Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 10/2016
- Pages: 1748-1755
- First Published: 23 September 2016
Highlights
Review
Hot Water Pretreatment of Lignocellulosic Biomass: An Effective and Environmentally Friendly Approach to Enhance Biofuel Production
- Pages: 1759-1770
- First Published: 19 July 2016
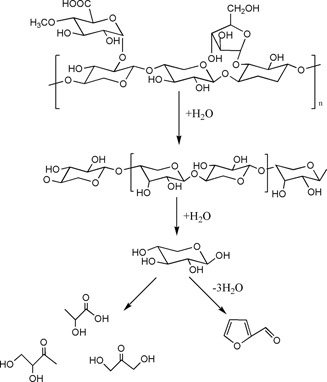
Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass is essential for overcoming its inherent recalcitrance prior to enzymatic hydrolysis and fermentation of its carbohydrate components into biofuels and bioproducts. Pretreatment of lignocellulosic biomass with hot water without chemicals is a particularly promising approach due to less safety and environmental concerns as well as relatively low costs.
Research Articles
Effect of Solvent on Nanoparticle Production of β-Carotene by a Supercritical Antisolvent Process
- Pages: 1771-1777
- First Published: 08 June 2016
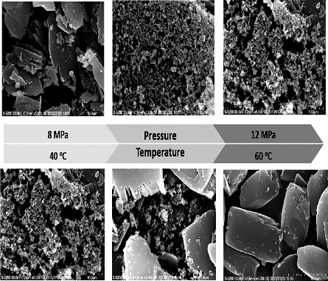
Micro- to nanosized particles of β-carotene could be successfully produced by solution-enhanced dispersion by supercritical fluids. Supercritical CO2 served as an antisolvent and optimum conditions for this process were evaluated. Ethyl acetate was found to be the best-suited solvent compared to dichloromethane, dimethylformamide, and hexane for production of nanoparticles.
Optimal Design of a Gas-to-Liquids Process with a Staged Fischer-Tropsch Reactor
- Pages: 1778-1784
- First Published: 24 May 2016
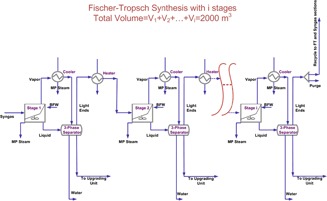
A natural gas-to-liquid hydrocarbons process with a staged cobalt-based Fischer-Tropsch reactor is optimized to maximize the wax production rate at the end of the reactor path. Staging of the Fischer-Tropsch reactor increases the production rate of wax. The carbon efficiency of the two-stage Fischer-Tropsch reactor is markedly higher compared to the single-stage reactor.
Mechanistic Modeling of Pollutant Removal, Temperature, and Evaporation in Chemical Air Scrubbers
- Pages: 1785-1796
- First Published: 11 May 2016
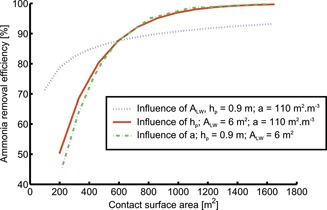
A mechanistic model for a countercurrent chemical air scrubber was set up based on the concentrations of incoming pollutants, the air temperature, and the relative humidity. The model was validated against experimental data from a conventional fattening pig housing facility, demonstrating that it was well able to describe the behavior of a countercurrent chemical air scrubber.
Catalytic Upgrading of Phenolic Oil by Etherification with Methanol
- Pages: 1797-1803
- First Published: 06 July 2016
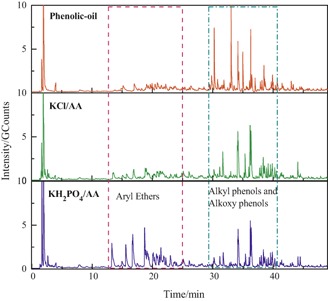
Upgrading of phenolic oil by etherification with methanol using potassium salts supported by activated alumina (AA) as catalysts was investigated in order to reduce the polarity and acidity of the product oil. The catalyst KH2PO4-AA exhibited the best performance due to its dehydration and anti-coking property. Alkoxy phenols exerted an inhibiting effect on etherification of alkyl phenols.
