Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Deciphering the connection: Diabetes, pericyte dysfunction, and their impact on cardiovascular health
- First Published: 25 February 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
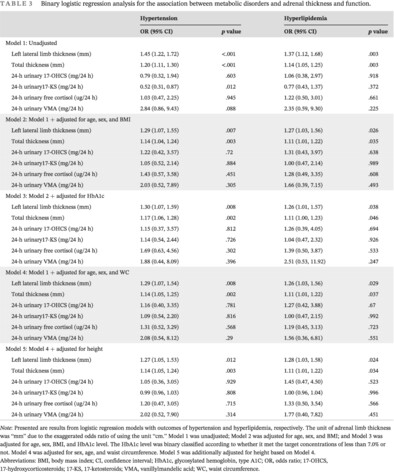
Adrenal limb thickness is associated with metabolism profiles in patients with diabetes: A cross-sectional study
- First Published: 26 September 2023
Highlights
- Adrenal thickness is independently associated with abdominal obesity, proteinuria, existing hypertension, and dyslipidemia.
- Cortisol may mediate the association between adrenal thickness and abdominal obesity.
- Adrenal physiology may have an essential role in the metabolism of patients with diabetes.
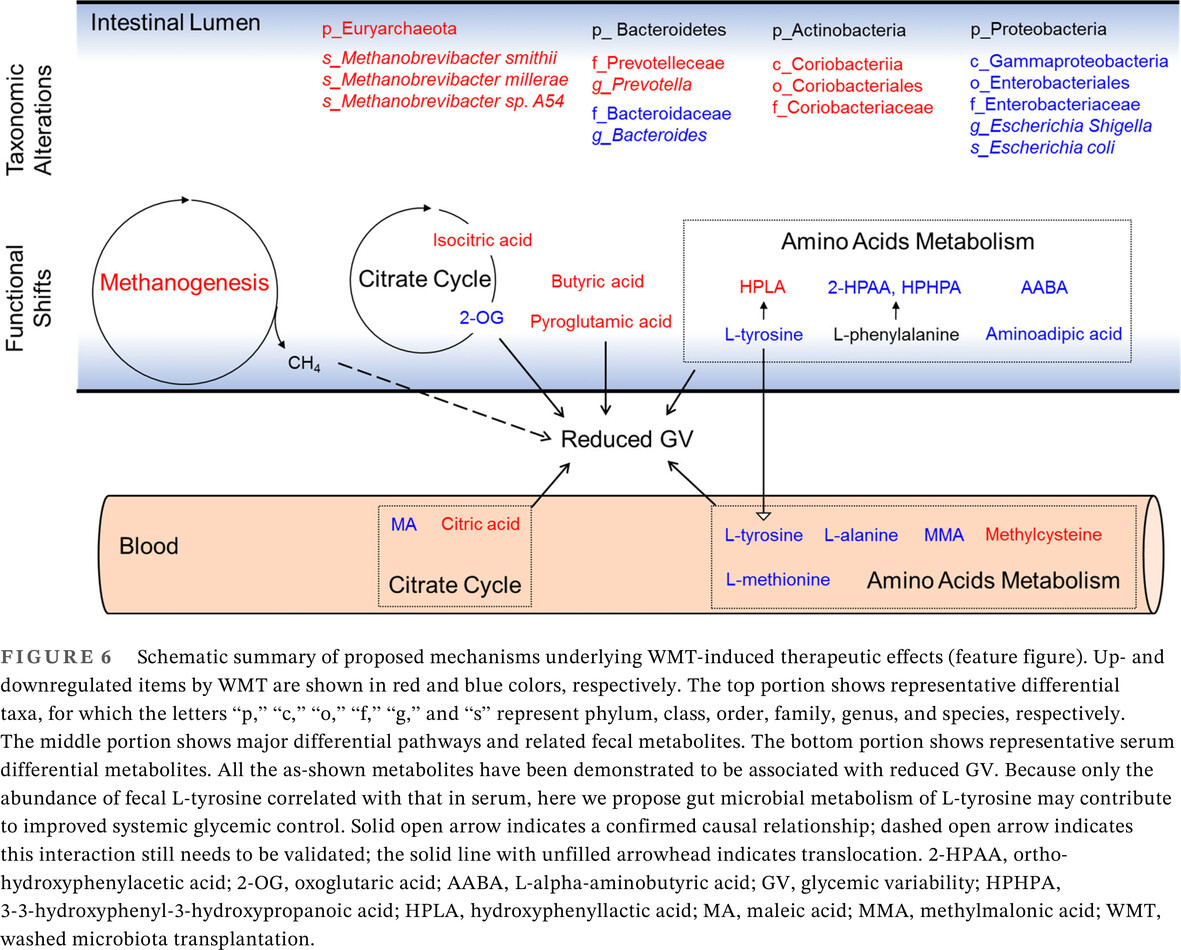
Washed microbiota transplantation reduces glycemic variability in unstable diabetes
- First Published: 17 October 2023
Highlights
- Washed microbiota transplantation (WMT) reduces glycemic variability in patients with unstable diabetes.
