Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Measurement of renal function: Should cystatin C be more widely used for people with diabetes?
- First Published: 28 January 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
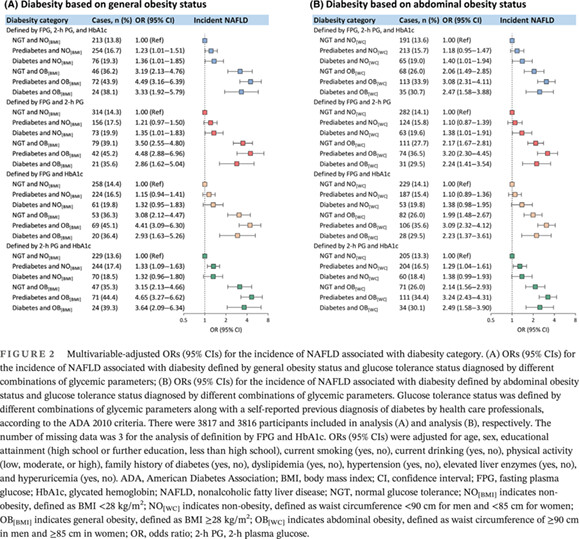
Diabesity phenotype in relation to the incidence and resolution of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: A prospective cohort study
- First Published: 16 August 2023
Highlights
- Obesity determines the association pattern of diabesity with the incidence of NAFLD.
- The combined phenotype of glucose intolerance and obesity drives diabesity-related likelihoods of NAFLD resolution.
- Our findings suggest that diabesity should be incorporated into NAFLD management programs to prioritize risk stratifications and guide personalized strategies for the prevention and control of NAFLD.
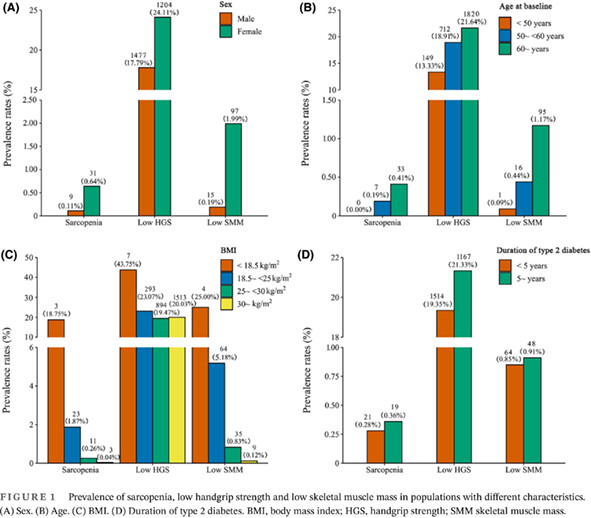
Associations between handgrip strength and skeletal muscle mass with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality in people with type 2 diabetes: A prospective cohort study of the UK Biobank
