Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 139, Issue 42
- First Published: 01 October 2022
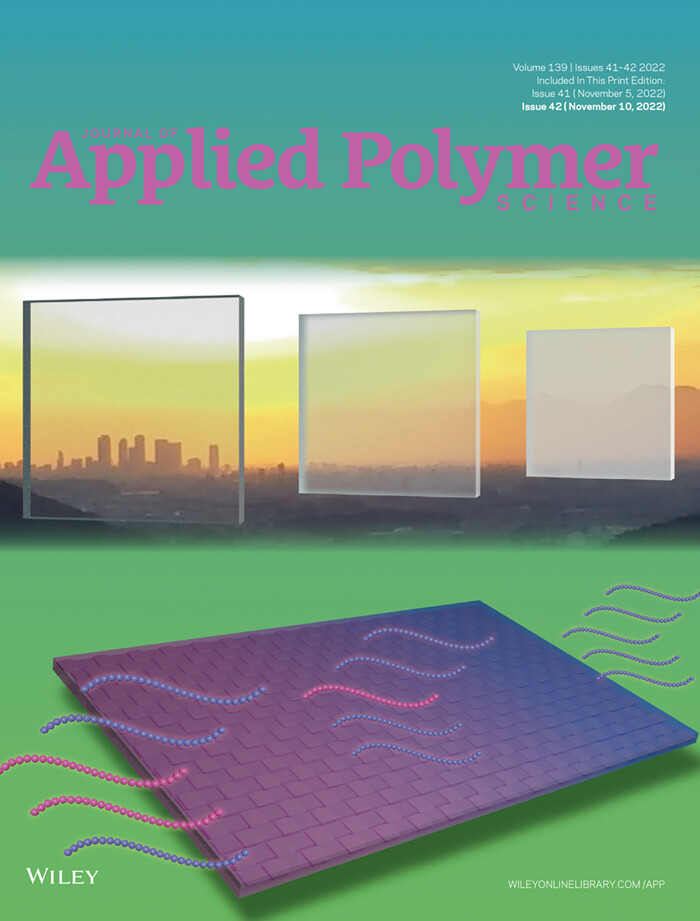
The cover image by Takayuki Hirai, Yoshimi Muraoka, and Hirotaka Okamoto shows transparent composites achieved by refractive index matching between glass fiber textiles and polymer blends of polycarbonate (PC) and polycaprolactone (PCL). The PC/PCL blend shows good transparency due to its miscibility, and refractive index matching between glass fiber and PC/PCL blend can be achieved by optimizing a composition ratio of PC and PCL. The transparent composite was obtained by impregnating the refractive index adjusted PC/PCL into a woven glass fiber. The composite shows optical transparency and excellent mechanical properties. DOI: 10.1002/app.52925
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLES
Strong, transparent composites based on glass-fiber textile and a polycarbonate–polycaprolactone blend with matching refractive indices
- First Published: 26 July 2022
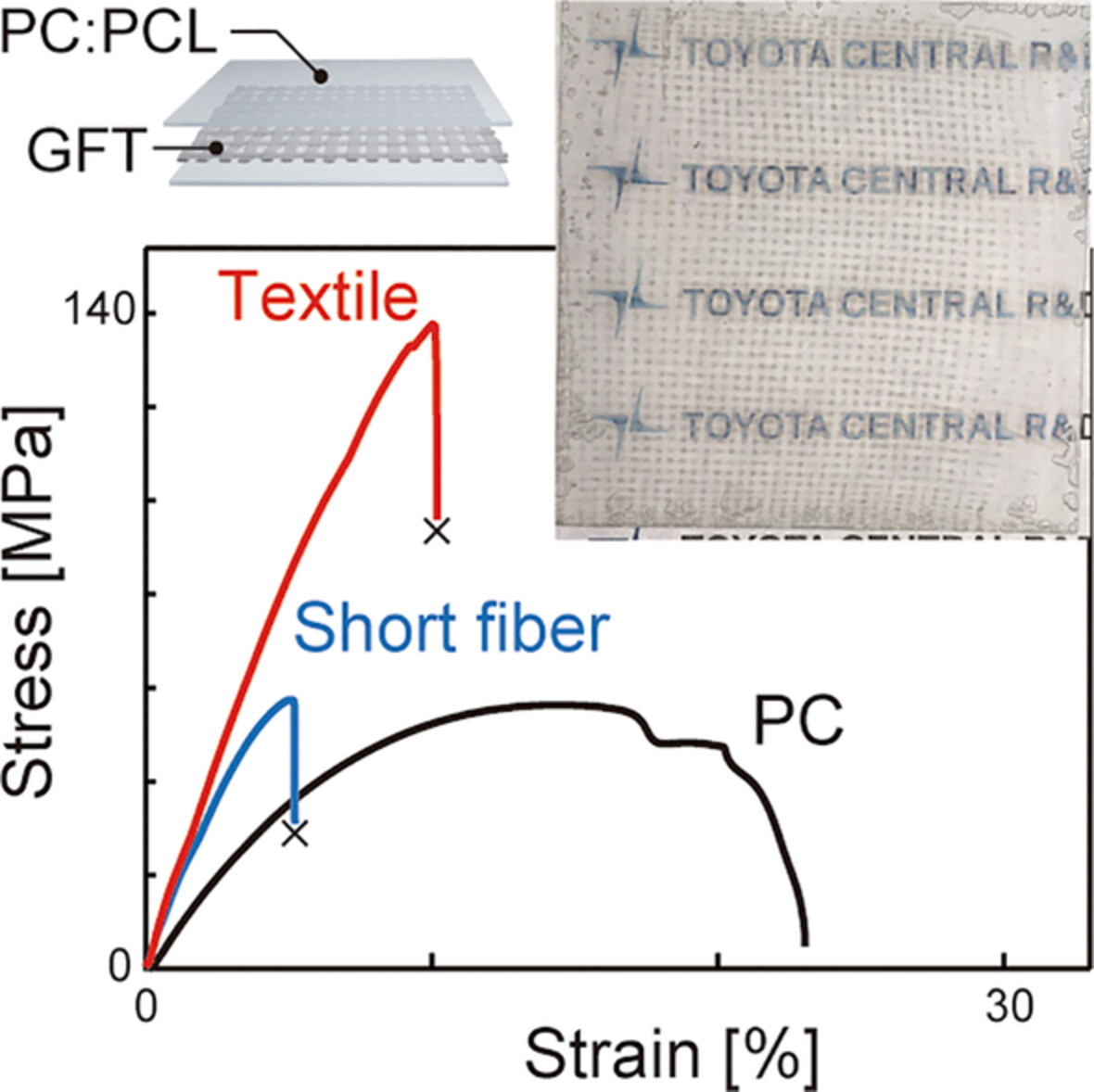
A transparent composite is developed based on E-glass fiber and a polymer blend by refractive index matching. Polycarbonate (PC) and polycaprolactone (PCL) is used as the matrix of the composite due to their miscibility and refractive index adjustability of PC–PCL blends. The impregnation of a glass-fiber textile with an optimized PC–PCL blend produces a strong, transparent composite.
Construction of antifouling and antibacterial polyhexamethylguanidine/chondroitin sulfate coating on polyurethane surface based on polydopamine rapid deposition
- First Published: 13 August 2022
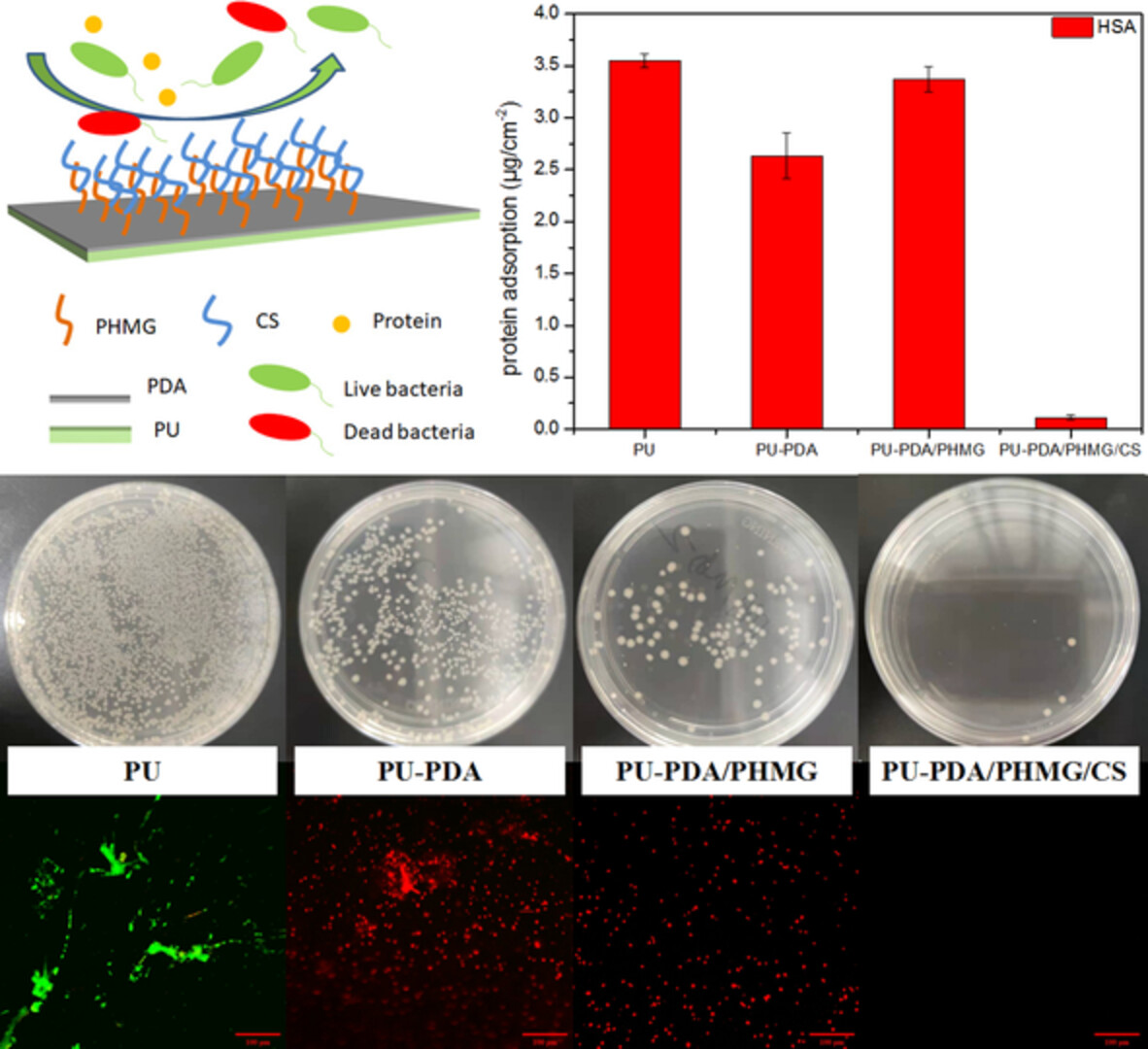
This article develops an antifouling and antibacterial coatings on PU surface based on PDA fast deposition. The coatings contain antibacterial agents polyhexamethyleneguanidine (PHMG) and hydrophilic polysaccharide chondroitin sulfate (CS), which endow surface with excellent anti-protein adsorption property and antibacterial ability. And the whole preparation process is environmentally friendly, which ensures the coatings good bio-compatibility.
Flexible polymeric biomaterials from epoxidized soybean oil, epoxidized oleic acid, and citric acid as both a hardener and acid catalyst
- First Published: 11 August 2022
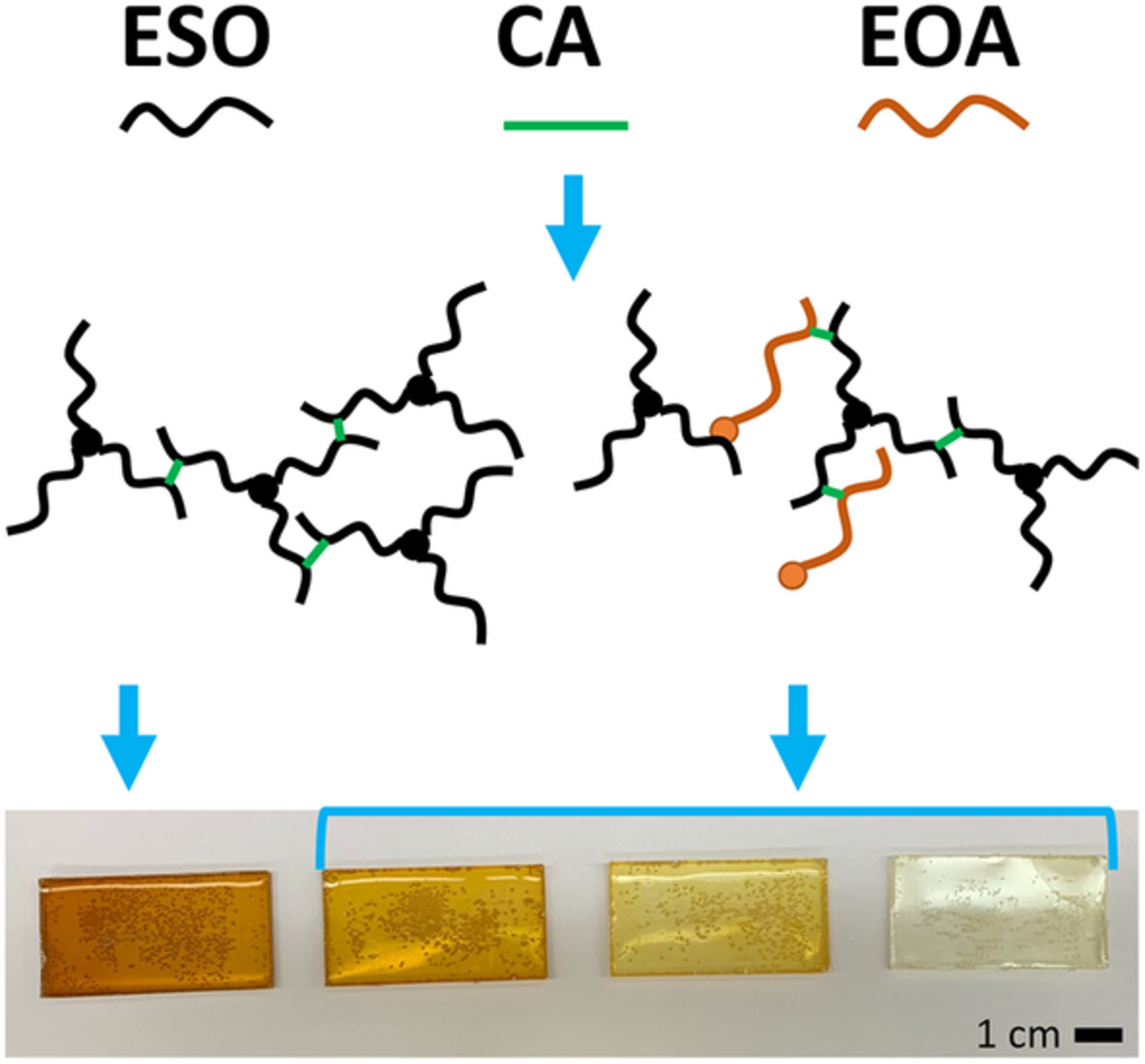
Flexible bio-based polymeric materials were produced by combining epoxidized soybean oil (ESO), aqueous citric acid solutions, and varying amounts of epoxidized oleic acid (EOA), followed by heating at 95°C for 24 h. Their mechanical properties can be tuned with EOA: increasing EOA decreases stiffness and increases stretchiness. These materials are also impermeable to water, making them promising bio-bases alternatives to plastics.