- WMT alters the composition and function of gut microbiome as revealed by 16S rRNA gene sequencing and metagenomics.
- WMT led to changed profiles of fecal and serum metabolites that are correlated with improved glycemic control.
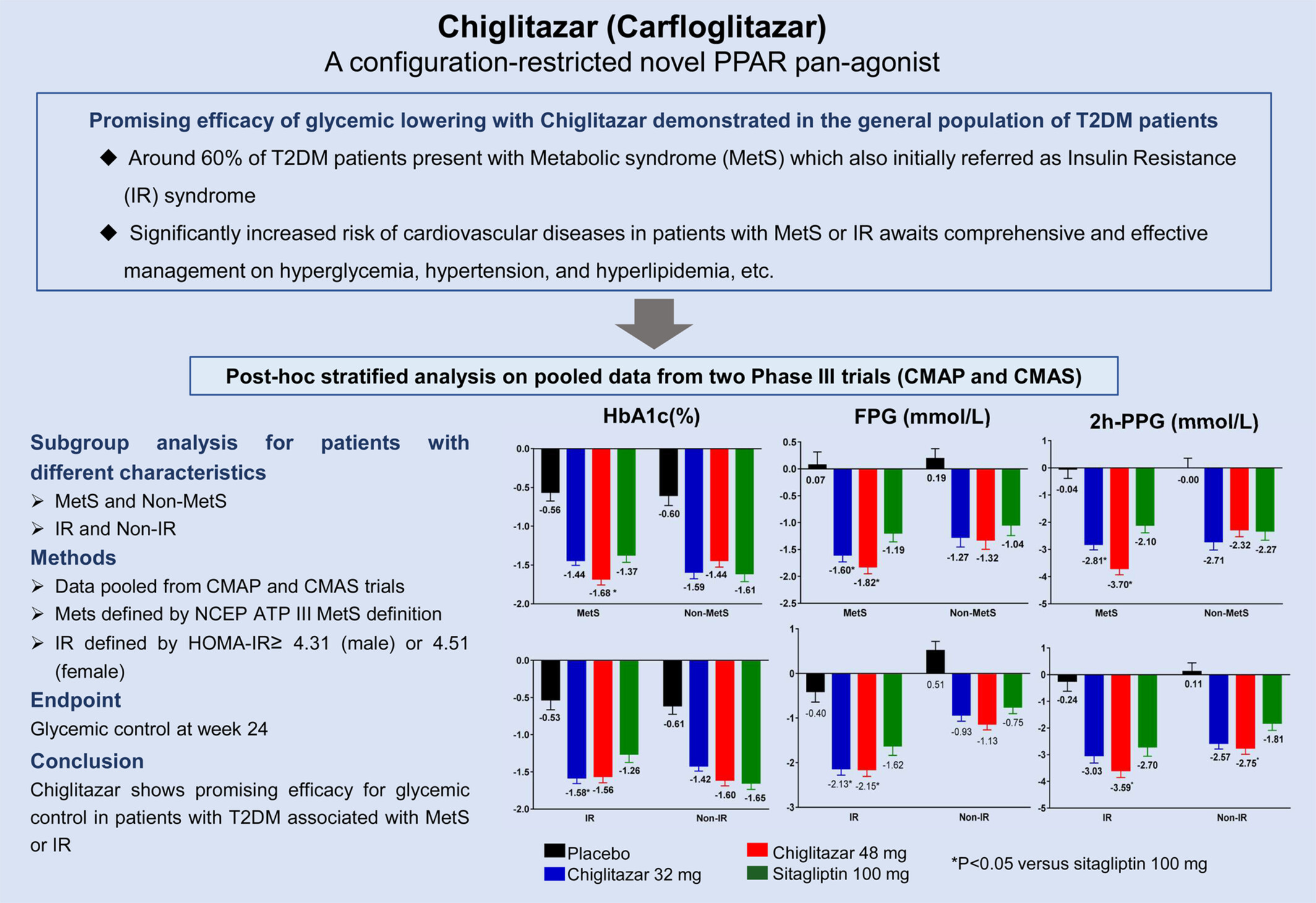
Impact of chiglitazar on glycemic control in type 2 diabetic patients with metabolic syndrome and insulin resistance: A pooled data analysis from two phase III trials
- First Published: 18 October 2023
Highlights
- Risk for atherosclerotic disease increases when type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is associated with metabolic syndrome (MetS).
- T2DM patients who present with MetS or insulin resistance show better improvement with the chiglitazar treatment. These results indicate a preferable population for chiglitazar treatment.
