Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cover Picture: Chem. Eng. Technol. 5/2017
- Page: 793
- First Published: 24 April 2017

The Thermocouples. Copyright: Petr Kluson
The image shows a series of thermocouples for temperature monitoring of the single-pellet string bed reactor. This unique reactor design with a 3-m long meandering channel integrates the heating/cooling system. It is well suited for accommodating highly exothermic catalytic reactions up to temperatures of 400 °C. The long reactor bed enables to reach high flow velocities and thus allows the investigation of the reactions under industrially relevant conditions in a laboratory environment.
Editorial Board
Editorial Board: Chem. Eng. Technol. 5/2017
- Page: 794
- First Published: 24 April 2017
Overview
Overview Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 5/2017
- Page: 795
- First Published: 24 April 2017
Highlights
Editorial
CHISA – Worldwide Meeting for Chemical Engineers in the Heart of Europe
- Page: 798
- First Published: 24 April 2017
Review
Fluid-Solid Adsorption in Batch and Continuous Processing: A Review and Insights into Modeling
- Pages: 799-820
- First Published: 23 January 2017
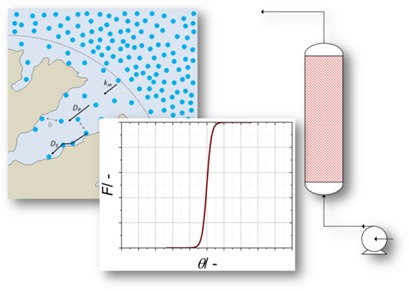
Existing state-of-the-art models for interpretation of equilibrium and kinetic experimental data for fluid-solid adsorption are reviewed. All aspects are covered, from particle scale to the design of industrial adsorption columns. A parametric study on an adsorption column is performed, testing the influence of the main physical parameters on the breakthrough curves.
Research Articles
Biomethane Production from Biogas by Separation Using Thin-Film Composite Membranes
- Pages: 821-828
- First Published: 23 January 2017
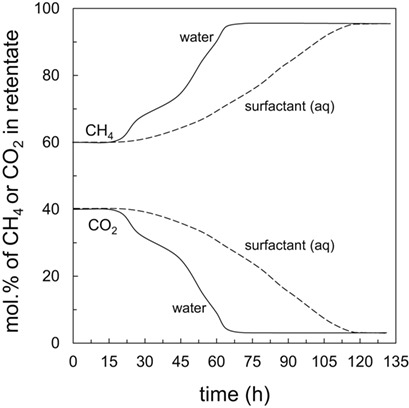
Raw biogas from a sewage plant was purified by a single-step separation method to a quality consistent with compressed natural gas standards. A membrane separation process based on a water-swollen thin-film composite membrane with polyamide skin layer was successfully applied for effective simultaneous removal of H2S and CO2 due to the good transport properties of this membrane.
Detection of Microscale Mass-Transport Regimes in Supercritical Fluid Extraction
- Pages: 829-837
- First Published: 20 January 2017
A generalized model of a particle-scale supercritical-fluid-extraction process is introduced. It is demonstrated that up-to-date experiments only allow identification of the initial extraction rates, which decrease or remain constant with time, depending on the assumed internal extraction regime. A methodology to detect the extraction regime in the particle is suggested.
Industrial Process Design for the Production of Aniline by Direct Amination
- Pages: 838-846
- First Published: 20 January 2017
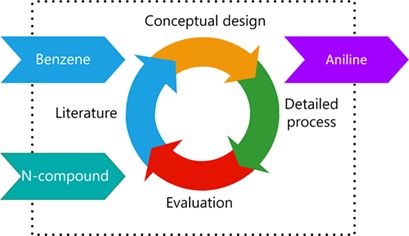
Aniline is a frequently used bulk chemical. Since today's synthetic routes suffer from low atomic efficiencies, a systematic approach was used to develop a process to produce aniline from benzene by direct amination. The proposed process can deliver a significant amount of high-quality steam and is economically and technically feasible.
