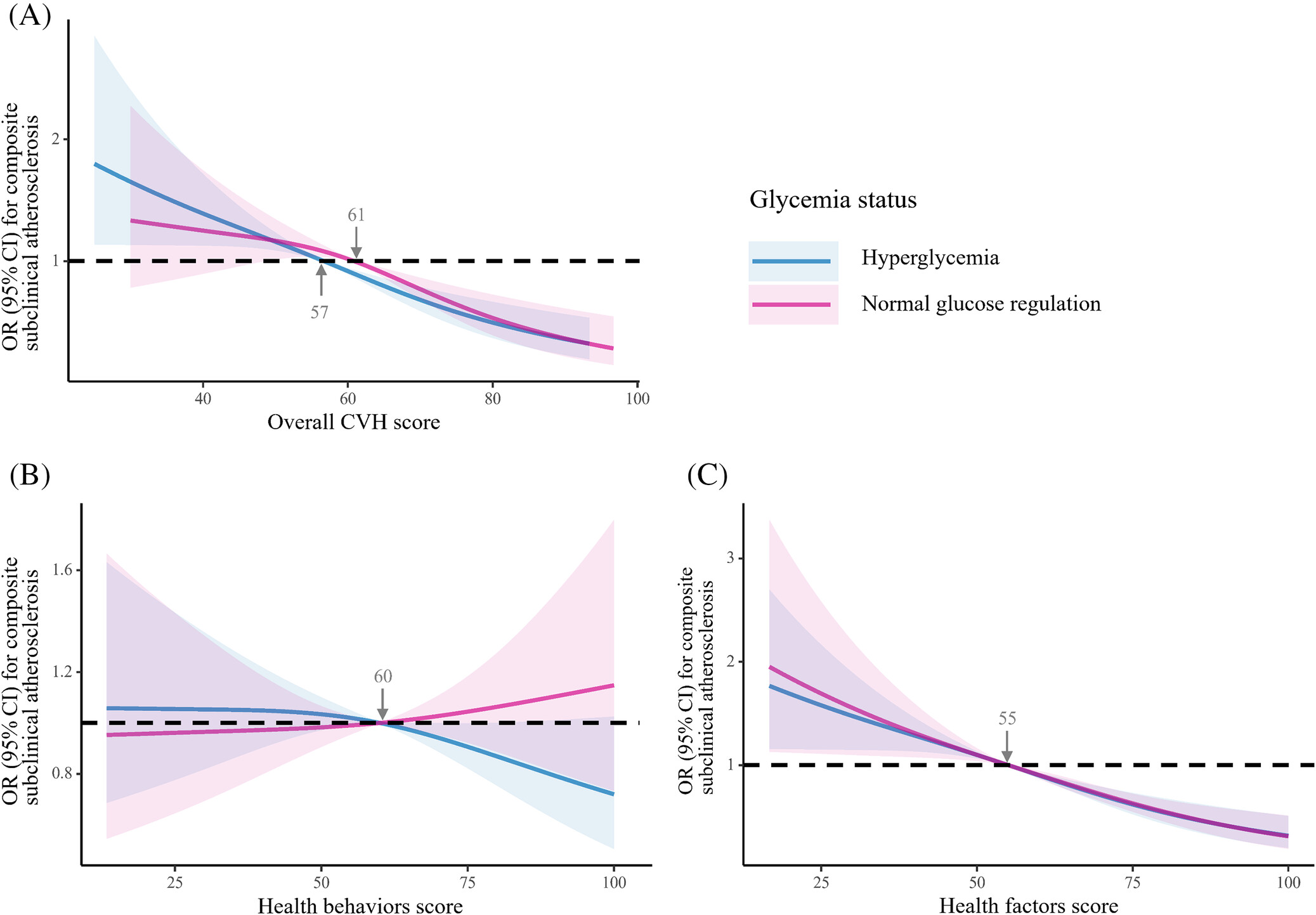
Highlights
- Participants with hyperglycemia who had high score of CVH exhibited no significant excess risk of subclinical atherosclerosis.
- Improvement in CVH during a median follow-up of 4.3 years showed a beneficial effect on reduced risk of subclinical atherosclerosis in individuals with hyperglycemia, compared with those who had normal glucose regulation and stable CVH.
- Promoting the adherence to, and the improvement of, both healthy behaviors and factors was a key strategy to tackle the onset of atherosclerosis.
Association between coffee consumption and metabolic syndrome: A cross-sectional and Mendelian randomization study
- First Published: 10 October 2024
Highlights
- Coffee consumption ≤2 cups/day inversely linked to metabolic syndrome (MetSyn).
- No causal relationship between coffee intake and MetSyn.
- High coffee consumption (4+ cups/day) associated with central obesity.
- Ground coffee showed stronger inverse association with MetSyn than instant coffee.
- Use of artificial sweetener with coffee linked to MetSyn and its components.
