Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
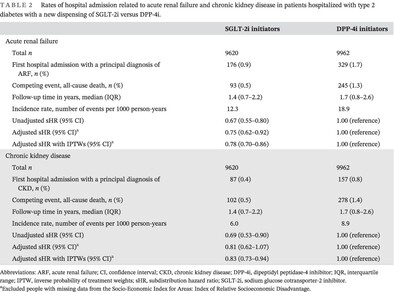
The association between sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors vs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and renal outcomes in people discharged from hospital with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
- What are the new findings?
This was the first Australian study using real-world data to show SGLT-2is reduce ARF and CKD compared to DPP-4is in people with type 2 diabetes. The rates of hospital admissions for ARF and CKD in people with type 2 diabetes were 22% and 17% lower, respectively, among SGLT-2i initiators compared to DPP-4i initiators.
- How might this have an impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
Efficacy and safety of bexagliflozin compared with dapagliflozin as an adjunct to metformin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A 24-week, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled, phase 3 trial
- First Published: 07 April 2024
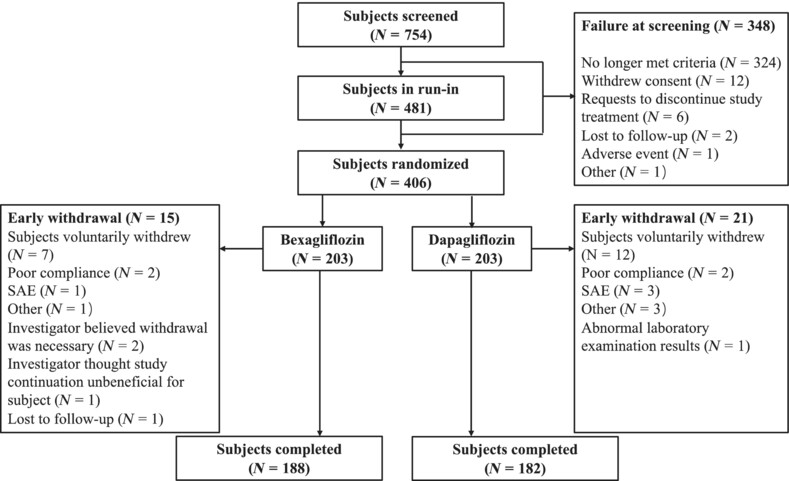
Highlights
- This is the first randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trial collecting data on the efficacy and safety of bexagliflozin compared to that of dapagliflozin in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Bexagliflozin provides identical efficacy in improving key efficacy parameters including glycated hemoglobin, fasting plasma glucose, 2-h postprandial blood glucose, and clinical response without an increase in adverse events compared with dapagliflozin.
Pedal medial arterial calcification in diabetic foot ulcers: A significant risk factor of amputation and mortality
- First Published: 07 April 2024
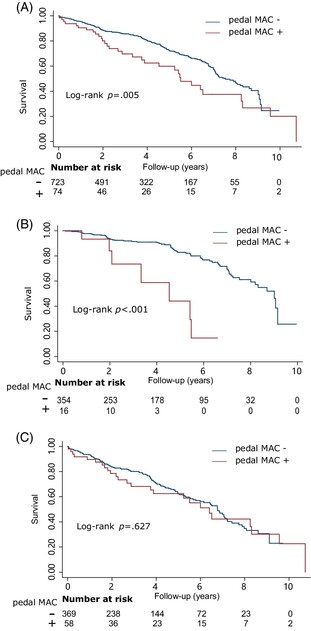
Highlights
- The impact of pedal medial arterial calcification (MAC) on individuals with diabetic foot ulcers (DFUs) remains uncertain.
- This study revealed a significant association between pedal MAC and both amputation and mortality in individuals with DFUs. Furthermore, pedal MAC demonstrated additional predictive value for amputation beyond that of PAD alone.
- The findings underscore the importance of preventing and reversing MAC in individuals with DFUs.
RESEARCH LETTERS
Association of healthy sleep pattern with lower risk of acute myocardial infarction mortality among people with diabetes: A prospective cohort study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
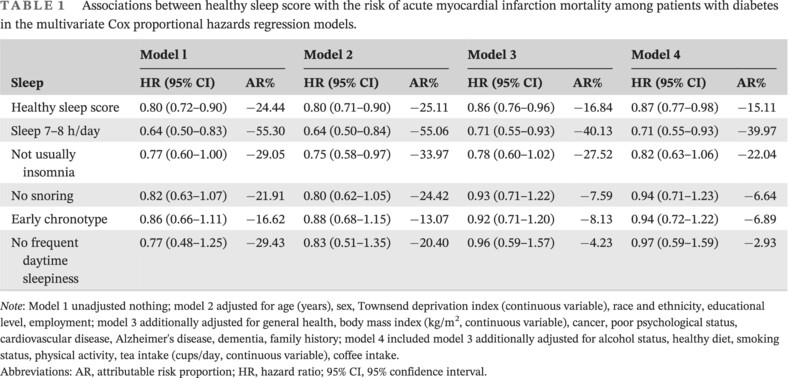
Highlights
- This large cohort study investigated a potential association between sleep pattern and acute myocardial infarction mortality among individuals with diabetes.
- Healthy sleep score showed a linear relationship with acute myocardial infarction mortality among people with diabetes.