Physicochemical Processes Occurring inside Clusters Consisting of FCC Catalyst Particles
- Pages: 847-853
- First Published: 23 January 2017
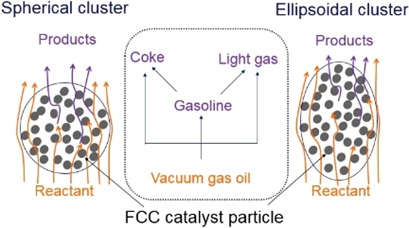
Knowledge about transport phenomena and catalytic reactions occurring inside clusters is important for understanding the multiscale behavior of the fluid catalytic cracking (FCC) riser. Transport phenomena and chemical reactions inside the cluster are studied with 3D computational fluid dynamics models to predict convective heat transfer between the gas and catalyst particles.
Multiphysics Model of a Fluorine Electrolysis Cell
- Pages: 854-861
- First Published: 23 January 2017
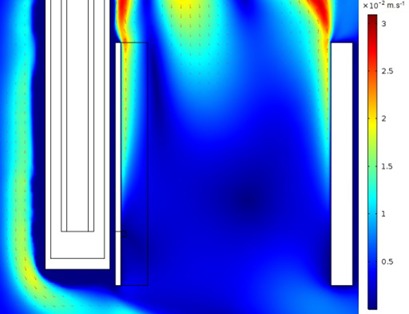
Gaseous fluorine production is fundamental for the nuclear industry as it is used to produce uranium hexafluoride. A model was built to simulate the main phenomena involved in fluorine electrolysis. Experiments were carried out and comparisons with simulated results were drawn to validate the model. It was then possible to better understand the species transport close to the electrode surfaces.
Liquid Mixing Time in Dense Solid-Liquid Stirred Tanks
- Pages: 862-869
- First Published: 23 January 2017
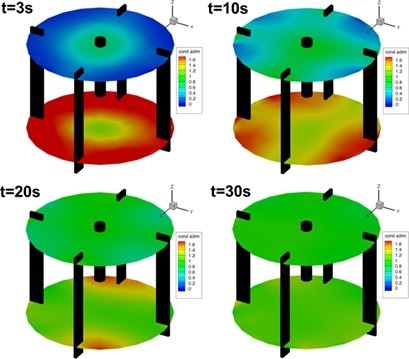
The liquid mixing time in solid-liquid stirred tanks is difficult to determine due to the effect of particle fluctuations and the opaqueness of the slurry. Different methods for the post-processing of raw data collected by electrical resistance tomography are evaluated. A robust approach for the identification of liquid mixing times in dense solid-liquid suspension is suggested.
Evaluation of Benzylamine Production via Reductive Amination of Benzaldehyde in a Slurry Reactor
- Pages: 870-877
- First Published: 23 January 2017

Benzylamine is a common industrial chemical and an intermediate in the manufacture of many chemical specialties. Although the reductive amination of benzaldehyde with ammonia may seem to be a comparably convenient alternative to benzylamine production by benzonitrile hydrogenation, the present study shows some features which can make this production process less favorable.
Volumetric Mass Transfer Coefficient in Fermenters: Scale-up Study in Viscous Liquids
- Pages: 878-888
- First Published: 23 January 2017
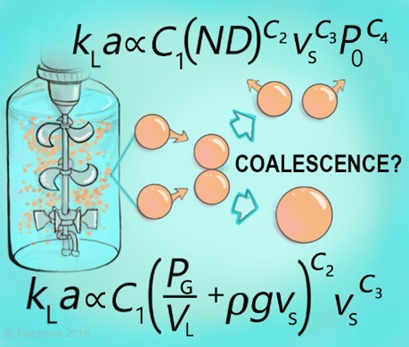
Scalable correlations for volumetric mass transfer coefficient in viscous batch for various impellers were developed. With the aim to determine a design parameter for industrial fermenters, volumetric mass transfer coefficients were measured in laboratory and pilot plant vessels. A viscous batch behavior similar to that of non-coalescent batches was observed.
