Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 139, Issue 41
- First Published: 23 September 2022

The cover picture by Dagmar D'hooge shows the micrographs of different ABS based mono- and hybrid nanocomposite filaments for 3D printing applications. Developing new feedstock materials for fused filament fabrication with increased properties is challenging and by designing hybrid materials, it is possible to optimize the dispersion of nanoparticles and increase the properties of the final materials. DOI: 10.1002/app.52922
ISSUE INFORMATION
Editorial Board, Aims & Scope, Table of Contents
- First Published: 23 September 2022
REVIEW
Effect of synergy between pyrolysis carbon black and carbon nanofibers on composite properties
- First Published: 06 August 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
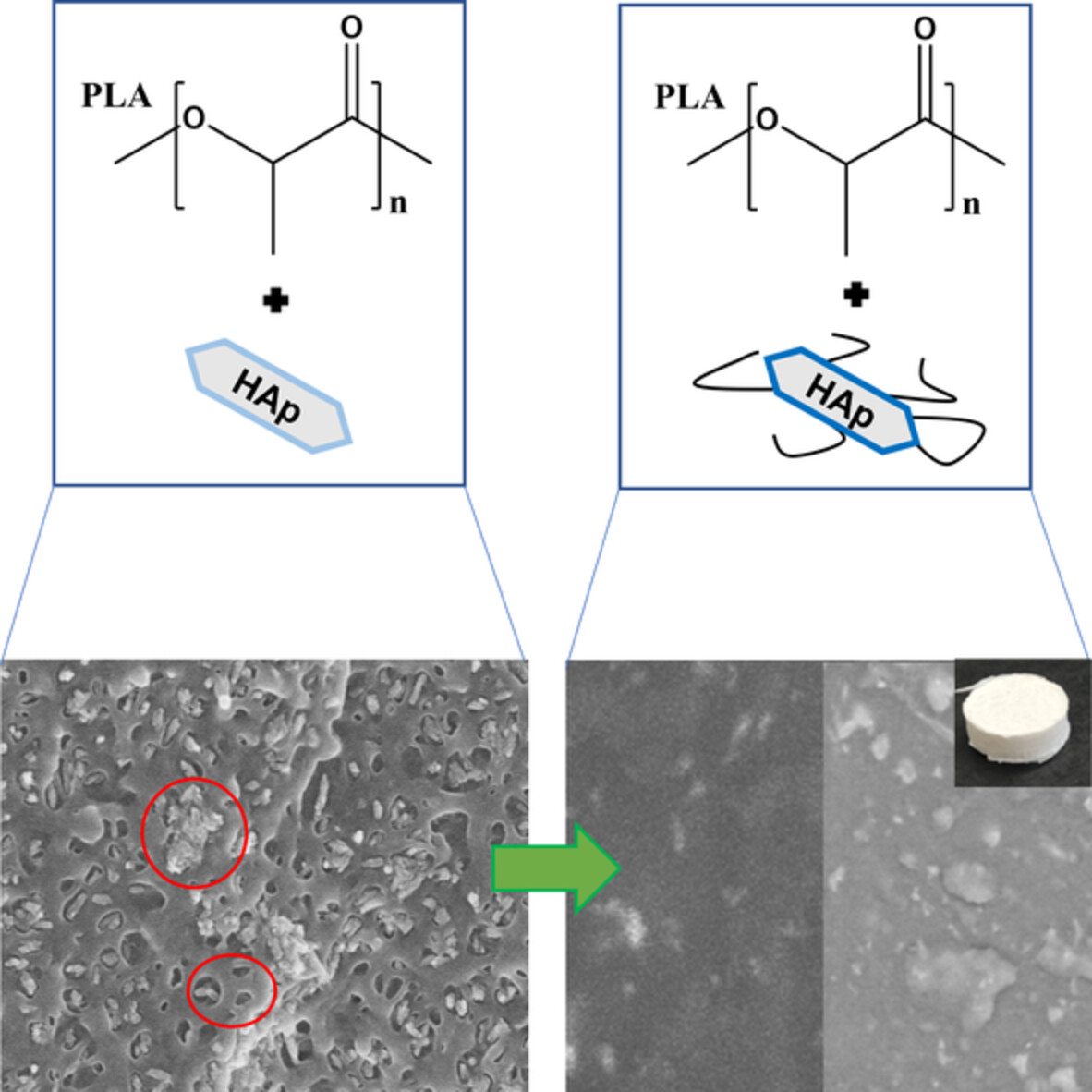
A simple approach for a PEG-b-PLA-compatibilized interface in PLA/HAp nanocomposite. From the design of the material to the improvement of thermal/mechanical properties and bioactivity
- First Published: 13 August 2022
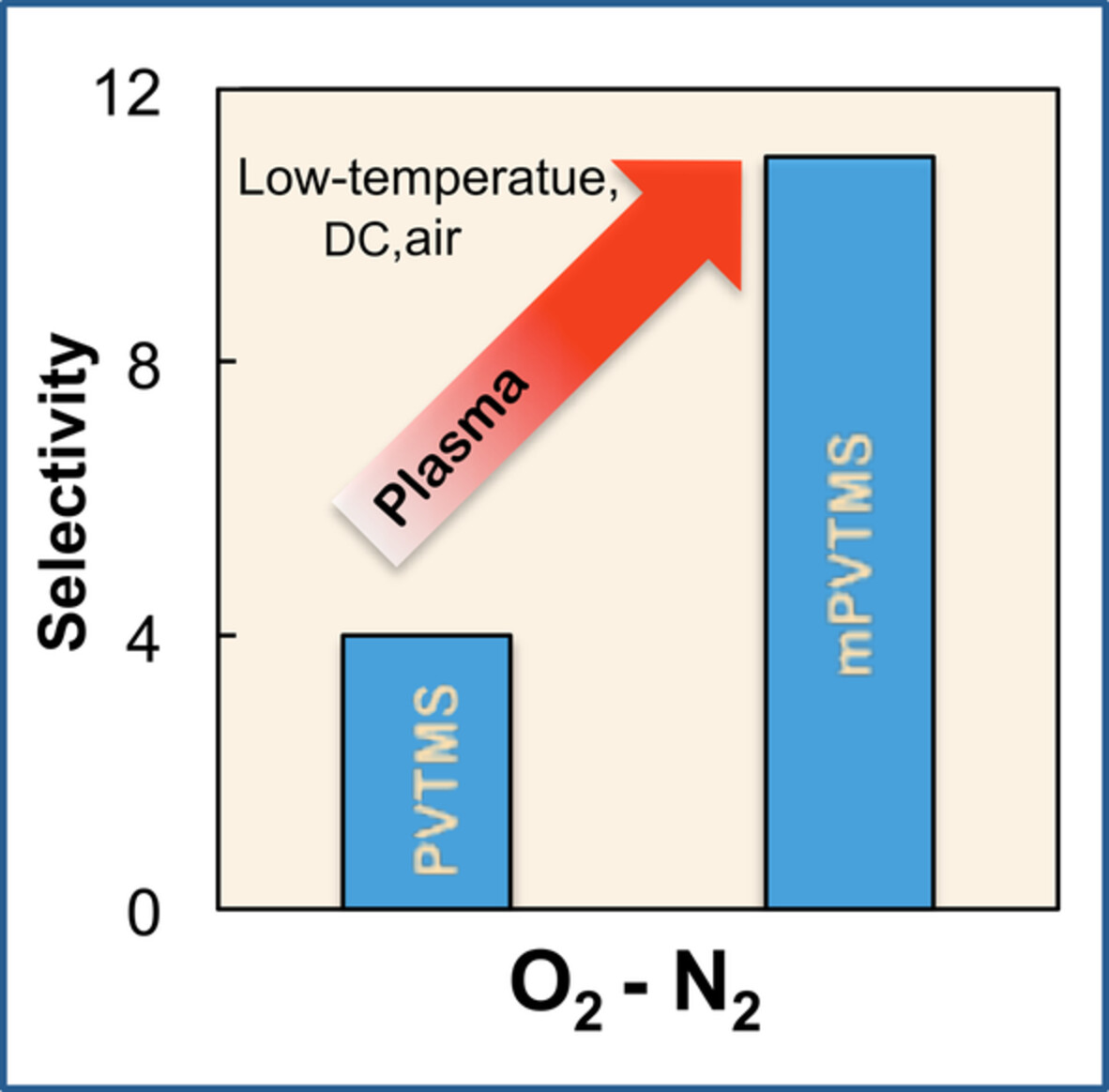
The gas permeability properties of poly(vinyltrimethylsilane) treated by low-temperature plasma
- First Published: 13 July 2022
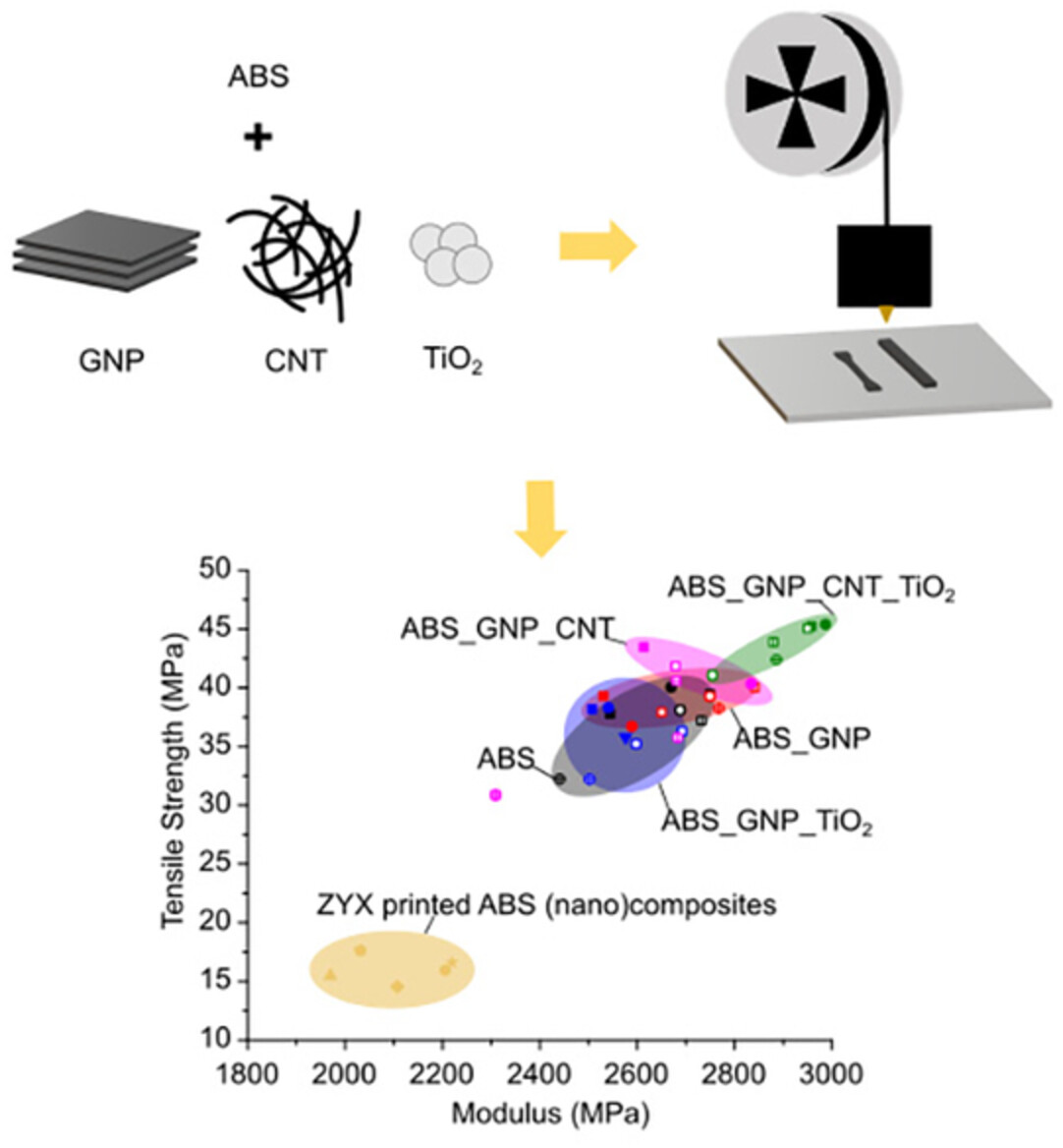
Exploiting mono- and hybrid nanocomposite materials for fused filament fabrication with acrylonitrile butadiene styrene as polymer matrix
- First Published: 28 July 2022
Synthesis of cyclotriphosphazene-containing imidazole as a thermally latent hardener for epoxy resins and its application in carbon fiber reinforced composites
- First Published: 01 August 2022
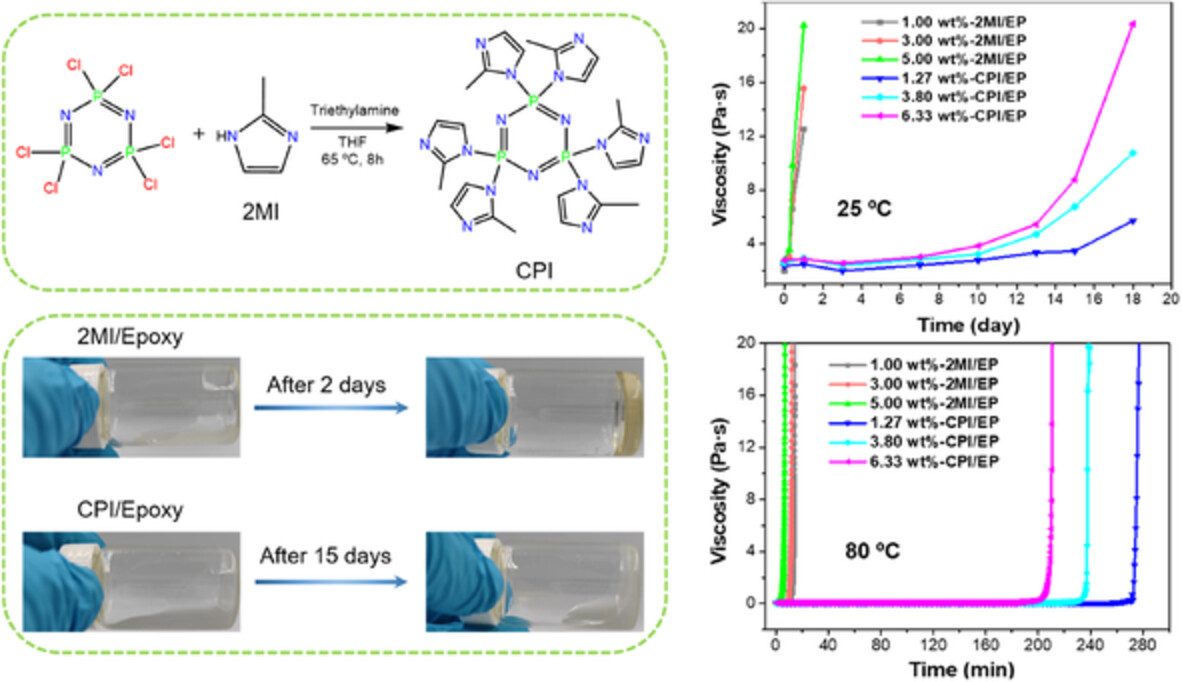
A cyclotriphosphazene-containing imidazole (CPI) hardener for epoxy resins was successfully prepared. The prepared CPI exhibits dramatically improved thermal latency toward epoxy monomers at both room temperature and 80°C. The epoxy resins cured by CPI show comparable thermal and mechanical properties compared with the epoxy resins cured by conventional imidazole hardeners.
