Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
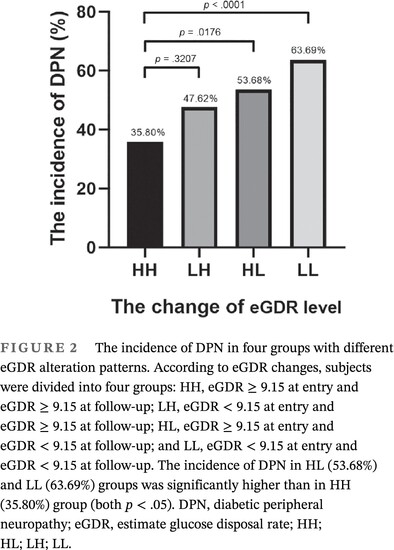
Estimated glucose disposal rate predicts the risk of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in type 2 diabetes: A 5-year follow-up study
- First Published: 15 January 2024
Highlights
- After 5.91 years, 198 of 366 (54.1%) participants with type 2 diabetes progressed to diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN).
- Subjects with low baseline estimated glucose disposal rate (eGDR < 9.15) had significantly higher risk of DPN at the end of follow-up (odds ratio = 1.75), even after adjusting for other known DPN risk factors.
- Diabetic patients with low eGDR are more prone to DPN and, therefore, require more intensive screening and more attention.
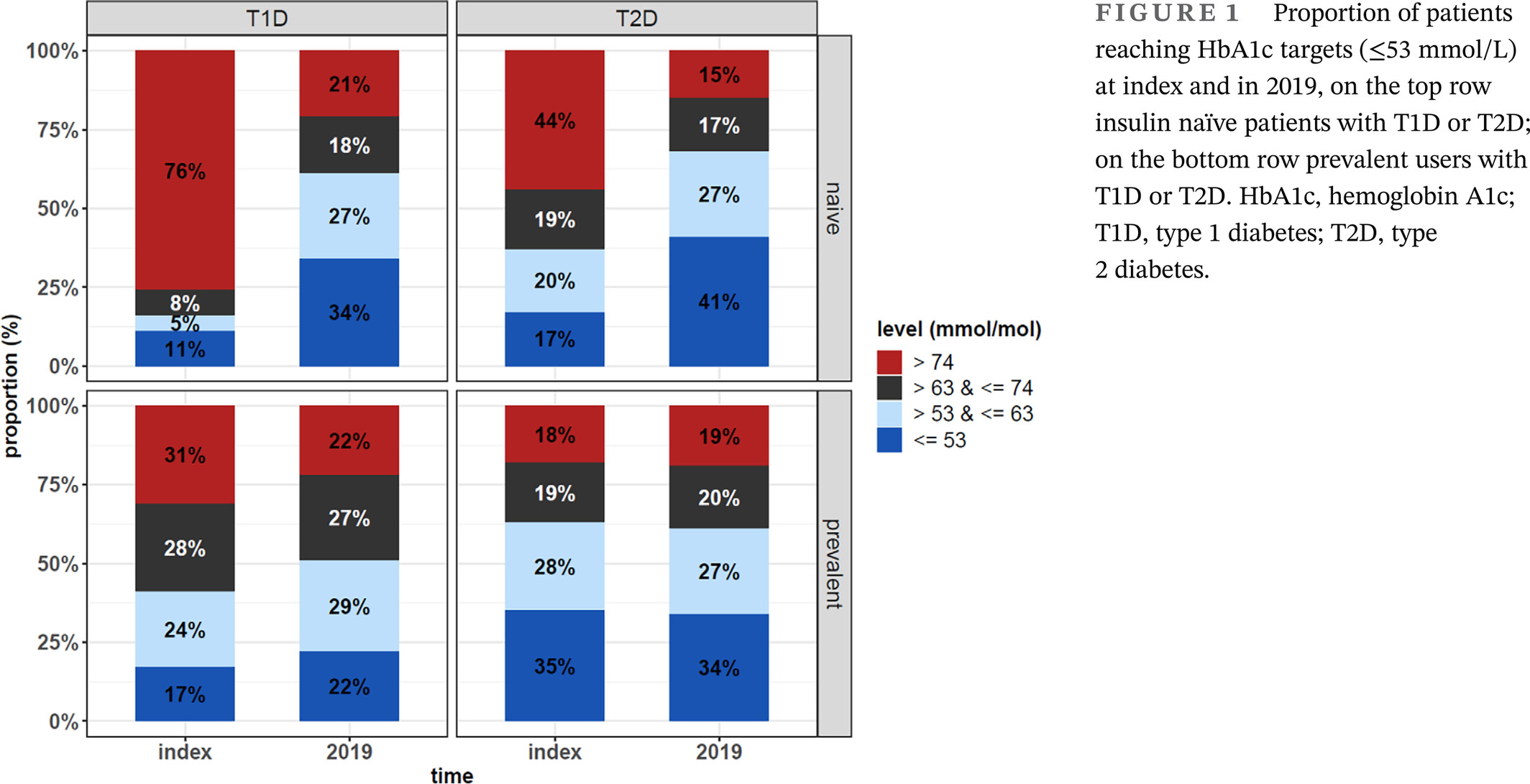
Trends in clinical characteristics, medication use, and glycemic control in insulin-treated patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes in Finland in 2012–2019: Nationwide real-world evidence study
- First Published: 25 January 2024
Highlights
- This Finnish nationwide real-world evidence study used national identity numbers to link data from several registries to identify 145 020 people with diabetes treated with insulin.
- Medication use has evolved with newer generation insulin and noninsulin diabetes medications between 2012 and 2019.
- Despite the aging population, glycemic control of insulin users has remained stable or improved between 2012 and 2019 in Finland.