- First Published: 22 August 2023
Highlights
- The prevalence of low handgrip strength and skeletal muscle mass was higher in women and in patients with long-duration diabetes and increased with increasing age and decreasing body mass index.
- All-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality risk showed a linear decreasing trend with increasing handgrip strength, whereas skeletal muscle mass showed a U-shaped nonlinear relationship with all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality risk.
- Low handgrip strength was a better predictor of all-cause mortality and cardiovascular mortality risk than low skeletal muscle mass.
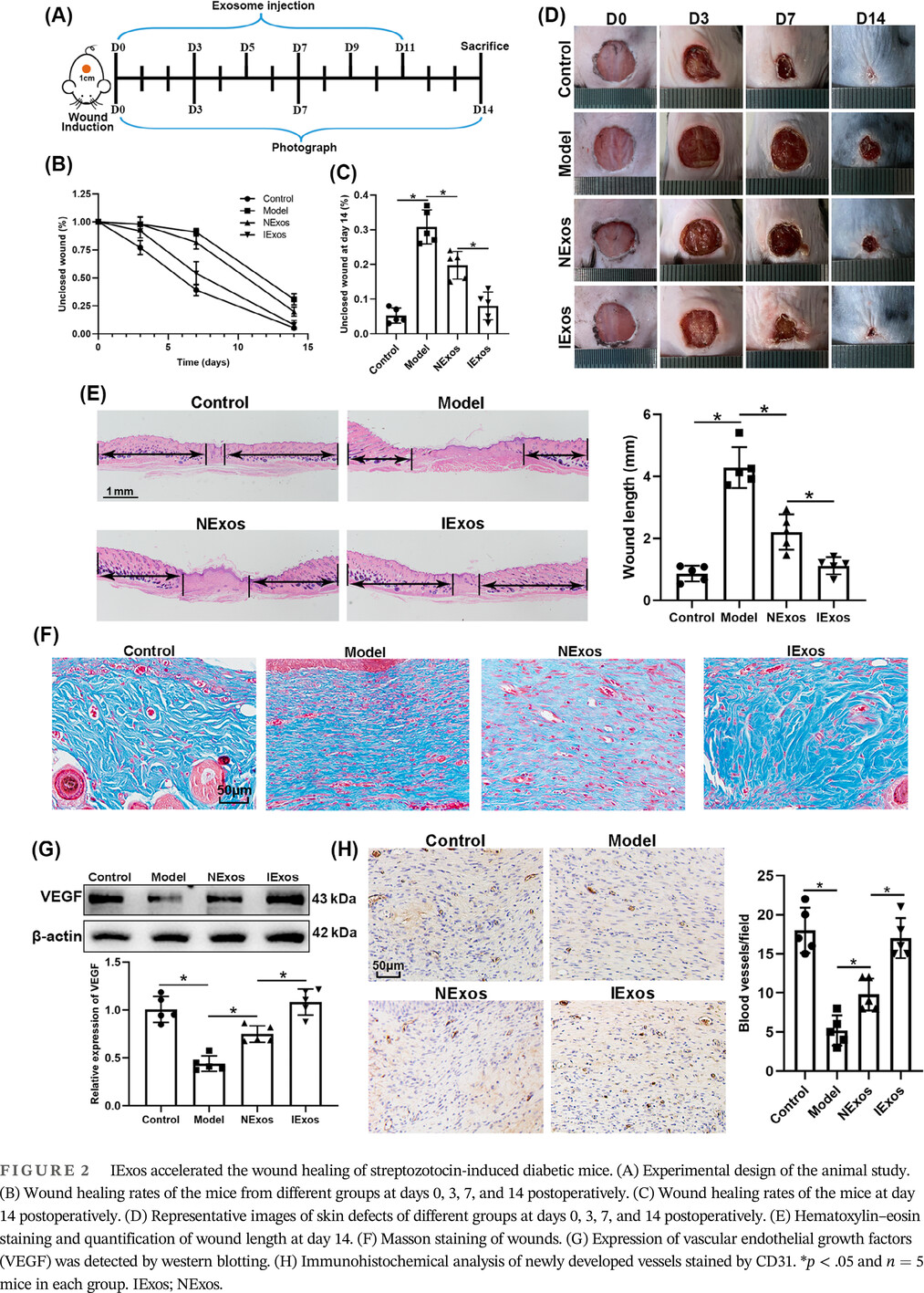
IFN-γ enhances the therapeutic efficacy of MSCs-derived exosome via miR-126-3p in diabetic wound healing by targeting SPRED1
- First Published: 30 August 2023
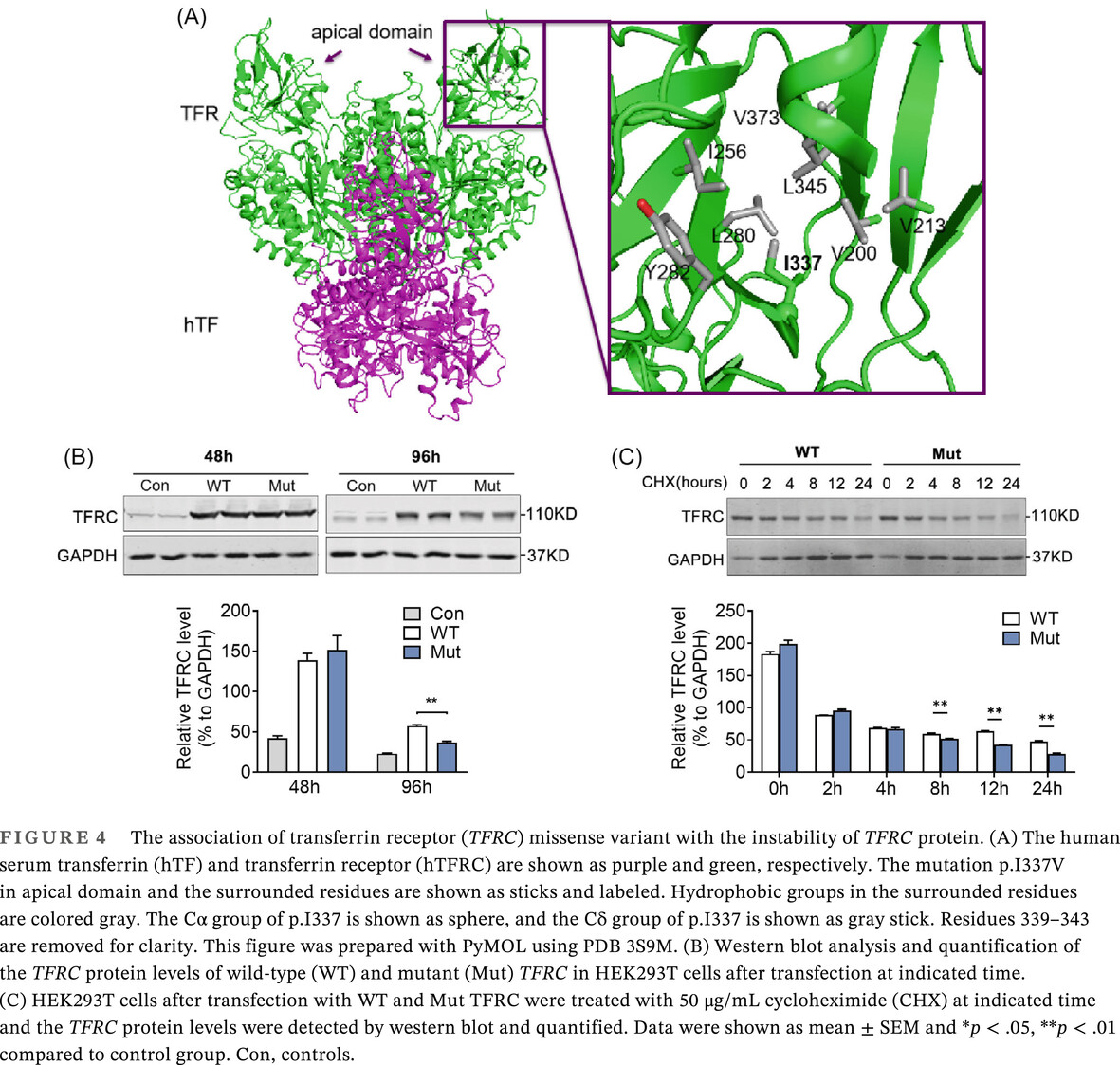
Transferrin receptor levels and its rare variant are associated with human obesity
- First Published: 30 August 2023
Highlights
