Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Fast Peel-Off Ultrathin, Transparent, and Free-Standing Films Assembled from Low-Dimensional Materials Using MXene Sacrificial Layers and Produced Bubbles (Small Methods 3/2022)
- First Published: 21 March 2022

Front Cover
In article number 2101388, Ling, Song, and coworkers developed a novel and scalable method that enables one to rapidly and intactly detach ultrathin and transparent films assembled from various low-dimensional materials. By adopting a layer of MXenes as the interlayer and foaming agent, ultrathin films can be peeled off in tens of seconds. The demonstrated method allows for making multifunctional films with ultrathin, transparent, and flexible features.
Inside Front Cover
P-Doped SiOx/Si/SiOx Sandwich Anode for Li-Ion Batteries to Achieve High Initial Coulombic Efficiency and Low Capacity Decay (Small Methods 3/2022)
- First Published: 21 March 2022

Inside Front Cover
In article number 2101052, Kim, Yoon, Cho, and co-workers provided new sandwich-structured trilayer Si thin-film anodes demonstrating enhanced electrical conductivity and Li-ion diffusion coefficient from the synergy between structural properties and P-doping. Consequently, a Si anode with the highest initial Coulombic efficiency of 90.4% is achieved, thereby exhibiting superior electrochemical properties as anode material for advanced Li-ion batteries.
Inside Back Cover
Mapping Conductance and Switching Behavior of Graphene Devices In Situ (Small Methods 3/2022)
- First Published: 21 March 2022

Inside Back Cover
In article number 2101245, Dyck and co-workers demonstrated that by using graphene as the deposition substrate, hydrocarbon contaminants primarily diffuse along the surface at high temperatures. This property enables a surface barrier to block the ingress of contaminant material. Usually, scaling direct-write lithography techniques to the atomic scale faces a significant challenge from unwanted contaminant materials. Here, a reaction-diffusion model is introduced to describe the observed diffusion.
Back Cover
Less-Energy Consumed Hydrogen Evolution Coupled with Electrocatalytic Removal of Ethanolamine Pollutant in Saline Water over Ni@Ni3S2/CNT Nano-Heterostructured Electrocatalysts (Small Methods 3/2022)
- First Published: 21 March 2022

Back Cover
In article number 2101195, Fu and co-workers developed an effective countermeasure for both energy and environmental challenges by integrating electro-oxidation removal of organic pollutants with energy-efficient hydrogen production in saline water. The as-synthesized core/shell Ni@Ni3S2/carbon nanotubes nano-heterostructures are competent for stably electro-oxidizing ethanolamine pollutant in saline water at the anode with long-term working stability at high current densities, which not only suppresses oxygen/chlorine evolution reactions but also decreases the energy cost to boost hydrogen production.
Masthead
Reviews
Fabrication Technologies for the On-Chip Integration of 2D Materials
- First Published: 07 January 2022

With a compact footprint, low energy consumption, high scalability, mass producibility, and unique structures with distinctive properties, 2D layered materials are revolutionizing chip-scale integrated devices. This paper reviews state-of-art fabrication techniques for the integration of 2D materials, including material synthesis, on-chip transfer, film patterning, property tuning/modification, 2D van der Waals heterostructures, finishing with current challenges and future perspectives.
Toward a New Generation of Fire-Safe Energy Storage Devices: Recent Progress on Fire-Retardant Materials and Strategies for Energy Storage Devices
- First Published: 04 February 2022
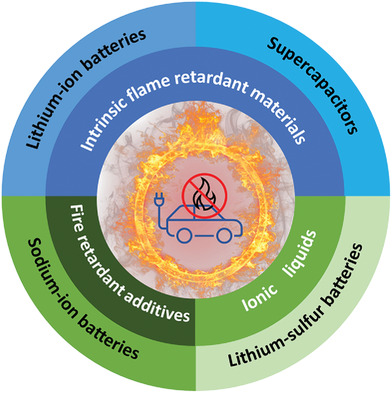
Fire incidents emanating from electric devices are frequent, especially based on lithium-ion batteries which are employed as the powerhouses of such devices. This review provides a comprehensive and critical summary of the progress achieved so far, as well as future directions and perspectives on the design of fire-safe energy storage materials.