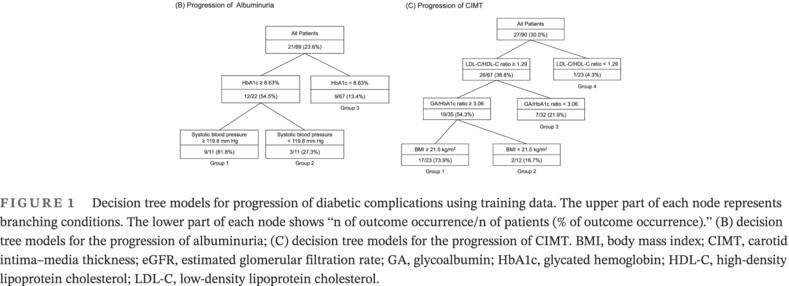
Evaluation of changes in glycemic control and diabetic complications over time and factors associated with the progression of diabetic complications in Japanese patients with juvenile-onset type 1 diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 18 October 2023
Highlights
- Glycemic control and complications were examined in Japanese patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus.
- Glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) and urinary albumin excretion rates improved over time.
- HbA1c, glycemic excursion, and blood pressure are related to diabetic nephropathy.
- HbA1c levels, glycemic excursion, lipid levels, and body mass index are associated with atherosclerosis.
The efficacy and safety of beinaglutide alone or in combination with insulin glargine in Chinese patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who are inadequately controlled with oral antihyperglycemic therapy: A multicenter, open-label, randomized trial
- First Published: 20 October 2023
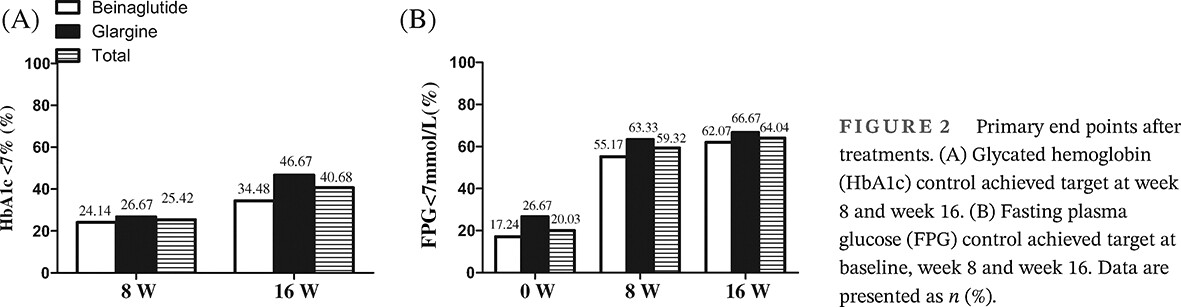
Highlights
- This was the first-ever multicenter, open-label, randomized trial to compare the hypoglycemic efficacy and safety of beinaglutide versus insulin glargine (IGlar) or beinaglutide combined with IGlar.
- Beinaglutide combined with IGlar attenuated fasting plasma glucose further and improved the proportion of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) reaching their glycemic target relative to beinaglutide alone.
- Beinaglutide reduced systolic blood pressure and improved lipid parameters in patients with T2DM.
- The hypoglycemic outcome with beinaglutide was related to the patients' baseline fasting C-peptide.
Associations of concurrent early-life famine exposure and adulthood obesity with type 2 diabetes mellitus in middle-aged Chinese
- First Published: 26 October 2023

Highlights
- Central overweight/obesity in adulthood is associated with the increased risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus, but the effect of early-life famine exposure is not very clear.
- The fetal period is probably a sensitive time window for the risk of type 2 diabetes mellitus, and central obesity in adulthood also plays a crucial role.
- Although lifestyle modification in adulthood will provide a degree of prevention, the long-term benefit may also come from the improvement of early life growth and development.
Comparison of medical resources and costs among patients with coronary heart disease and impaired glucose tolerance in the Acarbose Cardiovascular Evaluation trial
- First Published: 01 November 2023
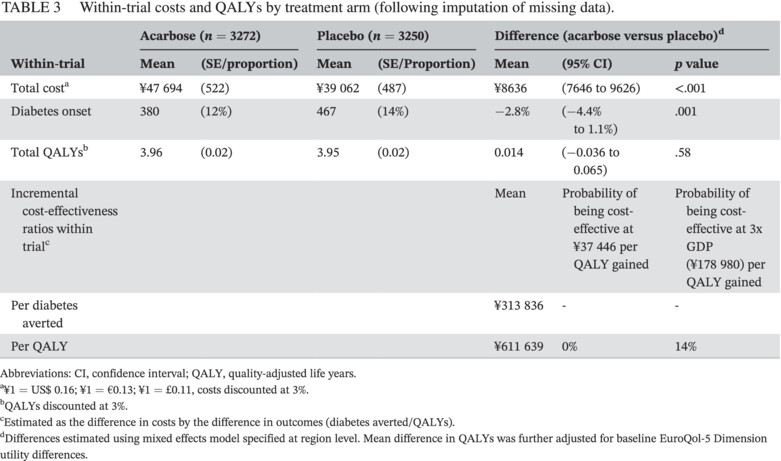
Highlights
- The Acarbose Cardiovascular Evaluation trial compared quality adjusted life years (QALYs) and costs of acarbose relative to placebo in participants with coronary heart disease and impaired glucose tolerance in China.