- Of five sleep habits, adequate sleep duration was associated with lowest risk of acute myocardial infarction mortality.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Independent and interactive associations of heart rate and obesity with type 2 diabetes mellites: A population-based study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
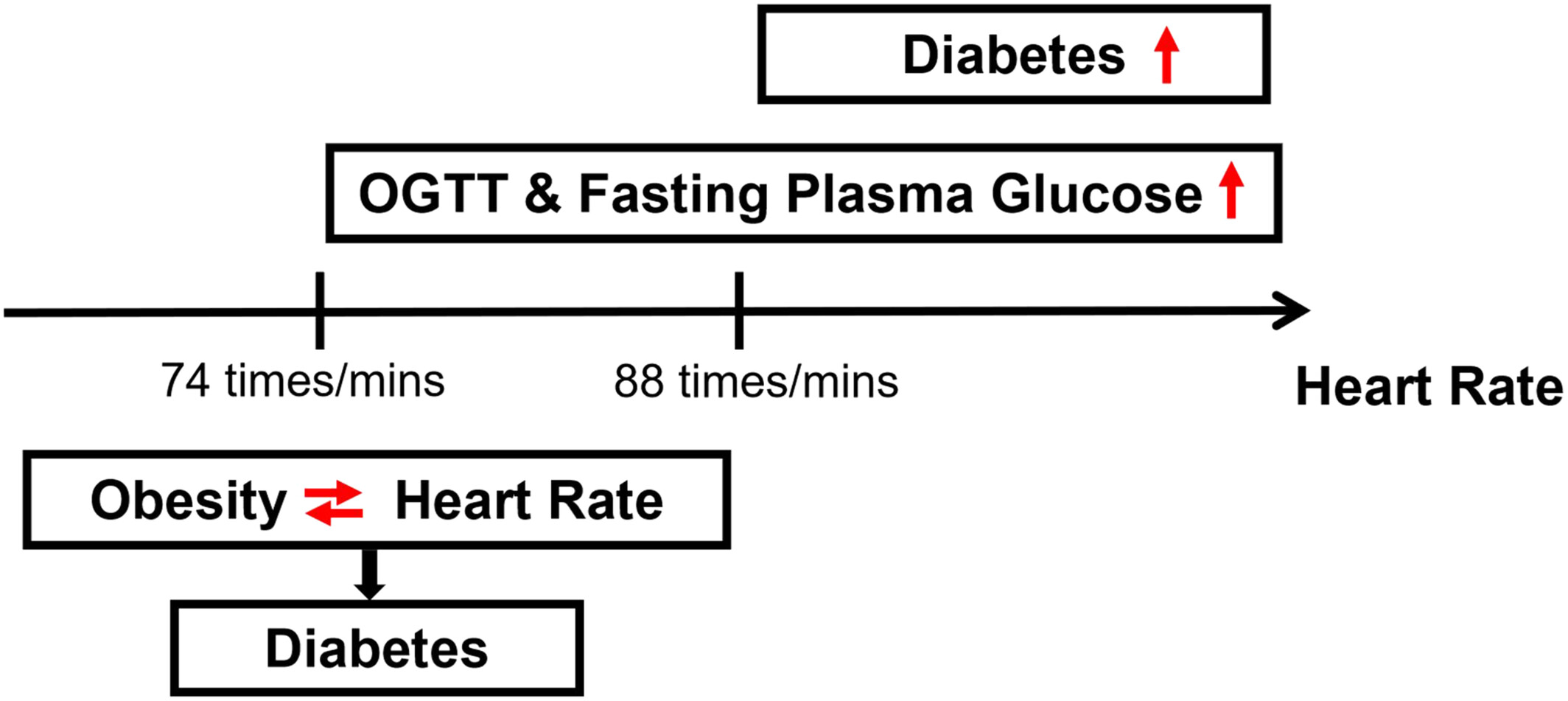
Highlights
- With the increase of heart rate (HR) level, high levels HR was associated with increasing risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- HR was in interaction with obesity, associating with incidence of T2DM in diabetic patients with HR < 74 beats/min.
- HR could be used as an independent assessment factor for diabetic patients with HR > 88 beats/min.
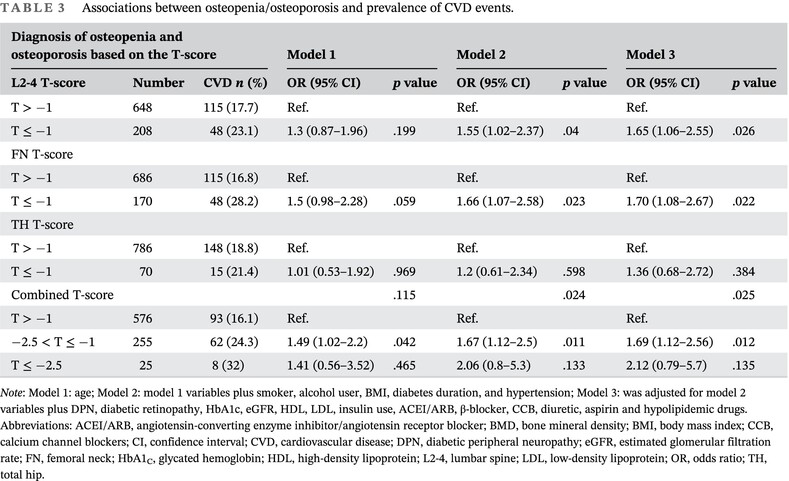
Association of cardiovascular disease prevalence with BMD and fracture in men with T2DM
- First Published: 07 April 2024
Highlights
- This is the first study to explore the association between bone mineral density, fracture, and the prevalence of cardiovascular disease in men with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- We have drawn the restricted cubic spline curve and revealed that femoral neck bone mineral density, total hip bone mineral density, and cardiovascular disease have a linear negative correlation.
- The previous fracture was independently associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease.
