Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Editorial Board
Overview
Contents
Contents: Chem. Eng. Technol. 11/2016
- Pages: 1984-1989
- First Published: 21 October 2016
Highlights
Editorial
Essay
Continuous and Intensified Laboratory Process Development at Clariant
- Pages: 1993-1995
- First Published: 21 September 2016

The conversion of batch processes to continuous operating regimes presents multiple advantages. The laboratory process development in specialty chemical industry also has to be adapted accordingly for this purpose. Its implementation in the process development department at Clariant is described focusing on a general approach of a process transfer on laboratory scale.
Review
Oxidative Coupling of Methane: Opportunities for Microkinetic Model-Assisted Process Implementations
- Pages: 1996-2010
- First Published: 25 August 2016

Natural gas reserves are a rich source of methane that can be used as feedstock for the production of ethene via oxidative coupling. Finding a mathematical formula for a highly active and selective catalyst can save years of trial and error in catalyst research and reactor design. Microkinetic modeling is a powerful tool in the development of next catalyst generations.
Research Articles
Catalytic Methane Combustion on a Pt Gauze: Laser-Induced Fluorescence Spectroscopy, Species Profiles, and Simulations
- Pages: 2011-2019
- First Published: 21 July 2016
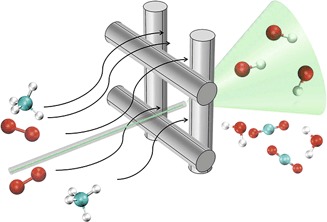
The investigation of oxidation reactions on Pt/Rh gauze catalysts is challenging due to their high reaction rate and complexity. Concentration profiles of OH• radicals, which represent an indicator species for these reactions, are measured for the catalytic combustion of methane in a single Pt-gauze reactor. CFD simulations of the profiles show that the reaction proceeds partly at the Pt surface and partly in the gas phase.
Periodic Operation with Modulation of Inlet Concentration and Flow Rate. Part I: Nonisothermal Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor
- Pages: 2020-2028
- First Published: 10 August 2016
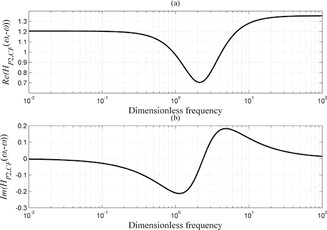
The nonlinear frequency response method is used to evaluate possible improvement of a nonisothermal CSTR by forced periodic operation. Simultaneous modulation of inlet concentration and flow rate can lead to significant improvement. Optimal forcing parameters maximizing the product yield are defined. Significant increases in product yield are obtained for both low and high forcing frequencies.
Three-Phase Heterogeneously Catalyzed Oxidative Esterification – Relevance of Oxygen Mass Transport
- Pages: 2029-2034
- First Published: 06 October 2016
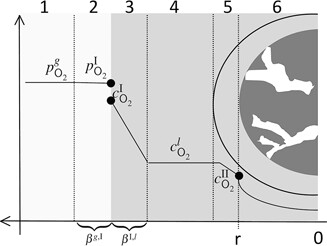
The field of applicable reactor setups for oxidative esterification, which is a green and mild alternative to classic routes, is extended to a fixed-bed recycle reactor with oxygen presaturation in the recycle. To investigate this three-phase reaction, a proper approach is the technical separation of gas-to-liquid mass transfers by introducing a gas absorption column in the liquid recycle flow.
