Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 139, Issue 40
- First Published: 15 September 2022

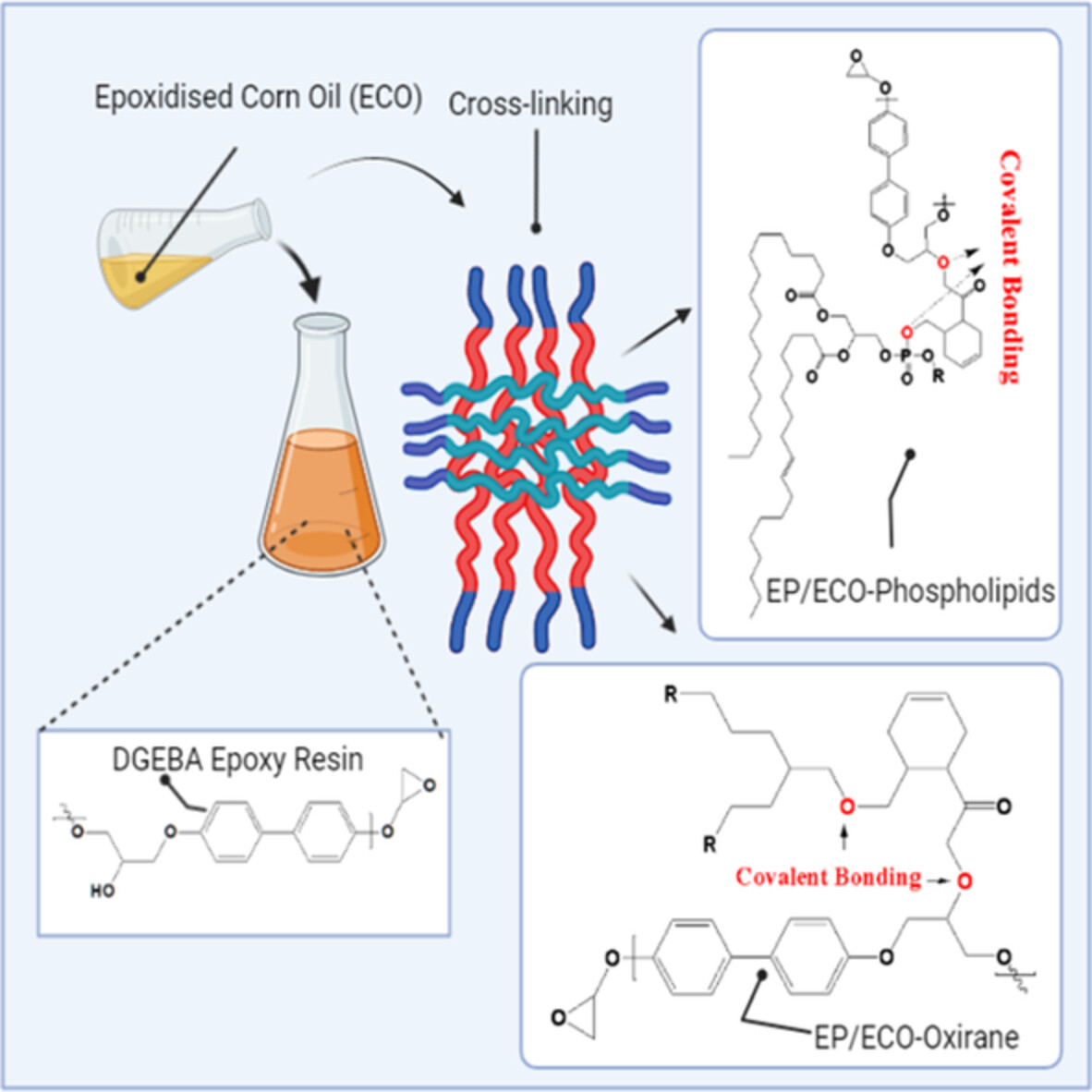
The cover image created by Maurelio Cabo Jr., and his colleagues show the aromatization of DGEBA epoxy resin aromatic rings to epoxidized corn oil aliphatic chains result in interaction and functionalization of phospholipids and hydroxyl radicals developing high brittleness yet lower flammability with an excellent reduction of carbon monoxide and carbon dioxide emission from commercialized polymer resins. DOI: 10.1002/app.52874
ISSUE INFORMATION
Editorial Board, Aims & Scope, Table of Contents
- First Published: 15 September 2022
REVIEWS
Polyphthalamide polymers: A review on synthesis, properties, and advance manufacturing and emerging applications
- First Published: 17 August 2022
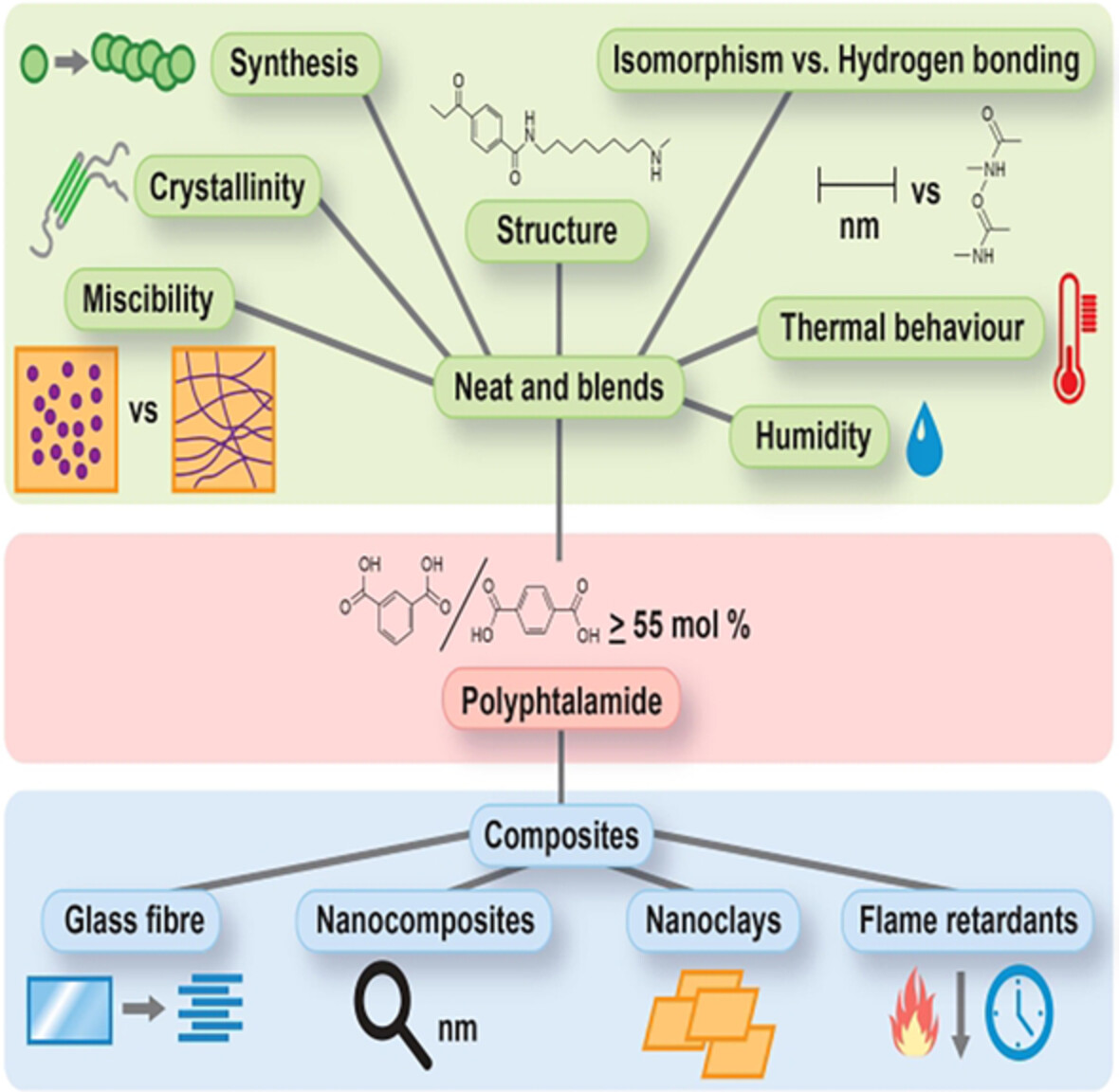
The family of polymers under the name ofpolyphthalamide (PPA) is utilized in many specialized areas as a result of itshigh thermomechanical properties, chemical resistance, etc. This articleprovides a thorough review of the research literature available by representingthe many avenues of research in both the basic understanding of properties aswell as in very specialized engineering applications.