COMMENTARIES
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Financial conflicts of interest among authors of clinical practice guidelines for diabetes mellitus in Japan
- First Published: 10 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
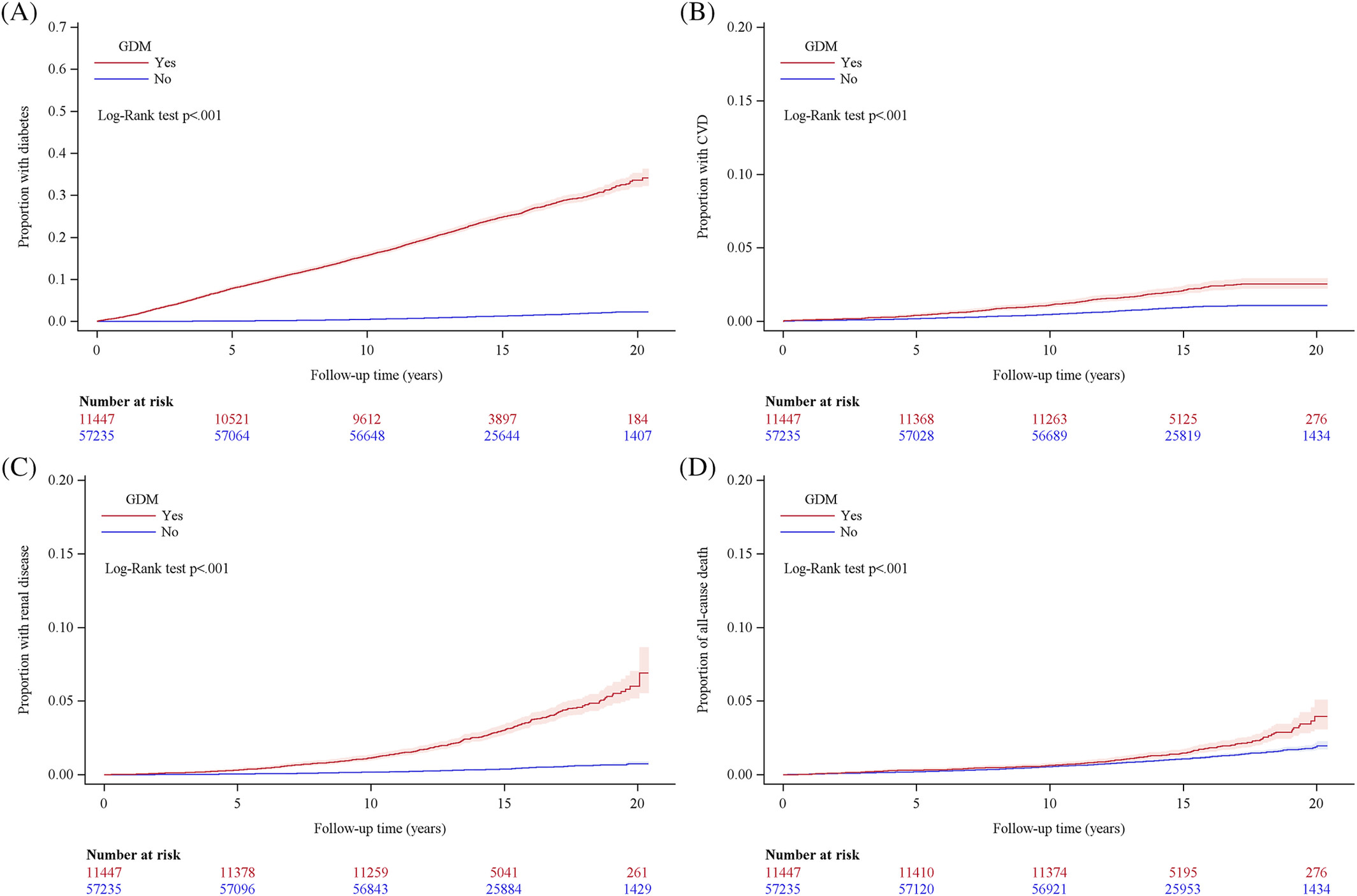
Increased risk of cardiovascular and renal disease, and diabetes for all women diagnosed with gestational diabetes mellitus in New Zealand—A national retrospective cohort study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
- Women diagnosed with gestational diabetes were significantly more likely to develop renal disease, have a major cardiovascular event, and develop hypertension and dyslipidemia following delivery compared with women without diabetes in pregnancy.
- The risk of developing type 2 diabetes for these women remains 20 times higher than for women without diabetes in pregnancy, despite knowledge of this association for over 50 years.
- European women diagnosed with gestational diabetes have the highest risk of developing type 2 diabetes compared with Māori, Pacific, and Asian women.
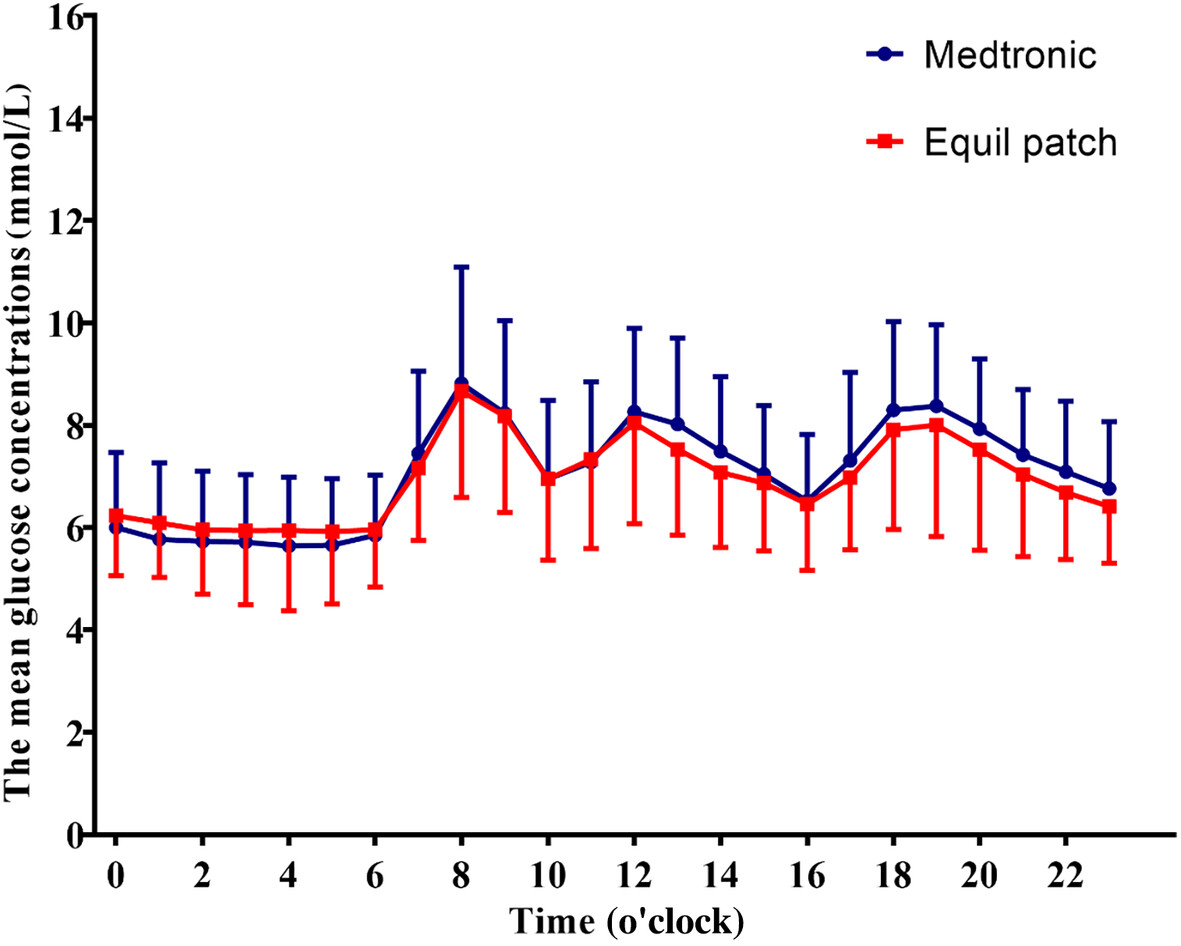
Comparing Equil patch versus traditional catheter insulin pump in type 2 diabetes using continuous glucose monitoring metrics and profiles
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
- This study was based on different parameters calculated from continuous glucose monitoring data and demonstrated that the Equil patch insulin pump has similar efficacy in clinical practice as the Medtronic MMT-712 insulin pump.
