Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
The association between sodium glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitors vs dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and renal outcomes in people discharged from hospital with type 2 diabetes: A population-based cohort study
- First Published: 10 April 2024
Highlights
- What are the new findings?
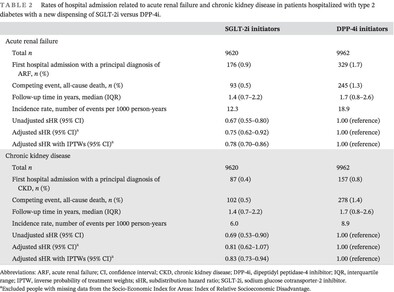
This was the first Australian study using real-world data to show SGLT-2is reduce ARF and CKD compared to DPP-4is in people with type 2 diabetes. The rates of hospital admissions for ARF and CKD in people with type 2 diabetes were 22% and 17% lower, respectively, among SGLT-2i initiators compared to DPP-4i initiators.
- How might this have an impact on clinical practice in the foreseeable future?
Antenatal oral glucose tolerance test abnormalities in the prediction of future risk of postpartum diabetes in women with gestational diabetes: Results from the LIVING study
- First Published: 06 May 2024
Highlights
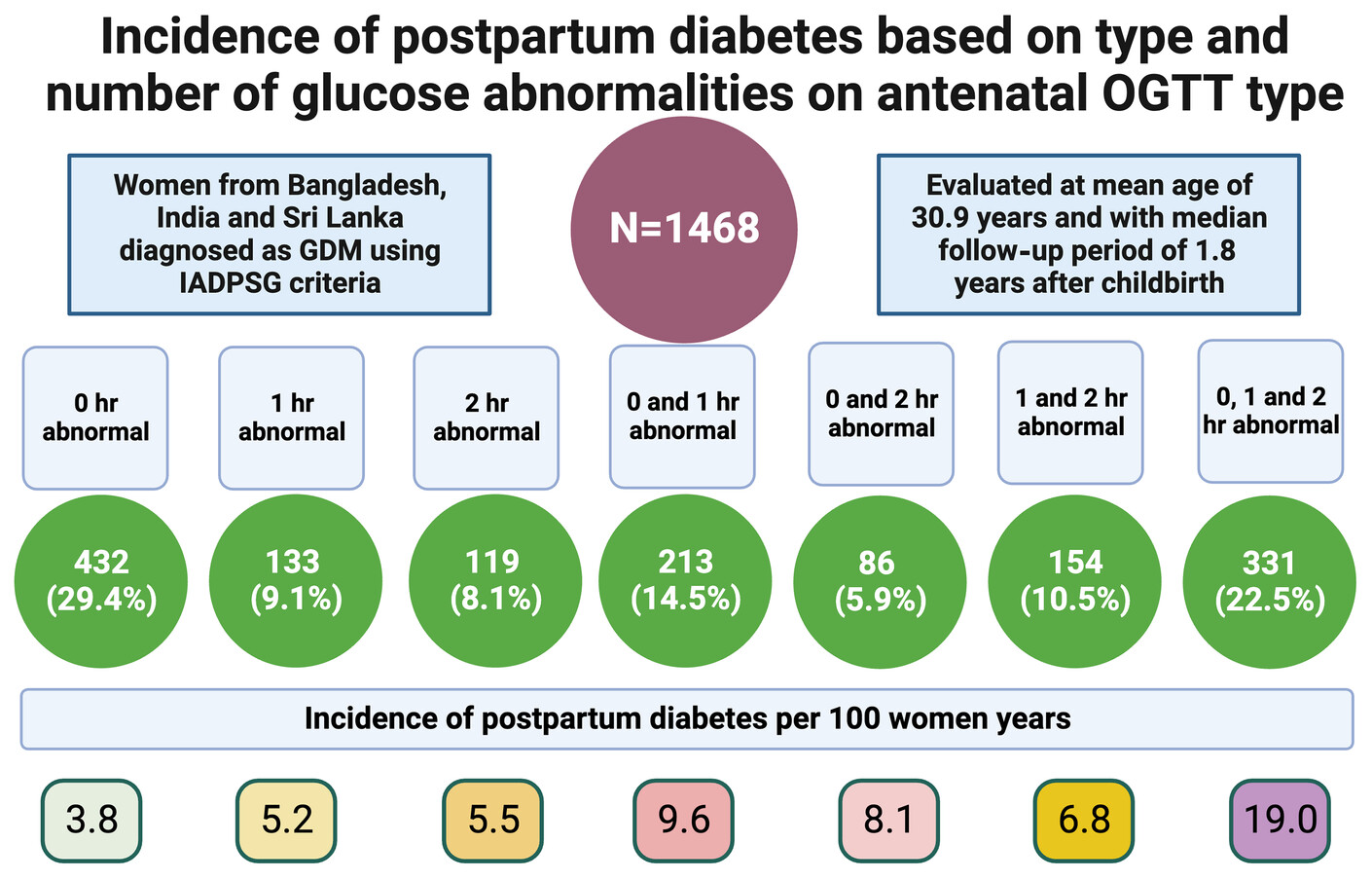
