Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Plant sprout foods: Biological activities, health benefits, and bioavailability
- First Published: 28 May 2021
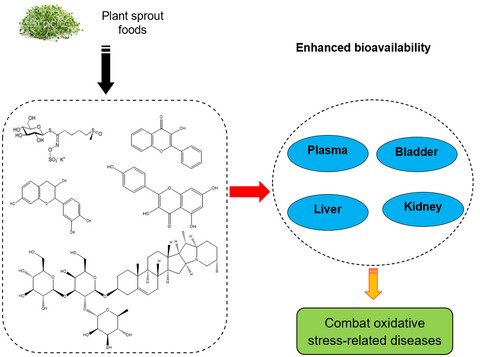
Plant sprout foods exhibit a lot of biological activities including anti-inflammatory, antioxidative, anticancer, antidiabetes, anti-infection, and antiviral activities. Up to the present moment, plant sprout foods have received much attention due to their abundance, good bioavailability, and health benefits for human. This review highlights the biological activities of different plant sprout foods (viz., broccoli sprout, buckwheat sprout, wheat sprout, mung bean sprout, soybean sprout, and adkuzi bean sprout) using in vitro model, animal model, and human model. Furthermore, the bioavailability of plant sprout foods is also discussed.
Dietary foods containing nitric oxide donors can be early curators of SARS-CoV-2 infection: A possible role in the immune system
- First Published: 09 August 2021
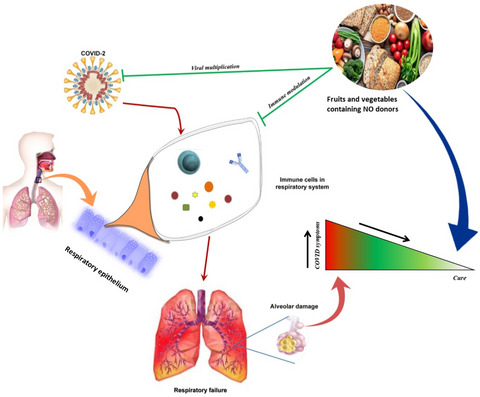
Studies on biological nitric oxide (NO) and its anti-viral activity have uncovered several surprising discoveries. The majority of the foods we eat on a daily basis are high in dietary NO donors, which have been scientifically demonstrated to helps in preventing immune-mediated respiratory tract infections. It was found that nitrite and nitrate-rich natural food supplementation can stop the progression of COVID-19 infection by acting on several immunological pathways. It is recommended that continue to consume a nutritious diet that promotes good health.
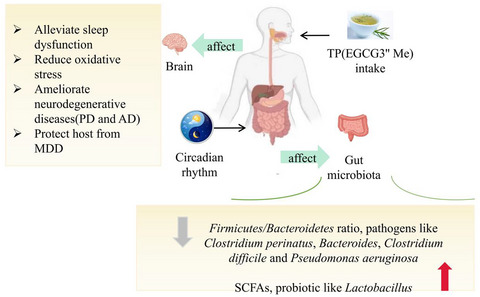
The interaction effect between tea polyphenols and intestinal microbiota: Role in ameliorating neurological diseases
- First Published: 19 July 2021
Sulforaphane as a potential remedy against cancer: Comprehensive mechanistic review
- First Published: 05 August 2021
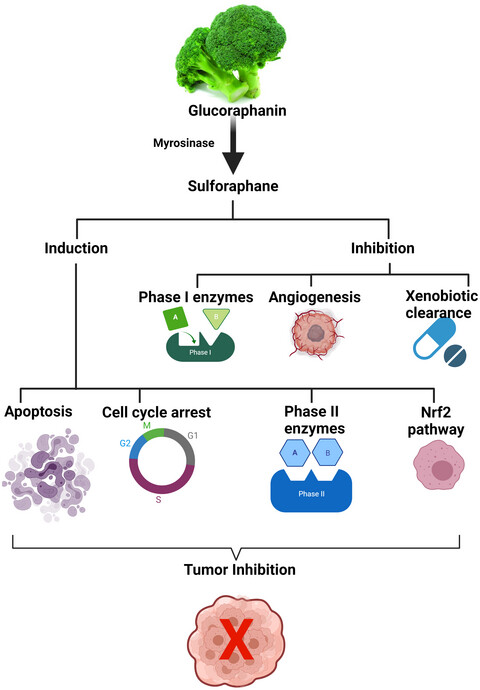
- Sulforaphane is a potent anticancer agent with proven tumor inhibition activities
- Activation of Nrf2 is its signature pathway for anticancer effects