REVIEW ARTICLES
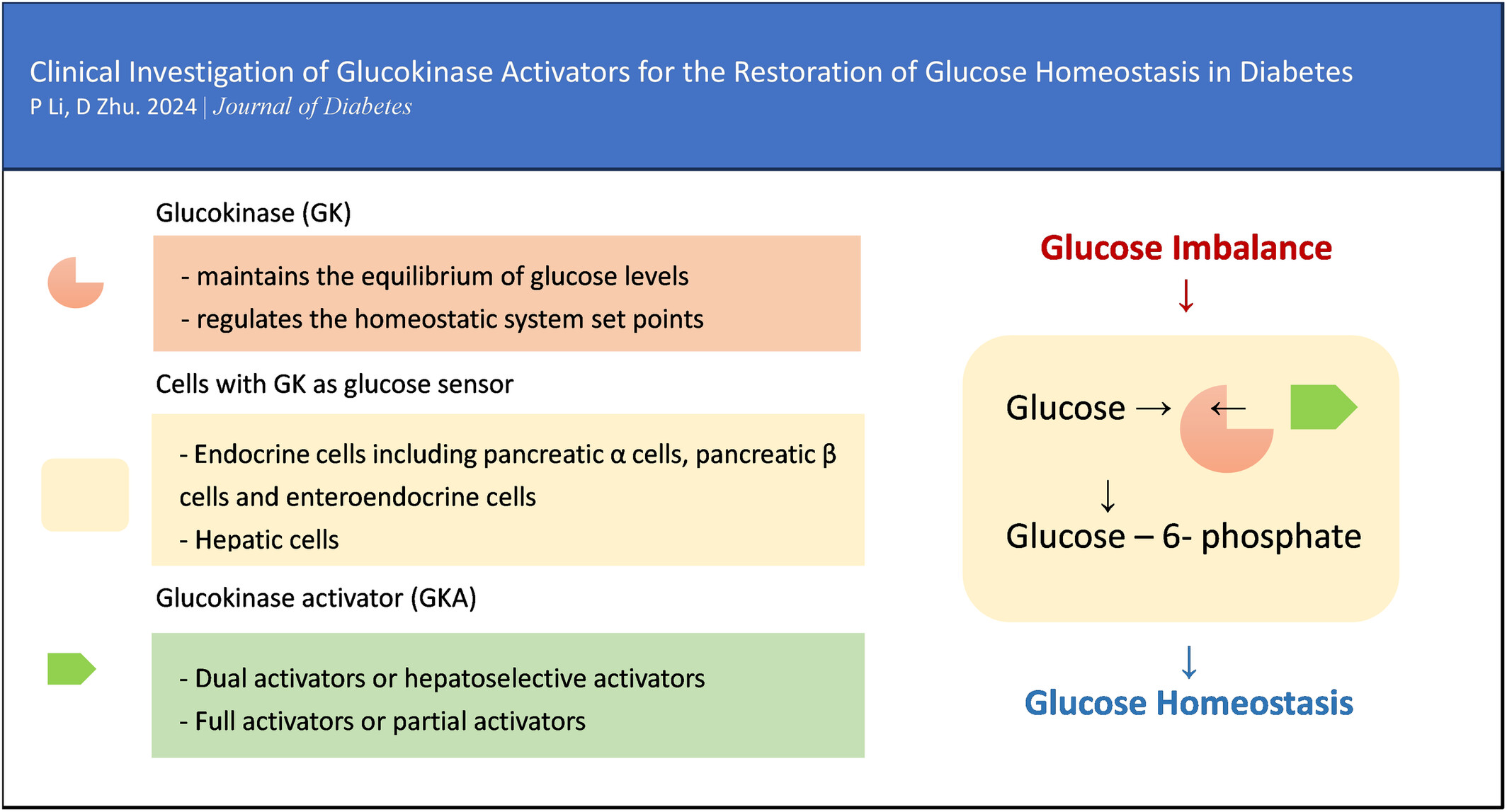
Clinical investigation of glucokinase activators for the restoration of glucose homeostasis in diabetes
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Highlights
- The crucial role of glucokinase (GK) in the homeostatic system maintains the balance of glucose levels.
- GK also influences the secretion of essential endocrine hormones like glucagon and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1).
- Studies in a broader population of patients with diabetes and prediabetes will provide greater clinical evidence for the long-term effects of GK activation.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Gamma-glutamyl transferase and the risk of all-cause and disease-specific mortality in patients with diabetes: A nationwide cohort study
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Highlights
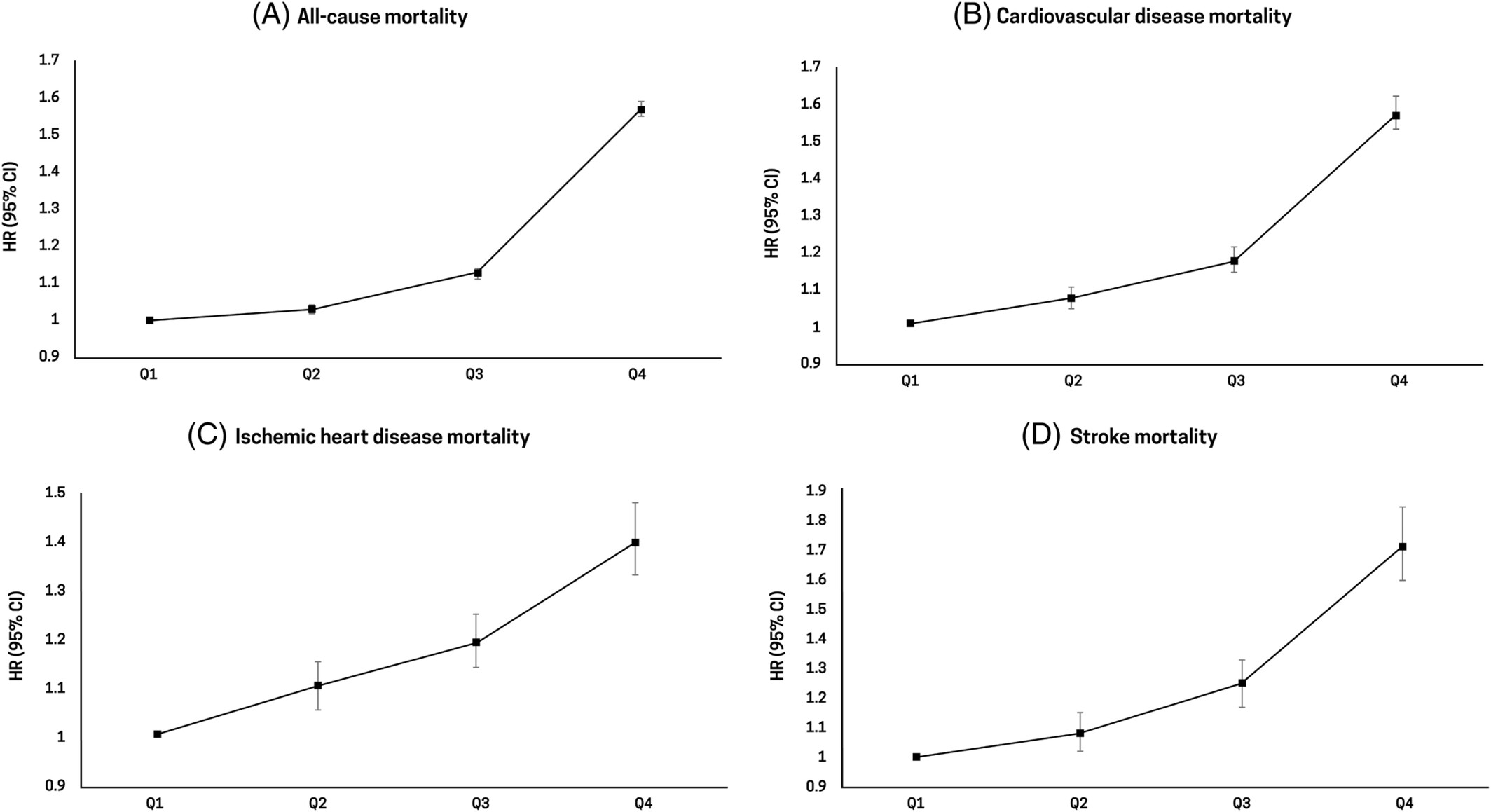
- This Korean nationwide population-based cohort study analyzed the overall and disease-specific mortality according to serum gamma-glutamyl transferase (GGT) levels in patients with type 2 diabetes.
