Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
COVER IMAGE
Cover Image, Volume 139, Issue 16
- First Published: 08 February 2022

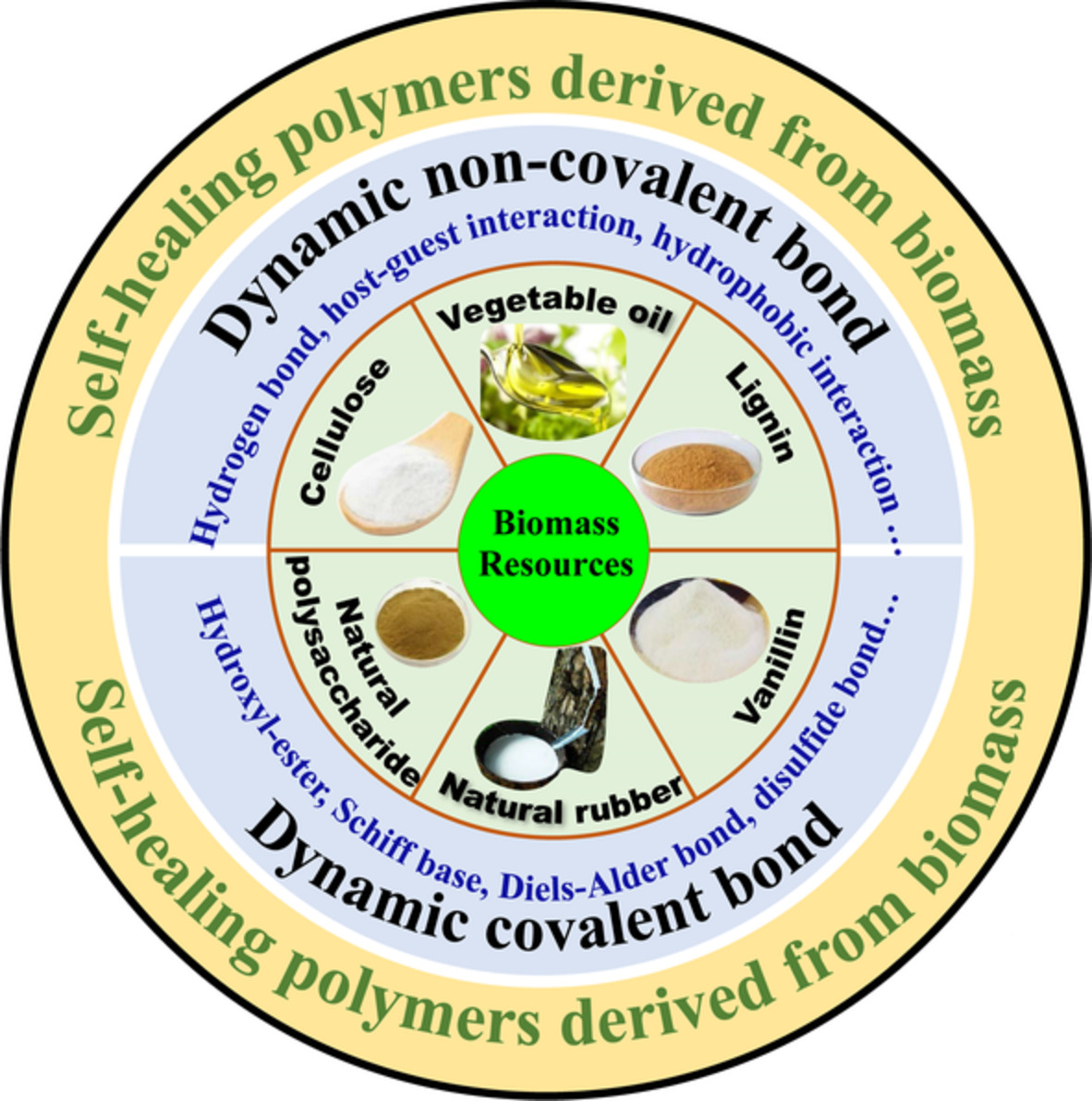
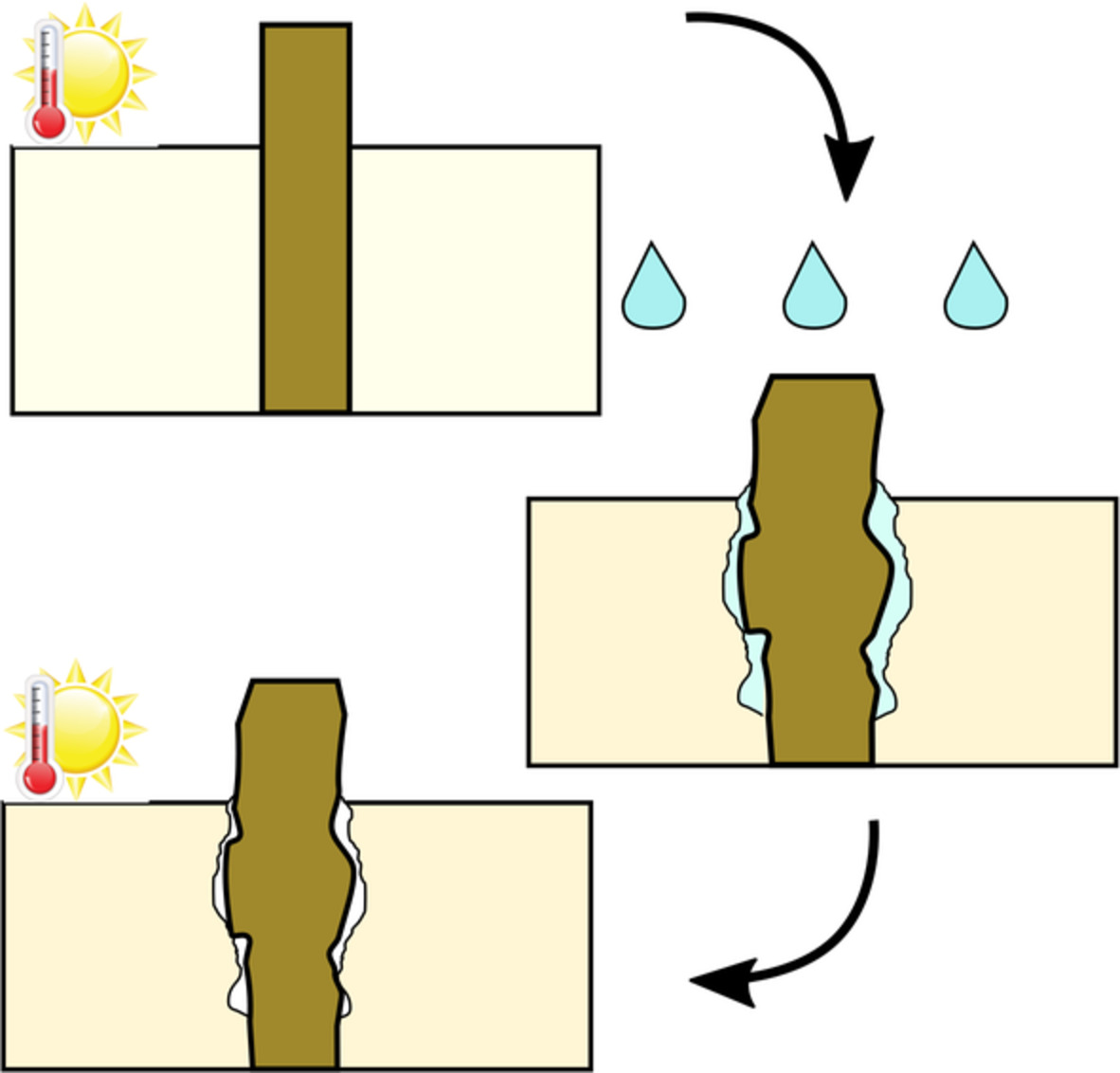
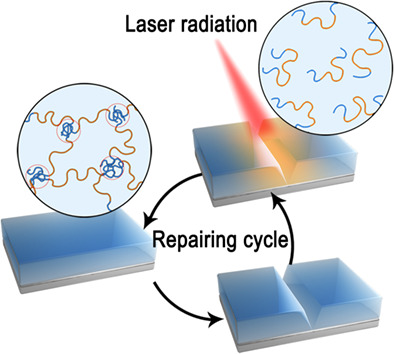
The cover image by Yufeng Ma and Puyou Jia shows the recent progress of biomass-based self-healing polymers. The self-healing polymer materials derived from biomass resources can reduce the dependence on traditional non-renewable resources such as petroleum. The structures and properties of biomass-based self-healing polymer materials are of great significance for their processing, recycling, and self-healing. The research progress of bio-based self-healing polymer materials based on dynamic non-covalent bonds and dynamic covalent bonds including hydroxyl ester, Schiff base, disulfide bond, and hydroxyl urethane derived from vegetable oil, lignin, cellulose, vanillin, and natural rubber. DOI: 10.1002/app.51977
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
Recent progress of biomass based self-healing polymers
- First Published: 02 December 2021
ARTICLES
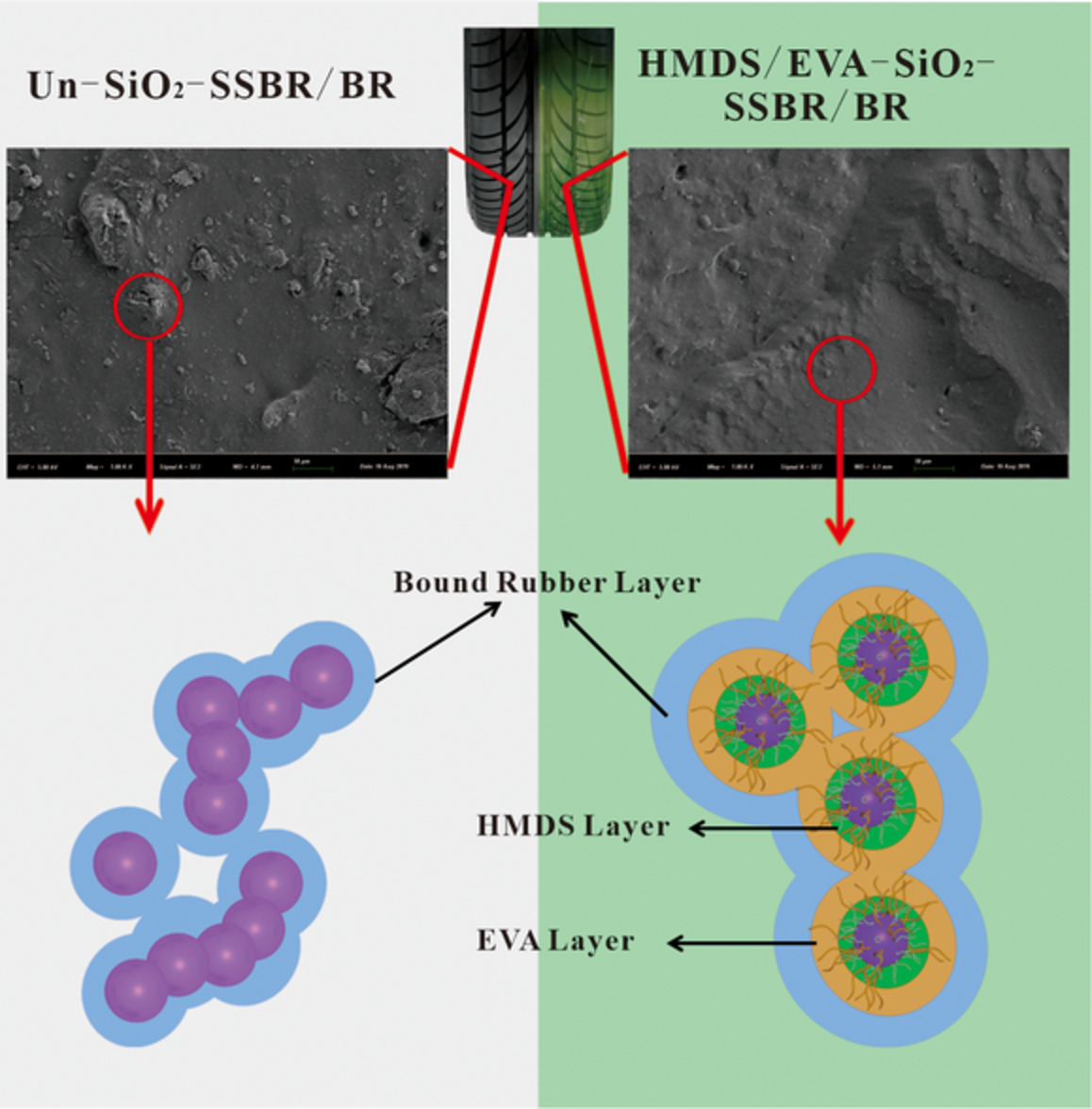
Double-layer modified silica with potential reinforcement for solution polymerized styrene-butadiene rubber/butadiene rubber composite