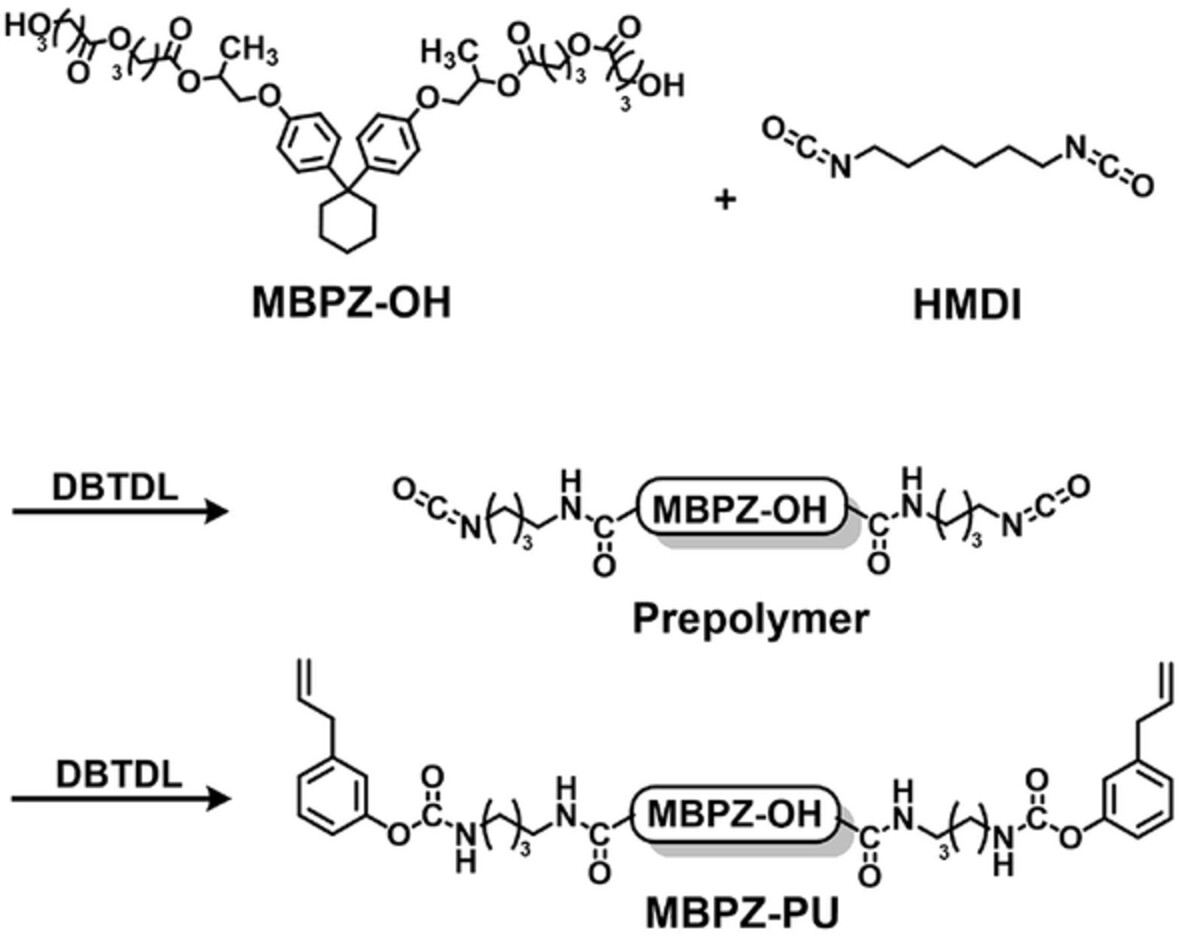
Polyol and polyurethane containing bisphenol-Z: Synthesis and application for toughening epoxy
- First Published: 17 August 2022
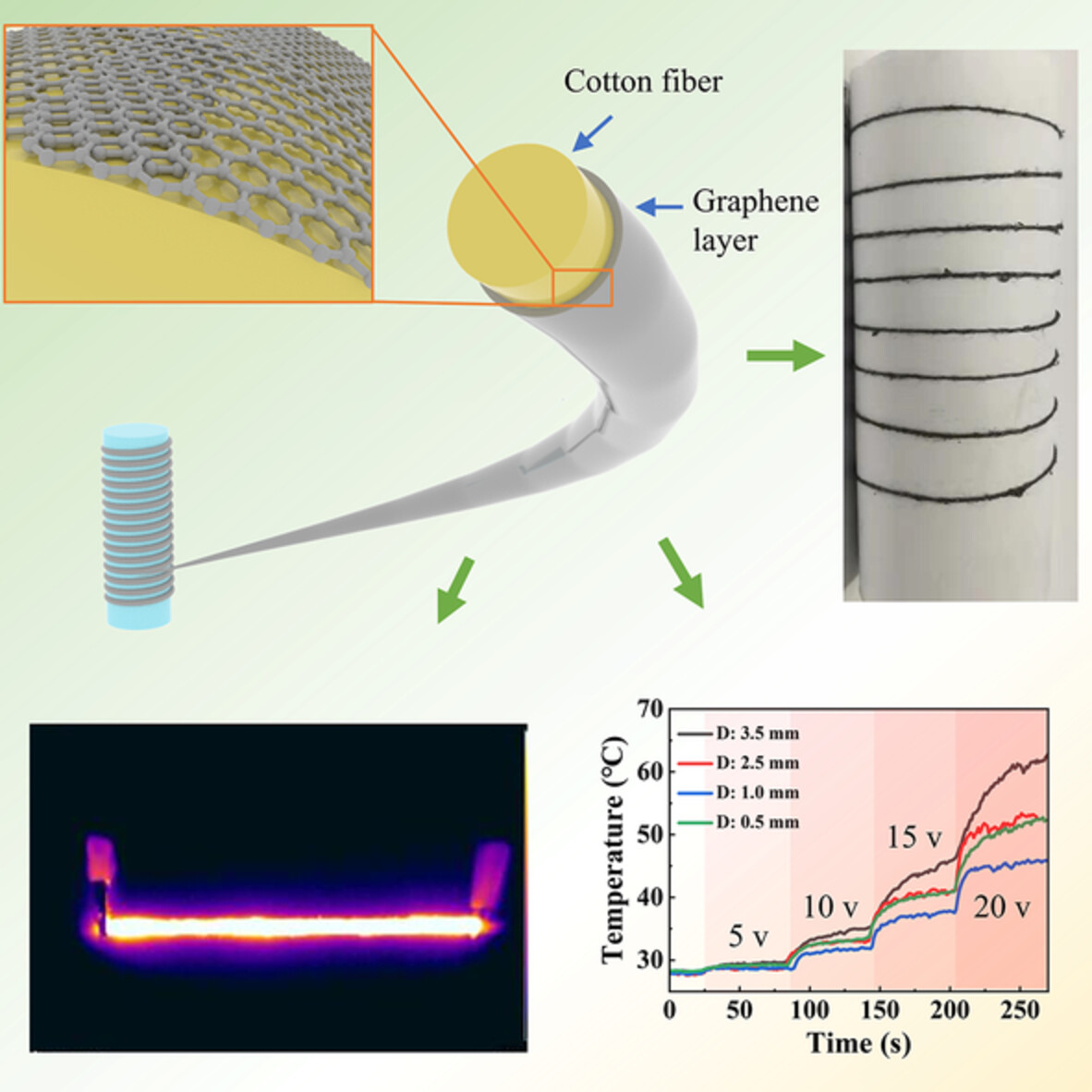
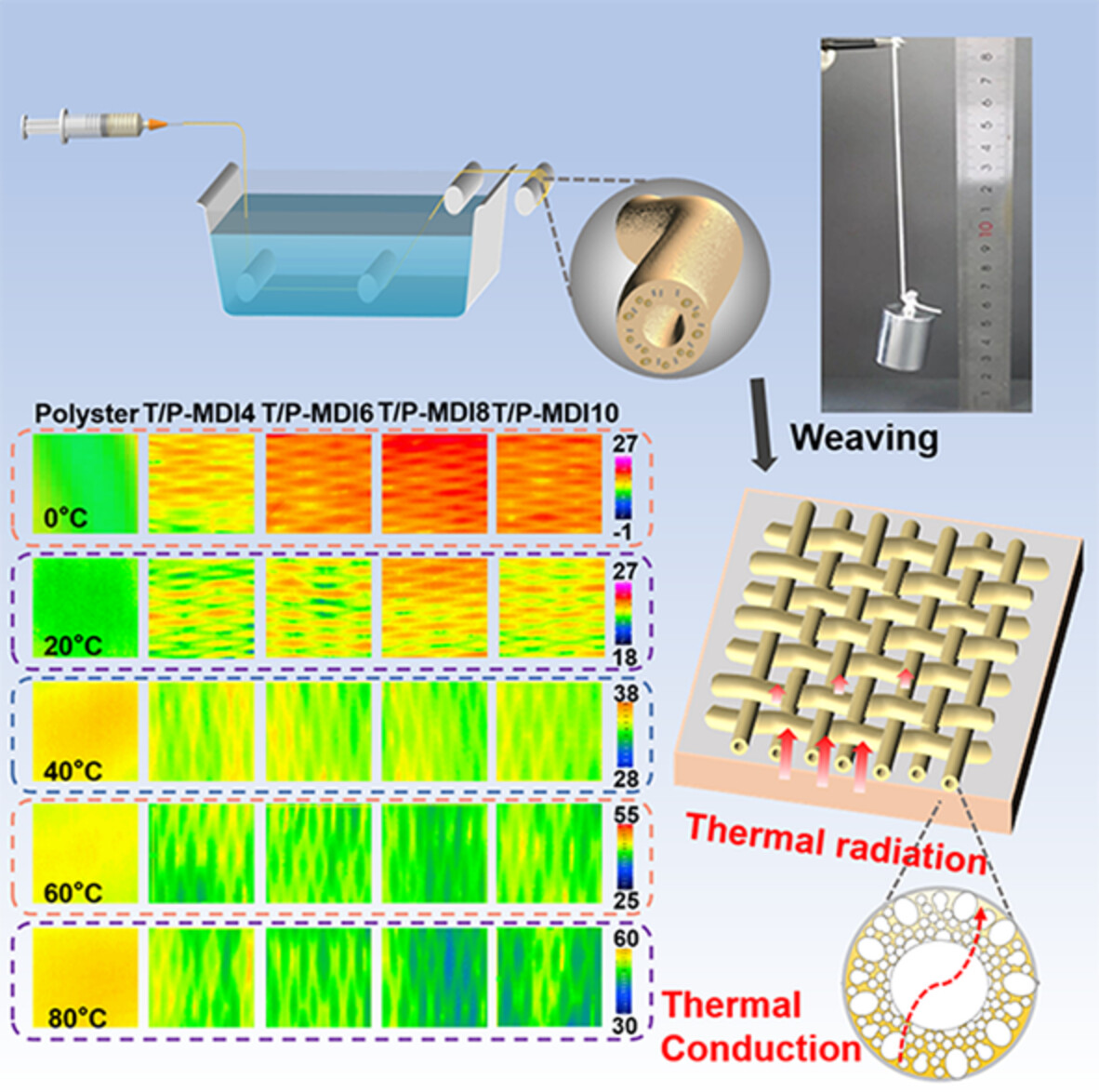
High-performance electric heating yarns based on graphene-coated cotton fibers
- First Published: 12 August 2022
Anti-fouling performance of polyamide microfiltration membrane modified with surfactants
- First Published: 12 August 2022
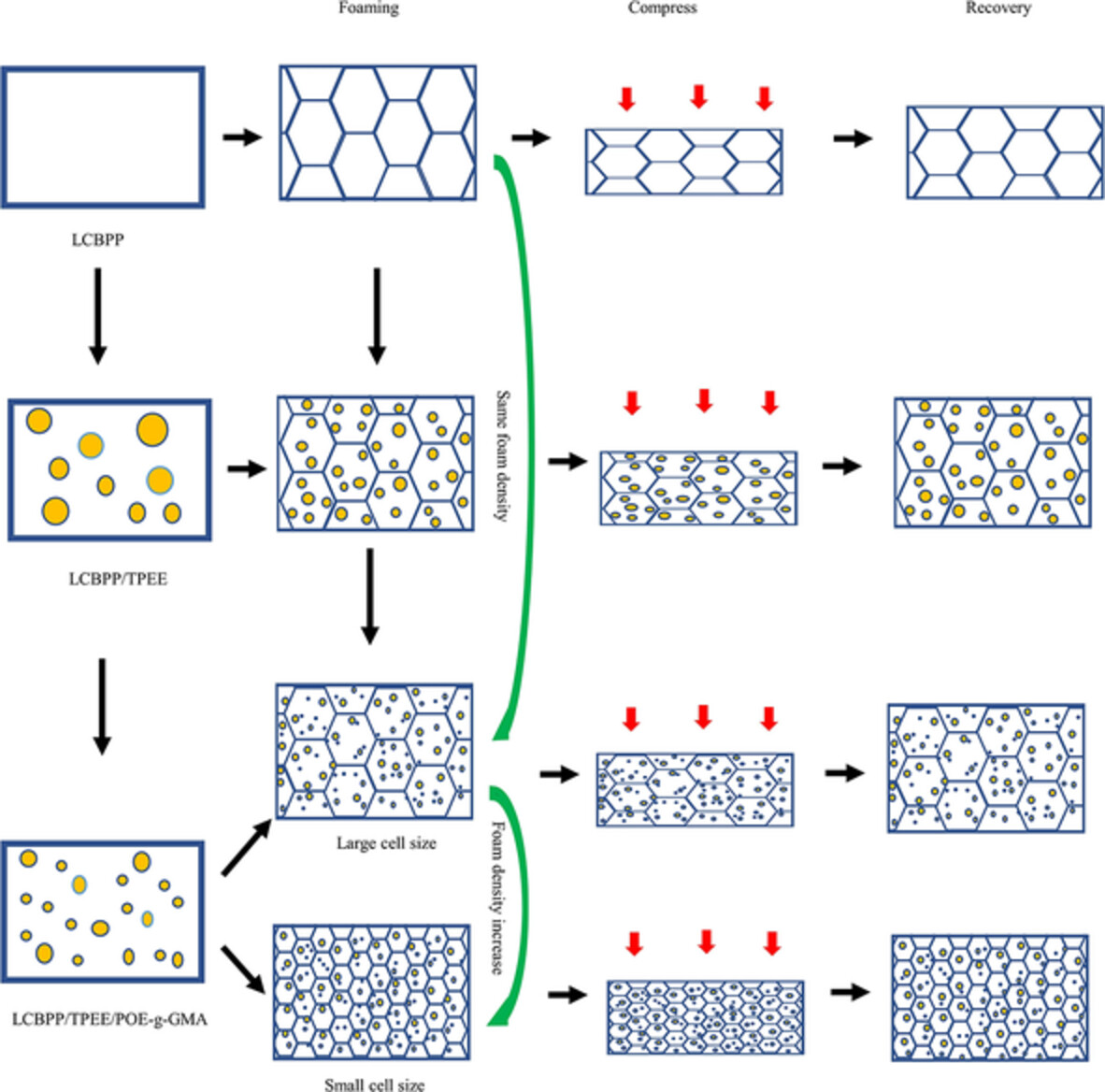
Fabrication strategy for long-chain branched polypropylene foams with high resilience and compressive strength
- First Published: 11 August 2022
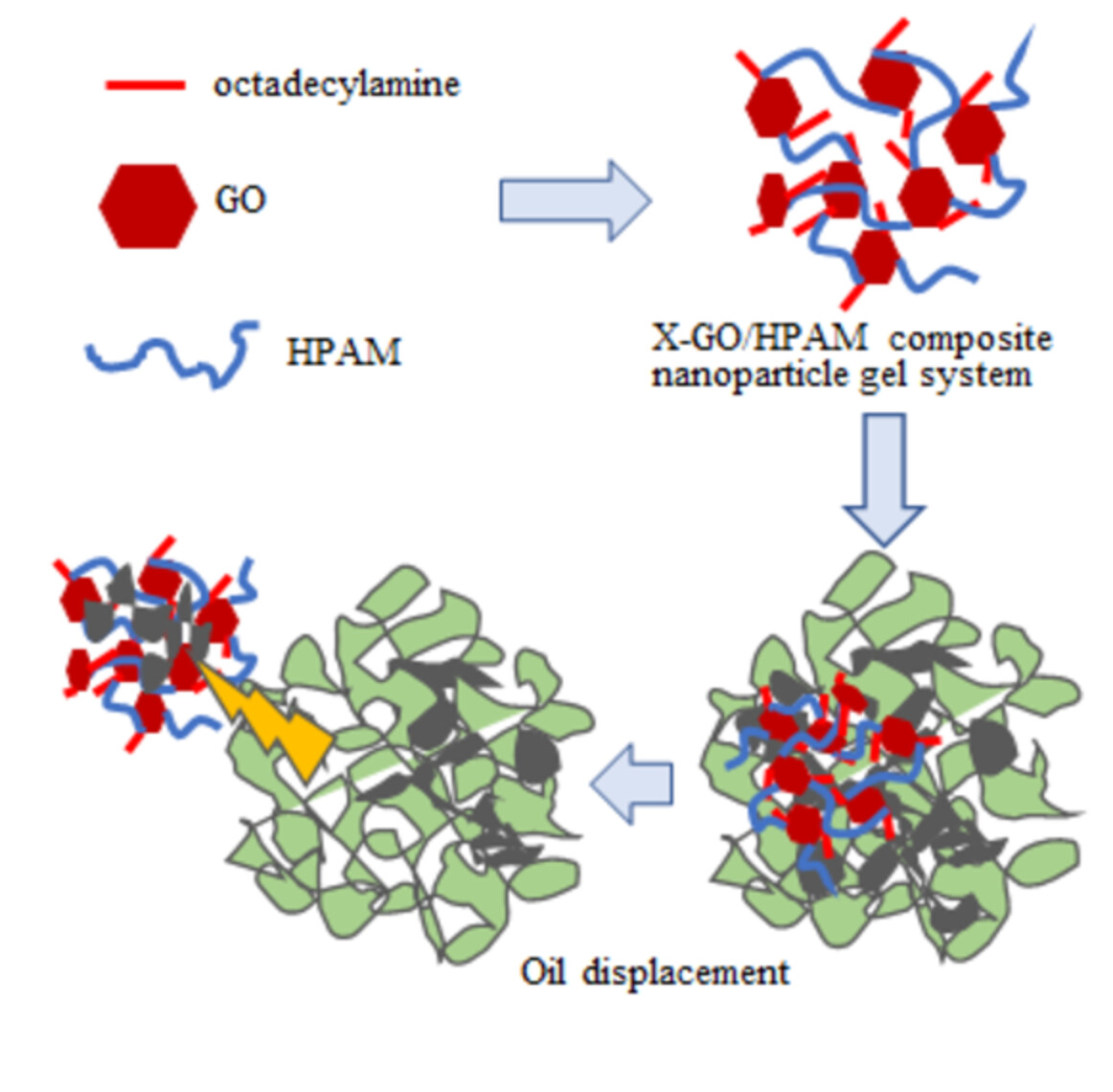
Preparation and properties of modified graphene oxide / polyacrylamide composite nanoparticle gel system
- First Published: 15 August 2022
Large-scalable polar bear hair-like cellular hollow fibers with excellent thermal insulation and ductility
- First Published: 13 August 2022
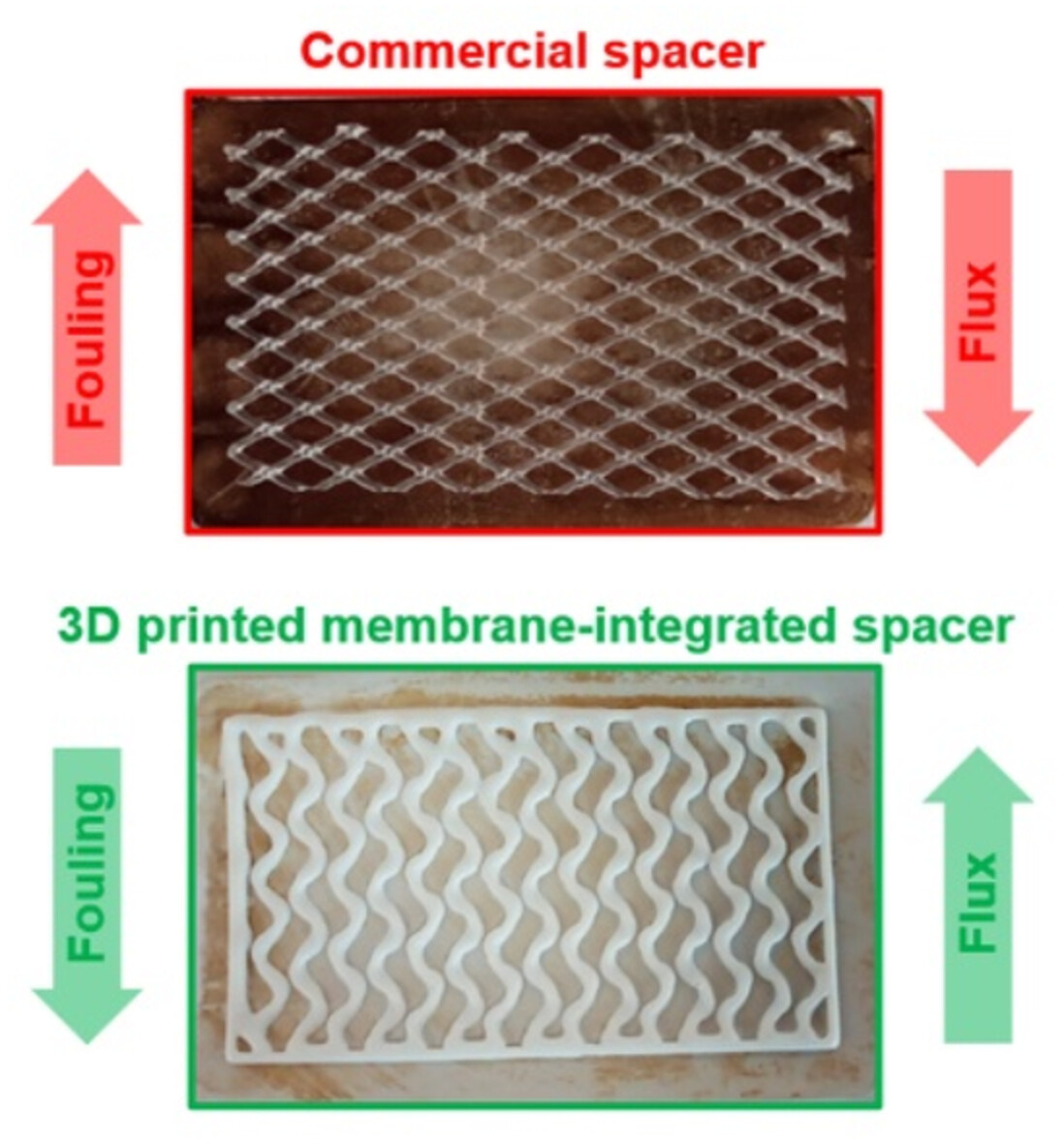
3D printed membrane-integrated spacers for enhanced antifouling in ultrafiltration