Ensemble Correntropy-Based Mooney Viscosity Prediction Model for an Industrial Rubber Mixing Process
- Pages: 1804-1812
- First Published: 24 May 2016
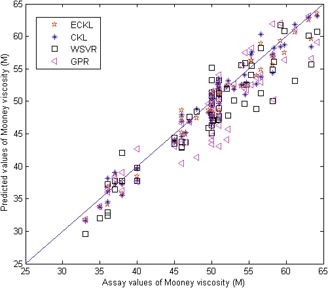
A correntropy kernel learning (CKL) method is proposed for robust soft sensor modeling of nonlinear industrial processes with outlier samples. Then, an ensemble CKL (ECKL) method is formulated by introducing the simple bagging strategy. Application to an industrial rubber mixing process demonstrates the superiority of ECKL in terms of better prediction performance.
Numerical Analysis of Header Structure Improvement in a Plate-Fin Heat Exchanger
- Pages: 1813-1820
- First Published: 04 May 2016
An innovative header structure with a plain baffle inside for improving the flow uniformity of plate-fin heat exchangers is proposed. Flow distribution and pressure drop characteristics in conventional and modified headers of heat exchangers are compared. A performance effectiveness factor is introduced to predict the effects of the proposed structure.
Acceleration of Anti-Markovnikov Hydroamination in the Synthesis of an Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient
- Pages: 1821-1827
- First Published: 10 March 2016
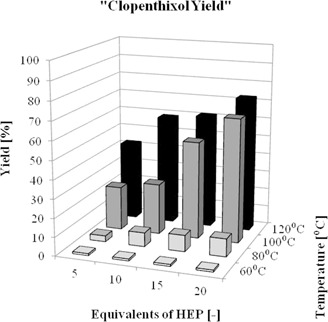
Slow chemical reactions are not suitable and a big challenge for continuous manufacturing modes in the modern pharmaceutical industry. It is therefore important to perform accelerations of such reactions. Significant speeding up of an anti-Markovnikov hydroamination reaction is achieved either via microwave radiation with tetrahydrofuran as solvent or a solvent-free approach.
Ozonation of Pyrolytic Aqueous Phase: Changes in the Content of Phenolic Compounds and Color
- Pages: 1828-1834
- First Published: 24 May 2016
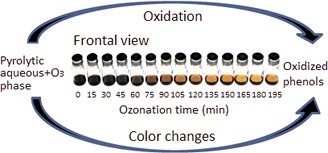
The pyrolytic aqueous phase attained from biomass fast pyrolysis used as substrate to generate bioproducts by microorganisms contains phenol inhibitors which must be removed. Ozonation turned out to be an efficient method for their reduction during which the dark color of samples diminished as a function of ozonation time. Thus, color changes were associated with the reduction of phenols.
Reducing Time to Market by Innovative Development and Production Strategies
- Pages: 1835-1844
- First Published: 22 July 2016
European chemical companies are exposed to increasing cost pressure. To maintain compet-itiveness, various technical and organizational approaches are applied to minimize costs, accelerate the development process, and optimize and improve the flexibility of the production. Examples for such techniques are described and their potential for time and cost reduction is demonstrated.
Heterogeneous Reactor Modeling of an Industrial Multitubular Packed-Bed Ethylene Oxide Reactor
- Pages: 1845-1857
- First Published: 03 May 2016
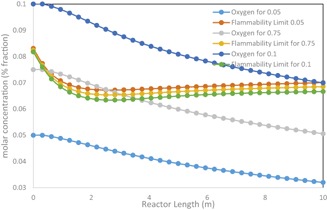
Based on the Aspen Custom Modeler, a one-dimensional heterogeneous model of a multitubular packed-bed ethylene oxide (EO) reactor was developed. The model predicts the behavior of the EO reaction and demonstrates the extent of catalyst utilization over time and along the length of the reactor or catalyst bed. Optimum feed flow, oxygen concentration, and feed pressure conditions were identified.
Investigation of Aggregation Kernel and Simulation of Cohesive Particle Flow
- Pages: 1858-1866
- First Published: 02 June 2016
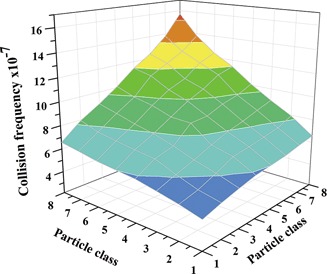
Aggregation is an essential process of cohesive particle flow. To simulate this process in fluidized beds, a modified model coupled with the population balance equation has been developed. In order to test its performance and assess its validity, the proposed model was successfully applied to simulate the aggregation process of cohesive particles in a fluidized bed.