- First Published: 22 November 2021
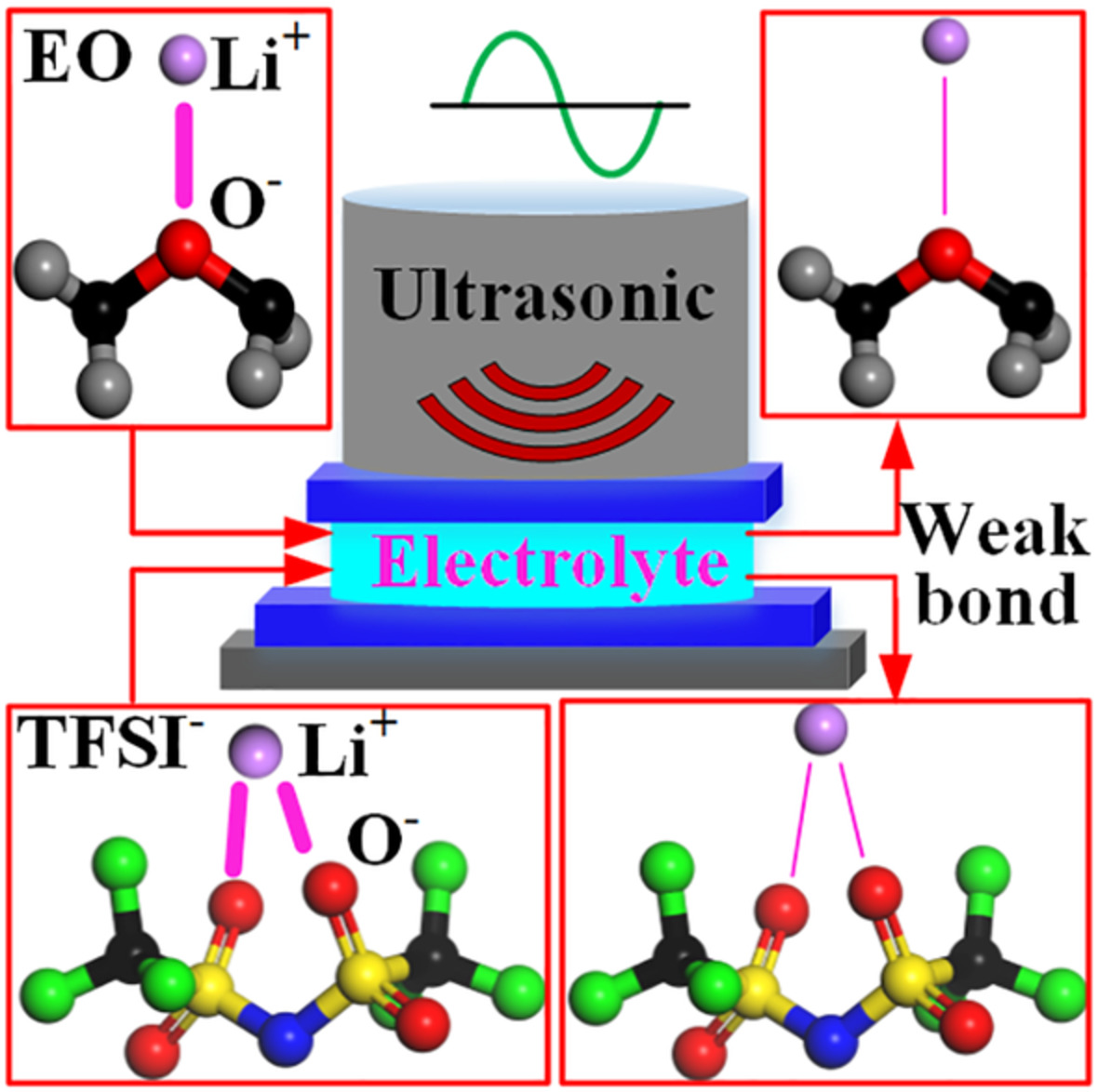
Mechanism of enhanced lithium-ion transport in solid polymer electrolytes assisted by ultrasonic vibration
- First Published: 24 November 2021
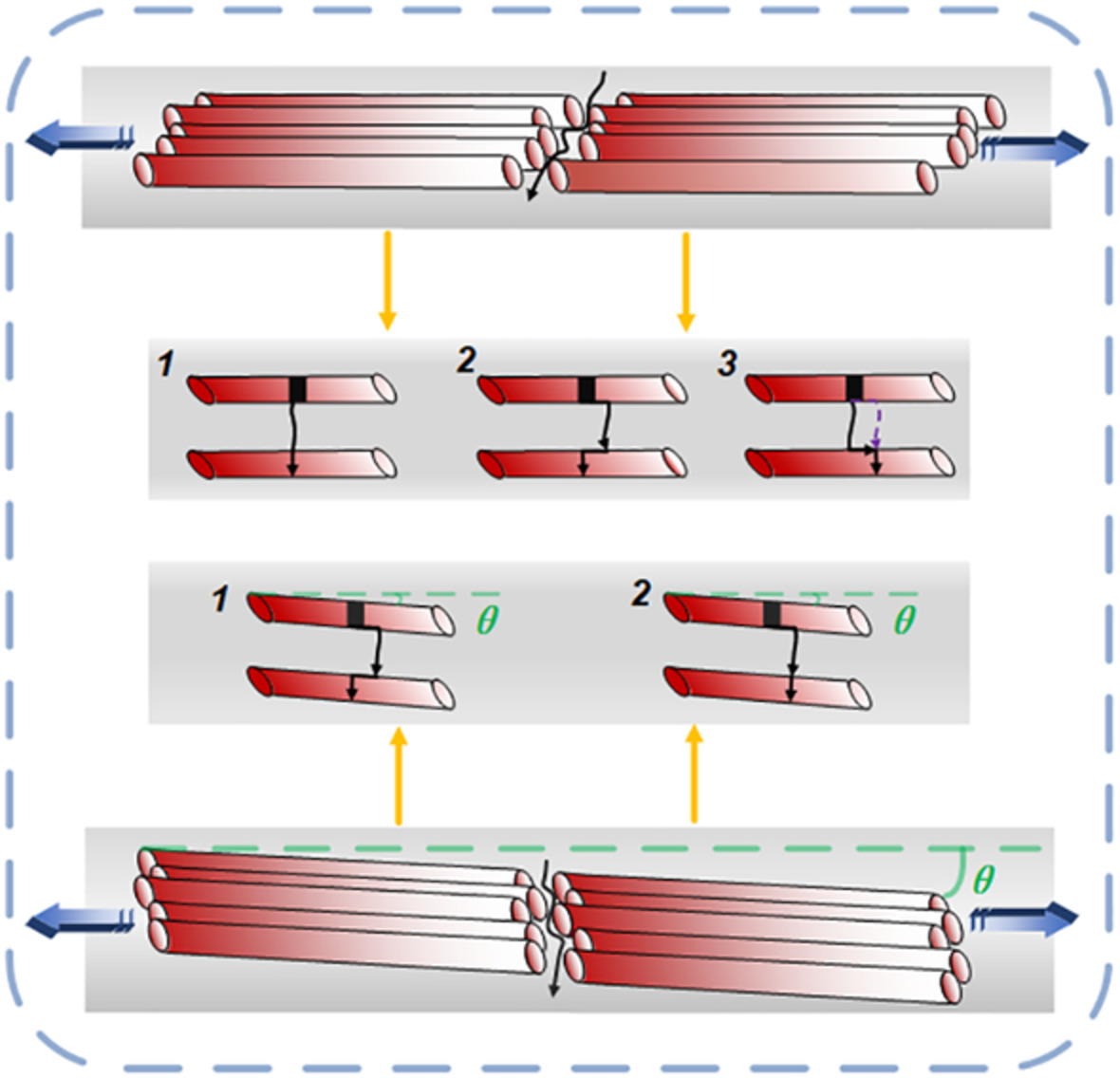
Angle-ply orientation-dependent failure behaviors of carbon fiber reinforced polymer laminates
- First Published: 21 November 2021
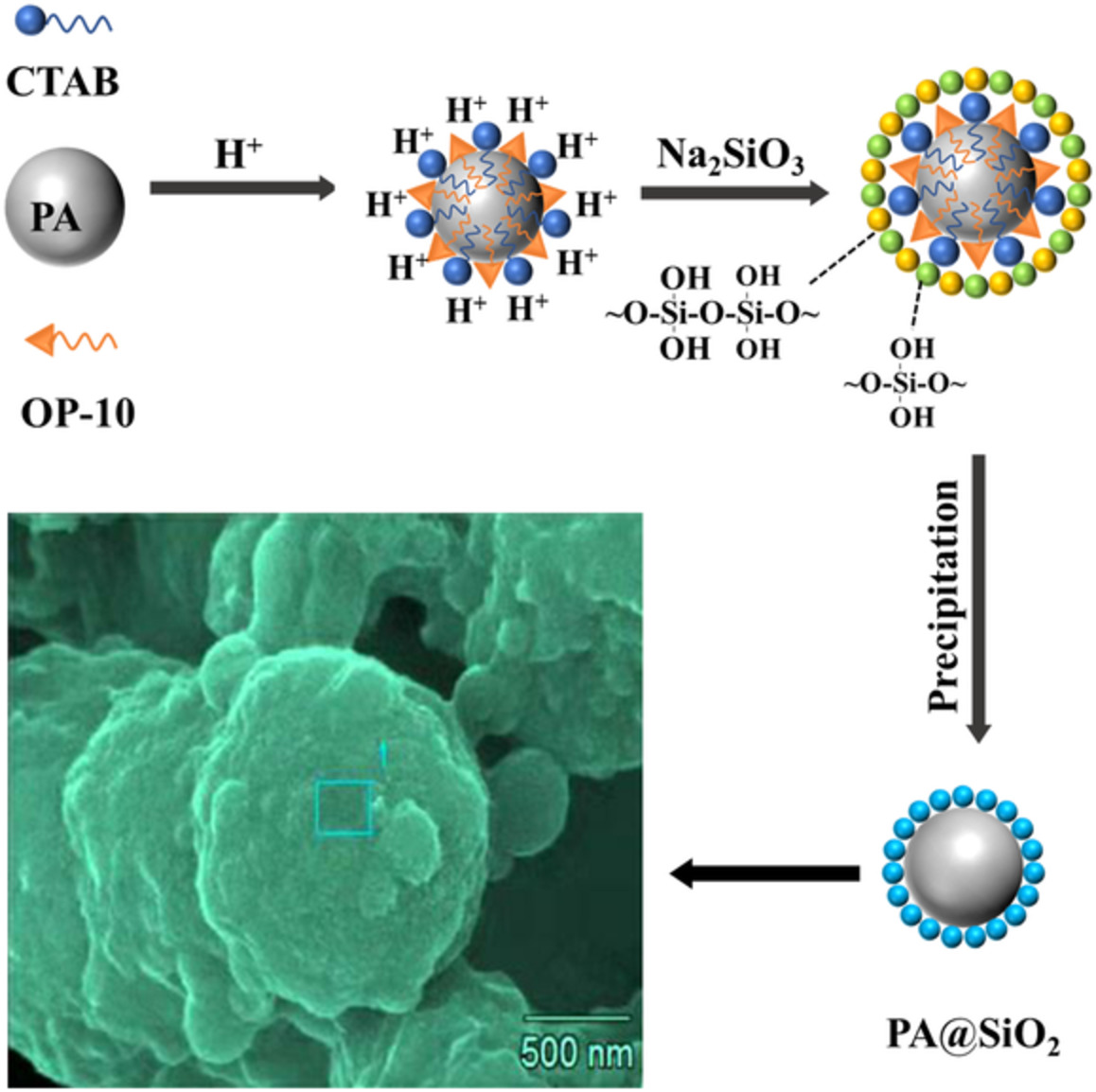
Process and performance of palmitic acid @silica phase-change microcapsules using chemical precipitation method
- First Published: 29 November 2021
Synthesis, rheological characterization, and proposed application of pre-polyglycerol sebacate as ultrasound contrast agent based on theoretical estimation
- First Published: 27 November 2021
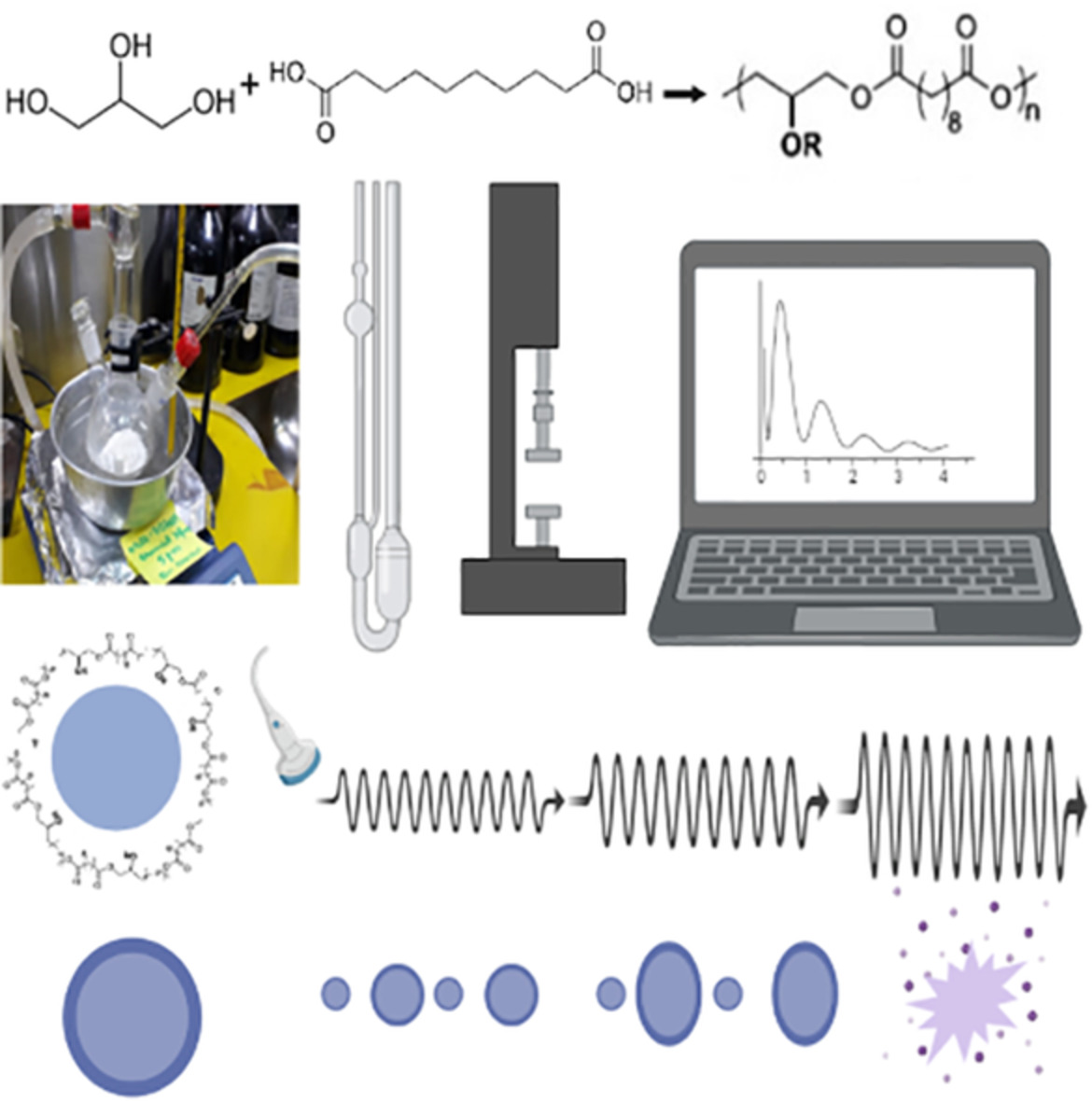
Polyglycerol sebacate (PGS) is a biocompatible elastomer prepared via a two-step melt condensation reaction. The mechanical properties of the cured polymer have been extensively explored for tissue engineering applications; however, properties of pre-polymer (pre-PGS) remained limited. The study focuses on the rheological characterization of pre-PGS and its potential as an ultrasound contrast agent predicted via its oscillatory response in a simulated acoustic field.