- The acarbose group reported numerically higher QALYs than the placebo group.
- Total costs per participant, including study drug, were significantly higher for the acarbose group compared with placebo.
Changes in the prevalence of diabetes and control of risk factors for diabetes among Chinese adults from 2007 to 2017: An analysis of repeated national cross-sectional surveys
- First Published: 05 November 2023
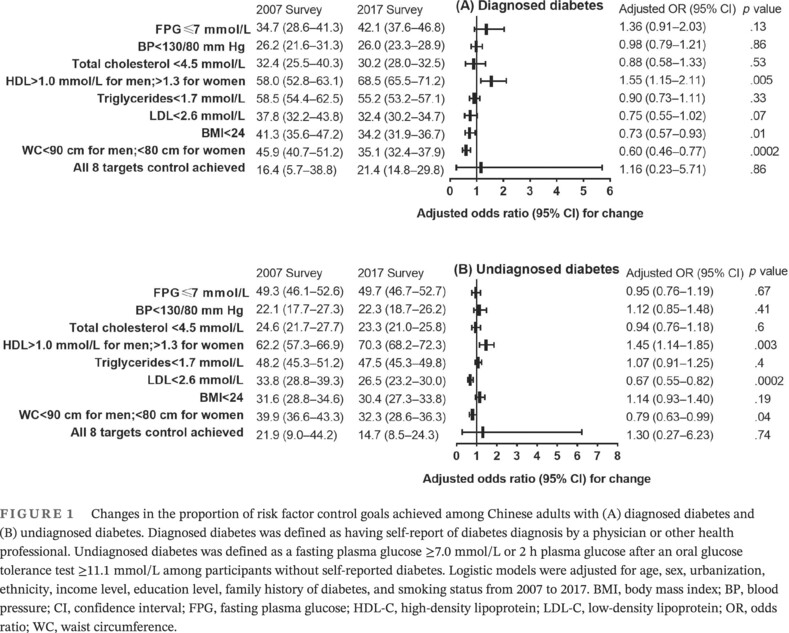
Highlights
- The prevalence of total diabetes and diagnosed diabetes significantly increased among adults in China between 2007 and 2017
- Waist circumference and the lipid accumulation product index were significantly increased among the overall and diabetic populations
- Only one fifth of patients diagnosed with diabetes had achieved all eight risk factor control goals in 2017
Cardiovascular disease risk in early-onset vs late-onset type 2 diabetes in China: A population-based cross-sectional study
- First Published: 06 November 2023
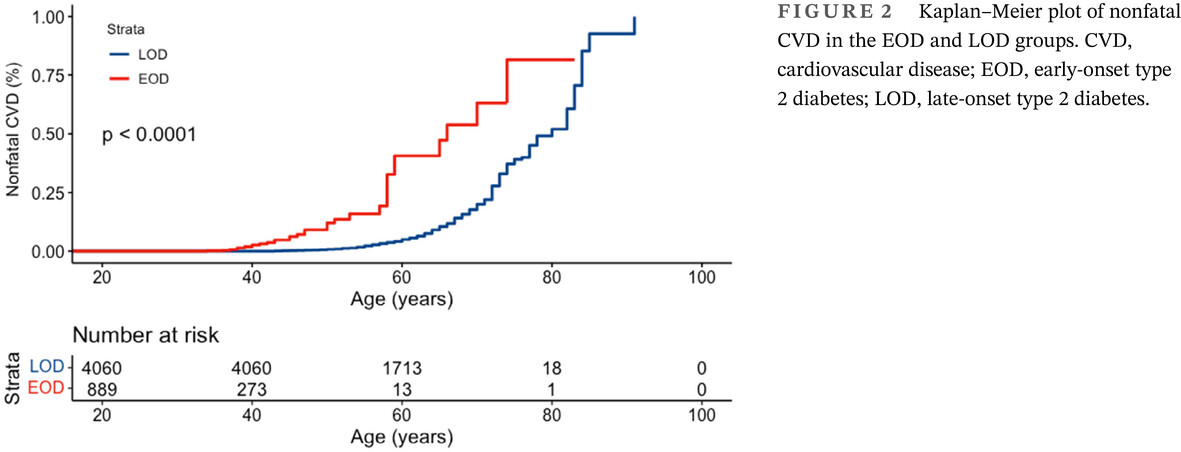
Highlights
- The study emphasizes the importance of implementing individualized prevention, intervention, and management strategies tailored to early-onset type 2 diabetes patients to address their heightened risk of nonfatal cardiovascular diseases.