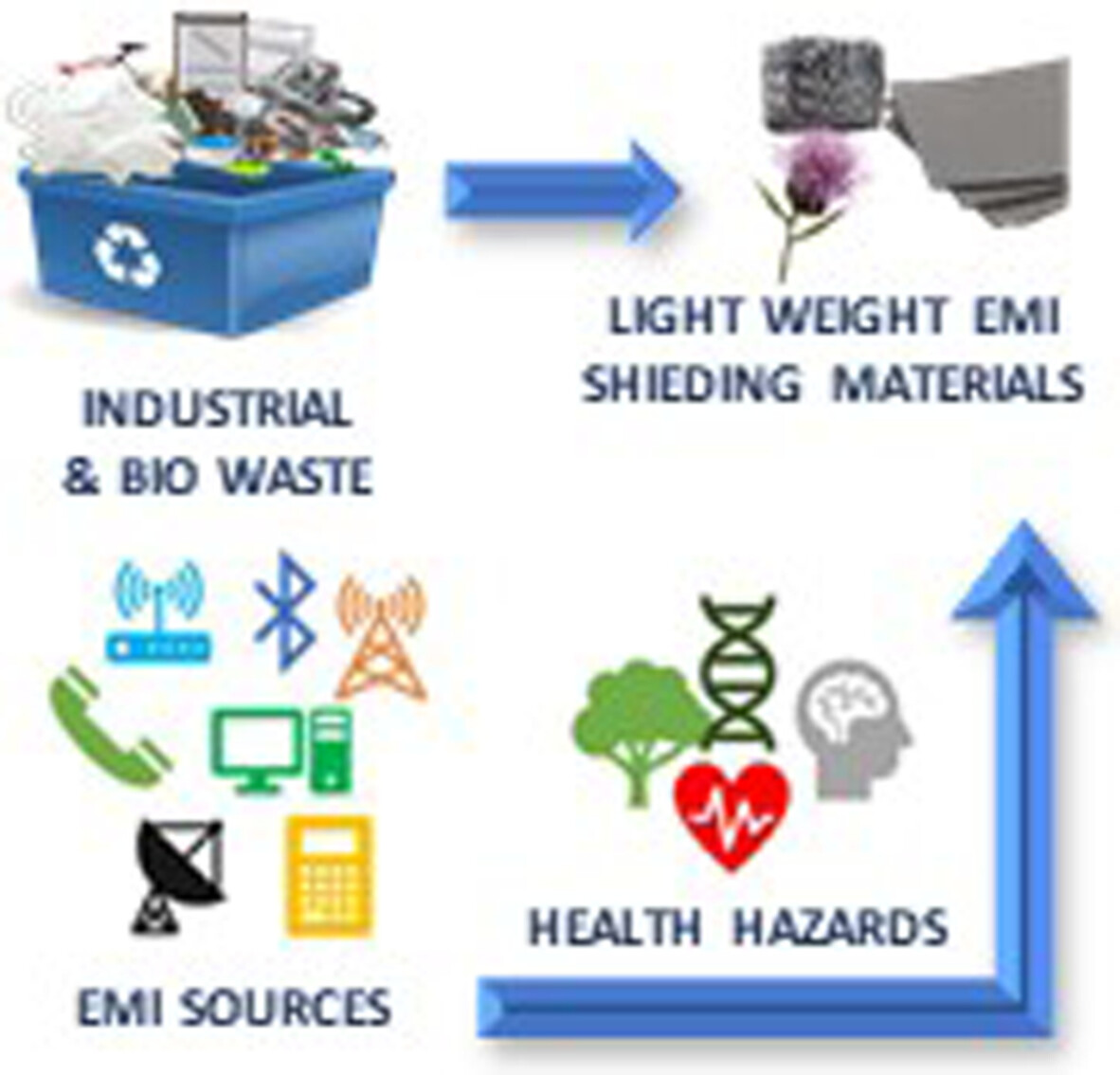
From waste to wealth: A critical review on advanced materials for EMI shielding
- First Published: 08 August 2022
RESEARCH ARTICLES
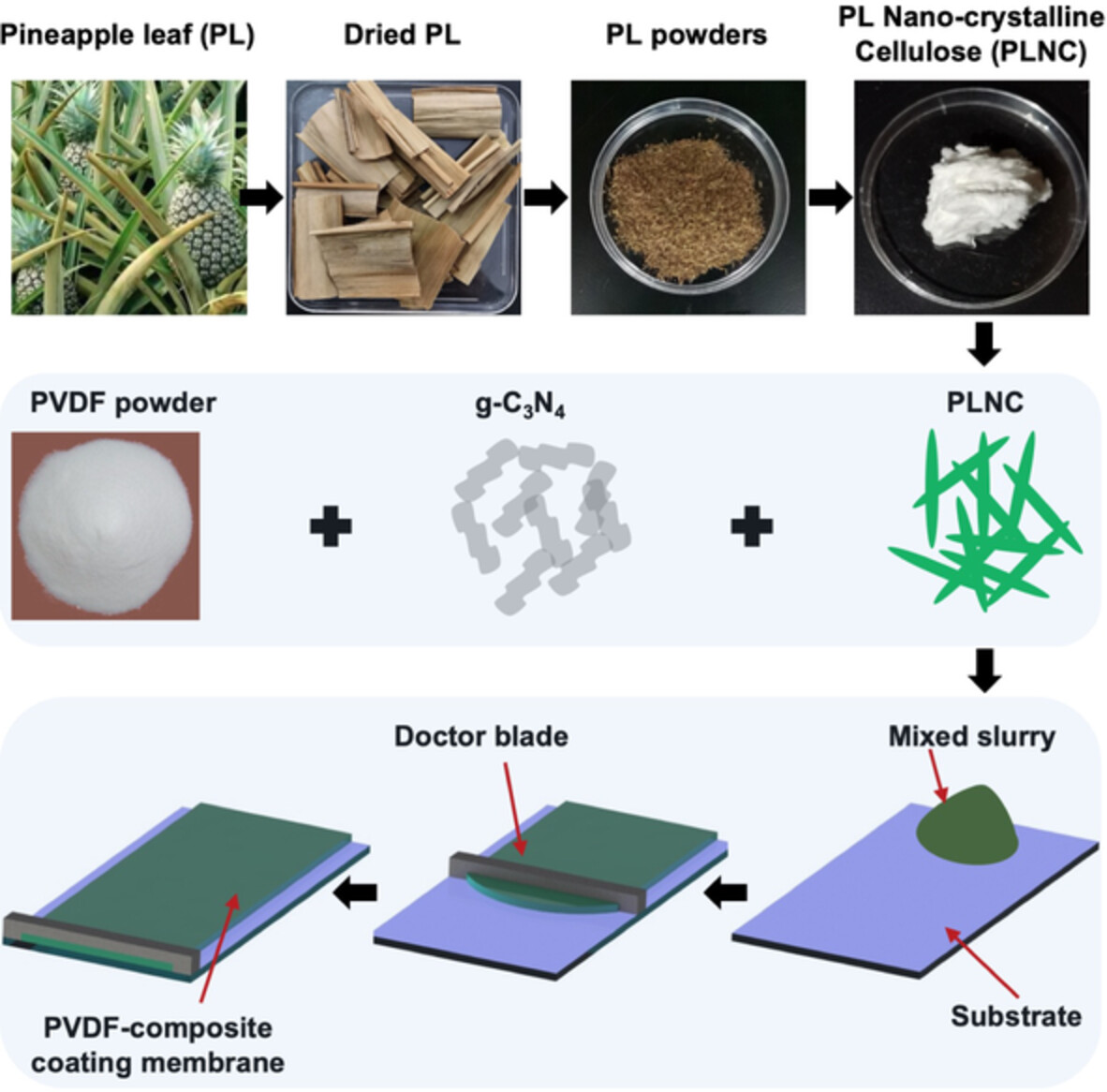
Improvement of PVDF composite membrane performance by using nanocrystals cellulose from waste pineapple leaf and g-C3N4
- First Published: 13 July 2022
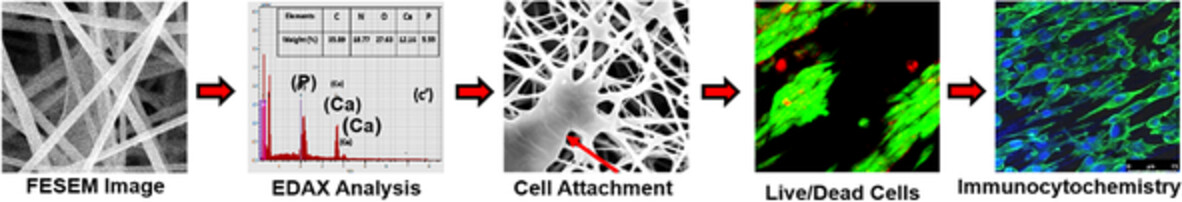
Enhancing physicochemical, mechanical, and bioactive performances of monetite nanoparticles reinforced chitosan-PEO electrospun scaffold for bone tissue engineering
- First Published: 03 August 2022
Study of the impact of epoxidized plant oil phospholipids and hydroxyl radicals on crosslinked epoxy resins
- First Published: 03 August 2022
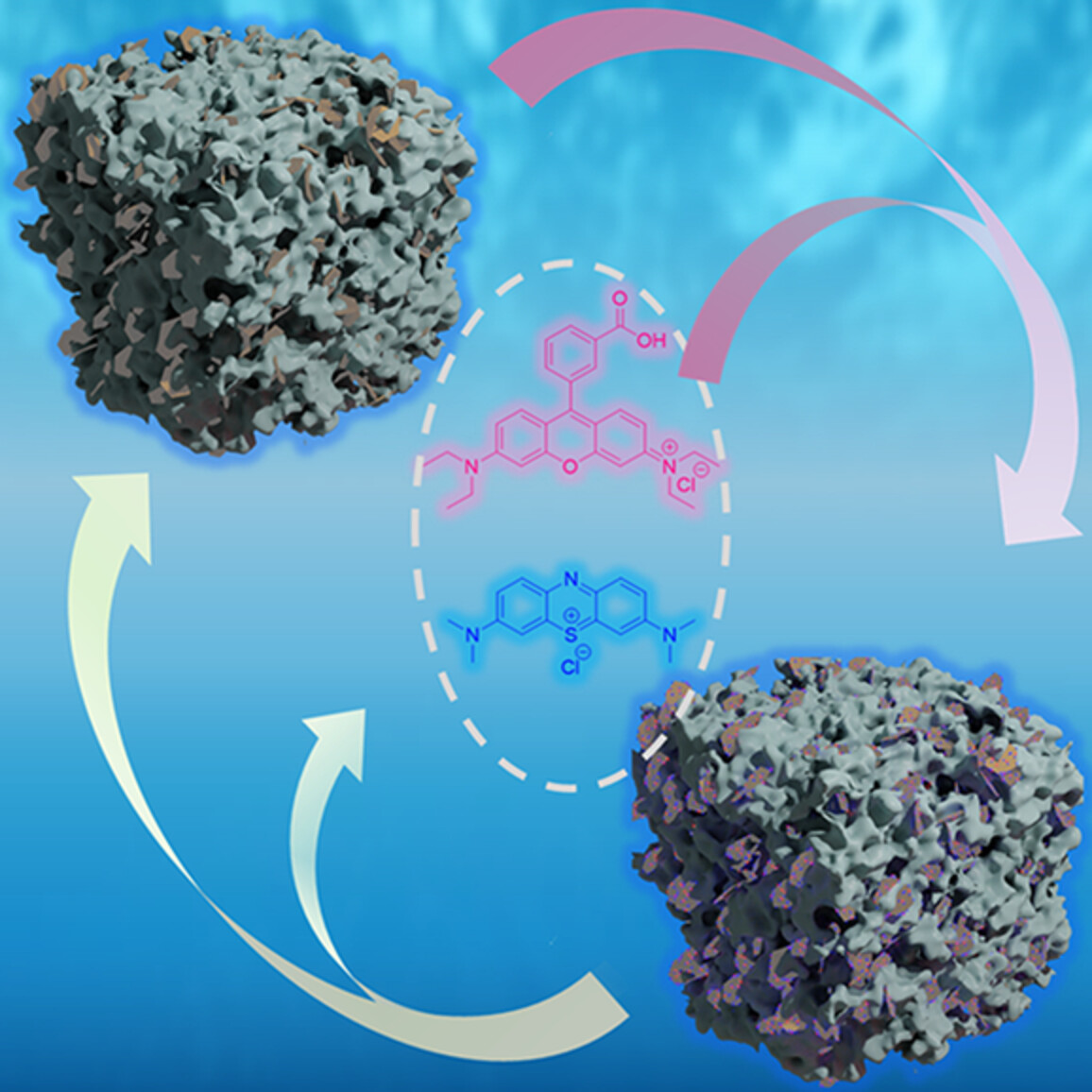
Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for the recognition of ellagic acid
- First Published: 30 July 2022
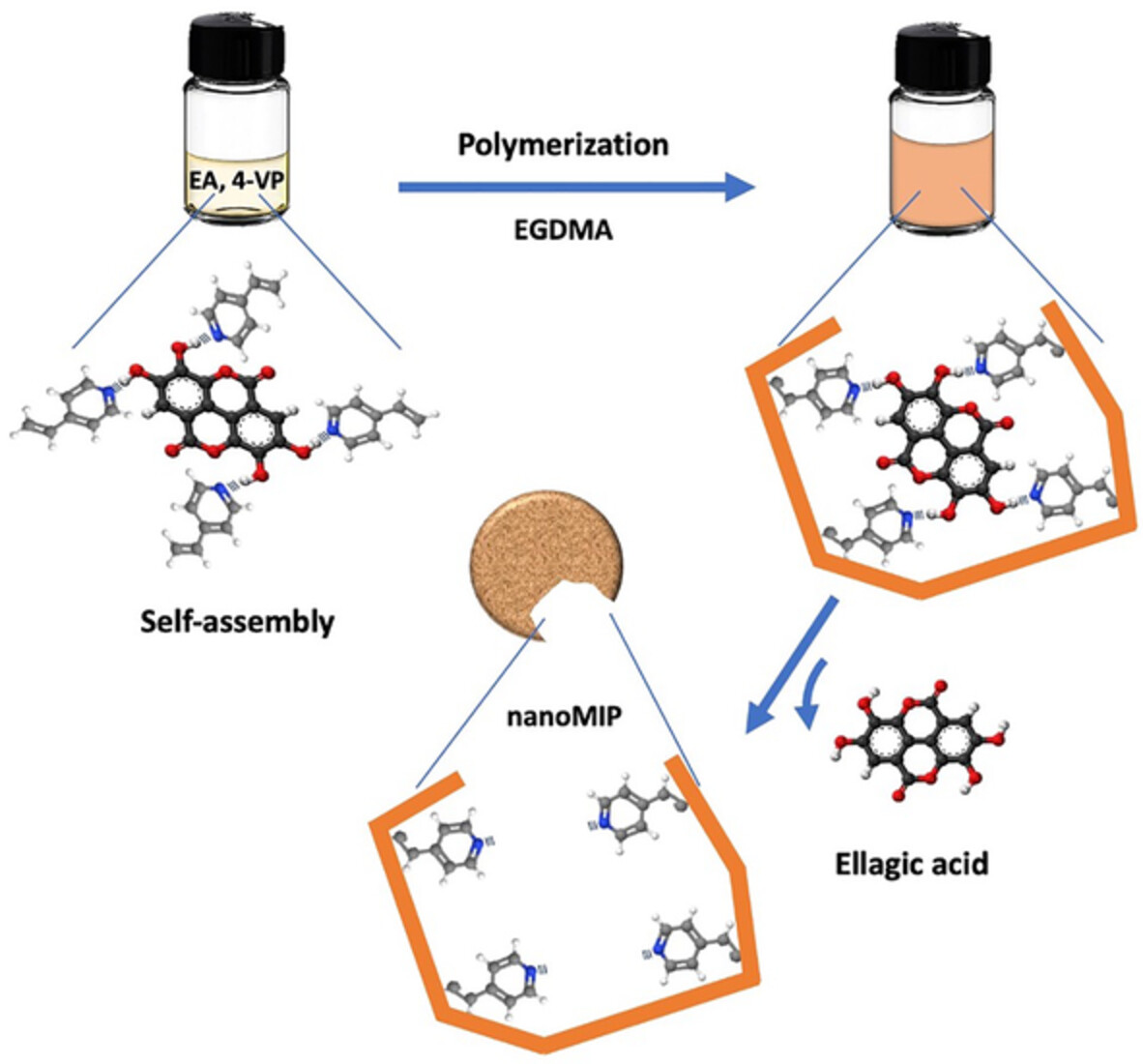
We create molecularly imprinted nanoparticles for the recognition of ellagic acid (EA). We develop a straightforward, efficient, and environmentally friendly precipitation polymerization method to synthesize nanoMIPs. We employ nanoMIPs-based dispersive solid-phase extraction to extract EA from pomegranate peels.