Rigid and conductive lightweight regenerated cellulose/carbon nanotubes/acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene nanocomposites constructed via a Pickering emulsion process
- First Published: 27 November 2021
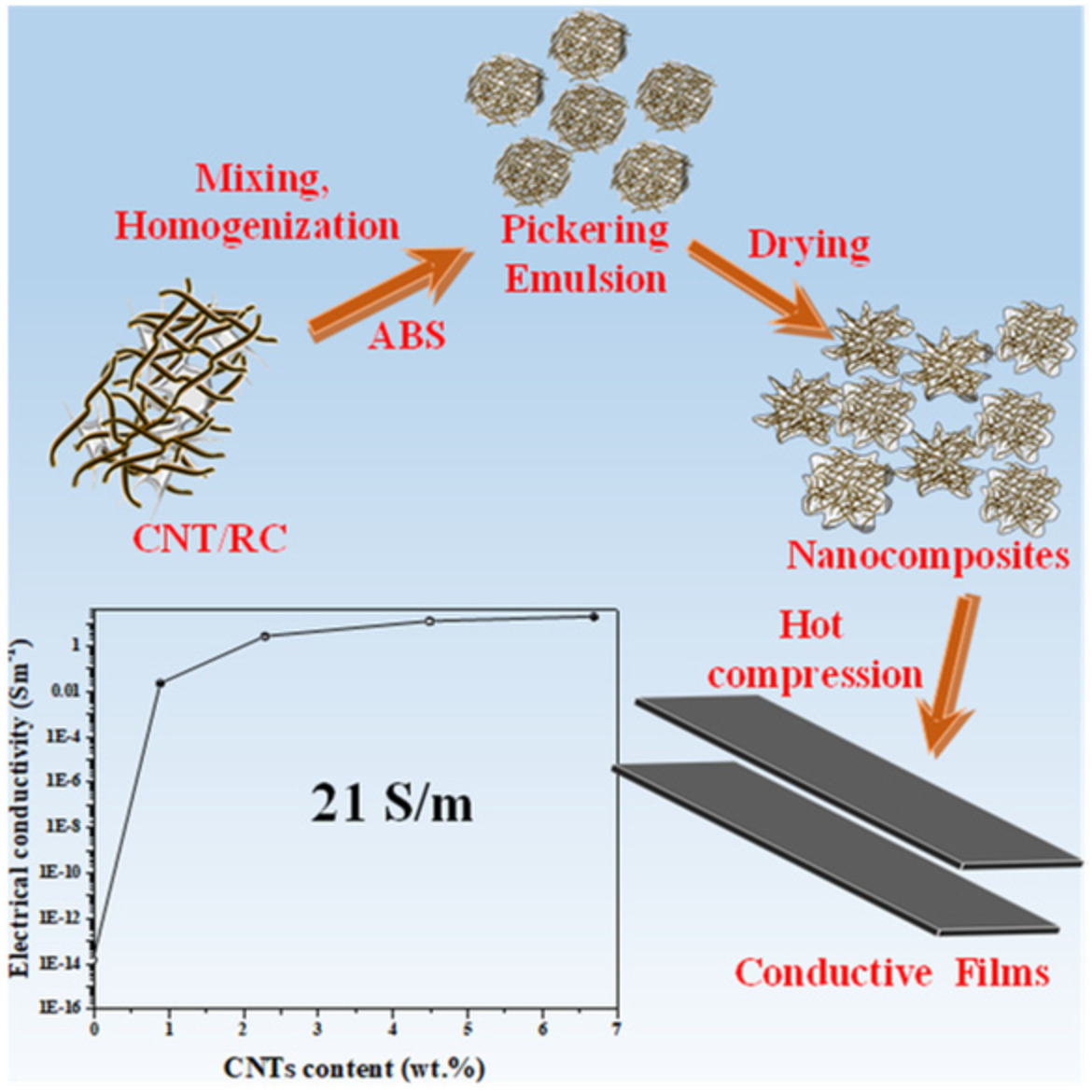
CNTs were homogeneously dispersed in acrylonitrile–butadiene–styrene (ABS) matrix with the aid of regenerated cellulose (RC), via an easy and cost-effective Pickering emulsion approach to form conductive nanocomposites, which possessed an electrical conductivity of up to 21 Sm−1 with 6.7 wt.% CNTs incorporation.
Optimization of interface microstructure of high-strength-high-modulus polyimide fibers composites utilizing waterborne polyamide and hybrid sizing agent
- First Published: 27 November 2021
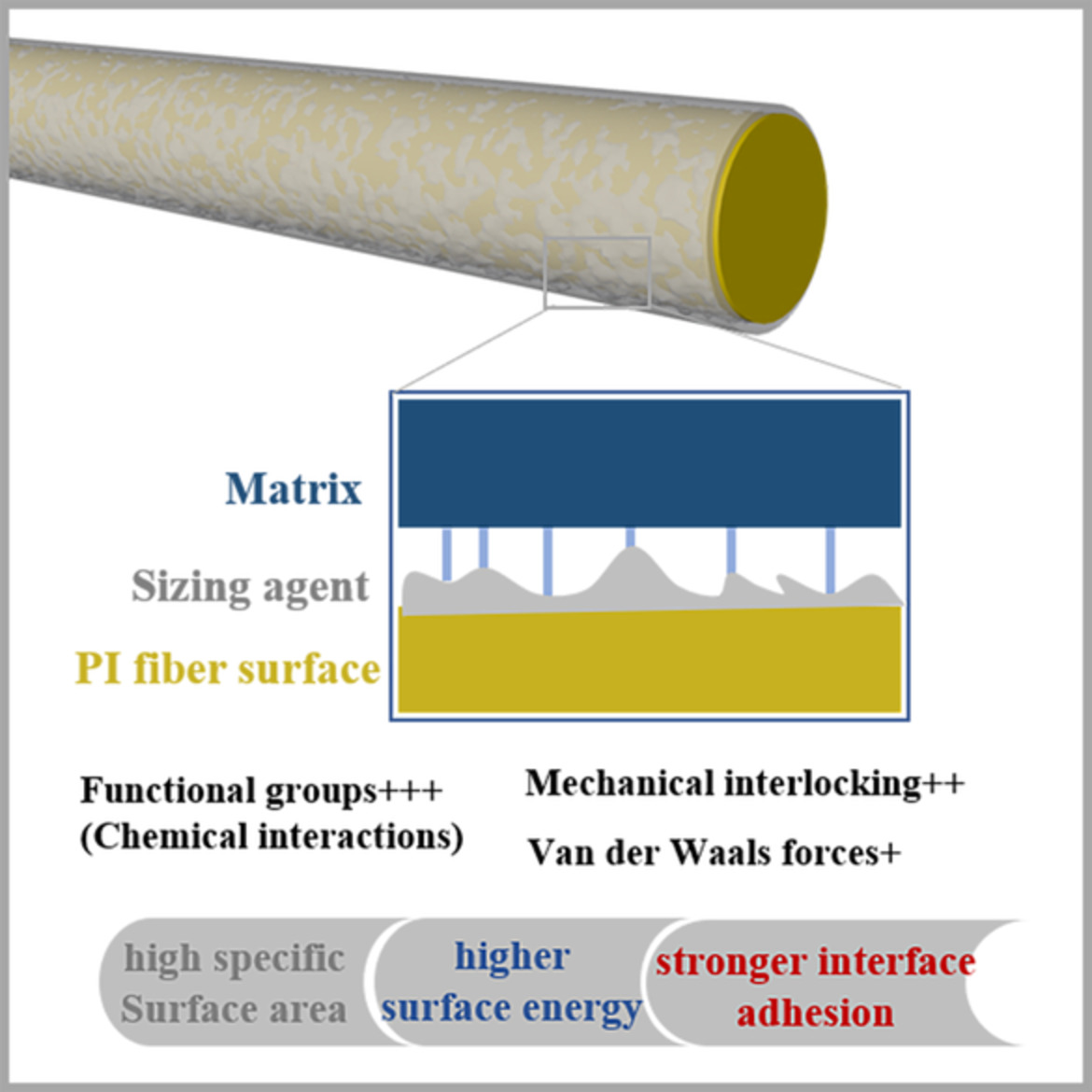
In this work, a waterborne polyamide (WPA) sizing agent was used to modify PI fibers to enhance the interface adhesion strength between the PI fibers and epoxy (EP) resin matrix. In addition, the hybrid sizing agent generated by WPA and waterborne EP (WEP) sizing agent exhibited the highest interface adhesion with 168.65% and 28.62% increment obtained for interfacial shear strength and interlaminar shear strength compared with unsized PI fiber reinforced EP resin composites.
Synthesis and characterization of 1,3-butadiene-containing hyperbranched conjugated polymers as a selective chemosensors for Fe3+ ions
- First Published: 22 November 2021
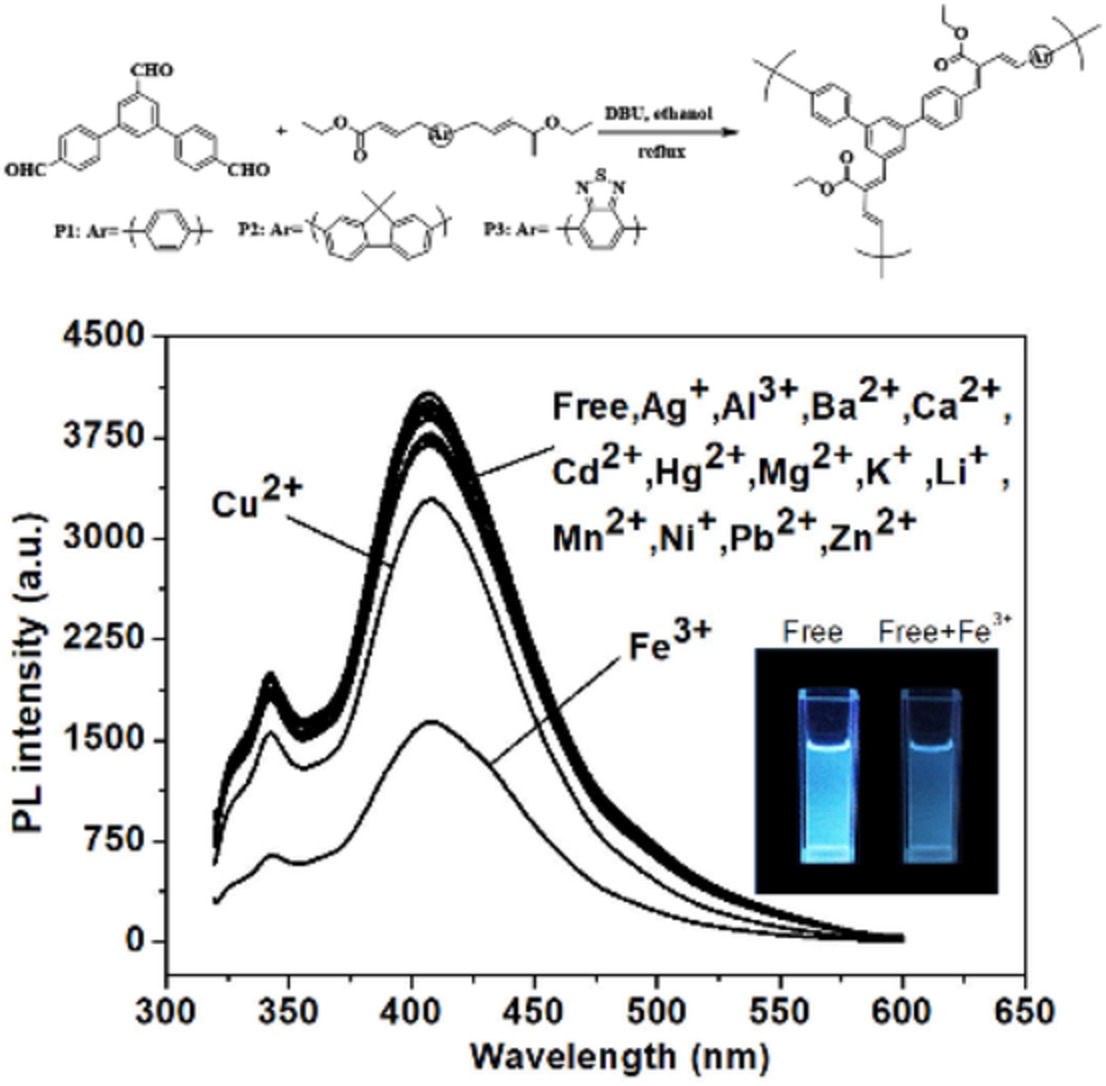
Hyperbranched conjugated polymers containing different aryl group appended with carboxylic ester groups were synthesized by metal-free catalyzed polymerization. The synthesized polymers were highly sensitive and selective towards Fe3+ ions in organic solvents and aqueous solution. The obtained results also demonstrated that the different aryl moieties in the backbone mainly affect the energy band as well as a less affect towards their selective detection of Fe3+ ions.