Adsorption of C1–C4 Alcohols, C4–C5 Isoolefins, and their Corresponding Ethers over Amberlyst™35
- Pages: 889-899
- First Published: 23 January 2017
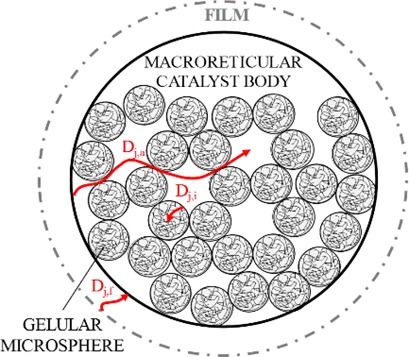
Ethers obtained from C1–C4 primary alcohols and C4–C5 isoolefins are potential environmentally benign gasoline additives. Liquid- and gas-phase adsorption equilibrium constants of the alcohols, isoolefins, and ethers on Amberlyst™35 were estimated and thereof adsorption enthalpies and entropies. Macro- and micropore diffusion coefficients of the adsorbing species were calculated from experimental data by means of the moment technique.
Excess Adsorption Isotherms of Hydrogen on Activated Carbons from Agricultural Waste Materials
- Pages: 900-906
- First Published: 23 January 2017
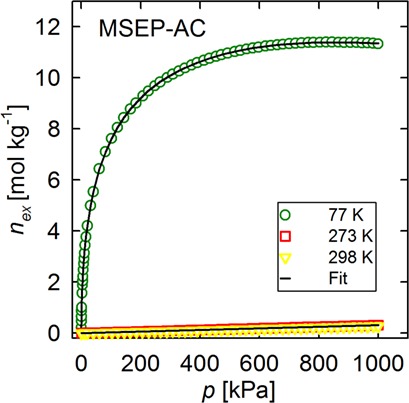
Hydrogen adsorption isotherms on four activated carbons at three temperatures and in a wide pressure range were determined. The obtained excess adsorption data were fitted by Henry's adsorption isotherm with excellent accordance at ambient temperatures. The Dubinin-Radushkevich adsorption isotherm was found to fit the excess adsorption data at cryogenic temperature with high accuracy.
Scale-Up of Oscillatory Helical Baffled Reactors Based on Residence Time Distribution
- Pages: 907-914
- First Published: 27 January 2017
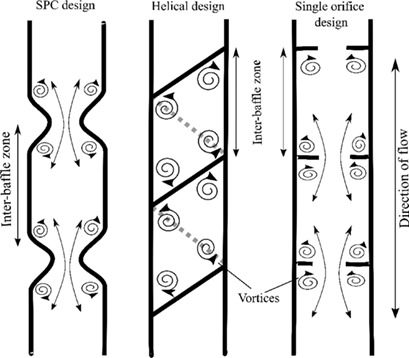
Residence time distributions were used to assess the scale-up of oscillatory helical baffled reactors over a wide range of Reynolds numbers and oscillation conditions. The scale-up correlation established to predict the plug flow behavior at various reactor scales describes the competing effects of an initial phase in which vortices develop and a second phase in which the vortices propagate further.
Cyclic Steady-State Behavior of a Fixed-Bed Adsorptive Reactor for Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction
- Pages: 915-926
- First Published: 27 January 2017
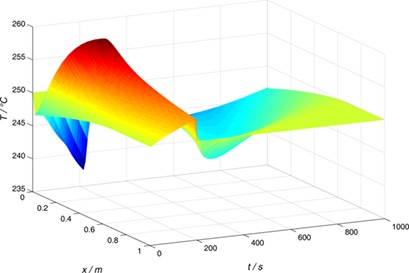
Activation of CO2 on an industrial scale is becoming increasingly important due to environmental concerns. The reverse water-gas shift reaction has been investigated for the production of syngas for methanol synthesis. The technical system has been modeled and optimized for the cyclic steady-state operation to evaluate the potential of this process.
Kinetic Energy Transfer between First Proper Orthogonal Decomposition Modes in a Mixing Tank
- Pages: 927-937
- First Published: 30 January 2017
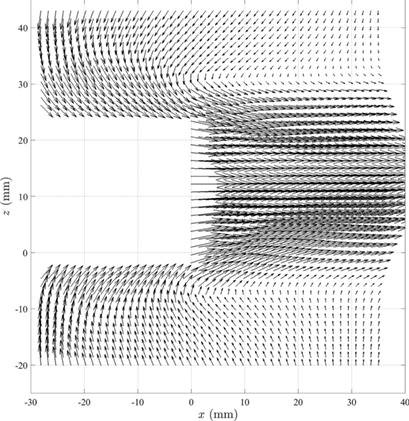
Hydrodynamics in a mixing tank was studied by 2D particle image velocimetry. Proper orthogonal decomposition was applied to the resulting data, enabling to reconstruct organized motion without the need of conditional averaging. Energetic exchanges between the first modes were considered locally. Transfer of the second mode on the fourth mode proved that a(4) evolves with a double pulsation.
