Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
New focuses on roles of communications between endoplasmic reticulum and mitochondria in identification of biomarkers and targets
- First Published: 02 November 2021
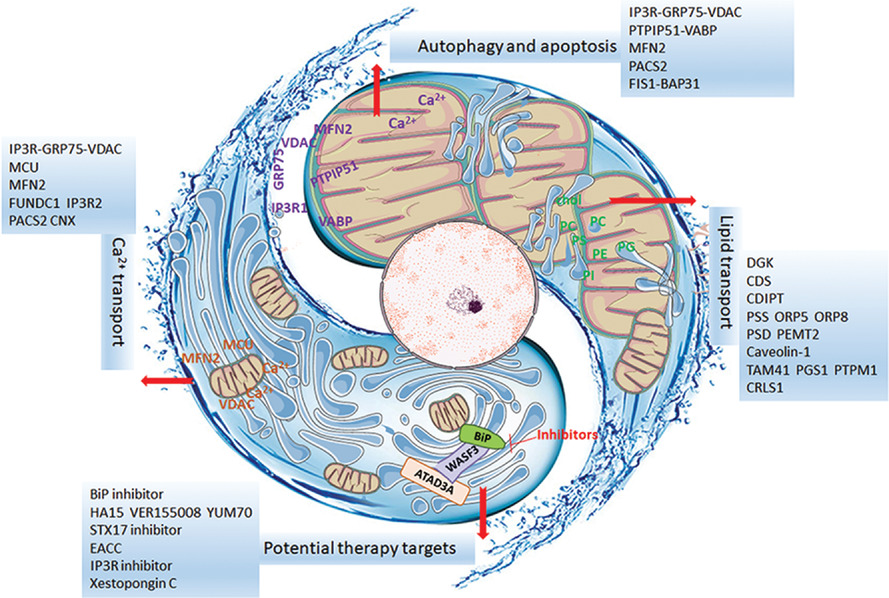
Highlights
1. The ER-Mt interactions are the important part of intracellular communication responsible for cell metabolism, development and death in the biological processes.
2. The ER-Mt regulations contribute to molecular mechanisms of diseases and vary among diseases, severities, stages and sensitivities to therapies.
3. The molecular signals during ER-Mt communication can be potential sources to discover and develop biology-, disease- and therapy-specific biomarkers and targets.
Altered lipidomic profiles in patients with and without osteonecrosis of the femoral head after 1-month glucocorticoid treatment
- First Published: 14 February 2021
Adipose-specific ATGL ablation reduces burn injury-induced metabolic derangements in mice
- First Published: 06 June 2021
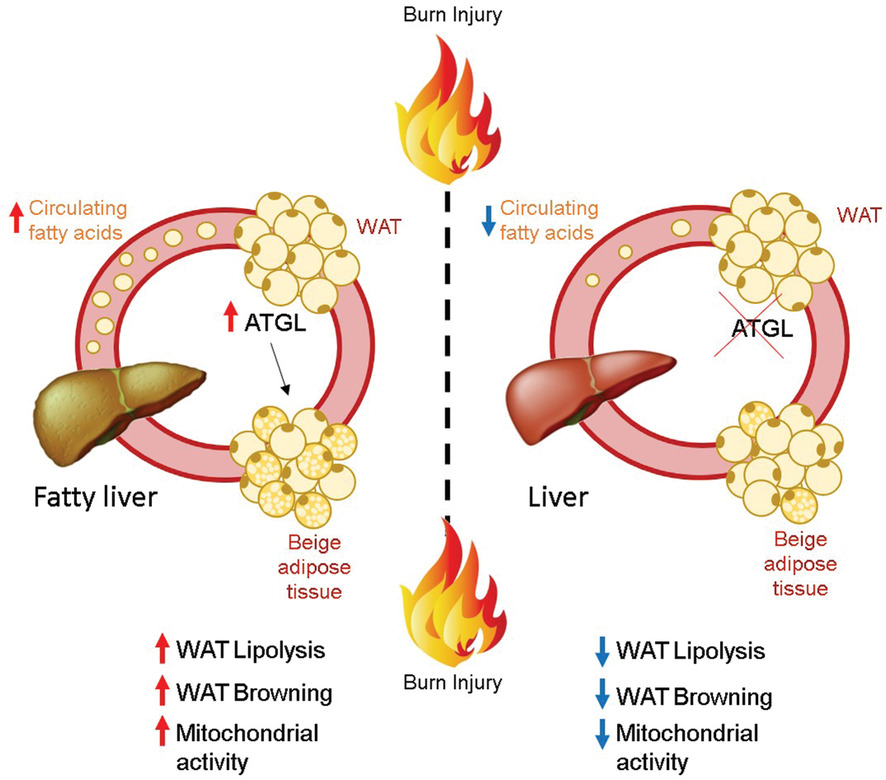
- A severe burn injury and its associated hypermetabolic response induces adipocyte dysfunction, fat catabolism, elevated fatty acids in the circulation and hepatic steatosis.
- Adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL) plays a central role in adipose lipolysis and lipid metabolism.
- Targeting adipose-specific ATGL post-burn injury diminishes WAT browning, reduces fatty acids in the circulation and protects against liver dysfunction.
SARS-CoV-2 spike protein alleviates atherosclerosis by suppressing macrophage lipid uptake through regulating R-loop formation on MSR1 mRNA
- First Published: 26 September 2021
Melatonin inhibits lipid accumulation to repress prostate cancer progression by mediating the epigenetic modification of CES1
- First Published: 06 June 2021
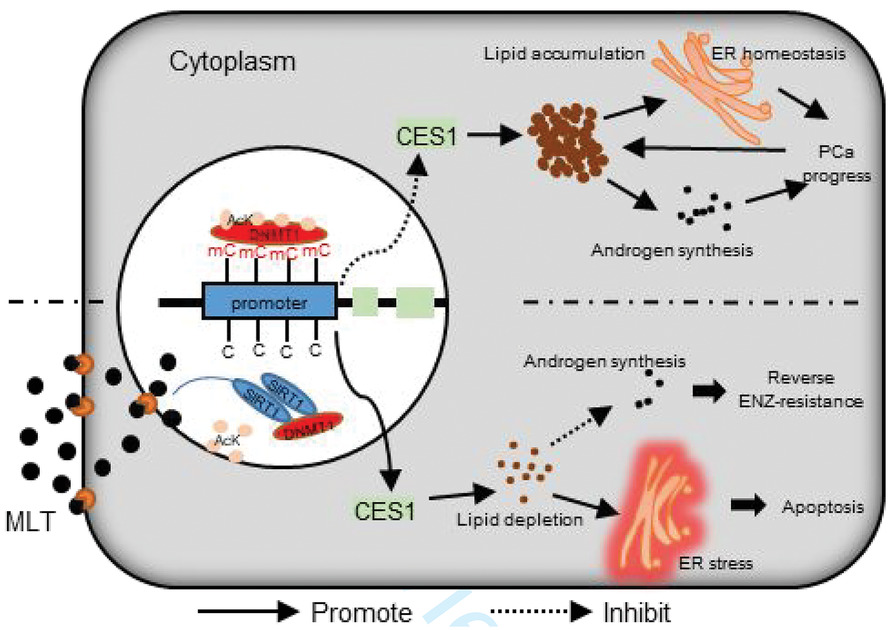
MLT regulated epigenetic modification of CES1 through SIRT1-mediated DNMT1 deacetylation. MLT-mediated CES1 expression induced lipid depletion, leading to ER stress-related apoptosis and blocking the intratumoral androgen synthesis that results in the inhibition of PCa progression and reversal of the enzalutamide resistance
Predicting the retinal content in omega-3 fatty acids for age-related macular-degeneration
- First Published: 30 June 2021
Deregulation of apolipoprotein C2 gene in cancer: A potential metabolic vulnerability
- First Published: 28 May 2021
Repurposing hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels as a novel therapy for breast cancer
- First Published: 04 November 2021
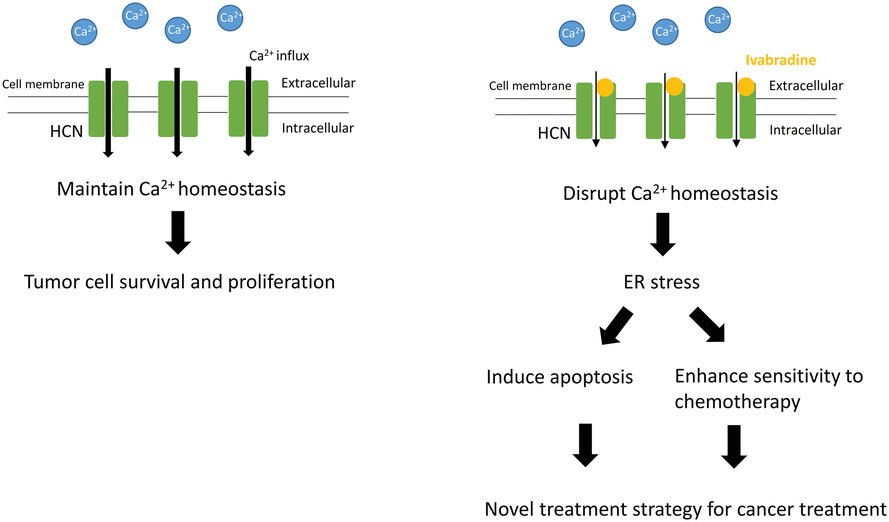
Overexpression of HCN provides advantages for the survival and proliferation of cancer cells. The addition of Ivabradine blocks HCN channels and affects intracellular homeostasis of Ca2+. Subsequently, this induces ER-stress and triggers apoptosis. Also, it makes the cancer cells become more sensitive to other chemotherapeutic agents.