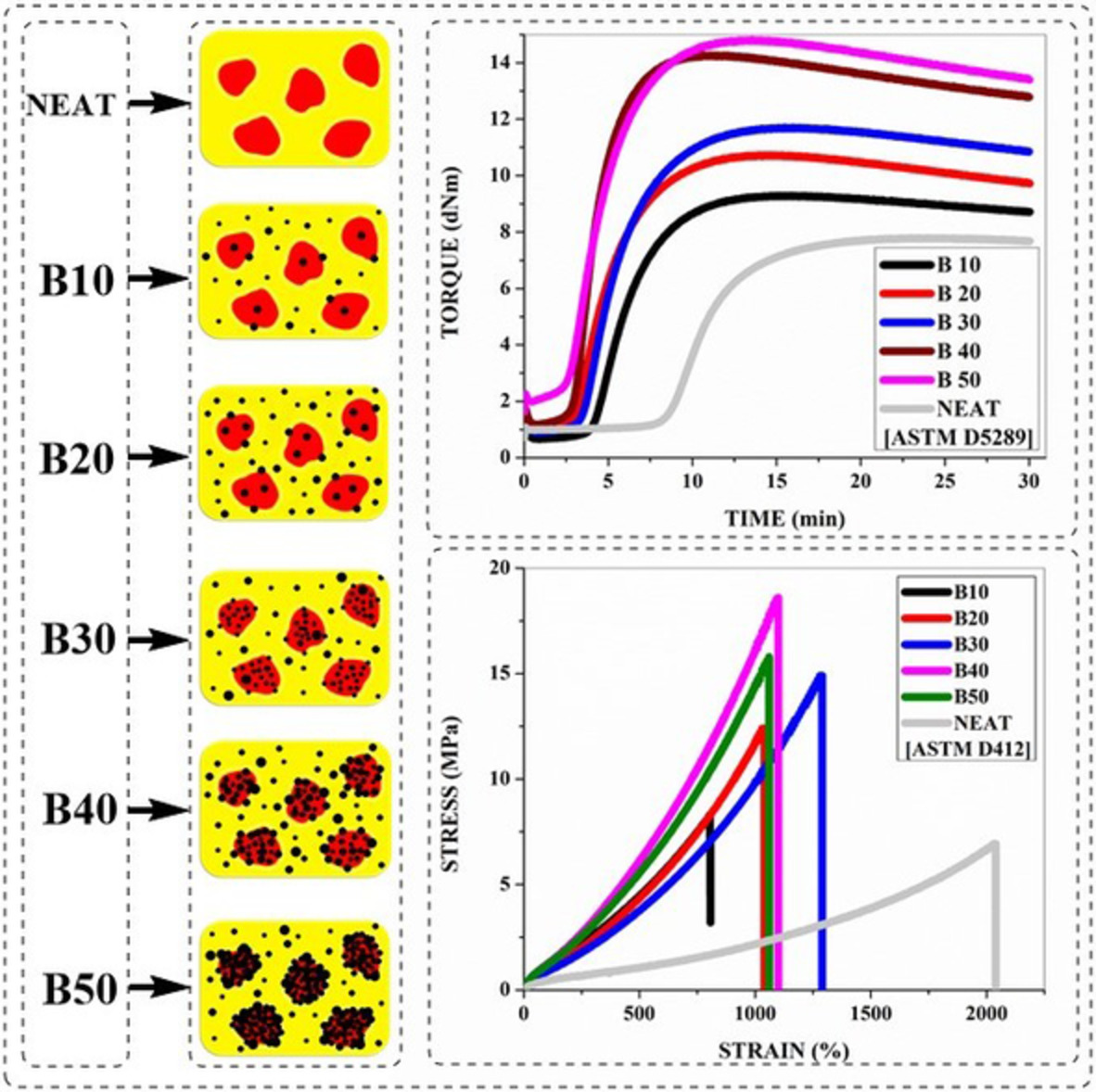
The effect of adding carbon black to natural rubber/butadiene rubber blends on curing, morphological, and mechanical characteristics
- First Published: 28 November 2021
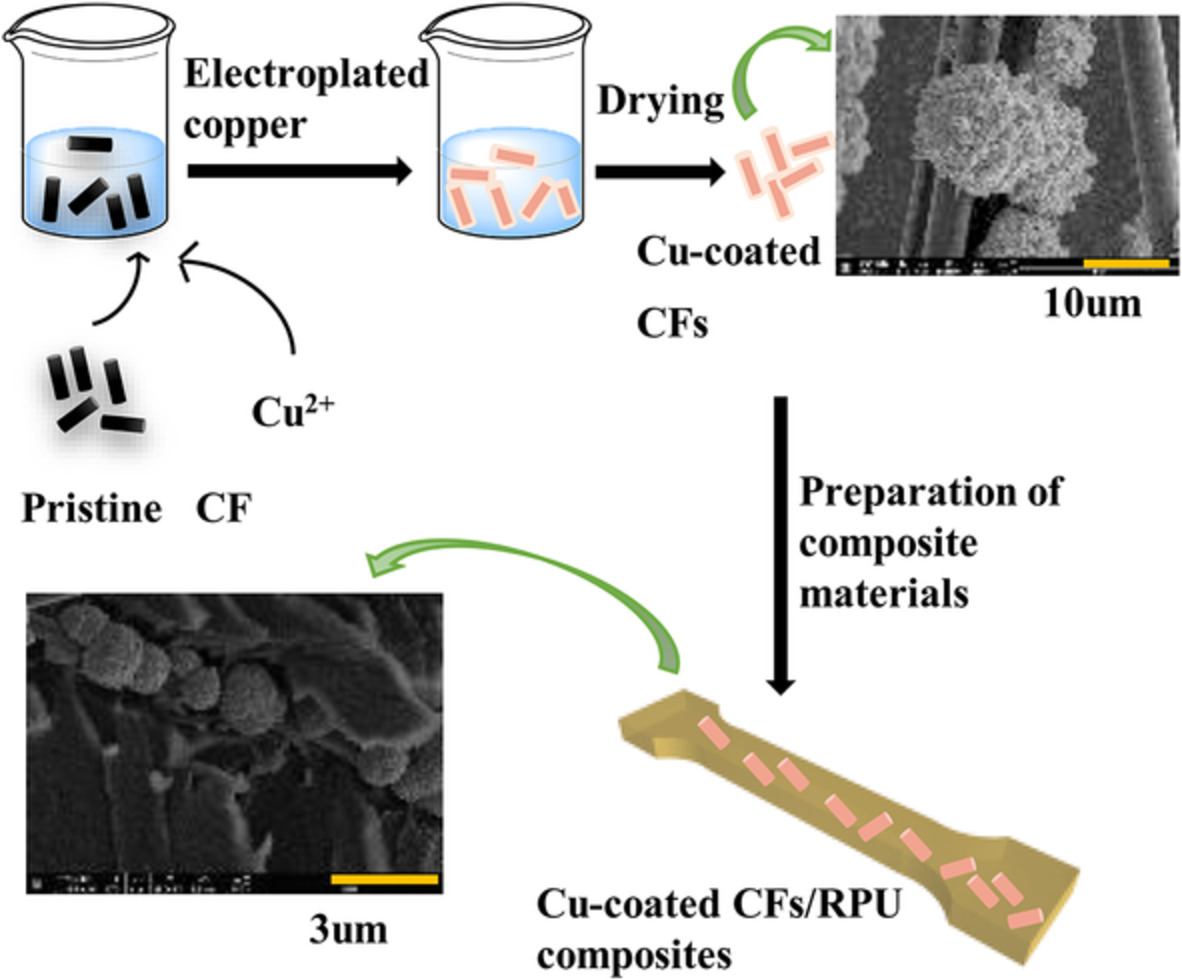
The effects of string-like copper plated short carbon fibers reinforced rigid polyurethane composites
- First Published: 24 November 2021
In situ monitoring of moisture uptake of flax fiber reinforced composites under humid/dry conditions
- First Published: 29 November 2021
Design of polyurea networks containing anticancer and anti-inflammatory drugs for dual drug delivery purposes
- First Published: 26 November 2021

The successful dual-drug release highlights the polyurea xerogel as a versatile carrier to combine anti-inflamatory and anticancer drugs into a single polymer matrix, opening new oportunities to develop functional materials containing different species for optical, health and environmental applications.
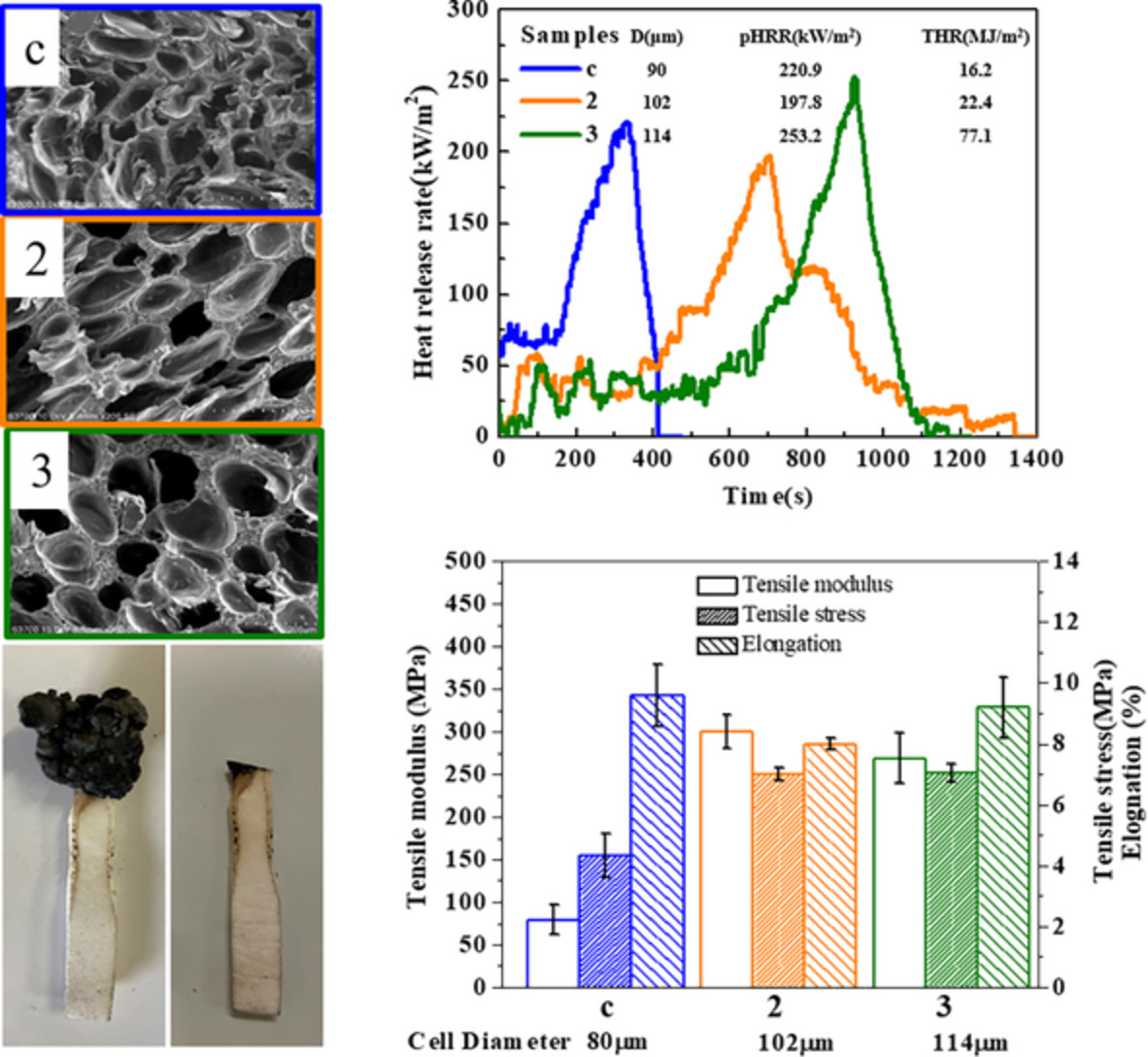
Halogen-free intumescent flame retardancy and mechanical properties of the microcellular polypropylene with low expansion ratio via continuous extrusion assisted by subcritical CO2
- First Published: 25 November 2021
Synthesis and characterization of high fluorine-containing polyimides with low-dielectric constant
- First Published: 30 November 2021
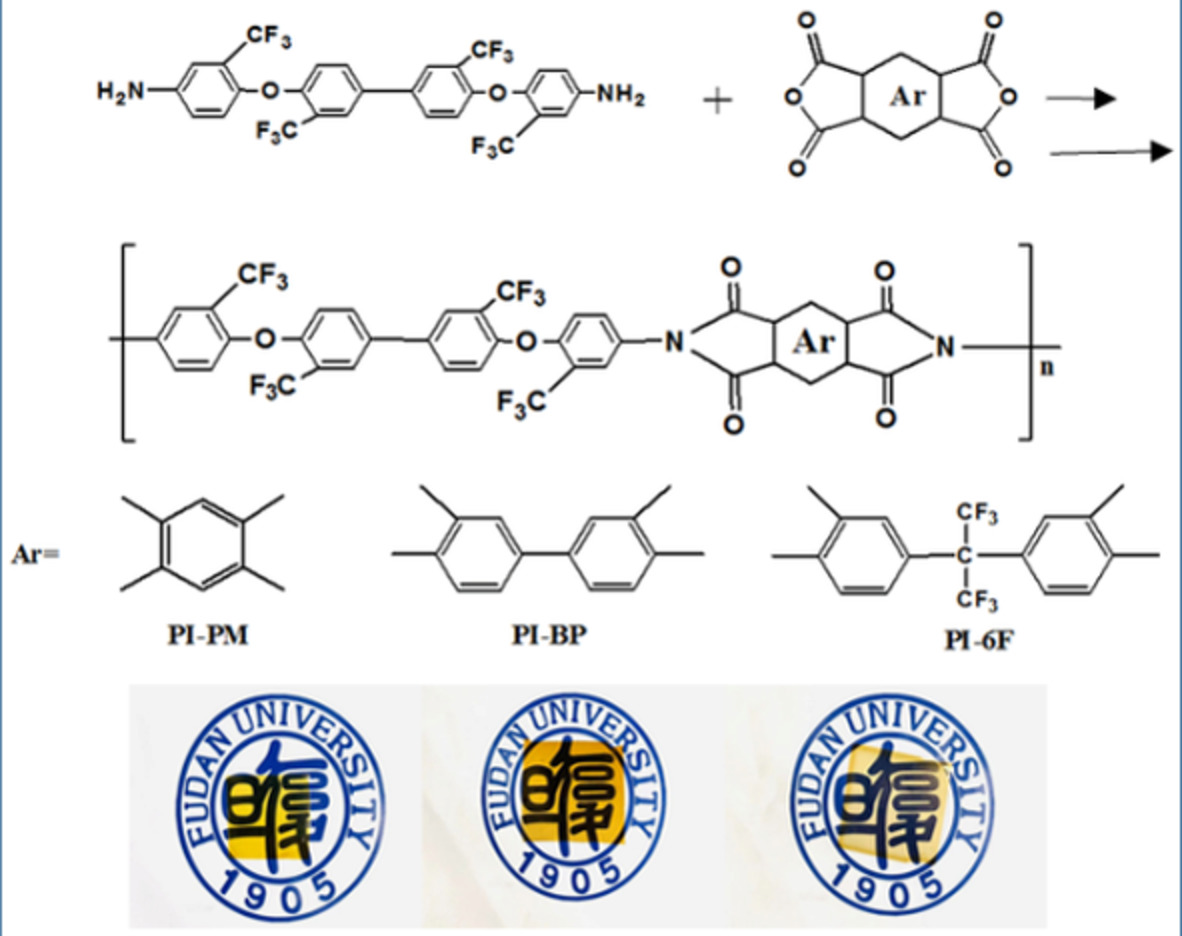
High fluorine-containing polyimides (HFPI) with high Tg, good thermal stability, high-optical transpancy, low-water absorption, and low-dielectric constant were prepared. The fluorine content of HFPI can reach as high as 32.6 wt%. The PI films showed low-Dk values of 2.68, 2.65, and 2.40 at 1 MHz, which were smaller than the commercial Kapton films (~3.2).