- This study demonstrated that the Equil patch insulin pump had similar efficacy in controlling glucose variability, reducing hyperglycemia, and managing hypoglycemic episodes in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients as the Medtronic MMT-712 insulin pump.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Advanced multifunctional hydrogels for diabetic foot ulcer healing: Active substances and biological functions
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
- A review was conducted of studies on the combination of hydrogels and diabetic foot ulcer pathogenesis.
- Various hydrogels were classified and elaborated based on their biological functions.
- The summary of biological functions provides guidance for future research and clinical application.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Association of obstructive sleep apnea symptoms with all-cause mortality and cause-specific mortality in adults with or without diabetes: A cohort study based on the NHANES
- First Published: 10 April 2024
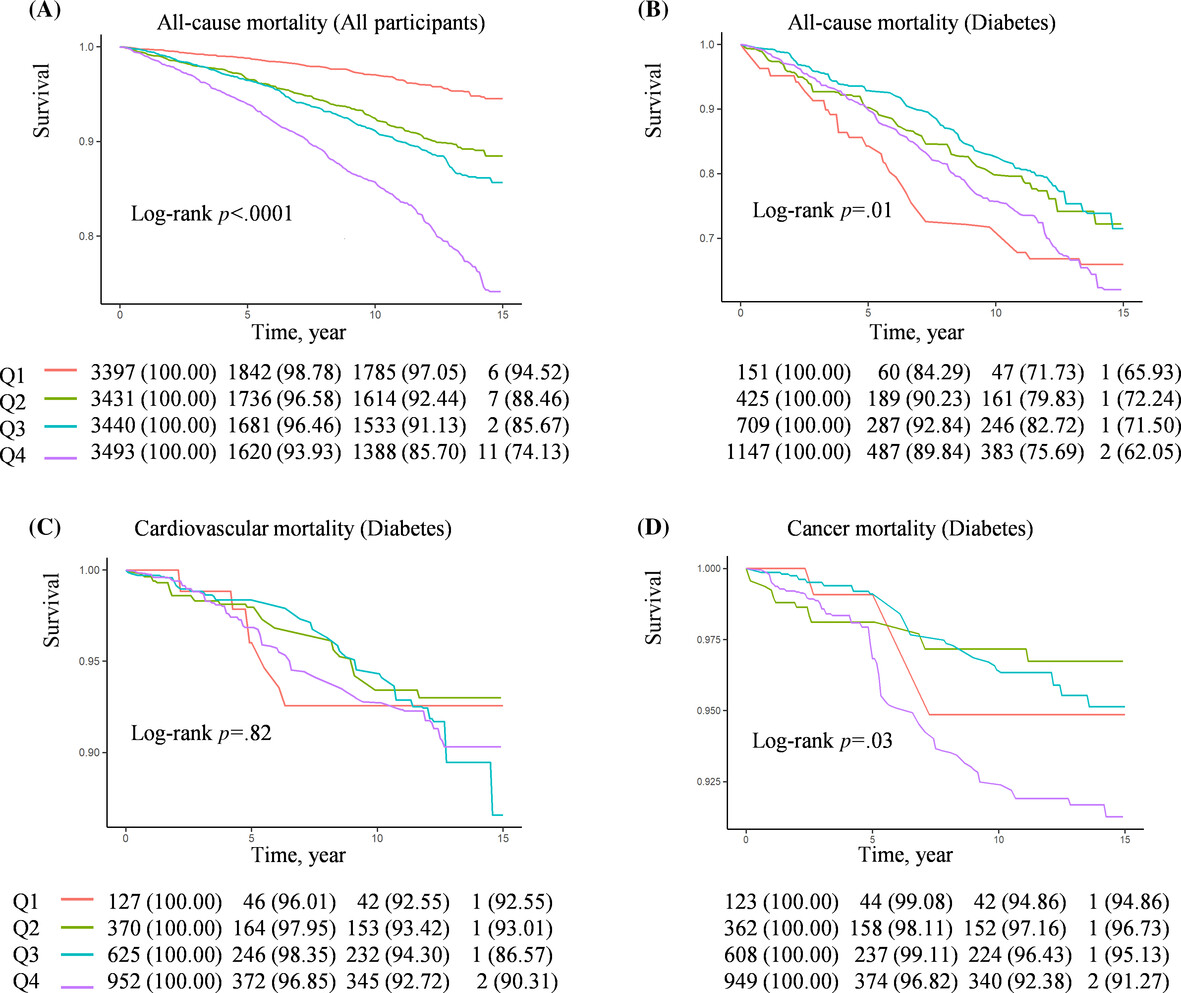
Highlights
- The study examined the association between obstructive sleep apnea symptoms (OSAS) and all-cause as well as cause-specific mortality in US individuals with and without diabetes, utilizing data from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey.