- First Published: 11 August 2022
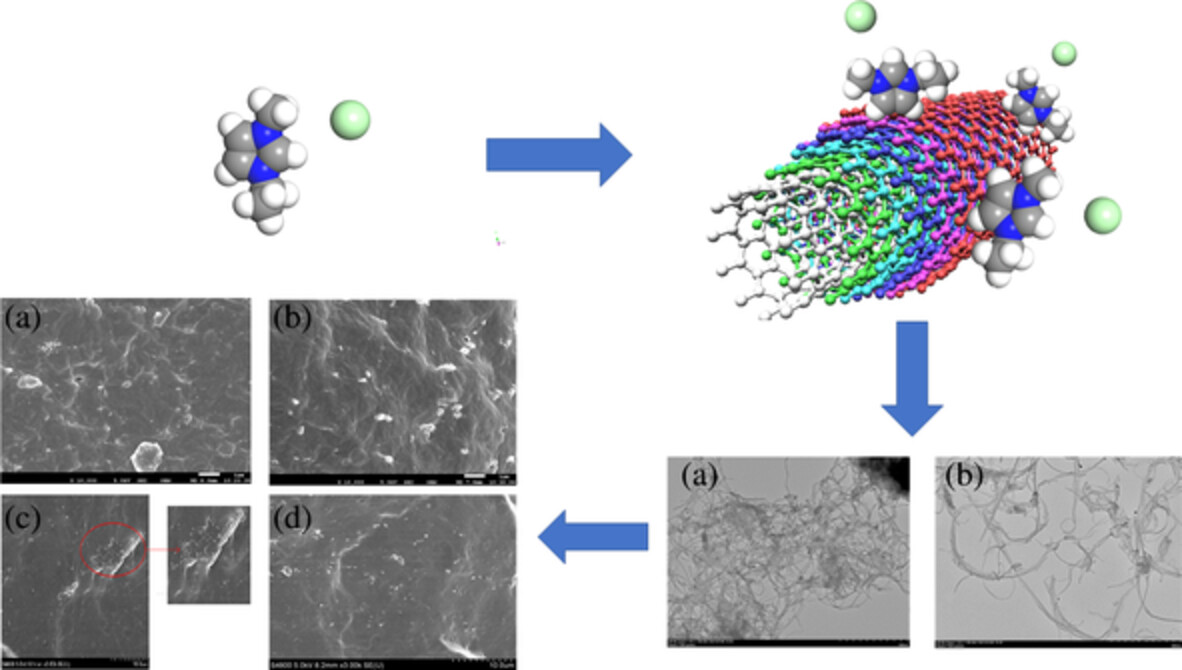
Effect of ionic liquid modified carbon nanotubes on the properties of nitrile butadiene rubber and nitrile butadiene latex nanocomposites
- First Published: 15 August 2022
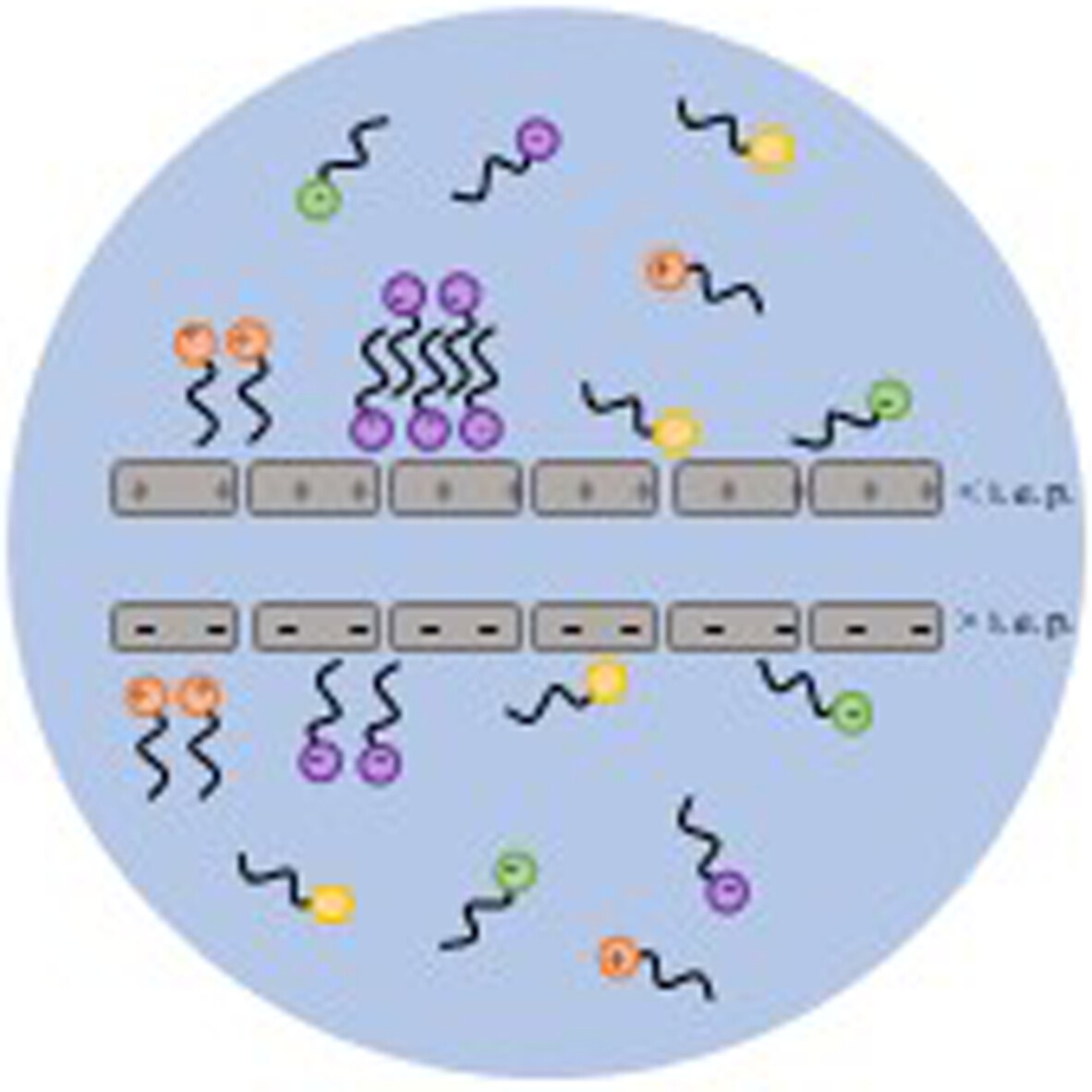
Development of poly(butyl acrylate-co-oleic acid) as biobased polymeric dispersant and its application in preparation of pigment concentrate
- First Published: 12 August 2022
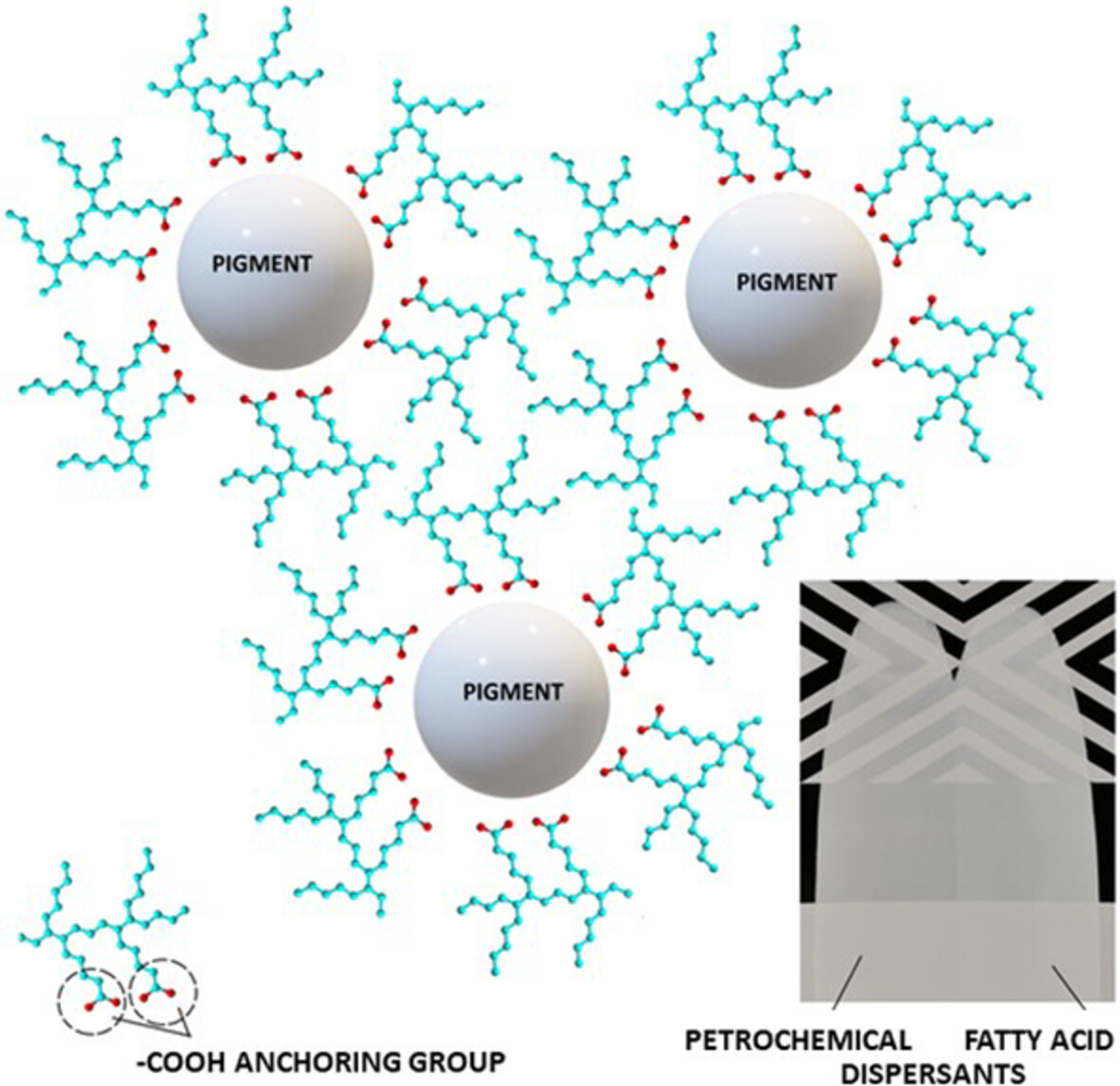
This image illustrates fatty acid-based polymeric dispersant in action, dispersing titania pigment effectively in pigment concentrate for surface coating application. The carboxyl group from oleic acid serves as effective pigment affinity group, allowing effective adsorption of the dispersant at the surface of the pigment, while the relatively long hydrocarbon side chain from the incorporated fatty acids provides good steric stabilization effect. The optical properties of coating produced from such pigment concentrate is of excellent quality.