- Of the 1468 South Asian women with gestational diabetes, 213 (14.5%) women developed diabetes over median follow-up 1.8 years after childbirth, an incidence rate of 8.7/100 women-years.
- The incidence rates for participants with any one, two, and three abnormal values on antenatal oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) were 4.3, 8.3 and 19.0/100 women years.
- The rates of future diabetes in this high-risk cohort varied considerably with antenatal OGTT values, providing the opportunity for targeted intervention to prevent future diabetes.
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists and kidney outcomes
- First Published: 04 October 2024
Highlights
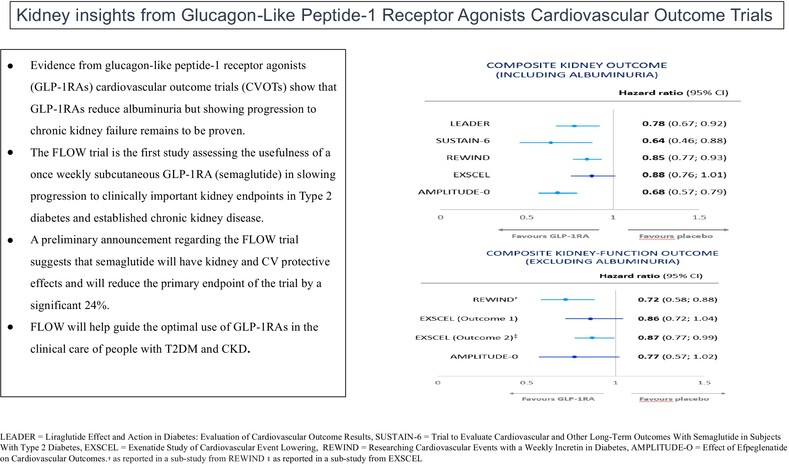
- Evidence from GLP-1RAs CVOTs show that GLP-1RAs reduce albuminuria but slowing of progression to chronic kidney failure remains to be proven.
- The FLOW trial is the first study assessing the usefulness of a once-weekly subcutaneous GLP-1RA (semaglutide) in slowing progression to clinically important kidney end points and protection form cardiovascular disease people with T2DM and established CKD.
- FLOW will help guide the optimal use of GLP-1RAs in the clinical care of people with T2DM and CKD.