Electronic Metal–Support Interaction Modulation of Single-Atom Electrocatalysts for Rechargeable Zinc–Air Batteries
- First Published: 17 January 2022
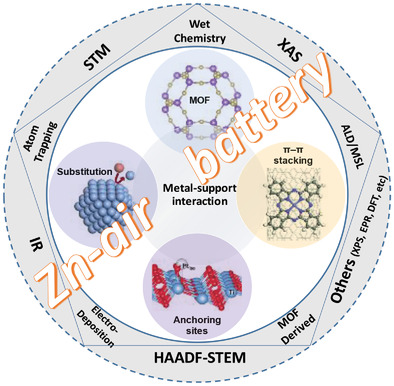
This review explores the development of single-atom catalysts (SACs) with a strong electronic metal–support interaction for rechargeable Zn–air batteries (ZABs). SAC design strategies and the impact of the metal atom coordination and substrate on the activity and stability are highlighted. This review serves as a framework for the rational design of SACs for high performance rechargeable ZABs.
Analysis and Performance Assessment of the Whole Genome Bisulfite Sequencing Data Workflow: Currently Available Tools and a Practical Guide to Advance DNA Methylation Studies
- First Published: 22 January 2022
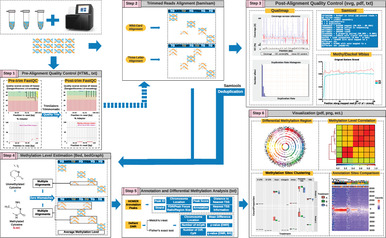
DNA methylation is an epigenetic mechanism controlling gene expression. Aberrant DNA methylation can indicate disease states, including cancer. This review analyzes the common methods used for studying DNA methylation. It compares the detailed experimental methodology of Whole-genome bisulfite sequencing using accessible and up-to-date analysis tools. It provided a step-by-step case study to guide new researchers in chromosomal aberrations research.
The Intracellular and Extracellular Microenvironment of Tumor Site: The Trigger of Stimuli-Responsive Drug Delivery Systems
- First Published: 20 January 2022
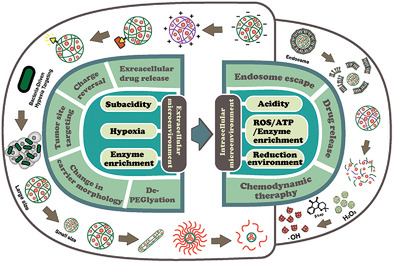
In this review, the abnormal biochemical indicators of the tumor microenvironment (TME) are introduced in detail from both the extracellular and intracellular aspects. In view of the various physiological barriers encountered during drug delivery, the strategy of constructing TME-responsive drug delivery systems (DDSs) is discussed. Finally, the authors prospect the development of TME-responsive DDSs by summarizing the typical research progress.
Research Articles
Fast Peel-Off Ultrathin, Transparent, and Free-Standing Films Assembled from Low-Dimensional Materials Using MXene Sacrificial Layers and Produced Bubbles
- First Published: 23 December 2021
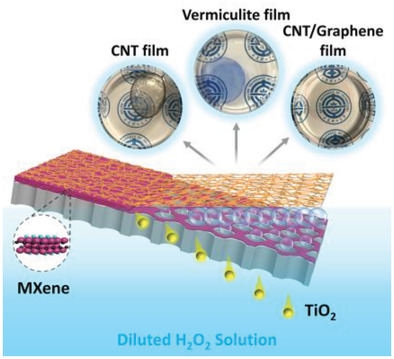
A versatile method is developed to rapidly peel off ultrathin and transparent films assembled from various low-dimensional materials (LDMs) by bubble buoying and dissolving the MXene interlayer from the layer-by-layer filtered MXene/LDM Janus films using diluted H2O2. The integrality and self-detaching rate of the LDM films are determined by the loading and reactivity of MXene.
P-Doped SiOx/Si/SiOx Sandwich Anode for Li-Ion Batteries to Achieve High Initial Coulombic Efficiency and Low Capacity Decay
- First Published: 28 November 2021
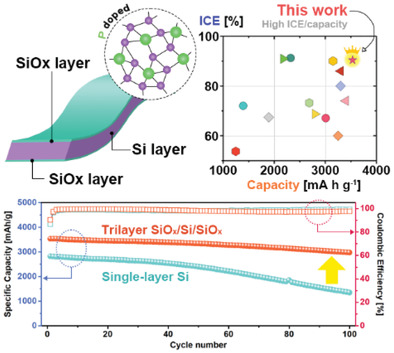
The P-doped silicon thin-film supporting more electrical conducting SiOx layers are fabricated, and high-performance lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are developed based on this anode. Attributed to the unique sandwich trilayer structure of the anode, these LIBs deliver high initial Coulombic efficiency, enhanced reversible capacity, low capacity decay, and prevent severe pulverization from volume change.