Toughening, highly thermostable, and flame retardant polylactic acid enabled by polyphosphazene microsphere
- First Published: 27 November 2021
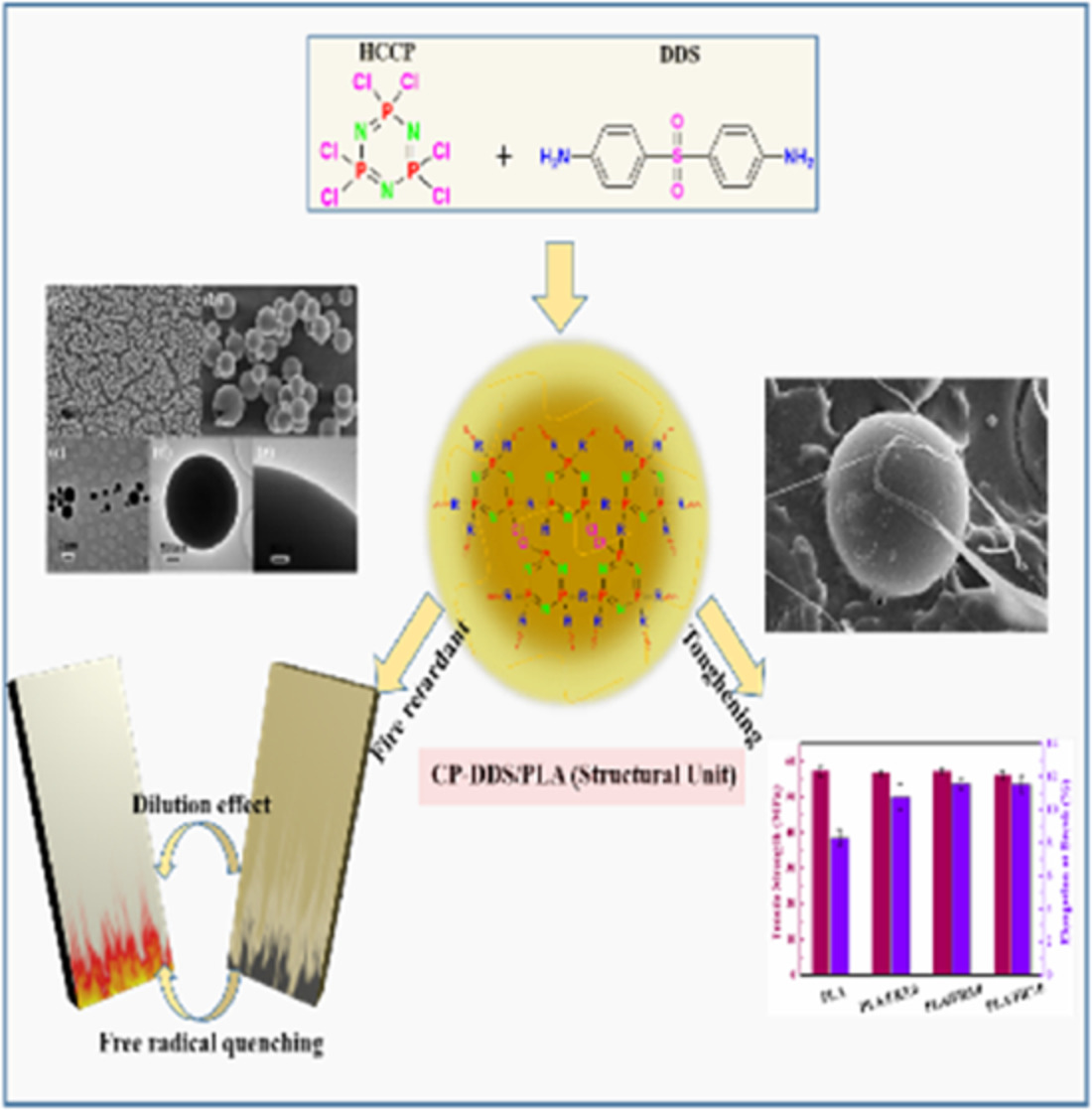
A novel poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-diaminodiphenyl sulfone) (CP-DDS) microsphere containing P/N/S elements was fabricated via the precipitation polymerization among hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene and 4,4′-diaminodiphenyl sulfone. This microsphere exhibited obvious effect in improving the flame retardancy and toughness of PLA. The fire-retardant materials prepared by this toughening microsphere are sufficient to cope with the challenges brought by complex environments, which are expected to be applied in more fields.
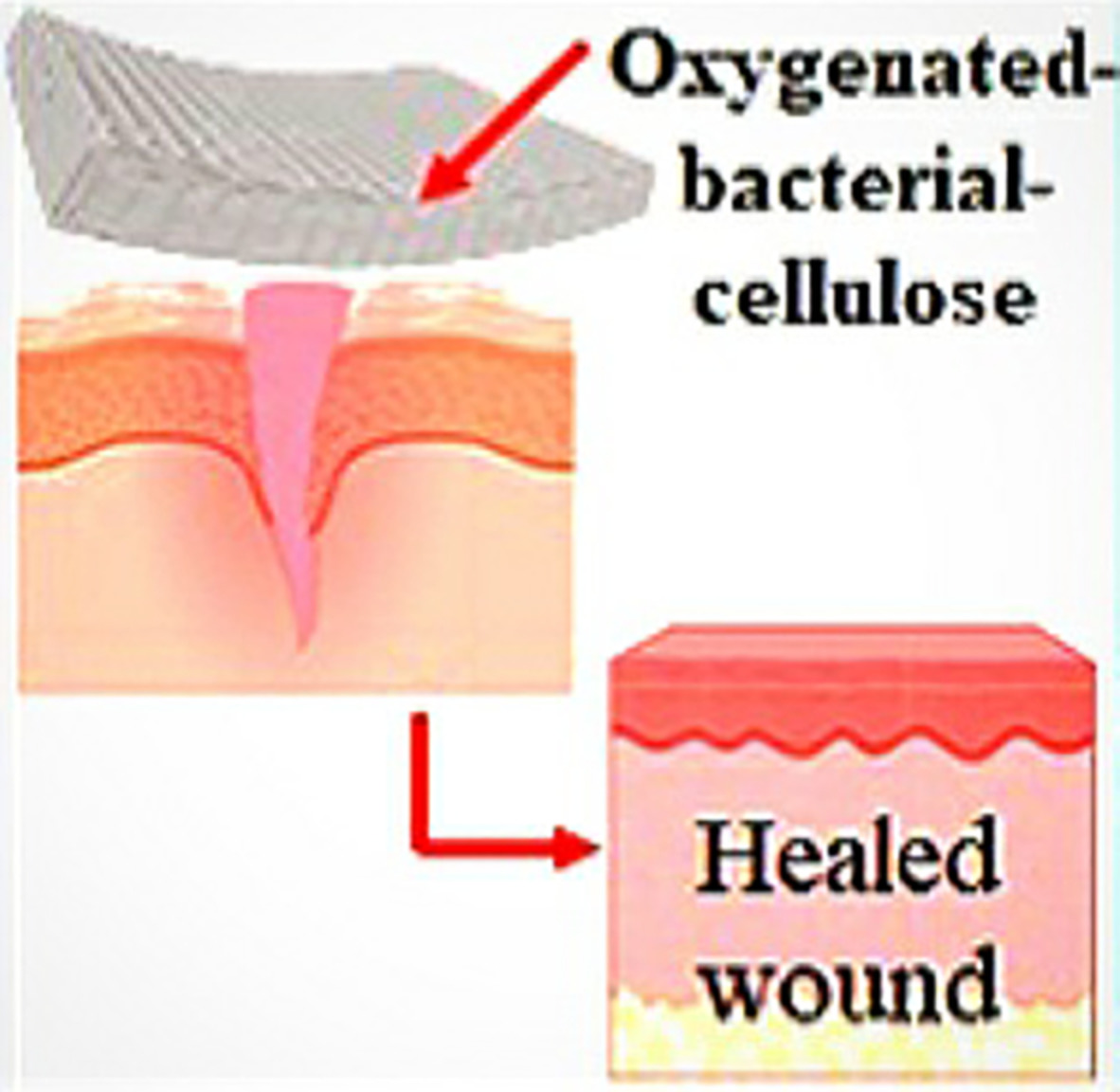
Oxygenated-bacterial-cellulose nanofibers with hydrogel, antimicrobial, and controlled oxygen release properties for rapid wound healing
- First Published: 27 November 2021
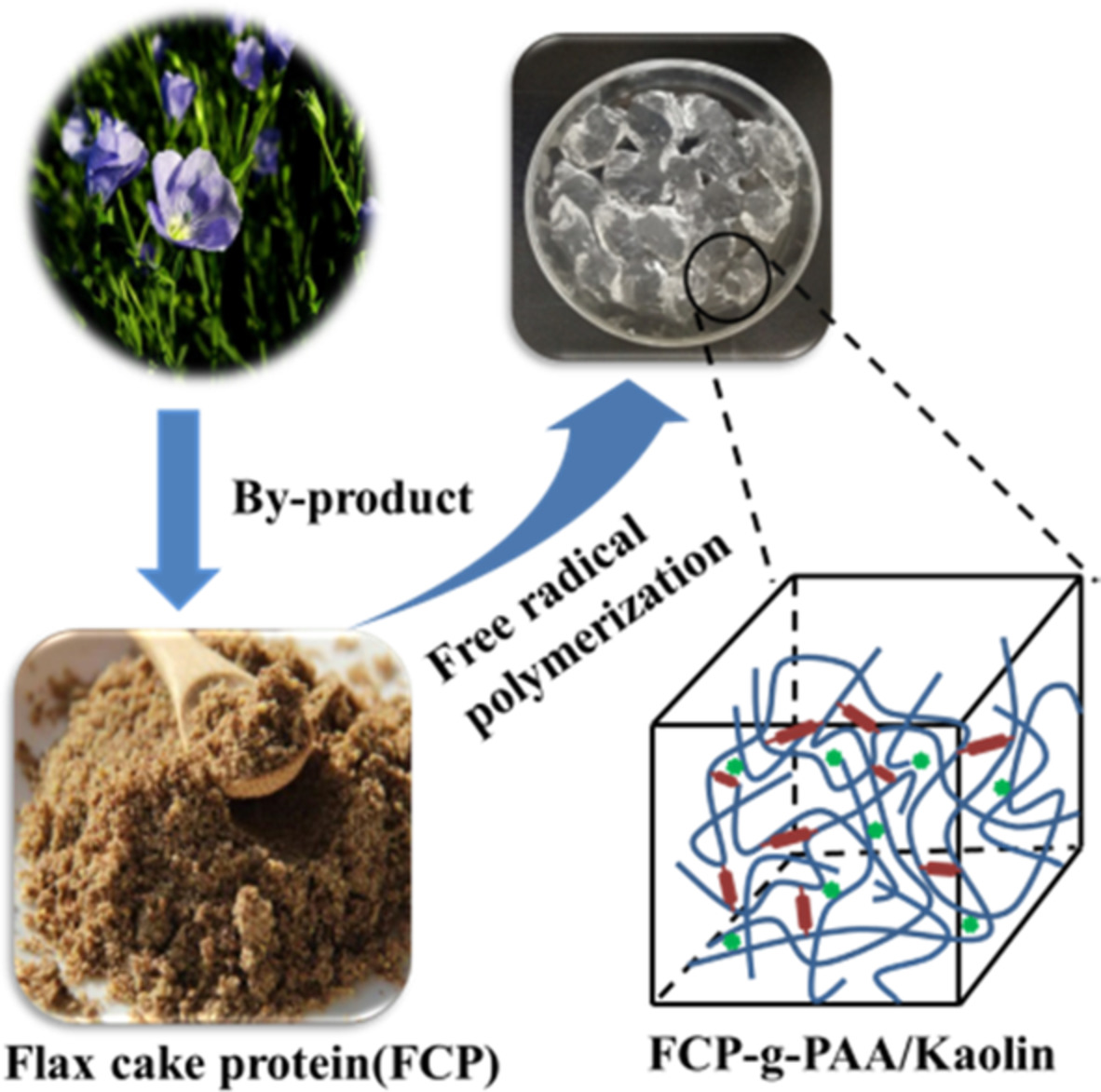
Preparation and properties of a biodegradability superabsorbent composite based on flax cake protein-g-poly (acrylic acid)/Kaolinite
- First Published: 30 November 2021
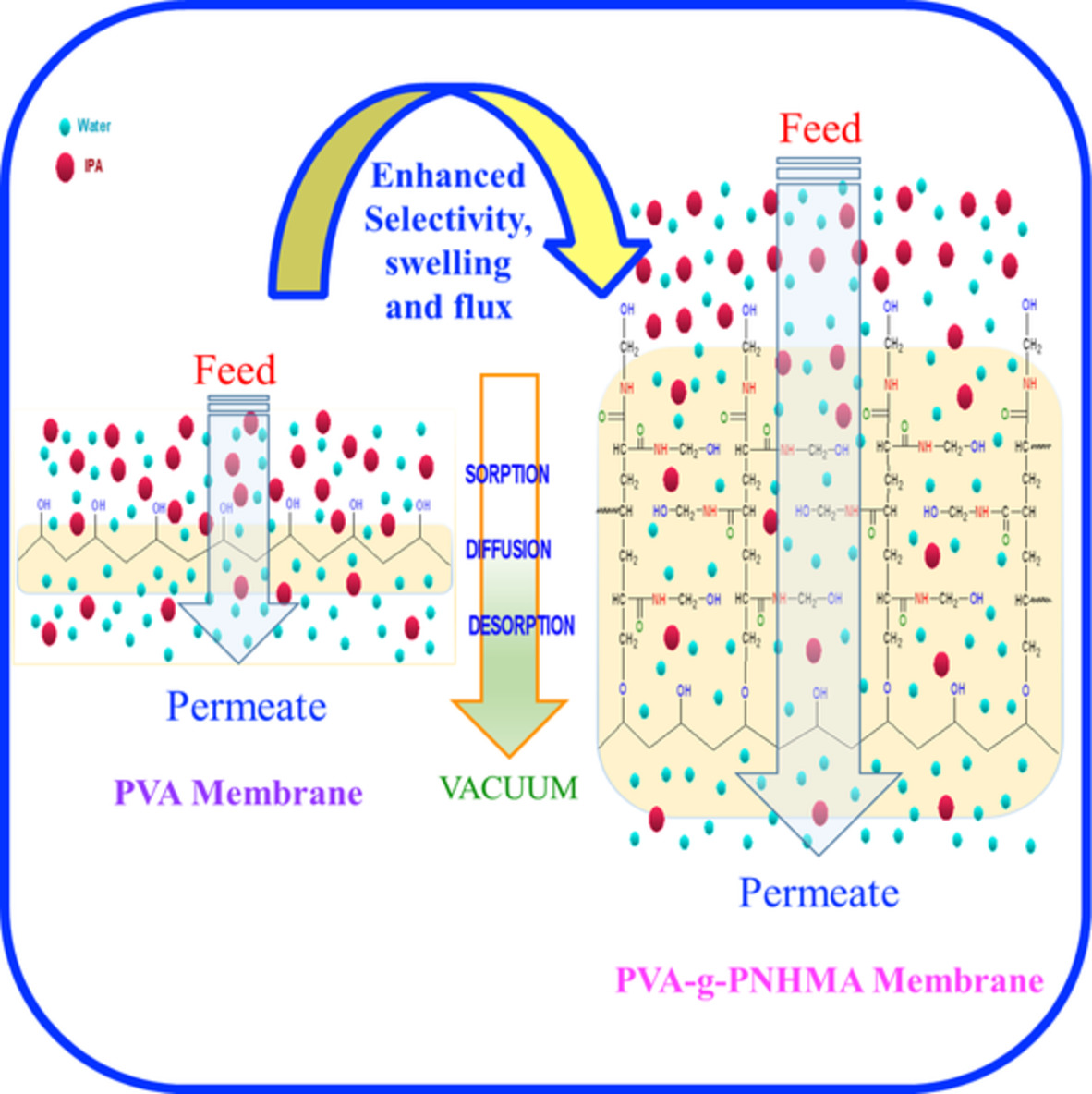
Pervaporation performance of poly(vinyl alcohol)-graft-poly(N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide) membranes for dehydration of isopropyl alcohol-water mixture