- Its activity largely depends upon its interactions at cellular levels via modulation of carcinogen metabolism & phase II enzymatic activities, cell cycle arrest, activation of Nrf2, cytotoxic, proapoptotic and apoptotic pathways
Immunity boosting nutraceuticals: Current trends and challenges
- First Published: 01 September 2021
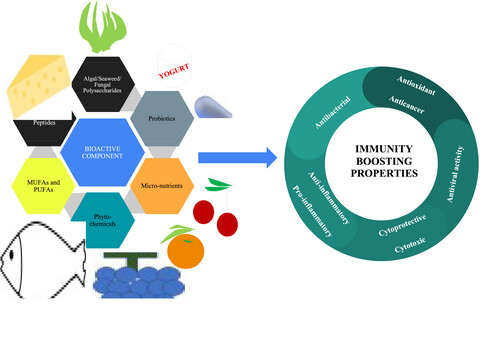
- The various bioactives present in foods synergistically contribute to the immunity-boosting properties and their administration can have a preventive and therapeutic action against chronic diseases.
- While some functional foods have immunostimulatory action for fighting off infections, some also possess immunosuppressive properties, which help in reducing the inflammation often encountered in autoimmune diseases and cytokine storms of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2.
- The antiviral, antibacterial, antioxidant and antitumor properties along with the immunomodulatory properties contribute to the immunity boosting potential of nutraceuticals.
Polysaccharides from traditional Asian food source and their antitumor activity
- First Published: 01 October 2021
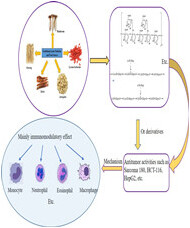
This paper introduced polysaccharides extracted from Asian traditional food source such as mushrooms, Ginseng,Salvia,Astragalus,Lycium barbarum etc. This review mainly focused on their structure, derivatives, antitumor activities and their mechanism of action in the last decades. The main mechanism of their antitumor was related to their immunopotentiating activity. It aimed to bridge traditional Asian ingredients with tumor and cancer curation in order to avoid side effect of traditional treatment.
Synergic effect of bee pollen and metformin on proliferation and apoptosis of granulosa cells: Rat model of polycystic ovary syndrome
- First Published: 08 February 2021
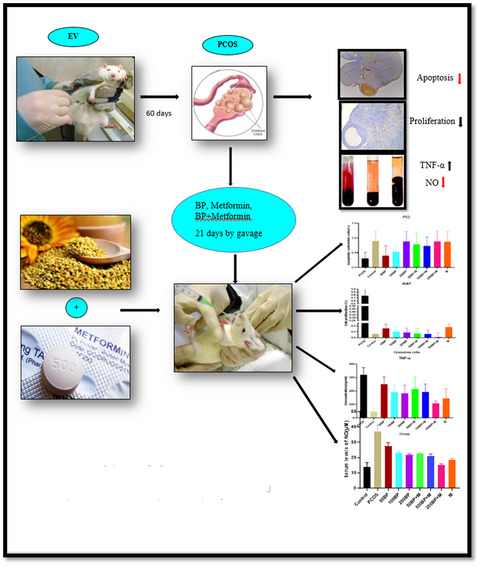
Bee pollen individually or synergistically with MET improved the symptoms of PCOS compared with control. Higher BP doses were more advantageous in this study and retrieved more significant changes. Based on the presence of various anti-oxidants, phytoestrogenic and phenolic compounds in BPE, this compound can be used as a potential therapeutic agent to treat PCOS.