Exploring factors associated with self-rated health in individuals with diabetes and its impact on quality of life: Evidence from the Survey of Health, Ageing, and Retirement in Europe
- First Published: 02 January 2024
Highlights
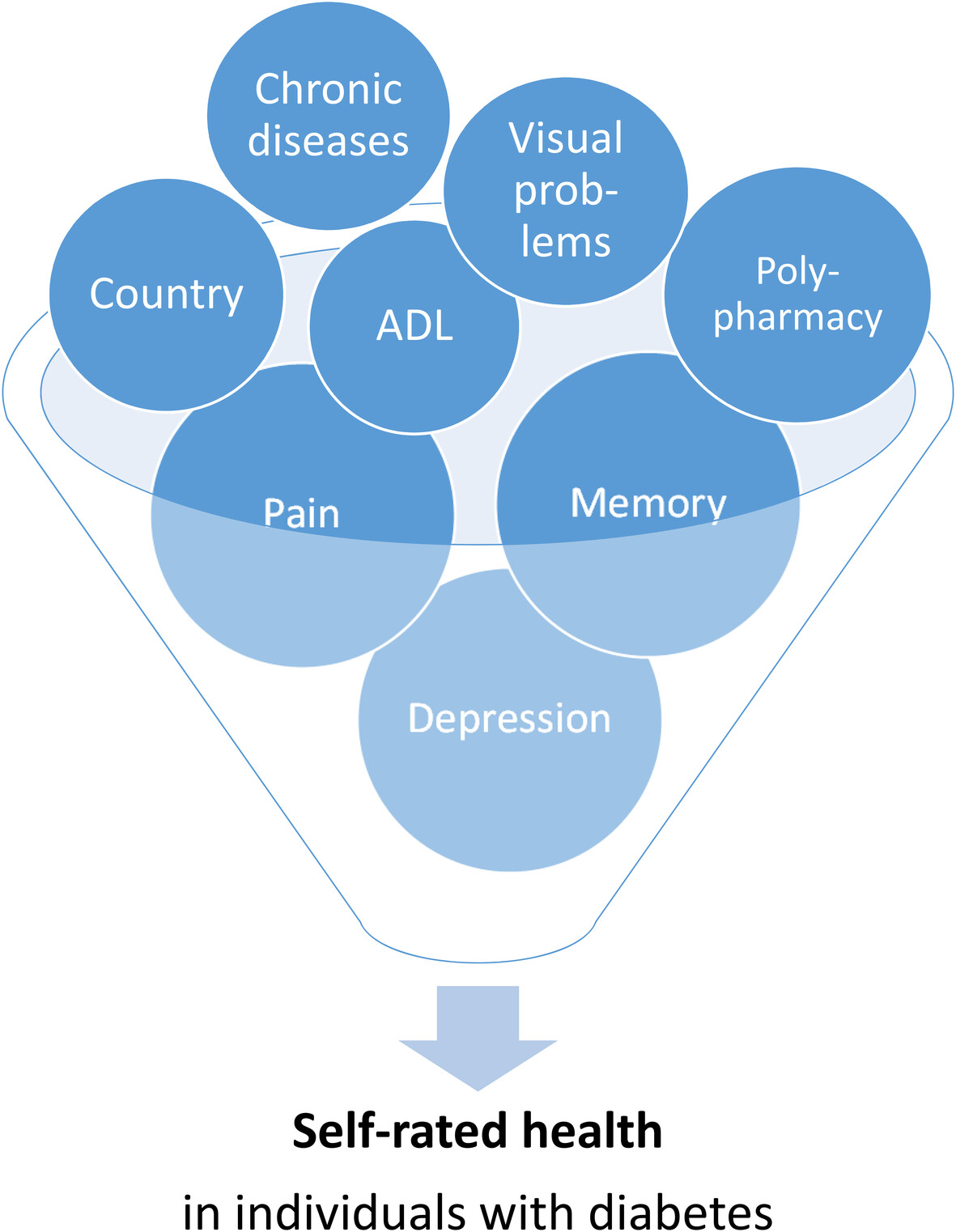
- Individuals with diabetes tend to report their health as less than very good more frequently compared to individuals without diabetes
- We have identified several factors that influence self-rated health in individuals with diabetes. Depression, pain, and memory function emerged as the most influential factors.
- Self-rated health was determined to be an independent predictor of quality of life.