Synthesis of a low viscosity amphoteric polyacrylamide and its application in oilfield profile control
- First Published: 18 August 2022
A low viscosity amphoteric polyacrylamide (LHPAM) was synthesized by causing the polymerization and substitution reaction. The synthesis was successfully characterized by FTIR, SEM, and EDS. It is proved by TG and DSC that LHPAM has good thermal stability, and found that LHPAM has strong flocculation through ultraviolet–visible spectrophotometer. It can be found from changing time, temperature, and viscosity that LHPAM has lower viscosity than HPAM. In addition, LHPAM can reacts with Cr3+ to form a gel that has longer gelation time and smaller resistance coefficient than HPAM, but the final gelation strength is the same. This study expands the application of HPAM in profile control and water shutoff, which is of great significance for enhanced oil recovery.
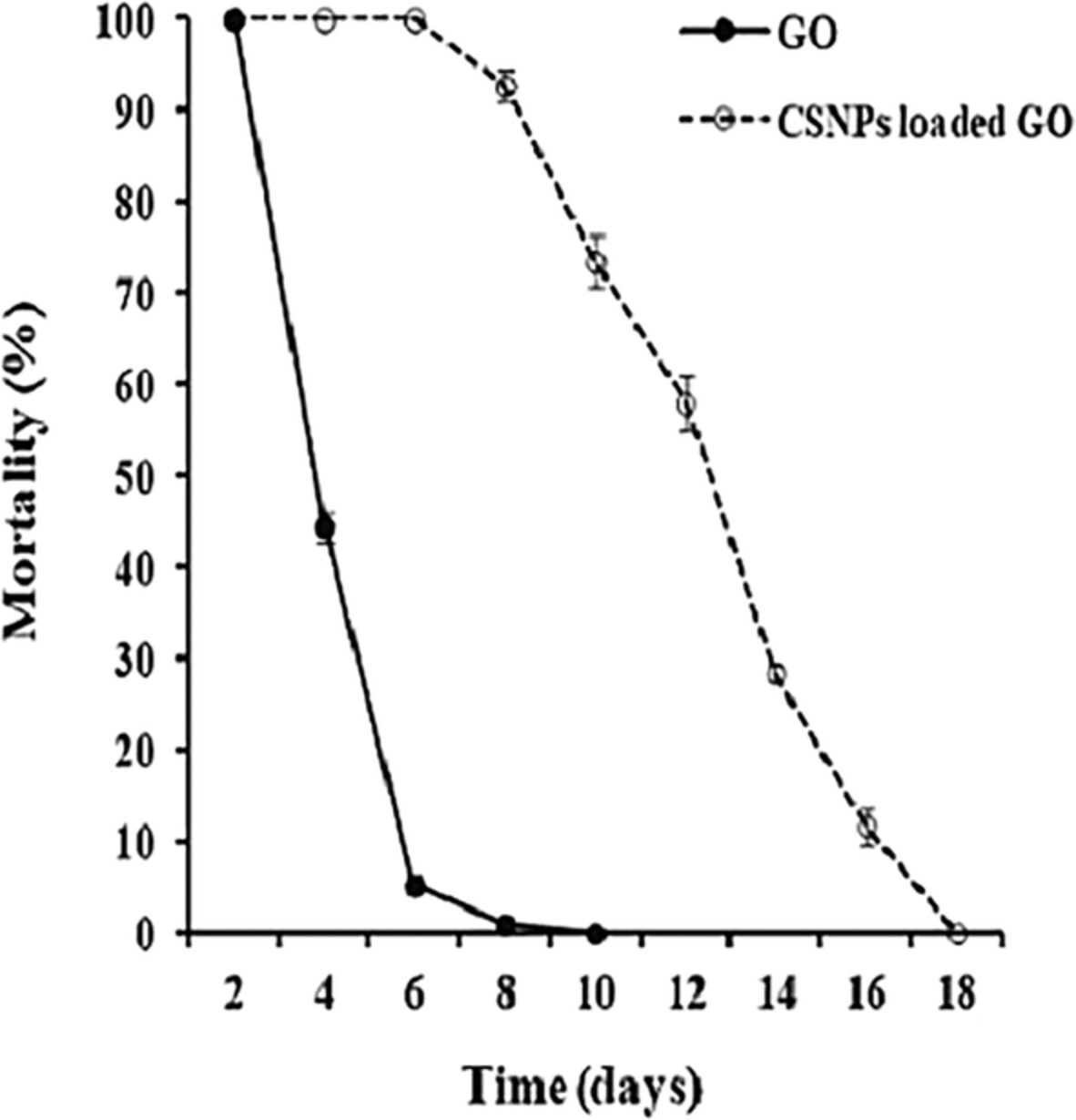
Polymeric nanoparticles containing different oils as insecticides against the storage pest Tribolium castaneum (Herbst) (Coleoptera: Tenebrionidae)
- First Published: 12 August 2022
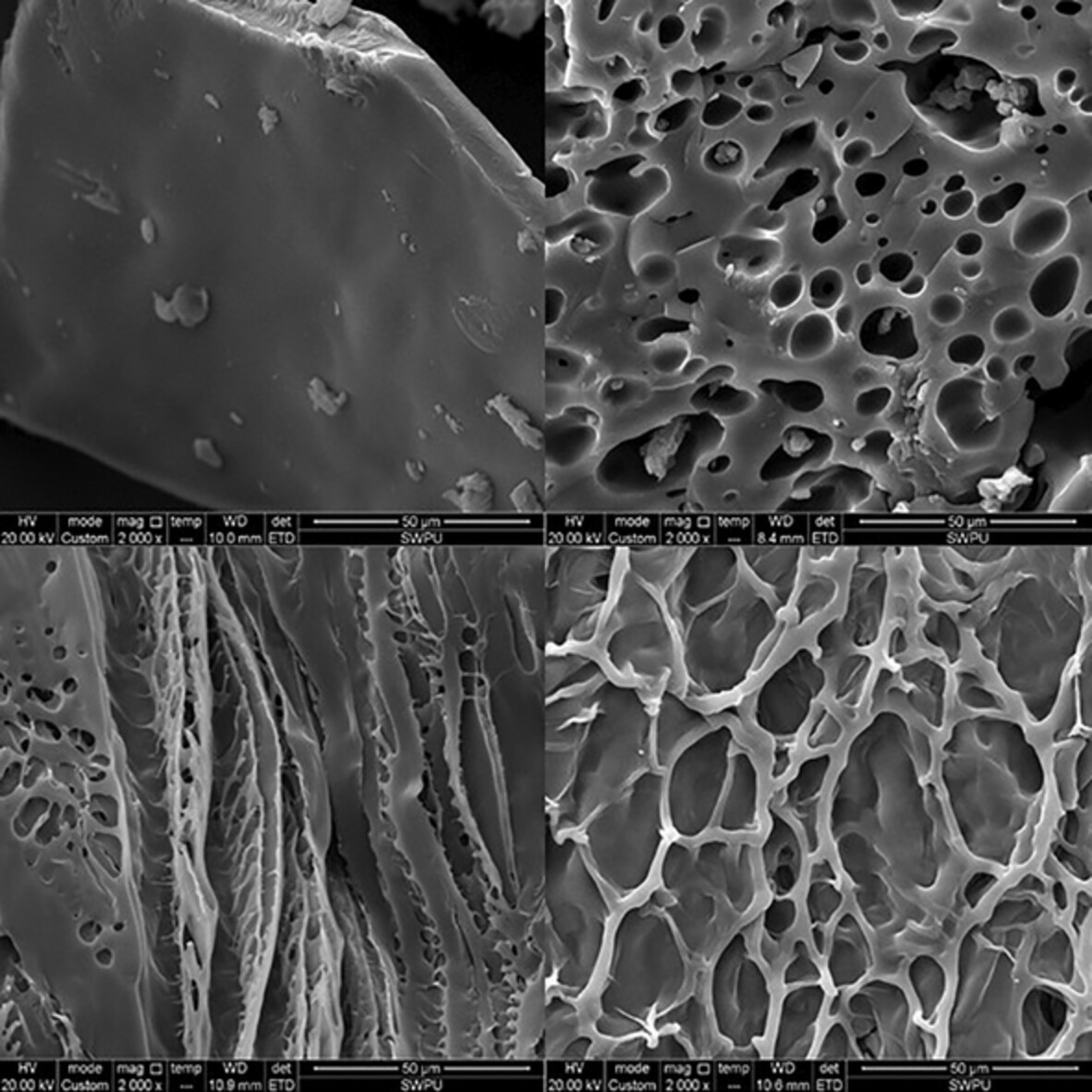
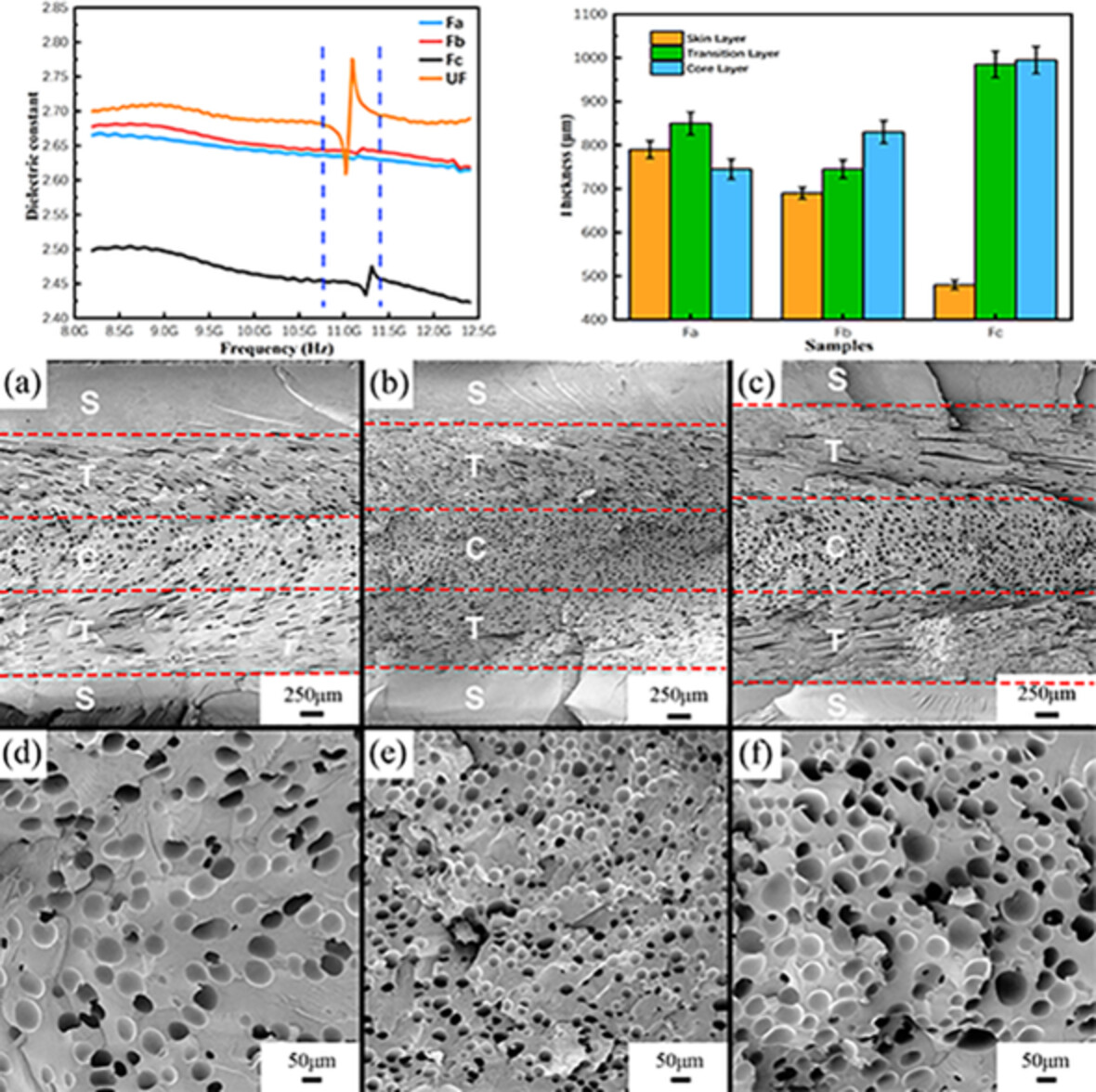
Lightweight, low temperature fatigue resistant, and low dielectric microcellular polyetheretherketone foams fabricated by microcellular injection molding