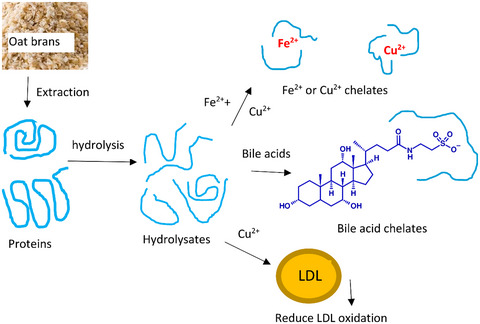
Inhibition of low-density lipoprotein oxidation, antioxidative and bile acid-binding capacities of hydrolyzed proteins from carbohydrase-treated oat bran
- First Published: 02 March 2021
Volatile aroma compounds and bioactive compounds of hawthorn vinegar produced from hawthorn fruit (Crataegus tanacetifolia (lam.) pers.)
- First Published: 02 March 2021
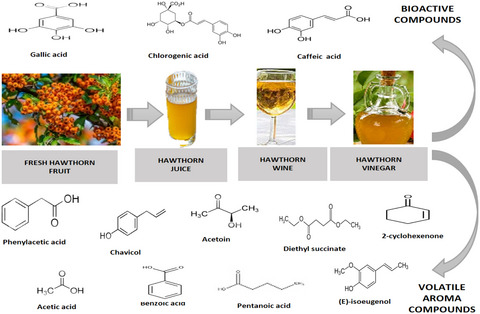
- Hawthorn vinegar is an innovative and alternative product.
- Hawthorn fruit is appropriate for production of vinegar with healthy and desired.
- The important volatile compounds of hawthorn vinegar are acetic acid, phenyl acetic acid, acetoin.
- The important phenolics of hawthorn vinegar are gallic and chlorogenic acids.
Identification of curcumin as a potential α-glucosidase and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibitor: Molecular docking study, in vitro and in vivo biological evaluation
- First Published: 04 April 2021
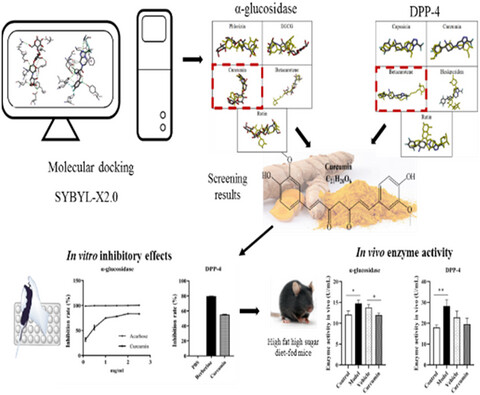
- Curcumin was identified as an inhibitor of α-glucosidase and dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 (DPP-4) according to molecular docking analysis.
- Curcumin showed inhibitory effects on α-glucosidase and DPP-4 in vitro.
- Curcumin alleviated diet-induced hyperglycemia partly through inhibiting the activities of α-glucosidase and DPP-4 in mice.