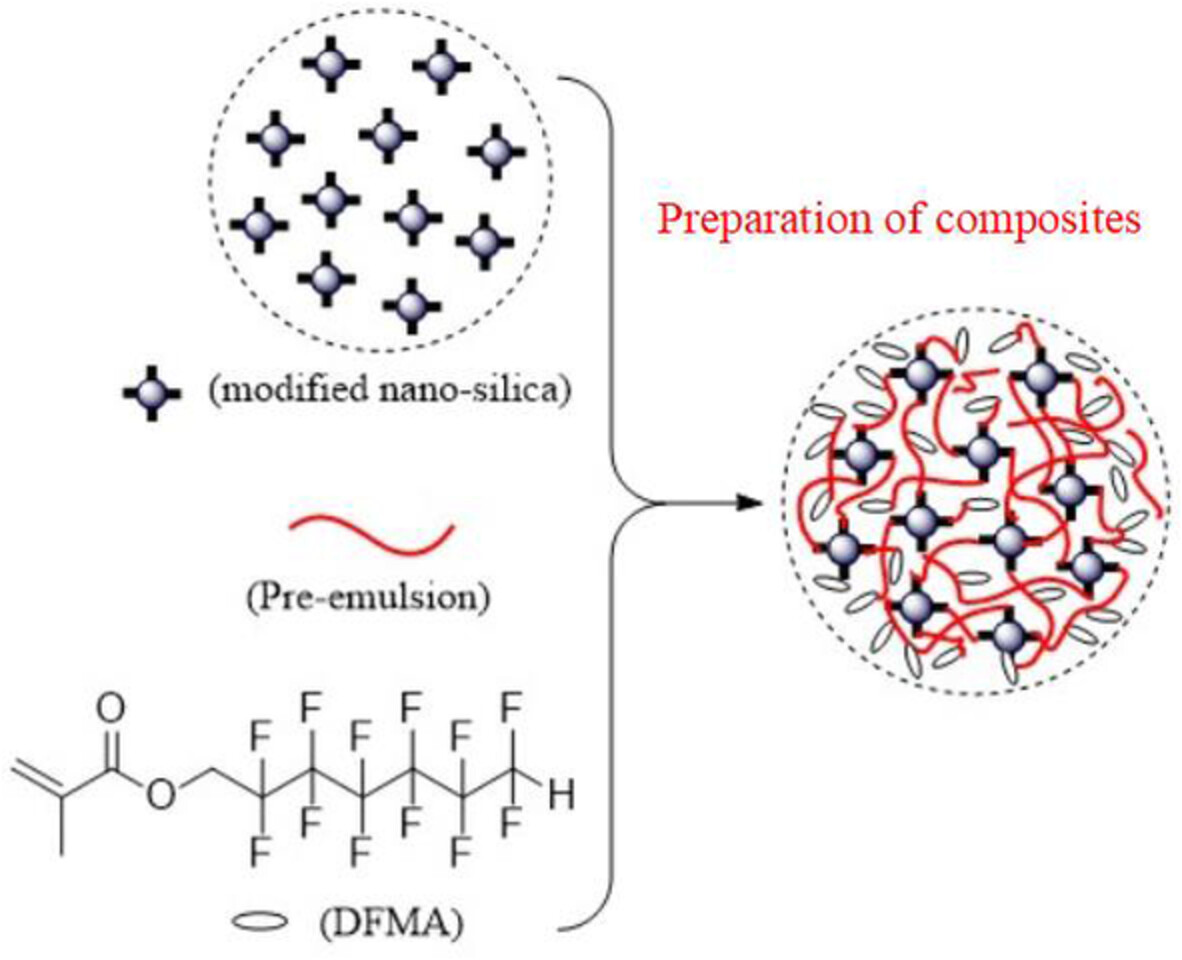
Nano-silica/fluorinated polyacrylate composites as surface protective coatings for simulated stone cultural relic protection
- First Published: 30 July 2022
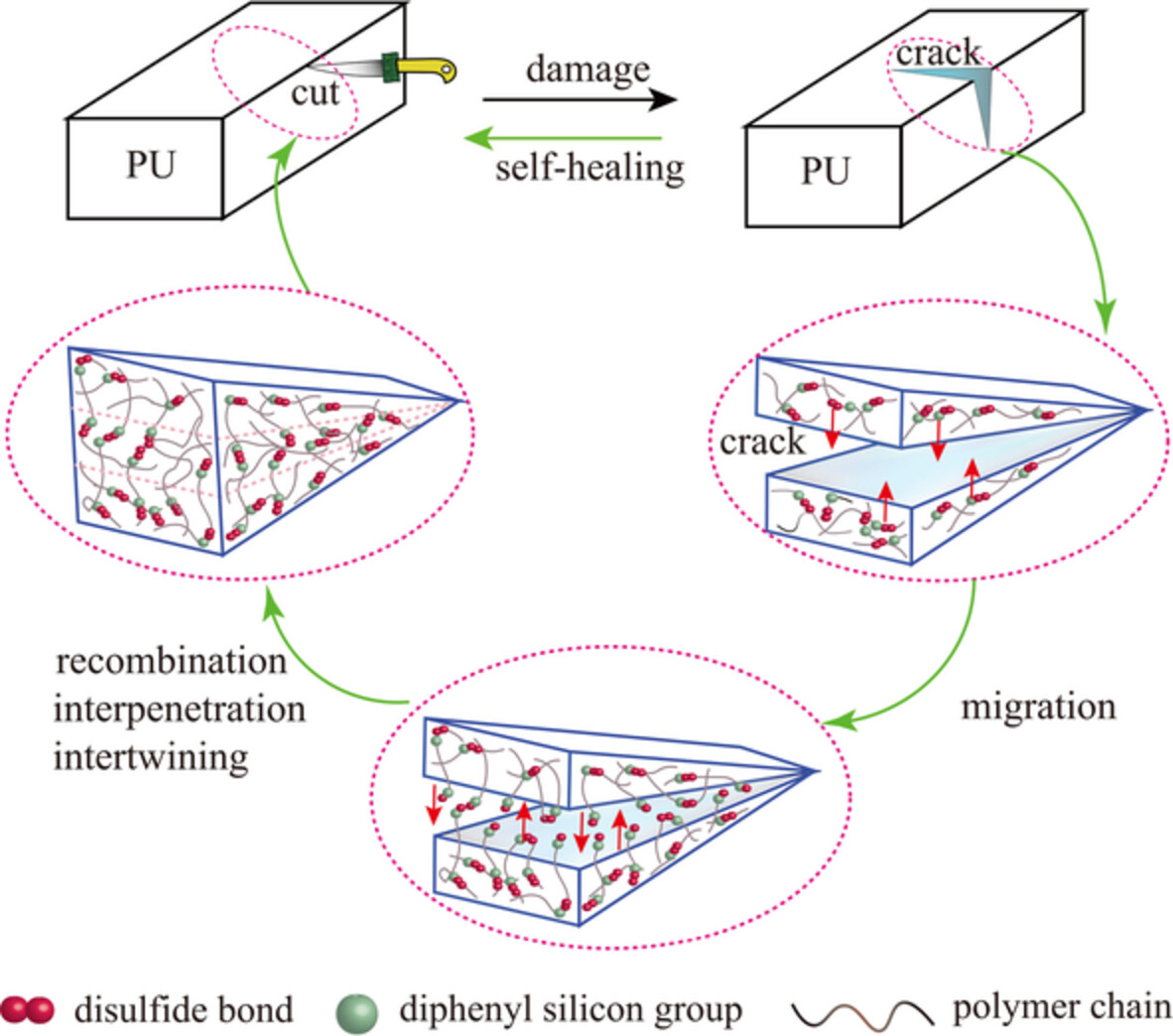
Synergistic effect of silicon-containing groups on the self-healing performance of polyurethanes based on disulfide bonds
- First Published: 03 August 2022
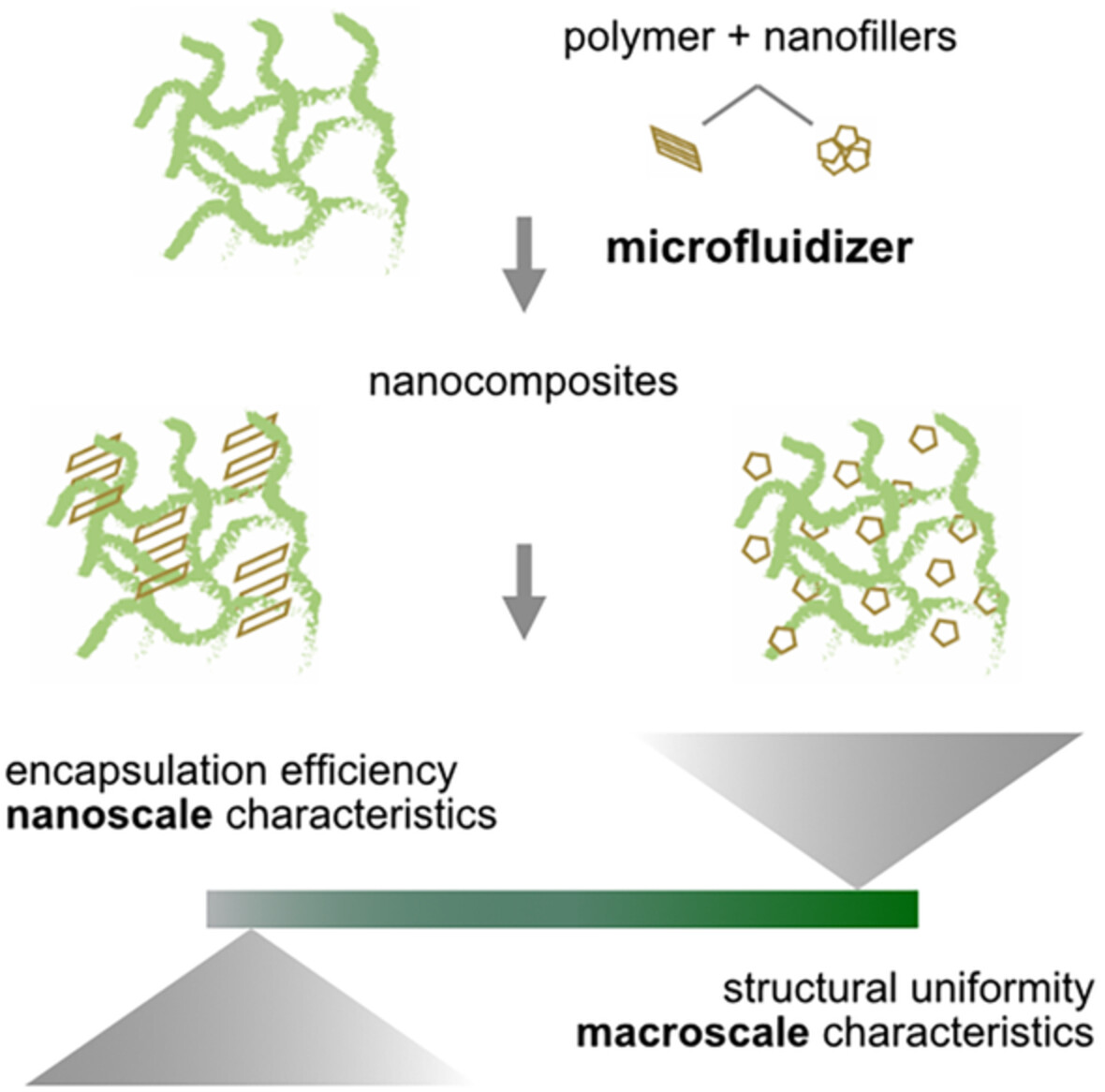
Microfluidic-assisted preparation of nano and microscale chitosan based 3D composite materials: Comparison with conventional methods
- First Published: 02 August 2022
Synthesis and property study of novel maleimide-cardanol based modifiers for epoxy resins
- First Published: 02 August 2022
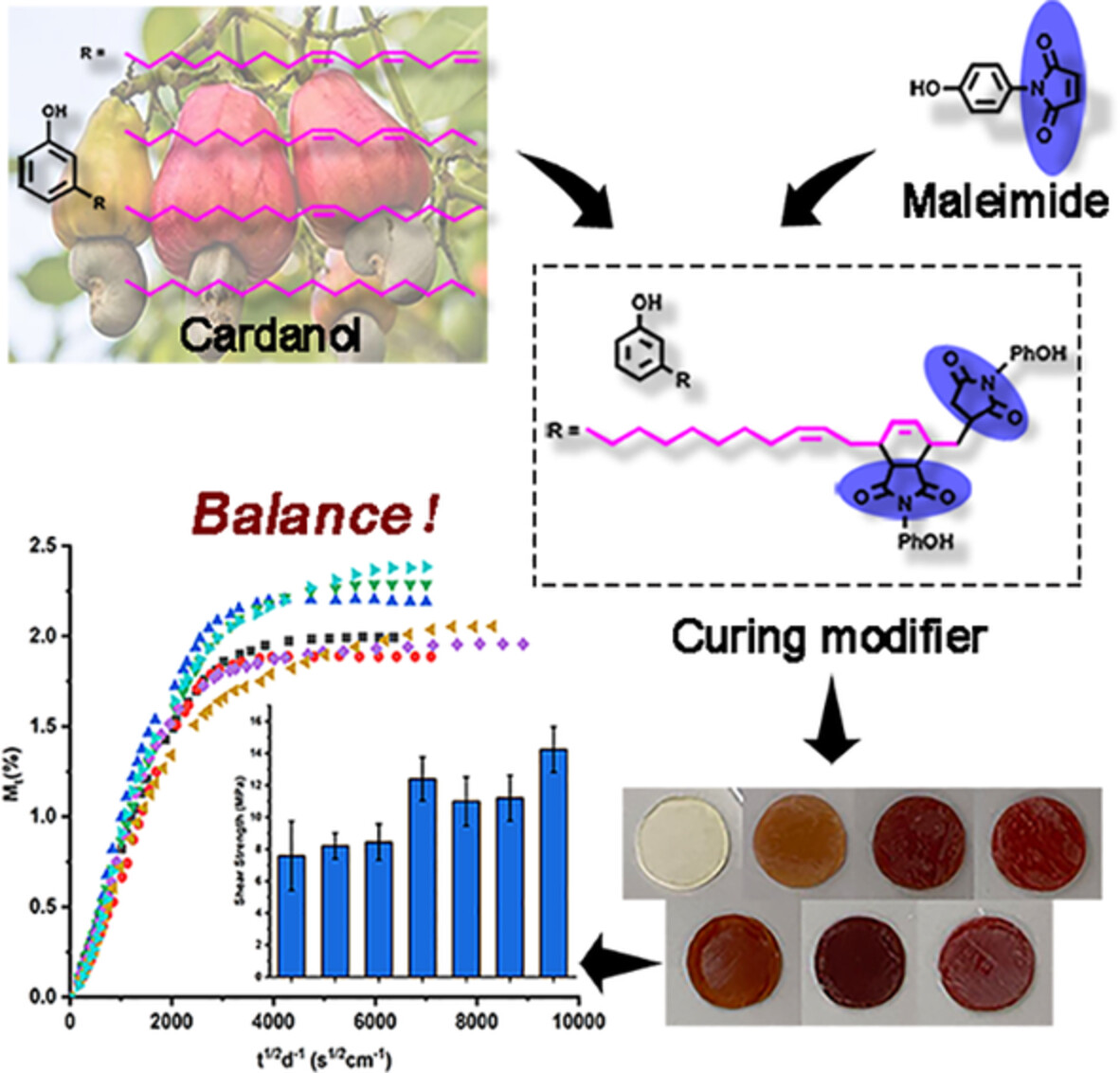
Epoxies with biomass-based maleimide-cardanol modifiers show lower curing activity and single glass transition temperature due to long flexible chain of cardanol. Besides, increased crosslinking density and high thermostability are attributed to the rigid