- GGT levels were positively associated with various causes of mortality, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, liver disease, respiratory disease, and infectious disease.
- Notably, the increased risk of all-cause mortality was more prominent in the subgroups of the young, underweight, and those with complications of type 2 diabetes.
- Serum GGT levels may be useful for the risk assessment of all-cause and disease-specific mortality among patients with type 2 diabetes.
Cost saving analysis of prediabetes intervention modalities in comparison with inaction using Markov state transition model—A multiregional case study
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Highlights
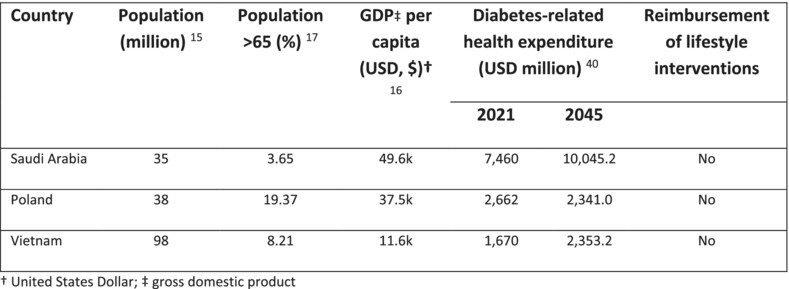
- Countries moving from low to middle income are most at risk from the type 2 diabetes (T2D) “epidemic” and may find implementing preventative measures challenging; yet prevention has largely been evaluated in developed countries.
- This study explored costs and benefits of various prediabetes management approaches in Poland, Saudi Arabia, and Vietnam, with the aim of facilitating resource use and planning decisions.
- Pharmacological and lifestyle prediabetes interventions offer promise for reducing T2D incidence. In the context of adherence concerns and funding/reimbursement challenges for lifestyle interventions, metformin alone may be an effective, cost-saving strategy.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Acellular fish skin grafts in the treatment of diabetic wounds: Advantages and clinical translation
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Highlights
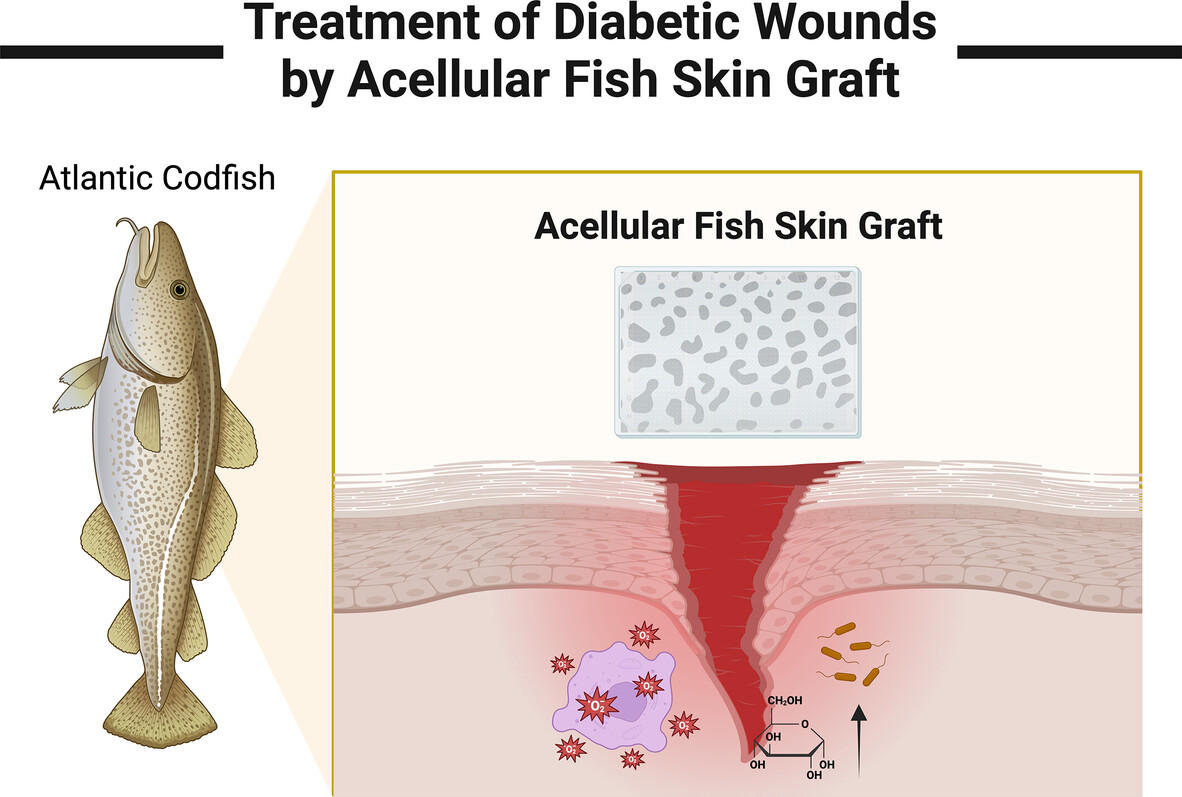
- Concisely included the latest research on the role of acellular fish skin grafts (AFSGs) in treating diabetic wounds, providing readers with a basic framework,
- This review outlined the therapeutic advantages and prospects of AFSGs,
- This work emphasized the role of cost-effectiveness in the treatment of diabetic wound dressings.
- We summarized the shortcomings and corrective measures of current AFSGs clinical trials.