Mapping Conductance and Switching Behavior of Graphene Devices In Situ
- First Published: 15 December 2021
Secondary electron e-beam induced current (SEEBIC) imaging is used to map conductive regions of supported graphene nanodevices in a scanning transmission electron microscope. Visualization of conductivity and connectivity enables mapping of supported graphene as well as revealing disconnects. Operando electric breakdown of several devices is performed, leading to nonohmic device response. Examination with SEEBIC reveals conductance switching.
Less-Energy Consumed Hydrogen Evolution Coupled with Electrocatalytic Removal of Ethanolamine Pollutant in Saline Water over Ni@Ni3S2/CNT Nano-Heterostructured Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 19 December 2021
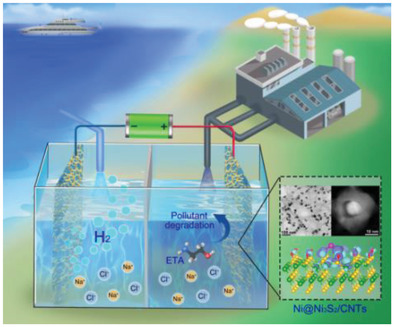
Ni@Ni3S2/carbon nanotubes nano-heterostructured electrocatalysts achieve the stable electro-oxidation of organic pollutant of ethanolamine in saline water at the anode with excellent working durability at a high current density of 100 mA cm−2, which not only suppresses oxygen and chloride evolution reactions but also decreases the energy cost to boost hydrogen production.
Frontispiece
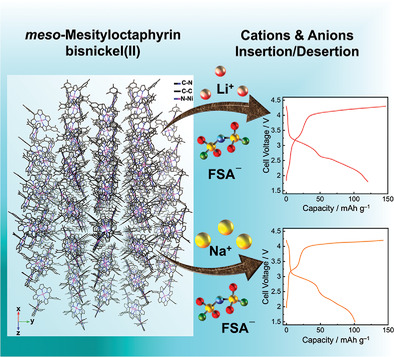
Octaphyrin(1.0.1.0.1.0.1.0) as an Organic Electrode for Li and Na Rechargeable Batteries (Small Methods 3/2022)
- First Published: 21 March 2022

Rechargeable Batteries
In article number 2101181, Hwang, Shin, and co-workers investigated Li- and Na- organic rechargeable secondary batteries using bisnickel(II) meso-mesityloctaphyrin(1.0.1.0.1.0.1.0), exhibiting high thermal stability and multiple oxidation states with extended π-conjugation pathways, as the active electrode material. The significant contribution of the pseudocapacitive processes over the diffusion-controlled processes proceeding in the cells induces fast charge/discharge performances and long-term cyclability.
Research Articles
Octaphyrin(1.0.1.0.1.0.1.0) as an Organic Electrode for Li and Na Rechargeable Batteries
- First Published: 25 November 2021
Editor's Choice
Formation of Unconventional Stoichiometric Na–Cl Magic-Number Nanoclusters and 2D Assembly on Ir(111)
- First Published: 27 January 2022
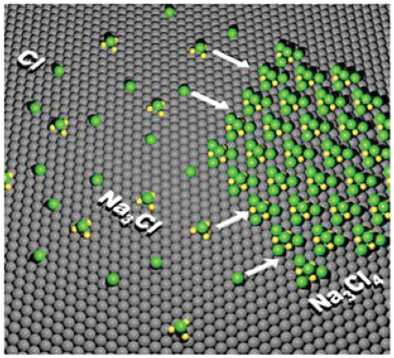
This work demonstrates that magic-number Na3Cl and 2D assembly of Na3Cl4 exist on an Ir(111) surface at room temperature. The 2D magic cluster assembly provides an opportunity to tailor the surface state electron gases via atomic-scale local gating and periodic templating, enabling a further exploration of exotic quantum states on metallic surfaces.