- Early-onset type 2 diabetes patients in China have a significantly higher age-standardized prevalence of nonfatal cardiovascular disease compared to late-onset type 2 diabetes patients.
- Early-onset type 2 diabetes patients tend to exhibit risk factors such as male gender, higher family history of diabetes, and unhealthy lifestyle behaviors (smoking, alcohol consumption, irregular physical activity), which contribute to their increased risk of nonfatal cardiovascular diseases.
- Early-onset type 2 diabetes with metabolic syndrome have an increased nonfatal cardiovascular disease risk compared to late-onset type 2 diabetes patients.
RESEARCH LETTERS
The potential blunting effect of metformin and/or statin therapy on physical activity-induced associations with HbA1c in type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 14 November 2023
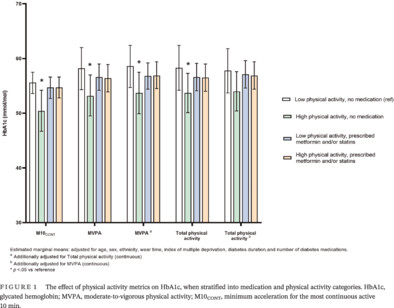
Highlights
- Our analysis indicates a potential blunting effect of metformin and/or statin therapy on physical activity-induced associations with HbA1c.
- The benefit of daily physical activity on glycemic control in people with type 2 diabetes is potentially more apparent in those prescribed neither metformin nor statin therapy.
- As physical activity is rarely prescribed in isolation of other background medications used to manage type 2 diabetes, the results of this analysis may help to maximize interventions delivered through routine clinical care, while allowing for personalization in prescribed physical activity and pharmacotherapy.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Association of remnant cholesterol and newly diagnosed early-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus in Chinese population: A retrospective cross-sectional study
- First Published: 14 November 2023
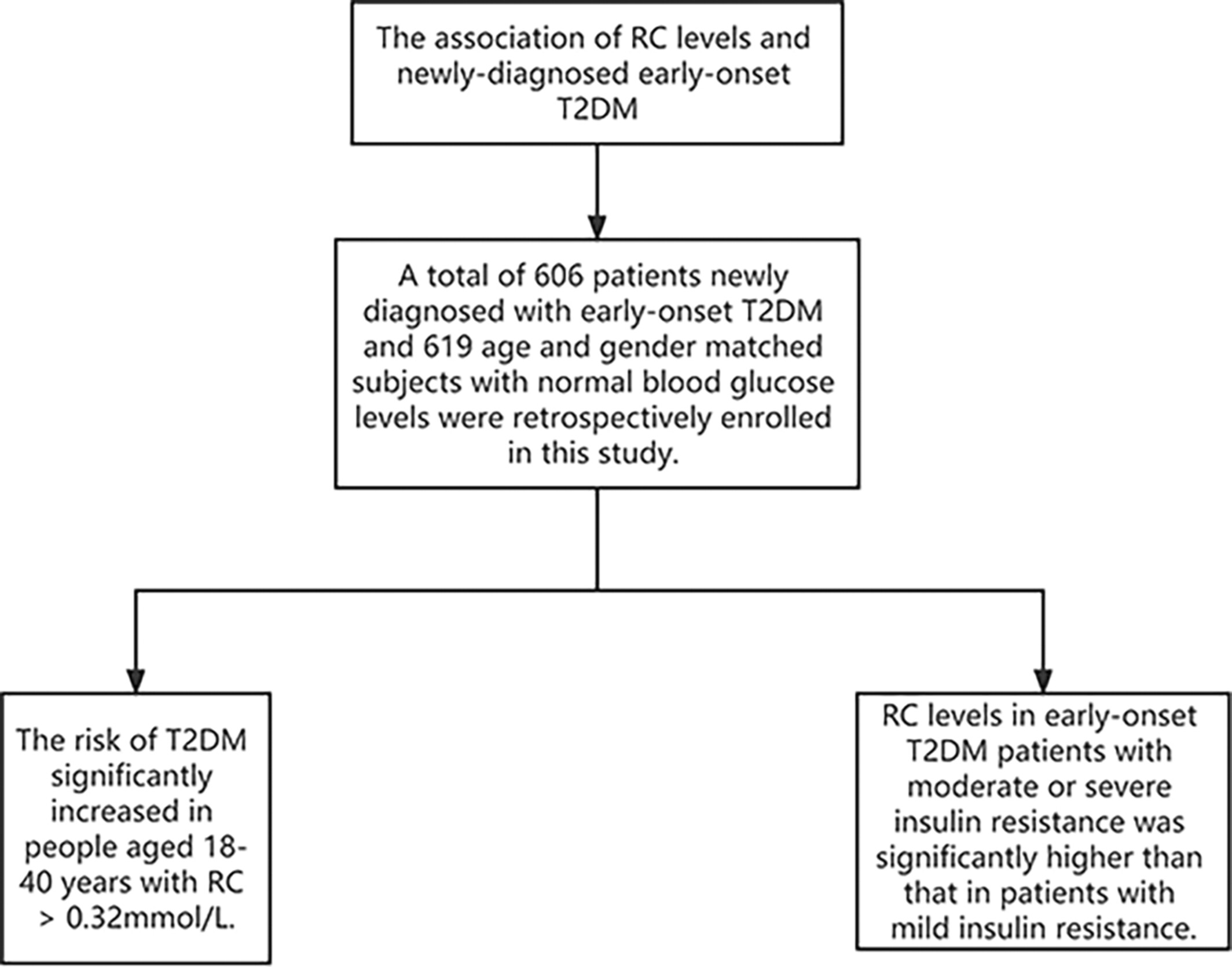
Highlights
- This study was the first to explore the association between remnant cholesterol (RC) levels and newly diagnosed early-onset type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM).