Kinetics of Isophorone Synthesis via Self-Condensation of Supercritical Acetone
- Pages: 1867-1874
- First Published: 24 May 2016
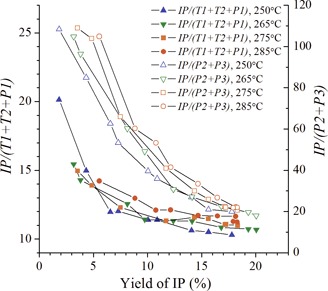
In a kinetic study, isophorone synthesis by self-condensation of supercritical acetone catalyzed by aqueous KOH in a tubular flow reactor is investigated. Two isophorone selectivity indicators were introduced to evaluate the effect of temperature. Higher reaction temperatures led to improved isophorone selectivity and favored the reversion of reversible by-products.
Extraction of Anthocyanins Using a Laboratory Robot and Innovative Extraction Technologies
- Pages: 1875-1883
- First Published: 22 July 2016
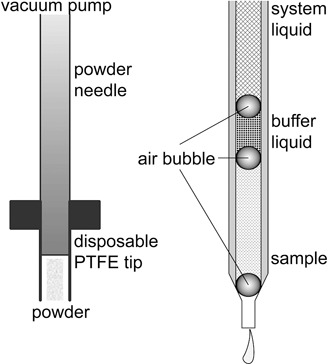
Natural plant extractions are performed using a fully automated laboratory robot to screen the most influential variables in the release of high-value chemicals from plant cells. Extraction parameters can be successfully determined and implemented using the robotic system. Reliability and quality of data is increased compared to manual measurements due to the consistent precision of the robot.
An Adaptive Pseudospectral Method for Constrained Dynamic Optimization Problems in Chemical Engineering
- Pages: 1884-1894
- First Published: 29 June 2016
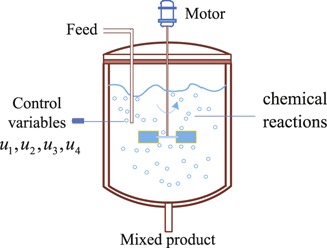
An adaptive pseudospectral method for constrained dynamic optimization problems is presented. To overcome limitations of the classical pseudospectral method, the proposed approach allows the division of the time interval and the number of collocation points in each subinterval to vary. The method proved to be efficient in enhancing the solution accuracy of dynamic optimization problems.
Coalescence Deformation of Bubble Pairs Generated from Twin Nozzles in CMC Solutions
- Pages: 1895-1902
- First Published: 06 July 2016
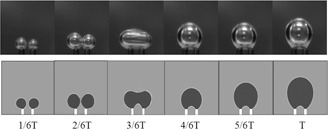
Understanding coalescing bubble deformation in non-Newtonian fluids is crucial for optimizing gas-liquid equipment design and for gaining an insight into multibubble behavior. Rheological characteristics of fluids are considered in numerical investigations of the coalescence regime of two bubbles generated at adjacent nozzles.
Particle-Scale Investigation of Heat Transfer in Radiation-Driven Char Gasification
- Pages: 1903-1911
- First Published: 06 July 2016
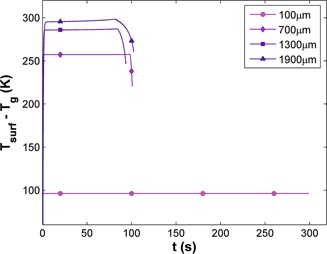
Solar thermal gasification has the potential to reduce pollutant discharge as it does not rely on combustion to produce heat. A dynamic model of a single char particle undergoing solar-driven gasification has been developed with accuracy and at low computational cost. Parameters such as the reactor conditions and particle diameter were found to influence the heat-transfer mechanisms.
Thermodynamics of Hydrogen Production Based on Coal Gasification Integrated with a Dual Chemical Looping Process
- Pages: 1912-1920
- First Published: 04 May 2016
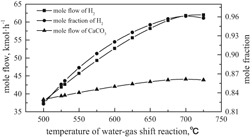
A novel hydrogen generation technology involving hydrogen production based on a coal gasification system integrated with a dual chemical looping process is proposed. Chemical looping air separation, coal gasification, and water-gas shift process are combined with chemical looping CO2 absorption. Potential advantages from a thermodynamic perspective are evaluated.
Analyzing the Adaption of Different Adsorption Models for Describing the Shale Gas Adsorption Law
- Pages: 1921-1932
- First Published: 10 August 2016
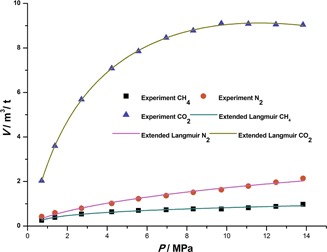
Different adsorption models were analyzed for describing the adsorption of CH4, N2, CO2, and their mixtures, representing shale gas. The modeling results show that the adsorption characteristics of most shale gas reservoirs obey those of type I on the macroscopic scale. Models suitable for predicting the adsorption of shale gas were identified.