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Glucose-sensitive structural color change of cholesteric liquid crystal formed by hydroxypropyl cellulose with phenylboronic acid moieties
- First Published: 06 August 2022
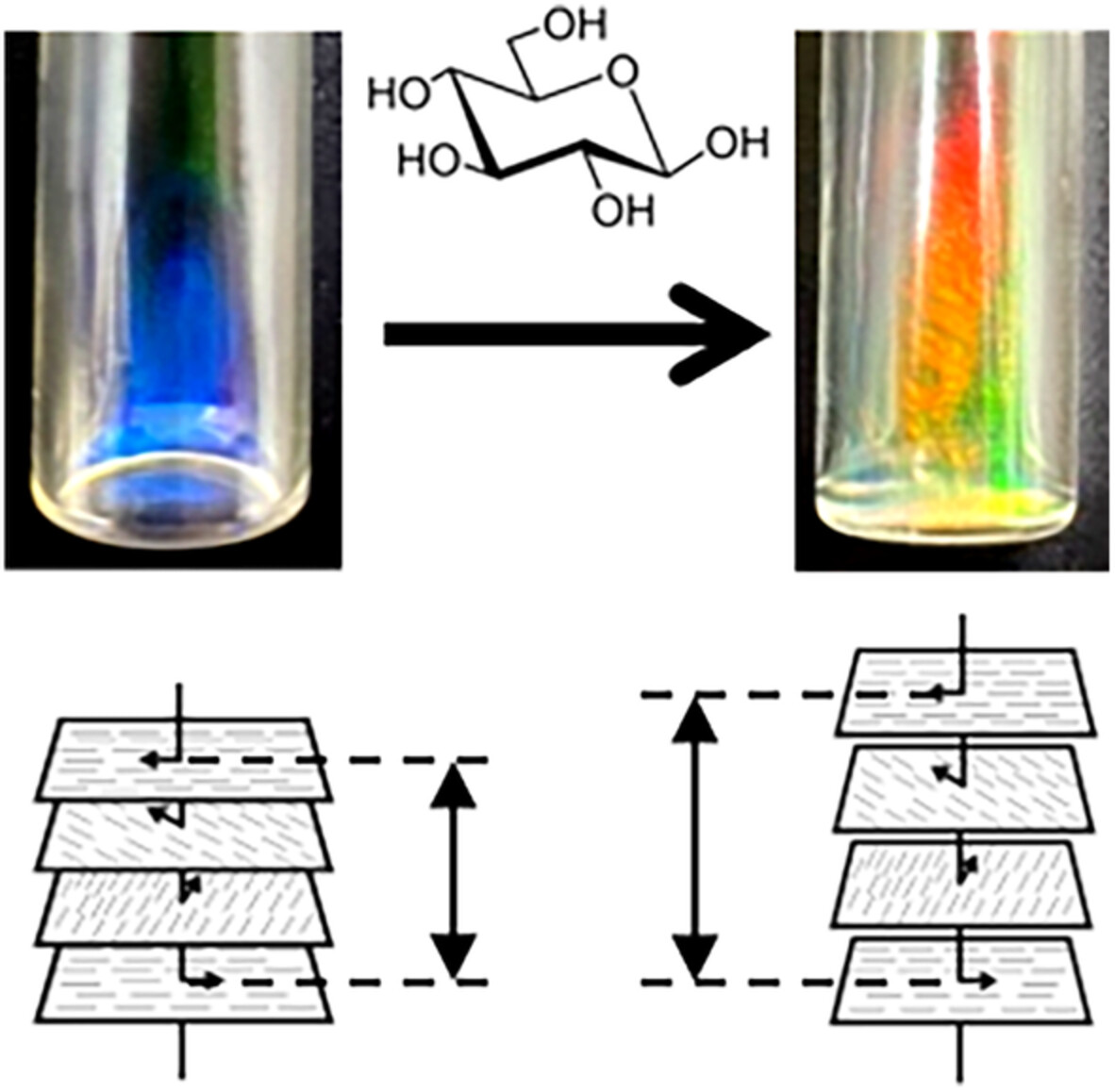
Hydroxypropyl cellulose with phenylboronic acid moieties (PBA-HPC) generates cholesteric liquid crystals (ChLCs) in aqueous solutions. The structural color of the PBA-HPC aqueous ChLC red shifts in response to glucose addition as a result of the formation of a complex between the PBA-side groups and glucose. This system can be useful as enzyme-free colorimetric glucose sensing.
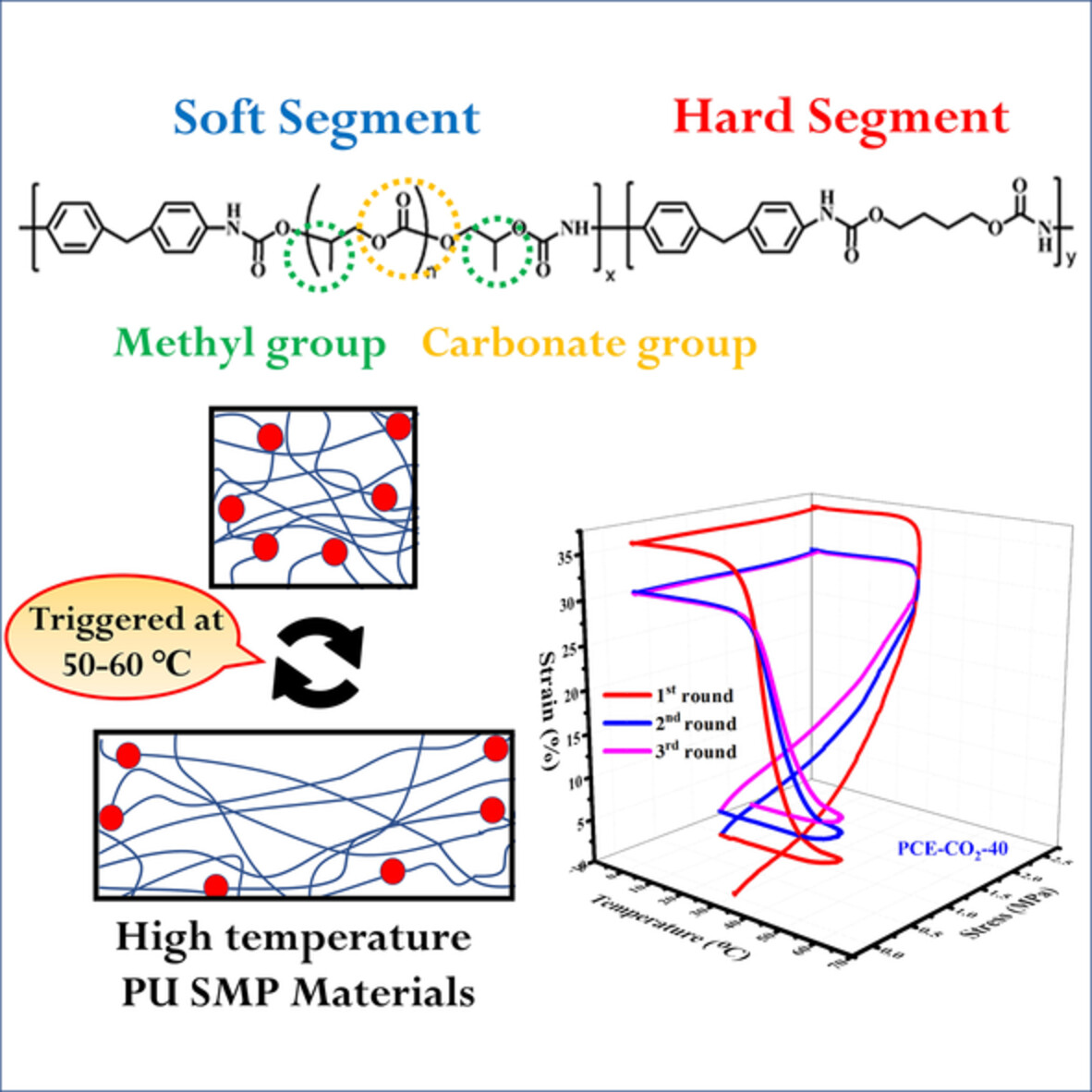
Tunable shape memory property polyurethane with high glass transition temperature composed of polycarbonate diols
- First Published: 05 August 2022
Hybrid modeling approach for polymer melt index prediction
- First Published: 15 August 2022

Hybrid modeling approach that combines the mechanistic modeling and machine learning is proposed to predict the melt index of a thermoplastic polymer during the polymerization process. The results of this research suggest that the prediction performance of the proposed hybrid model is greater than that of the traditional data-only machine learning model.