- First Published: 03 December 2021
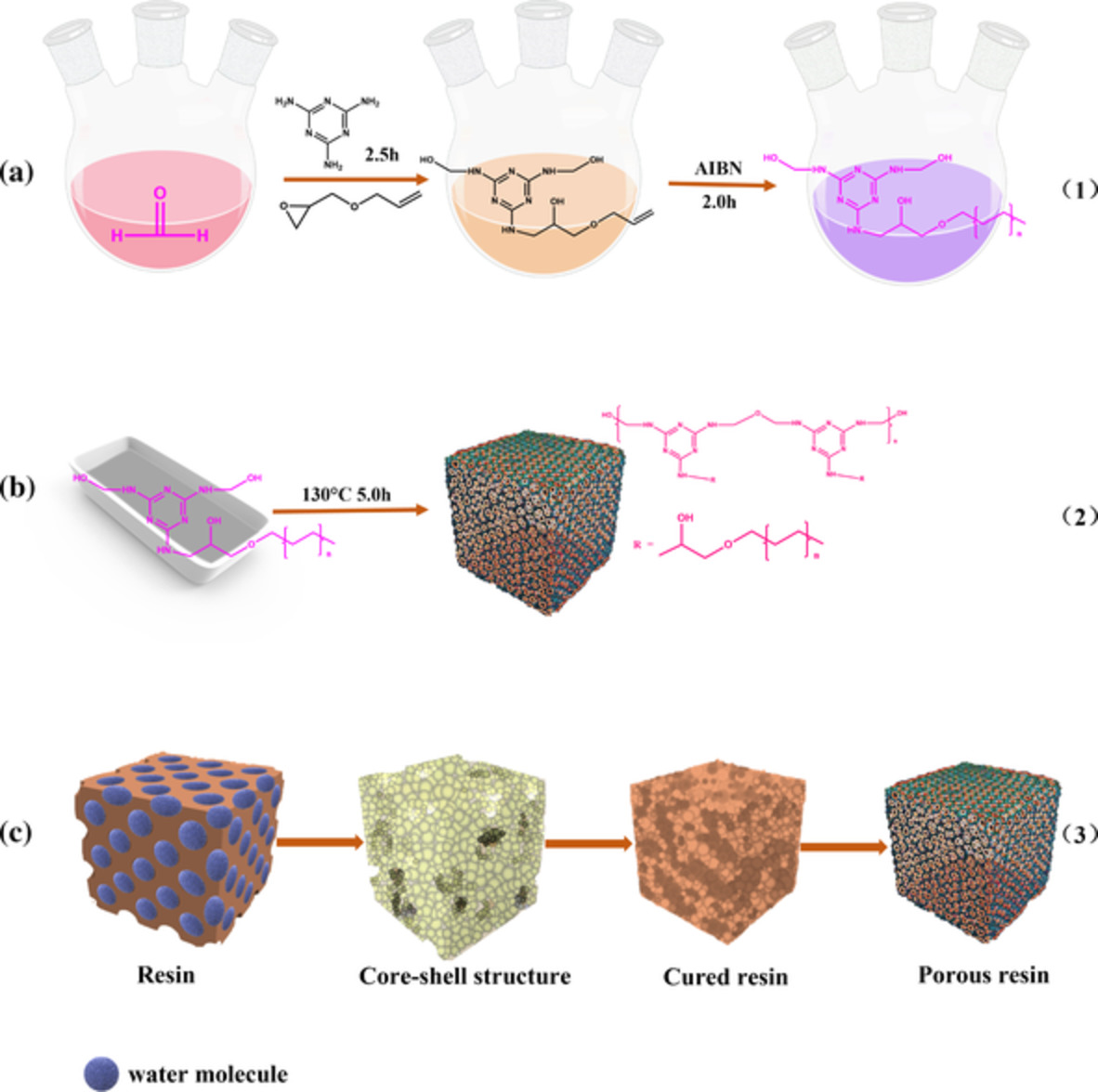
Novel hydroxyl-containing and thermo-dehydrocyclizable polycondensation polymers for multifunctional materials: Synthesis, properties, application
- First Published: 06 December 2021
Plasma sprayed thermal barrier coatings: Effects of polyamide additive on injection molding part quality
- First Published: 30 November 2021
Data-driven methodology to realize strong and broadband microwave absorption properties of polymer-fly ash cenosphere composite
- First Published: 03 December 2021
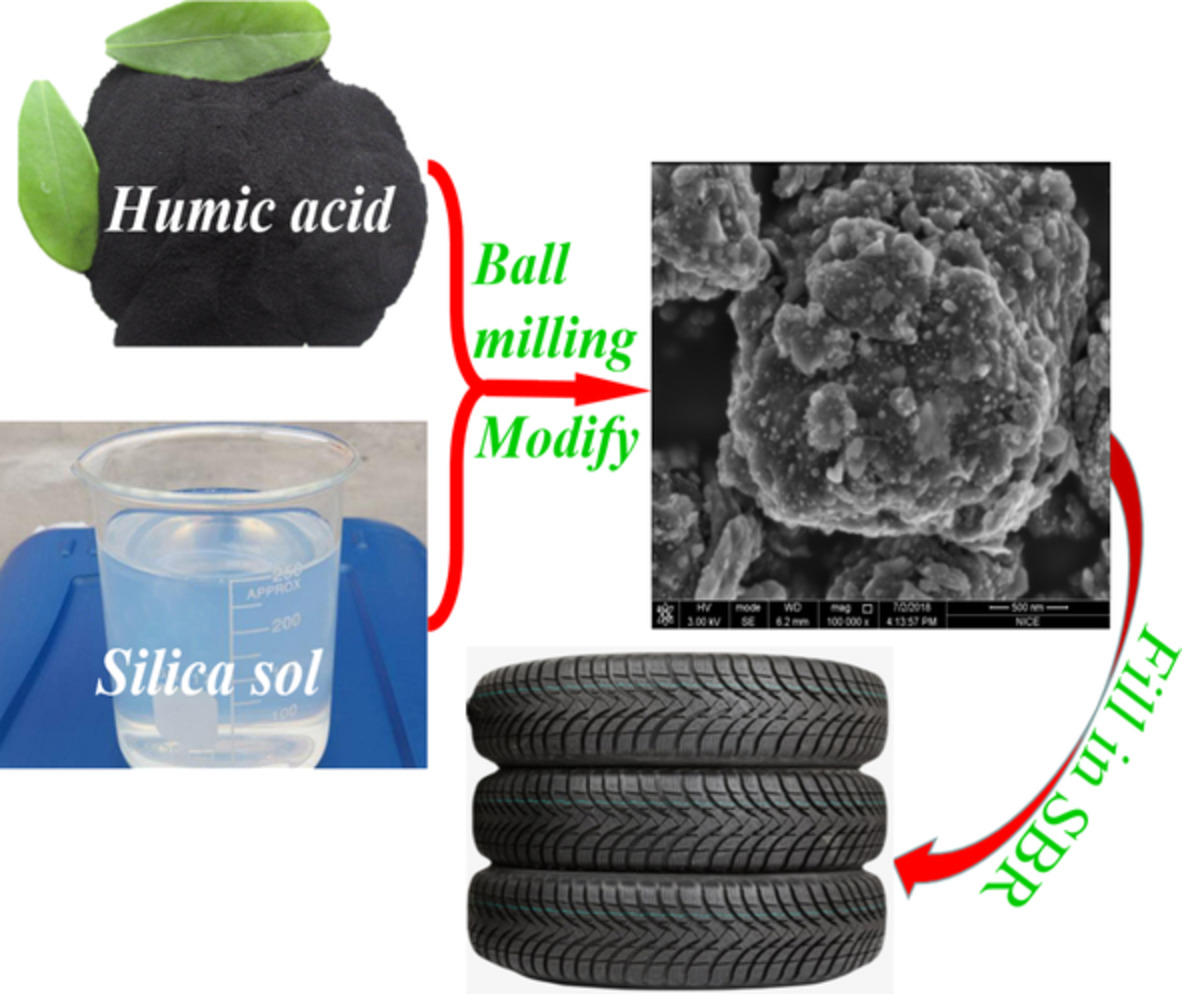
Preparation of an eco-friendly carbon–silicon dual-phase rubber filler with humic acid and silica sol
- First Published: 01 December 2021
Architecture of chitosan chains with sulfur-doped carbon dots along with decorating CeO2 nanoparticles for the photocatalytic application
- First Published: 03 December 2021
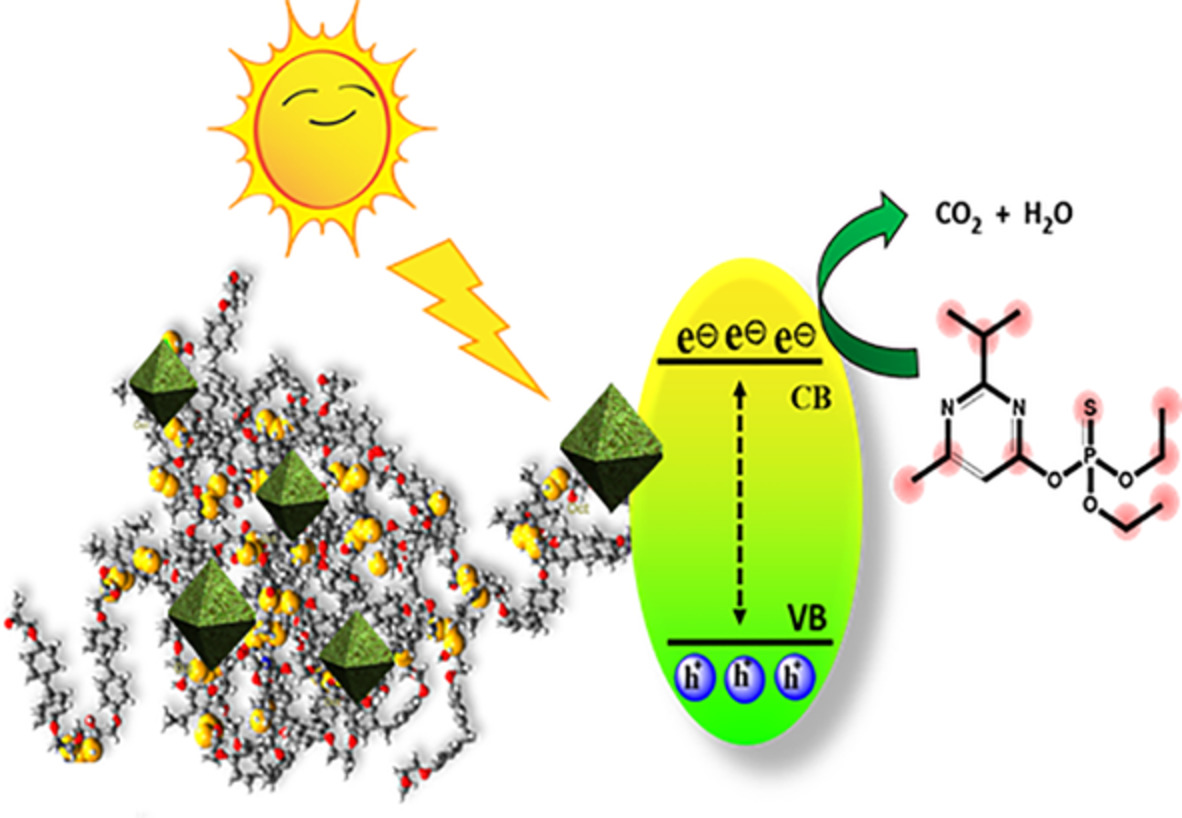
- A new simple method for the synthesis of paraformaldehyde was presented.
- Paraformaldehyde was applied to cross-linking of chitosan with sulfur-doped carbon dots through the methylene bridge.
- Reinforcing of photocatalytic properties was done by loading CeO2 NPs.
- This system effectively degraded Diazinon under visible light.