- Among patients without diabetes, OSAS was positively associated with all-cause, cardiovascular, and cancer mortality.
- For diabetes patients, the relationship between OSAS and the risk of all-cause mortality and cancer mortality exhibited L-shaped curves.
Mitochondria-associated membranes contribution to exercise-mediated alleviation of hepatic insulin resistance: Contrasting high-intensity interval training with moderate-intensity continuous training in a high-fat diet mouse model
- First Published: 10 April 2024
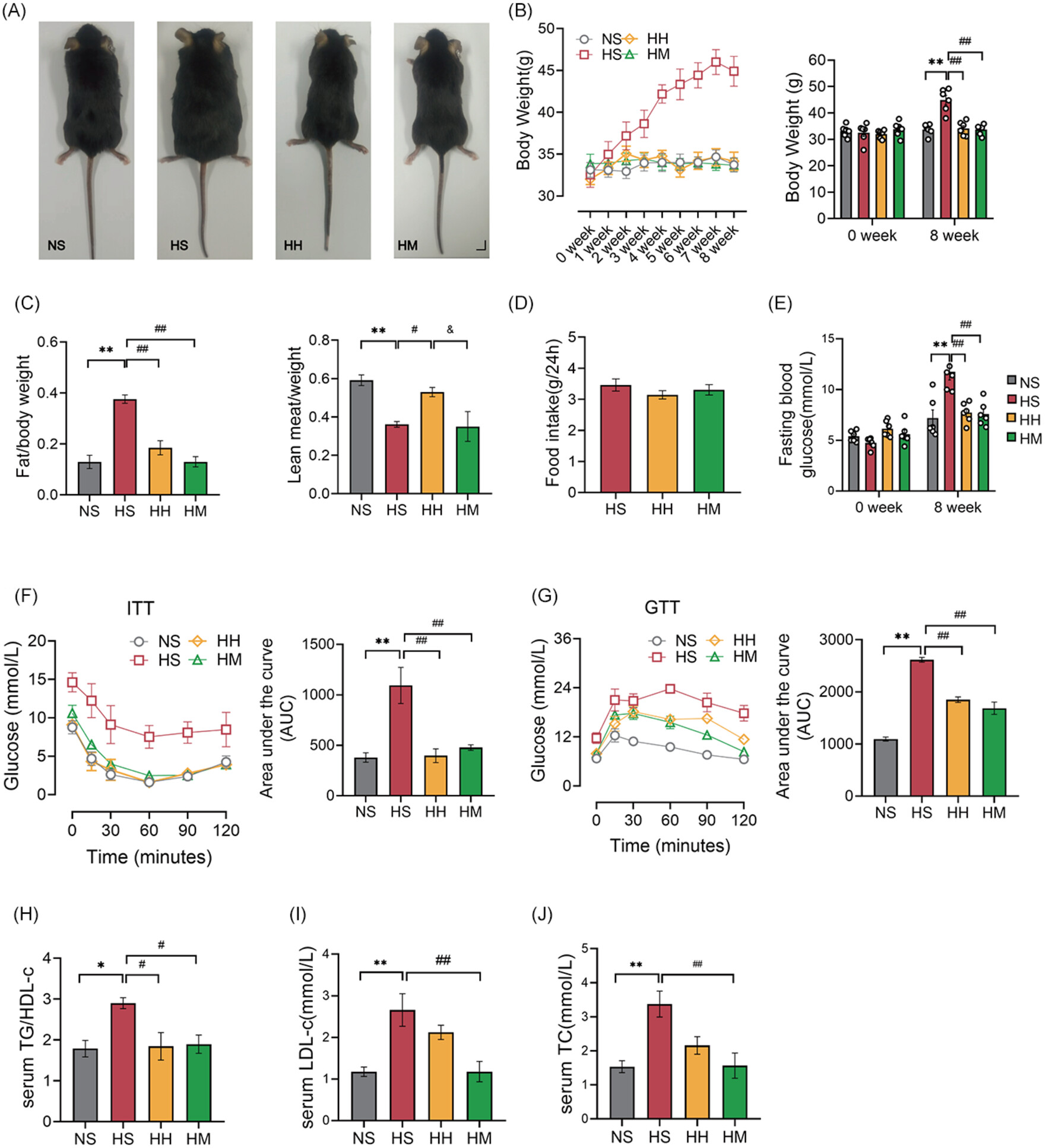
Highlights
- The reduction of hepatic mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) induced by high-fat diet (HFD) is related to the development of hepatic insulin resistance.
- Both high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) effectively reverse the reduction of hepatic MAMs induced by HFD.