- Evidence for contribution of transferrin receptor (Tfrc) and its variants for human thermogenic fat is limited. TFRC levels is elevated in activated human thermogenic fat from pheochromocytoma patients and downregulated in fat from overweight patients compared to their control subjects, respectively.
- Whole-exome sequencing of obese and matched control subjects suggests that a rare heterozygous missense variant p.I337V in TFRC shows a tendency to enrich in young, severely obese subjects.
- Structural and functional studies reveal impaired protein stability of the TFRC variant p.I337V compared to wild-type.
The effects of economic status on metabolic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus at 10 metabolic management centers in China
- First Published: 05 September 2023
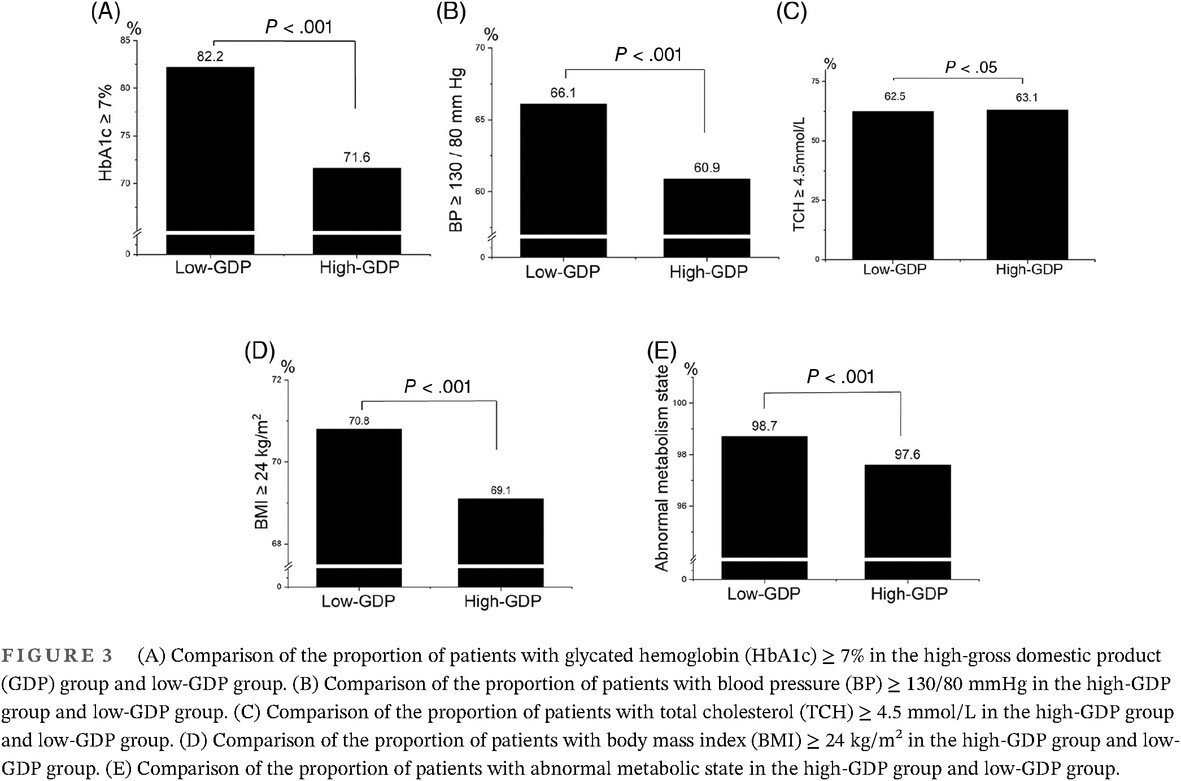
Highlights
- The risk of developing an abnormal metabolic state in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients with a higher gross domestic product per capita was significantly lower after adjustment for possible confounders.
