Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
LETTER TO THE JOURNAL
scICB: A pan-cancer database of human temporal immune checkpoint blockade therapy at single-cell transcriptomic resolution
- First Published: 28 April 2025
EDITORIAL
Complex, cell-type-specific role of EEPD1: Bridging TNF-α, inflammation and apoptosis in endothelial cells
- First Published: 15 May 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
Friend or foe: The paradoxical roles of cancer-associated fibroblasts in tumour immunotherapy
- First Published: 19 May 2025
INVITED LETTER
Senescence as a pathogenic driver in chronic kidney disease: From cellular fate to clinical stratification
- First Published: 19 May 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
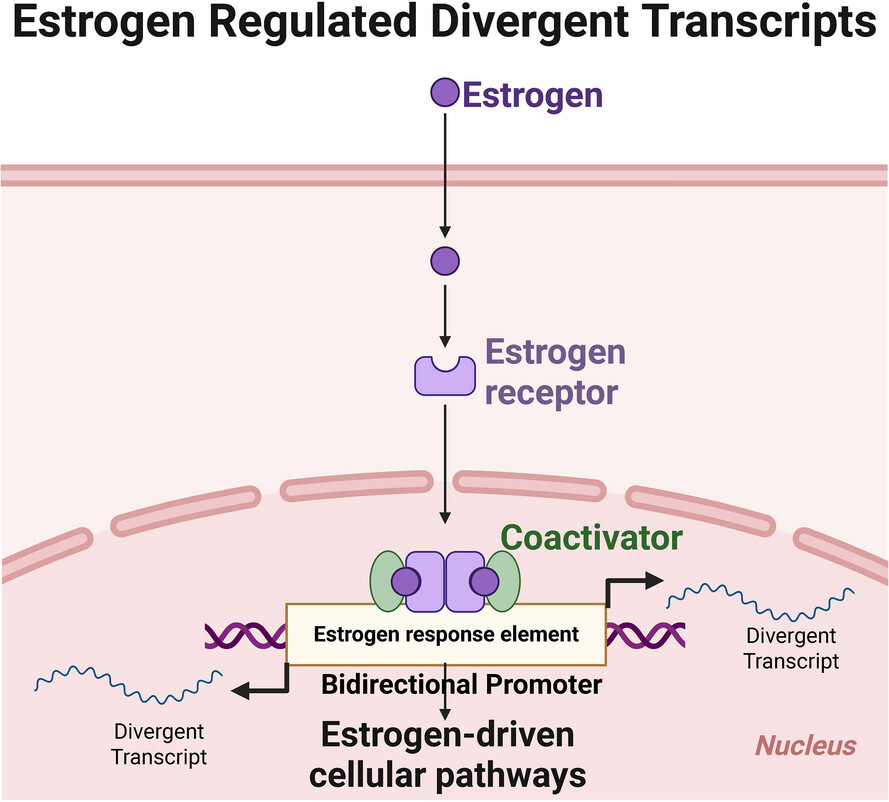
A snapshot of the role of estrogen-regulated divergent non-coding transcripts
- First Published: 25 May 2025
Current advances in the role of classical non-homologous end joining in hematologic malignancies
- First Published: 29 May 2025
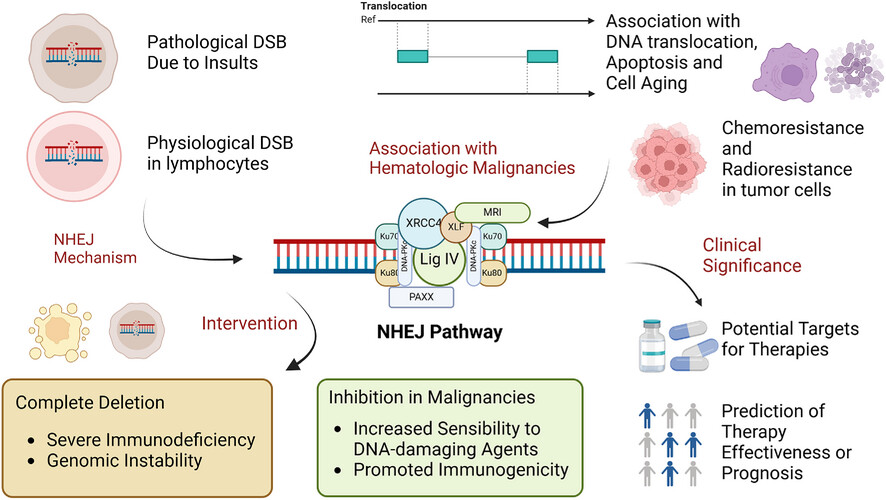
As depicted in the graphics, the classical NHEJ pathway can either take place in cells with DSBs or normal lymphocytes, reinforcing the stability of genome, and simultaneously maintaining the function of the immune system. While complete deletion causes immunodeficiency and tumourigenesis, some inhibitions could promote cancer therapies.