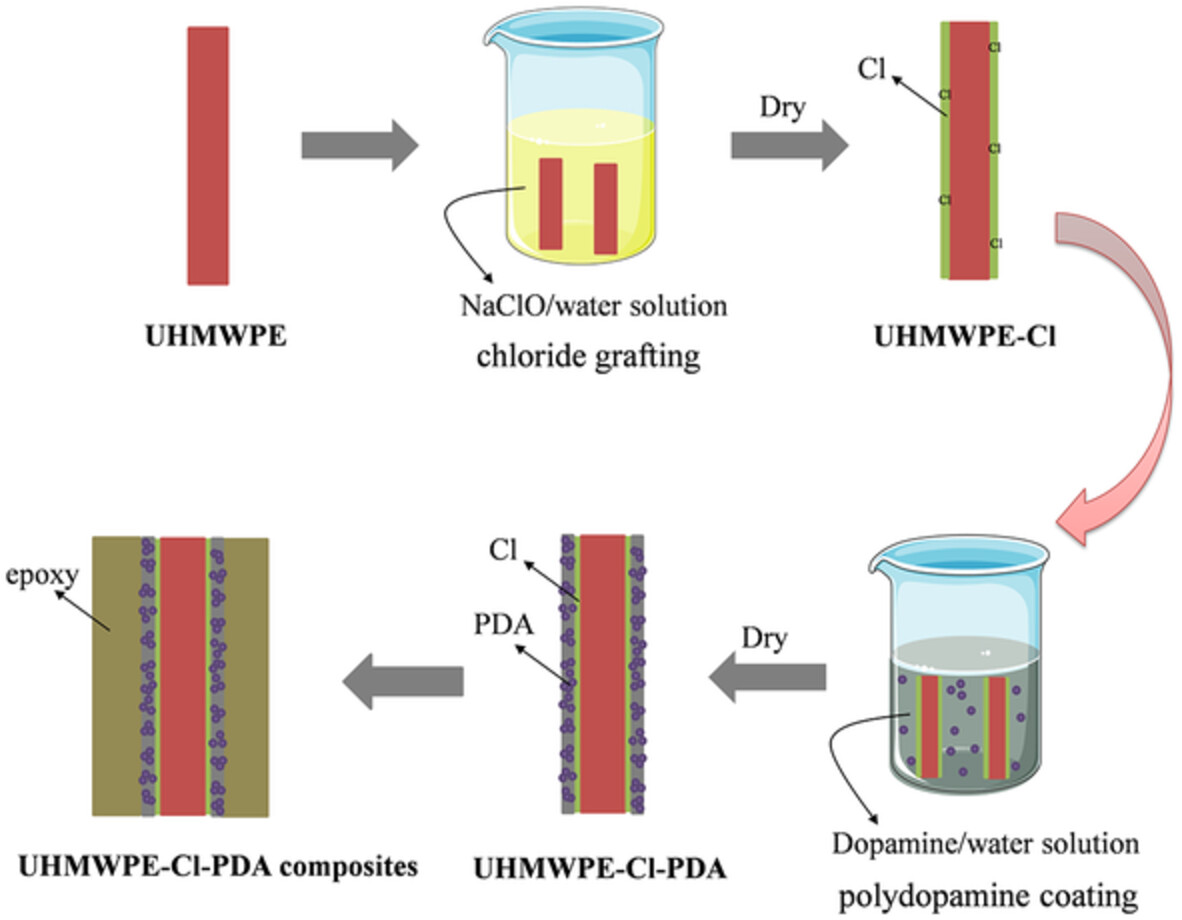
Surface modification of UHMWPE fibers with chlorination and polydopamine for enhancing the mechanical properties of composites
- First Published: 08 August 2022
Aggregation behavior of triblock terpolymer poly[n-butyl acrylate-block-N-isopropylacrylamide-block-2-(dimethylamino)ethyl acrylate] at the air/water interface
- First Published: 03 August 2022
Development of renewable thermosetting polymers based on grape seed oil derivatives
- First Published: 12 August 2022
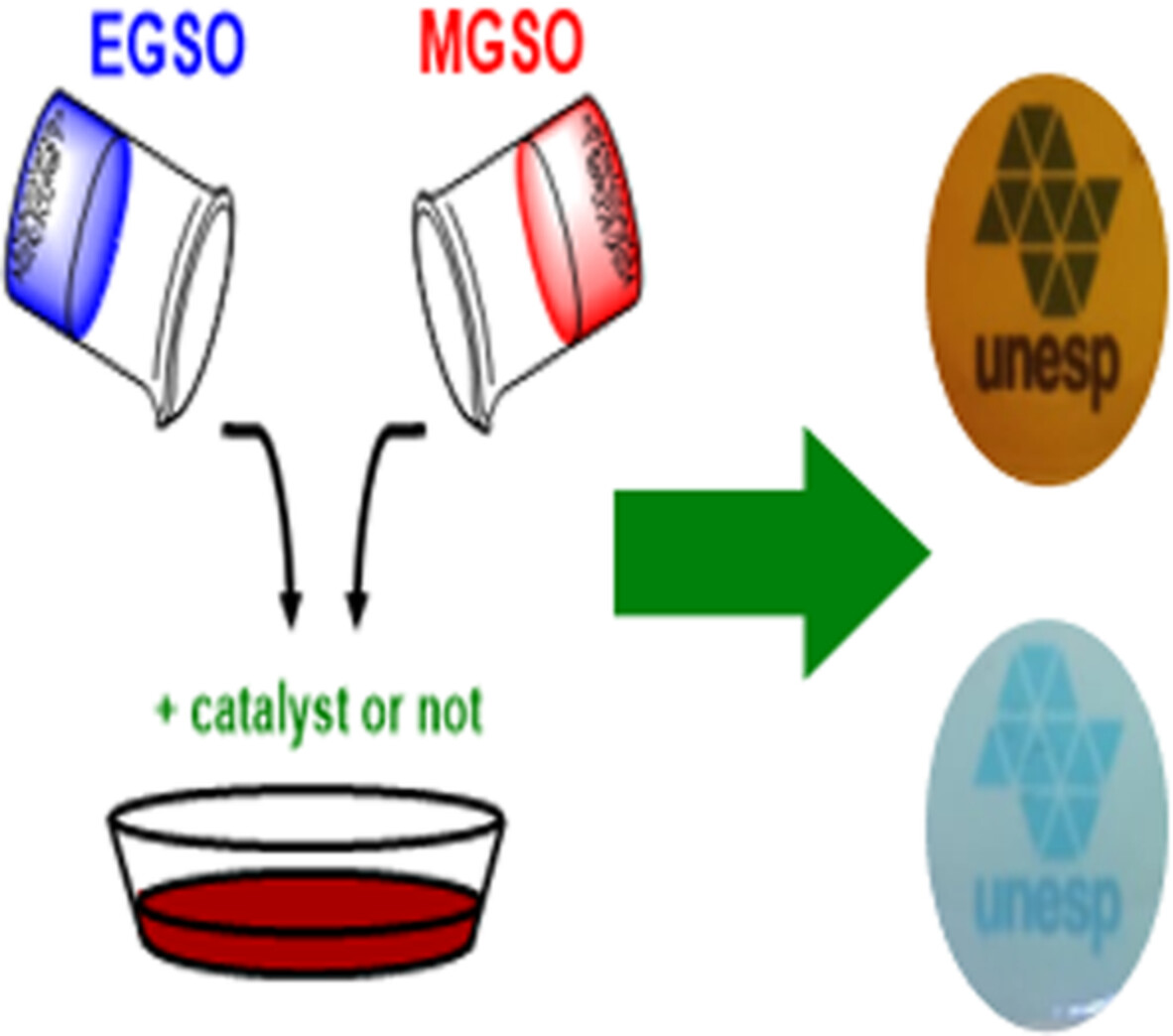
Renewable polymers were obtained from two grape seed oil monomers using different catalysts and also in absence of them. 1Im was the most selective catalyst and using 5.0 mol% was enough to almost suppress the etherification reaction. However, using 1% or 5% of 1Im did not change significantly the polymers final properties.
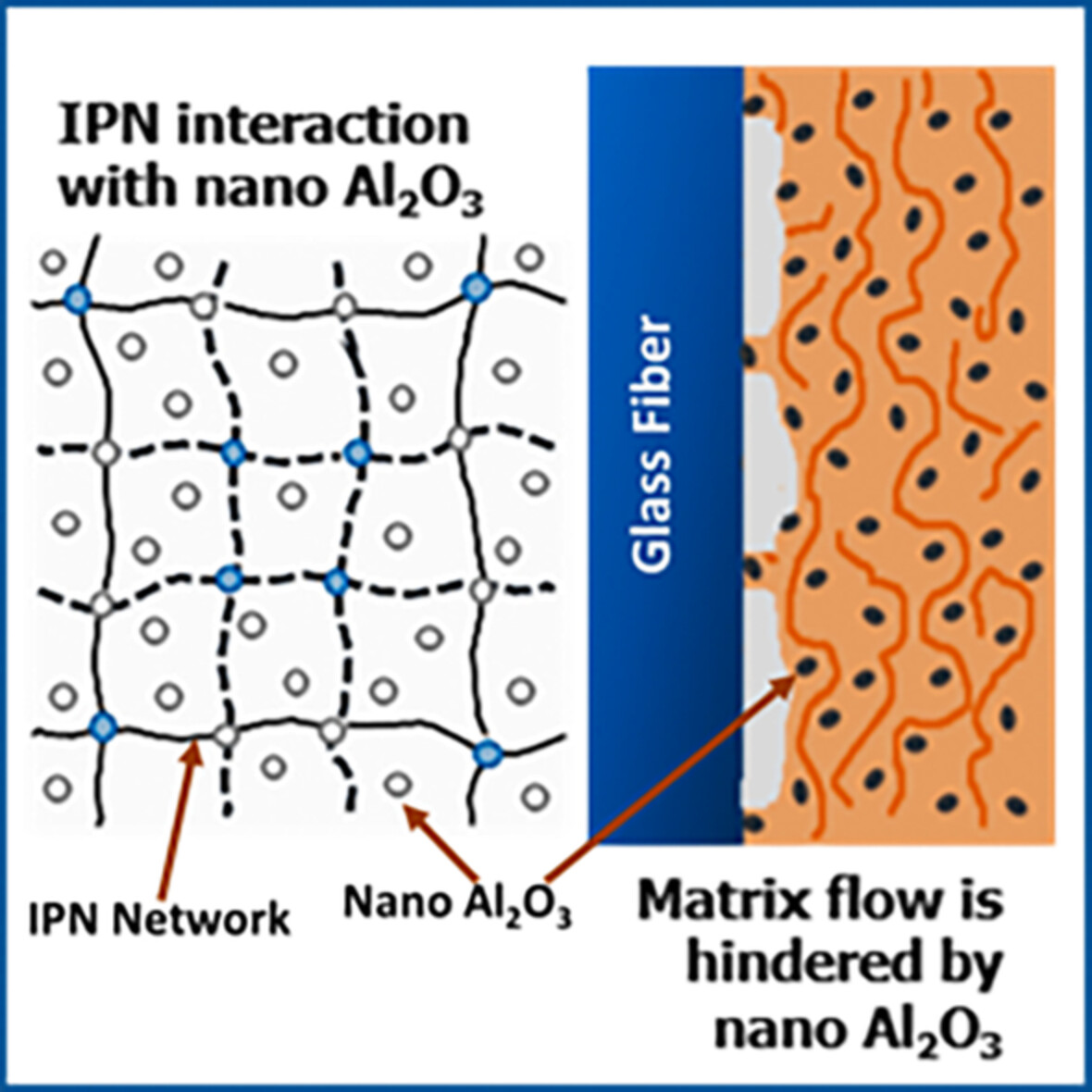
Elevated temperature mechanical behavior of nano Al2O3 embedded interpenetrating polymer network/glass fiber composites
- First Published: 11 August 2022
A high-performance self-healing polyurea material based on exchangeable aromatic disulfide
- First Published: 06 August 2022
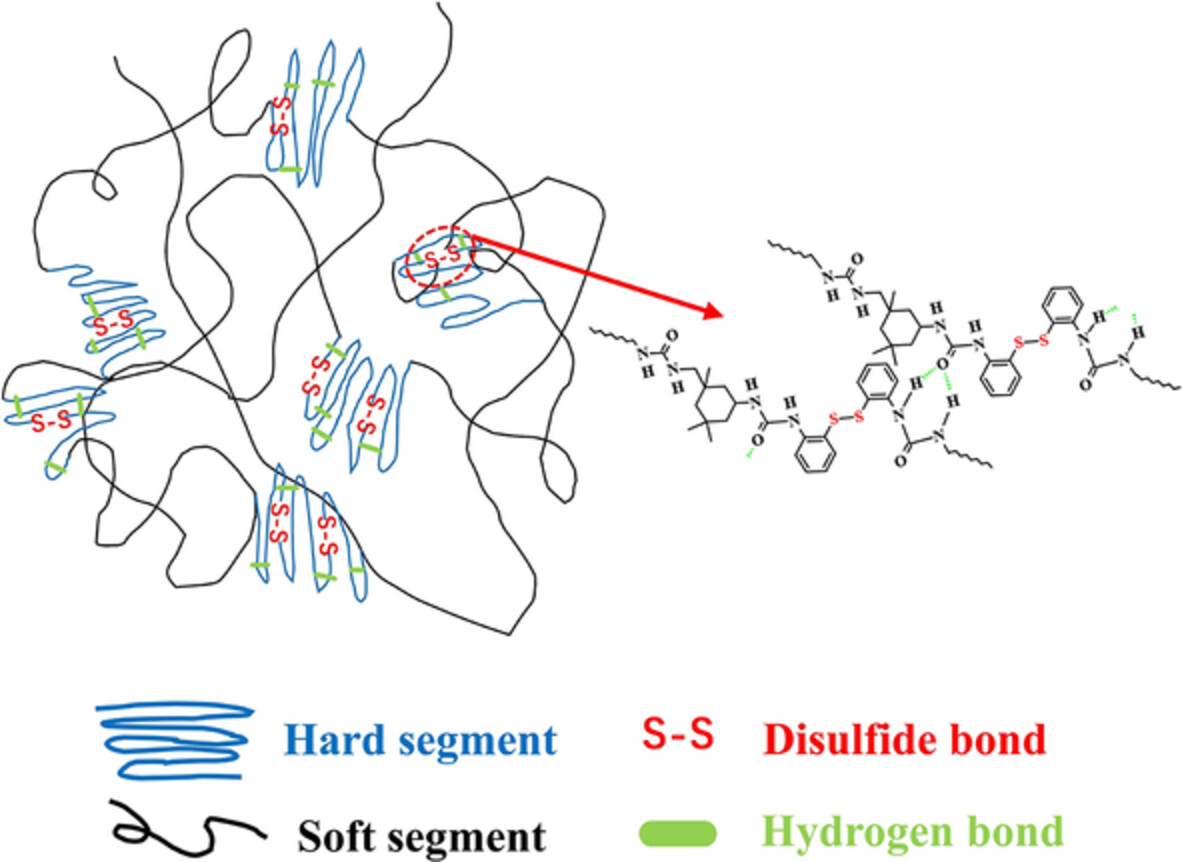
A series of polyureas with reversible disulfide bonds were designed and fabricated, and the effect of chain extender content on the microstructure, mechanical properties and self-healing ability of polyurea materials was investigated. The representative PU4 sample exhibited both superior mechanical properties and excellent self-repairing properties.