Structured Raney Nickel Catalysts for Liquid-Phase Hydrogenation
- Pages: 1933-1938
- First Published: 15 June 2016
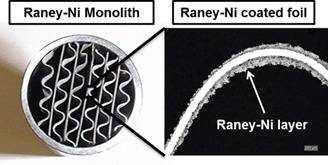
New structured catalysts based on Raney Ni were tested for the hydrogenation of glucose and o-nitrotoluene. The intrinsic catalytic activity of the Raney Ni monoliths was higher compared to that of the Raney Ni pellets, but lower than that of the corresponding slurry catalyst. The activity of the Raney Ni monolithic structure was significantly improved when applying a two-phase co-current flow.
Mass Transfer and Liquid-Film Formation in a Spray Tower for SO2 Removal in Sodium Hydroxide Solution
- Pages: 1939-1945
- First Published: 16 August 2016
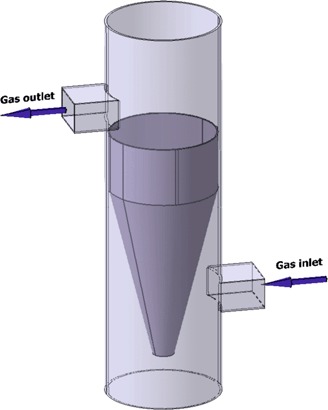
Spray towers enable the control of air pollution. The SO2 removal efficiency of such a tower was investigated under various operating conditions in terms of liquid flow rate, gas flow rate, and inlet SO2 concentration. The formation of a liquid film and its impact on the droplet flow rate down the tower was analyzed and correlations to predict the volumetric mass transfer coefficient are proposed.
Model-Based Optimization of a Photocatalytic Reactor with Light-Emitting Diodes
- Pages: 1946-1954
- First Published: 03 June 2016
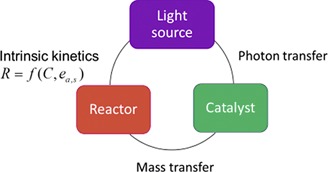
An LED-based photocatalytic reactor is modeled based on mass, momentum, and photon transfer equations. Different objective functions are formulated to find optimal values for reactor dimensions and the number and positioning of the light sources. The proposed approach facilitates the design of LED-based photocatalytic reactors by optimization of mass and photon transfer simultaneously.
Influence of Bubble Bouncing on Mass Transfer and Chemical Reaction
- Pages: 1955-1962
- First Published: 10 August 2016
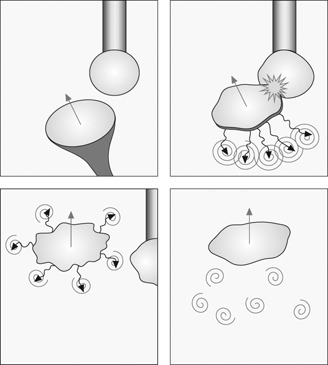
Bubble-induced turbulence and bubble-bubble interactions influence the gas-liquid mass transfer and mixing of reactants. Bubble bouncing leads to a deformation of the interfaces of two bubbles and is expected to affect the mass transfer rate. A Sherwood number correlation is developed to predict the mass transfer in dependency of the bouncing frequency.
Numerical Investigation of Flow Patterns and Concentration Profiles in Y-Mixers
- Pages: 1963-1971
- First Published: 19 July 2016
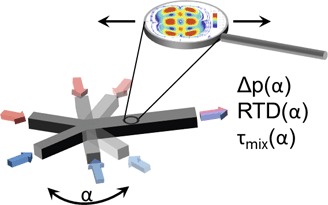
3D lattice Boltzmann method-based model simulations were performed to study the flow patterns and concentration distributions in a Y-mixer for different mixing angles. These simulations identified stratified laminar, vortex, and engulfment flow regimes. The residence time distributions for these flow patterns were characteristically different. Maximum mixing occurred in the 100° obtuse-angle Y-mixer.
Communication
Electrostatic Discharges of Droplets of Various Liquids during Splash Filling
- Pages: 1972-1975
- First Published: 08 June 2016

Electrostatics experts still do not know exactly whether splash filling of a vessel with a liquid may create an electrostatic hazard or not. This second part of the research project Splash Filling answers the question whether electrostatic discharges do occur during splash filling of several liters and which safety precautions may be necessary.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 10/2016
- Page: 1979
- First Published: 23 September 2016