five-membered ring structure of maleimide. In addition, adhesion properties, equilibrium water sorption and diffusion coefficient are related to the polarity of HPM.
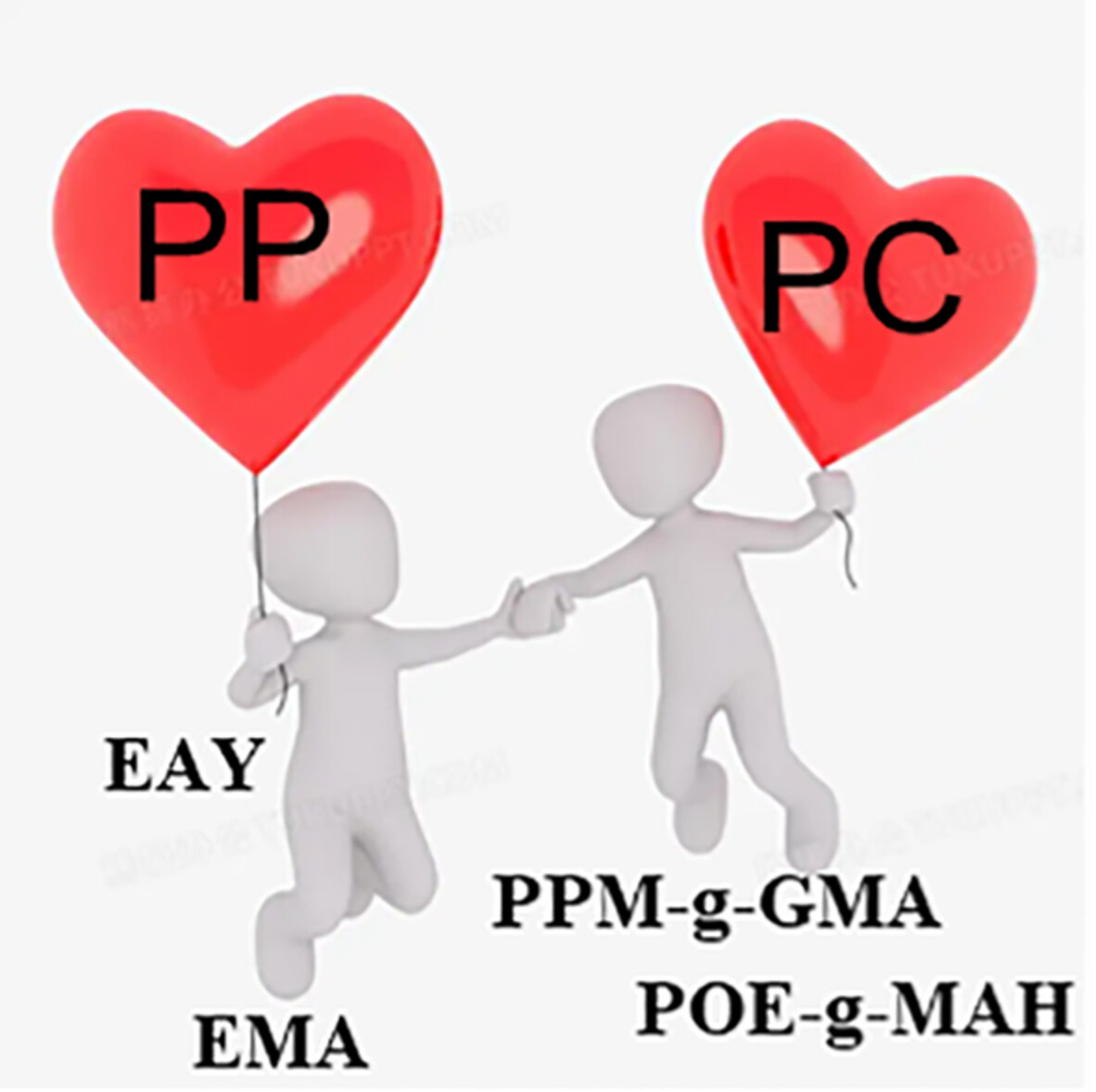
Effect of compatibilizer on the structure and property of polycarbonate/polypropylene alloys
- First Published: 04 August 2022
Light-driven self-healing castor oil based polyurethane film with enhanced mechanical properties
- First Published: 28 July 2022
Synthesis and fabrication of biobased thermoplastic polyurethane filament for FDM 3D printing
- First Published: 03 August 2022
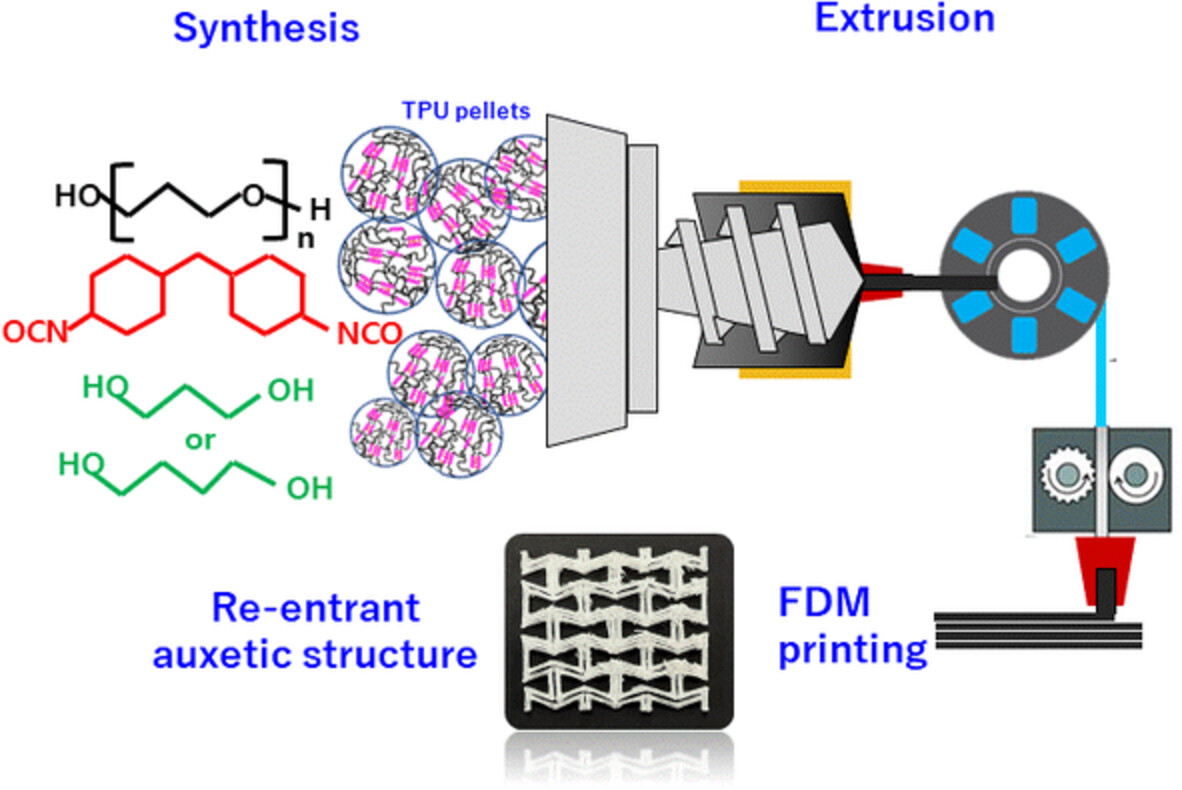
In the present study, a soft actuator-grade thermoplastic polyurethane (TPU) was synthesized and then processed into a filament for FDM 3D printers during a melt-extrusion process using synthesized pellets. Chemical, thermal, and mechanical properties of the manufactured TPU filaments were characterized. Auxetic re-entrant TPU samples were then printed with the manufactured filament.