- A healthy lifestyle had an additive effect on achieving glycemic goals, even in individuals with a better economic status.
Association of visceral fat area or BMI with arterial stiffness in ideal cardiovascular health metrics among T2DM patients
- First Published: 08 September 2023
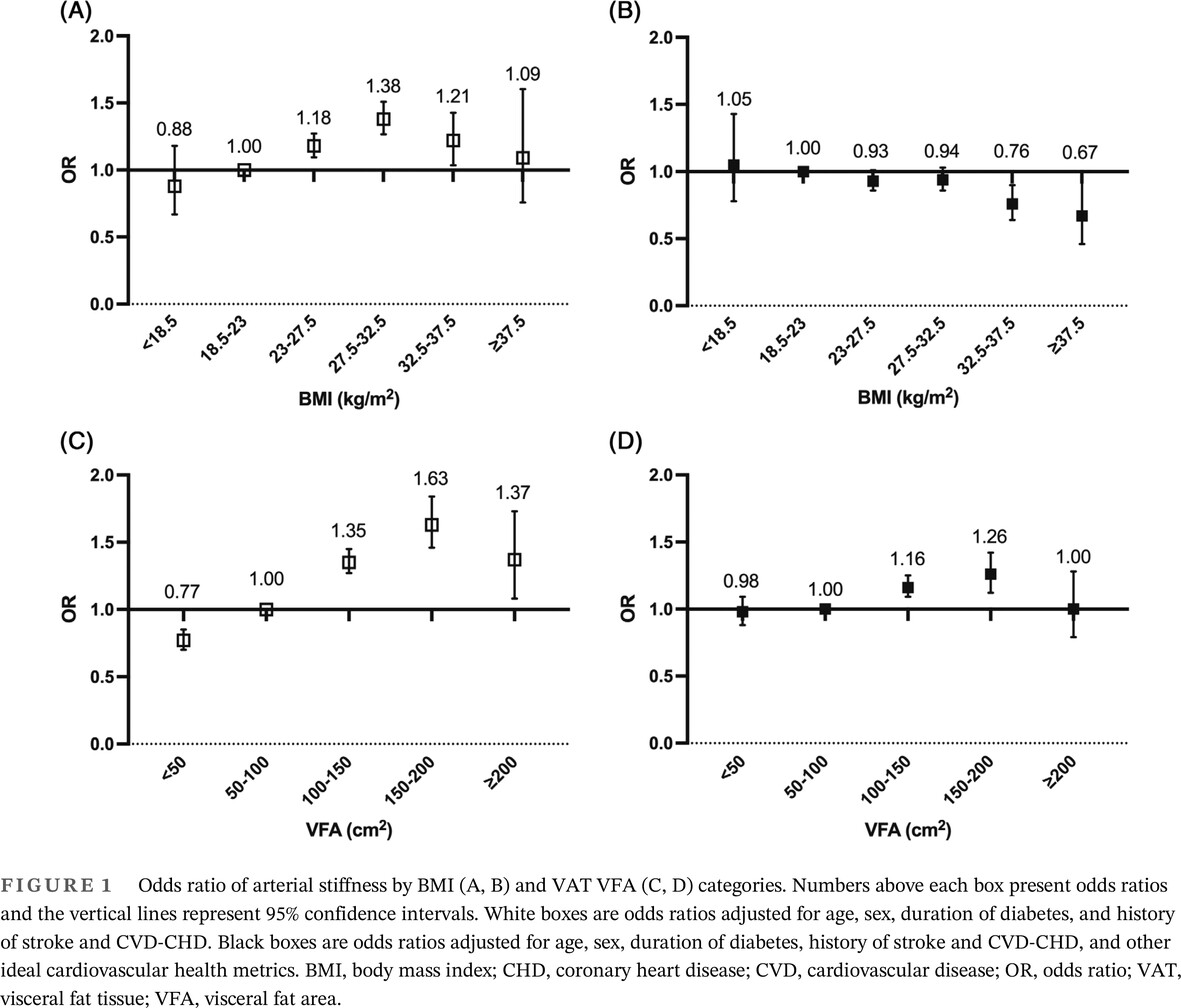
Highlights
- This is a multicenter study to compare the association of visceral fat area (VFA) or body mass index (BMI) with the presence of arterial stiffness combined with other ideal cardiovascular health metrics (ICVHMs).