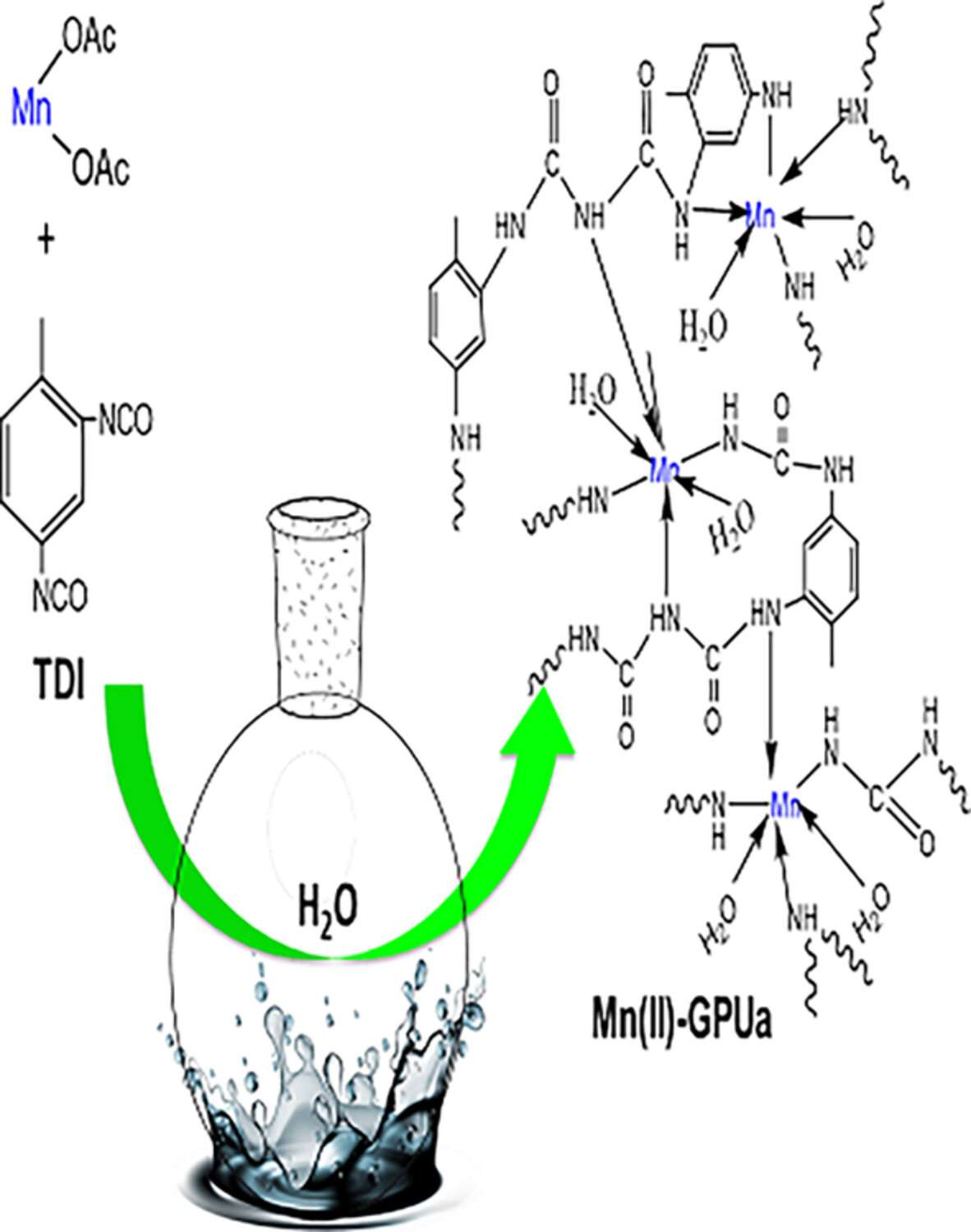
Development of nanostructured green divalent manganese-coordinated polyurea
- First Published: 08 August 2022
Synthesis of new copolyimides containing pyridine and morpholine groups for gas separation through molecular design and simulation
- First Published: 18 August 2022
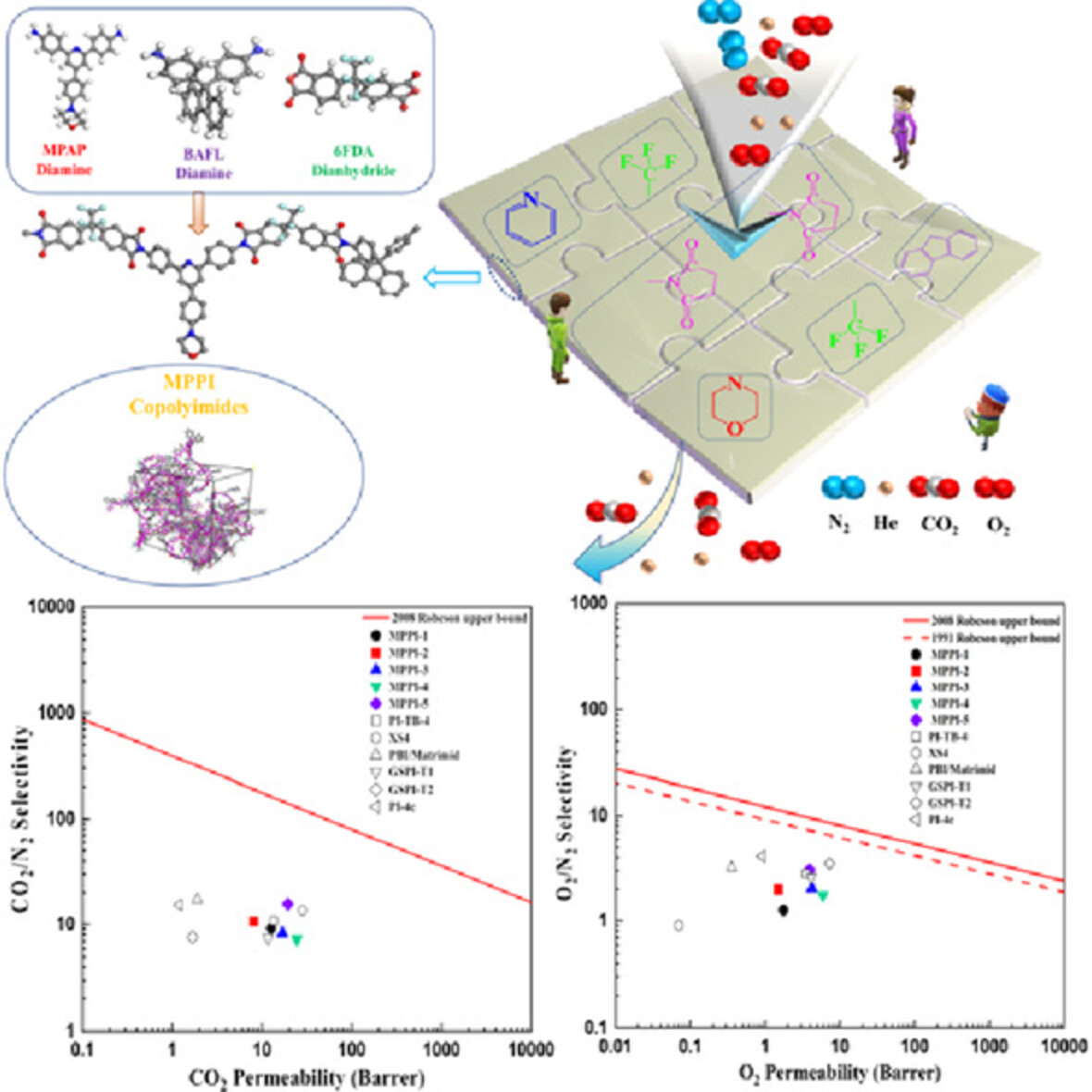
Via a one-step copolymerization reaction, a kind of new morpholinyl polyimide was synthesized and characterized, and also applied in gas separation field. This morpholinyl polyimide displays outstanding properties and respectable gas separation applications. Through molecular simulation, the simulation results further confirmed the reliability of experimental data.