INVITED LETTER
Endothelial single-cell sequencing: A new way to understand endothelial biomedicine
- First Published: 02 June 2025
REVIEW ARTICLE
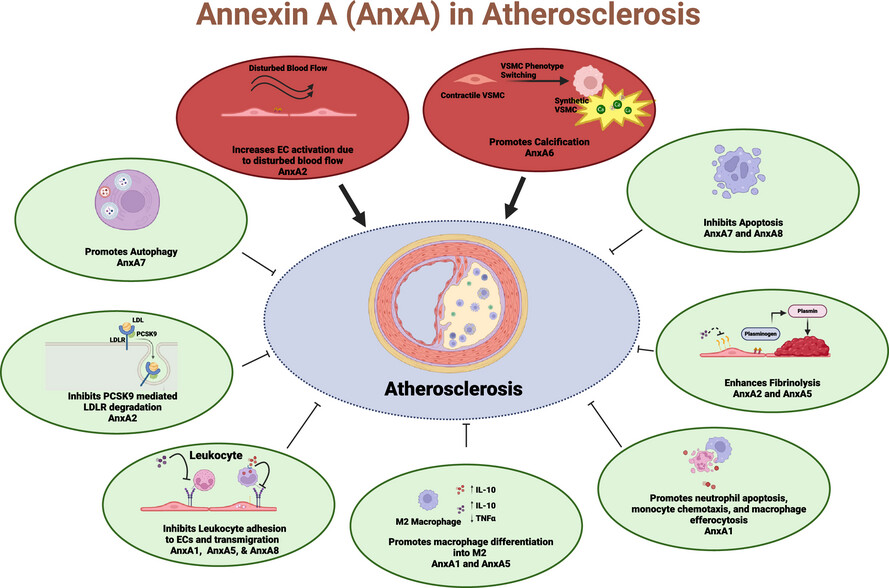
Therapeutic potential of the annexin A family in atherosclerosis
- First Published: 22 June 2025
Bridging viral hepatitis and liver cancer: Emerging concepts in pathogenesis and therapeutic innovation
- First Published: 23 June 2025
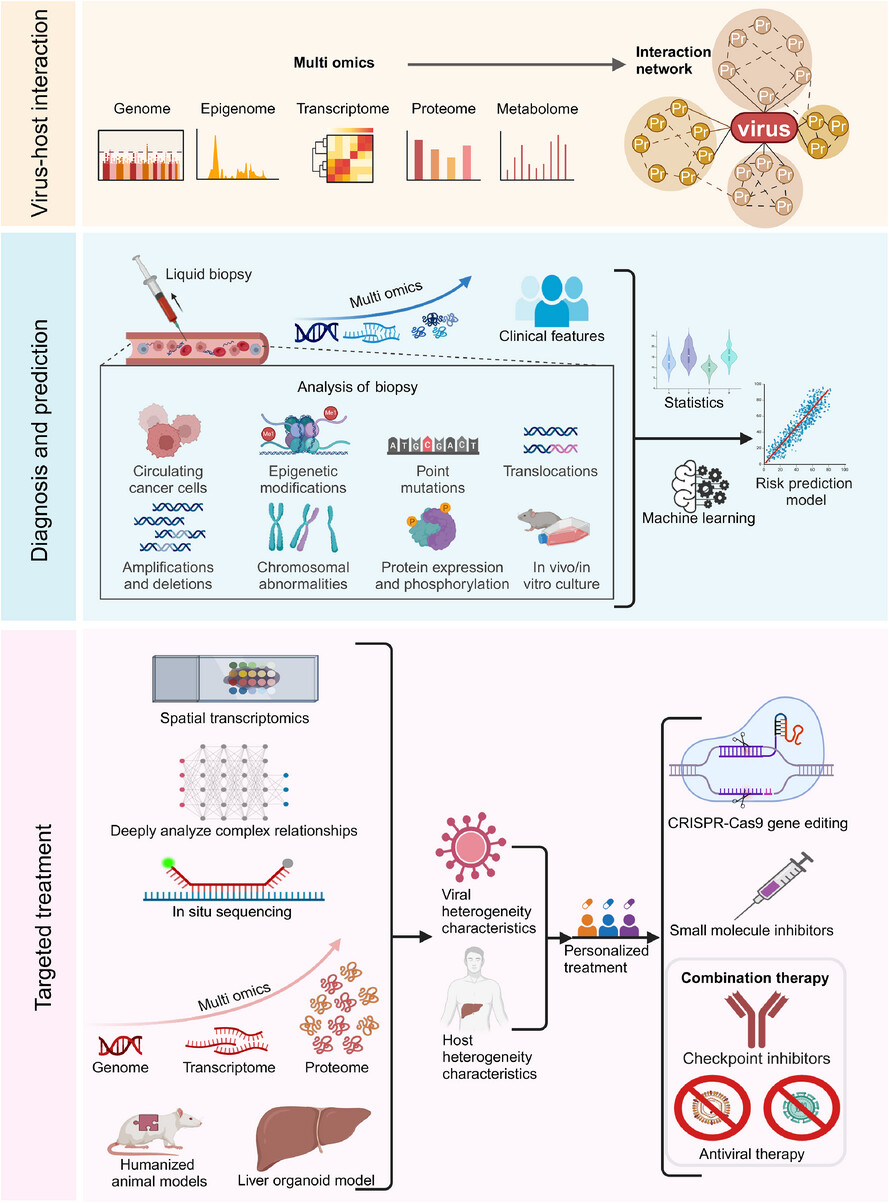
This review elucidates distinct (hepatitis B virus [HBV] DNA integration, oncoproteins; hepatitis C virus [HCV] metabolic dysregulation, fibrosis) and shared (chronic inflammation, epigenetic alterations, genomic instability) molecular mechanisms driving viral hepatitis (HBV/HCV)-induced hepatocellular carcinoma. It