- VAT VFA appears to be more relevant to cardiovascular risk and be more optimal than BMI for obesity assessment in the ICVHMs in Chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients.
GSK-3β activation mediates apolipoprotein E4-associated cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A multicenter, cross-sectional study
- First Published: 12 September 2023
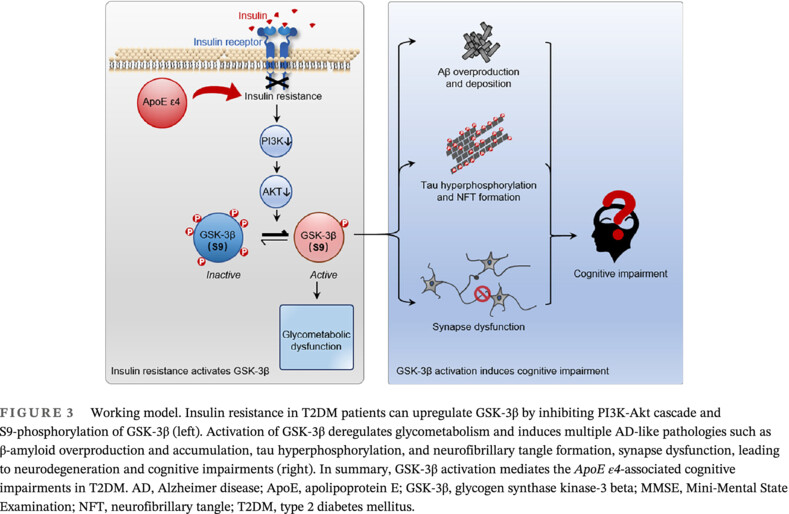
Highlights
- The association of ApoE polymorphism with cognitive impairment in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) was inconclusive. Moreover, it is not reported whether and how glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β), a crucial kinase in insulin resistance and Alzheimer disease-like pathologies, play a role in linking ApoE ε4 and cognitive impairment.
- We revealed that ApoE ε4, but not ApoE ε2, was a risk factor of cognitive impairment in Chinese Han population. GSK-3β activation acts as a mediator between ApoE ε4 and cognitive impairment.
- These data reveal a novel role ApoE ε4 and GSK-3β in T2DM-associated cognitive deficits. Targeting GSK-3β, such as inhibitor, could be a constructive strategy in preserving the cognitive function in T2DM patients but need further proof.
Exercise ameliorating myocardial injury in type 2 diabetic rats by inhibiting excessive mitochondrial fission involving increased irisin expression and AMP-activated protein kinase phosphorylation
- First Published: 18 September 2023
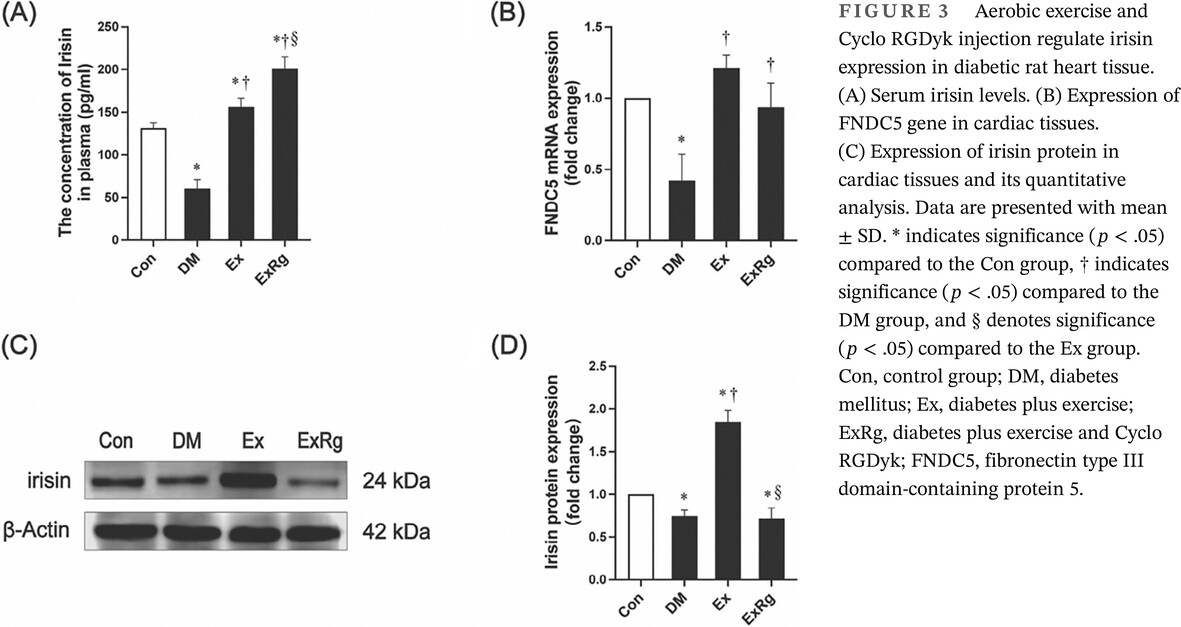
Highlights
- Exercise reduced cardiac fibrosis and injuries, and improved over-mitochondrial fission in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) rat hearts.