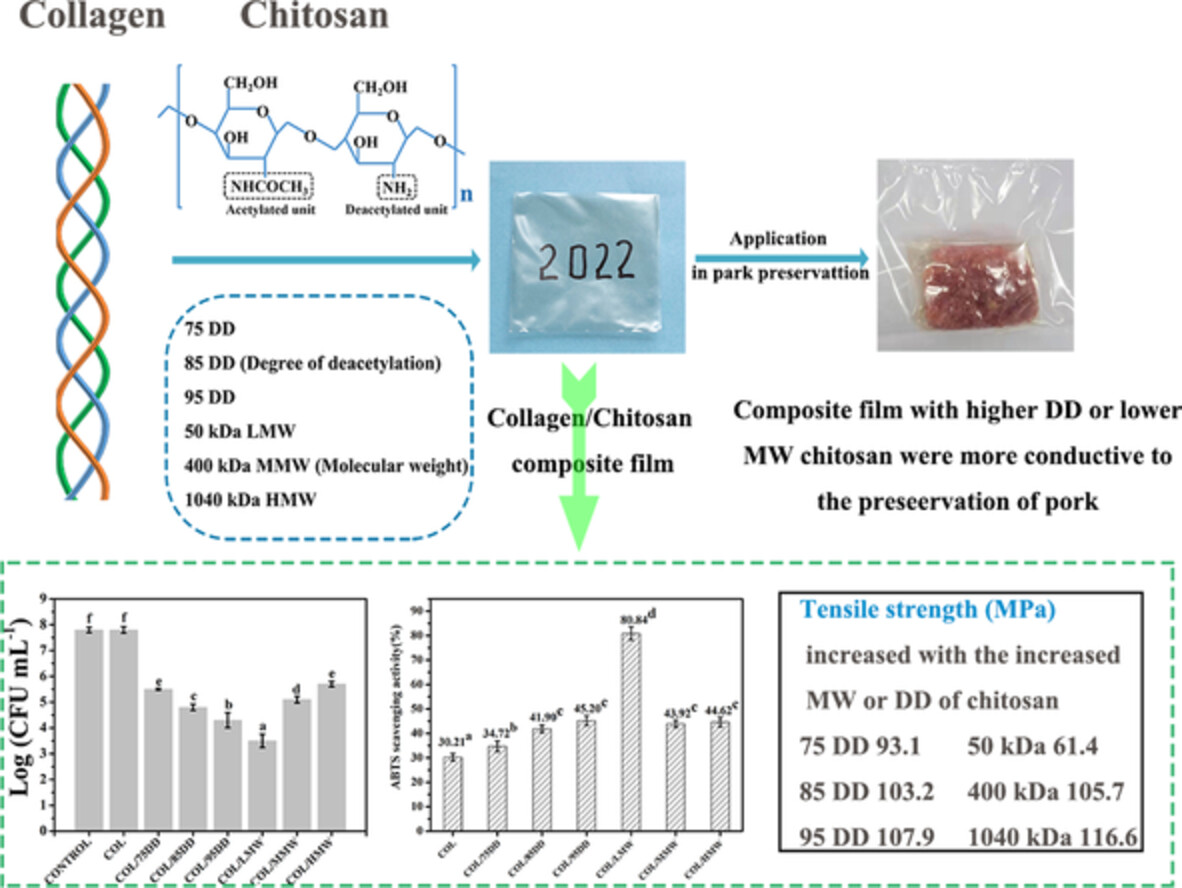
Effects of chitosan molecular weight and deacetylation degree on the properties of collagen-chitosan composite films for food packaging
- First Published: 05 August 2022
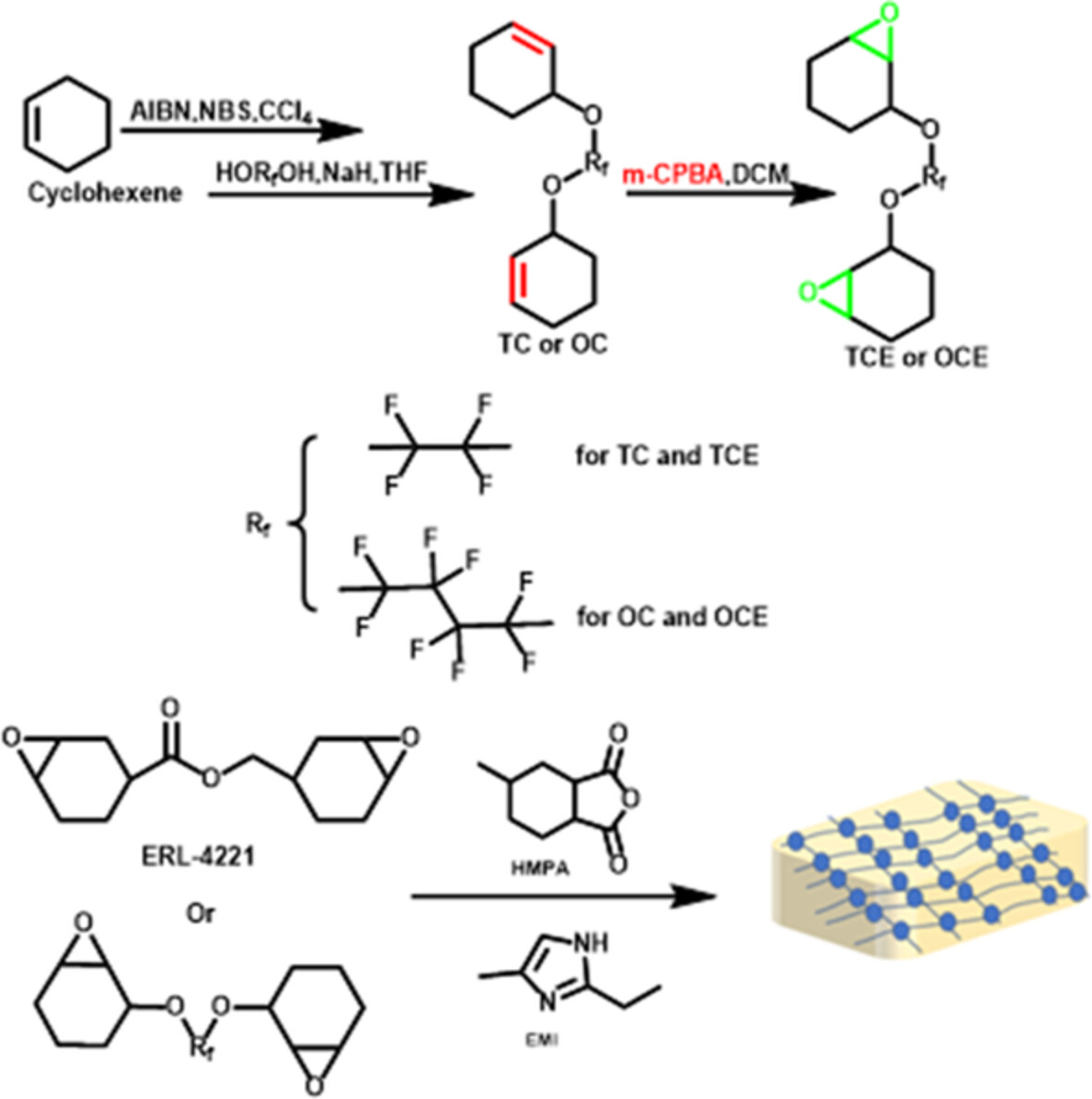
Synthesis and properties of cycloaliphatic diepoxides containing fluorinated linker
- First Published: 11 August 2022
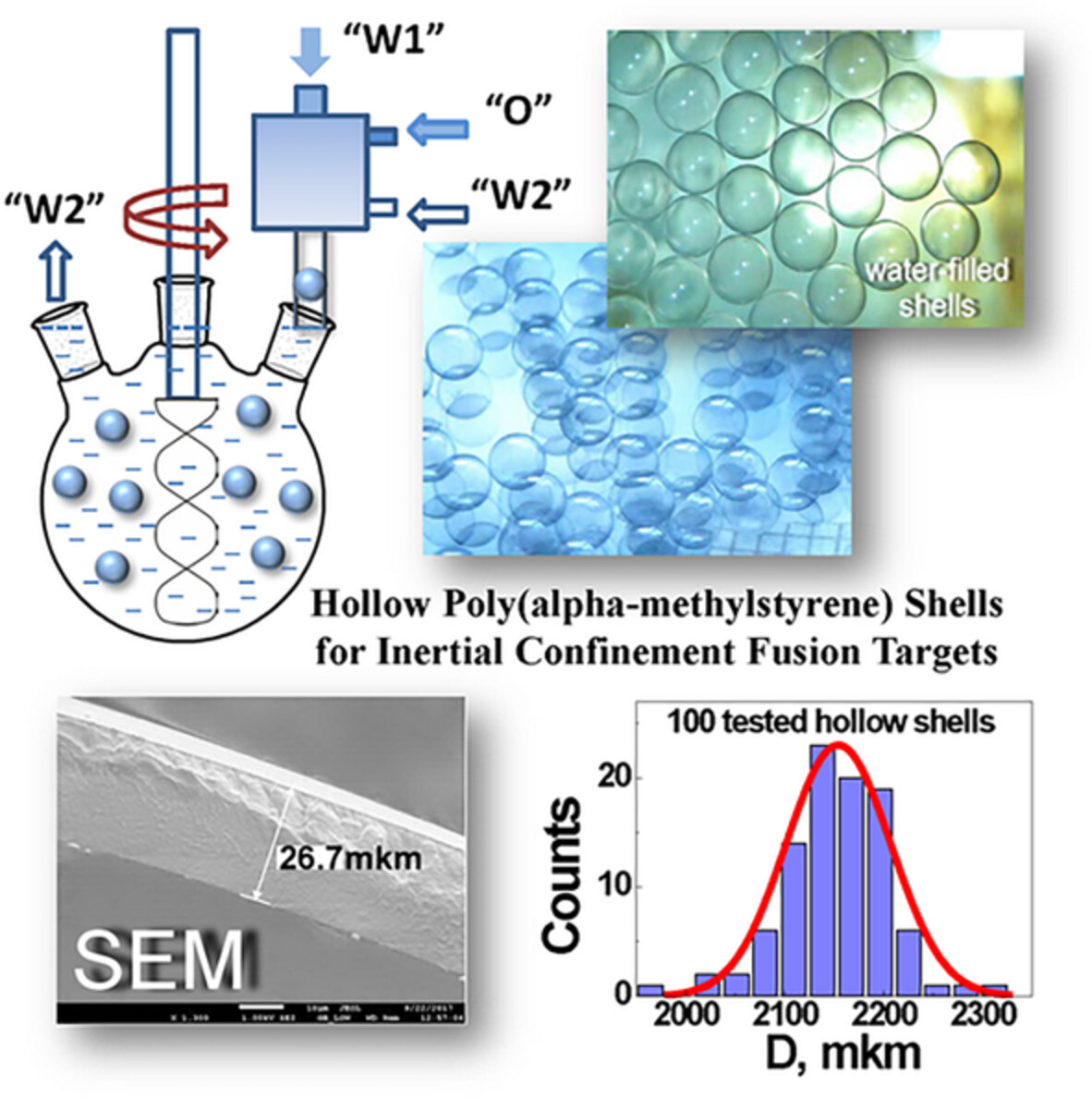
Fabrication of hollow poly(alpha-methylstyrene) shells for inertial confinement fusion targets
- First Published: 12 August 2022
Eco-friendly superabsorbent hydrogels based on starch, gellan gum, citric acid, and nanoclays for soil humidity control
- First Published: 11 August 2022
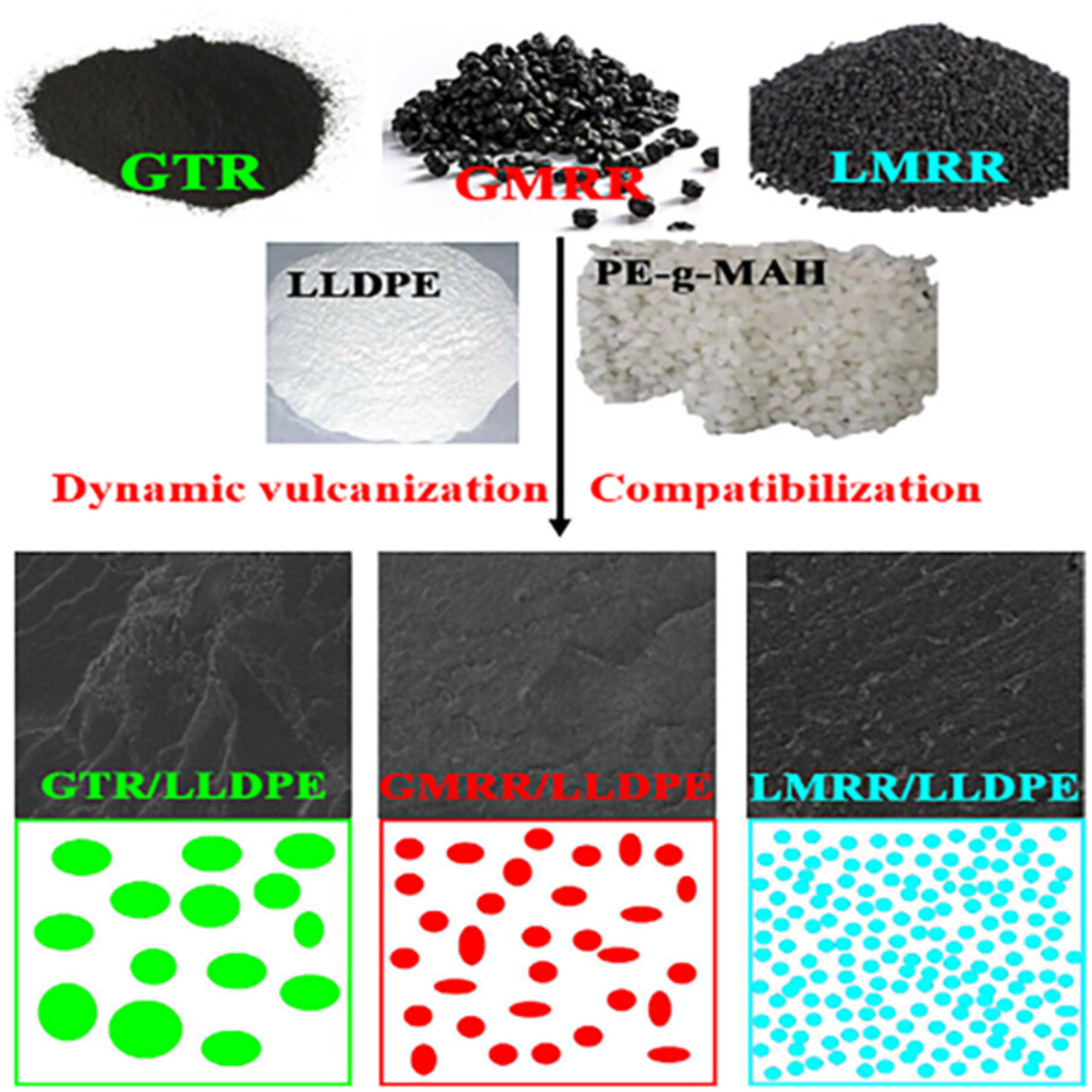
Compatibilized thermoplastic elastomers based on highly filled polyethylene with ground tire rubber
- First Published: 05 August 2022
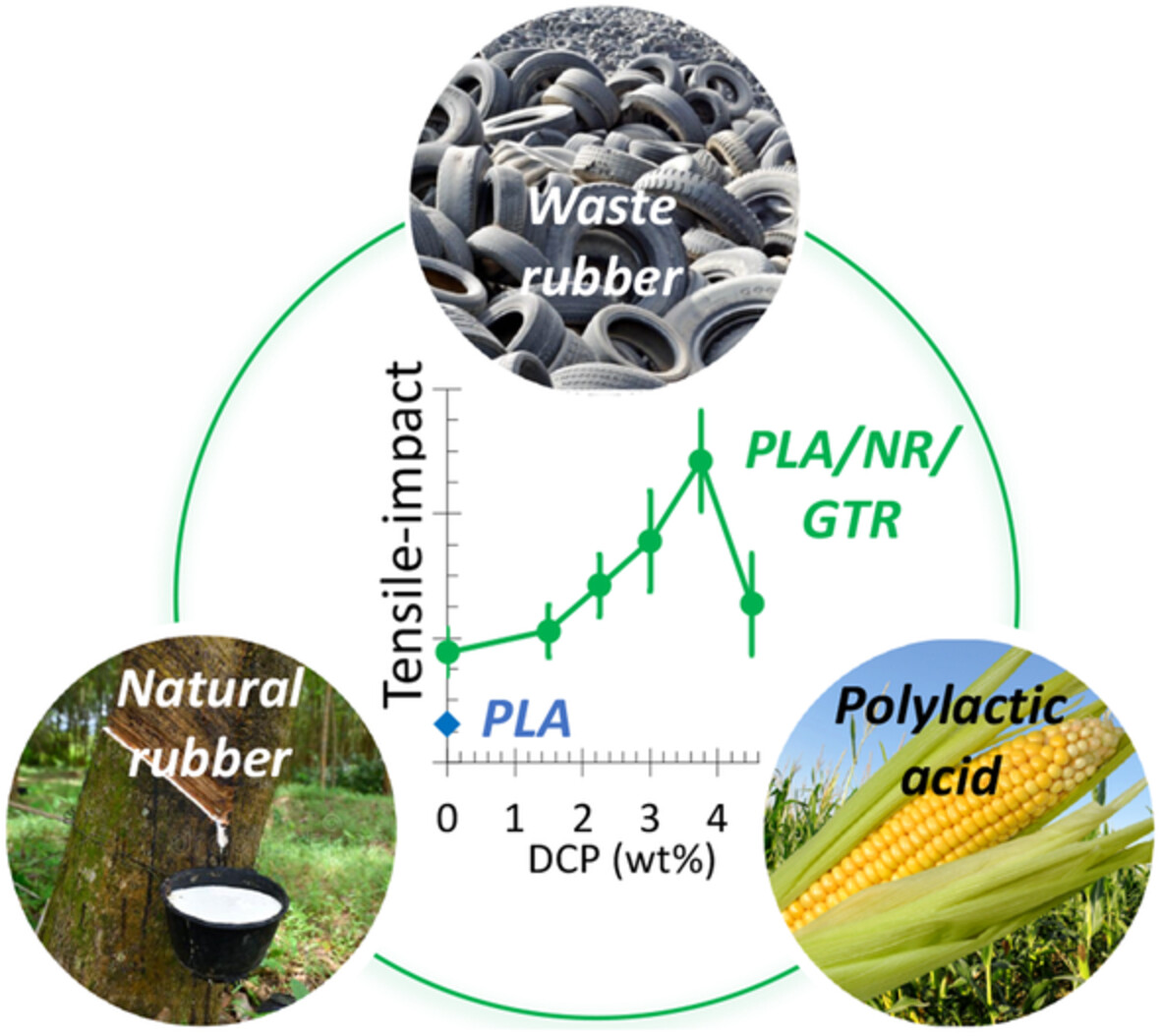
Dynamically vulcanized polylactic acid/natural rubber/waste rubber blends: Effect of the crosslinking agent on the morphology and tensile properties