Glioma glycolipid metabolism: MSI2–SNORD12B–FIP1L1–ZBTB4 feedback loop as a potential treatment target
- First Published: 12 May 2021
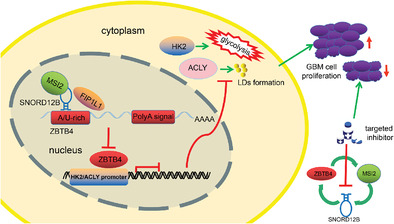
1. MSI2 expression was significantly upregulated in GBM, binding to SNORD12B and improving SNORD12B expression by increasing its stability.
2. SNORD12B regulated alternative polyadenylation process of transcriptional repressor ZBTB4 by competitively combining with FIP1L1.
3. ZBTB4 transcriptionally suppressed the expression of HK2, ACLY, and MSI2, forming a positive feedback regulatory loop to regulate the glycolipid metabolism and proliferation of GBM cell.
Apolipoprotein C-II induces EMT to promote gastric cancer peritoneal metastasis via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway
- First Published: 09 August 2021
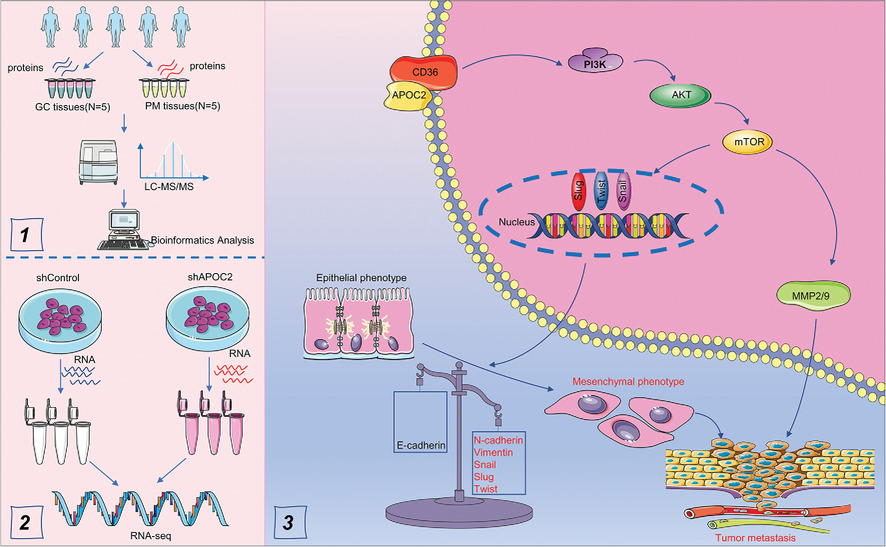
Tandem Mass Tags identified differentially expressed proteins (DEPs) between peritoneal metastasis (PM) and gastric cancer tissues, and showed that APOC2 was highly expressed in PM tissues.
APOC2 cooperates with CD36 to regulate EMT process via PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling, which eventually promotes tumor progression and peritoneal metastasis in gastric cancer.