- We explored the resistance that may be encountered by AFSGs in various stages of clinical studies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
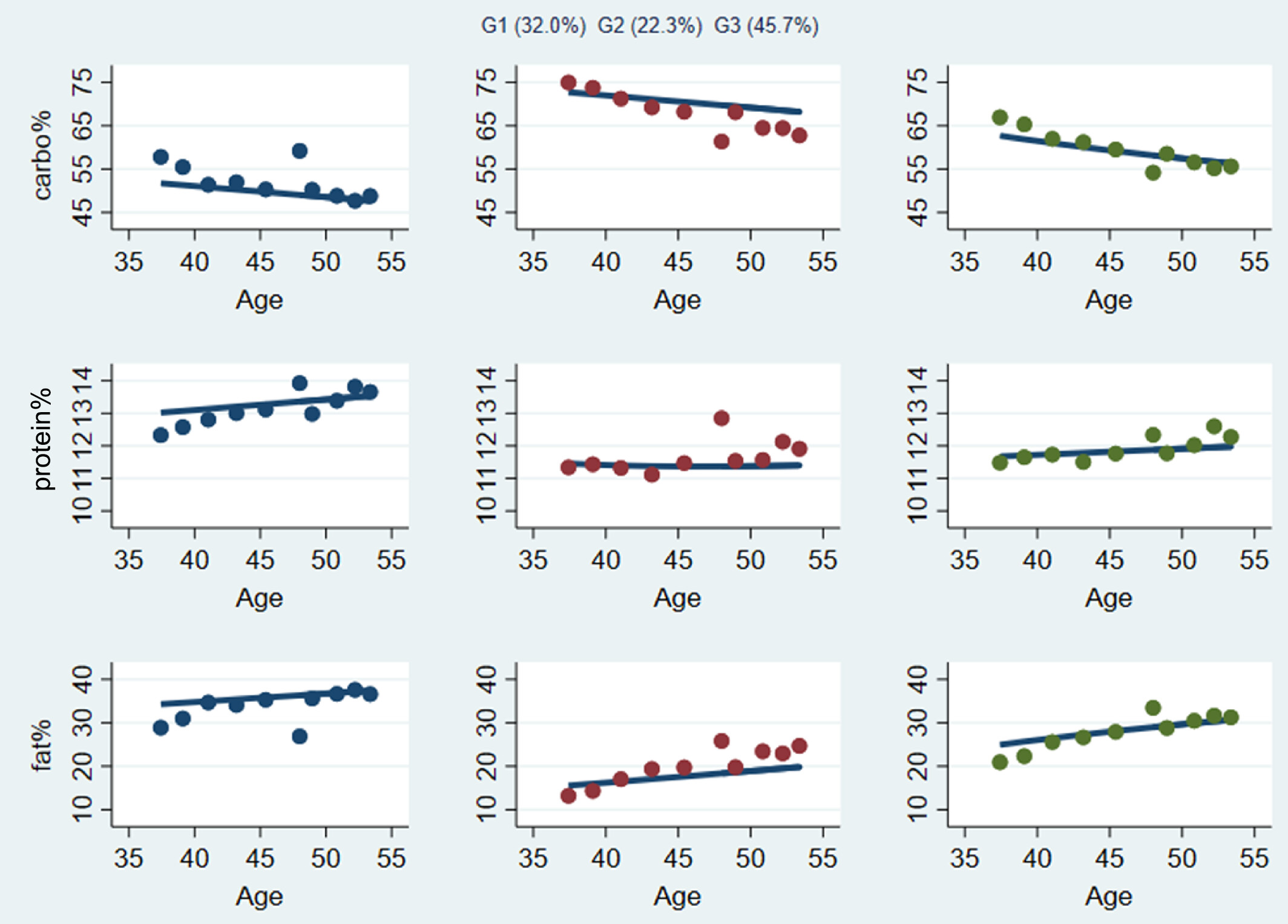
The association between multiple trajectories of macronutrient intake and the risk of new-onset diabetes in Chinese adults
- First Published: 09 May 2024
The metabolic effects of habitual leg shaking: A randomized crossover trial
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Highlights
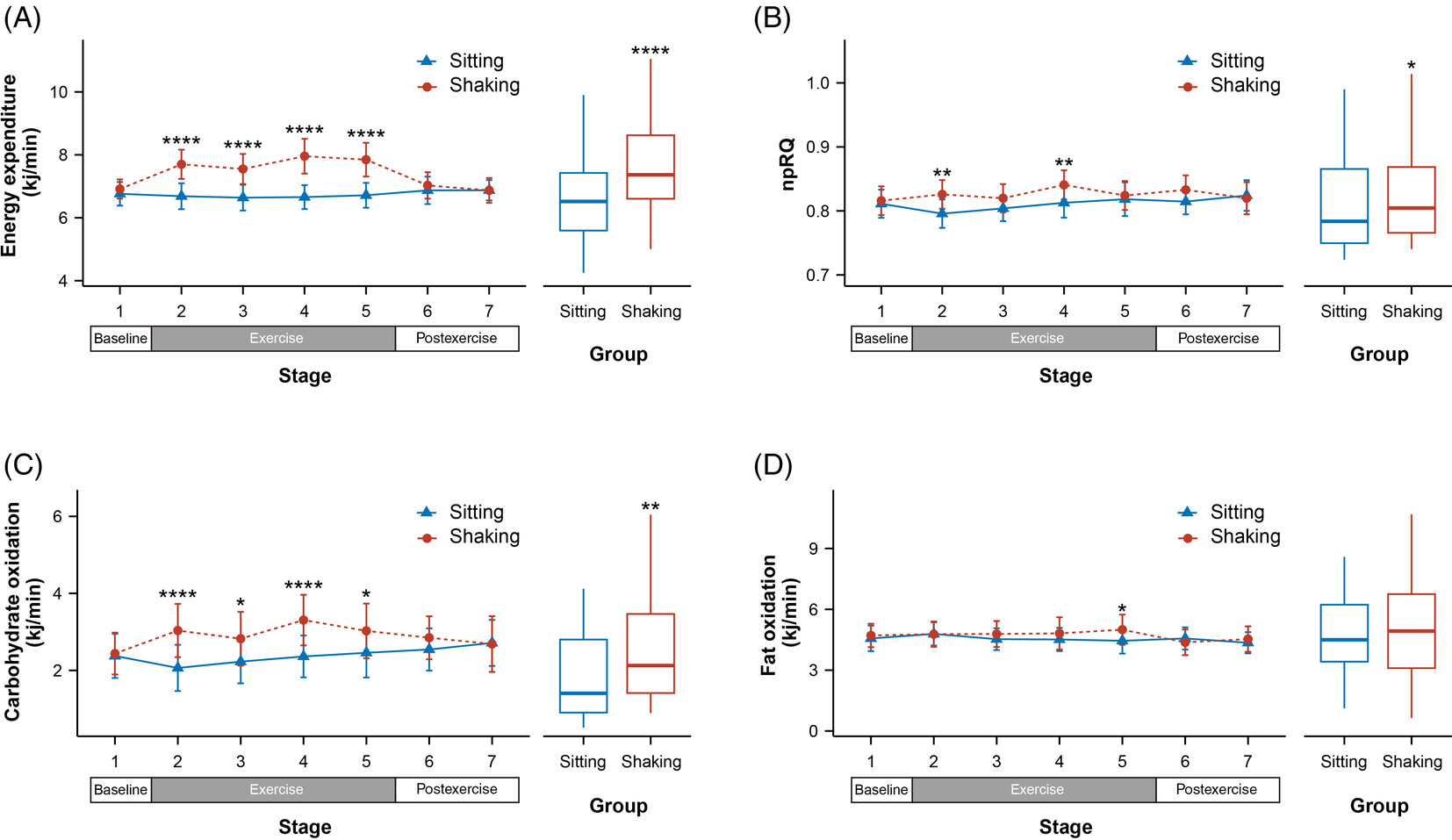
- Previous research has established the detrimental effects of sedentary behavior on obesity and chronic diseases. Efforts to mitigate heightened sedentary behavior through measures such as promoting elevated physical activity or incorporating extended standing and exercise during sedentary intervals have faced challenges in implementation.