- First Published: 10 August 2022
Bentonite-PDMS composite foams for oil spill recovery: Sorption performance and kinetics
- First Published: 12 August 2022
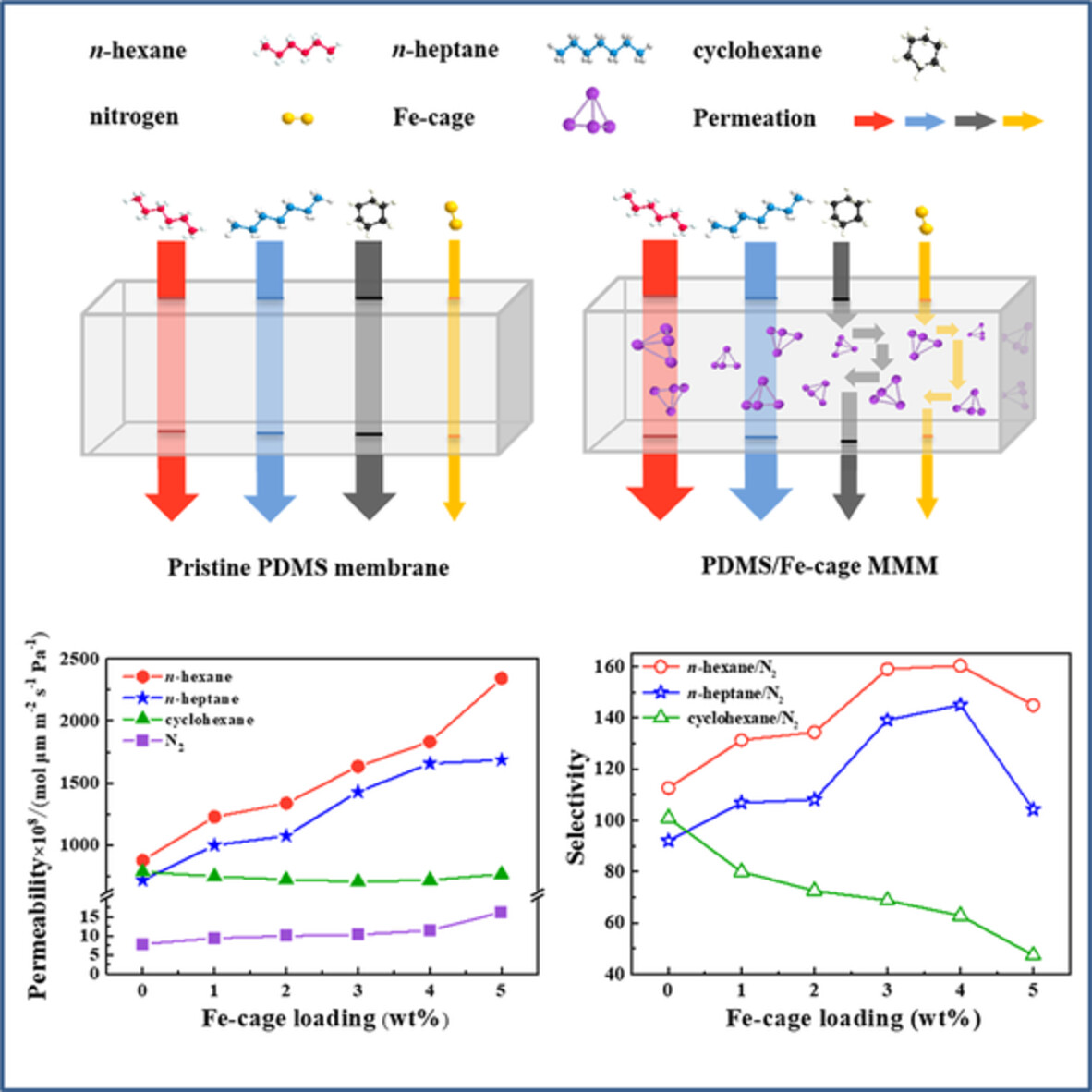
Tailor-made iron-organic molecular cage embedded polydimethylsiloxane membranes via emulsion casting technique for efficient VOCs removal
- First Published: 17 August 2022
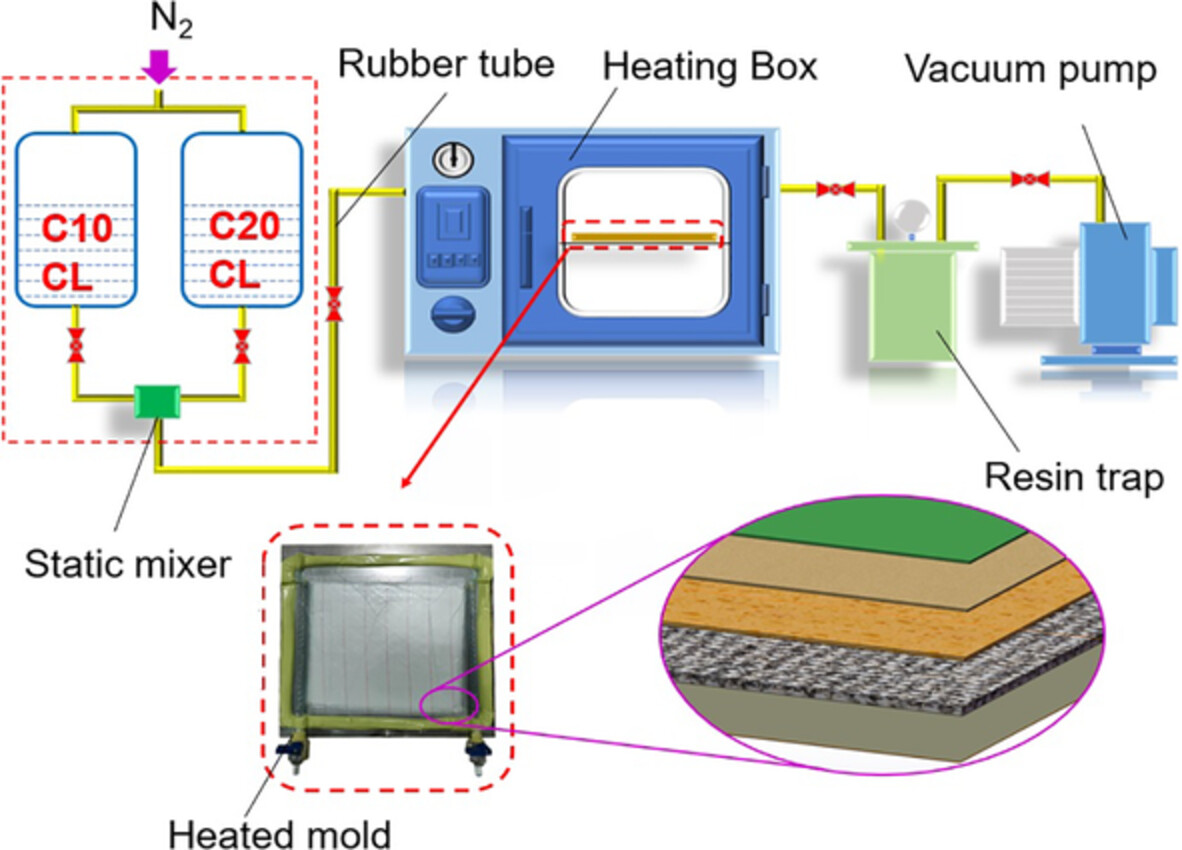
Optimization of process parameters for the preparation of continuous glass fiber-reinforced Nylon 6 composites by vacuum bagging process
- First Published: 18 August 2022
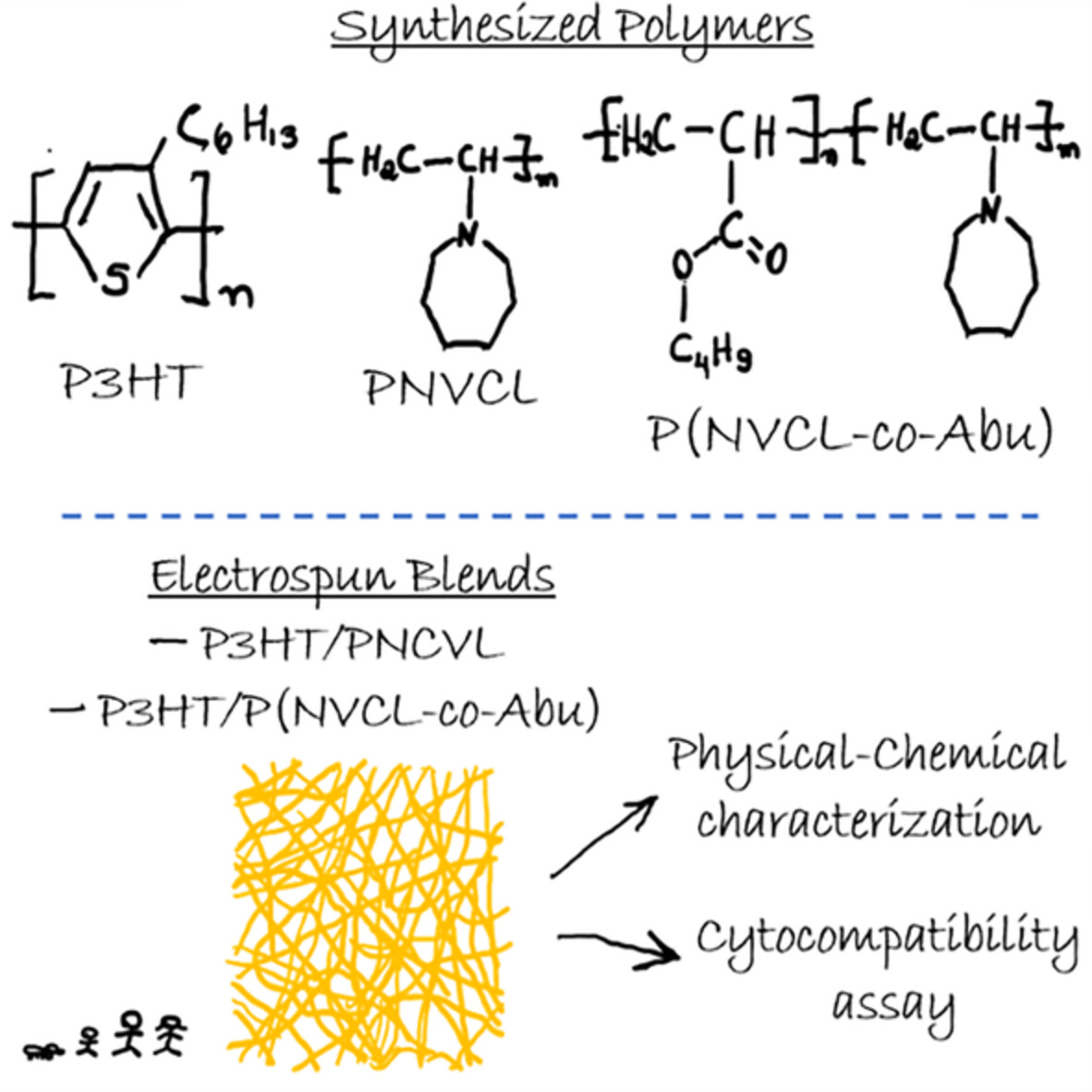
Development of scaffolds based in blends of poly(N-vinylcaprolactam) and poly(N-vinylcaprolactam-co-butylacrylate) with poly(3-hexylthiophene) for tissue engineering: Synthesis, processing, characterization, and biological assay
- First Published: 06 August 2022
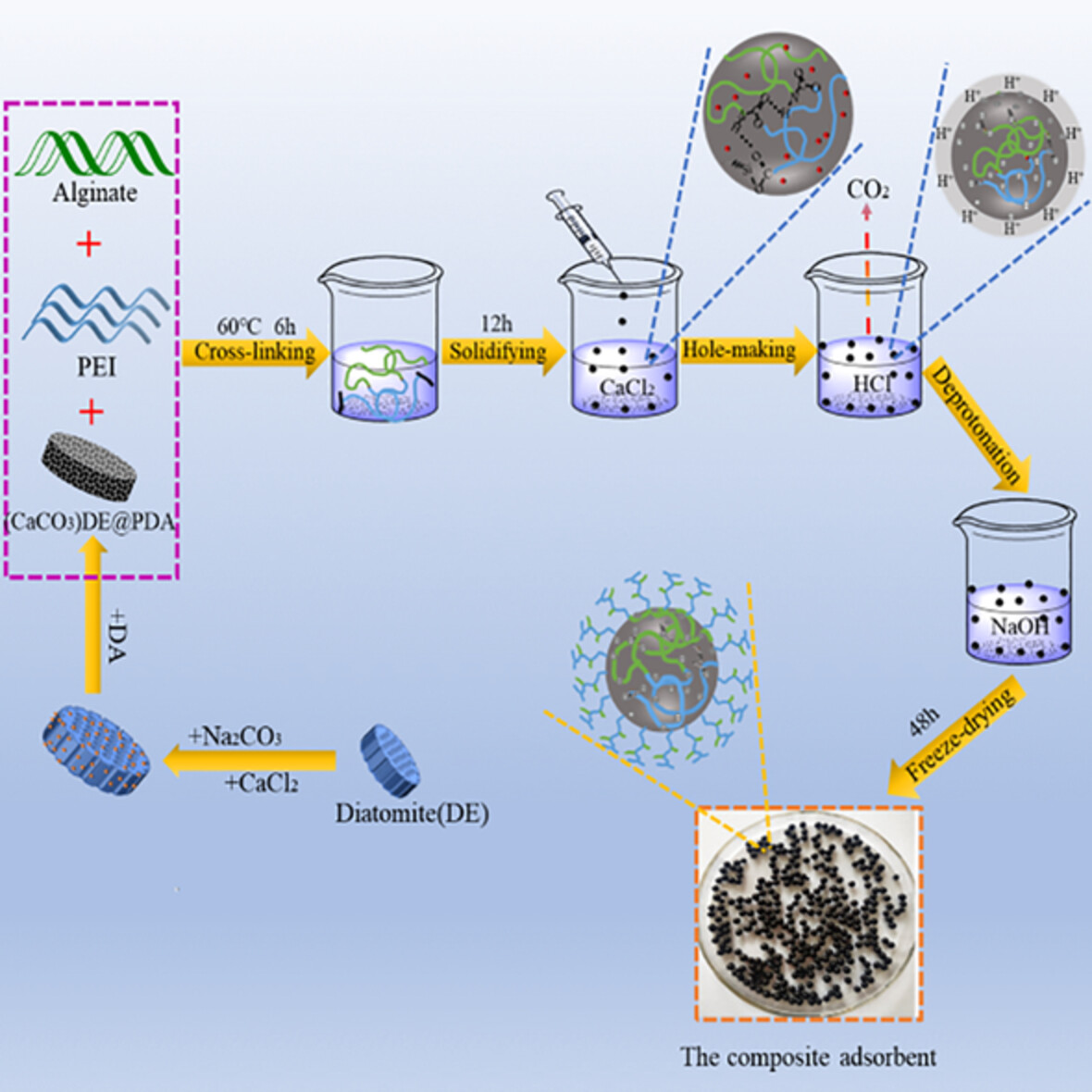