- We found that the risk of T2DM was increased when people aged 18–40 years had RC >0.32 mmol/L.
- RC level was correlated to the degree of insulin resistance.
Effect of MAFLD on albuminuria and the interaction between MAFLD and diabetes on albuminuria
- First Published: 16 November 2023
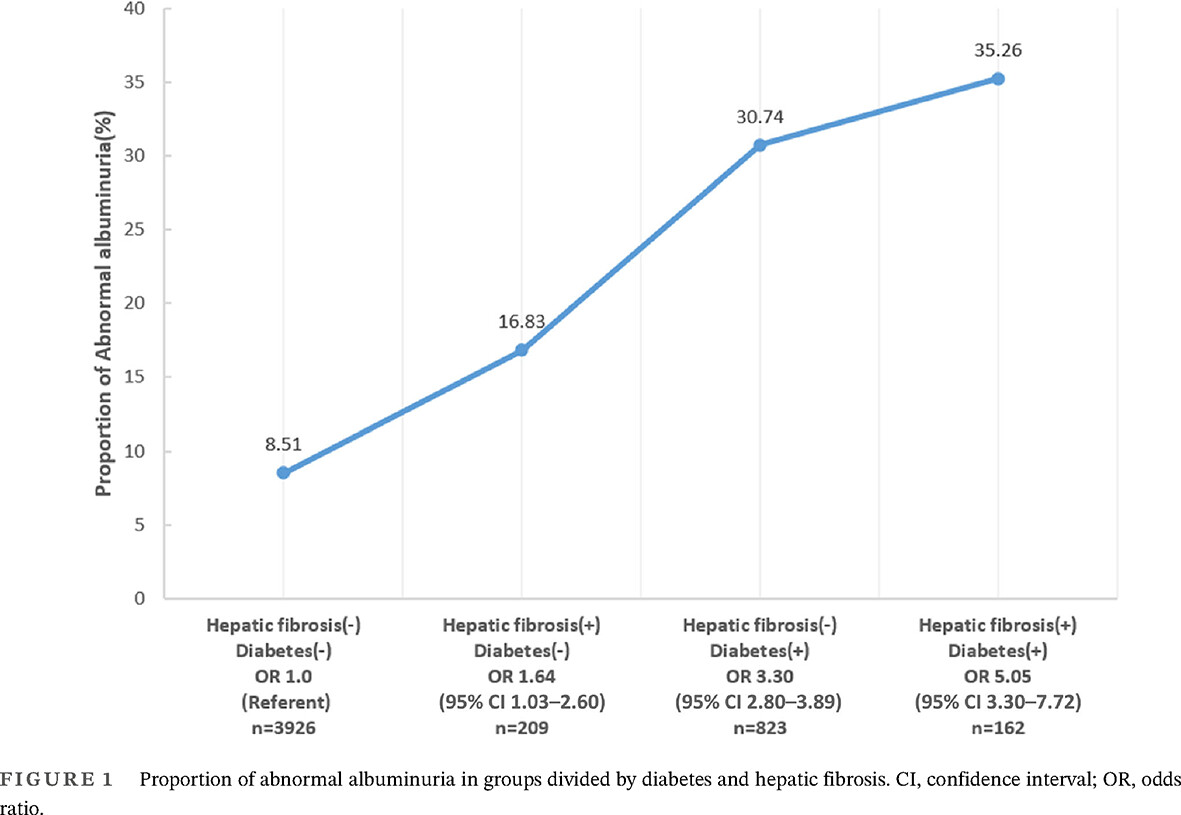
Highlights
- Data of 5119 participants from the American 2017–2018 National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey were analyzed.