Physical activity modifies the association between atherogenic index of plasma and prediabetes and diabetes: A cross-sectional analysis
- First Published: 13 October 2024
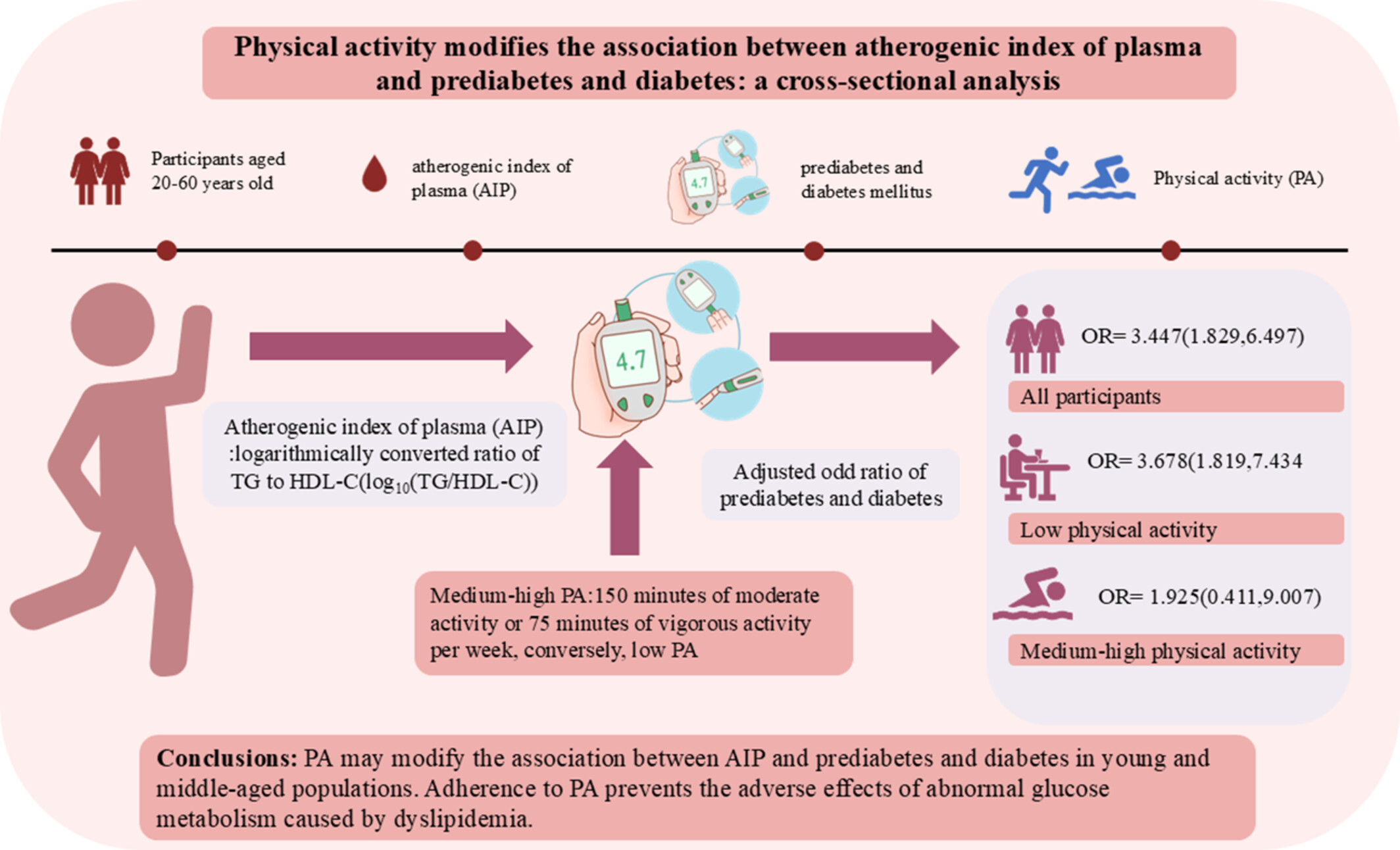
Highlights
- After adjusting for confounders, AIP was positively correlated with prediabetes and diabetes, showing a greater effect in the low PA group and a nonsignificant relationship in the high PA group.
- Restricted cubic spline showed that in midlife populations, AIP was directly associated with prediabetes and diabetes prevalence when AIP > −0.16, and the reverse was not significant.
- PA can modify the link as regards AIP with prediabetes and diabetes, especially in females.
Interactive correlations between artificial light at night, health risk behaviors, and cardiovascular health among patients with diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 13 October 2024
Highlights
- This study can help solve and expand public health problems by exploring the environmental factors of diabetes combined with cardiovascular disease and moving the problem forward.
- Artificial light at night (ALAN) is not only related to cardiovascular health but also plays a role in the development of cardiovascular disease together with other factors.
- By focusing on ALAN and green space at the same time, potential correlations between complementary factors can be discovered.
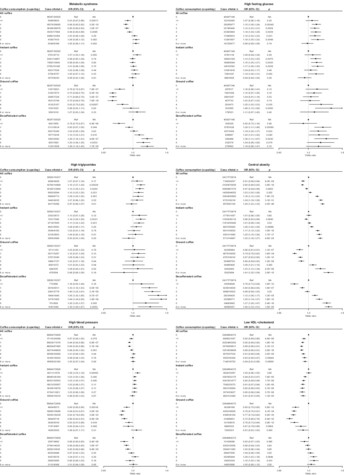
Major adverse cardiovascular events’ reduction and their association with glucose-lowering medications and glycemic control among patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study using electronic health records
- First Published: 21 October 2024
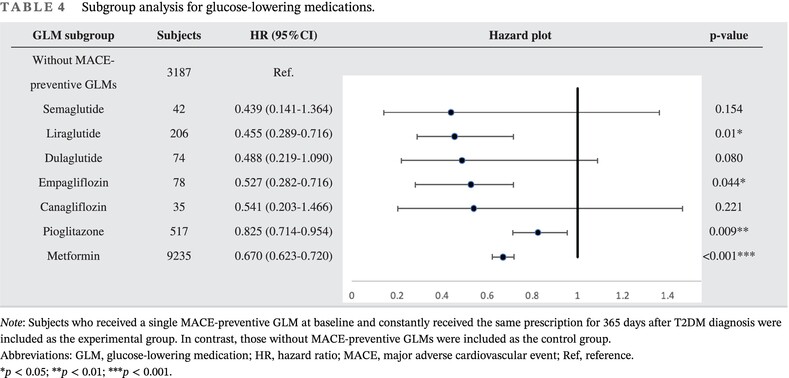
Highlights
- Good baseline glycemic control (GC) can reduce the risk of future major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) by 16.3%.
- MACE risk increases as the Hemoglobin A1c variability score (HVS) increases, and the HVS boundaries differ between good GC and poor baseline GC.