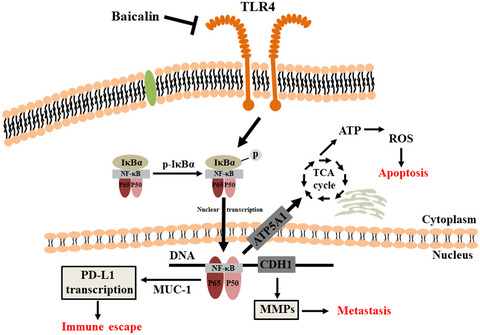
Baicalin triggers apoptosis, inhibits migration, and enhances anti-tumor immunity in colorectal cancer via TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway
- First Published: 20 March 2021
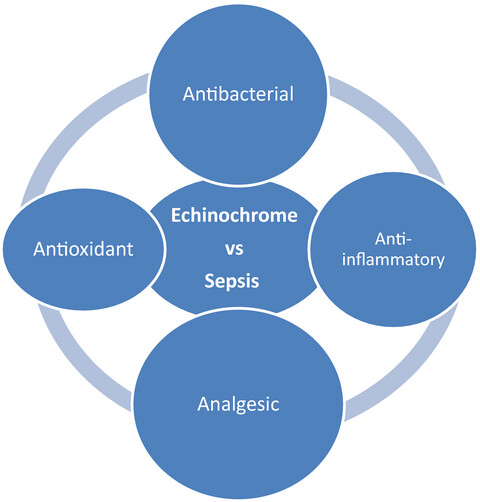
Echinochrome pigment extracted from sea urchin suppress the bacterial activity, inflammation, nociception, and oxidative stress resulted in the inhibition of renal injury in septic rats
- First Published: 19 April 2021
Polyphenols from Arctium lappa L ameliorate doxorubicin-induced heart failure and improve gut microbiota composition in mice
- First Published: 17 April 2021
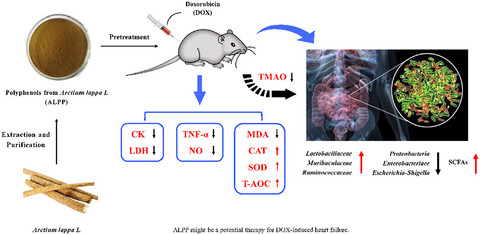
Polyphenols from Arctium lappa L (ALPP) was purified and identified by HPLC-MS. ALPP contains 16 kinds of polyphenols, among which arctiin was the most abundant ingredient. Animal experiments proved that ALPP pretreatment significantly reduced the activities of casein kinase and lactate dehydrogenase, lowered the levels of inflammatory indexes and alleviated antioxidant stress in doxorubicin-induce mice, thus leading to a reduced heart failure syndrome. In addition, ALPP could modulate gut microbiota and enhance production of short chain fatty acids.
An insight on the nature of biochemical interactions between glycyrrhizin, myricetin and CYP3A4 isoform
- First Published: 23 June 2021
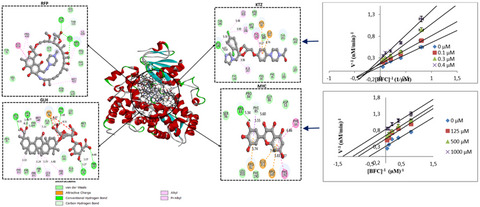
- The mechanism of modulatory roles of glycyrrhizin (GLH) and myricetin (MYC) on the CYP3A4 was investigated in silico and in vitro.
- MYC uncompetitively inhibited CYP3A4, while GLH had no inhibitory effect in vitro.
- In vitro results were consistent with the in silico and the ADME predictions, where MYC compared well with ketoconazole, a known CYP3A4 inhibitor.
- Considering its pharmacokinetic properties, GLH was suggested as a probable CYP3A4 inducer.
- MYC and GLH could potentiate clinically vital drug-drug interactions.