- Exercise increased serum irisin levels and cardiac irisin expression in T2DM rats; blocking irisin signaling by agent-cyclo RGDyk diminished the protective effects of exercise on T2DM rat hearts.
- The ameliorative effect of exercise on myocardial injury in T2DM may be achieved through the regulation of the AMP-activated protein kinase-Drp1 signal by the myokine irisin to improve mitochondrial overfission.
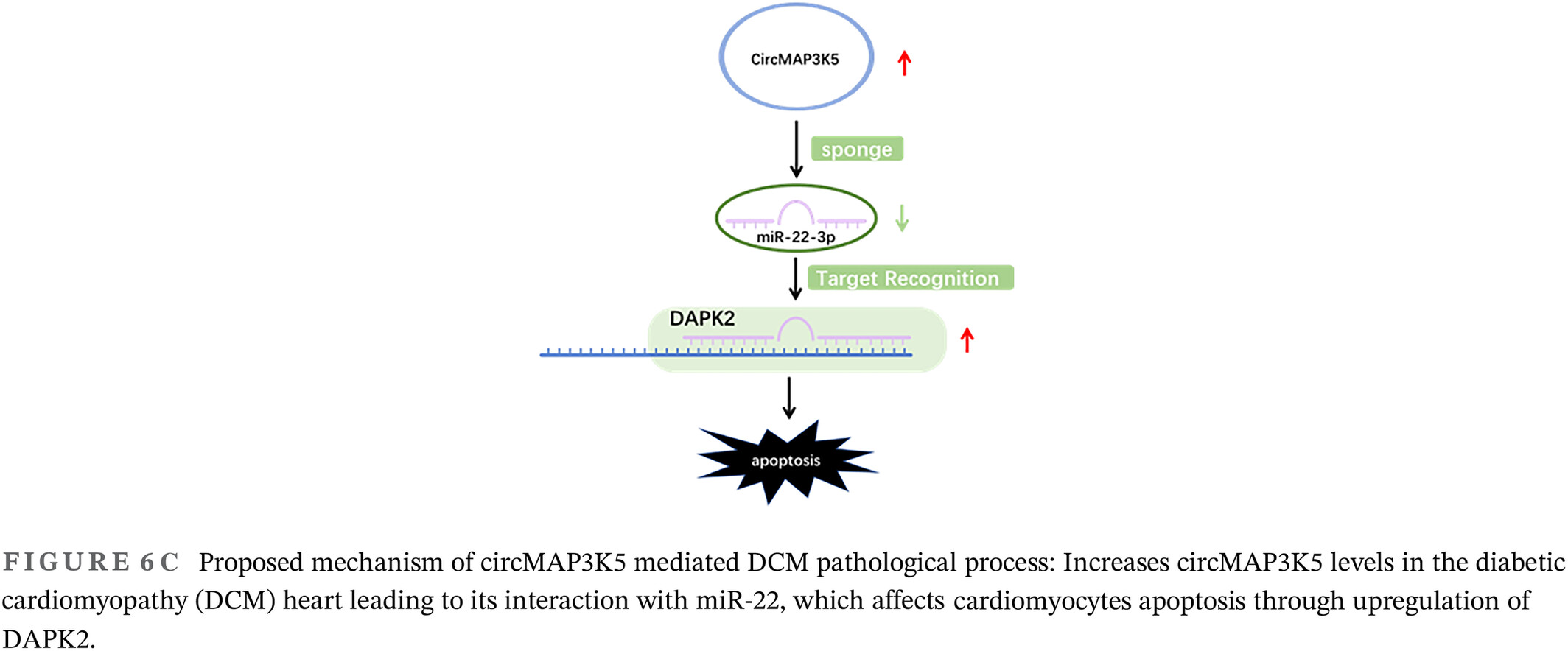
CircMAP3K5 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy by regulating miR-22-3p/DAPK2 Axis
- First Published: 21 September 2023
Highlights
- Novel mediated cardiomyocyte apoptosis in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM) mediated by a new regulator, circRNA mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase 5 (circMAP3K5).