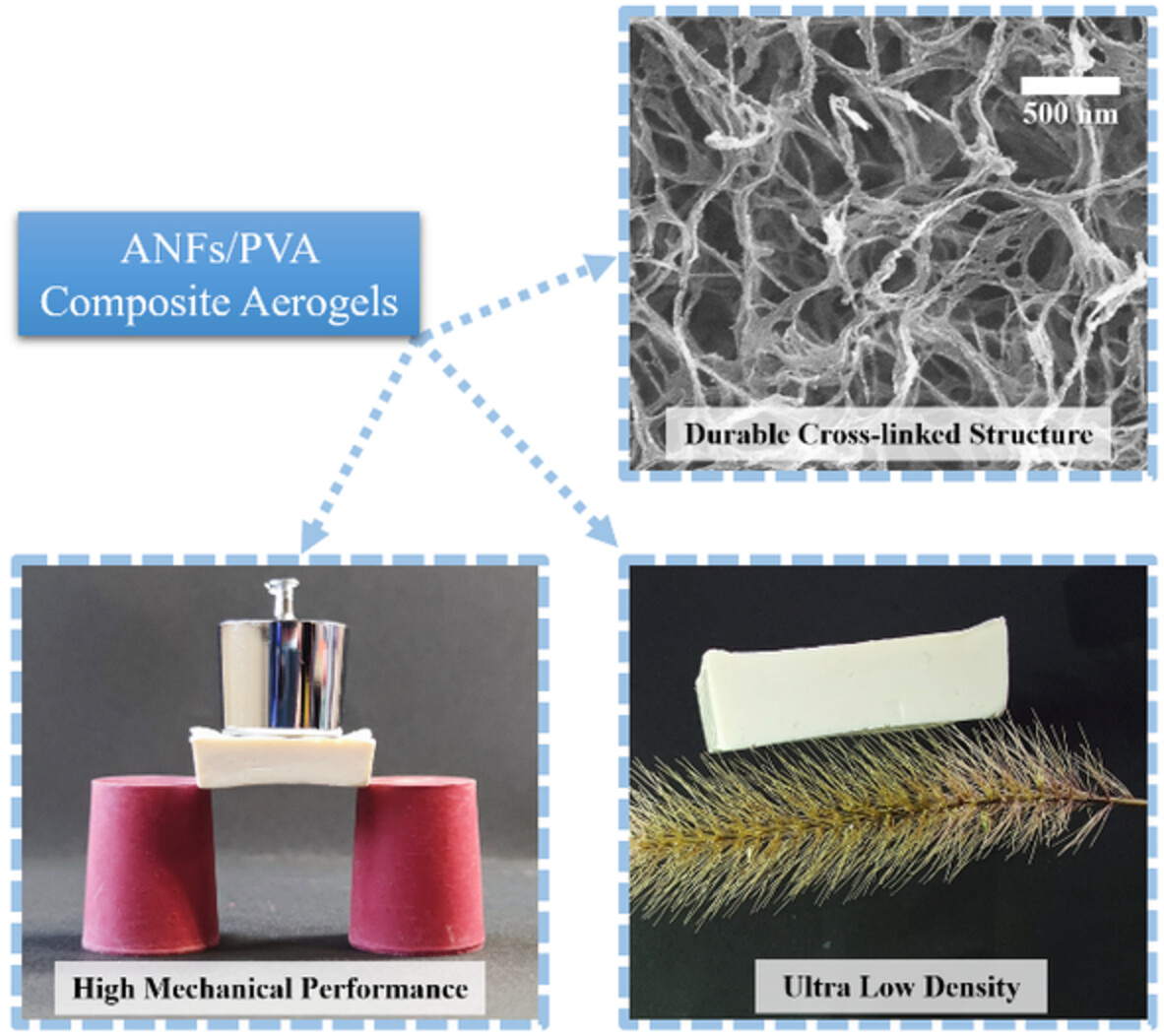
Investigation of the influences of the molecular weights and dosage ratios of polyvinyl alcohol on para-aramid nanofibers/polyvinyl alcohol composite aerogels
- First Published: 02 August 2022
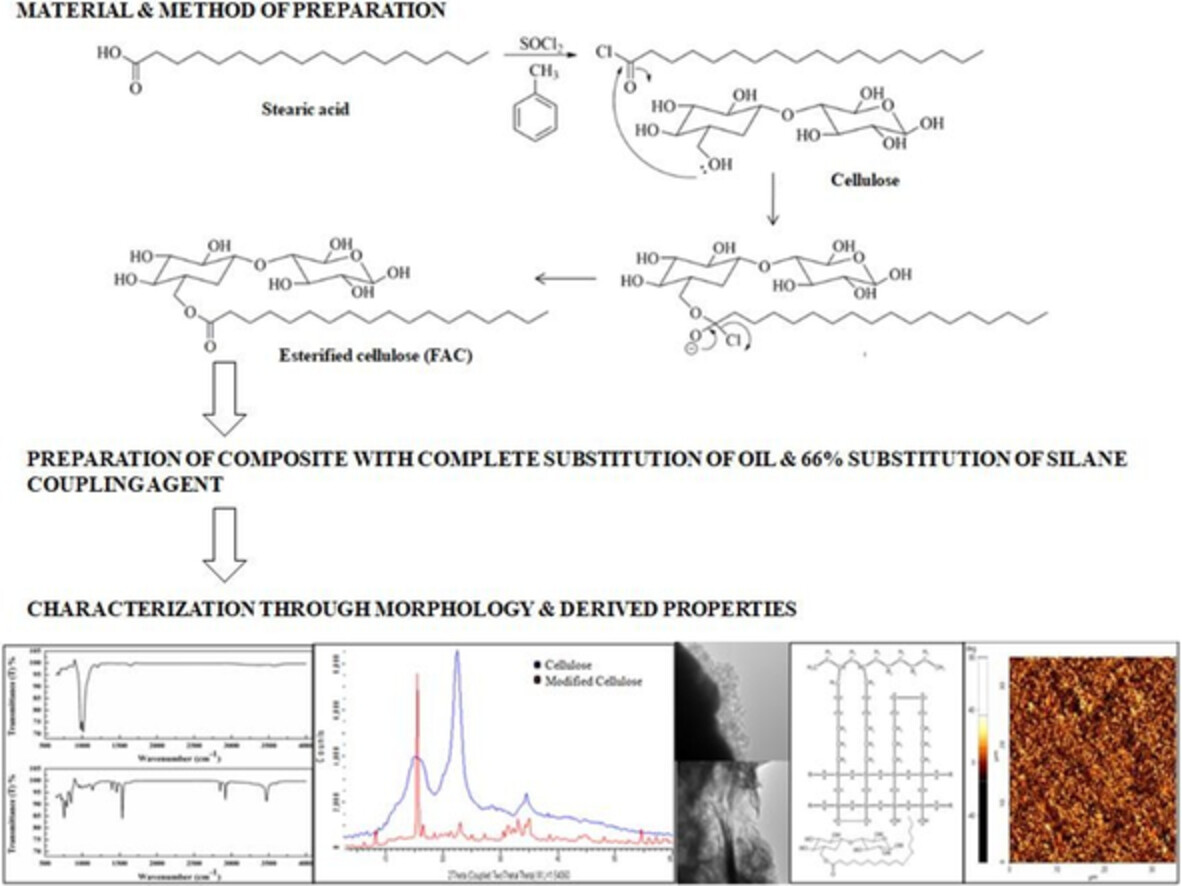
Fatty acid modified cellulose: Preparation and application as green multi-functional additive in a tyre tread formulation
- First Published: 04 August 2022
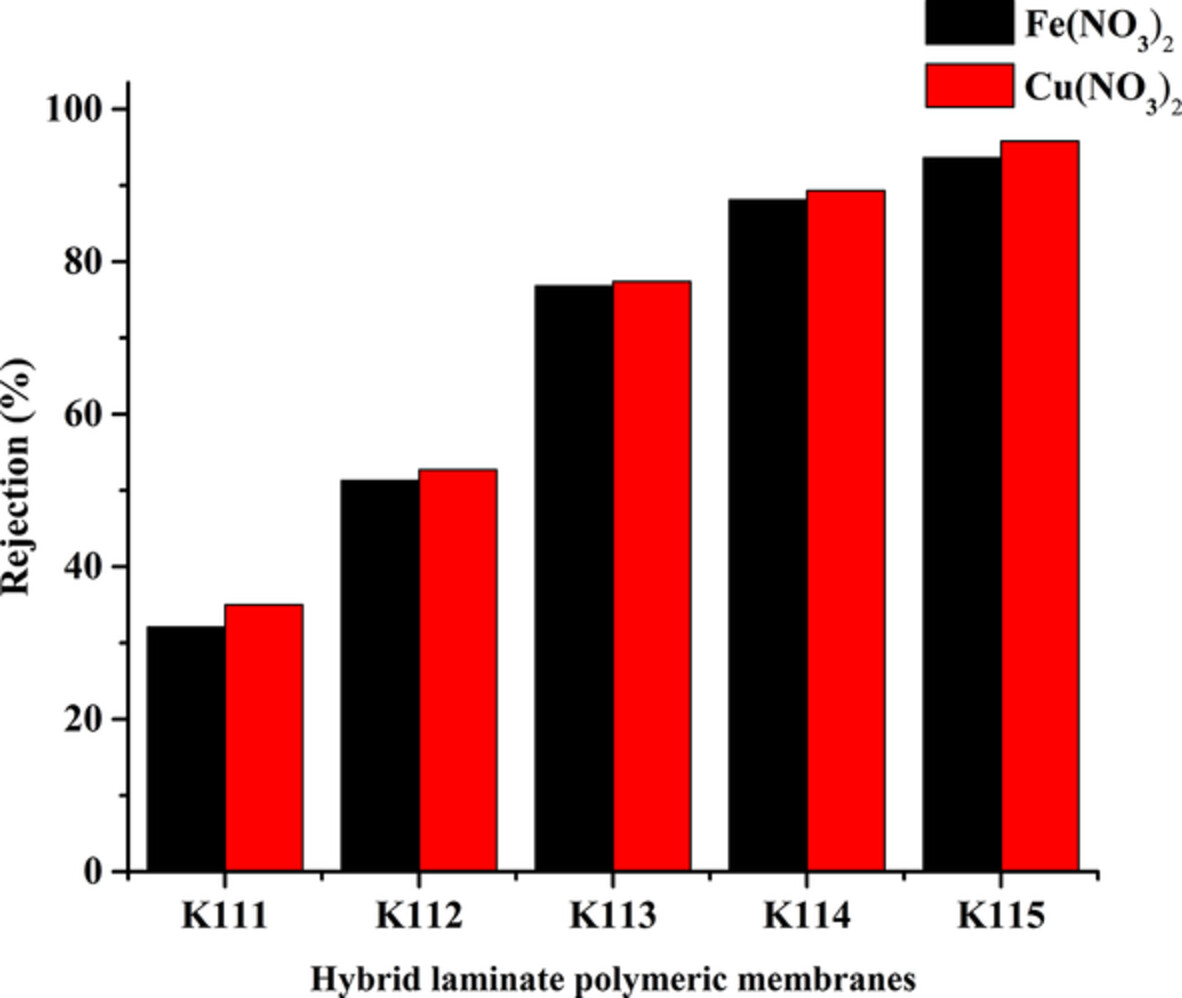
Deportment of cobalt bismuth nanoferrites in Kevlar-supported cellulose acetate membranes for heavy metal-salts rejection profile
- First Published: 03 August 2022
High heat-resistant (250°C) epoxy resin composites with excellent dielectric properties
- First Published: 08 August 2022
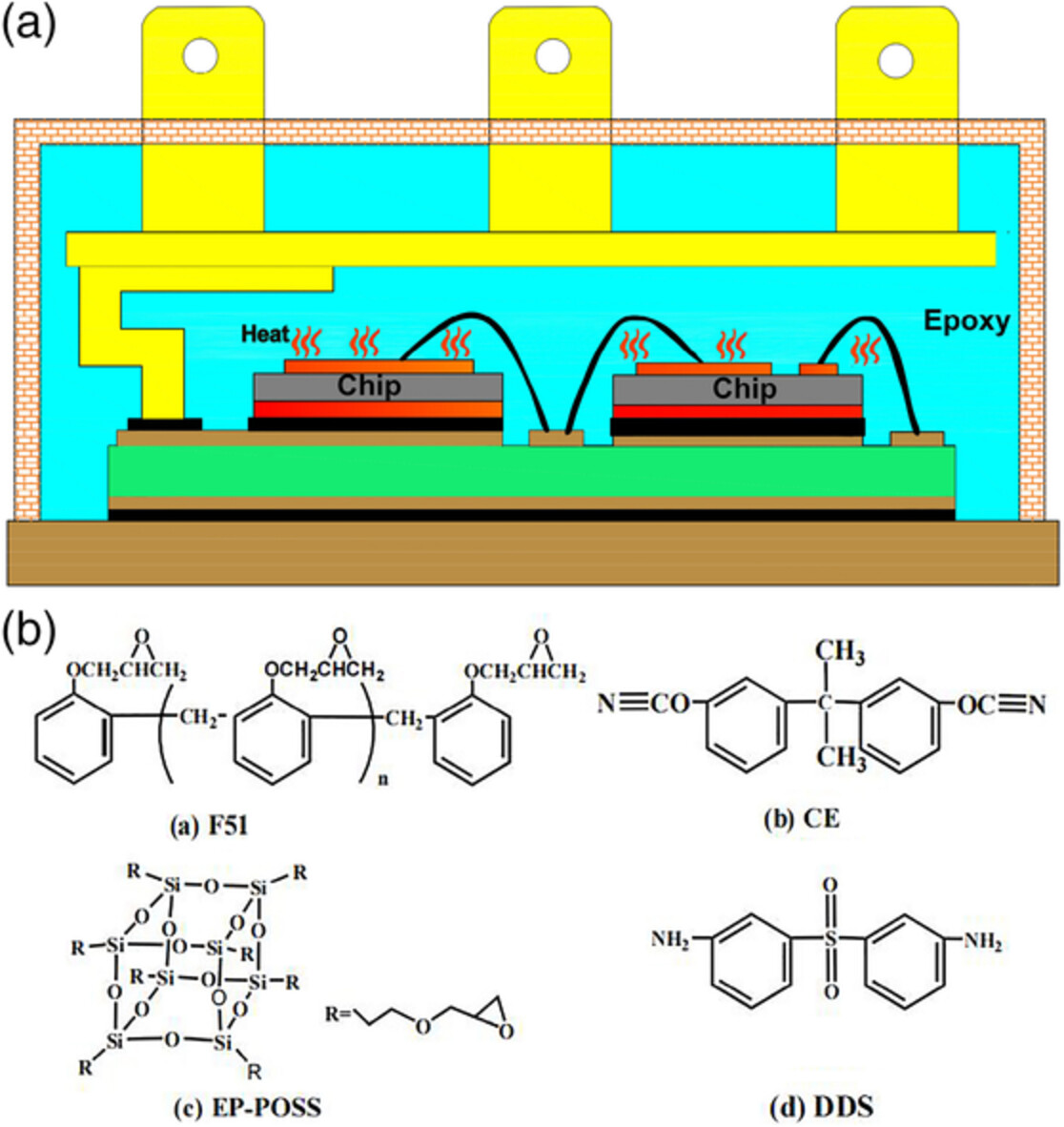
An all-organic high heat-resistant epoxy resin packing material for insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) encapsulation was prepared by modifying epoxy with cyanate (CE) and EP-POSS. Compared with epoxy, which not only has low