Buchholzia coriacea seed (wonderful kolanut) alleviates insulin resistance, steatosis, inflammation and oxidative stress in high fat diet model of fatty liver disease
- First Published: 28 June 2021
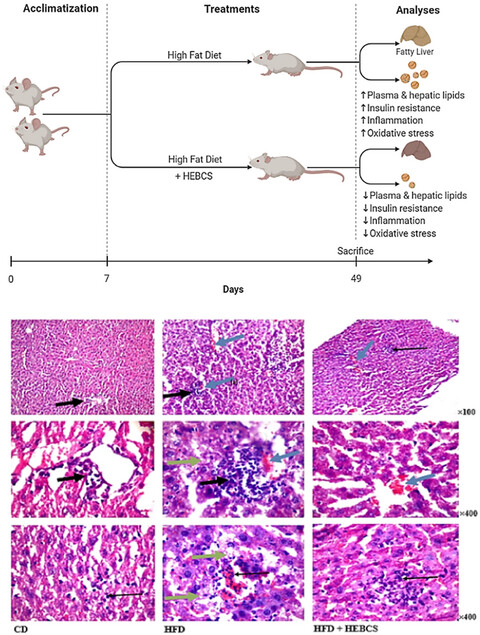
- Bioactive polyphenols and alkaloids were identified in hydroethanolic extract of Buchholzia coriacea seed (HEBCS).
- HEBCS exerts multiple therapeutic actions in alleviating high fat diet (HFD) induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) in mice.
- HEBCS alleviates insulin resistance, metabolic dysfunction, steatosis, inflammation, and oxidative distress in this model of NAFLD.
YY-11, a camel milk-derived peptide, inhibits TGF-β-mediated atherogenic signaling in human vascular smooth muscle cells
- First Published: 27 July 2021
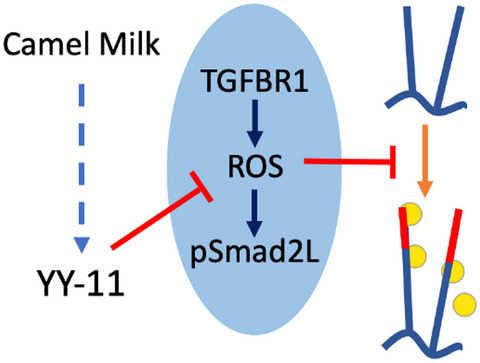
Camel milk-derived peptide YY-11 inhibits TGF-β stimulated ROS and downstream transcription factors Smad2 phosphorylation in the linker region. Atherosclerosis commences with the binding of lipids to elongated glycosaminoglycan chains on proteoglycans. TGF-β stimulated the expression of genes associated with glycosaminoglycan chain elongation. YY-11 inhibits TGF-β stimulated expression of elongation genes and as such supports the notion that camel milk may be a suitable nutritional product to prevent atherosclerosis.
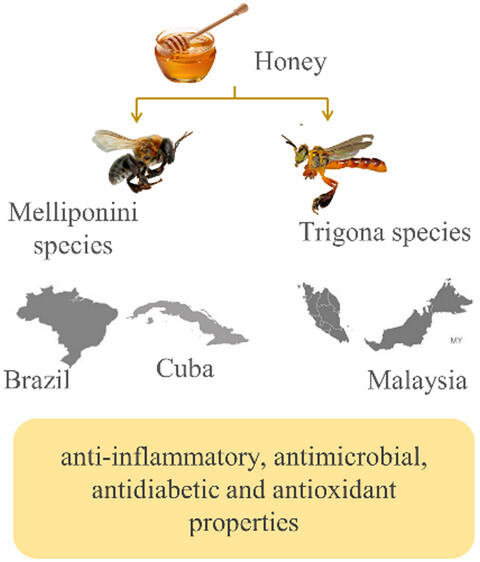
Stingless bee honey: An overview of health benefits and main market challenges
- First Published: 02 August 2021
Triterpenoid acids from medicinal mushroom Inonotus obliquus (Chaga) alleviate hyperuricemia and inflammation in hyperuricemic mice: Possible inhibitory effects on xanthine oxidase activity
- First Published: 15 September 2021
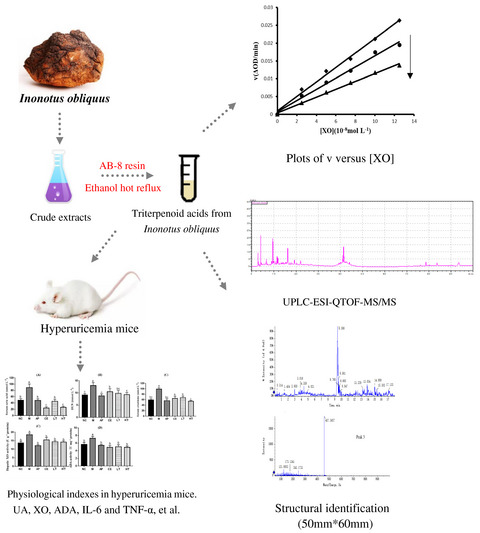
- Triterpenoid acids from Inonotus obliquus (TAIO) effectively inhibited in vitro and in vivo xanthine oxidase activity.