Sympathetic Neurostress Drives Osteoblastic Exosomal MiR-21 Transfer to Disrupt Bone Homeostasis and Promote Osteopenia
- First Published: 16 December 2021
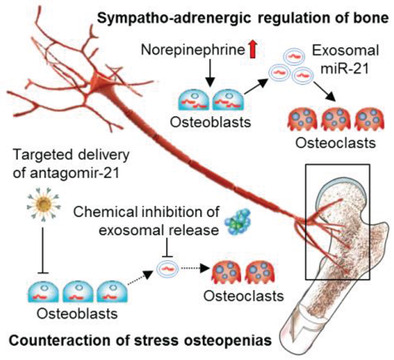
It was discovered that sympatho-adrenergic cues provoke transcription response of miR-21 in osteoblasts, which is transferred via exosomes to dictate osteoclastogenesis and disrupt bone homeostasis. It is further shown that pharmacological inhibition of exosome release by clinically-relevant drugs, dimethyl amiloride or omeprazole, and targeted delivery of antagomir-21 to osteoblasts are effective in ameliorating osteopenias against isoproterenol and depression stresses.
Quantitative Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) of Magnetically Confined Bacteria Enables Early Detection of Human Bacteremia
- First Published: 03 February 2022
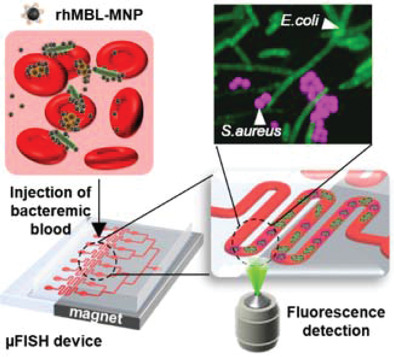
For early detection of bacteremia, a new diagnostic platform is developed using fluorescence in situ hybridization in a microfluidic device (μFISH). Pathogens in bacteremic blood are enriched by recombinant human mannose-binding lectin-coated magnetic nanoparticles (rhMBL-MNP) and magnetically captured in the μFISH device. The FISH-labeled bacteria are fluorescently visualized and quantified.
Amorphous/Crystalline Heterophase Ruthenium Nanosheets for pH-Universal Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 26 December 2021
Free-standing Ru nanosheets with amorphous/crystalline heterophases are successfully synthesized, which outperform both of their amorphous and crystalline counterparts during the hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) in pH-universal electrolytes. The formation of interphase is the key to increase the HER performance. Meanwhile, the amorphous/crystalline heterophase structure also shows improved stability when compared with its pure amorphous and crystalline counterparts.
DNA Origami Calibrators for Counting Fluorophores on Single Particles by Flow Cytometry
- First Published: 07 January 2022
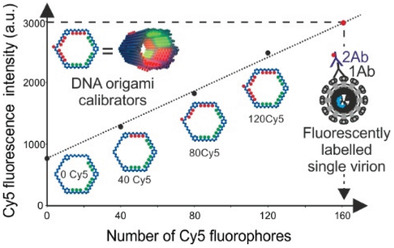
DNA-origami nanobeads for fluorescence/antigen quantification using flow cytometry (FCM). FCM is a high-throughput fluorescence-based technique for multiparameter analysis of individual particles, including cells and nanoparticles. Each bead is decorated with a specific number of calibrator fluorophores and a fluorescent trigger domain with an alternative fluorophore for proper detection in an FCM setup.
In Situ Detection of Lithium-Ion Battery Pack Capacity Inconsistency Using Magnetic Field Scanning Imaging
- First Published: 13 January 2022
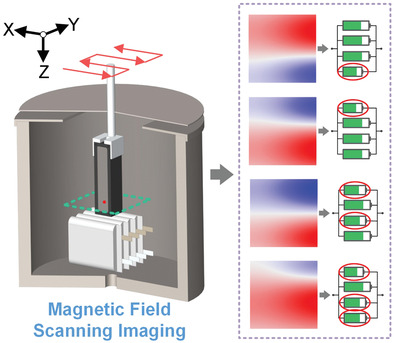
Magnetic field scanning imaging is a key tool in in situ detection of a lithium-ion battery pack. The influence of cell current and magnetic susceptibility on the magnetic field changes is first discussed and then the detection technique for battery pack capacity inconsistency is proposed. The feasibility and practicality of employing this technique in the battery pack with multicells is demonstrated.
Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Reveals the Temporal Diversity and Dynamics of Cardiac Immunity after Myocardial Infarction
- First Published: 13 January 2022

Temporal regulation of cardiac immunity is strongly associated with the onset, progression, and outcomes of myocardial infarction (MI). The study of time-series scRNA-seq on the whole cardiac immune cells isolated from the left anterior descending coronary artery ligation mice and the tanshinone IIA-treated mice sheds light on the underlying pathology of MI.