- New signaling pathways mediating cardiomyocyte apoptosis in DCM.
- CircMAP3K5 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis through the miR-22-3p-DAPK2 axis in DCM.
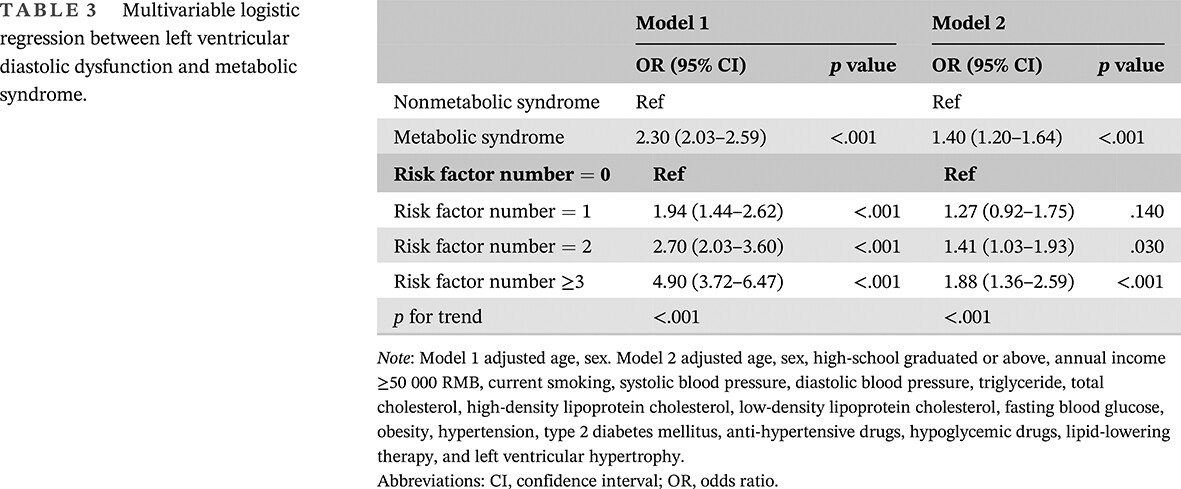
Positive additive interaction effects of age, sex, obesity, and metabolic syndrome on left ventricular dysfunction
- First Published: 24 September 2023
Highlights
- Left ventricular dysfunction such as left ventricular diastolic dysfunction (LVDD) and impaired global longitudinal strain (GLS) were important causes of cardiac events in cardiovascular high-risk population.
- Metabolic disorders play a key role in the progression of left ventricular dysfunction, therefore, the prevention of metabolic syndrome (MetS) in women, elderly, and obese individuals might reduce the burden of LVDD and left ventricular systolic dysfunction.
- The study first analyzed LVDD and GLS by echocardiography in a large community population, providing new insights for community target organ damage screening in MetS.
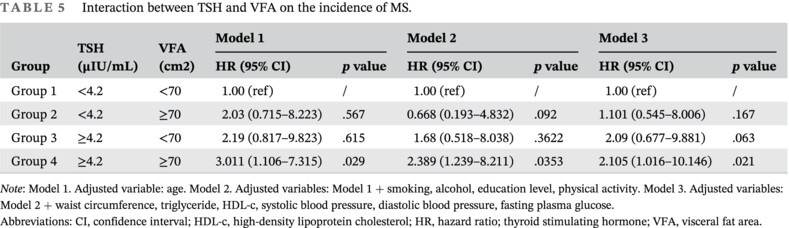
Accumulative prediction values of serum thyroid stimulating hormone and visceral adipose tissue for metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women: A 10-year follow-up study of Chinese population
- First Published: 25 September 2023
Highlights
- Elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and visceral fat area (VFA) were critical factors for the prevalence of MS during postmenopause independently