- Subjects with MACE-preventive glucose-lowering medications (GLMs) at baseline had 0.681 times lower MACE risk.
- Among all MACE-preventive GLMs, semaglutide potentially had the higher MACE-preventive effect (hazard ratio [HR]: 0.439; CI: 0.141–1.364), while pioglitazone (HR: 0.825; CI: 0.714–0.954) had the least in relative.
Protective effect of regular physical activity against diabetes-related lower extremity amputation
- First Published: 22 October 2024
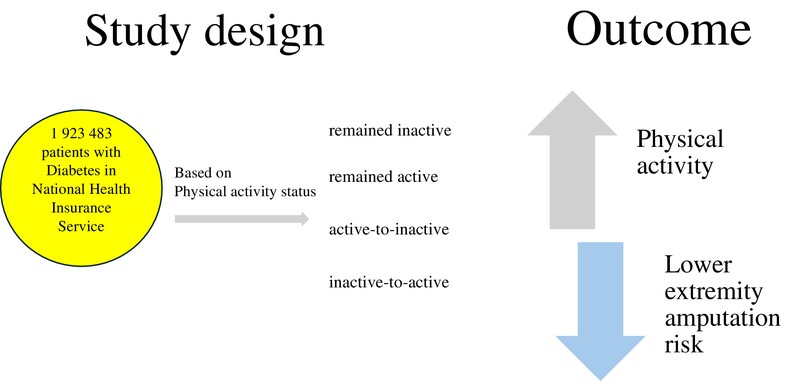
Highlights
- Regular physical activity has a protective effect lower extremity amputation in individuals with diabetes.
- There is evidence suggesting a proportional relationship between levels of physical activity and the reduction of amputation risk, with vigorous-intensity activities demonstrating the most significant advantages.
The potential adverse effects of hypodermic glucagon-like peptide -1 receptor agonist on patients with type 2 diabetes: A population-based study
- First Published: 22 October 2024
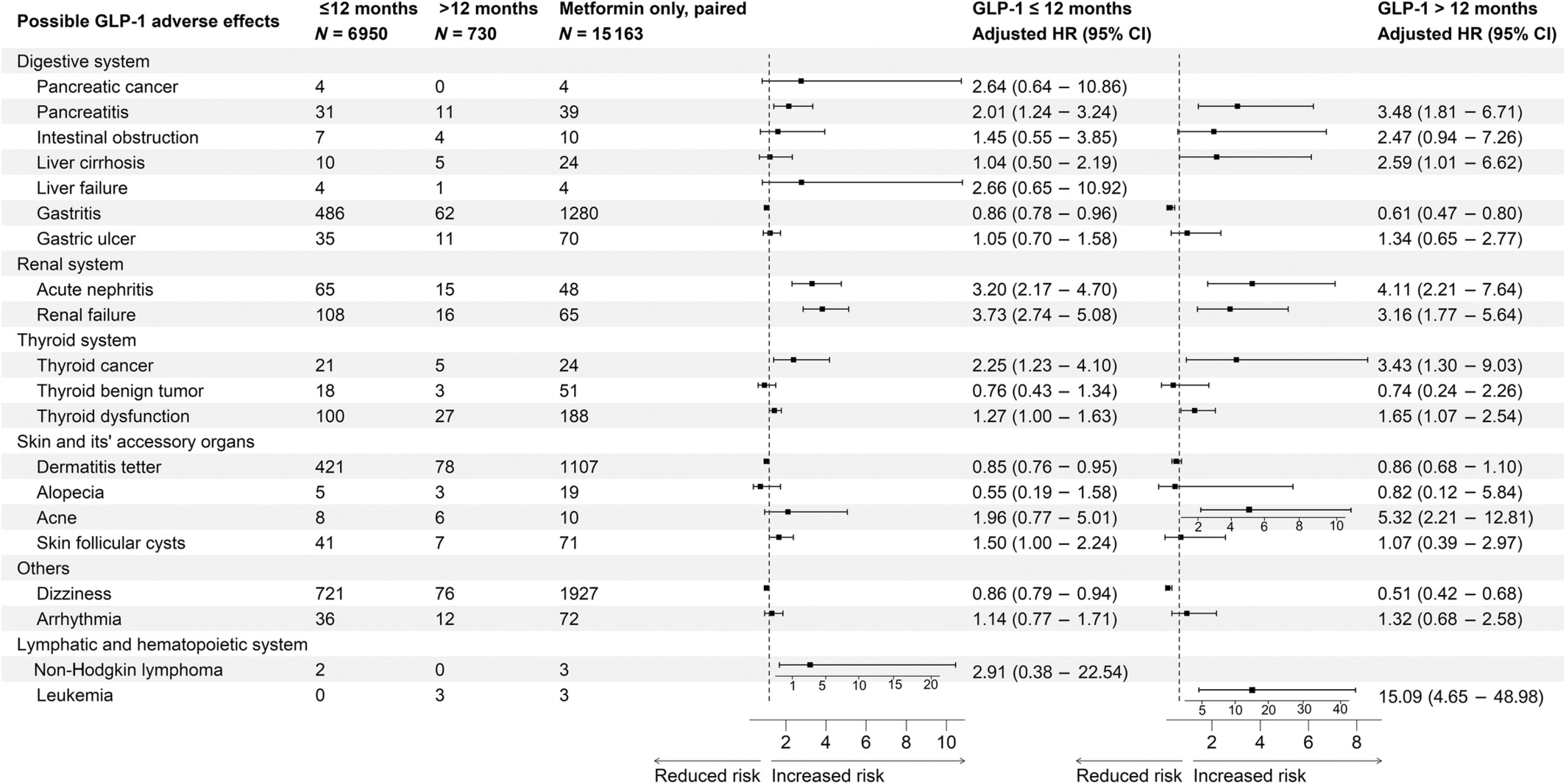
Highlights
- GLP-1 RAs may increase the incidence risks of various adverse outcomes.