Manipulating Stable Layered P2-Type Cathode via a Co-Substitution Strategy for High Performance Sodium Ion Batteries
- First Published: 15 January 2022
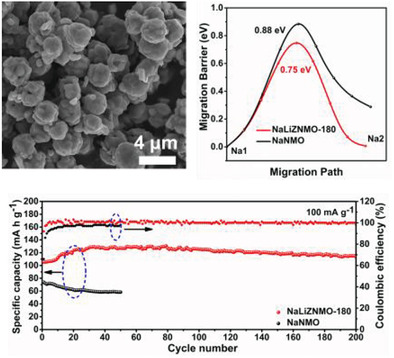
The co-substitution of Li and Zn for Ni sites in the transition metal layers contributes to lower migration energy barriers, fast Na+ diffusion and a stable structure. Therefore, the Na0.7Li0.06Zn0.06Ni0.21Mn0.67O2 (NaLiZNMO) cathode material with microsphere structure prepared via a modified solvothermal method, followed by a solid-state reaction has eminent cycle life and superior rate performance.
Magneto-Electrodeposition of 3D Cross-Linked NiCo-LDH for Flexible High-Performance Supercapacitors
- First Published: 15 January 2022
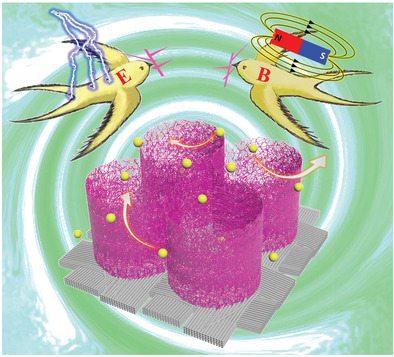
High magnetic fields are first introduced during the electrodeposition of NiCo-layered double hydroxide (LDH). Owing to magneto-hydrodynamic effect induced by magnetic field-electric field coupling, not only the loading mass increases significantly, but also a 3D cross-linked nest-like structure with abundant exposed active sites is constructed, leading to a substantial improvement of electrochemical performance of NiCo-LDH as the electrode material for supercapacitors.
Damage-Free Charge Transfer Doping of 2D Transition Metal Dichalcogenide Channels by van der Waals Stamping of MoO3 and LiF
- First Published: 17 January 2022
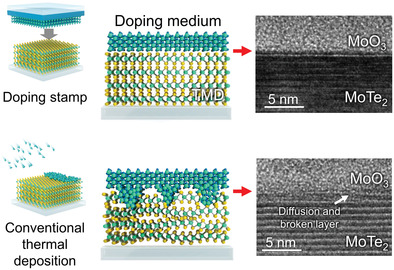
Damage-free charge transfer doping methods using MoO3- and LiF-deposited polydimethylsiloxane stamp are demonstrated for 2D-like thin transistor channels. Both p-MoTe2 and n-MoS2 channels are successfully doped by such a stamping method, also displaying a hysteresis-minimized device performance. Because defect-free doping is hardly achieved by the conventional method using a direct thermal deposition, the stamping method is regarded novel and worthy.
1-Chloronaphthalene-Induced Donor/Acceptor Vertical Distribution and Carrier Dynamics Changes in Nonfullerene Organic Solar Cells and the Governed Mechanism
- First Published: 22 January 2022
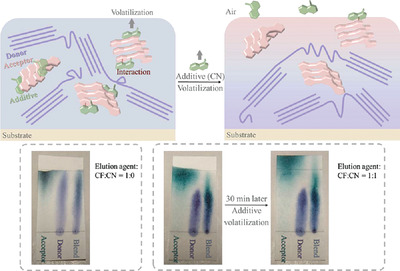
1-Chloronaphalene (CN) has been extensively employed as an additive to improve the donor/acceptor crystallization/phase segregation in organic solar cells. However, this work further uncovers that CN can tune the donor/acceptor vertical distribution in the blend film, which is revealed to be the dominant factor leading to the significantly improved efficiency and finally contributes to a best efficiency of 18.29%.
