Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
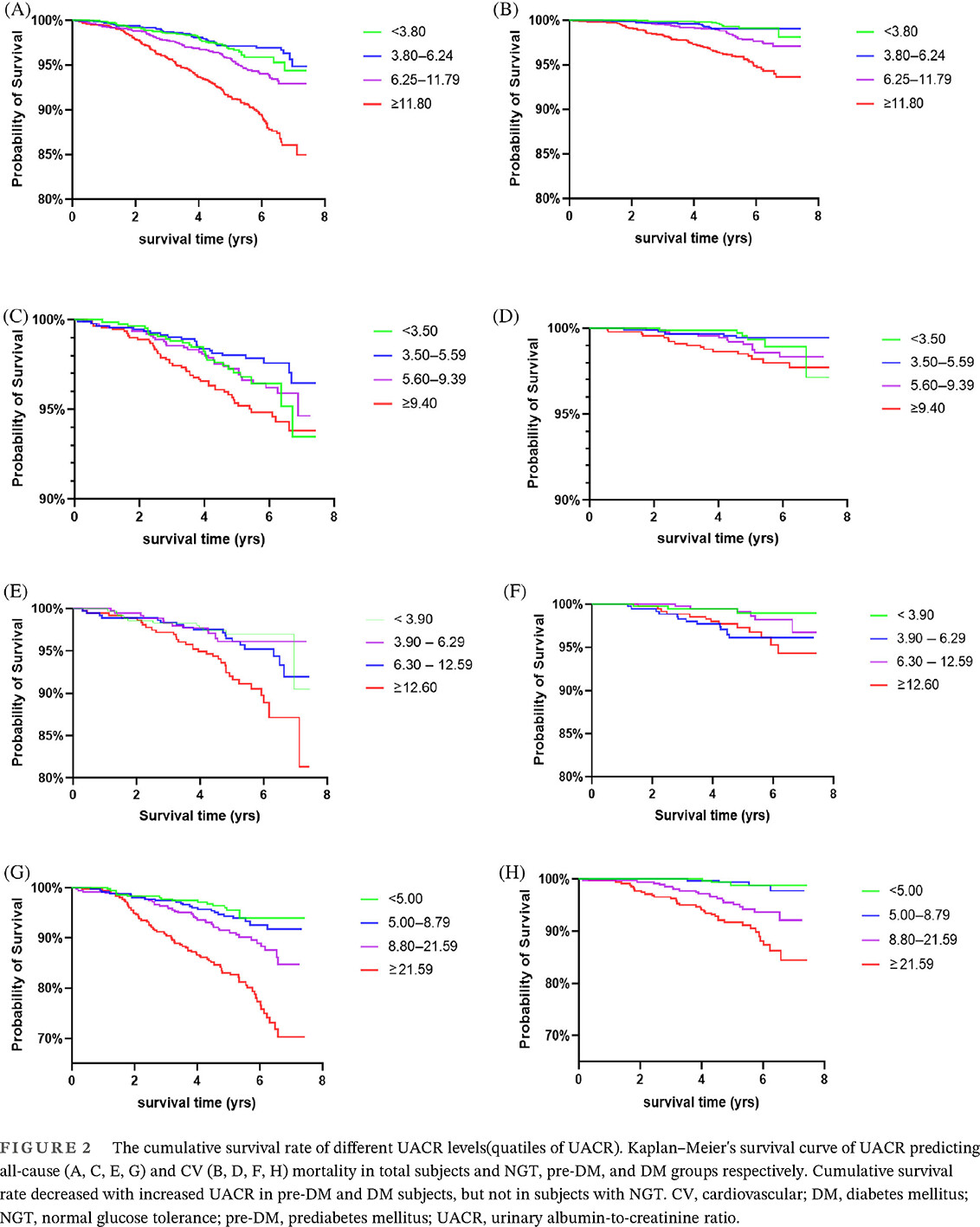
Lower urinary albumin-to-creatinine ratio predicted all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in Chinese population with diabetes and prediabetes—The Shanghai Changfeng cohort study
- First Published: 20 November 2023
Highlights
- The study firstly revealed that the relationship between UACR and mortality was different in subjects with different status of glucose metabolism. UACR was an important predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with pre-DM and DM but not in subjects with normal glucose tolerance.