- TAIO strengthened antioxidant activity and regulated inflammation in hyperuricemia mice.
- Eight compounds including triterpenoids were identified by Ultra performance liquid chromatography electrospray quadrupole time of flight mass spectrometry.
Impact of Thymus vulgaris extract on sodium nitrite-induced alteration of renal redox and oxidative stress: Biochemical, molecular, and immunohistochemical study
- First Published: 26 March 2021
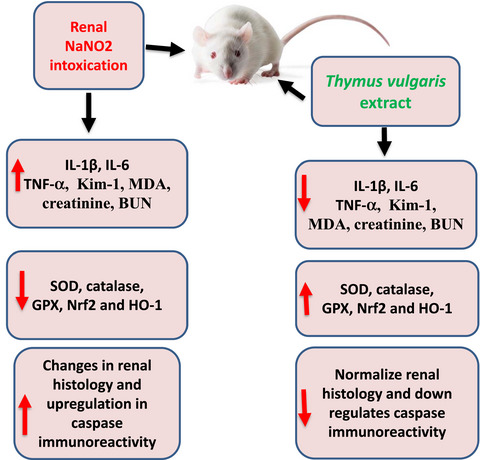
Thymus vulgaris ameliorated NaNO2 induced alteration in renal redox and antioxidant activity.
- NaNO2 has a variety of toxic effects on the organs in the human body.
- NaNO2 caused inflammation and alteration in genes associated with renal antioxidant activity.
- Thyme has the potential to inhibit the side impacts associated with NaNO2 toxicity in kidney.
Masseter muscle and gingival tissue inflammatory response following treatment with high-fructose corn syrup in rats: Anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of kefir
- First Published: 16 April 2021
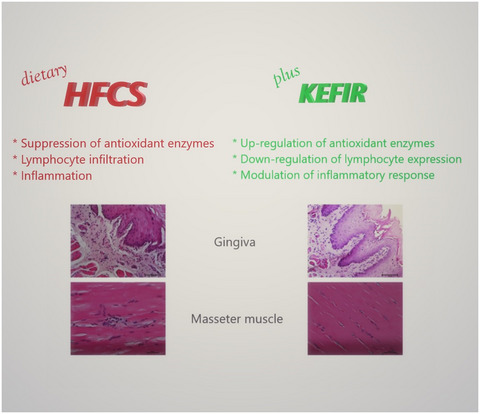
Dietary high-fructose corn syrup (HFCS) causes inflammation by suppressing antioxidant capacity in the masseter muscle and gingival tissue. Kefir provides the recovery of antioxidant enzymes as catalase, GPx, SOD-1, SOD-2, and Nrf2 in the masseter muscle and gingival tissue. Kefir reduces inflammation via suppresses the proinflammatory structures as HFCS-induced IL-6, IL-1β, IL-11, and TNF-α proteins in the masseter muscle and gingival tissue.