- Prolonged use (over 12 months) of GLP-1 RAs may further elevate these risks.
- Cautions were strongly recommended in clinical practice with risk–benefit balance, particularly for risks of pancreatitis, acute nephritis, kidney failure, thyroid cancer/dysfunction.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Overview of oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetes
- First Published: 22 October 2024
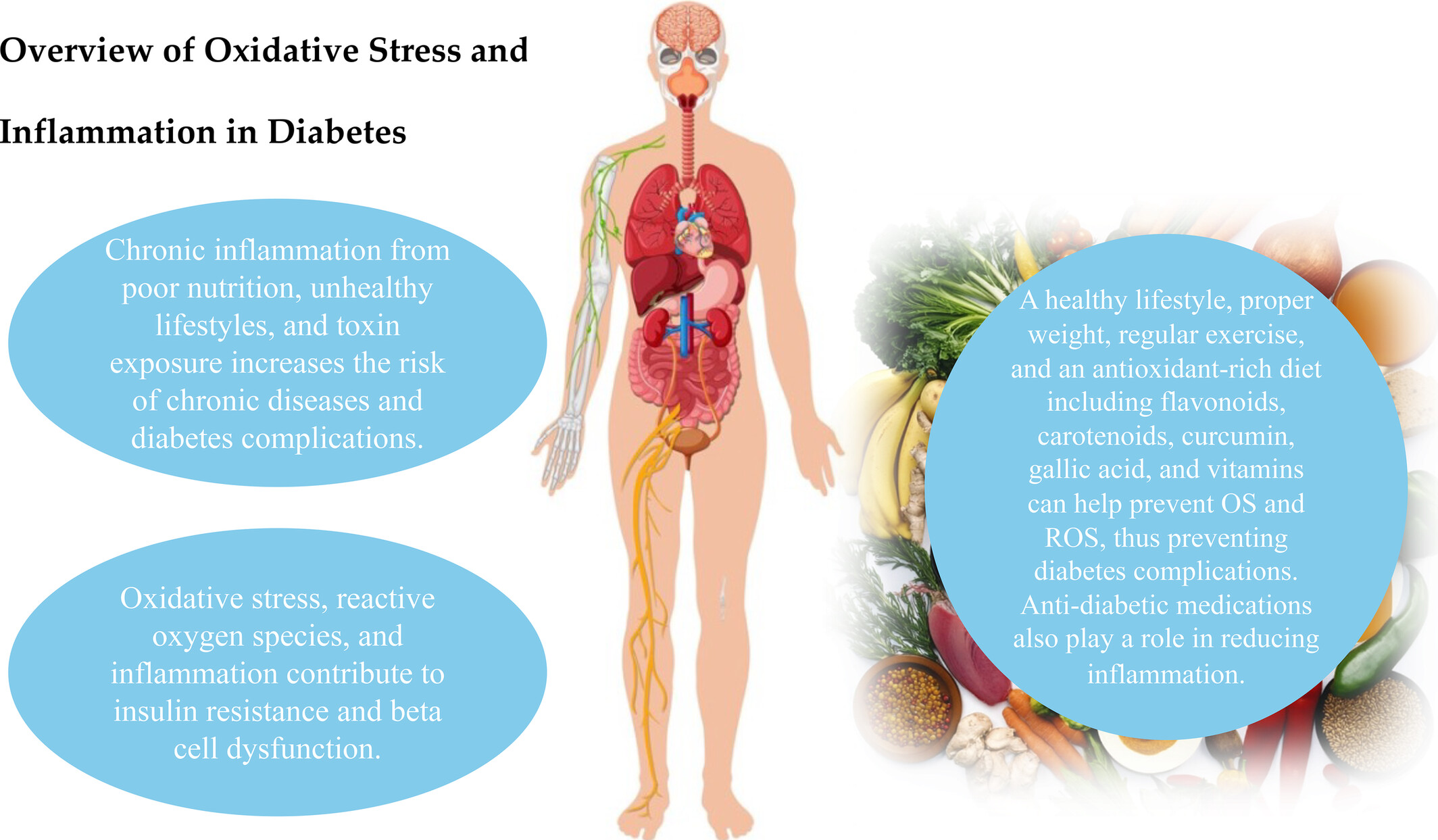
Highlights
- Chronic inflammation from poor nutrition, unhealthy lifestyles, and toxin exposure increases the risk of chronic diseases and diabetes complications.
- OS, ROS, and inflammation contribute to insulin resistance and β-cell dysfunction.
- A healthy lifestyle, proper weight, regular exercise, and an antioxidant-rich diet including flavonoids, carotenoids, curcumin, gallic acid, and vitamins can help prevent OS and ROS, thus preventing diabetes complications.