Construction of a novel double network polymer composite and evaluation of its highly efficient adsorption properties for copper ions
- First Published: 11 August 2022
Electromagnetic interference shielding of thermally exfoliated graphene/polyurethane composite foams
- First Published: 12 August 2022
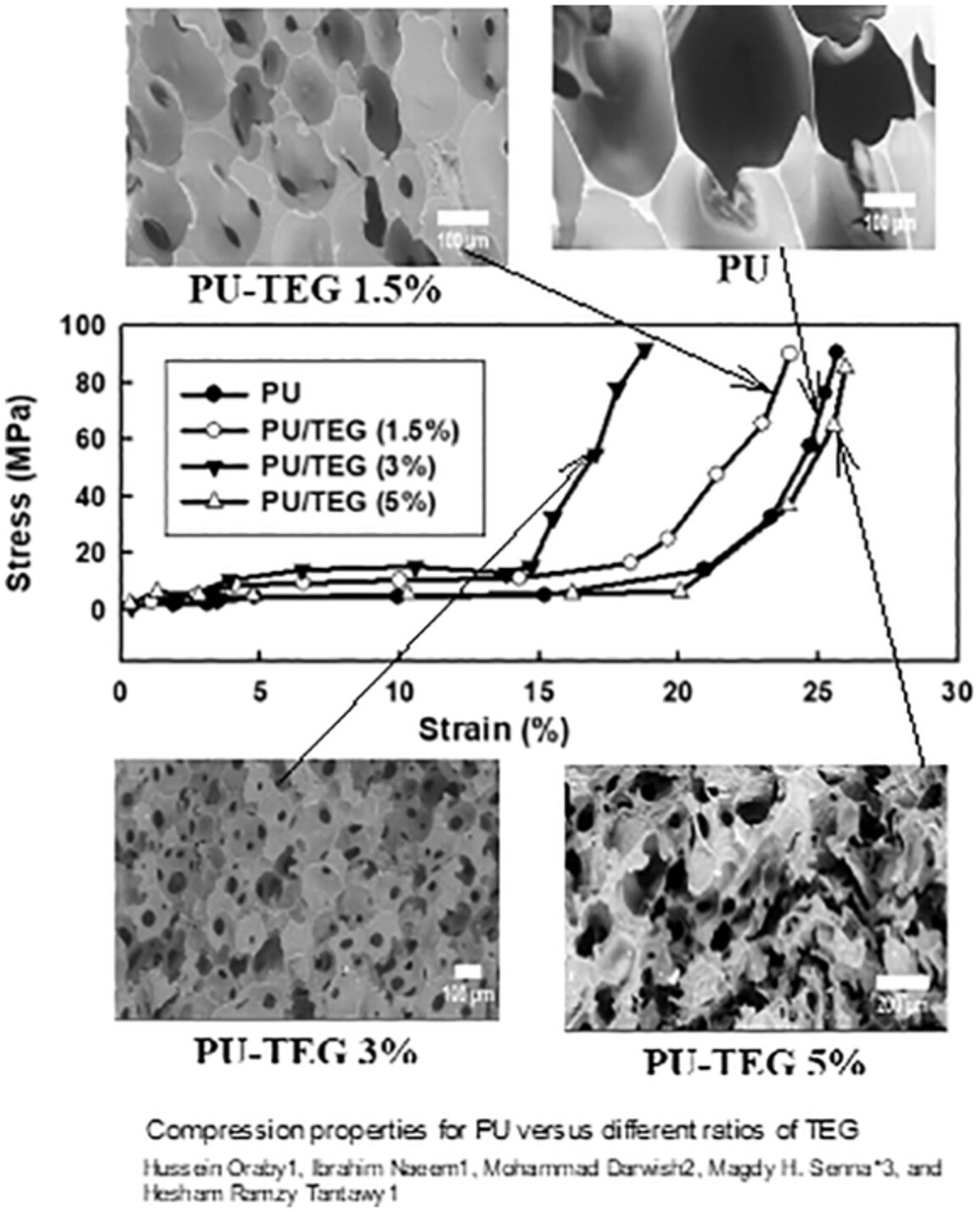
Thermally exfoliated graphene (TEG)/polyurethane (PU) composite samples were prepared for application in electromagnetic interference shielding (EMIS). The composite foam with 5 wt% TEG content exhibits the highest SE. The loading of 3 wt%, TEG resulting in a compromise between SE and mechanical characteristics. The findings highlight the potential applicability of the composite for EMIS applications.





![Aggregation behavior of triblock terpolymer poly[n-butyl acrylate-block-N-isopropylacrylamide-block-2-(dimethylamino)ethyl acrylate] at the air/water interface](/cms/asset/87c6cdea-f419-4da8-bb86-2634e3ec9ff5/app52989-toc-0001-m.jpg)