- In our study, hepatic steatosis was measured by ultrasound transient elastography and hepatic fibrosis was detected by FibroScan.
- It was revealed that metabolic associated fatty liver disease (MAFLD) with hepatic fibrosis is an independent risk factor for abnormal albuminuria, whereas MAFLD without hepatic fibrosis is not associated with abnormal albuminuria.
- MAFLD with or without hepatic fibrosis was not associated with CKD.
- There were neither additive interaction nor multiplicative interaction between hepatic fibrosis and diabetes on the prevalence of abnormal albuminuria.
Long noncoding RNAs as potential diagnostic biomarkers for diabetes mellitus and complications: A systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 23 December 2023
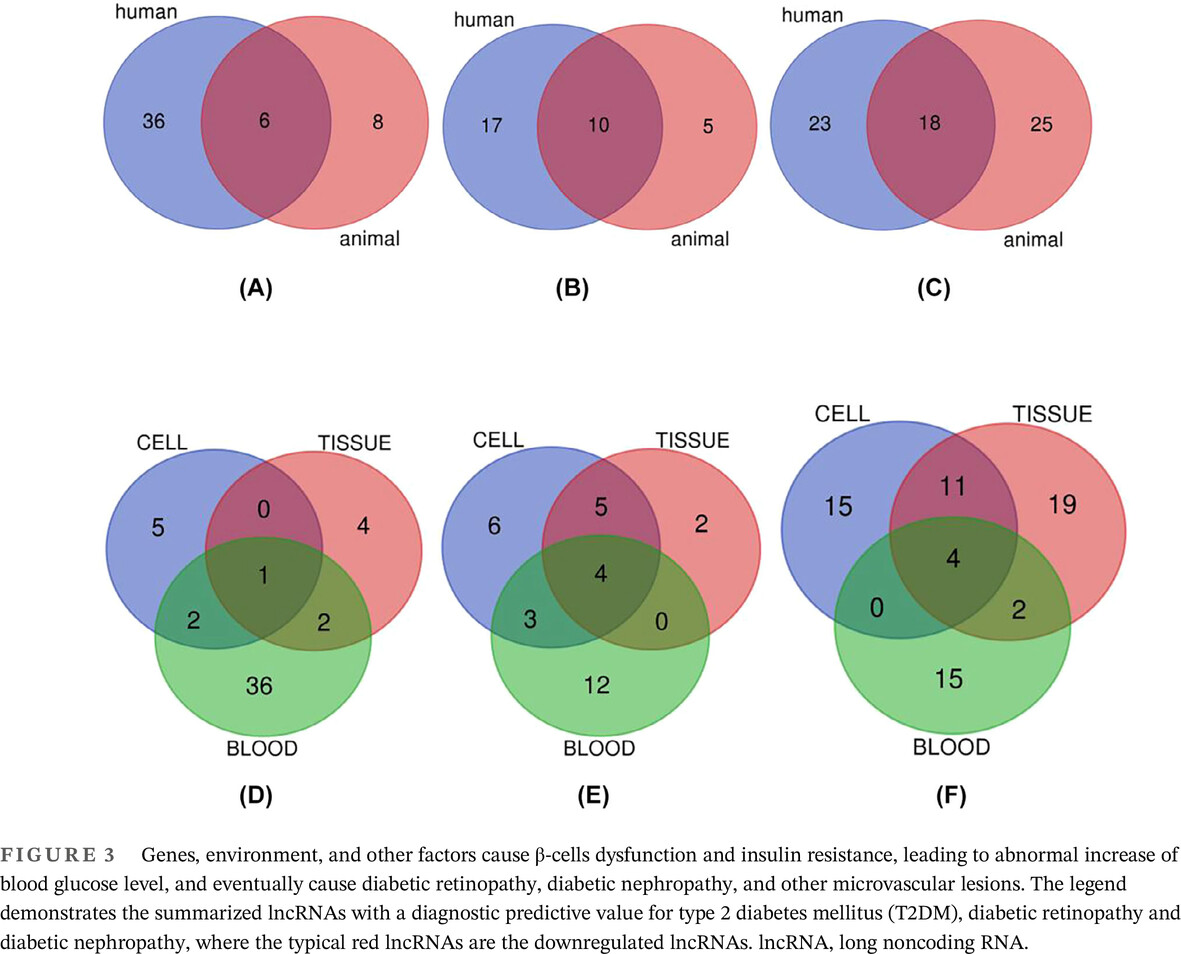
Highlights
- Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) may be associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and related complications.
- We performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of related published literature.
- LncRNAs had T2DM diagnostic area under the curve of 0.84, sensitivity of 0.79, and specificity of 0.75.