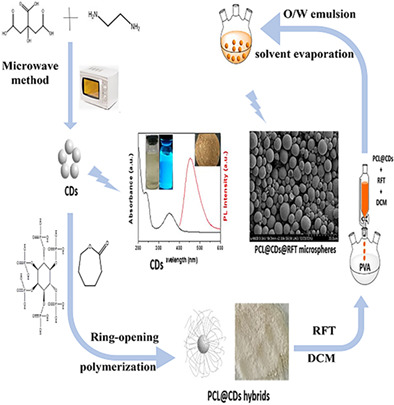
Eco-friendly PCL@CDs biomaterials via phytic acid, CDs-cocatalyzed polymerization for rifapentin delivery
- First Published: 09 December 2021
Celgard/PIM-1 proton conducting composite membrane with reduced vanadium permeability
- First Published: 01 December 2021
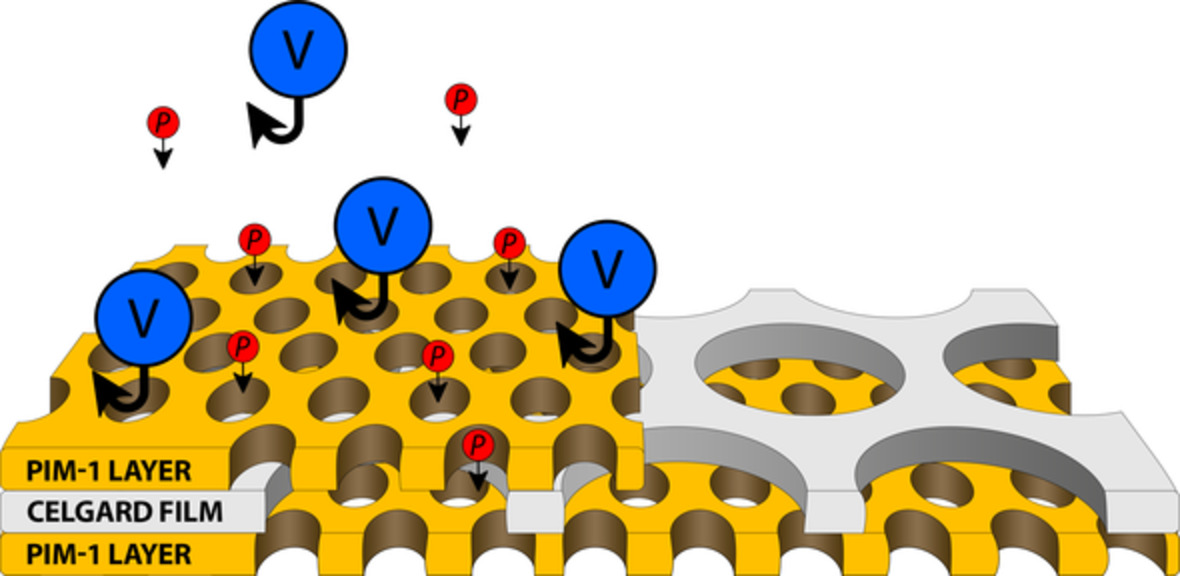
The use of renewable energy sources requires the development of more efficient devices for its storage and timely release, such as vanadium flow batteries (VFB). In order to optimize the VFB properties, we proposed a composite based on a porous polyolefin matrix and a polymer with internal microporosity PIM-1 as an ion-conducting membrane. PIM-1 pores with diameter less than 2 nm provide size-screening of H3O+/hydrate vanadium ions. The resulting structure demonstrates improved selectivity, which allows it to be used for real applications.
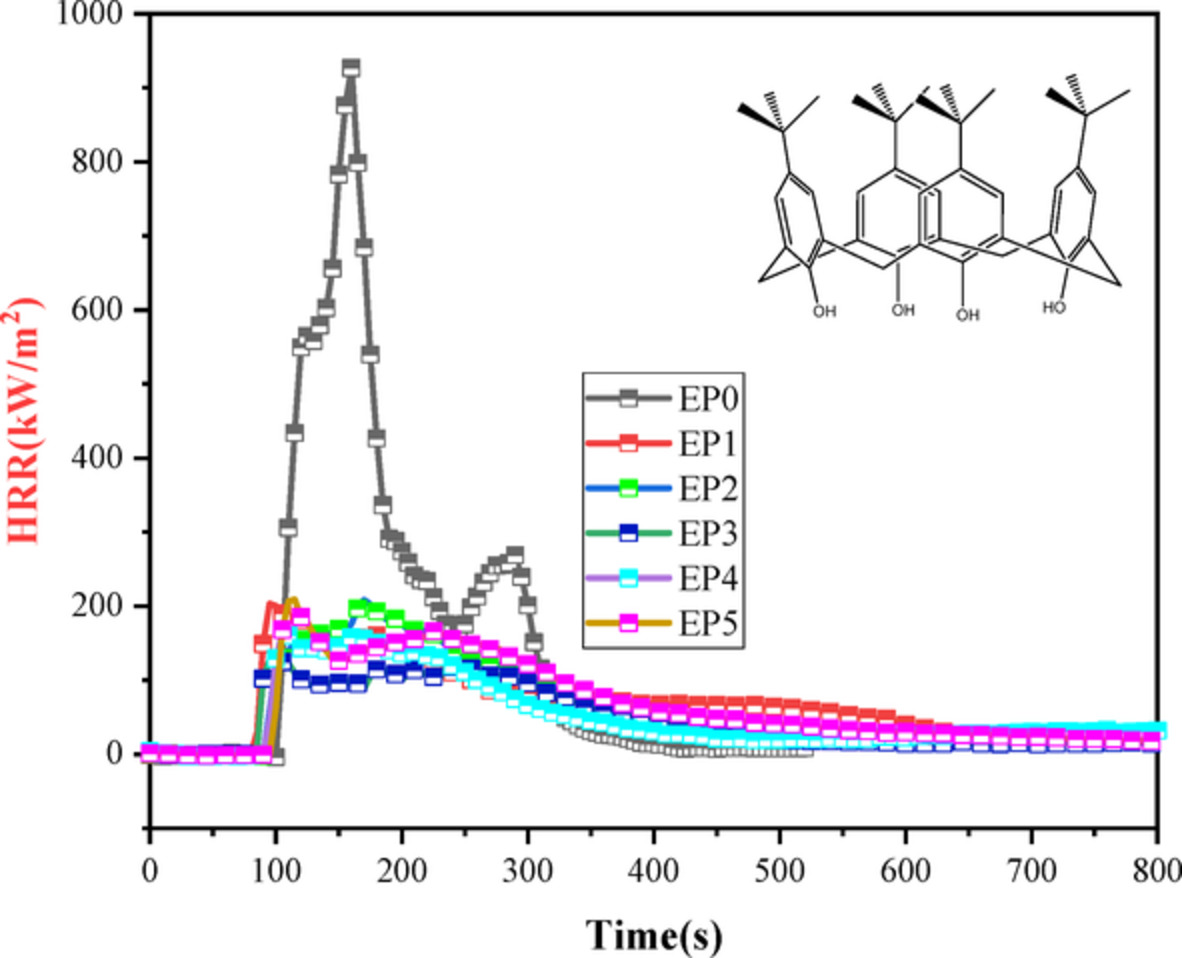
Synthesis of novel calixarene-based intumescent flame retardant and application of flame retardant epoxy resin
- First Published: 04 December 2021
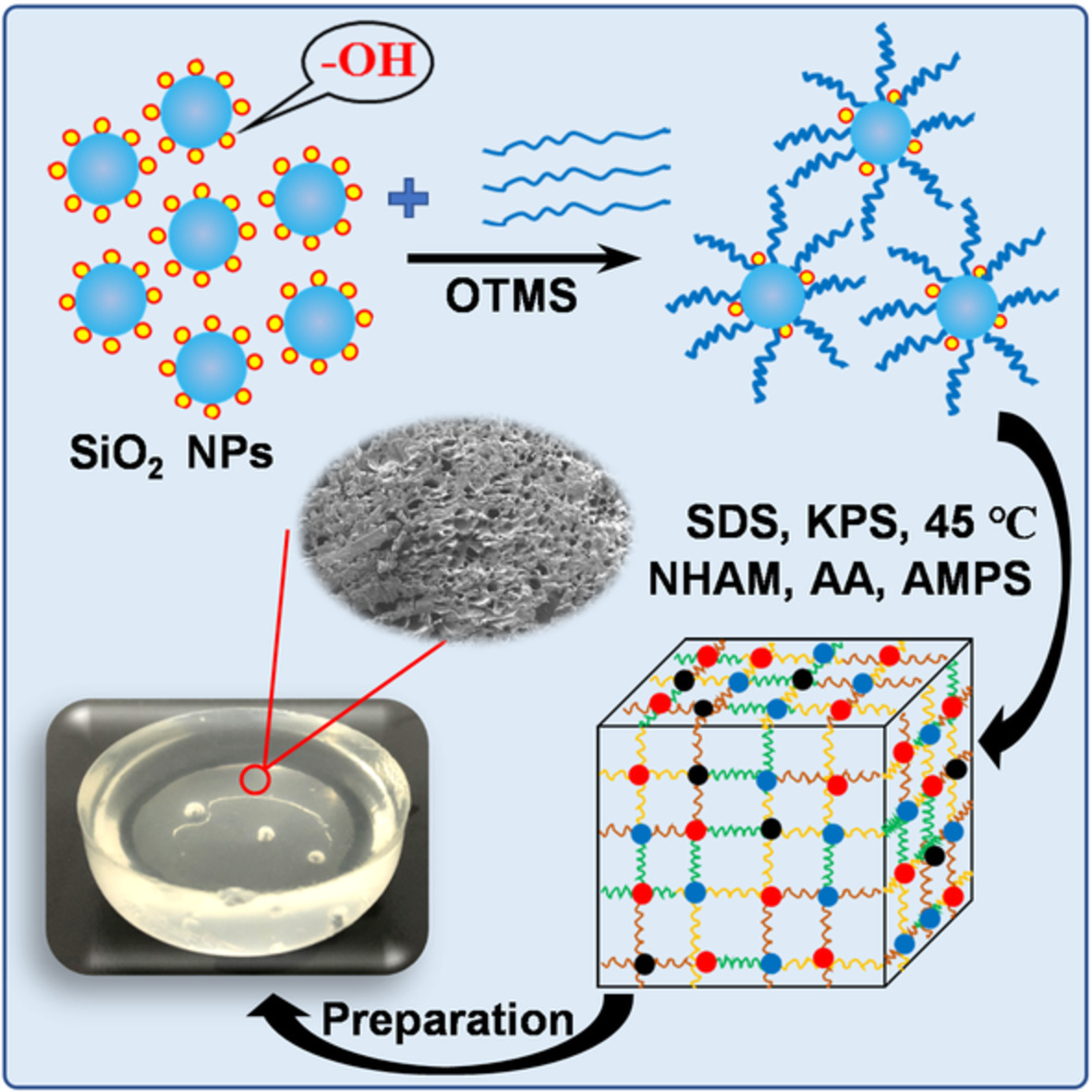
Improving the mechanical performance of P(N-hydroxymethyl acrylamide/acrylic acid/2-acrylamido-2-methylpropanesulfonic acid) hydrogel via hydrophobic modified nanosilica
- First Published: 03 December 2021
Preparation and characterization of self-emulsifying poly(ethylene glycol) methyl ether methacrylate grafted polyacrylate copolymers modified by waterborne polyester
- First Published: 02 December 2021
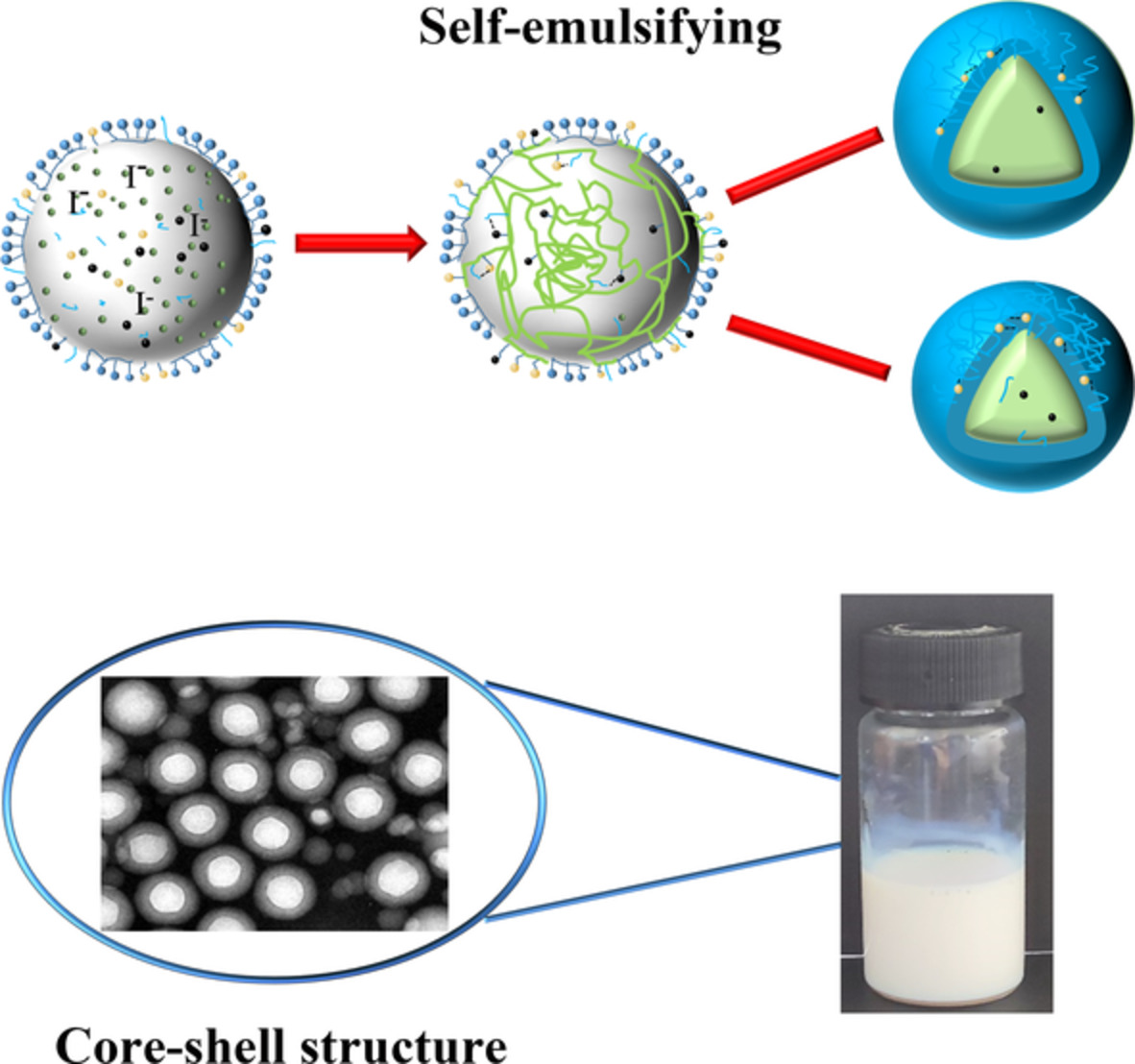
The polyacrylate with core-shell structure was prepared without any emulsifier. The molecular weight of the polyacrylate modified by waterborne polyester was up to 2.5×104 g·mol-1 under the premise of 20% hydroxyl monomer content and 50% solid content. The film cured with melamine formaldehyde resin showed excellent water resistance, adhesion, hardness and tensile property.