Multifunctional biocompatible films based on pectin-Ag nanocomposites and PVA: Design, characterization and antimicrobial potential
- First Published: 17 August 2022
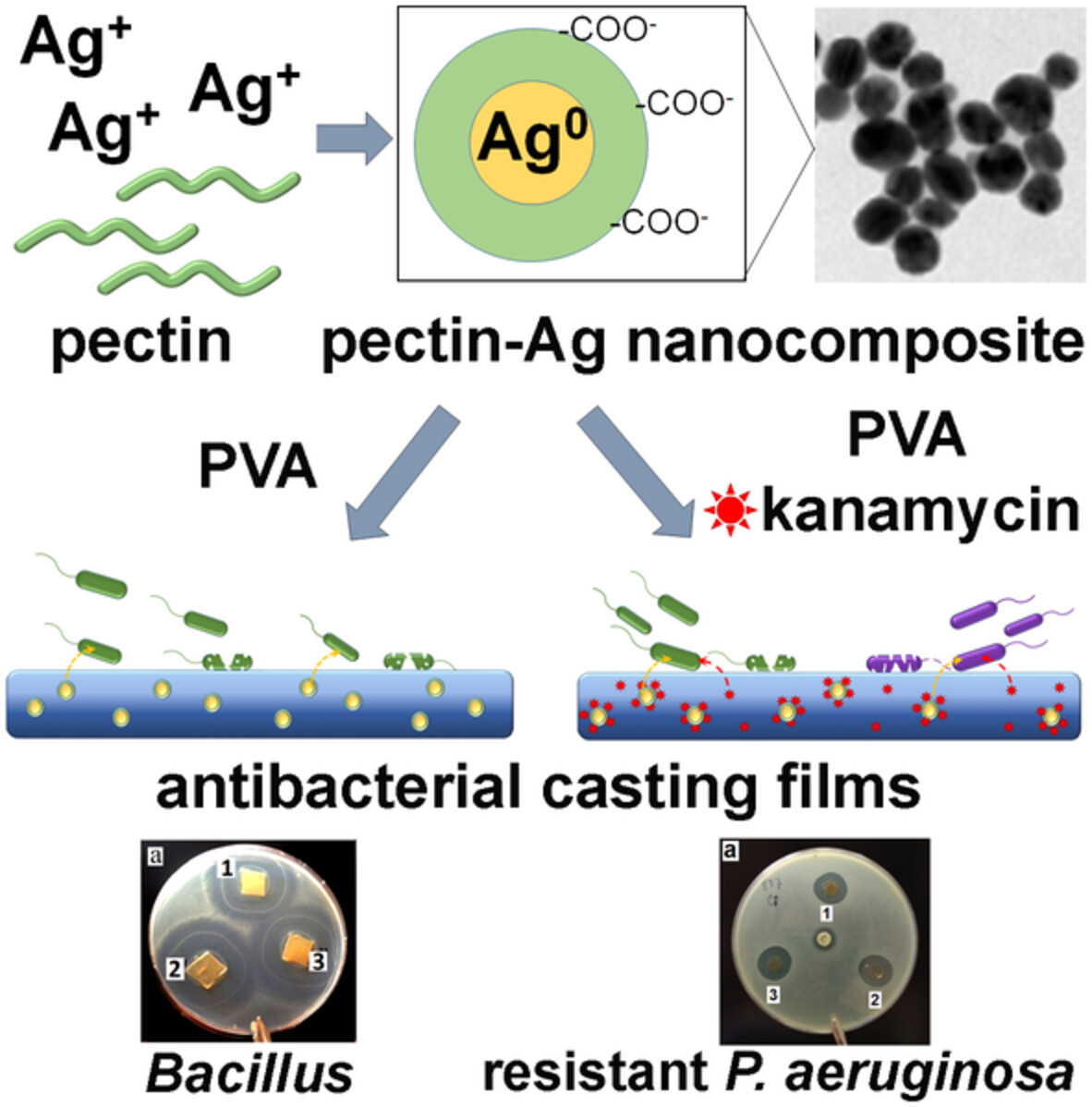
This study introduces a comparative assay of physicochemical, mechanical, and antibacterial properties of the films based on pectin-Ag nanocomposites, synthesized by “green chemistry” method, and polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) with different molecular weight. Prolonged release of antibiotic kanamycin (KAN) and antimicrobial effect of pectin-Ag/PVA/KAN films against gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria have been demonstrated.
Activation of R-BAPB polyimide with cold plasma dielectric barrier discharge for improvement of cell-material interaction
- First Published: 12 August 2022
Influence of physical aging of ferroelectric vinylidene fluoride copolymer films on their structural and electrophysical characteristics
- First Published: 16 August 2022
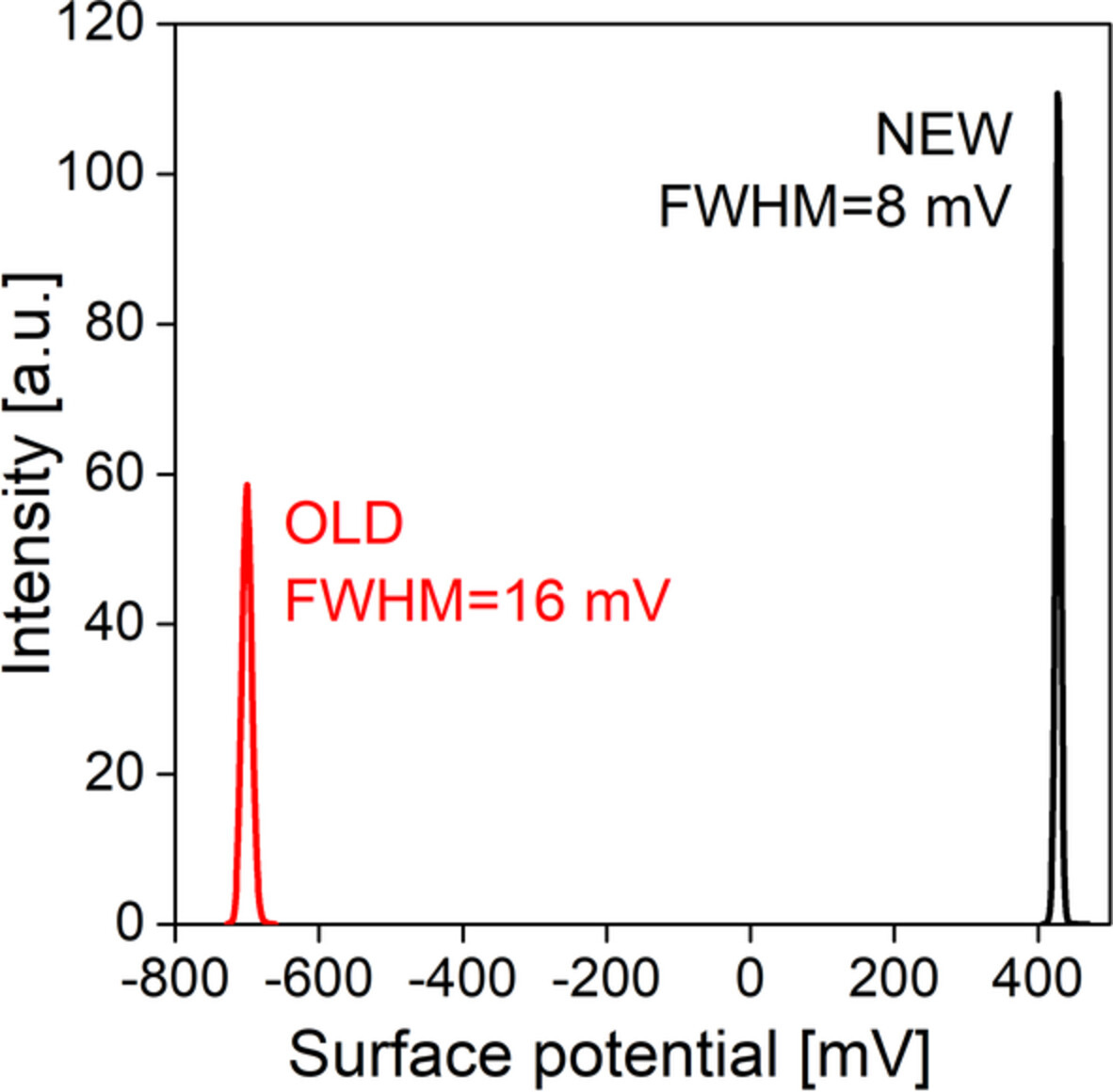
The use of the ferroelectric materials in hybrid nanogenerators based on triboelectricity requires the information on their surface potential. The latter was studied by the Kelvin-mode method on VDF-HFP copolymer films obtained by crystallization from solution in ethyl acetate. Freshly prepared films have a positive surface potential. Exposure of such a film at room temperature for 4 years is accompanied by structural changes: increase in the volume degree of crystallinity, but its strong decrease in the surface. The observed decrease occurs due to displacement of the amorphous phase chains, which contains sections of chains with monomer units attached in the "wrong" position, into the surface. Such structural changes are accompanied by significant changes in the surface potential, which changes its sign.