Scaling the Velocity Gradients in a Vessel Agitated by a Rushton Turbine
- Pages: 938-945
- First Published: 27 January 2017
Scaling of fluctuation velocity gradients was investigated in a vessel agitated by a Rushton turbine. The squared time-averaged dimensionless local fluctuation velocity gradient was found to be proportional to the squared impeller Reynolds number, and the effect of PIV resolution on the fluctuation velocity gradient must be always taken into account when the PIV method is used for determining the gradient.
Mass Transfer from Small Droplets Suspended in a Turbulent Fluid
- Pages: 946-955
- First Published: 04 March 2017

The mechanism and efficiency of mass transfer in two-phase liquid-liquid systems were investigated in a high-shear in-line rotor-stator mixer. The multifractal model of drop breakage and the model of mass transfer by Favelukis and Lavrenteva were applied to identify the energetic efficiency of drop breakage and mass transfer. A calibration curve enabled direct interpretation of the experimental results.
Modeling Suspension Cultures of Microbial and Mammalian Cells with an Adaptable Six-Compartment Model
- Pages: 956-966
- First Published: 04 March 2017
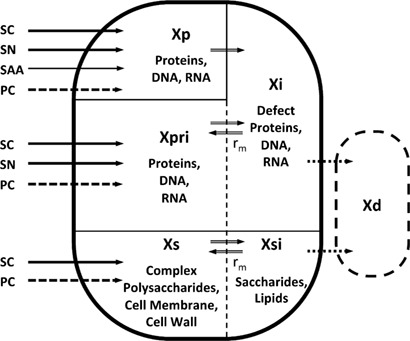
The development of process models can be time consuming and laborious. To remedy this, a highly adaptable six-compartment model has been created, which is able to describe the time courses of important state variables and the growth behavior of bacteria, yeast, fungi, and animal cells. The model can be adapted to a new process by parameter estimation. This reduces the modeling effort significantly.
A Probabilistic-Statistical Model of the Particle Classification Process in Small Hydrocyclone Classifiers
- Pages: 967-972
- First Published: 04 March 2017
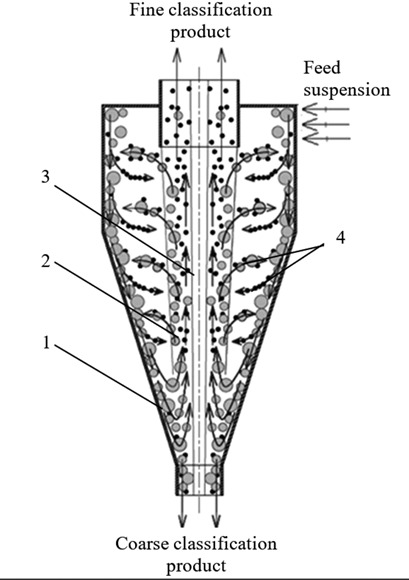
In response to modern chemical engineering requirements, solid fine fractions with particle sizes of less than 5 µm are classified in liquid-solid polydisperse systems in hydrocyclone classifiers of small sizes. An analytical probabilistic-statistical model is developed by using diffusion-type equations, in particular, the Fokker-Planck-Kolmogorov equation.
Effect of Copper-based Catalyst Support on Reverse Water-Gas Shift Reaction (RWGS) Activity for CO2 Reduction
- Pages: 973-980
- First Published: 28 March 2017
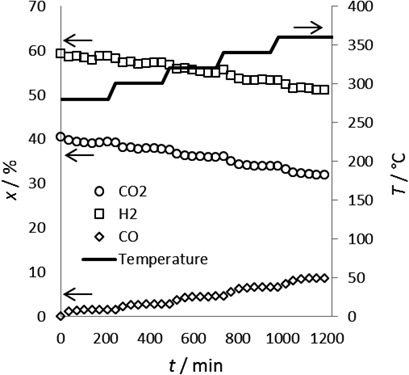
The reverse water gas shift reaction is a promising green process for syngas production. Numerous metal catalysts have been reported, but not much research has been done on the effects of the support. Five Cu catalysts with different supports were synthesized, characterized, and tested in a packed-bed reactor to determine the effect of the support on catalyst morphology, chemistry, and activity.