- The optimal cutoff point of UACR for prediction was about 17 mg/gCr, which was far below the current diagnostic cutoff point for microalbuminuria (30 mg/gCr).
- Earlier interventions of albuminuria should be initiated at much earlier stage of diabetic nephropathy, even at the normal stage of urine protein excretion, to ultimately reduce the burden of death in all the patients with hyperglycemia.
Open Access
oa
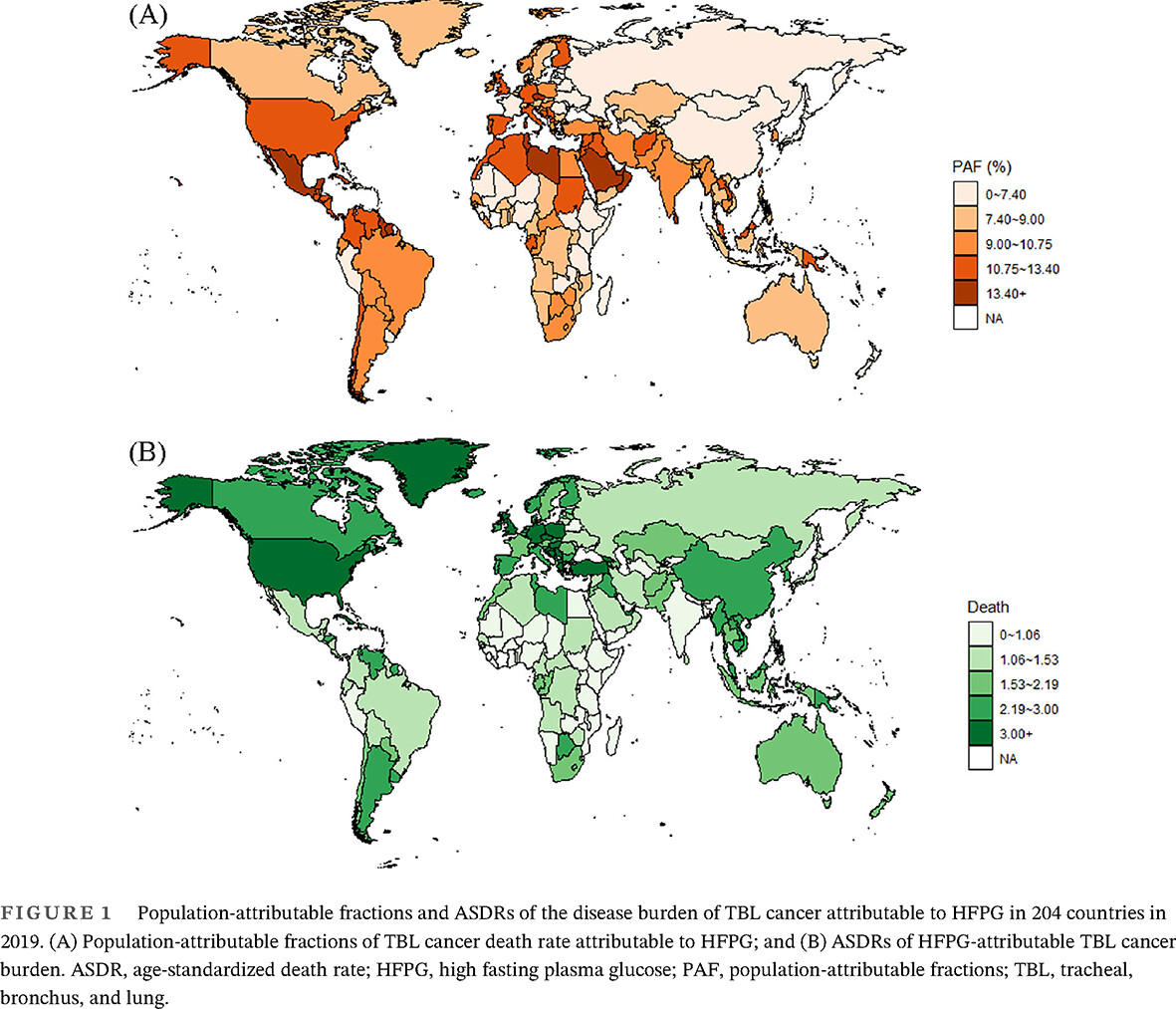
Global, regional, and national burden of tracheal, bronchus, and lung cancers attributable to high fasting plasma glucose: A systematic analysis of global burden of disease 2019
- First Published: 27 November 2023
Highlights
- High fasting plasma glucose (HFPG) increased the risk of development and worsen the prognosis of Tracheal, bronchus, and lung (TBL) cancer, we evaluated the global disease burden of TBL cancer attributable to HFPG.