- MICT is more beneficial in increasing the formation of hepatic MAMs in HFD mice compared to HIIT.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Kisspeptin a potential therapeutic target in treatment of both metabolic and reproductive dysfunction
- First Published: 10 April 2024
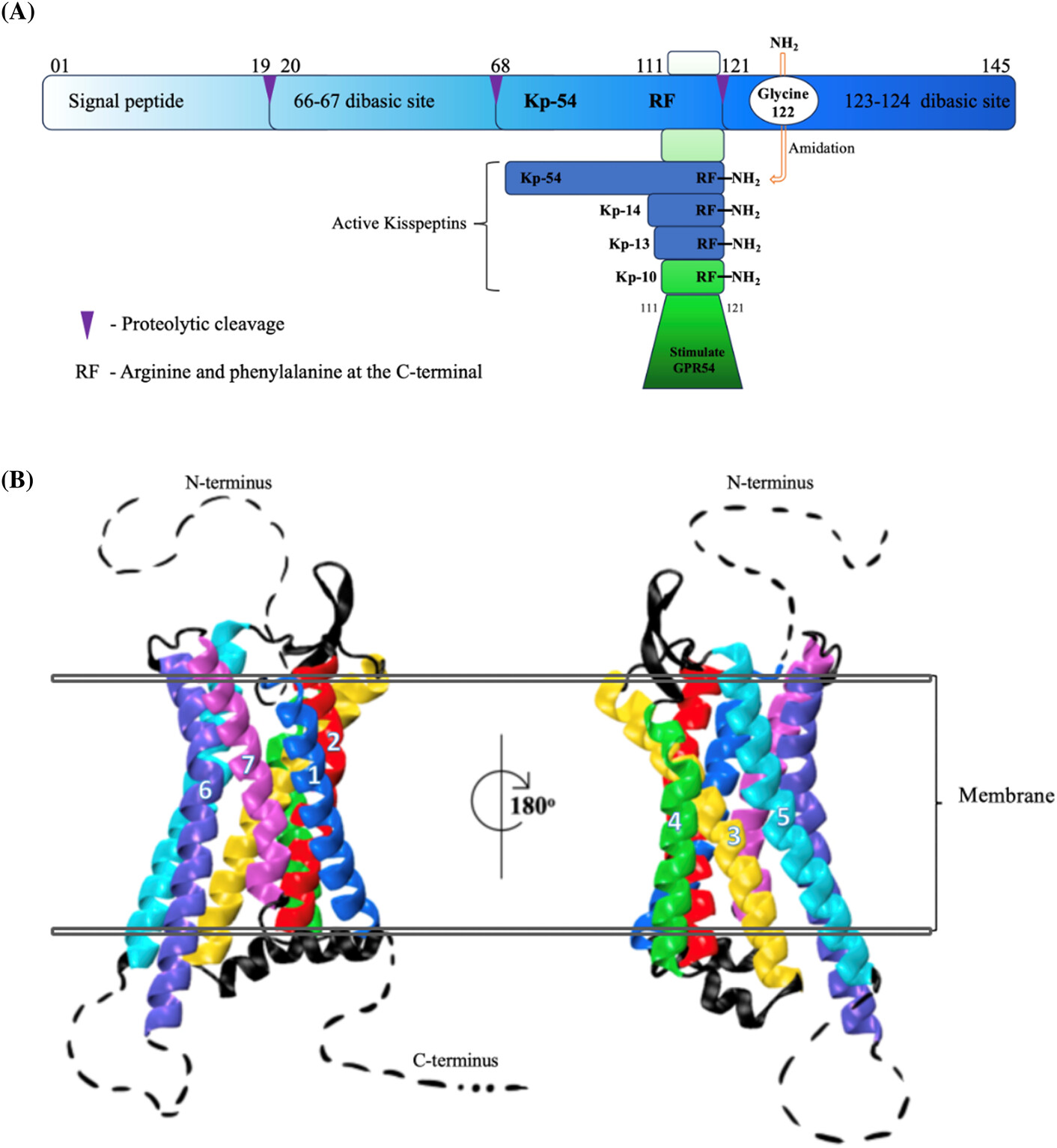
Highlights
- Kisspeptins (KPs) were first discovered to have antimetastatic action. Historically, a role in reproduction was demonstrated. Today, there is growing experimental and clinical evidence that KPs and their receptors regulate metabolism.
- Disruption of KP and receptor interaction provides an interesting approach to treating metabolic conditions, as well as reproductive disorders.
- Clinical trials have focused mainly on treating reproductive dysfunctions; however, greater understanding of the biology and mechanisms of action of KPs is being used in the therapeutic armory against insulin-related dysfunctions.
- Linkage between reproduction and metabolism via the KP system also allows for therapeutic targeting.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
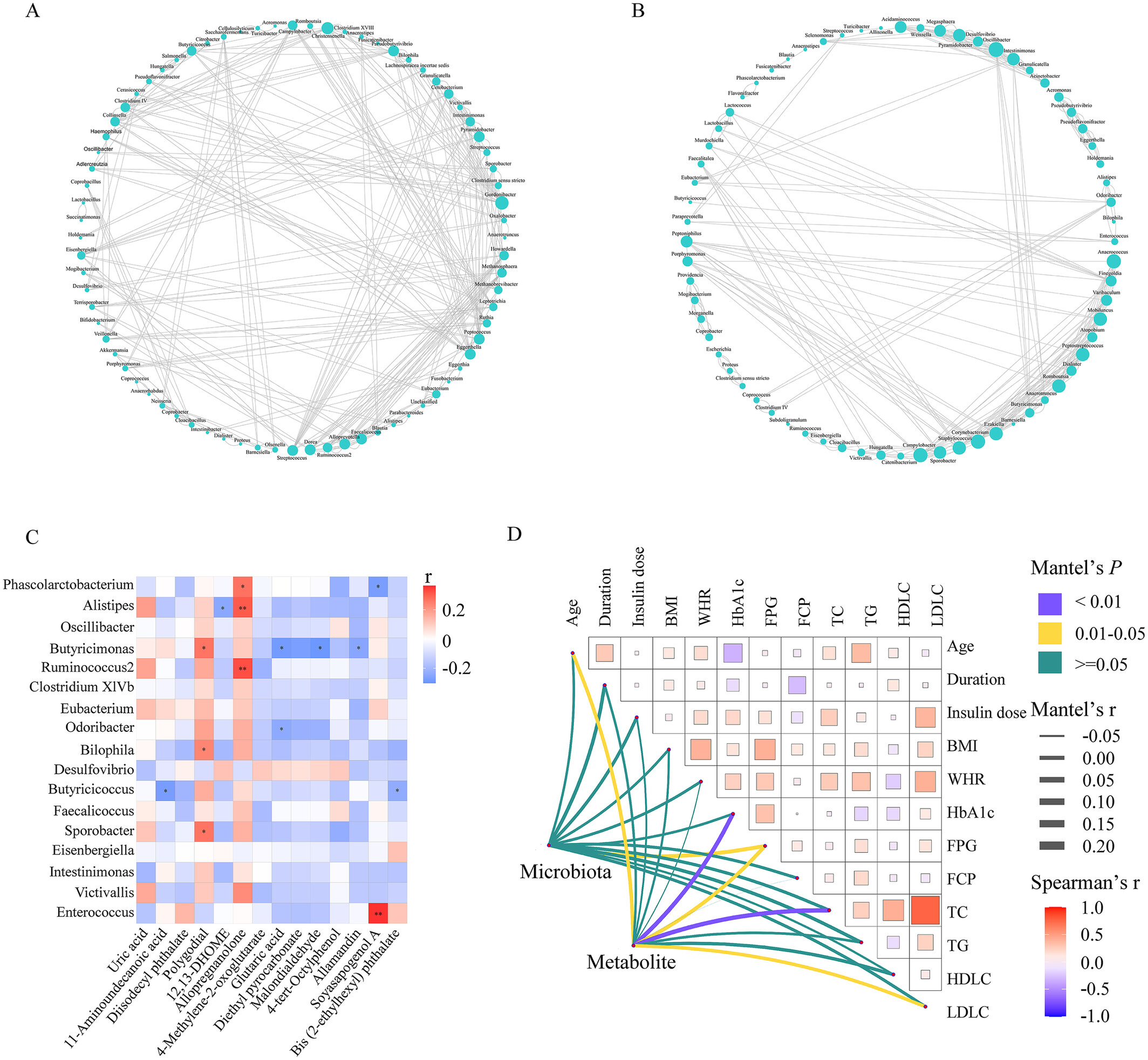
Microbial and metabolomic profiles of type 1 diabetes with depression: A case–control study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Further learning of clinical characteristics and imaging manifestations of nonketotic hyperglycemic hemichorea
- First Published: 07 April 2024