Vernonia amygdalina stimulates muscle glucose uptake and modulates redox activities and functional chemistry in oxidative hepatic injury
- First Published: 31 May 2021
Effects of Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium and grapefruit juice on the pharmacokinetics of omeprazole in rats
- First Published: 02 June 2021
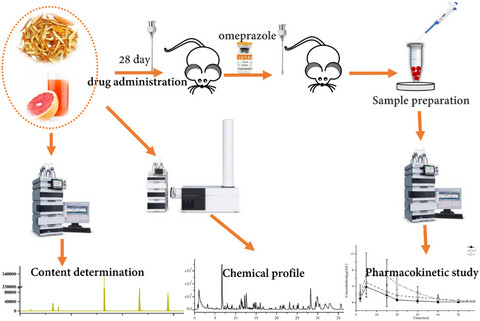
- Higher bioavailability of omeprazole was observed after prolonged multiple pretreatments with the Citri Reticulatae Pericarpium (CRP) and grapefruit juice (GFJ).
- The systemic exposure of omeprazole should be monitored when concomitant administration with CRP and GFJ.
- The effect on the pharmacokinetics of omeprazole may be attributable to the inhibition of hepatic cytochrome P450 enzymes by the flavonoids and furanocoumarins.
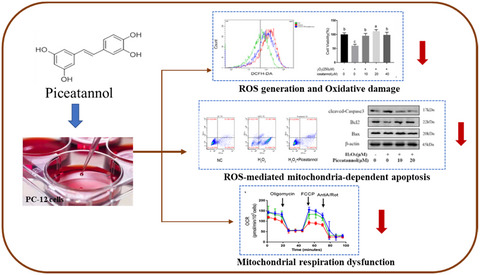
Piceatannol alleviate ROS-mediated PC-12 cells damage and mitochondrial dysfunction through SIRT3/FOXO3a signaling pathway
- First Published: 16 June 2021
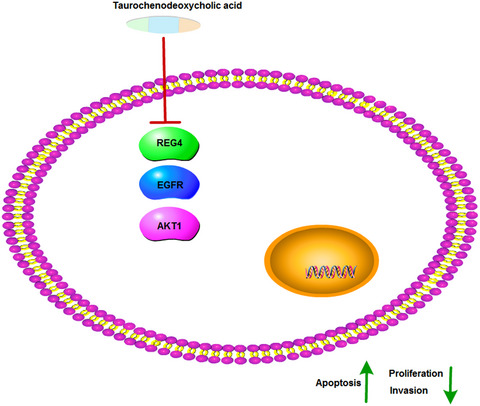
Taurochenodeoxycholic acid inhibits the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer and induces its apoptosis
- First Published: 18 July 2021
Evidence for antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential of mango (Mangifera indica L.) in naproxen-induced gastric lesions in rat
- First Published: 05 August 2021
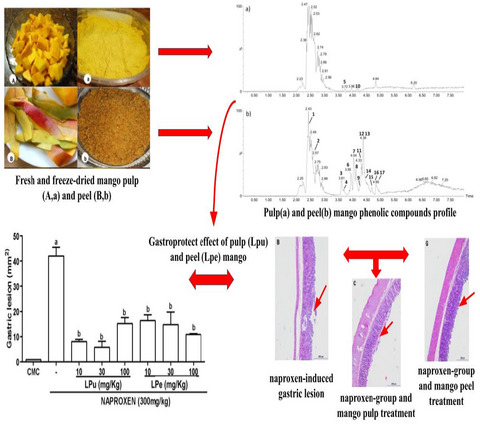
Epidemiological studies have shown that products with antioxidant activity can be used as potential agents in the treatment and prevention of chronic inflammatory diseases, such as gastric ulcers. Our study showed the possibility of using mango extracts as antioxidants and gastroprotectants, opening a new perspective in which a cheap and abundant food and its industrial residues can be transformed into pharmacological alternatives or applied as adjuvants in the treatment of chronic inflammatory diseases induced by oxidative stress.