- HFPG-attributable TBL cancer burden increased globally from 1990 to 2019, and approximately 8% of TBL cancer burden was attributable to HFPG in 2019.
- Men, people over 70 years of age were vulnerable subgroups in HFPG-attributable TBL cancer.
- Integrated cancer prevention and control measures are needed, with control of metabolic disorders as one of the key elements.
Open Access
oa
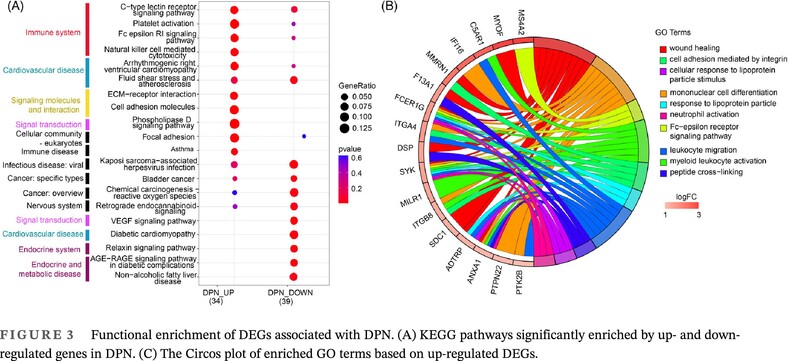
Diagnostic biomarker for type 2 diabetic peripheral neuropathy via comprehensive bioinformatics analysis
- First Published: 29 November 2023
Highlights
- Differentially expressed genes between diabetic peripheral neuropathy (DPN) and normal controls are mainly enriched in immune-related pathways.
- Three immune genes—FCER1G, PTK2B, and SYK—were identified as diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for DPN.