dielectric constant, but also can endure 250°C of operating temperature. A mechanism that forming of oxazolidone and triazine rings restricts movement of carriers and degrading of cross-linked networks was proposed for the improvement of dielectric and thermal performances.
Polydimethylsiloxane/carboxylated hydroxylated multiwalled carbon nanotubes/polyimide composite membrane wearable flexible piezoresistive tactile sensor device with microsphere array
- First Published: 03 August 2022
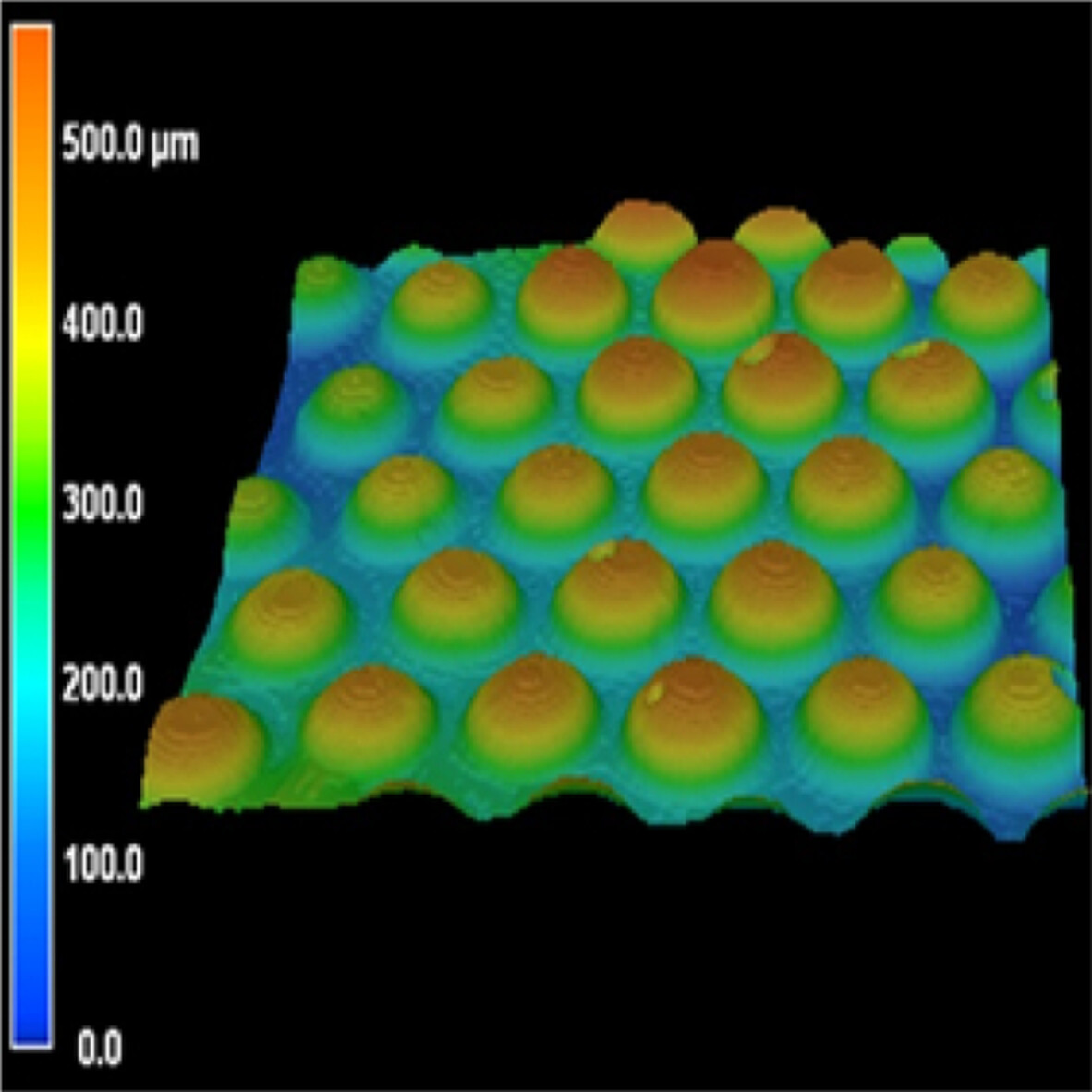
This research proposed a flexible piezoresistive tactile sensor (FPTS) device with imprinted microsphere array to realize the accurate and stable acquisition of human motion data. The electromechanical response curves of piezoresistive tactile sensor consisting of PDMS/MWCNT-COOH/PI composite membrane with double-sided microsphere shows that the detection limits can reach 0.0289 kPa, and the sensitivity is 1.139 kPa−1. The sensor has high stability, especially when the wearing radius of curvature is more than 30 mm.