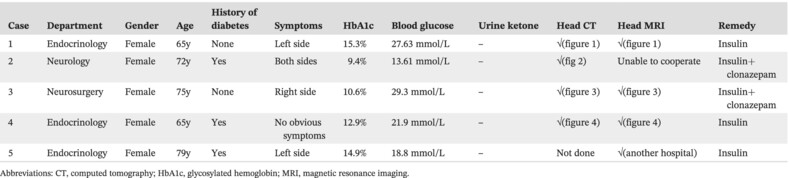
Highlights
- Nonketotic hyperglycemic hemichoea (NH-HC) is a rare complication of diabetes. Because it may involve the departments of endocrinology, neurology, and neurosurgery, it is often missed diagnosed or misdiagnosed.
- NH-HC has a range of relevant clinical and imaging features, but the clinical heterogeneity is large, and not all patients have typical findings.
- We analyzed the clinical manifestations and imaging features of the disease through five related cases to provide some ideas for the future clinical diagnosis and treatment of NH-HC. How to quickly and accurately identify this disease in clinical work and treat it as soon as possible is the top priority.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Traditional and emerging strategies using hepatocytes for pancreatic regenerative medicine
- First Published: 10 April 2024
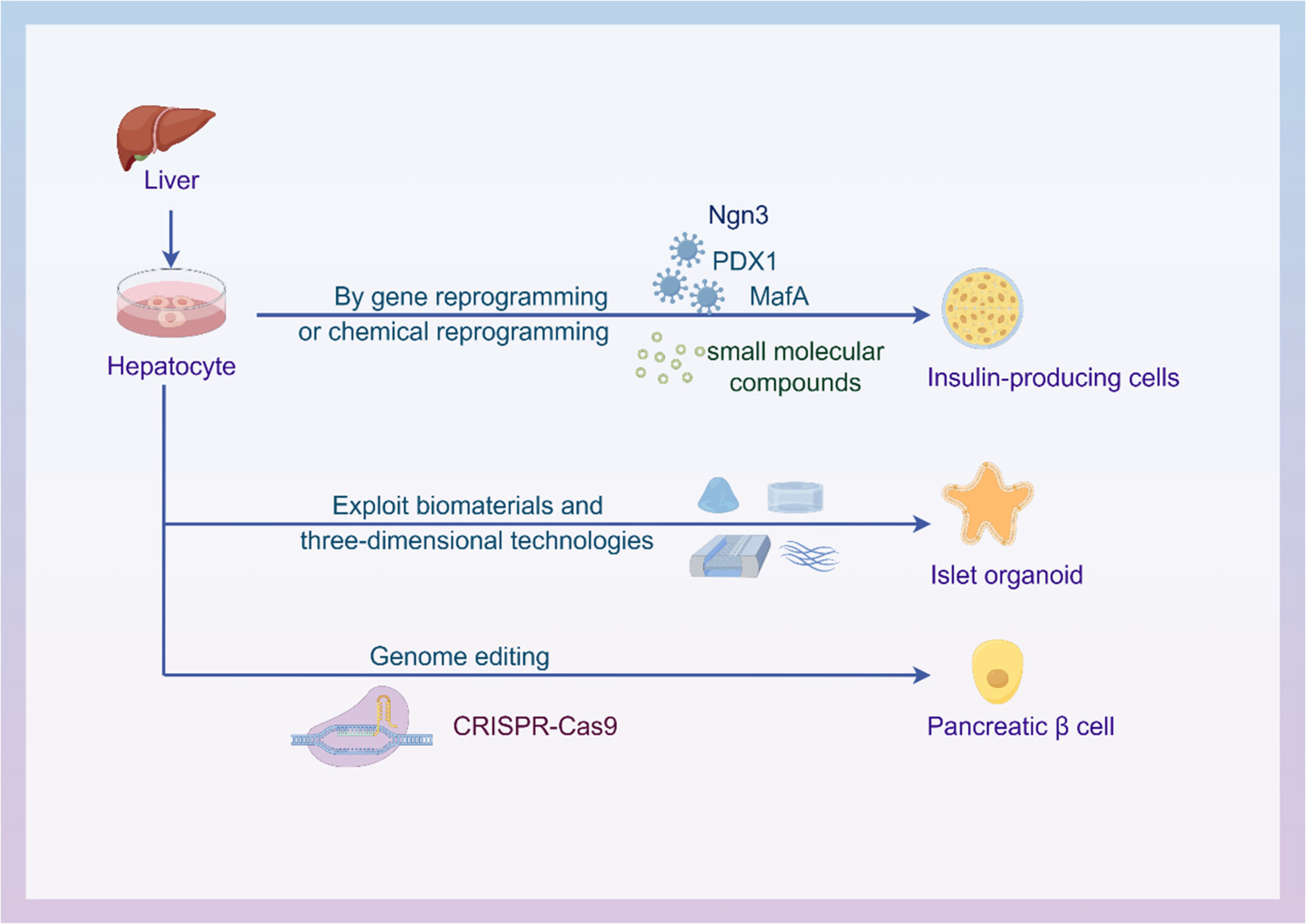
Highlights
- At present, the traditional and emerging strategies using hepatocyte-derived islet-like cells for diabetic cell replacement therapy have made extensive and far-reaching progress. Gene reprogramming and chemical reprogramming technology are traditional strategies with potential, and organoid technology as an emerging strategy has also been widely studied. Clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/Cas9 gene editing also provides new opportunities and challenges for the development of organoid technology.