Improvement of structural vibration damping performance of SMCs through SMC/TPE sandwich structures
- First Published: 15 August 2022
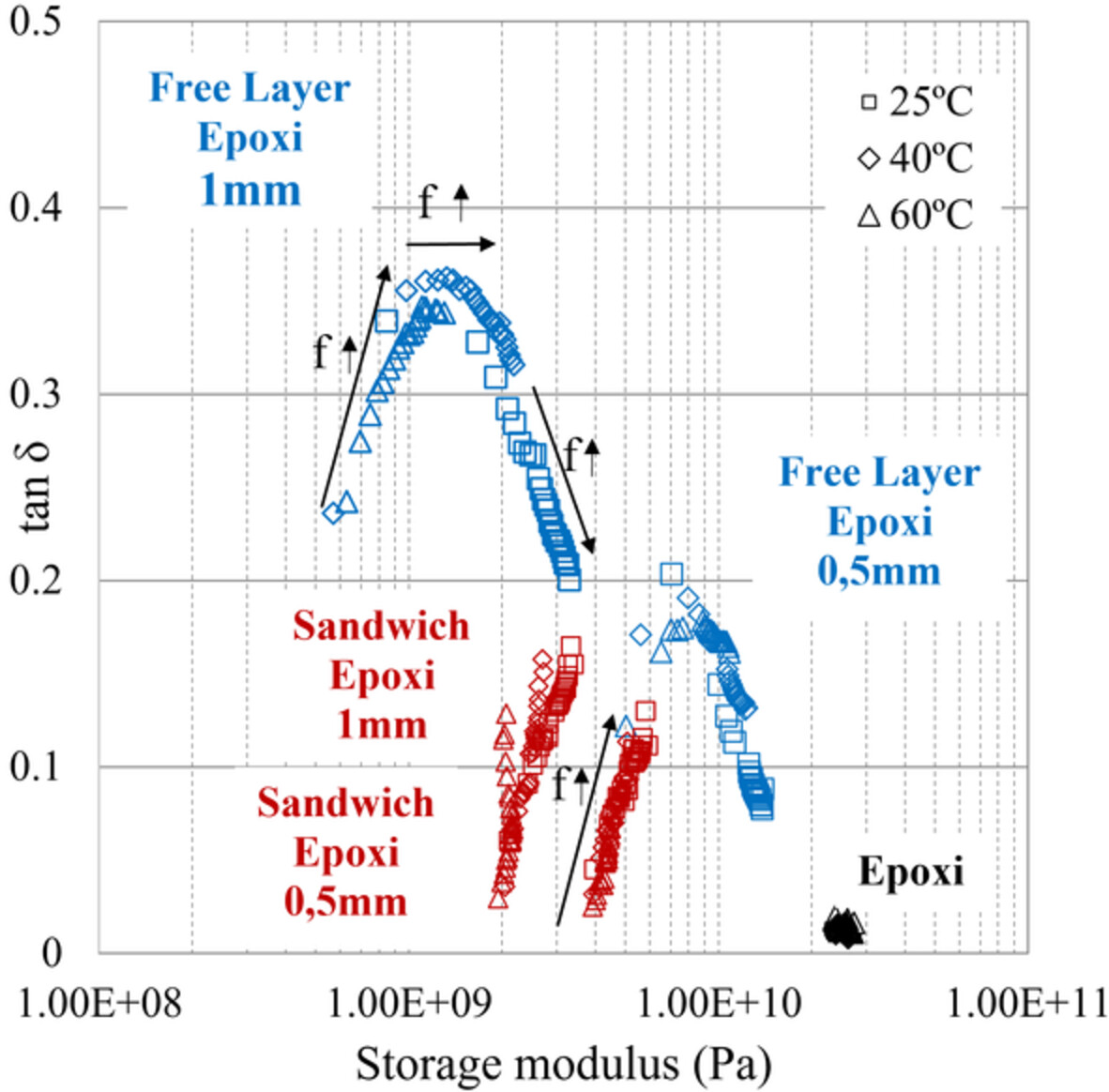
The vibration damping capabilities of Sheet Molding Compounds are enhaced by generating bi-material structures by means of the addition of Thermoplastic elastomer material layers.The bi-material structures can be construted by sandwich structures or by free layer damping structures. Each strategy implies several pos and cons regarding to the damping capabilities, overal mechanical performance and resistance to temperature.Sandwich structures show the most promising balance of the quoted variables.
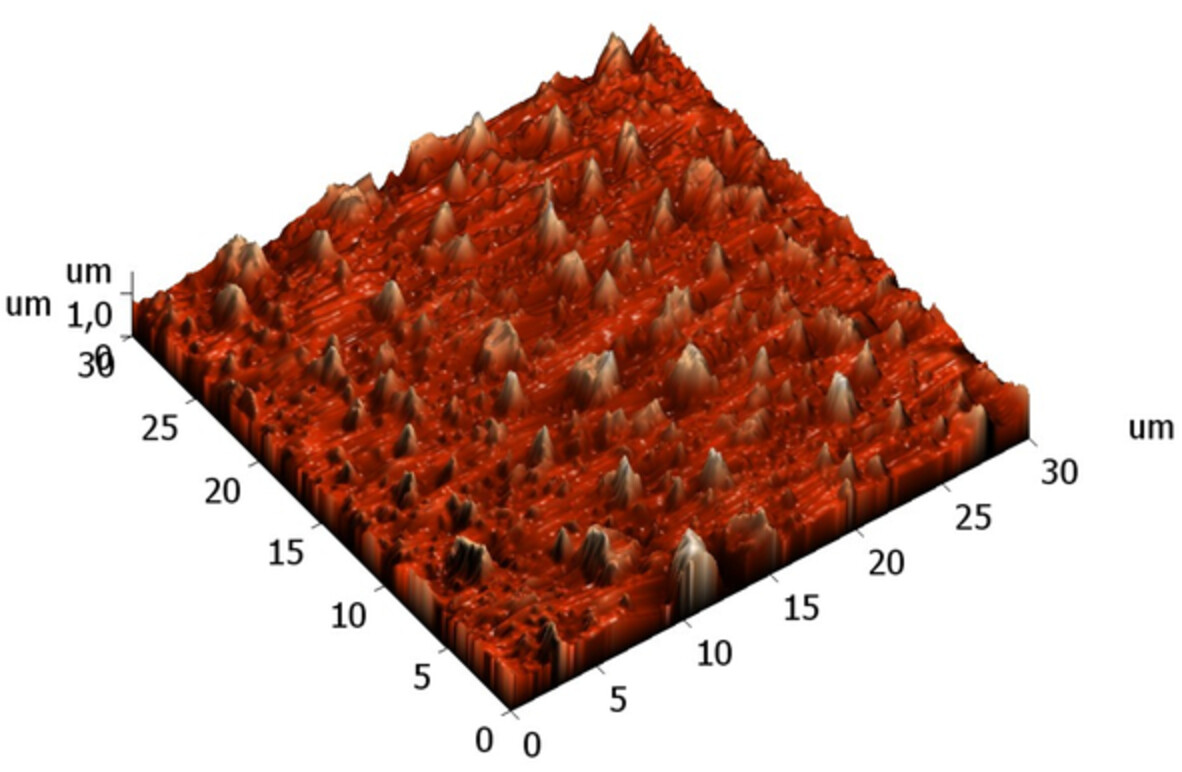
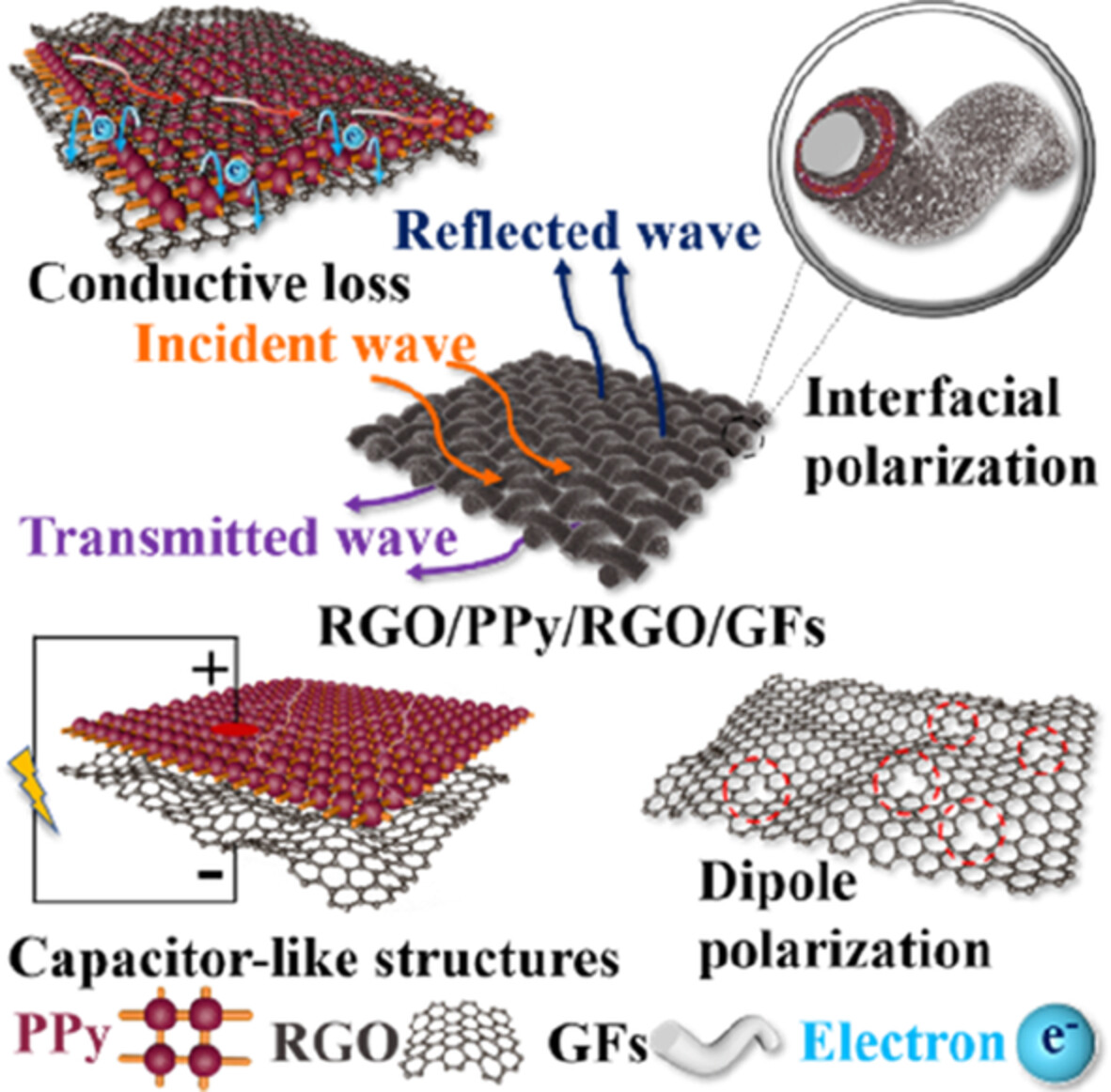
Constructing reduced graphene oxide and polypyrrole coatings on glass fiber to enhance its absorbing performance
- First Published: 11 August 2022
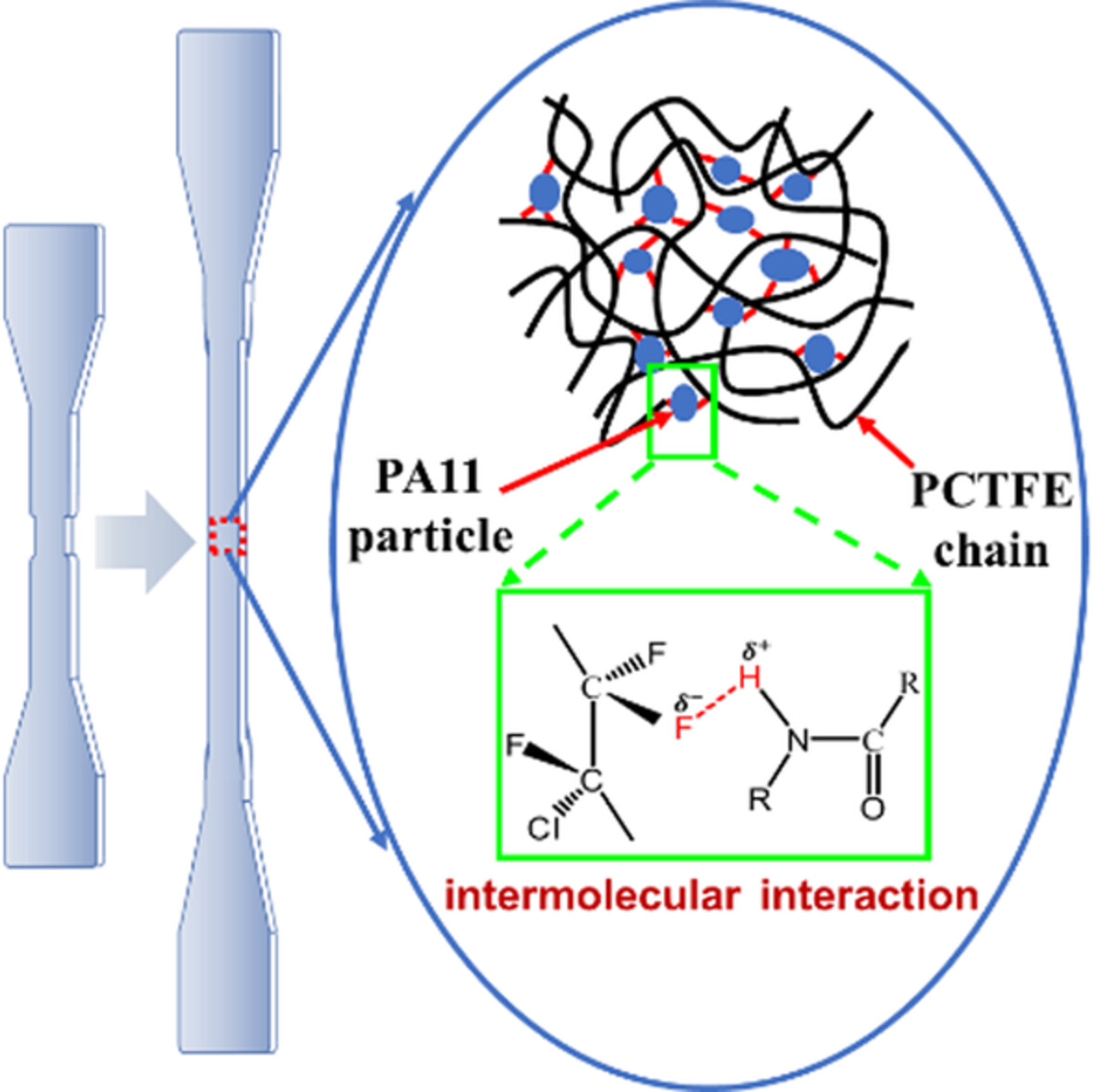
Mechanical properties and microstructure of polychlorotrifluoroethylene toughened by polyamide 11 based on intermolecular interaction
- First Published: 16 August 2022
Development of high-performance partially biobased thermoset polyester using renewable building blocks from isosorbide, 1,3-propanediol, and fumaric acid
- First Published: 29 August 2022
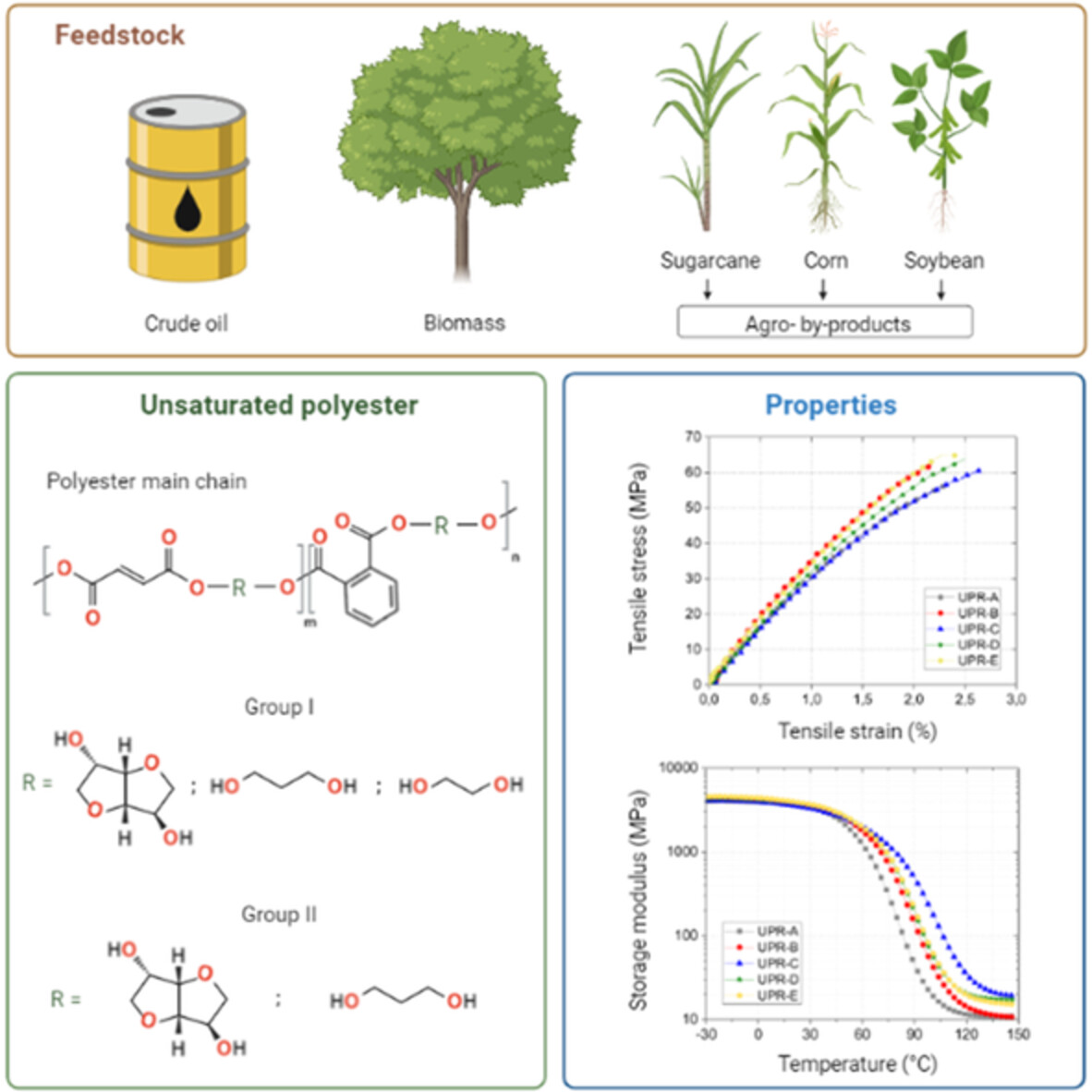
This article presents the development of biobased unsaturated polyesters based on building blocks synthesized with monomers produced from renewable raw materials, namely, isosorbide, 1,3-propanediol, and fumaric acid, with petroleum-derived phthalic anhydride. A blend between styrene and a less toxic acrylate-type monomer (2-hydroethyl methacrylate) is used as a reactive diluent, resulting in biobased crosslinked resins suitable for various high-performance applications.