Aryl-aryl linked two-dimensional covalent organic frameworks/cellulose composite monolith with hierarchical structure for aqueous dyes adsorption
- First Published: 01 August 2022
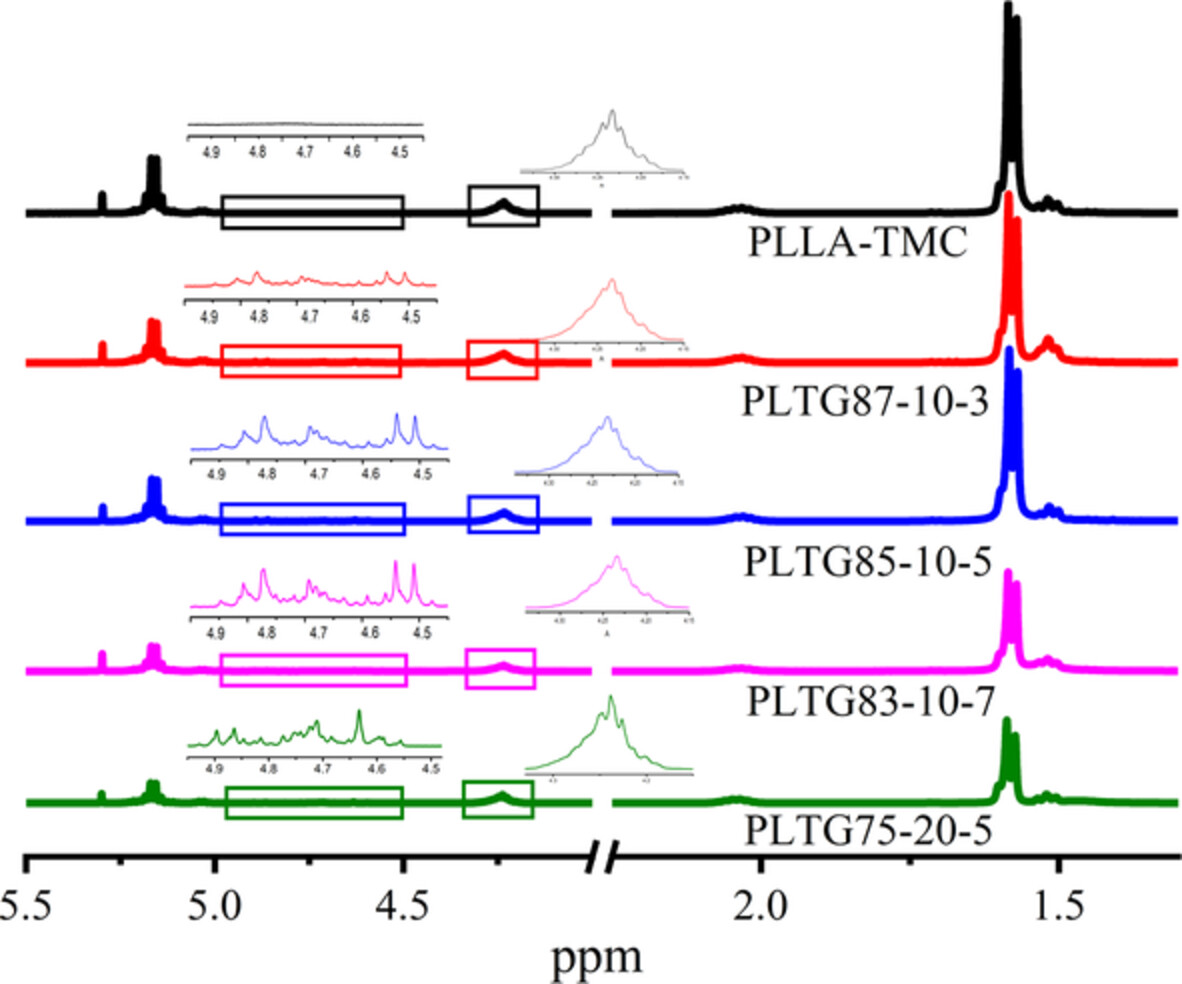
Structure, properties, and in vitro degradation behavior of biodegradable poly(L-lactic acid)-trimethylene carbonate-glycolide terpolymer
- First Published: 02 August 2022
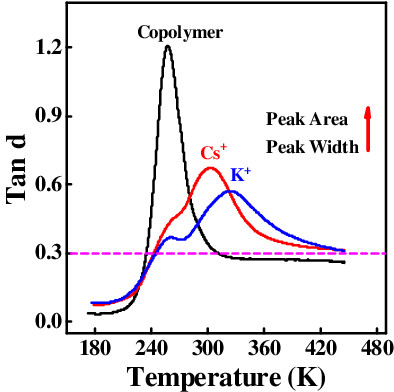
Damping properties of acrylate polymers mediated by ionic coordination
- First Published: 05 August 2022
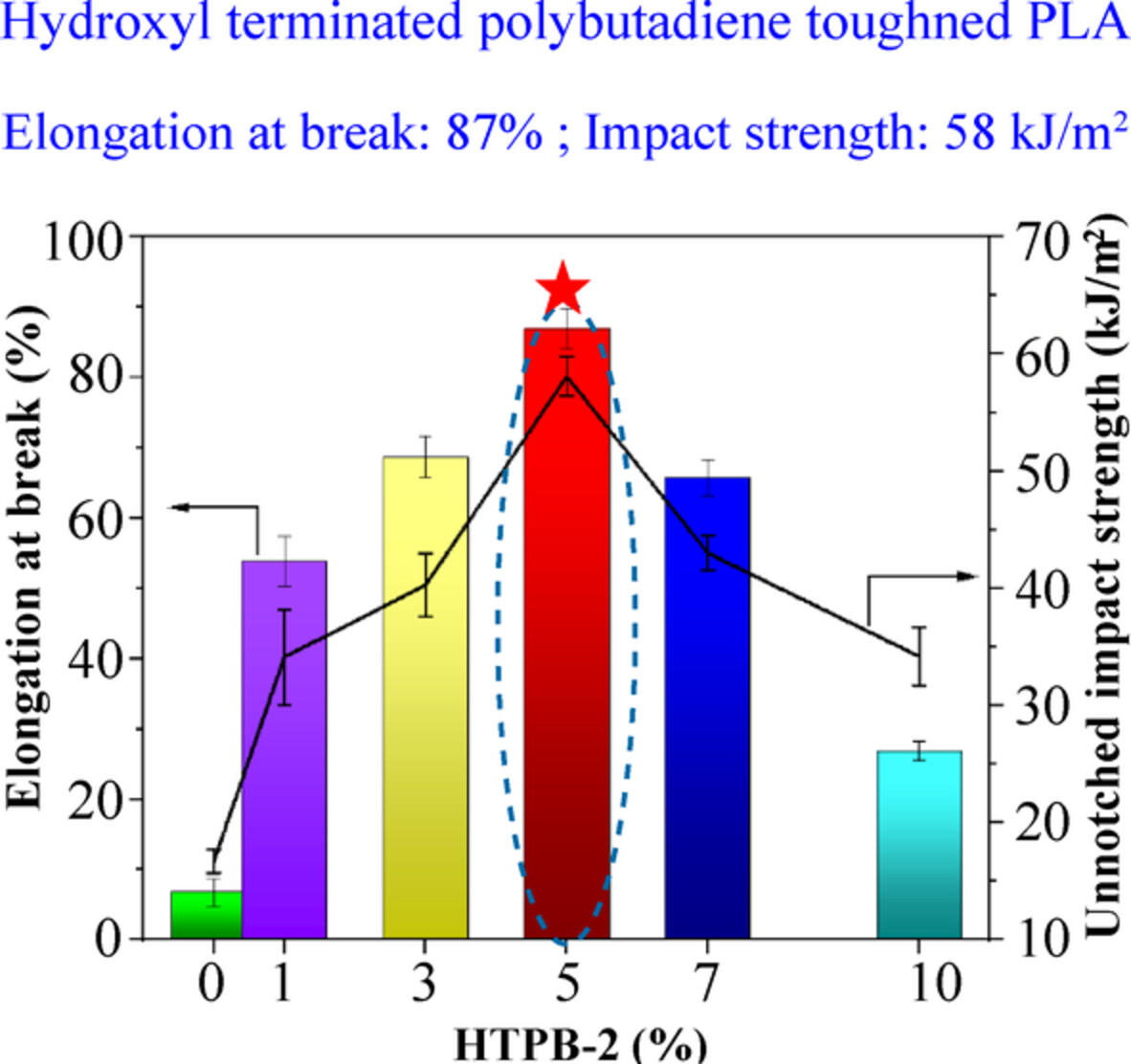
Enhancing toughness of poly(lactic acid) by regulating the hydroxyl value and viscosity of hydroxyl terminated polybutadiene
- First Published: 29 July 2022
Wet continuous mixing technique based on full formula of carbon black
- First Published: 10 August 2022
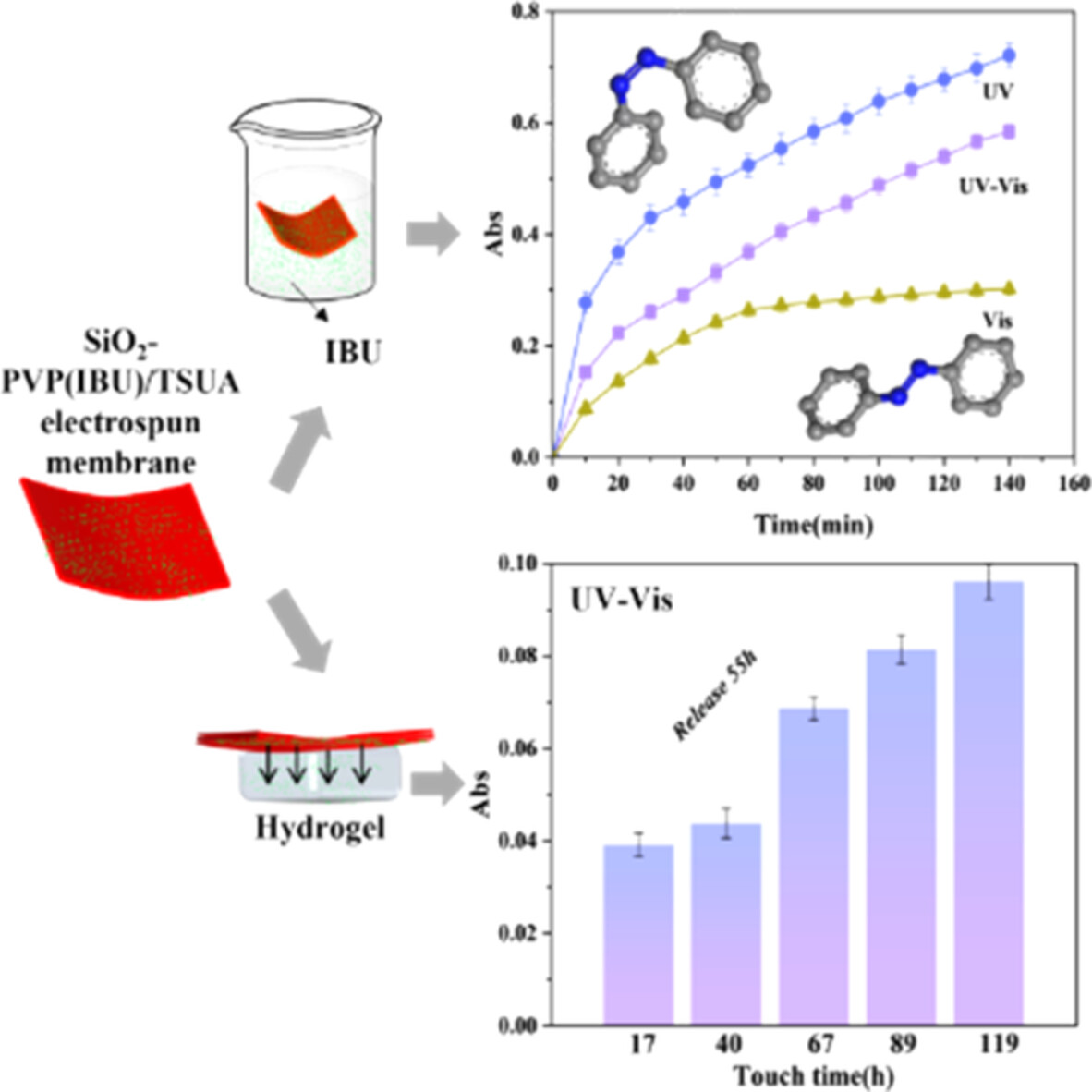
Drug release behaviors of flexible SiO2-polyvinyl pyrrolidone electrospun membranes responsive to multiple stimuli
- First Published: 01 August 2022
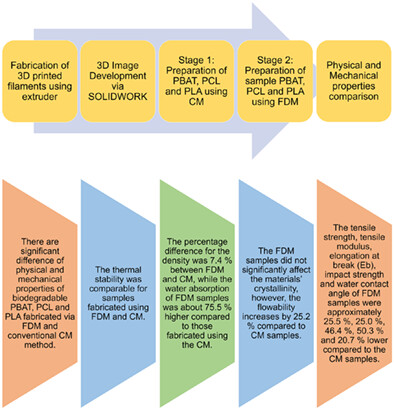
Comparison of physical and mechanical properties of biodegradable polybutylene adipate terephthalate, polycaprolactone, and poly(lactic acid) fabricated via fused deposition modeling and conventional molding
- First Published: 04 August 2022
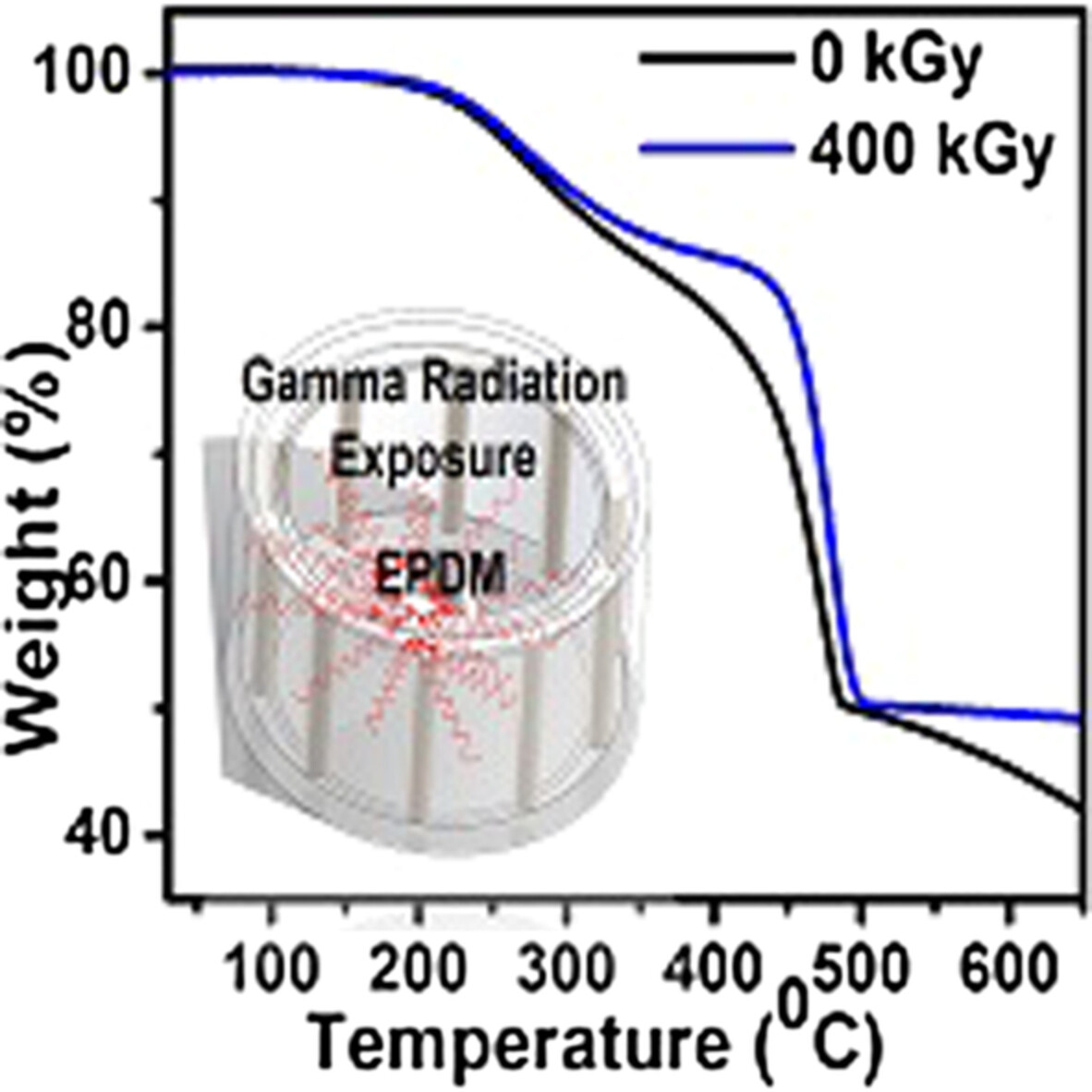