- Our study confirmed that habitual leg shaking effectively increased energy expenditure by approximately 16.3%, elevated the metabolic equivalent to a nonhealthy level, enhanced carbohydrate oxidation, improved blood oxygen saturation and minute ventilation, while avoiding additional cardiovascular burden.
- Leg shaking offers a simple and feasible approach to enhance physical activity without disrupting daily routines.
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injection therapy in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes
- First Published: 25 April 2024
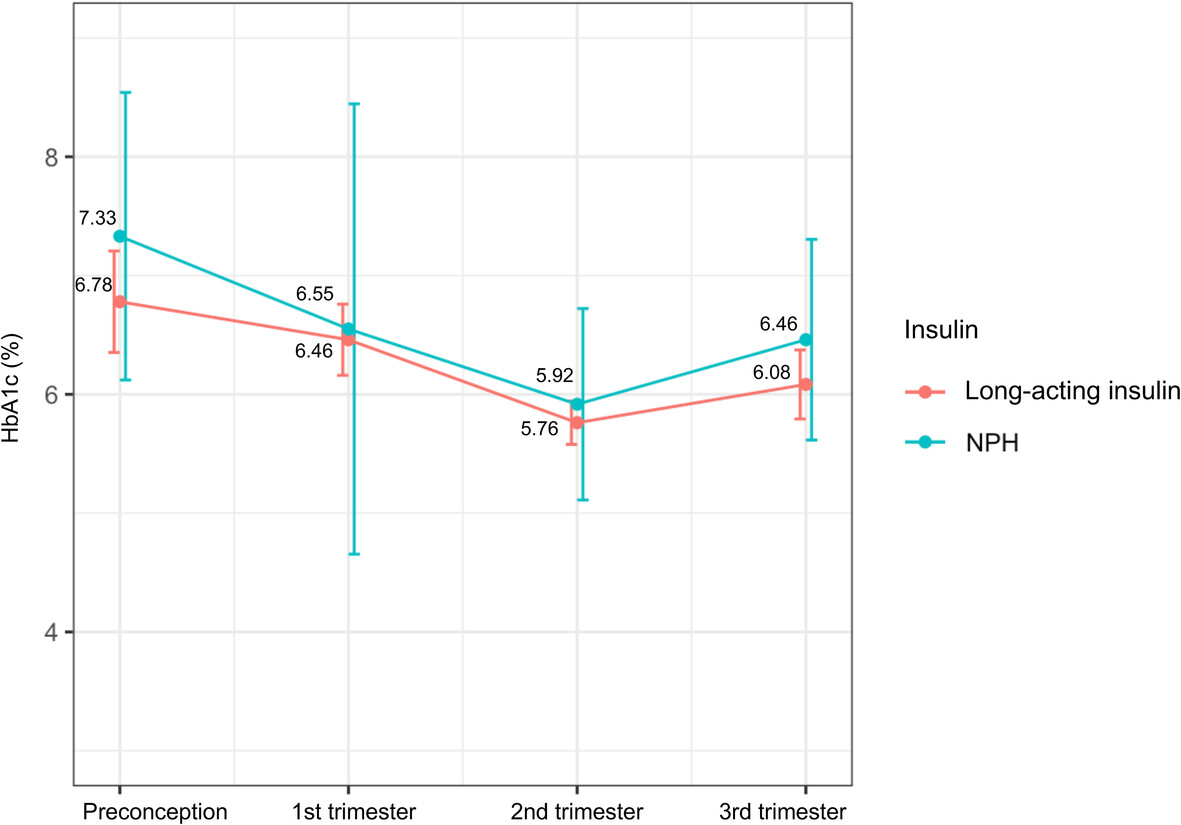
Highlights
- This study is the first to evaluate the effects of multiple daily injection and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy among Chinese pregnant women with type 1 diabetes.
- We found that pregnant women with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy had better glycemic control in the third trimester than those on multiple daily injection therapy.
- Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion users had a significant decline in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level from preconception to the third trimester.
- There was a nonsignificant lower HbA1c level for women treated with long-acting insulin, compared with neutral protamine Hagedorn.
Epidemiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents: A 50-year, single-center experience
- First Published: 25 April 2024
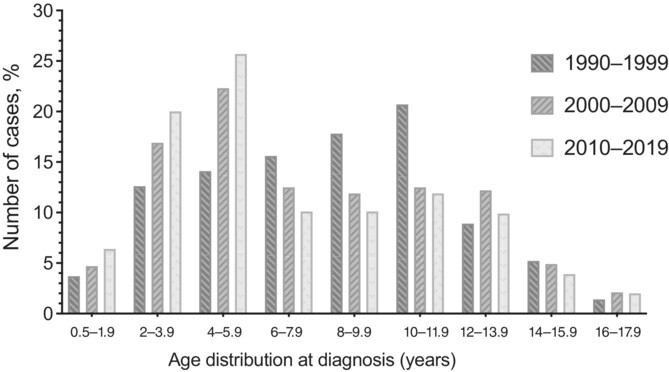
Highlights
- This study provides important data from a single quarternary reference center where cases with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) come from a wide range of geographical distribution over 50 years and may well reflect secular trends in T1DM in Turkey.
- The mean age at diagnosis was 9.5 ± 4.0 years from 1969 to 1990, and it significantly decreased to 7.1 ± 3.6 years over the subsequent 50 years. Similarly, age at diagnosis peaked at 12–14 years between 1969 and 1990, then fell to 10–11.9 years between 1990 and 1999, and to 4–5.9 years between 2000–2009 and 2010–2019.
- Although the percentage of patients diagnosed <6 years of age is gradually increasing, the percentage diagnosed between ages of 6 and 11.9 years is decreasing, and the percentage diagnosed ≥12 years remained stable.
- Approximately half of the patients had ketoacidosis at the time of diagnosis and the frequency of presentation with DKA did not decrease, but the severity decreased slightly.
- Although the frequency of patients with mild DKA increased over time, frequency of patients with moderate DKA decreased; however, no significant difference was observed among patients with severe ketoacidosis.