Cobalt Oxide Catalysts on Commercial Supports for N2O Decomposition
- Pages: 981-990
- First Published: 06 March 2017
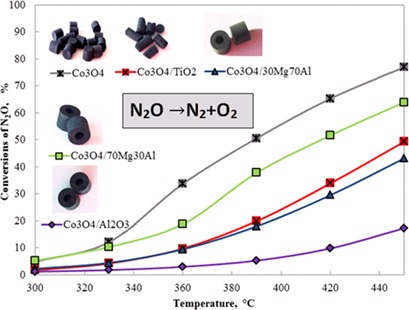
Cobalt-based catalysts exhibit excellent activities for the decomposition of N2O, a pollutant contributing to the greenhouse effect. Difficulties in the formation of Co3O4 can be circumvented by supporting the active cobalt spinel phase on an appropriate support. Co3O4 oxide catalysts prepared on different commercial supports with various Mg and Al concentrations are characterized aiming at a catalyst for industrial application.
Simple Apparatus for the Measurement of Total Pressure of Polymer-Solvent Mixtures
- Pages: 991-996
- First Published: 06 March 2017
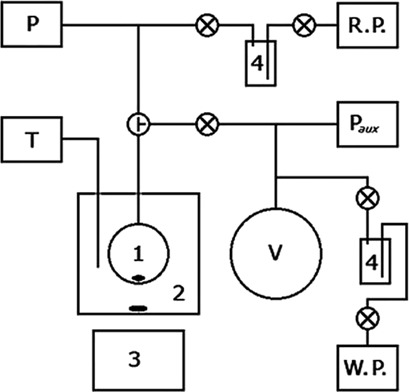
Determination of the vapor pressure of solutions with high polymer concentrations by conventional methods is challenging. A simple new setup to determine phase equilibria in systems containing one nonvolatile component was designed and applied to measure the pressure above three different water-poly(ethylene glycol) systems and these data were compared with published and predicted data.
Comparison of Flat and Hollow-Fiber Mixed-Matrix Composite Membranes for CO2 Separation with Temperature
- Pages: 997-1007
- First Published: 06 March 2017
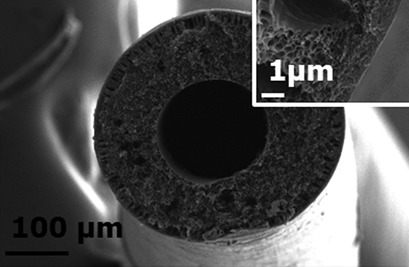
The change of geometry of CO2-permselective and thermally resistant mixed-matrix membrane self-standing materials as coating layers on flat and hollow-fiber polymer-compatible supports is evaluated. Reduction of selective layer thickness and influence of temperature to keep the high permselectivity and thermal stability in advanced membrane configurations are considered.
Substitute Composition of Naphtha Based on Density, SIMDIST, and PIONA for Modeling of Steam Cracking
- Pages: 1008-1015
- First Published: 28 March 2017
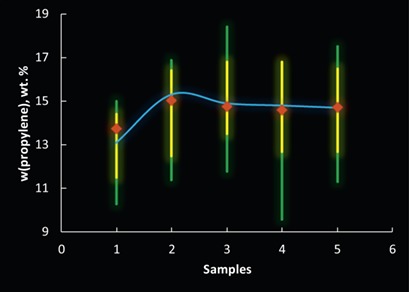
Secondary naphtha streams are considered as potential feedstocks for steam cracking. Naphtha characterization by density, SIMDIST, and PIONA is methodologically analyzed using a method for substitute composition generation. A large set of naphthas can be virtually mixed for given values of empirical characteristics and provide significantly variable yields of steam cracking products.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 5/2017
- Page: 1016
- First Published: 24 April 2017