A Self-Powered Triboelectric Hybrid Coder for Human–Machine Interaction
- First Published: 27 January 2022
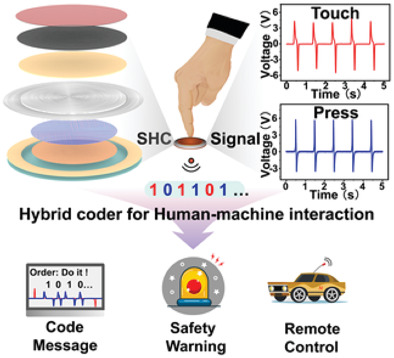
A self-powered hybrid coder (SHC) based on a dual-mode triboelectric nanogenerator is developed for human–machine interaction. The actions of finger touch and pressing can send a hybrid signal consisting of Morse code and Gray code through the SHC, which has a potential to build a concise multifunctional human machine interface.
Anionic Redox Activities Boosted by Aluminum Doping in Layered Sodium-Ion Battery Electrode
- First Published: 27 January 2022
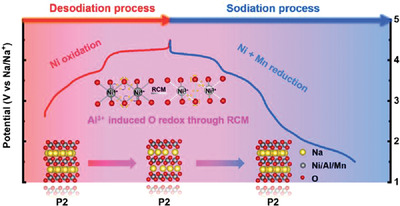
An appropriate amount of Al doping into the transition metal slabs of Na-deficient layered Na0.6Ni0.3Mn0.7O2 cathode materials can not only suppress the unfavorable P2–O2 phase transition but also boost the reversible oxygen redox through a reductive coupling mechanism between the isolated O 2p states in the NaOAl configuration and Ni4+ ions, leading to improved electrochemical performance.
Boosting Vascular Imaging-Performance and Systemic Biosafety of Ultra-Small NaGdF4 Nanoparticles via Surface Engineering with Rationally Designed Novel Hydrophilic Block Co-Polymer
- First Published: 02 February 2022
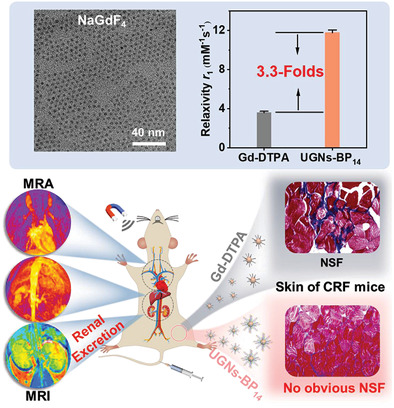
Ultra-small NaGdF4 nanoparticles are engineered with block copolymer into robust magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents with high imaging performance and excellent biosafety. The resultant renal clearable nanoagents exhibit remarkably higher relaxivity (11.8 mm–1 s–1 at 3.0 T) than clinical agent Gd-DTPA (3.6 mm–1 s–1), and negligible release of Gd3+ ions which significantly reduce the risks of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis.
Cell-Selective Encapsulation within Metal–Organic Framework Shells via Precursor-Functionalized Aptamer Identification for Whole-Cell Cancer Vaccine
- First Published: 02 February 2022
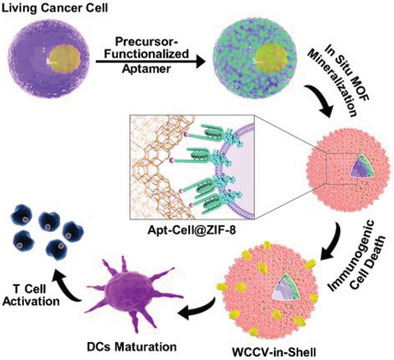
By harnessing the cell identification via precursor-functionalized aptamer, ZIF-8 is specifically in situ grown on living cancer cells at biocompatible condition, forming the integral whole-cell cancer vaccine (WCCV)-in-shell structure. With calreticulin surface exposure and entire tumor associated antigens, WCCV-in-shell has enhanced immunogenicity and shows the best preventive effect on tumorigenesis along with little safety concern.
Accelerated Hydrogen “Spill-Over” Enhances Anode Performance of Tensile Strained Pd-Based Fuel Cell Electrocatalysts
- First Published: 17 January 2022
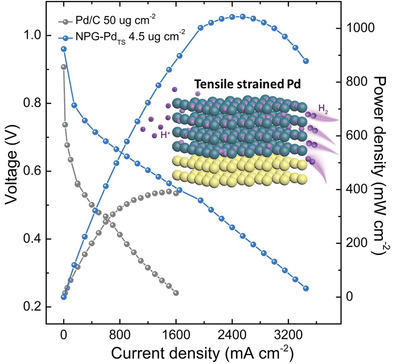
A tensile strained Pd anode with nanoporous structure exhibits outstanding proton exchange membrane fuel cells performance (>1 W cm–2) at an ultra-low Pd loading of 4.5 µg cm−2, due to a mechanism of accelerated hydrogen “spill-over” from its hydrogen storage lattices that greatly improve the anode activity.