Liraglutide does not increase heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction
- First Published: 03 January 2024
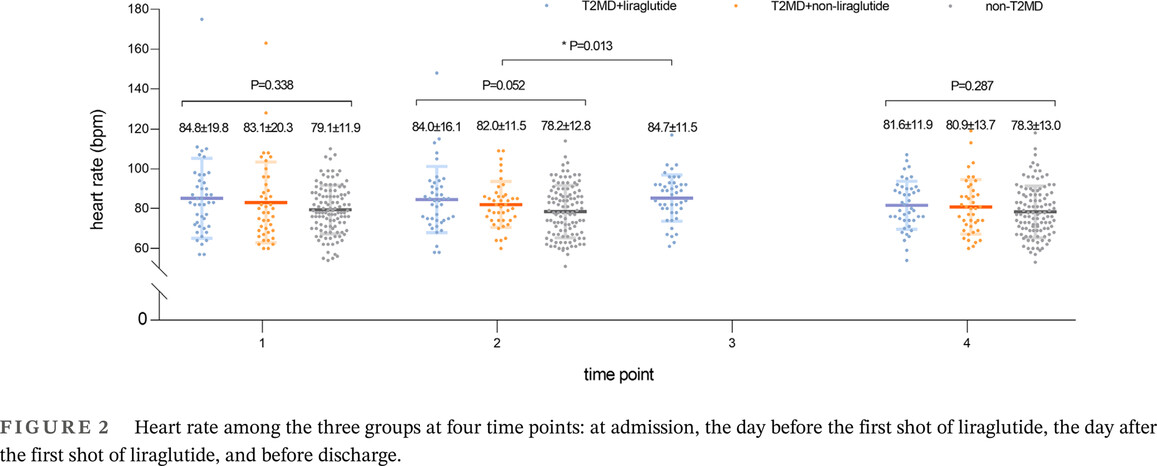
Highlights
- Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists have been shown to reduce all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in patients with Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
- Previous studies have found that liraglutide can increase the heart rate in patients, so the use of liraglutide should be controlled in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
- We found that liraglutide did not increase the heart rate of diabetic patients during acute myocardial infarction and it had no effect on blood pressure.
- Therefore, liraglutide is safe for use in the early stages of acute myocardial infarction.
Mitochondria-associated membranes contribution to exercise-mediated alleviation of hepatic insulin resistance: Contrasting high-intensity interval training with moderate-intensity continuous training in a high-fat diet mouse model
- First Published: 10 April 2024
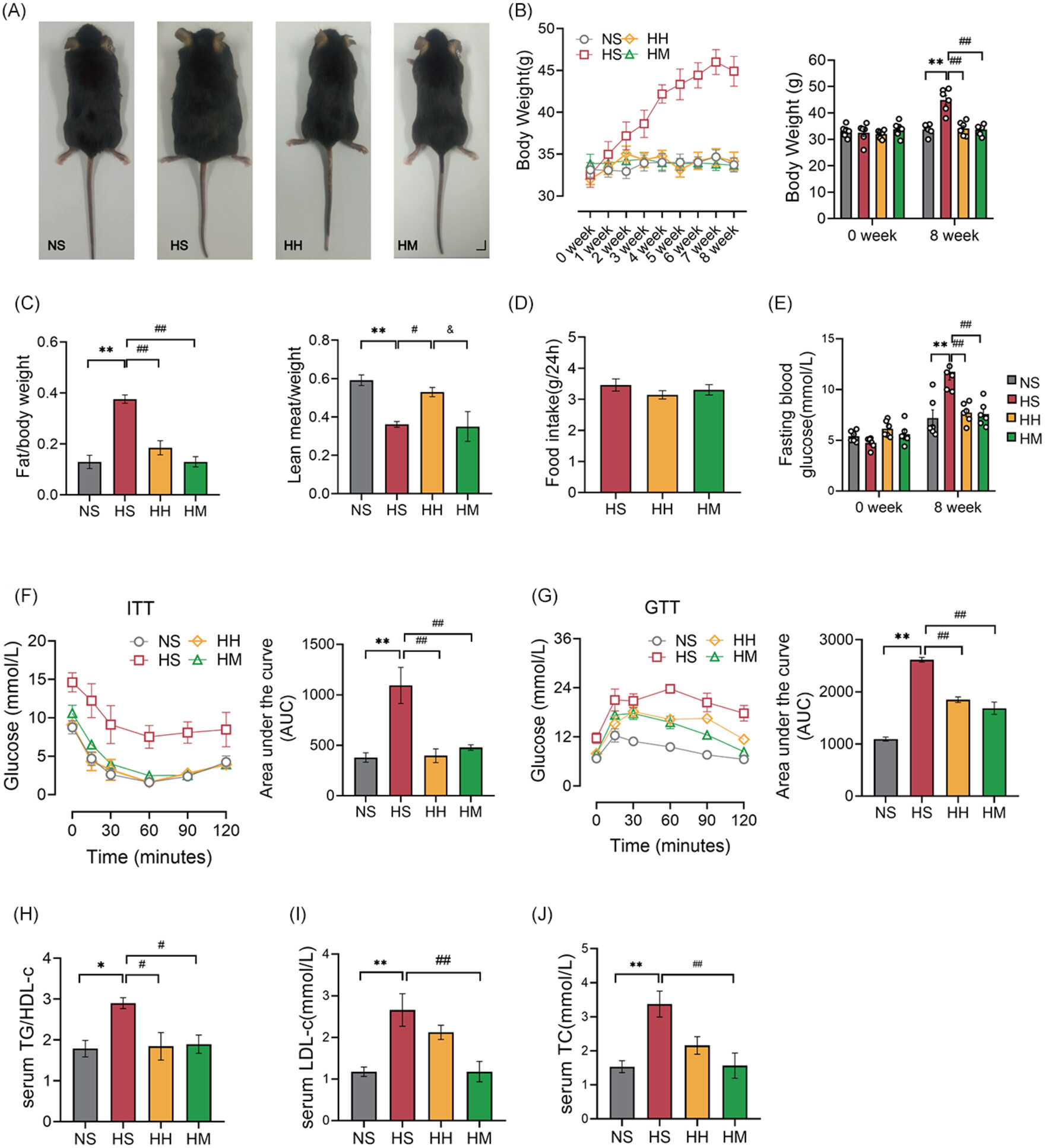
Highlights
- The reduction of hepatic mitochondria-associated membranes (MAMs) induced by high-fat diet (HFD) is related to the development of hepatic insulin resistance.