Prevalence of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and liver cirrhosis in Chinese adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 25 April 2024
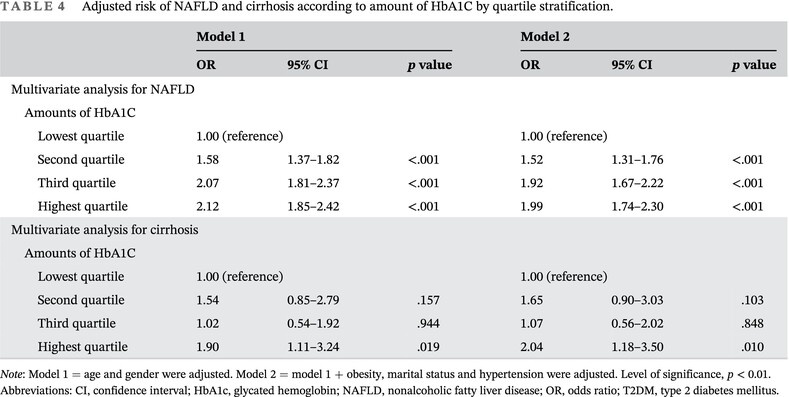
Highlights
- A nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) prevalence of 59.36% and a liver cirrhosis prevalence of 1.43% was found among type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) patients.
- Significant risk factors for NAFLD were identified, including age, gender, marital status, and obesity, with obesity showing a particularly strong positive association.
- The glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c)-NAFLD relationship displayed a linear pattern that mimicked an inverted L-shaped pattern. A significant positive association existed between HbA1c levels and NAFLD for HbA1c <8.00%, but this was not observed for HbA1c >8.00%.
Special Issue: Diabetes in South Asians
Diabetes and tuberculosis syndemic in India: A narrative review of facts, gaps in care and challenges
- First Published: 08 June 2023
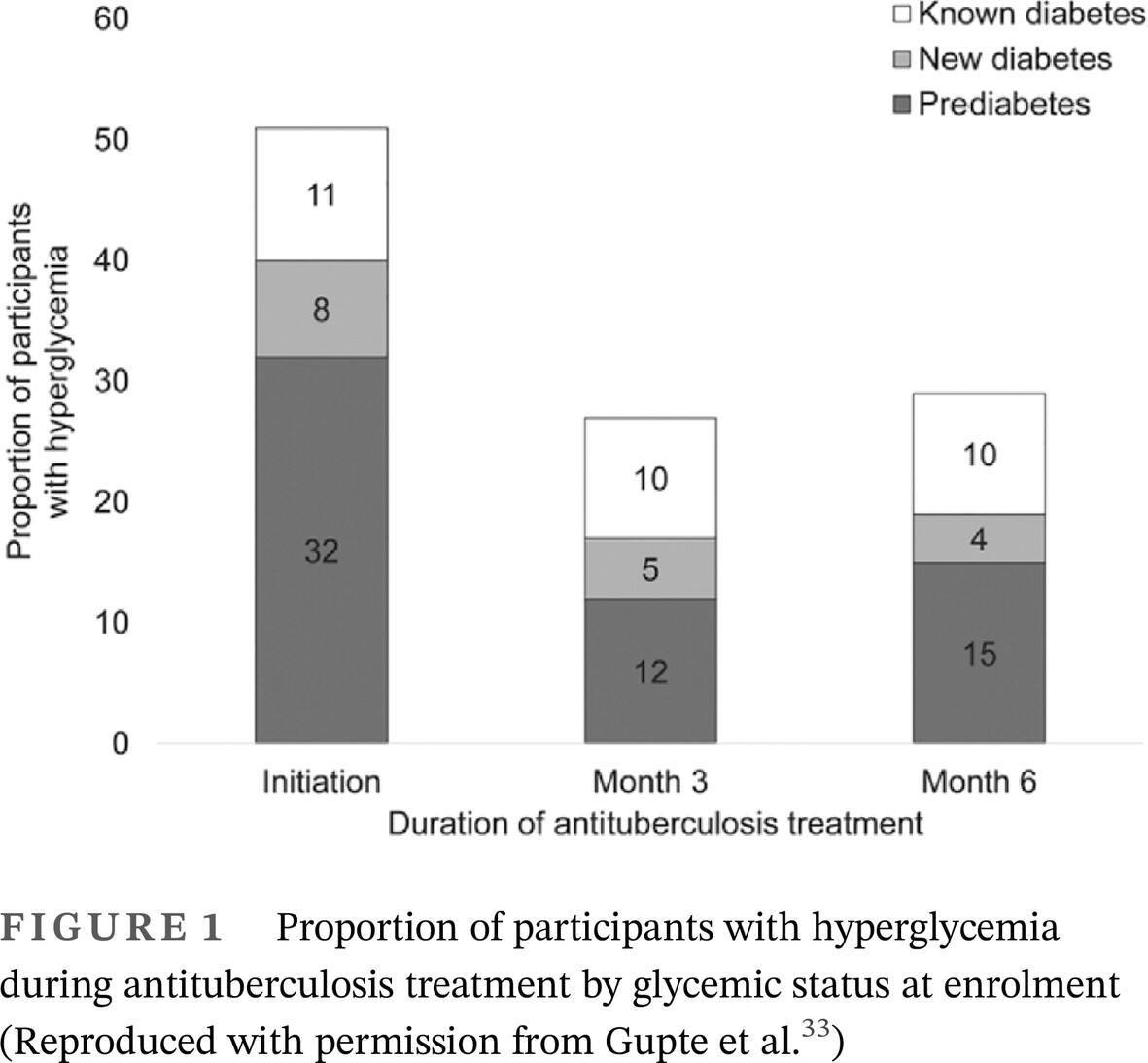
Highlights
- Some data suggest that coexistence of diabetes mellitus and tuberculosis substantially increases the failure of treatment of antituberculosis drugs.
- The COVID-19 pandemic has severely affected the healthcare delivery of tuberculosis-diabetes mellitus patients.
- The tuberculosis-diabetes mellitus syndemic needs a more aggressive focus to have a better outcome.