Systemic antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of yellow passion fruit bagasse extract during prostate cancer progression
- First Published: 02 August 2021
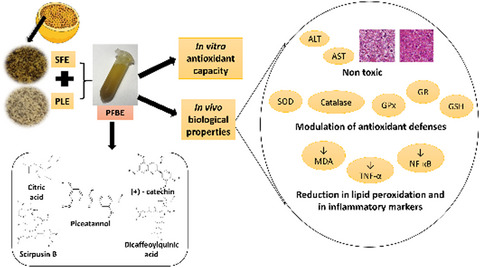
- Prostate cancer progression alters systemic oxidative and inflammatory parameters in the TRAMP model.
- Some phytochemicals were identified in passion fruit bagasse extract (PFBE), as piceatannol, scirpusin-B, (+)-catechin and dicaffeoylquinic acid, and citric acid.
- PFBE presented antioxidant properties in vitro and in vivo, as well as anti-inflammatory effects, and can act as an adjuvant during the initial steps of prostate cancer progression.
Effectiveness of a new rutin Cu(II) complex in the prevention of lipid peroxidation and hepatotoxicity in hypercholesterolemic rats
- First Published: 07 November 2021
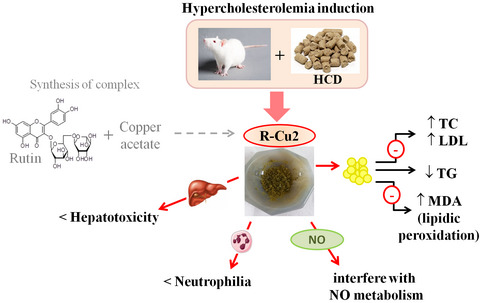
R-Cu2 activity on diet-induced hypercholesterolemia rats. The effect of R-Cu2 on lipids measurement: TC and LDL-induced increase inhibition; TG reduction; and lipidic peroxidation prevention maintaining the MDA at normal levels. The R-Cu2 also act modulating serum NO levels; reducing neutrophilia; and preventing histological changes in all evaluated liver zones.
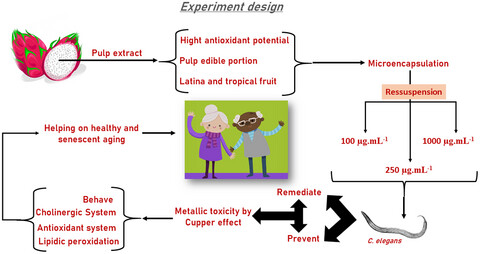
Pitaya fruit extract ameliorates the healthspan on copper-induced toxicity of Caenorhabditis elegans
- First Published: 03 January 2022
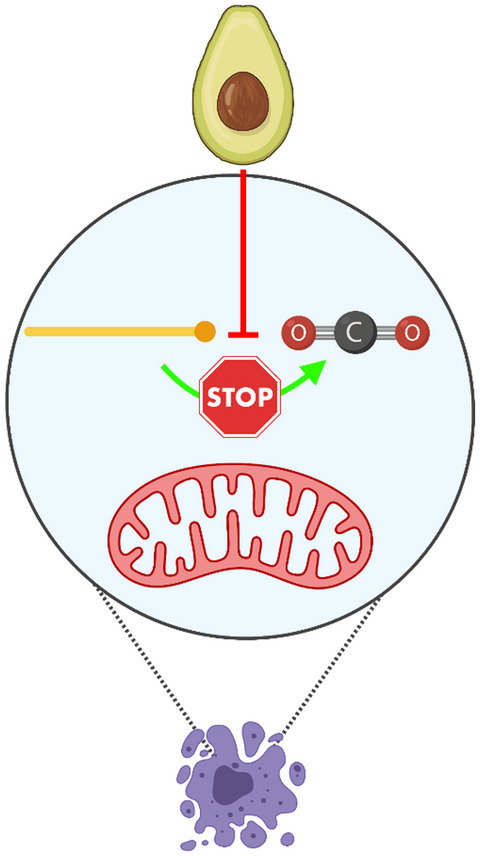
Avocado-derived avocadyne is a potent inhibitor of fatty acid oxidation
- First Published: 16 August 2021