- Gene expression of FCER1G, PTK2B, and SYK was negatively correlated with the cell proportion of resting natural killer cells, T follicular helper cells, and activated mast cells, but positively correlated with monocytes.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
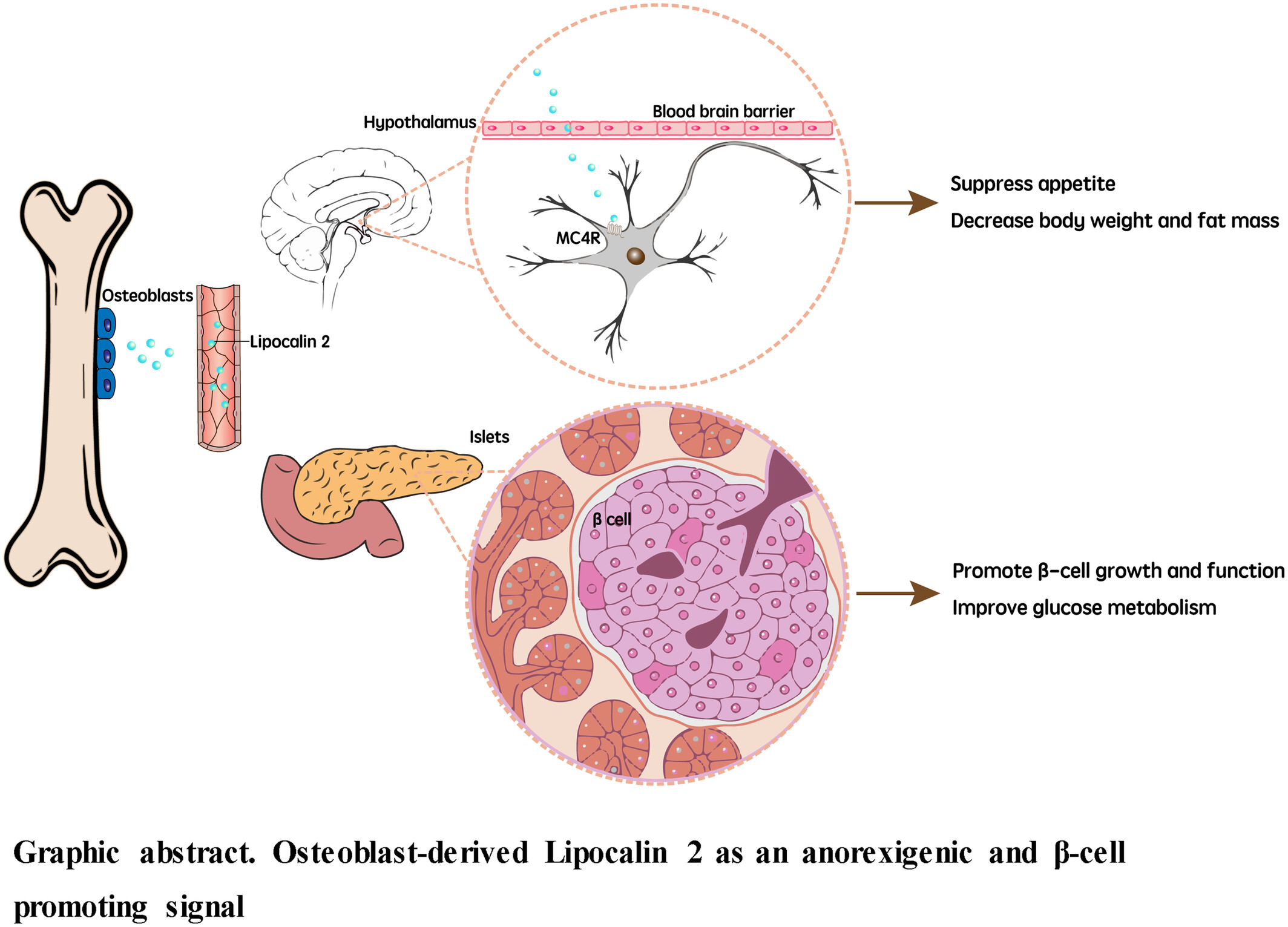
Lipocalin 2—A bone-derived anorexigenic and β-cell promoting signal: From mice to humans
- First Published: 30 November 2023
Highlights
- Lipocalin 2 (LCN2) suppresses appetite through melanocortin-4 receptor.
- LCN2 protects β-cell from damage and enhance their proliferation.
- LCN2 orchestrates energy metabolism by maintaining homeostasis of lipid metabolism in liver and supporting muscle regeneration.