A comparative study of the gut microbiome in Indian children with type 1 diabetes and healthy controls
- First Published: 28 June 2023
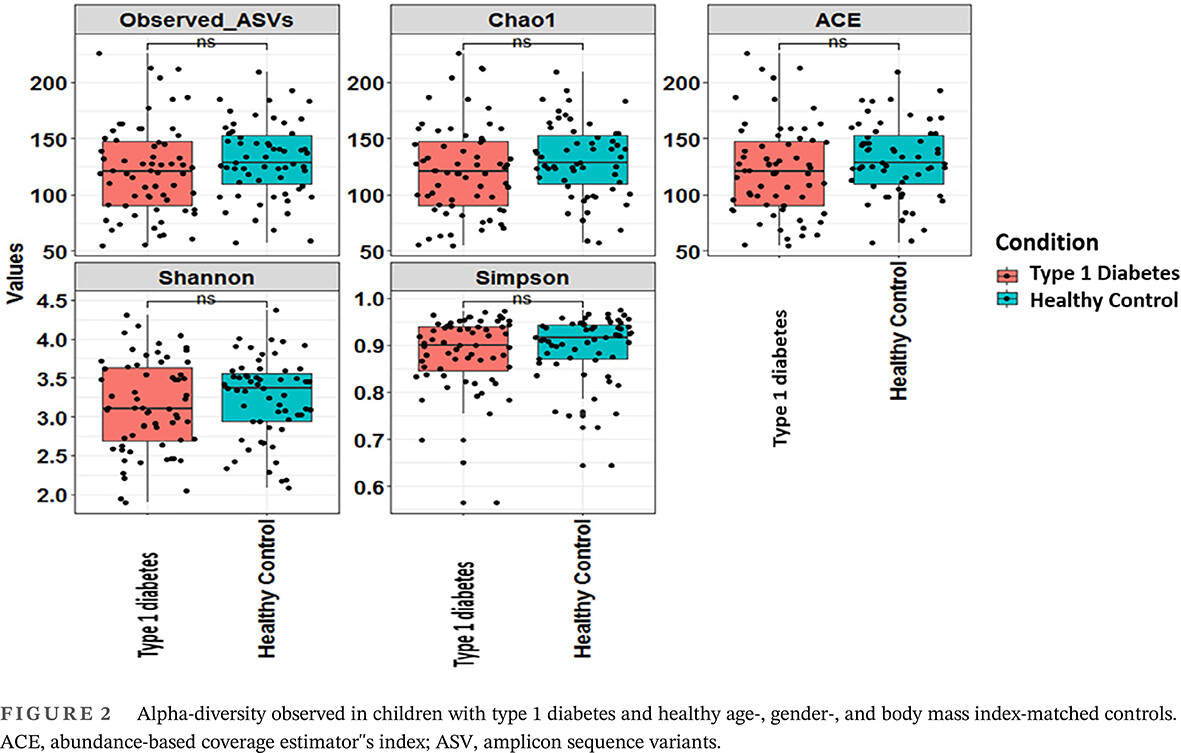
Highlights
- To best of our knowledge, this is the first study conducted to compare the gut microbiome of Indian children with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and healthy controls.
- There were significant differences observed in the gut microbiome profile at the genera level of children with T1DM as compared to controls, thus indicating a distinct gut microbial signature in children with type 1 diabetes.
- Short chain fatty acid producers may play an important role as significant predictor of glycemic control in Indian children with T1DM.
Cardiometabolic profile of women with a history of overt diabetes compared to gestational diabetes and normoglycemia in index pregnancy: Results from CHIP-F study
- First Published: 30 August 2023
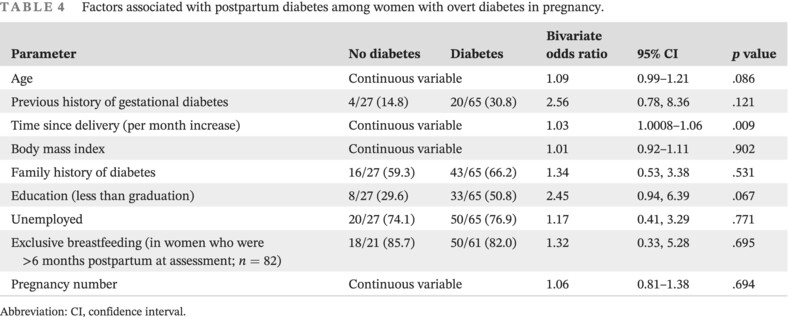
Highlights
- We evaluated the prevalence of postpartum diabetes among women with overt diabetes in pregnancy (ODiP).
- Diabetes was diagnosed in 65 (70.7%) women with ODiP at a median postpartum interval of 29 months.
- The prevalence of diabetes in the ODiP group was 47.4% among women tested in the first year postpartum, increasing to 86.8% among women tested at >3 years postpartum.
- Postpartum diabetes was more common when ODiP was diagnosed in the first (27/29, 93.1%) trimester of pregnancy.
- Postpartum diabetes was more common when ODiP was diagnosed based on glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) elevation before 15 weeks of gestation (19/20, 95.0%).
Clustering of health behaviors and their associations with cardiometabolic risk factors among adults at high risk for type 2 diabetes in India: A latent class analysis
- First Published: 06 May 2024
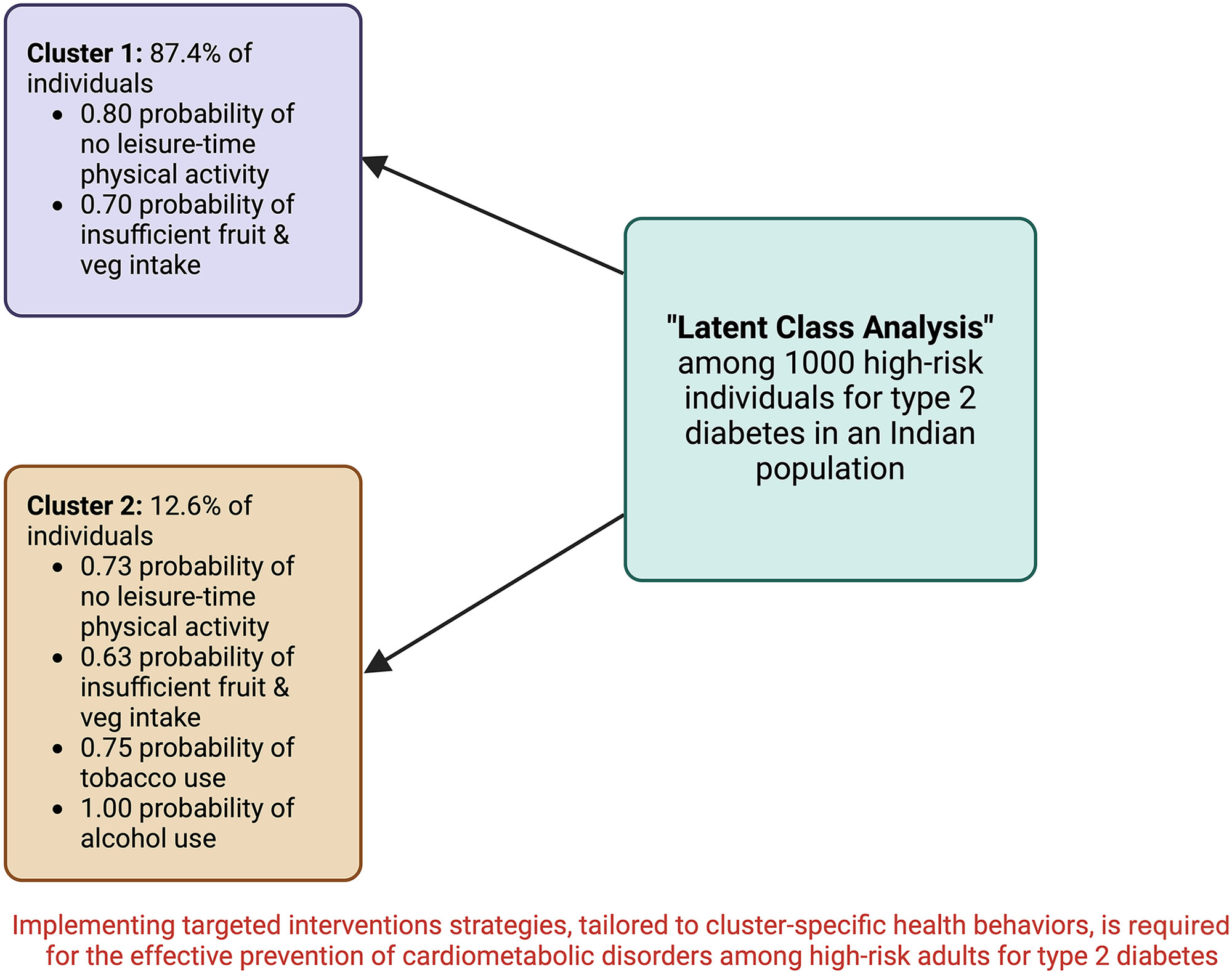
Highlights
- Two clusters of health behaviors were identified in a high-risk population for type 2 diabetes in an Indian setting.