COMMENTARIES
FSH regulates glucose-stimulated insulin secretion: A bell-shaped curve effect
- First Published: 10 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
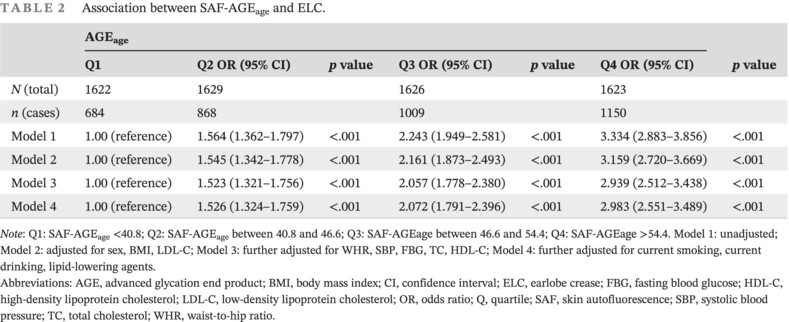
Association of advanced glycation end products with ear lobe crease: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
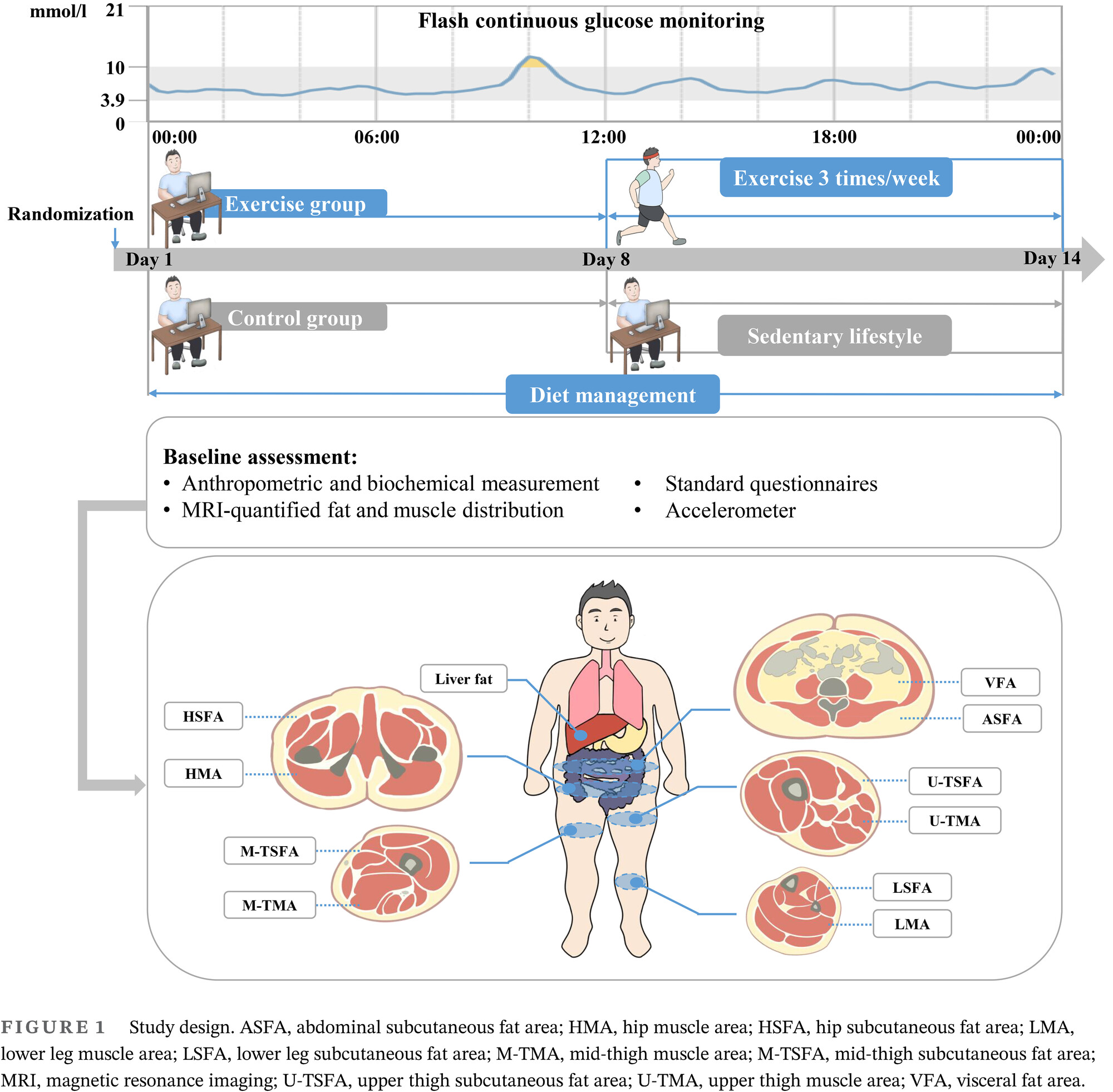
Exercise-induced improvement of glycemic fluctuation and its relationship with fat and muscle distribution in type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 07 April 2024