- Targeting LCN2 holds significant therapeutic potential for managing both metabolic disorders and cachexia.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
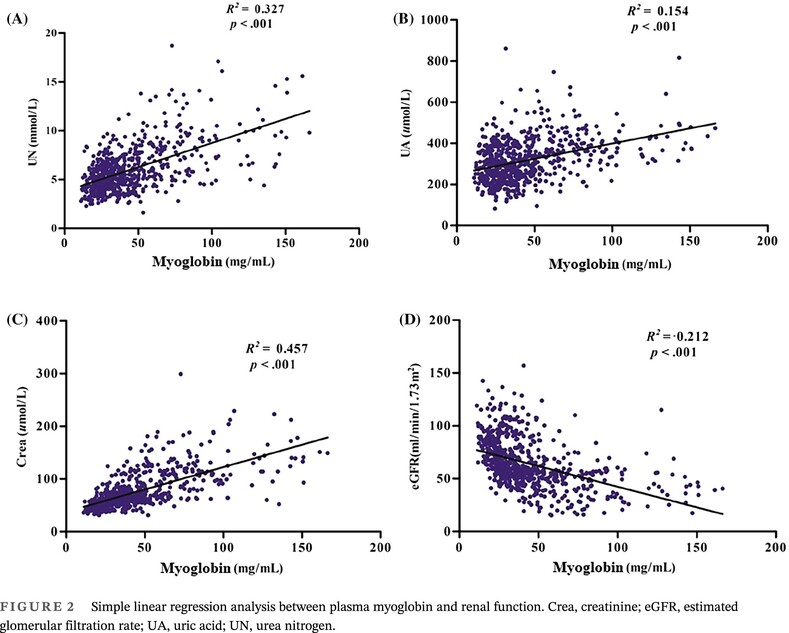
Elevated plasma myoglobin level is closely associated with type 2 diabetic kidney disease
- First Published: 30 November 2023
LETTERS TO THE EDITOR
Open Access
oa
Estimated glomerular filtration rate and risk of all-cause mortality
- First Published: 04 December 2023
REVIEW ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
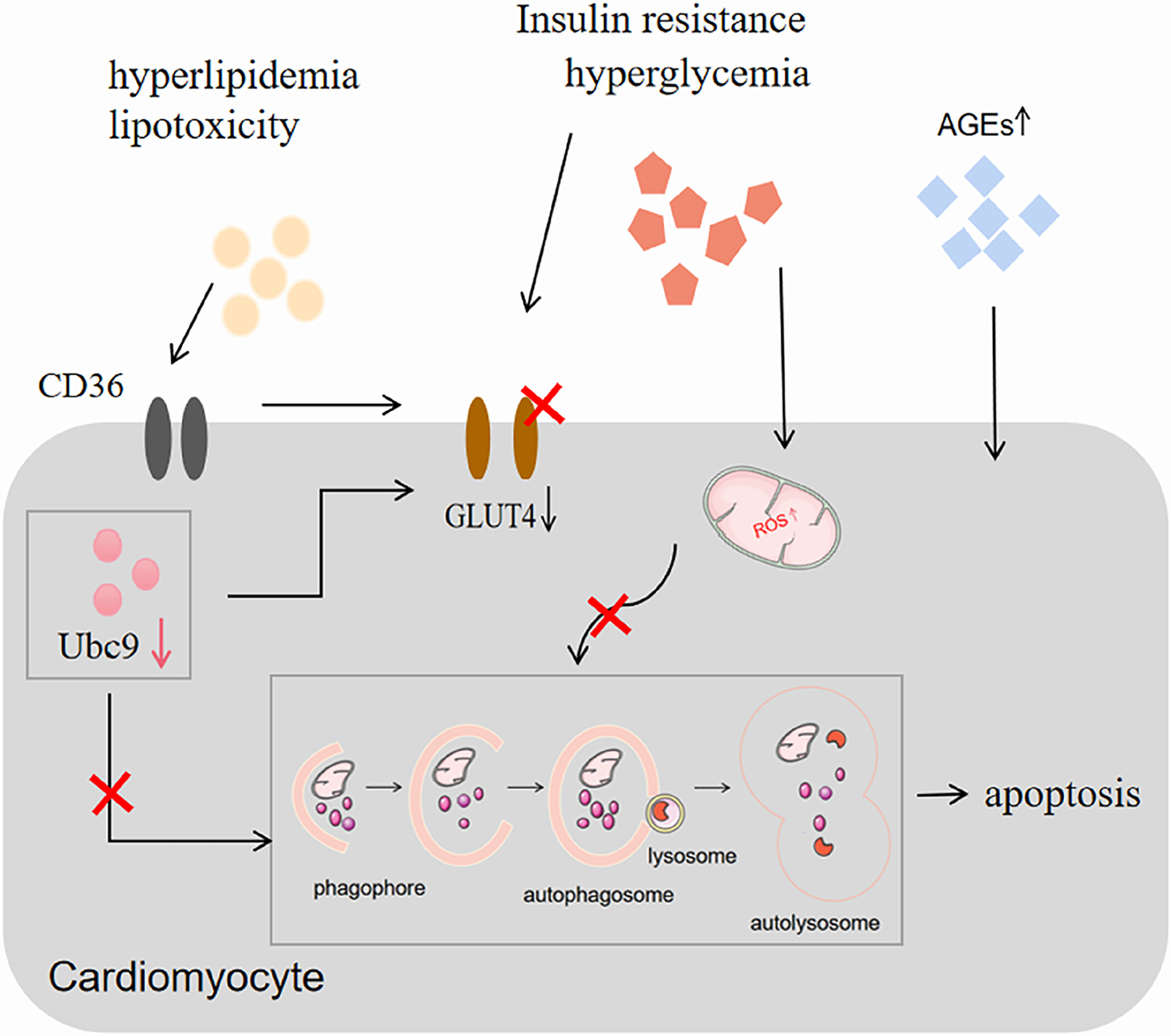
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 for regulating autophagy in diabetic cardiomyopathy: A mini-review
- First Published: 05 December 2023
Highlights
- Autophagy changes in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) were summarized.