- Both high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and moderate-intensity continuous training (MICT) effectively reverse the reduction of hepatic MAMs induced by HFD.
- MICT is more beneficial in increasing the formation of hepatic MAMs in HFD mice compared to HIIT.
Kidney function trajectories, associated factors, and outcomes in multiethnic Asian patients with type 2 diabetes
- First Published: 02 January 2024
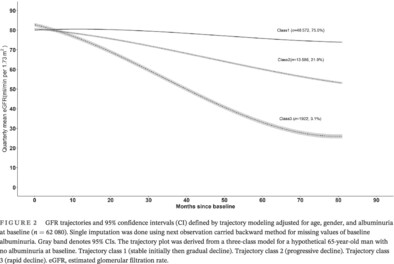
Highlights
- Three estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) trajectories were identified among Asian individuals with type 2 diabetes: stable initially then gradual decline (75%), progressive decline (21.9%), and rapid decline (3.1%)
- Multiple factors were associated with progressive or rapid eGFR decline (eg, women, low socioeconomic status, high hemoglobin A1c, and albuminuria)
- Progressive and rapid eGFR decline were associated with a higher risk of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD)
- Our results highlight the gender and social disparities in renal function decline and also underscore the potential benefit of multifactorial intervention targeting the modifiable risk factors to postpone ESKD.