- The concomitant elevated VFA and serum TSH levels were indeed a menopause-related phenomenon that interacted with each other and appeared to co-contribute to the increased risk of MS during the postmenopausal period
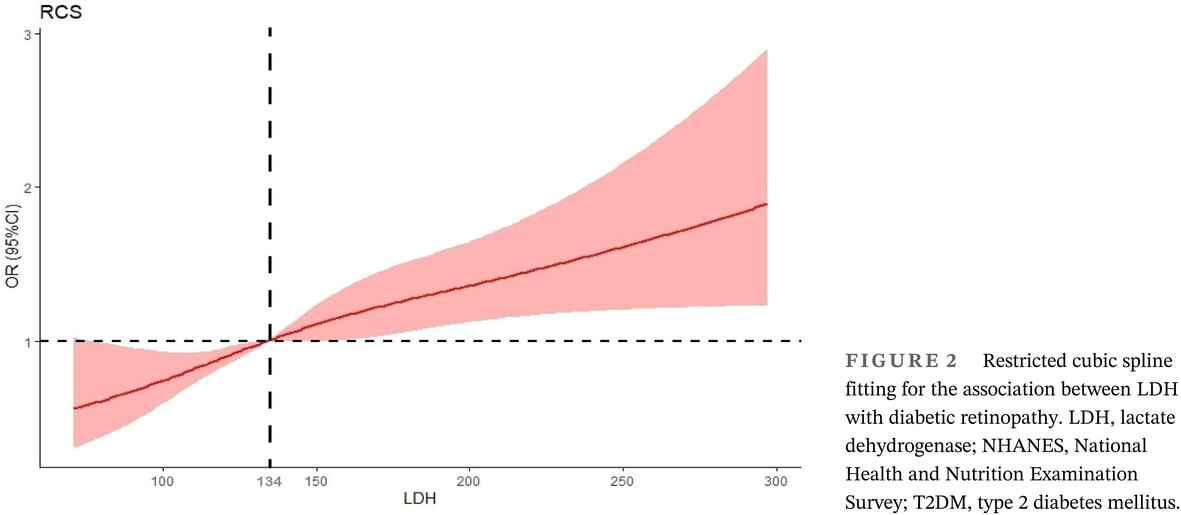
Association of lactate dehydrogenase and diabetic retinopathy in US adults with diabetes mellitus
- First Published: 25 September 2023
Highlights
- There are limited studies to reveal the association between lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) and diabetic retinopathy (DR). Our findings were the initial ones to demonstrate a positive correlation between the rise in LDH levels and the prevalence of DR. Our study revealed that diabetic individuals exhibiting LDH levels > 134 U/L were found to have a statistically significant elevation in their probability of developing DR. After adjusting for other confounding factors, there was a relationship observed between LDH and the incidence of DR. Furthermore, our research indicates that individuals diagnosed with diabetes and coronary heart disease exhibit heightened susceptibility to DR.
Ten-year clinical characteristics of patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes: A single-center experience in China
- First Published: 26 September 2023
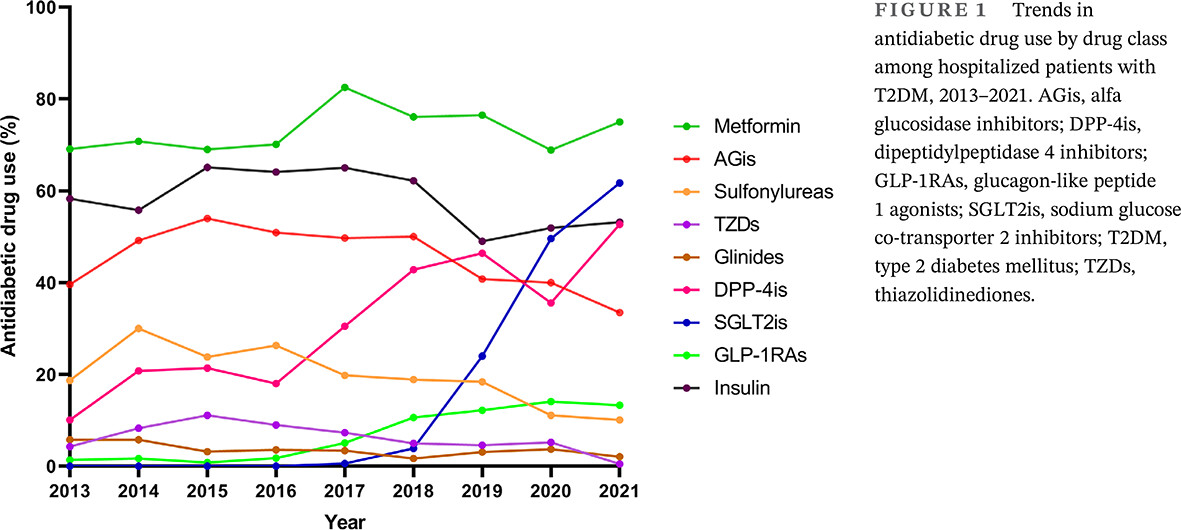
Highlights
- Early-onset type 2 diabetes refers to diabetes diagnosed before 40 years of age.
- Early-onset type 2 diabetes patients had worse glycemic control, higher weight and lipid levels, and higher risks of diabetic nephropathy.
- Patients with early-onset type 2 diabetes were more likely to use organ-protective drugs.