- The role of ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 (Ubc9) in DCM and the positive regulation of autophagy by Ubc9 were elucidated.
- Ubc9 may play an integral role in cardiac autophagy in DCM and Ubc9 is a potential target for regulating autophagy in DCM.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Open Access
oa
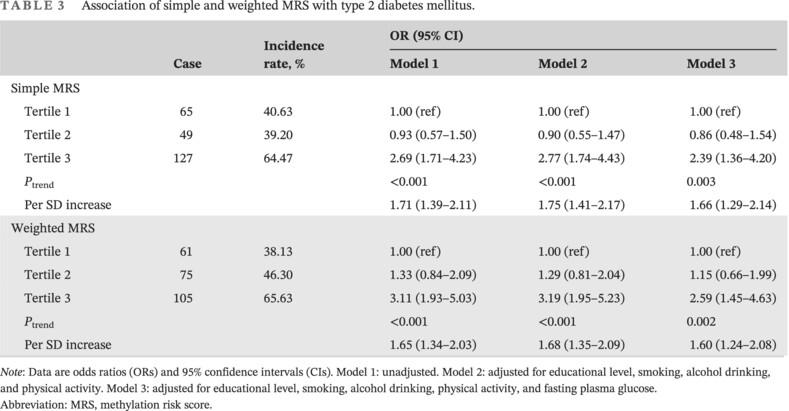
Association of methylation risk score with incident type 2 diabetes mellitus: A nested case–control study
- First Published: 07 December 2023
Highlights
- This is the first prospective nested case–control study based on the Chinese population to explore the relationship of methylation risk score (MRS) with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) risk.
- We calculated simple and weighted MRSs based on the methylation levels of 10 risk CpG sites of ATP-binding cassette G1 gene, fat mass and obesity associated gene, potassium voltage-gated channel member 1 gene, and thioredoxin-interacting protein gene before T2DM occurred.
- We found a significant positive association between MRS and the risk of T2DM incidence.
Open Access
oa
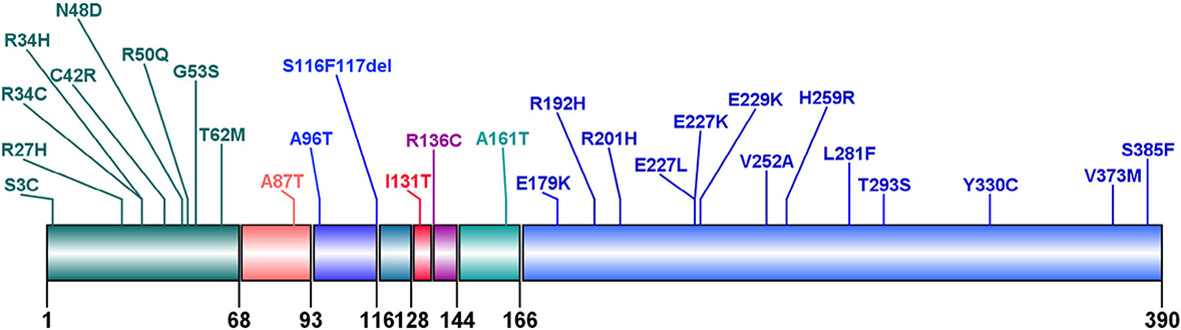
Clinical and genetic characteristics of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 13: A systematic review of the literature
- First Published: 14 December 2023
Highlights
- This is the first article to summarily describe clinical and genetic characteristics of maturity-onset diabetes of the young type 13 (MODY13).
- MODY13 was diagnosed later than other types of MODY and was associated with low fasting C-peptide.
- Mutation sites of MODY13 were mostly concentrated in N- and C-terminal intracellular domains.