- Individuals in cluster 1 (87.4% of participants) exhibited a high probability of not engaging in leisure-time physical activity and consuming insufficient amounts of fruits and vegetables. This pattern was also observed in cluster 2 (12.6% of participants) in addition to having a high likelihood for tobacco and alcohol use.
- These findings emphasize the importance of interventions targeting cluster-specific health behaviors to prevent cardiometabolic disorders among high-risk individuals for type 2 diabetes.
Antenatal oral glucose tolerance test abnormalities in the prediction of future risk of postpartum diabetes in women with gestational diabetes: Results from the LIVING study
- First Published: 06 May 2024
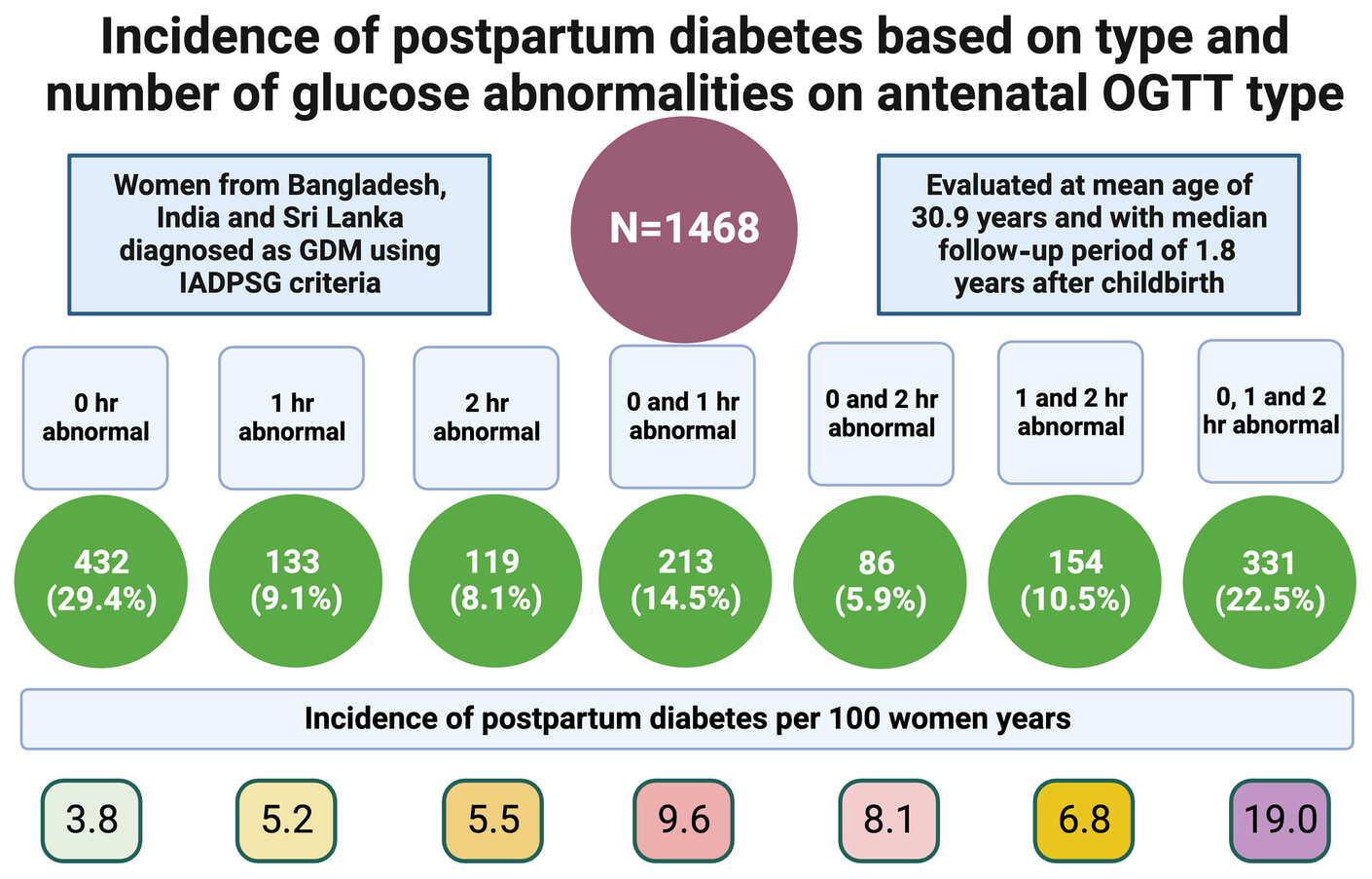
Highlights
- Of the 1468 South Asian women with gestational diabetes, 213 (14.5%) women developed diabetes over median follow-up 1.8 years after childbirth, an incidence rate of 8.7/100 women-years.
- The incidence rates for participants with any one, two, and three abnormal values on antenatal oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were 4.3, 8.3 and 19.0/100 women years.
- The rates of future diabetes in this high-risk cohort varied considerably with antenatal OGTT values, providing the opportunity for targeted intervention to prevent future diabetes.