Association between red cell distribution width/serum albumin ratio and diabetic kidney disease
- First Published: 26 June 2024
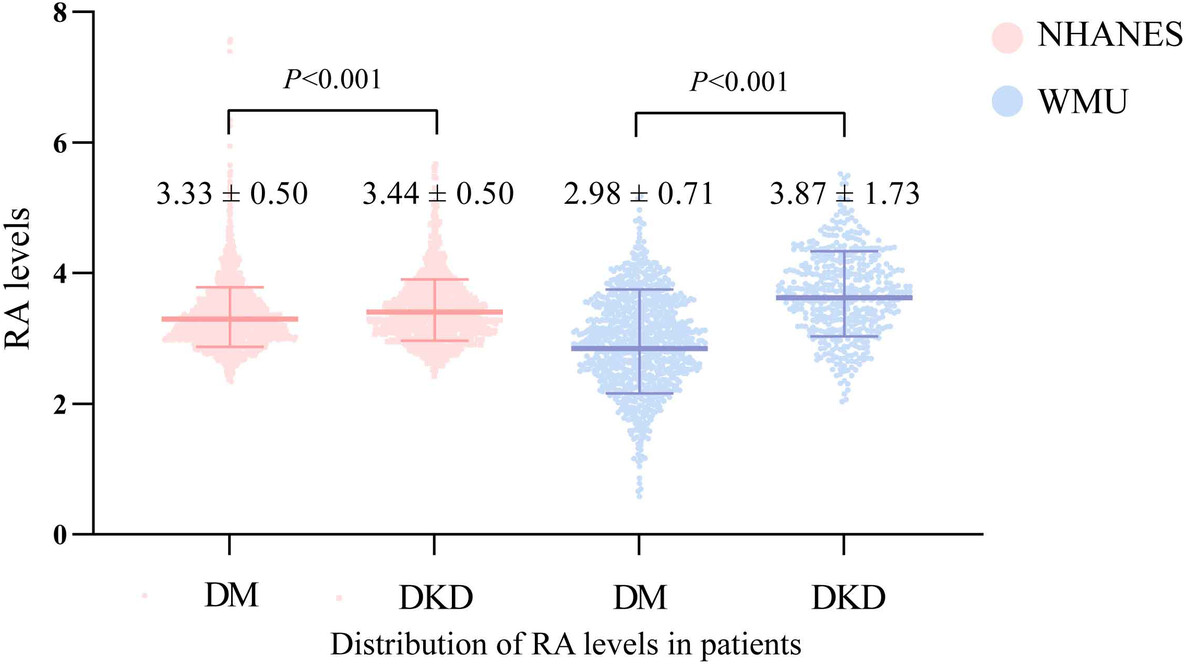
Highlights
- RA levels differ between DM and DKD patients in both the NHANES databases and WMU data.
- After accounting for confounders and using propensity score-matched analysis, both RA levels were found to be independently associated with DKD.
- The RA, a cost-effective and easily accessible biomarker, could be useful for risk stratification of DKD.
Glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists versus dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors and cardiovascular outcomes in diabetes in relation to achieved glycemic control. A Danish nationwide study
- First Published: 16 May 2024
Highlights
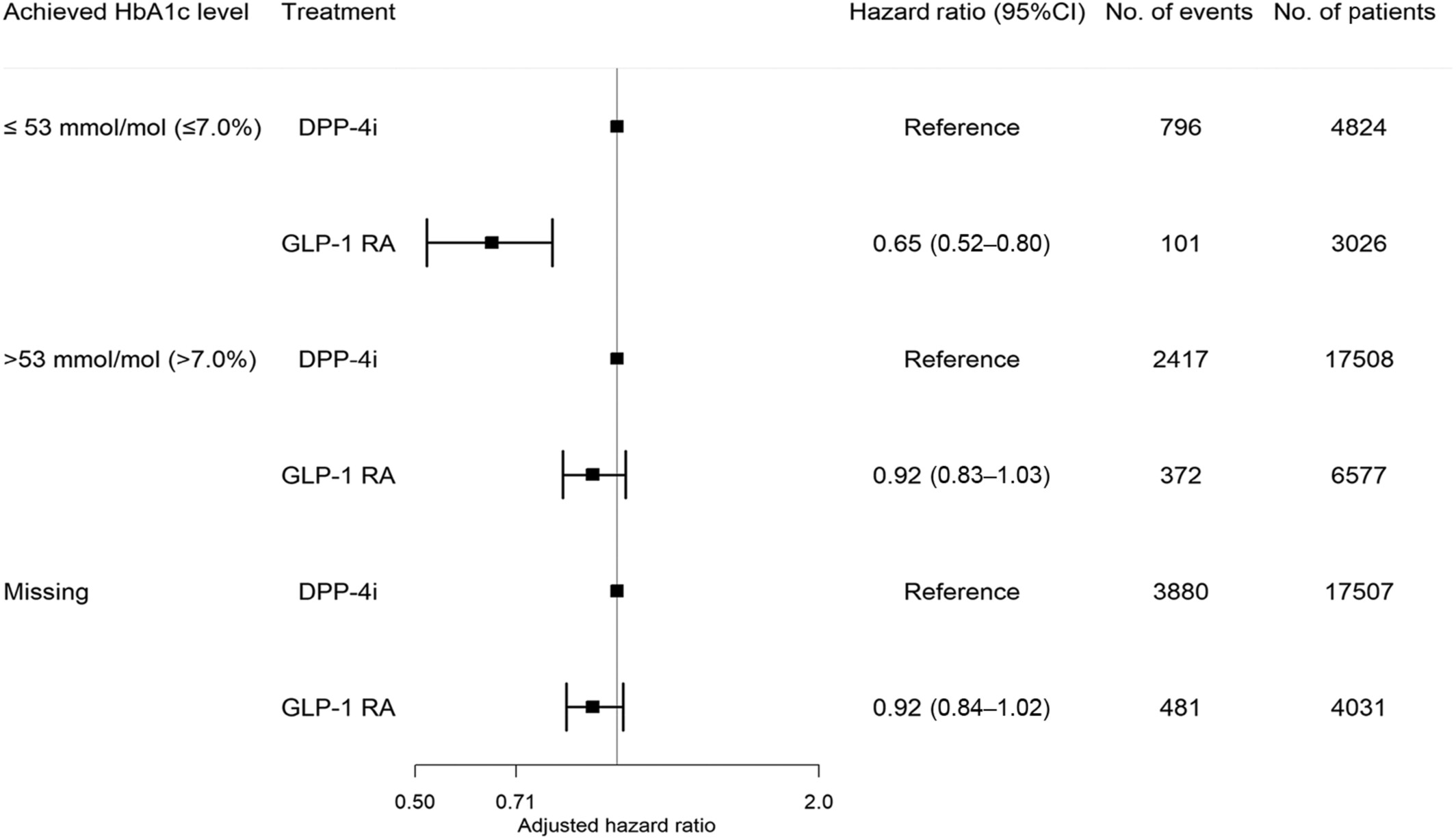
- Question: Does achieving the target glycemic level while on treatment with glucagon-like-peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA) compared to dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors (DPP-4i) reduce the rate of major adverse cardiovascular outcomes (MACE)?
- Findings: The rate of MACE among GLP-1 RA versus DPP-4i users was significantly reduced when achieving lower HbA1c levels: HbA1c ≤ 53 mmol/mol: 0.65 (0.52–0.80); HbA1c > 53 mmol/mol: 0.92 (0.83–1.03); missing HbA1c: 0.92 (0.83–1.03).
- Meaning: GLP-1 RA use was associated with a lower rate of MACE. The association was stronger in patients achieving the target glycemic level and weaker in patients not achieving the target glycemic level, suggestive of an interaction between achieved HbA1c level and GLP-1 RA.