- Anti-diabetic medications also play a role in reducing inflammation.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Chronic glycemic control influences the relationship between acute perioperative dysglycemia and perioperative outcome
- First Published: 22 October 2024
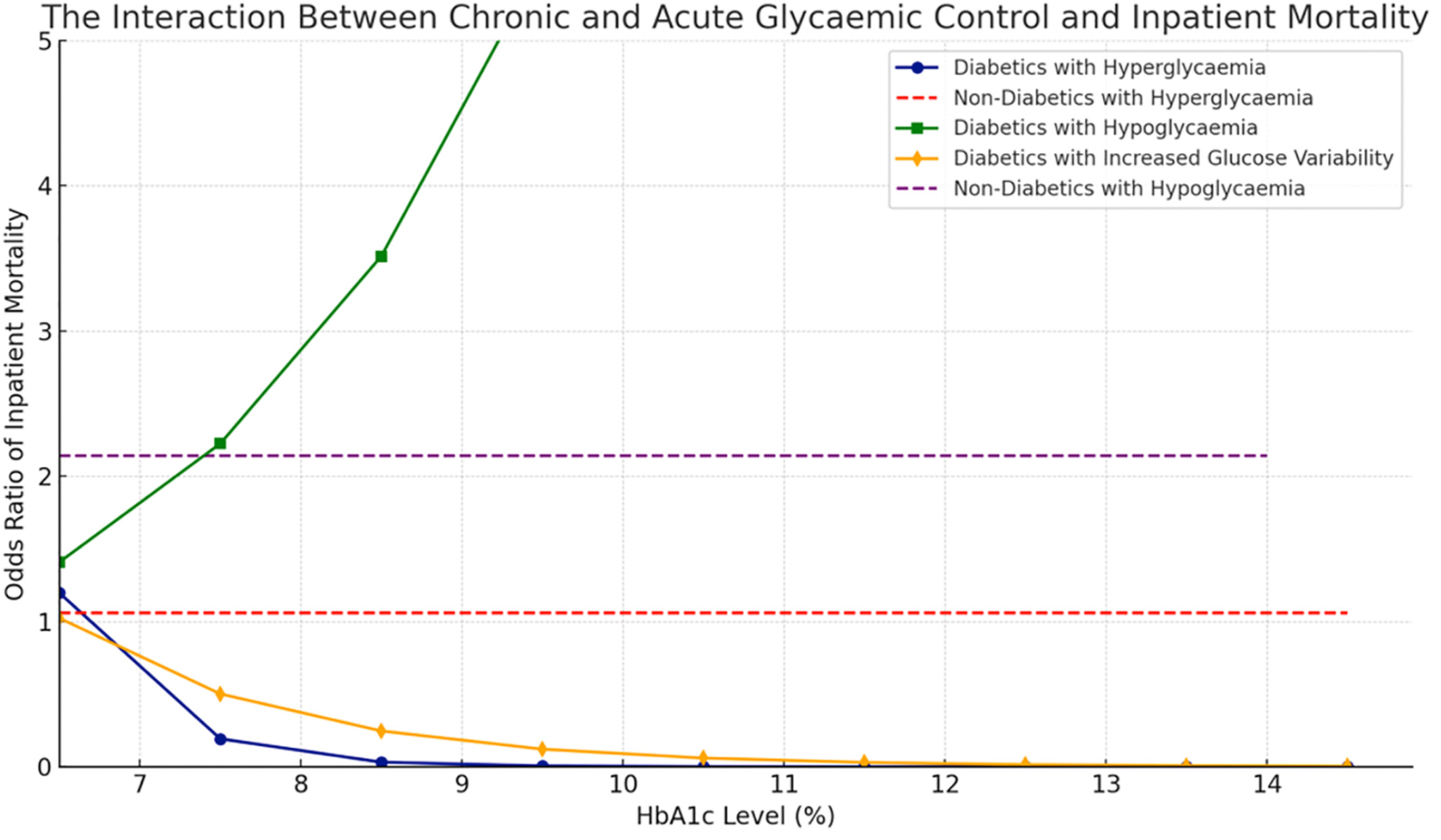
Highlights
- Based on our study of 52 145 surgical patients, in those with diabetes, prior exposure to hyperglycemia attenuates the impact of perioperative hyperglycemia and glycemic variability on inpatient mortality and intensive care unit (ICU) admission.
- The stress hyperglycemic ratio (SHR) may represent a more accurate and pertinent predictor of perioperative outcomes than the absolute definitions by serum titer (of >10, <4 or SD >1.7). This may be because the SHR uniquely considers the antecedent glycemic control.
- In patients without diabetes mellitus, all absolute thresholds of dysglycemia are associated with ICU admission, unlike those with diabetes, suggesting the need to use more relative measures such as the SHR.
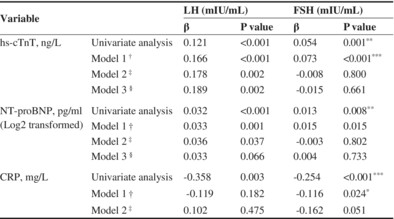
Luteinizing hormone is independently associated with high-sensitive cardiac troponin T elevation in postmenopausal T2DM patients: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 22 October 2024