Unraveling the Kinematics of Sperm Motion by Reconstructing the Flagellar Wave Motion in 3D
- First Published: 09 February 2022
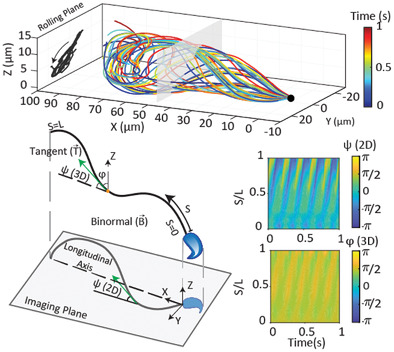
Sperm swim through the complex environment of the reproductive tract by propagating a 3D flagellar wave. However, traditional microscopy techniques only image and analyze the motion in 2D. An automated platform is demonstrated to resolve the flagellar dynamics in 3D by reconstructing the waveform in 3D using thin-lens approximation, indicating the weakly nonplanar and ambidextrous nature of the flagellar wave.
Investigations on the Electrochemical and Mechanical Properties of Sb2O3 Nanobelts by In Situ Transmission Electron Microscopy
- First Published: 08 February 2022
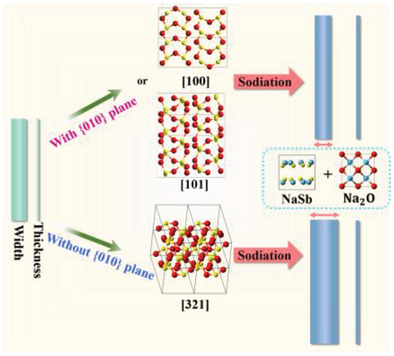
The sodiation/desodiation mechanism and mechanical properties of Sb2O3 nanobelts are revealed by in situ transmission electron microscopy. The Sb2O3 nanobelt shows anisotropic expansion and the orientation of the Sb2O3 nanobelt has great influence on the expansion ratio. In situ bending experiments suggest that the sodiated Sb2O3 nanobelts show satisfactory toughness and flexibility.
Polyoxometalate Ionic Sponge Enabled Dendrite‑Free and Highly Stable Lithium Metal Anode
- First Published: 12 February 2022
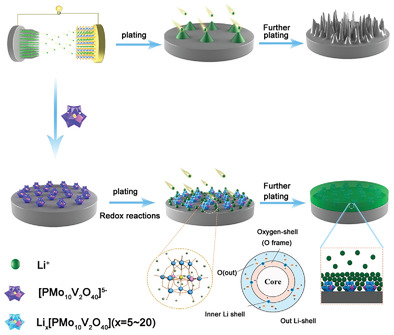
Polyoxometalates, endowed as “ionic sponge”, can be used for lithium metal batteries. They can adjust the uniform deposition of Li+ and form an ultra-stable solid electrolyte interphase layer even at high electroplating capacity of 3 mAh cm−2. This work presents an efficient mechanism for suppressing dendritic growth and forming a lithium-rich interface layer enabling secure Li-based batteries.
Semicrystalline SrTiO3-Decorated Anatase TiO2 Nanopie as Heterostructure for Efficient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 17 February 2022
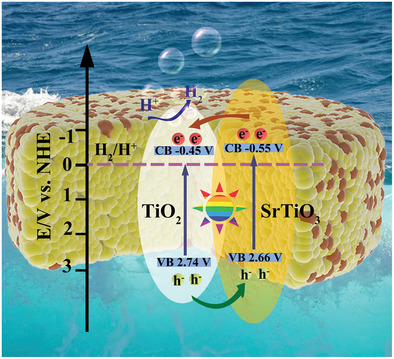
Semicrystalline SrTiO3 uniformly grows on metal organic framework-derived TiO2 surface via a simple and facile hydrothermal reaction. The synergy of nano-heterostructure and semicrystalline effect enables shorter carrier transfer path, lower charge transport resistance, faster electron/hole separating, and stronger interfacial charge coupling, leading to superior photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity and cycling stability.