- These values for diagnosing prediabetes were 0.65%, 82%, and 65%, respectively.
- Thus, lncRNAs may be promising diagnostic markers for T2DM and related complications.
Factors associated with diabetic foot ulcers and lower limb amputations in type 1 and type 2 diabetes supported by real-world data from the German/Austrian DPV registry
- First Published: 25 February 2024
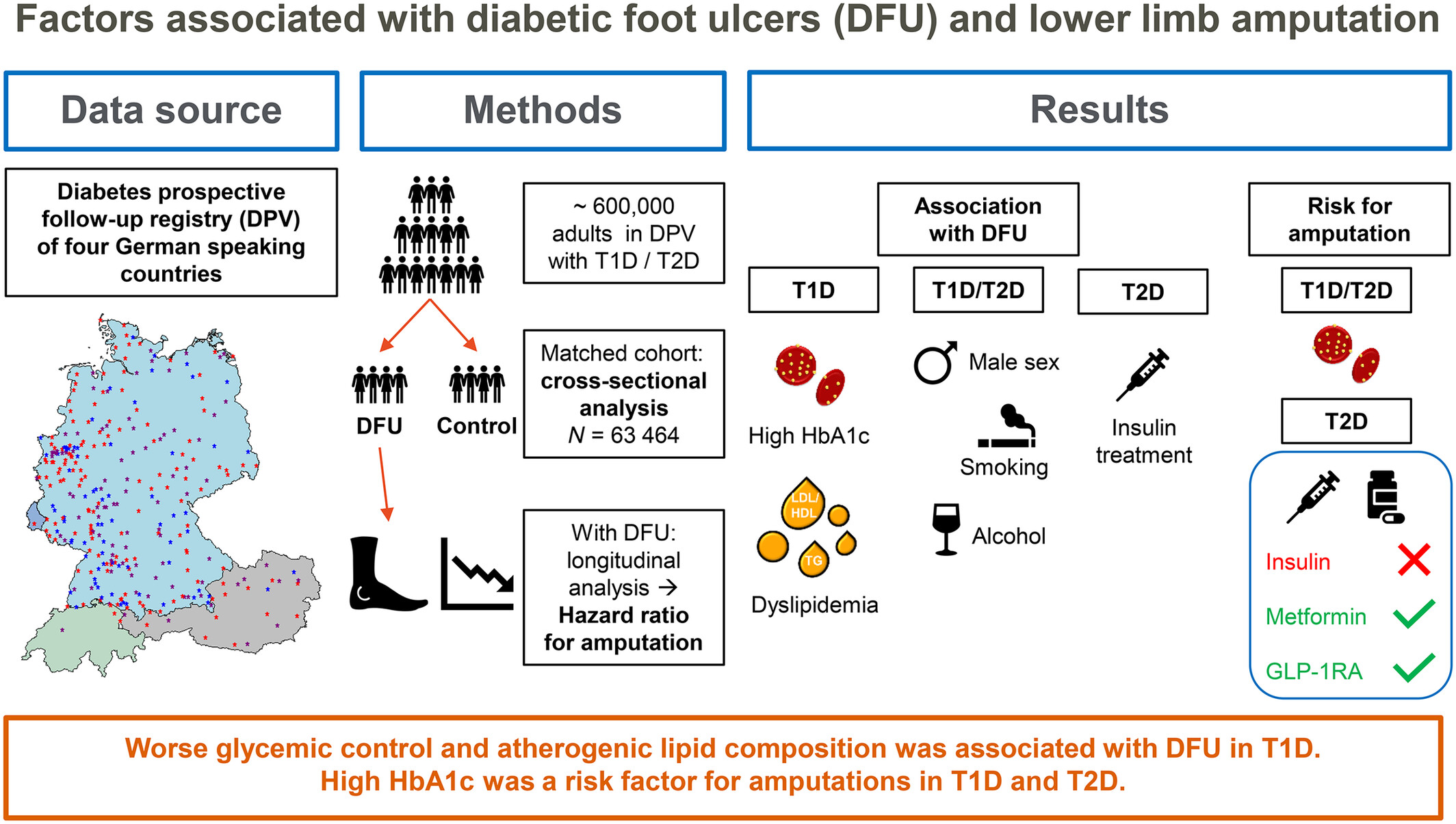
Highlights
- Poor glycemic control and high lipid levels were associated more closely with diabetic foot ulcers in type 1 compared to type 2 diabetes.
- Gender differences regarding the association of diabetic foot ulcers with metabolic outcomes were more pronounced in type 1 diabetes.
- Smoking and alcohol consumption might be important in developing foot ulcers but play a minor role in prevention of amputations.
- The role of oral hypoglycemic medication in development of diabetic foot ulcers should be further analyzed in type 2 diabetes.