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Healthy sleep score, acute myocardial infarction, and type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 24 October 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Potential mechanisms of metabolic reprogramming induced by ischemia–reperfusion injury in diabetic myocardium
- First Published: 25 October 2024
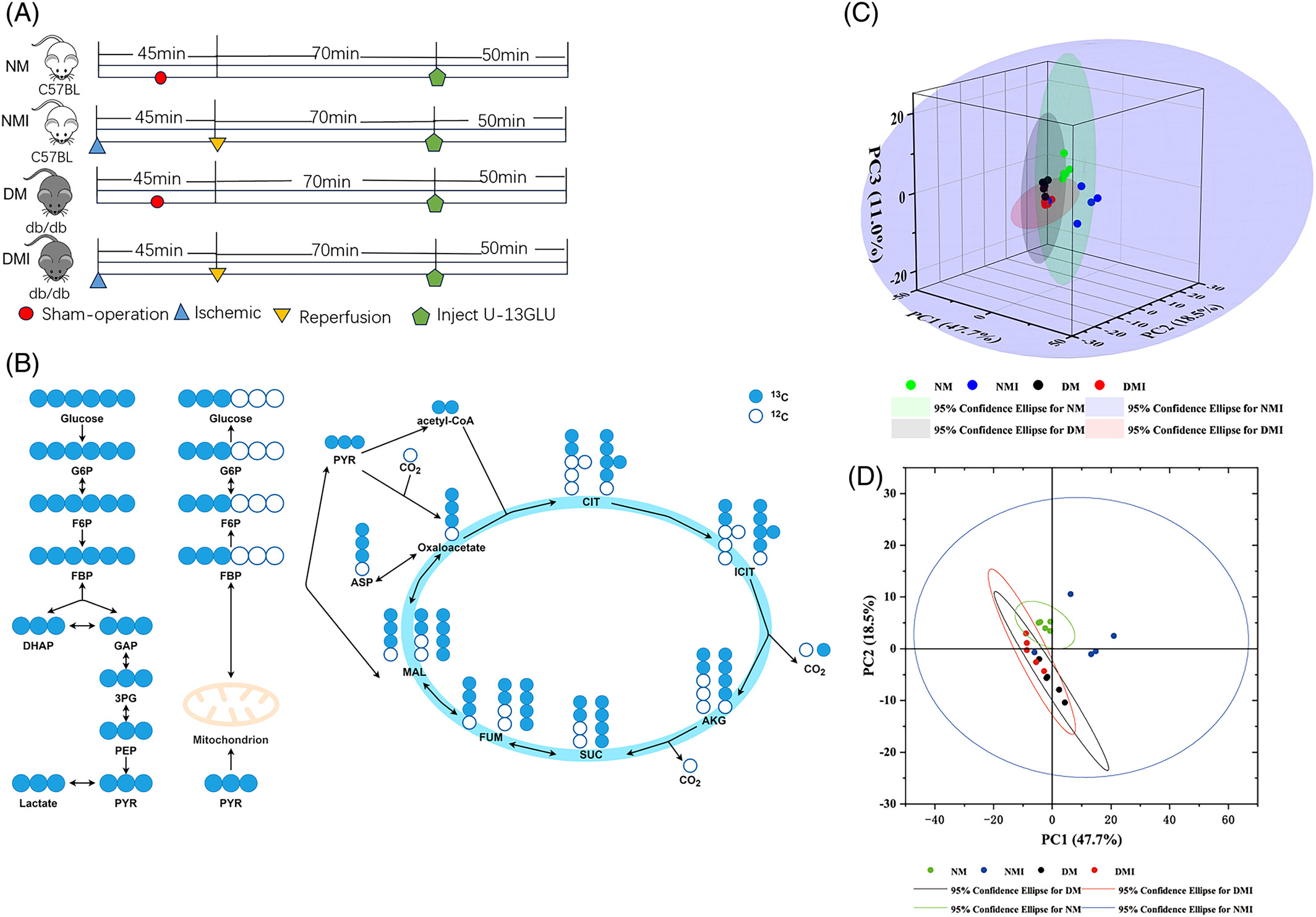
Highlights
- Diabetic myocardium undergoes changes in energy metabolism after ischemia–reperfusion injury (I/RI) and impacts myocardial vulnerability.
- Various advanced methods such as mass spectrometry coupled with gas chromatography or liquid chromatography (GC/LC–MS) as well as single-cell sequencing technology were used.
- Diabetic myocardium undergoes metabolic reprogramming after I/RI, which is mainly characterized by an overdependence on fatty acid metabolism for energy supply.
- Analysis revealed that myocardial subtype Cluster 0 was significantly increased in diabetic myocardium, and the differential gene was mainly enriched in fatty acid metabolism.
The relationship between glucose patterns in OGTT and adverse pregnancy outcomes in twin pregnancies
- First Published: 27 October 2024
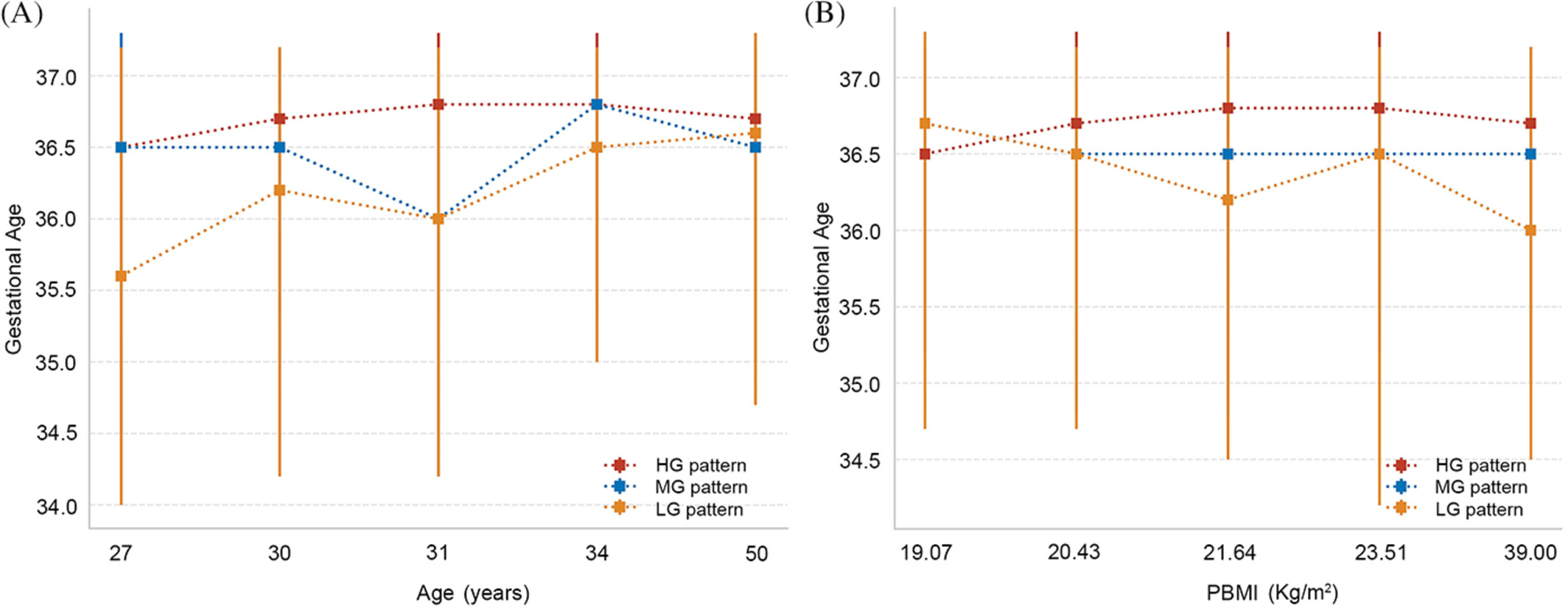
Highlights
- Latent mixture models identified LG, MG, and HG glucose patterns in pregnant women.