Reductive Calcination of Mineral Magnesite: Hydrogenation of Carbon Dioxide without Catalysts
- Pages: 2035-2041
- First Published: 10 August 2016
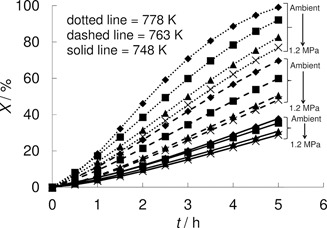
Catalytic hydrogenation of waste CO2 to value-added products such as methane or syngas is a promising technology. In reductive calcination, inorganic carbonates are calcined in a hydrogen atmosphere. Results are presented for the reductive calcination of mineral magnesite. Depending on process temperature and pressure, more than half of the CO2 is converted to either methane or syngas without admixure of catalysts.
Transferring Electrochemical CO2 Reduction from Semi-Batch into Continuous Operation Mode Using Gas Diffusion Electrodes
- Pages: 2042-2050
- First Published: 21 July 2016
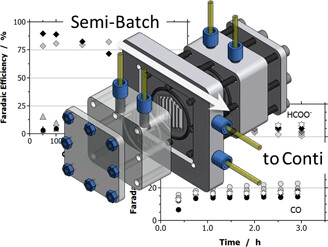
The transfer of electrochemical CO2 reduction into continuous mode of operation at industrially relevant current density is described. Technical realization is approached in terms of high reaction rates, continuous operation, and energetic efficiency using gas diffusion electrodes loaded with electrocatalyst nanoparticles, a microstructured flow cell, and electrolyte optimization.
Continuous-Flow Synthesis and Functionalization of Magnetite: Intensified Process for Tailored Nanoparticles
- Pages: 2051-2058
- First Published: 10 August 2016
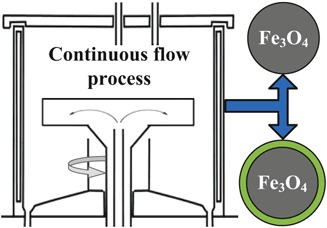
A continuous-flow process for tailored nanoparticles is established on a spinning disc reactor. Control over the particle properties, surface functionalization in a single step, and the absence of hazardous chemicals make this process especially reliable, efficient, and clean. Narrow particle size distributions along with high magnetizabilities qualify the ferrofluids for numerous applications.
Effect of Bed Height on the Performance of a Fixed Mo/HZSM-5 Bed in Direct Aromatization of Methane
- Pages: 2059-2065
- First Published: 15 August 2016
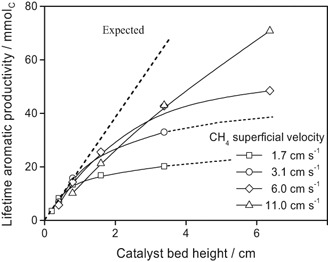
For extension of the catalytic lifetime of fixed catalyst bed reactors often the catalyst-overloading strategy is applied. The adaptability of this strategy to the Mo/HZSM-5 catalyst for non-oxidative methane dehydroaromatization was approved for the first time by evaluating the influence of bed height on the catalytic stability and lifetime aromatic productivity.
Dynamic Modeling of Fixed-Bed Fischer-Tropsch Reactors with Phase Change Material Diluents
- Pages: 2066-2076
- First Published: 15 August 2016
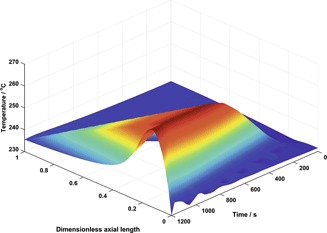
The concept of catalyst bed dilution using encapsulated phase change materials (PCM) in a Fischer-Tropsch fixed-bed reactor was investigated. The so-called α-model was modified and applied in order to study the time response of the reactor to various process disturbances. The effects of the thermal inertia introduced by the PCM on the reactor productivity are also discussed.
Prediction of Flow Patterns of Rotating Inclined Reactors by Using a Modified Permeability Approach
- Pages: 2077-2086
- First Published: 30 August 2016