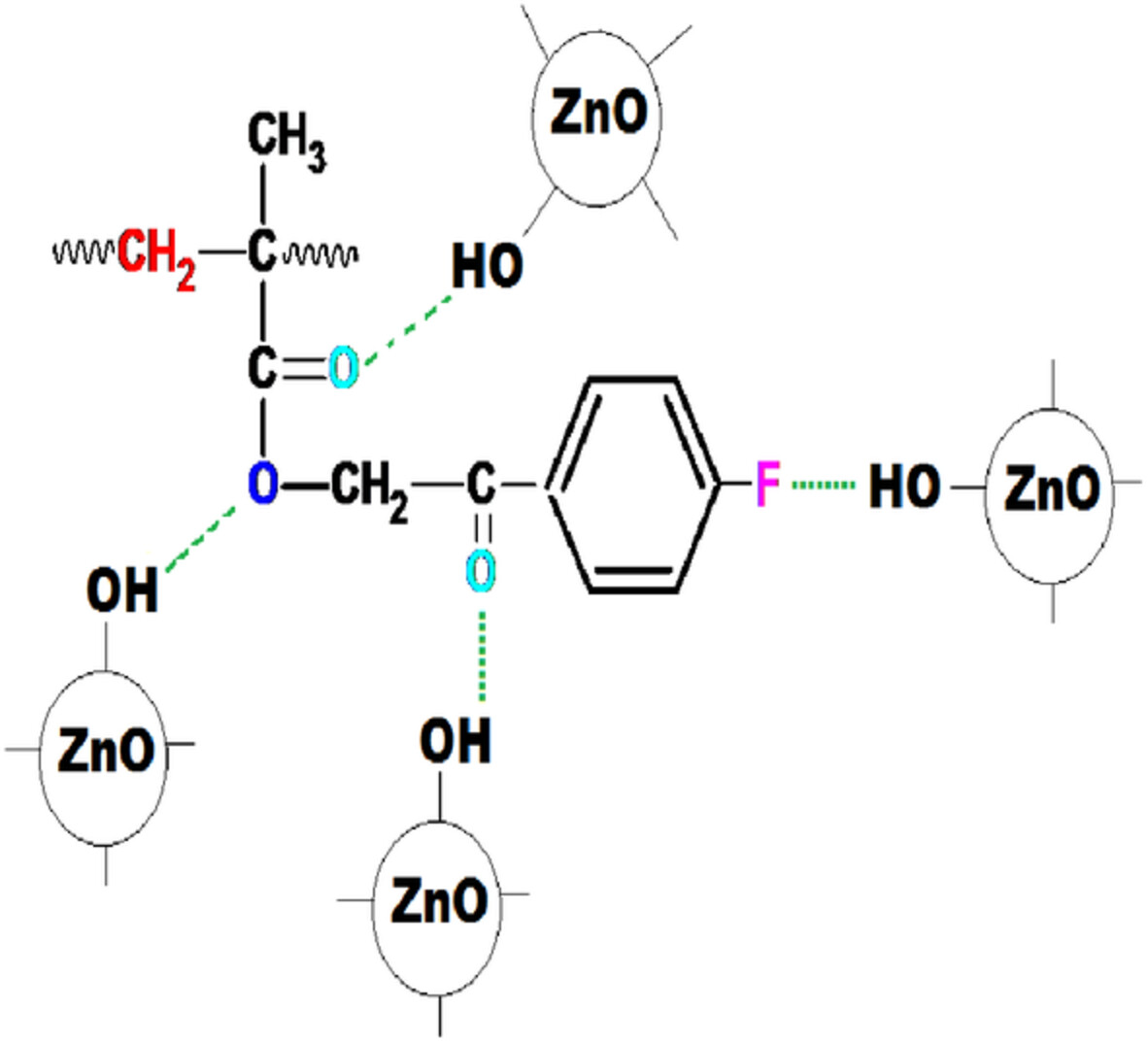
Synthesis of novel methacrylate-based nanocomposites containing ZnO via the hydrothermal method and determination of thermal, optical, and biocidal properties
- First Published: 16 August 2022
Preparation of BTCA-esterified cellulose nanocrystals and effects on mechanical and thermal properties of polypropylene composites
- First Published: 17 August 2022
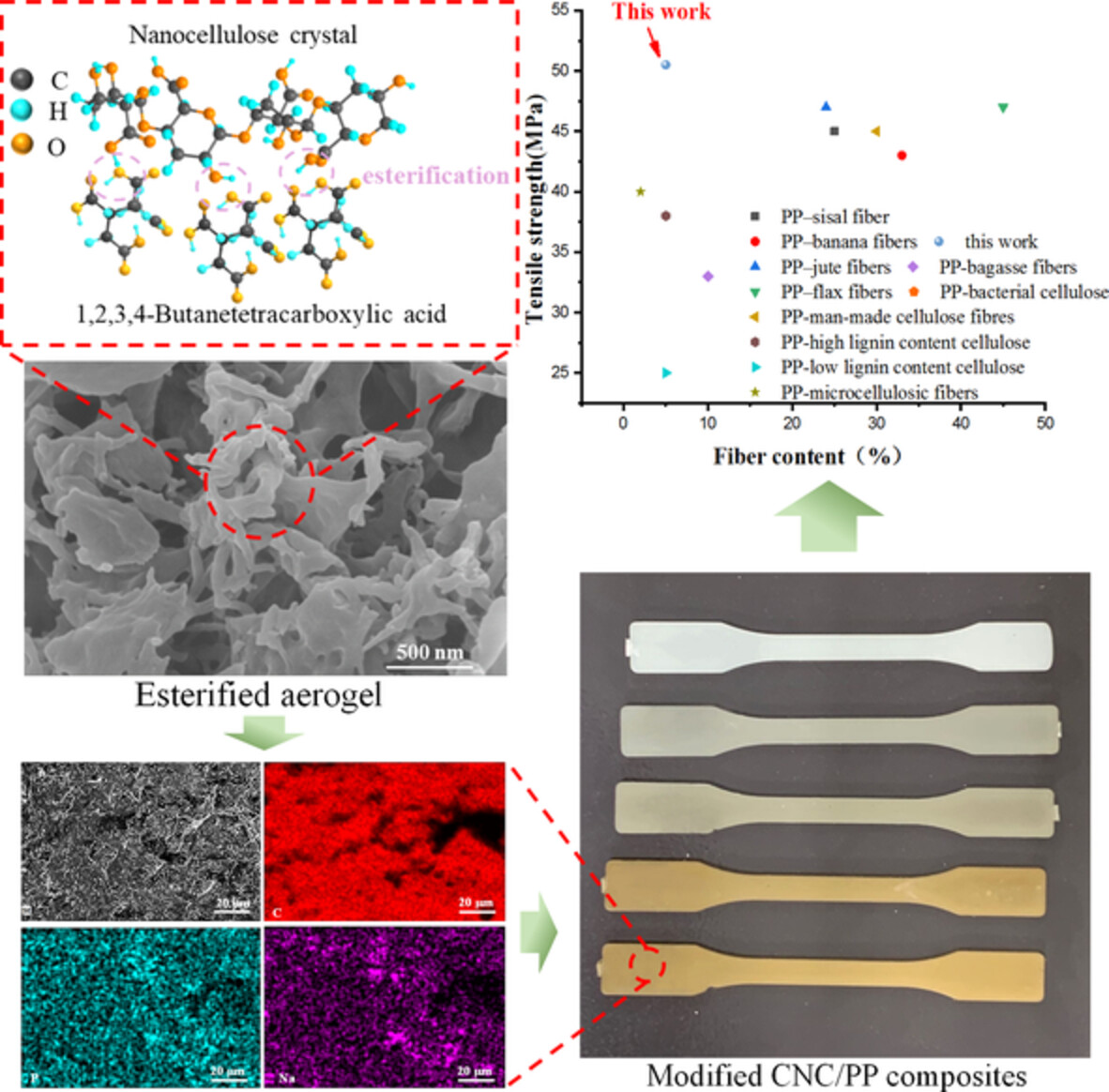
This study reports a feasible procedure to develop a nanocellulose-reinforced polypropylene composite prepared by melt extrusion with a twin-screw extruder. The tensile strength and thermal stability of the composite are improved, which indicated good compatibility between the nanocellulose fillers and the polymer matrices.
Influence of the structure of sub-micrometer core-shell rubber particles and matrix composition on the mechanical properties, morphological structure and deformation mechanism of rubber-modified polyphenylene oxide/polystyrene blends
- First Published: 15 August 2022
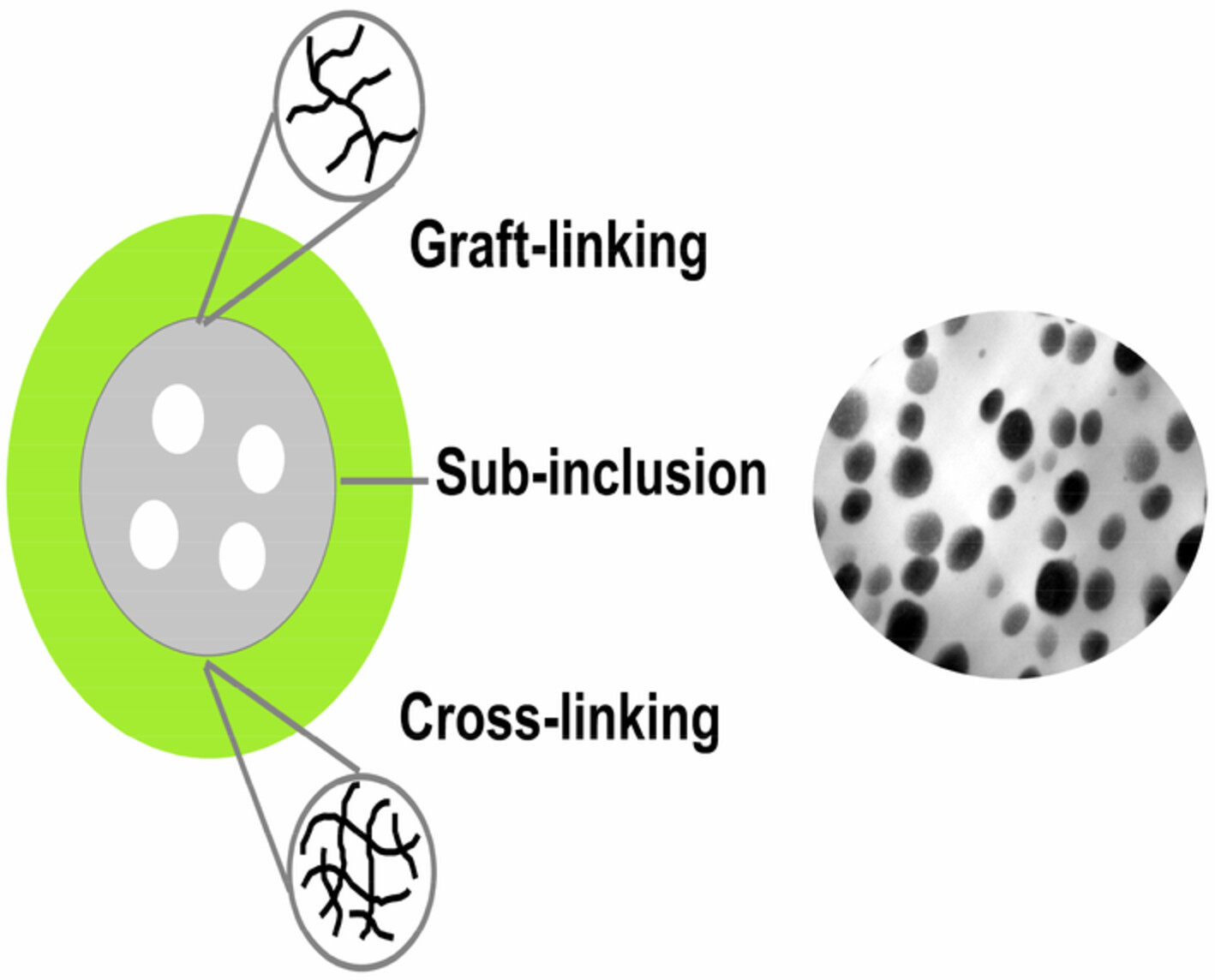
PB-g-PS graft copolymer with core-shell structure was prepared by emulsion polymerization. The matrix toughness was provided by the core phase (PB), while the shell phase (PS) has good compatibility with PPO, which ensured that the core-shell particles of PB-g-PS can be uniformly dispersed in the PPO/PS matrix. It is found that the impact toughness of PPO/PS blends can be effectively improved by controlling the core-shell ratio of PB-g-PS graft copolymer.