- The study compared maternal and neonatal traits and adverse outcomes across patterns, analyzing outcome trends from LG to HG.
- It assessed the glucose patterns' effects on delivery timing and neonatal adverse outcomes and evaluated these impacts by maternal characteristics.
Gut microbiota, serum metabolites, and lipids related to blood glucose control and type 1 diabetes
- First Published: 27 October 2024
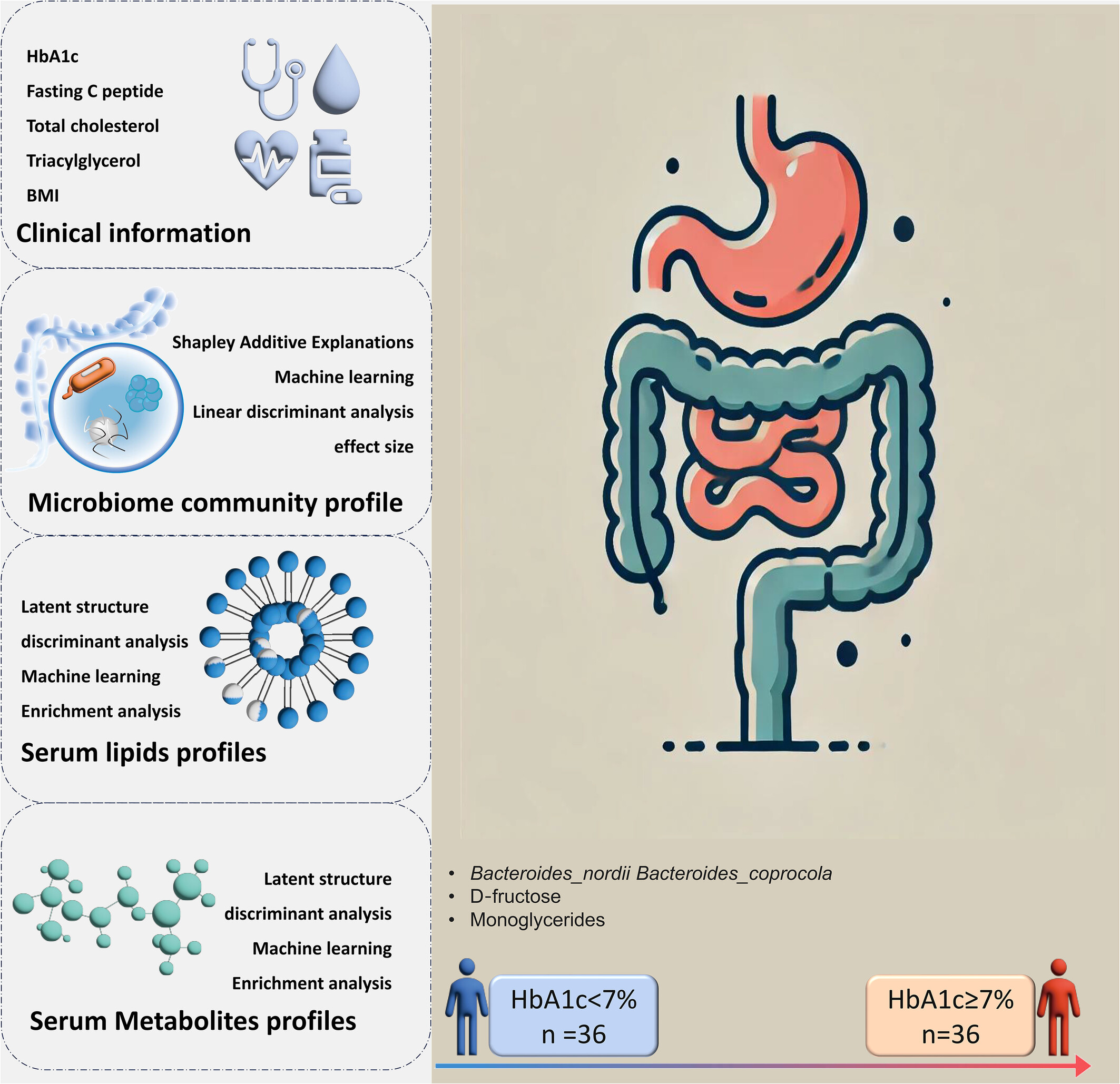
Highlights
- Our integrated multi-omics analyses revealed the potential glycemic control–microbiota–metabolite/lipid–T1D relationship.
- We identified several bacterial genera (e.g., Bacteroides_nordii, Bacteroides_cellulosilyticus) positively associated with the well glycemic control linked to T1D.
- Through comprehensive analysis, microbiota (Bacteroides_nordii, Bacteroides_coprocola), metabolites (D-fructose), and lipids (Monoglycerides) may serve as potential mediators that communicated the interaction between the gut, circulatory systems, and glucose fluctuations in T1D patients.