- The incidence rates of chronic complications were lower than type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
Open Access
oa
Impact of treatment with GLP-1RAs on suicide attempts in adults persons with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective comparative effectiveness study based on a global TriNetX health research database
- First Published: 19 March 2024
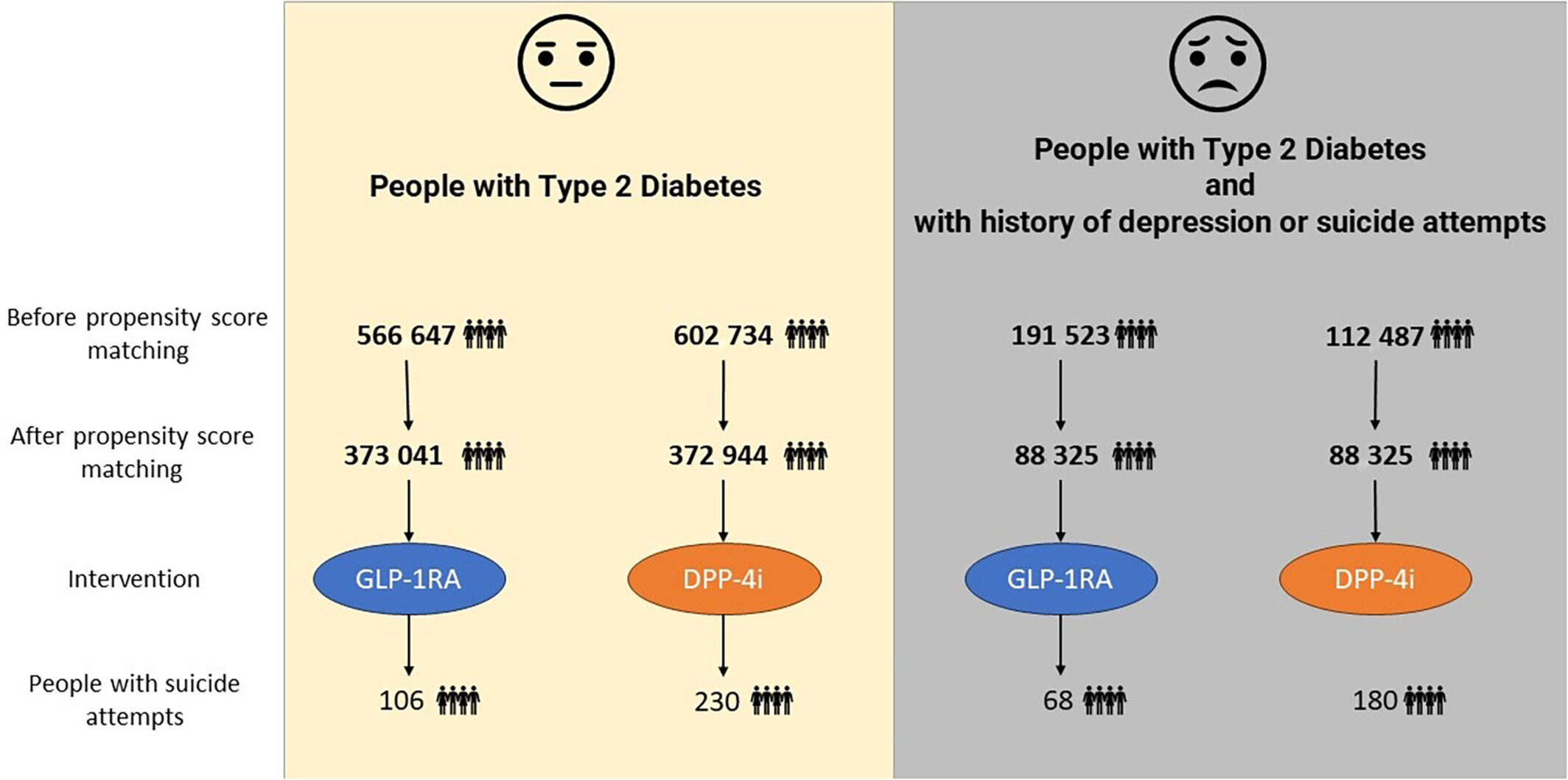
Highlights
- This retrospective cohort study utilized the TriNetX global database and showed that the use of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) is associated with lower suicide risk in people with type 2 diabetes (T2D).
- Further, the use of GLP-1RA was particularly associated with lower suicide risk compared with the use of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor (DPP-4i) in people with T2D with a history of depression or suicide attempts.
- Overall, based on these data, GLP-1RA might provide more protection for the risk of suicide attempts compared to DPP-4i in people with T2D.