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion versus multiple daily injection therapy in pregnant women with type 1 diabetes
- First Published: 25 April 2024
Highlights
- This study is the first to evaluate the effects of multiple daily injection and continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy among Chinese pregnant women with type 1 diabetes.
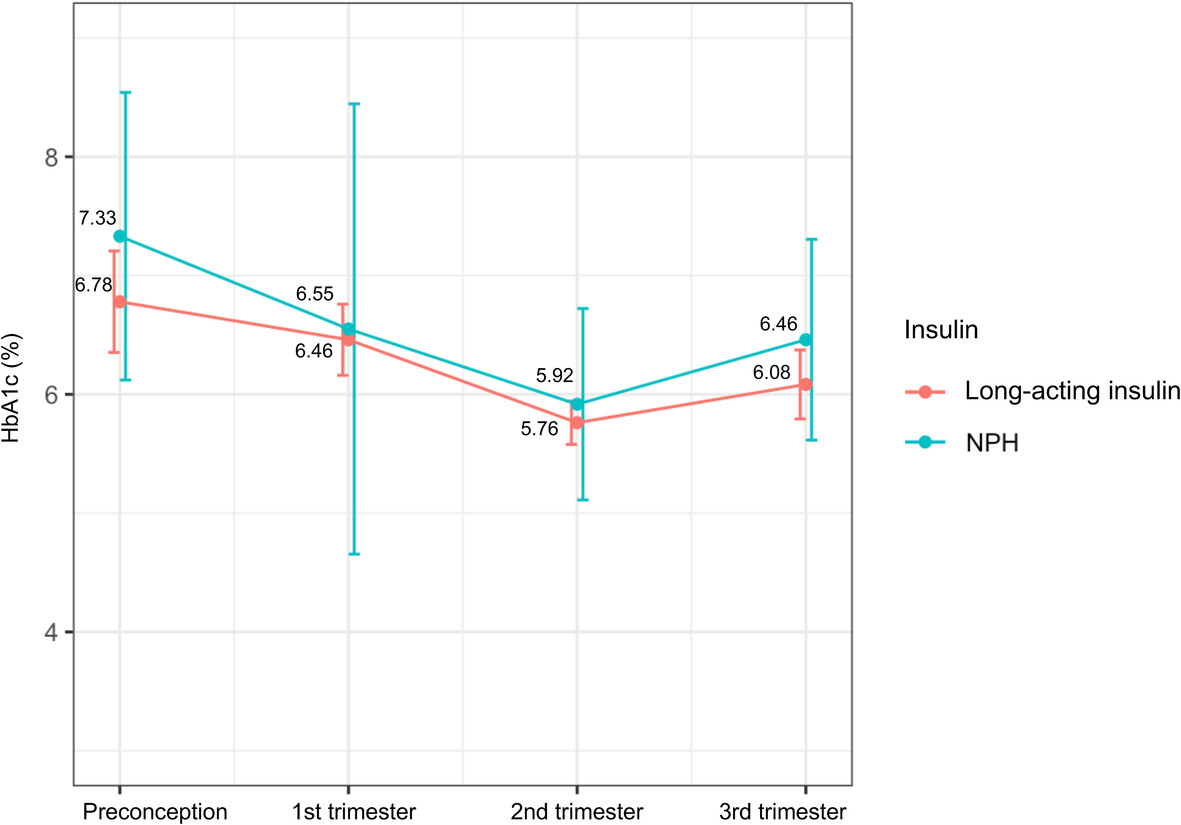
- We found that pregnant women with type 1 diabetes on continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion therapy had better glycemic control in the third trimester than those on multiple daily injection therapy.
- Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion users had a significant decline in glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) level from preconception to the third trimester.
- There was a nonsignificant lower HbA1c level for women treated with long-acting insulin, compared with neutral protamine Hagedorn.