highlights how viral infection remodels the tumour microenvironment and discusses emerging diagnostic, preventive and therapeutic strategies targeting these pathways.
Molecular mechanisms of ageing in cancer development and therapeutic response: Translational implications for precision oncology
- First Published: 23 June 2025
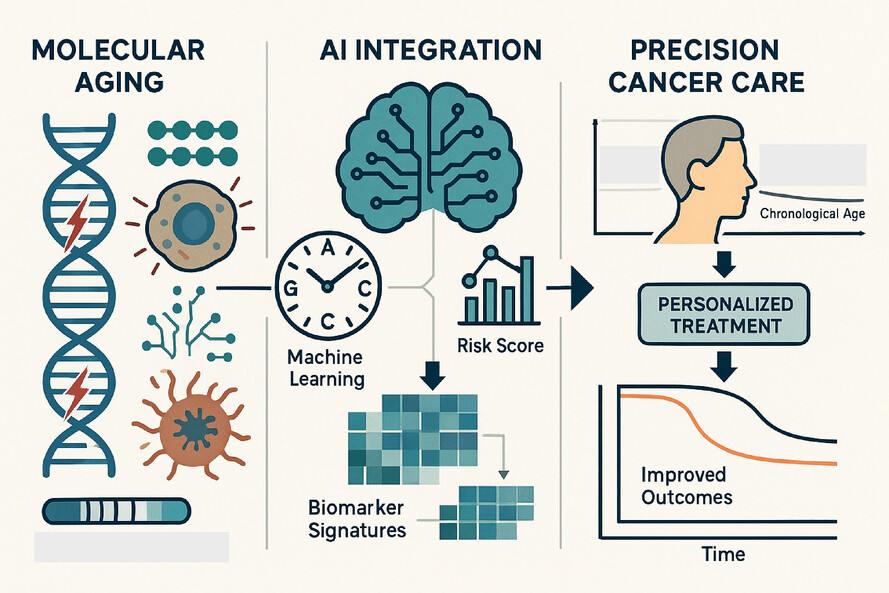
Molecular ageing mechanisms including genomic instability, cellular senescence, and epigenetic alterations drive cancer development while affecting therapeutic response. Artificial intelligence-powered biomarkers and ageing clocks enable precision oncology approaches that optimize treatment selection based on biological rather than chronological age, improving outcomes for older cancer patients.