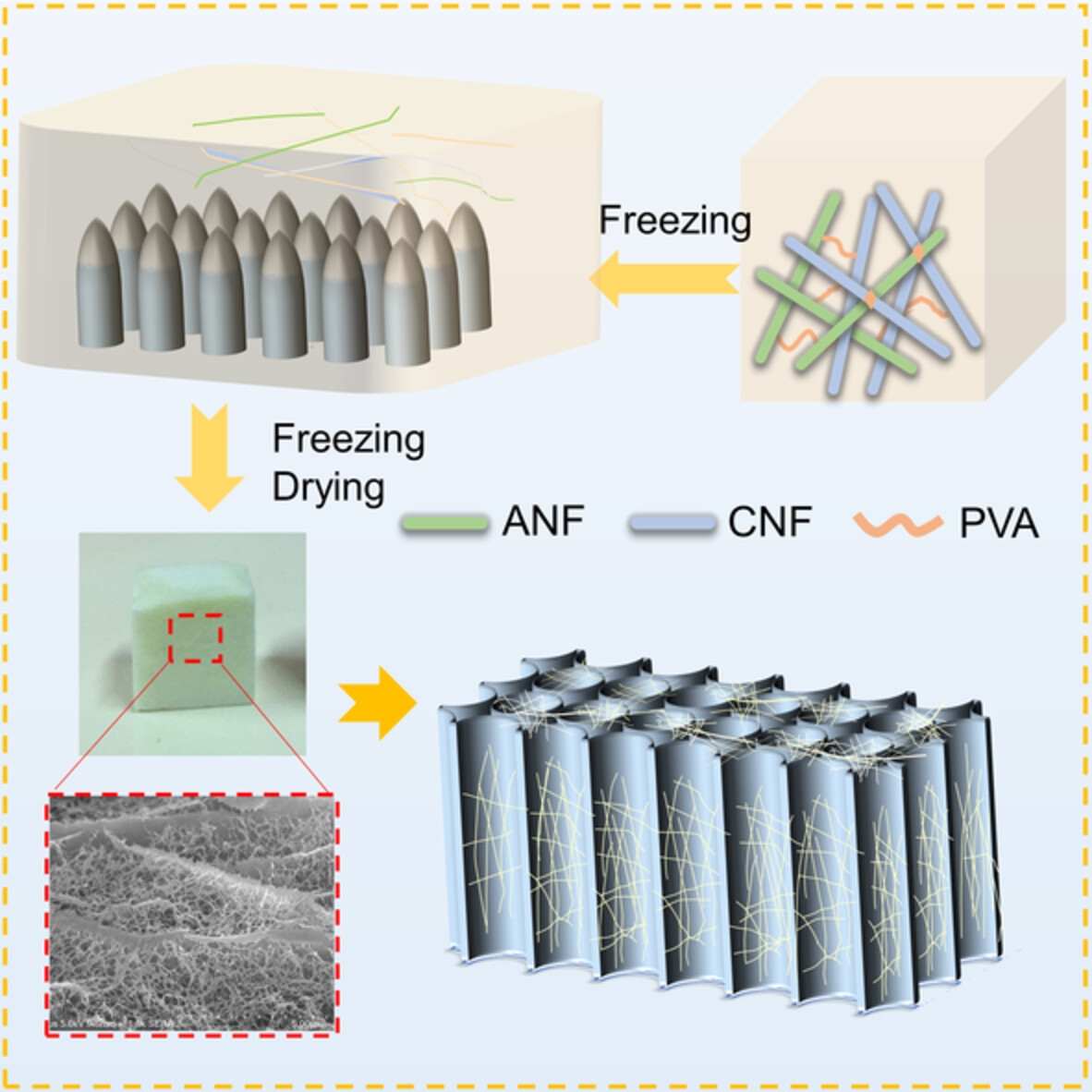
‘Rigid-soft’ synergistic effects to improve the microstructure and superflexibility properties of aramid nanofiber aerogel
- First Published: 24 August 2022
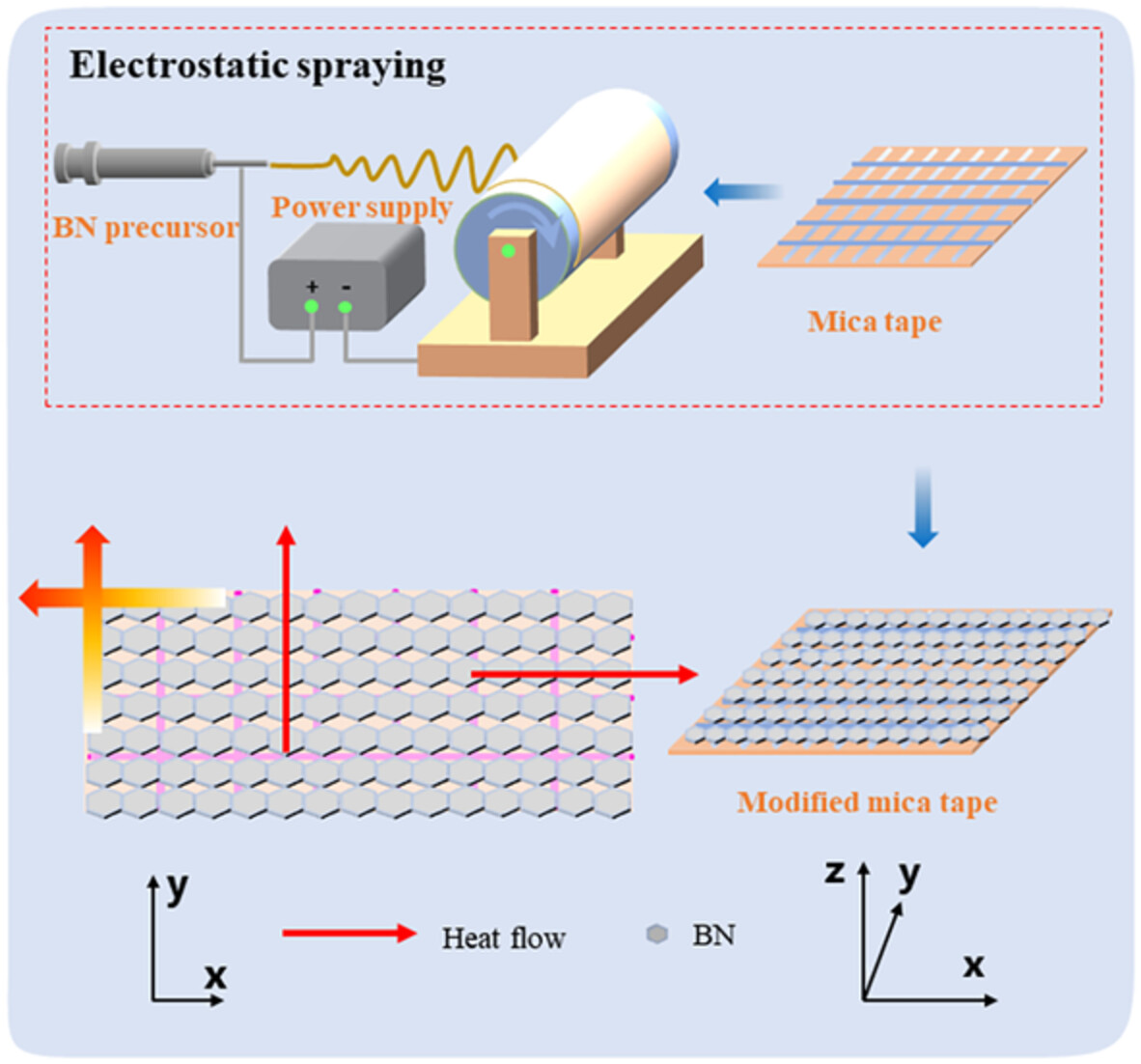
Enhanced thermal conductivity and insulation properties of mica tape with BN coating via electrostatic spraying technology
- First Published: 18 August 2022
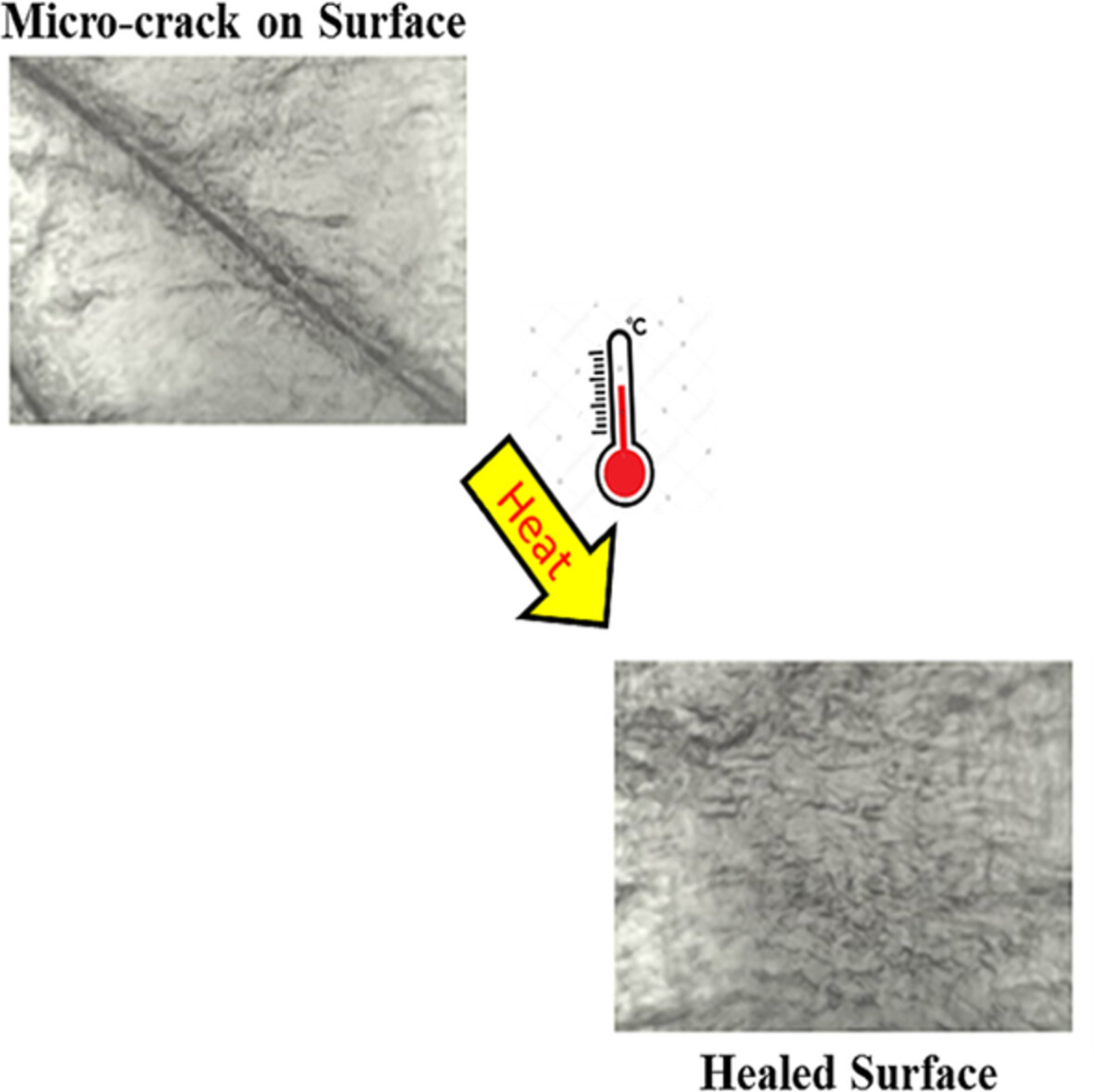
An innovative approach to develop self-healing materials from commercial tire-grade elastomers
- First Published: 01 September 2022
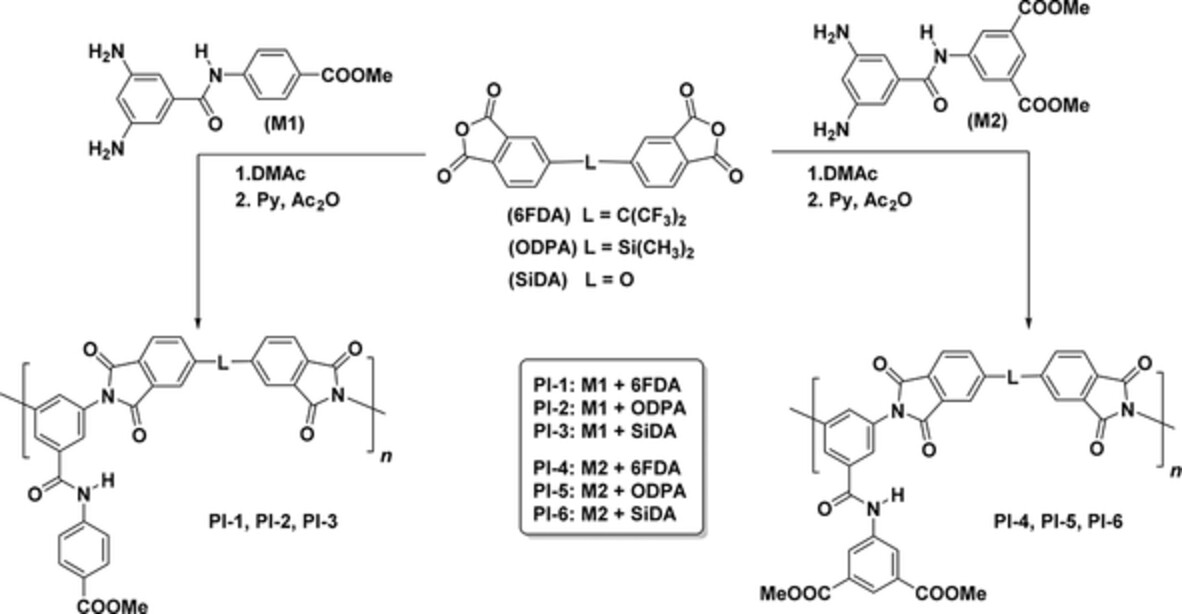
New polyimides containing methyl benzamidobenzoate or dimethyl benzamidoisophthalate as bulky pendant groups. Effects on solubility, thermal and gas transport properties
- First Published: 20 August 2022
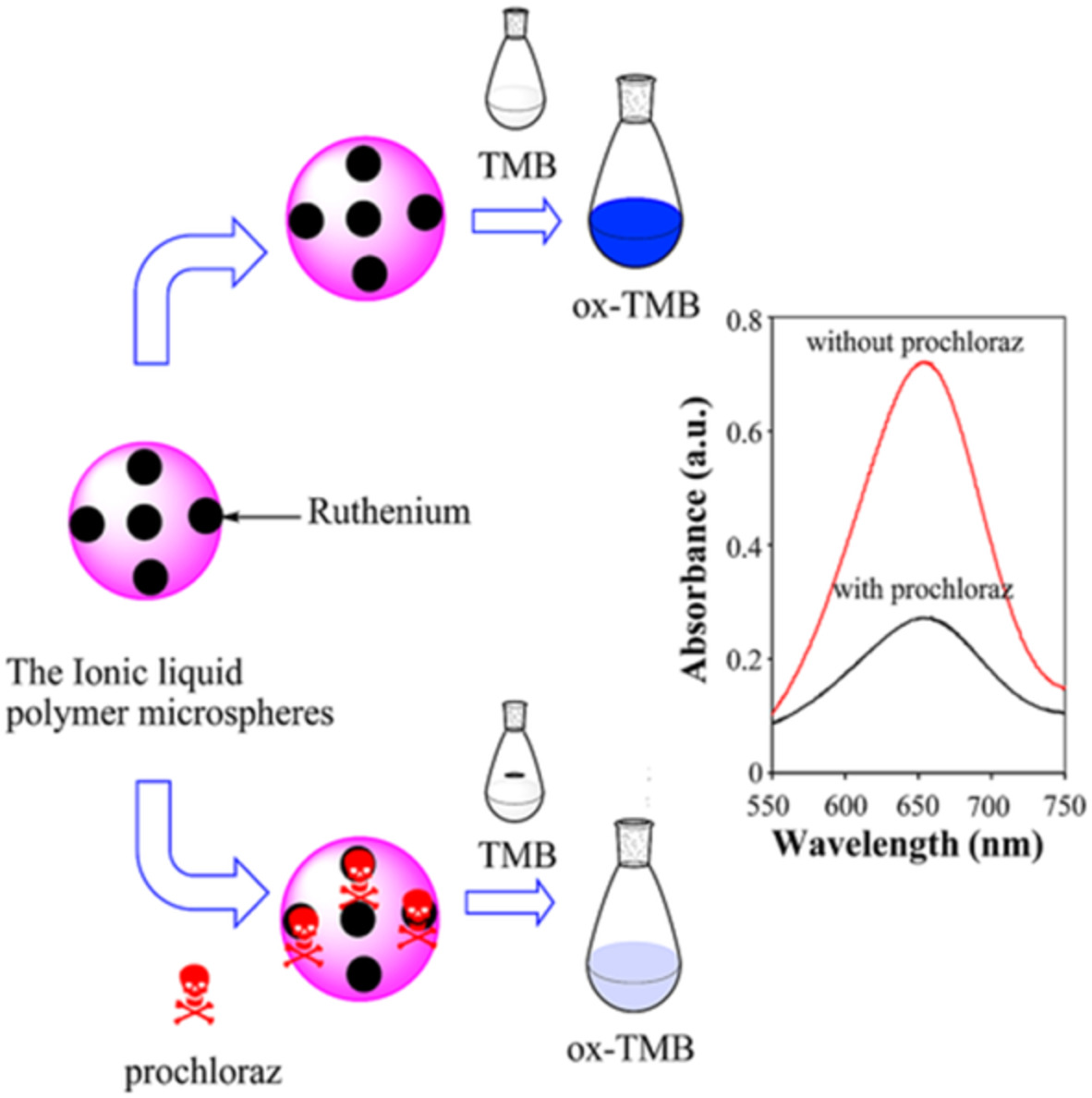