Thermal stability of gamma irradiated ethylene propylene diene monomer composites for shielding applications
- First Published: 05 August 2022
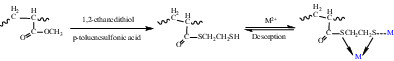
Synthesis of thiol-functionalized resin and its adsorption of heavy metal ions
- First Published: 06 August 2022
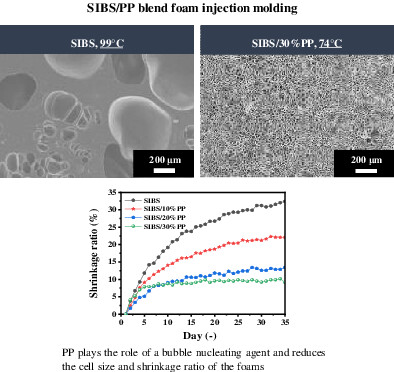
Microcellular foam of styrene–isobutylene–styrene copolymer with N2 using polypropylene as a crystallization nucleating and shrinkage reducing agent
- First Published: 11 August 2022
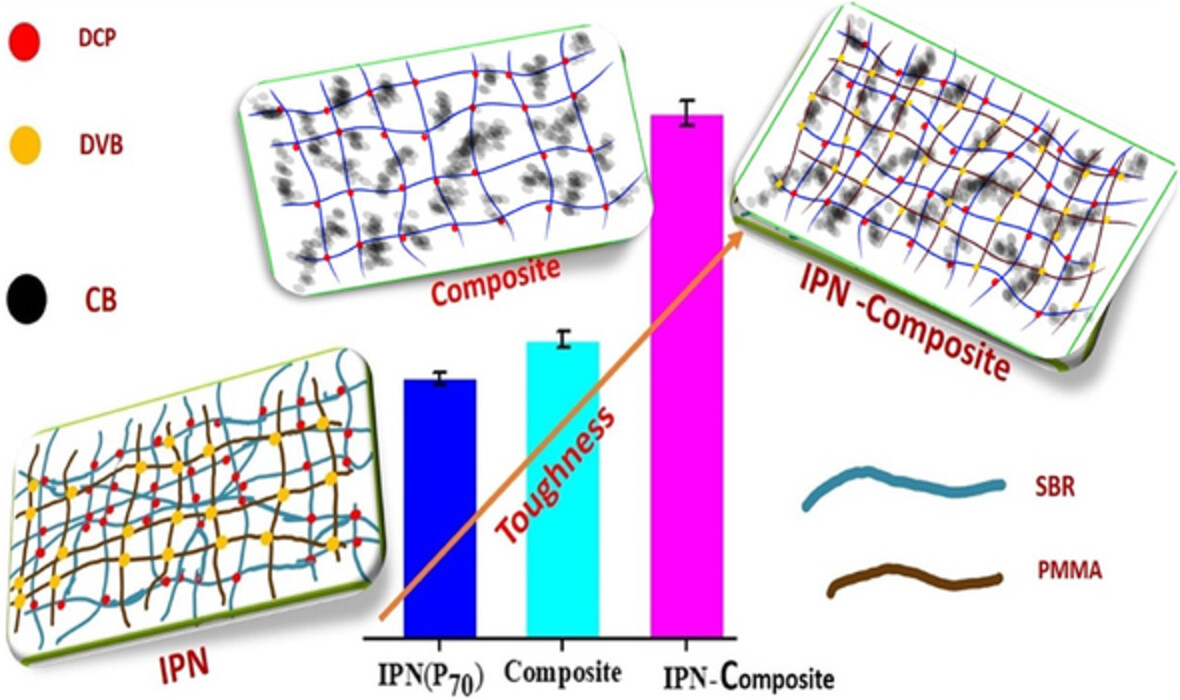
Super tough interpenetrating polymeric network of styrene butadiene rubber-poly(methyl methacrylate) incorporated with general purpose carbon black (N660)
- First Published: 13 August 2022
Evaluation and mechanism of interaction effect between thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer modified asphalt and fillers
- First Published: 19 August 2022
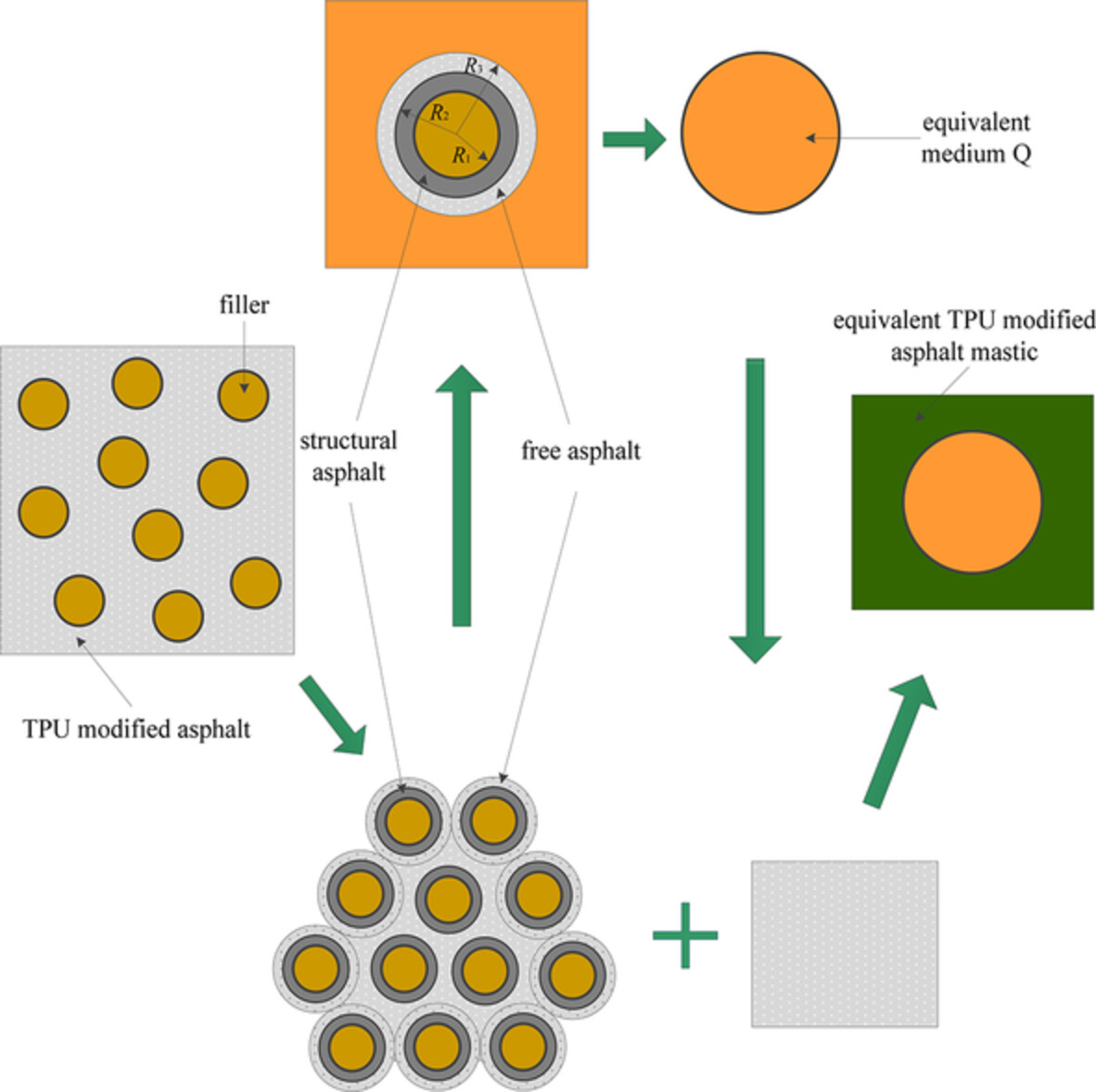
The structural asphalt and free asphalt can affect the macroscopic mechanical properties of asphalt mastic. Hence, TPU modified asphalt mastic can be regard as a two-phase composite material composed of TPU modified asphalt and filler. Its rheological characteristics and internal mechanism are affected by TPU modified asphalt and different kind of fillers.