A new type of reactor concept, a rotating inclined fixed bed reactor, leads to improvements in heterogeneous catalytic multiphase reactions. A comparison between experimental data and modeling by a computational fluid dynamics approach reveals that the model accurately predicts flow patterns. The model can be used to determine optimum operating conditions for various systems.
The Taylor-Couette Disc Contactor
- Pages: 2087-2095
- First Published: 06 October 2016

Liquid-liquid extraction is a leading technology that can increase the economic feasibility of separation processes and provides access to both a chemical reaction and separation in one reactor. For application in reactive bioseparations, the Taylor-Couette disc contactor may offer advantageous operation features. This paper investigates the hydro-dynamic characteristics of the Taylor-Couette disc contactor.
Thermal Decomposition of Sulfur Compounds and their Role in Coke Formation during Steam Cracking of Heptane
- Pages: 2096-2106
- First Published: 12 October 2016

Sulfur-containing additives influence product selectivity, coke deposition, and CO production in steam cracking processes. Four different sulfur compounds were tested in a pilot plant. Online 2D gas chromatography with sulfur chemiluminescence detection was applied to characterize the sulfur compounds and to quantify the product composition. In all cases, coke formation increased while CO formation decreased.
Analysis of Three-Phase Catalytic Fuel Synthesis Reactors for Flexible Operation
- Pages: 2107-2116
- First Published: 21 July 2016
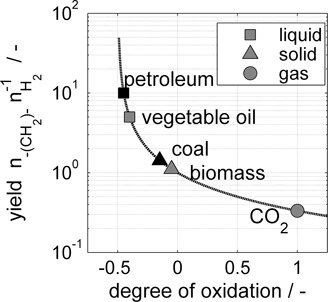
In a future energy system, flexible reactor operation may be needed if renewable electricity is converted to chemical energy carriers. The investigation of transient catalyst and reactor effects in three-phase catalytic synthesis reactors will help with the scale-up of industrial applications and can be applied to other synthesis reactions.
Control Strategy and Comparison of Tuning Methods for Continuous Lactide Ring-Opening Polymerization
- Pages: 2117-2125
- First Published: 25 August 2016
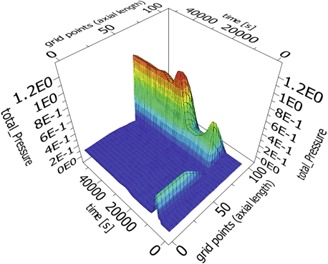
The closed-loop dynamics of a continuous process for the manufacturing of polylactic acid by ring-opening polymerization is studied by simulations. A control strategy is envisioned that dampens the negative effects of variations of monomer contaminants on the process. The implementation of the proposed control strategy can improve the operability, safety, and productivity of industrial plants.
Periodic Operation with Modulation of Inlet Concentration and Flow Rate Part II: Adiabatic Continuous Stirred-Tank Reactor
- Pages: 2126-2134
- First Published: 06 October 2016
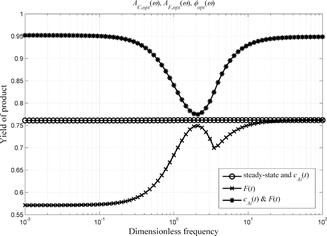
The nonlinear frequency response method is used to evaluate possible improvement of an adiabatic CSTR by forced periodic operation. The results are applied to a laboratory-scale reactor for hydrolysis of acetic anhydride. Significant increases in product yield are predicted for simultaneous modulation of inlet concentration and flow rate with optimized forcing parameters.
Structural and Operational Optimality of Adsorptive Reactors
- Pages: 2135-2141
- First Published: 22 August 2016
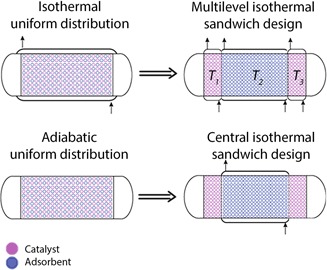
Reliable techniques and robust methodologies are provided by which a multifold improved performance of potential adsorptive reactors could be achieved and thus the industrial implementation of this up-and-coming technology is facilitated. The potential of temperature profiling to drive forward the macrostructuring of adsorptive reactors for optimizing the performance is demonstrated.
Modular and Scalable Fischer-Tropsch Reactor for Small-Scale Gas-to-Liquid Production
- Pages: 2142-2150
- First Published: 22 August 2016

A simulation study is performed on conceptual design for a Fischer-Tropsch reactor capable of providing the petroleum and hydrocarbon waste processing sectors with a low-cost and low-risk gas-to-liquid technology for monetizing small-size gas sources. The best candidate design is presented, being suitable for processing the associated gas usually flared at oil exploration and production sites.
Operation of a Small-Scale Demonstration Plant for Biodiesel Synthesis under Supercritical Conditions
- Pages: 2151-2163
- First Published: 15 August 2016
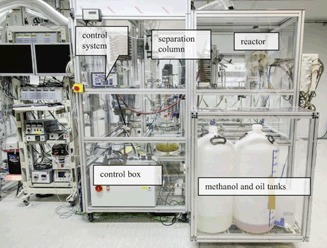
Heterogeneously catalyzed synthesis of biodiesel was performed under supercritical conditions in a newly designed small-scale demonstration plant. The simulation software Aspen Plus® was applied to find a strategy for minimization of the energy demand for the product purification stages. Acid-modified γ-Al2O3 and La2O3 supported by γ-Al2O3 were identified as most promising catalyst candidates.
Overview
Overview Contents: Chemie Ingenieur Technik 11/2016
- Page: 2167
- First Published: 21 October 2016