RESEARCH LETTER
Stratum corneum hydration levels are negatively correlated with HbA1c levels in the elderly Chinese
- First Published: 27 October 2024
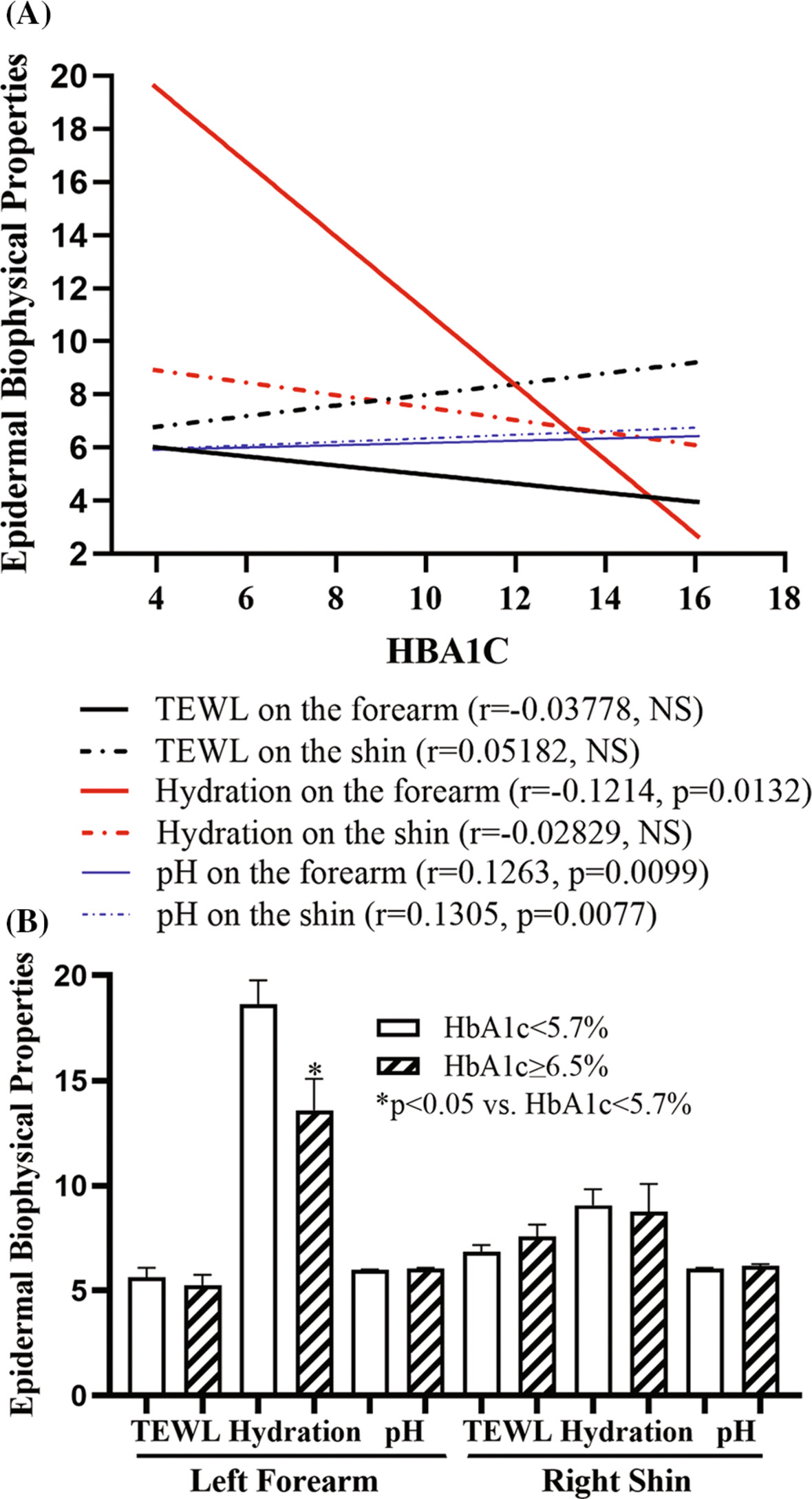
Highlights
- Stratum corneum hydration levels are negatively correlated with HbA1c levels and positively correlated with skin surface pH.
- Individuals with type 2 diabetes display lower levels of stratum corneum hydration.
- Because low stratum corneum hydration levels can increase circulating levels of proinflammatory cytokines, which are linked to the pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes, improvement in stratum corneum hydration can be an alternative approach in the management of type 2 diabetes.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Association of systolic blood pressure variability with cognitive decline in type 2 diabetes: A post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial
- First Published: 29 October 2024
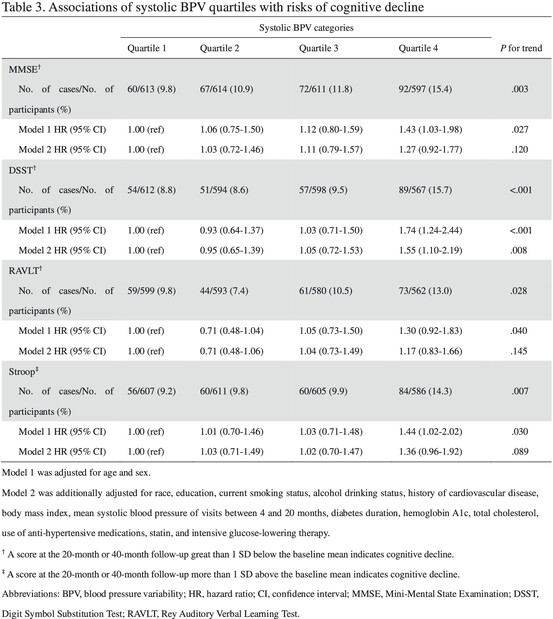
Highlights
- This post hoc analysis of the Action to Control Cardiovascular Risk in Diabetes Memory in Diabetes (ACCORD-MIND) substudy showed that high visit-to-visit systolic blood pressure variability (BPV) was associated with an increased risk of cognitive decline defined by the Digit Symbol Substitution Test (DSST) score.
- Further, visit-to-visit systolic BPV was positively associated with change in white matter lesion volume evaluated by brain magnetic resonance imaging.
- Visit-to-visit systolic BPV might play a role in the decline of cognitive function in individuals with type 2 diabetes.