Synthesis of ruthenium-based metal ionic liquid polymer microspheres as an artificial enzyme for colorimetric detection of prochloraz residues in strawberries
- First Published: 26 August 2022
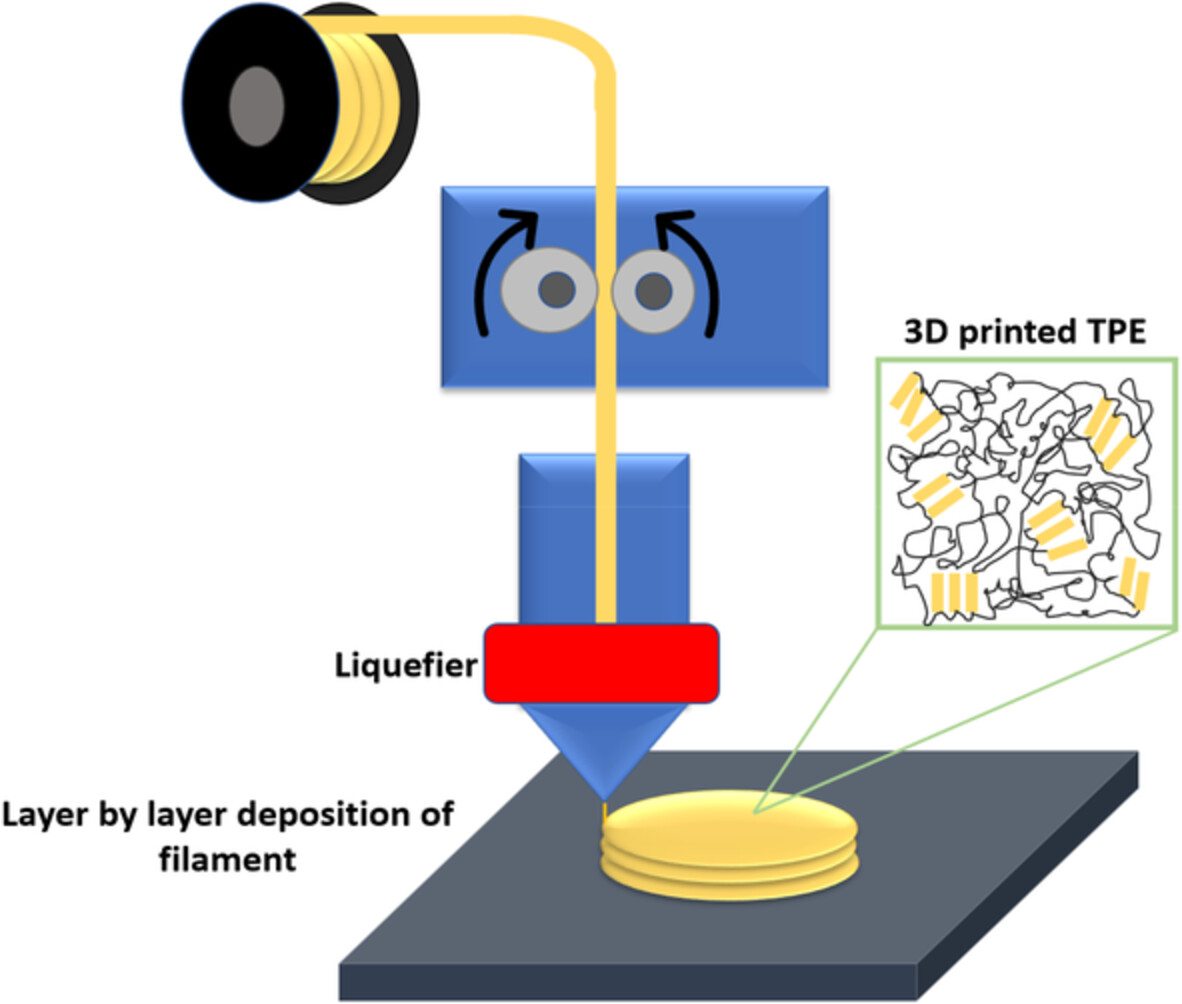
Development of material extrusion 3D printing compatible tailorable thermoplastic elastomeric materials from acrylonitrile butadiene styrene and styrene-(ethylene-butylene)-styrene block copolymer blends
- First Published: 18 August 2022
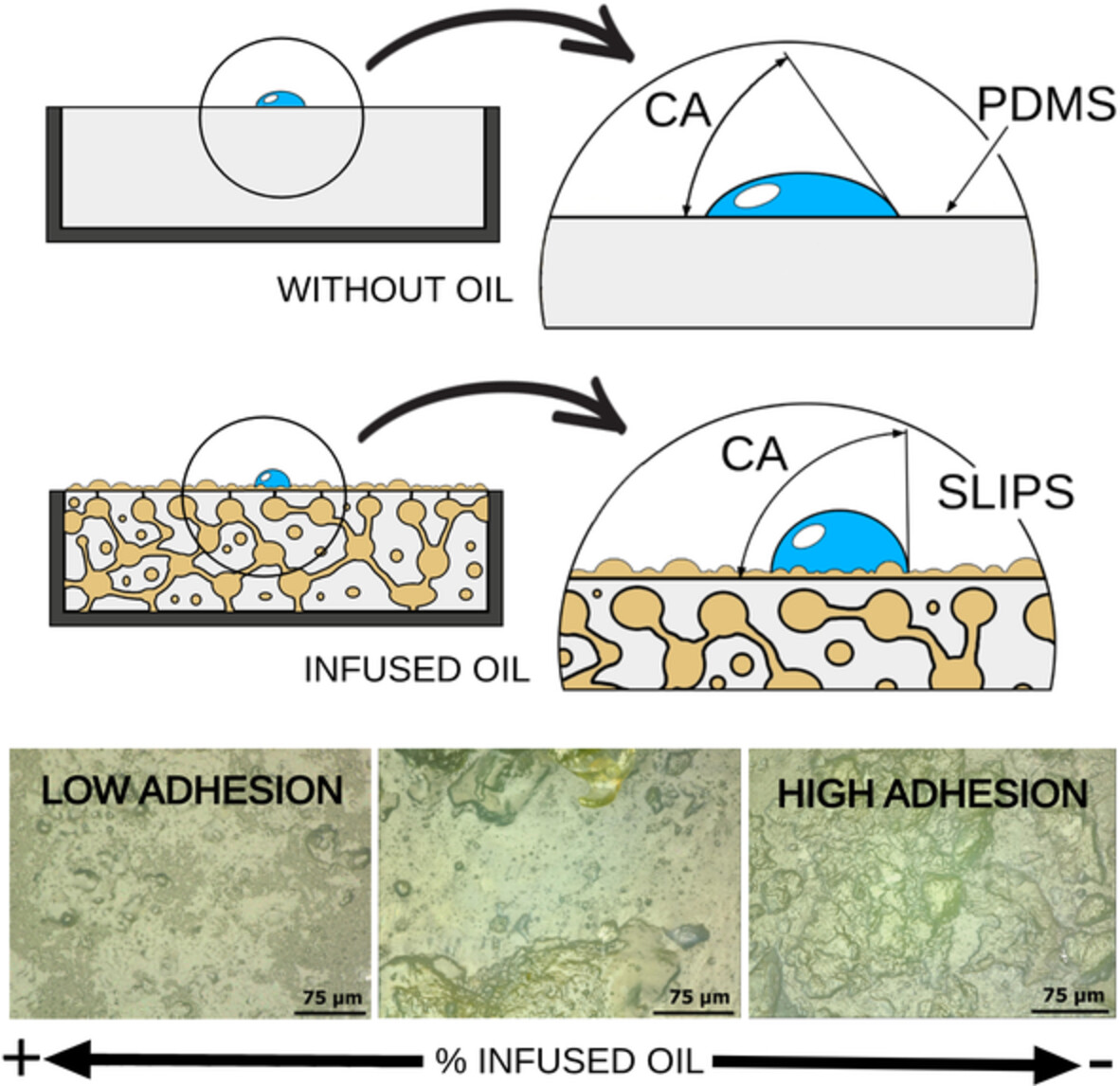
Advances in lubricated polydimethylsiloxane surfaces for polyurethane foam molding
- First Published: 24 August 2022
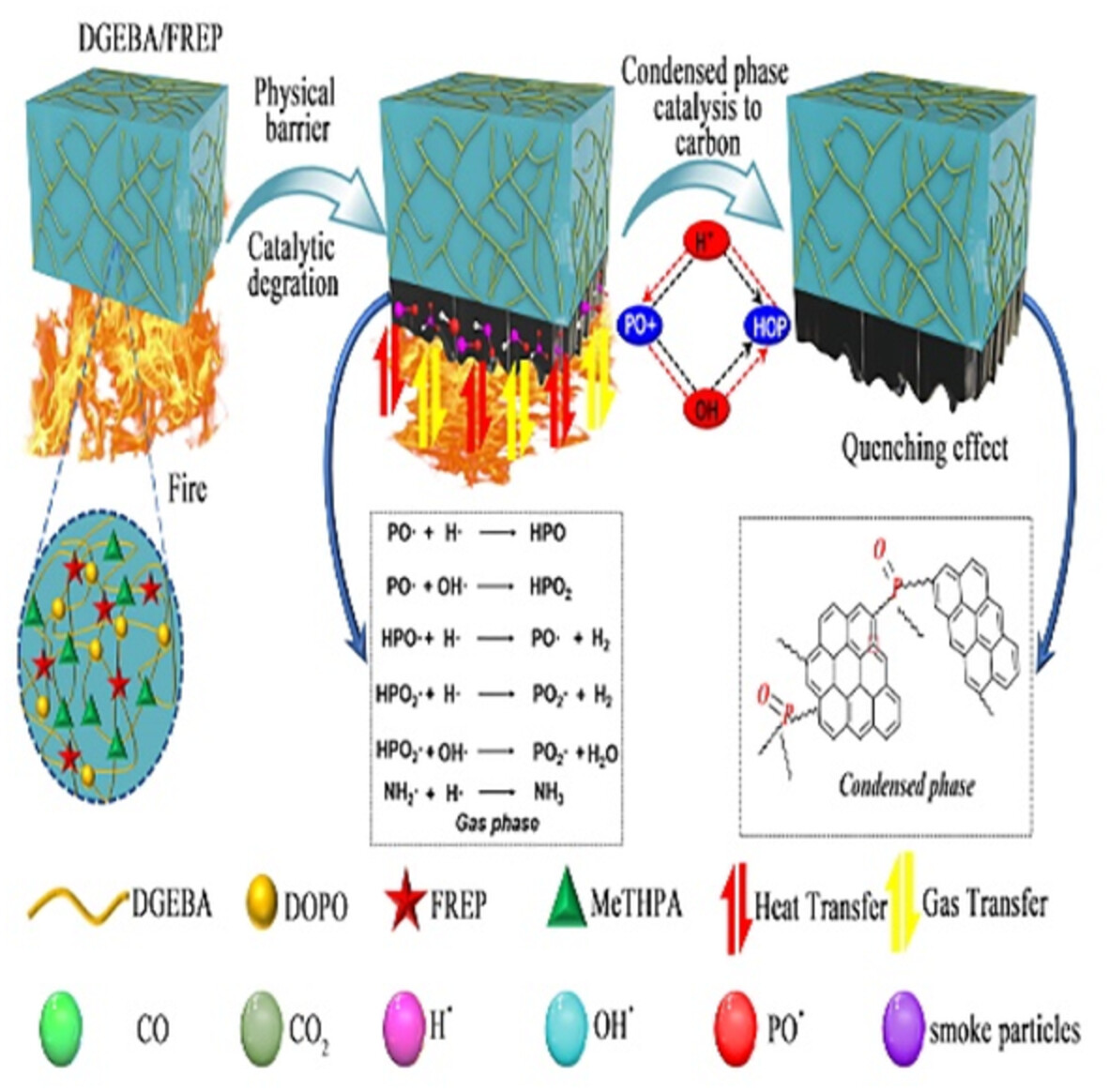
Preparation of a multifunctional flame retardant epoxy resin containing phosphorus and nitrogen and study of its properties
- First Published: 19 August 2022