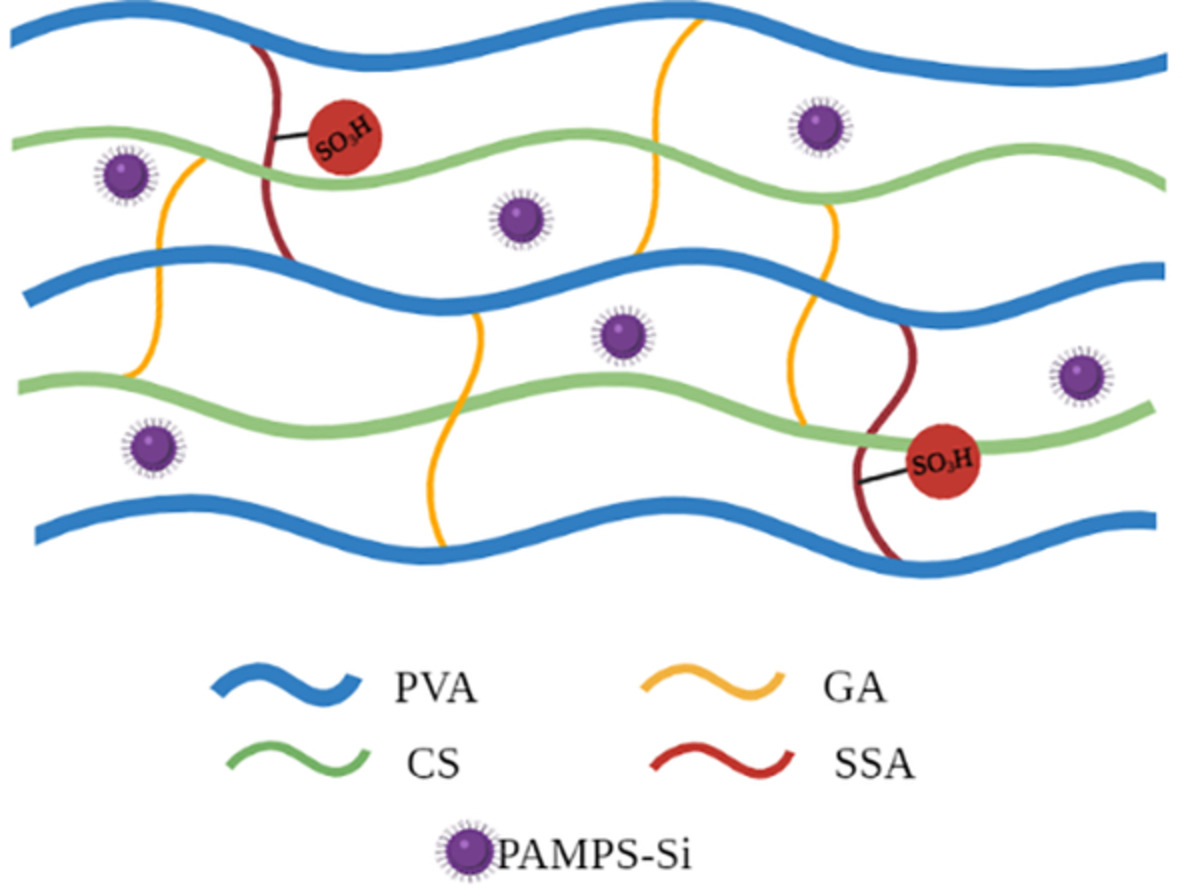
Composite proton conducting membranes from crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol)/chitosan and silica particles containing poly(2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propansulfonic acid)
- First Published: 02 December 2021
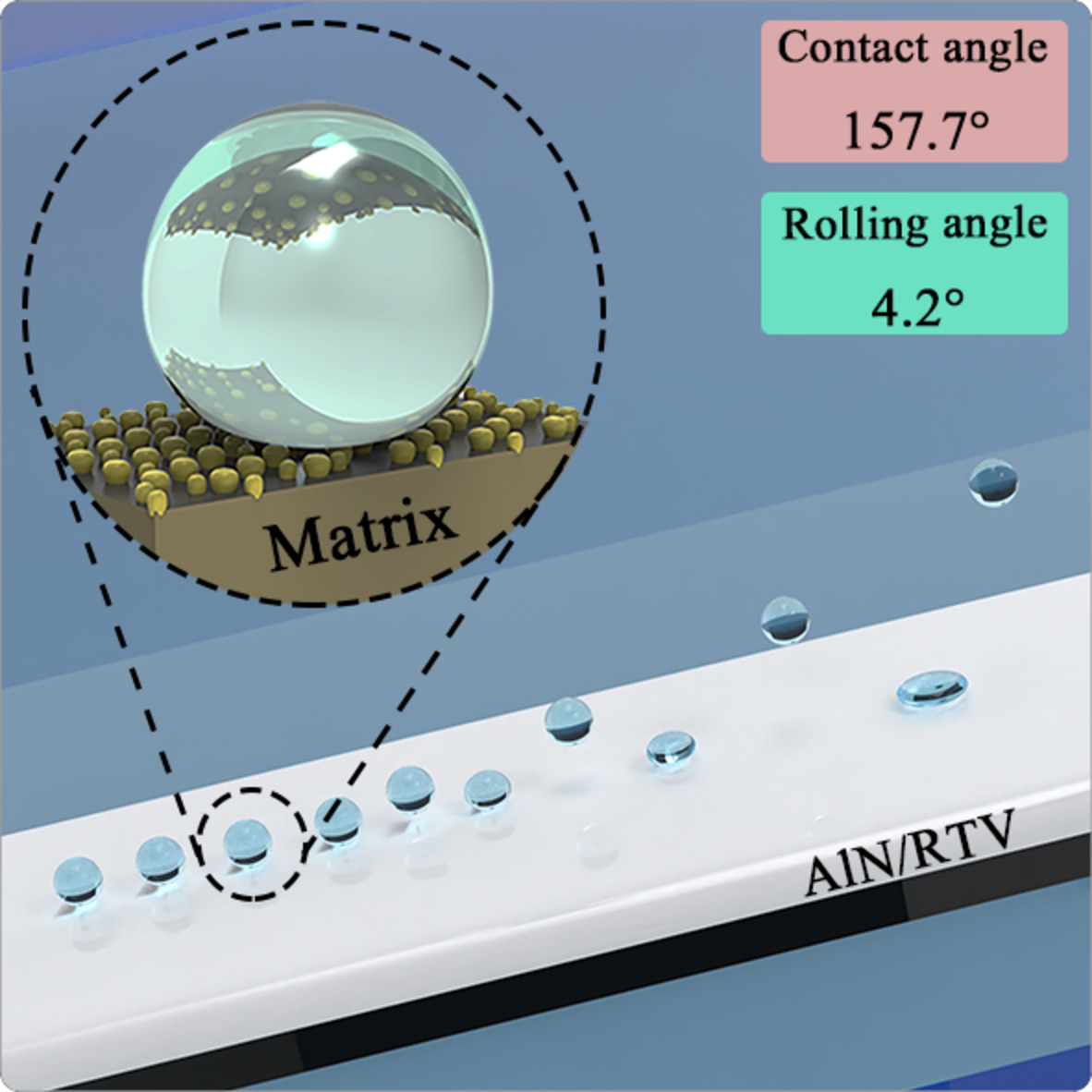
Investigation of self-cleaning and bouncing properties of superhydrophobic aluminum nitride/silicone rubber
- First Published: 02 December 2021
The influence of interfacial failure on the tensile S–N response of aged Arcan joints
- First Published: 07 December 2021
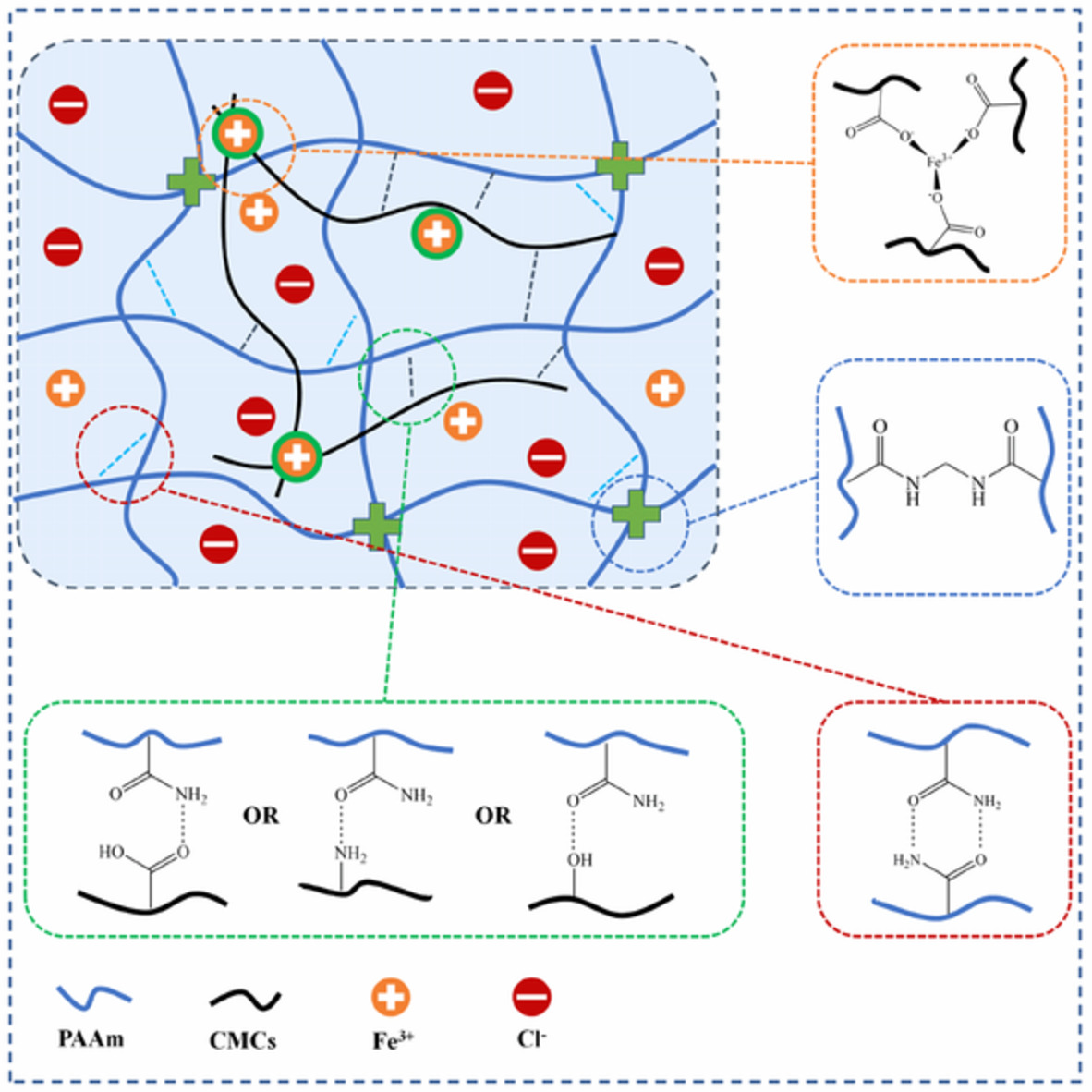
Polyacrylamide/carboxymethyl chitosan double-network hydrogels with high conductivity and mechanical toughness for flexible sensors
- First Published: 06 December 2021
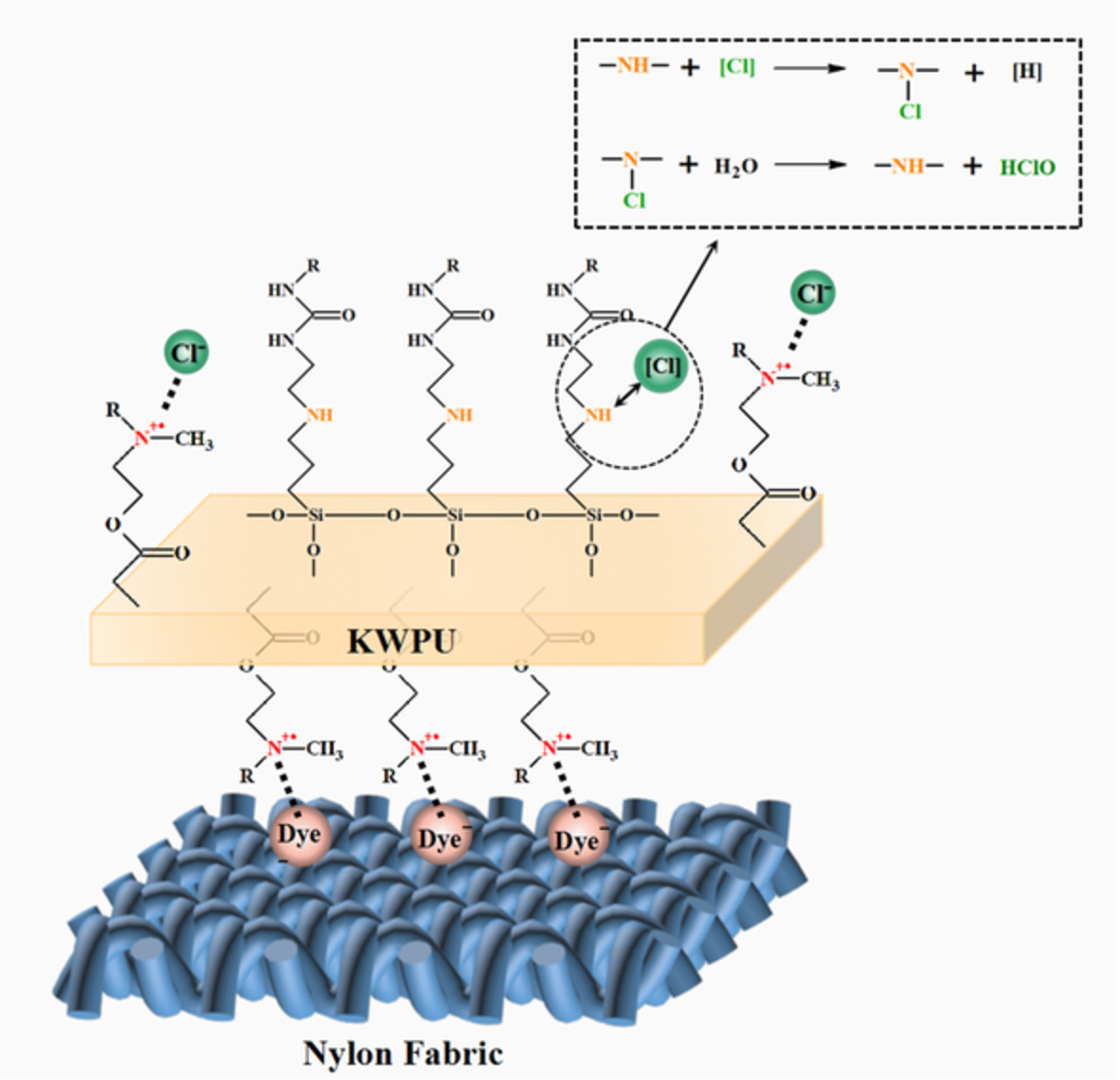
Synthesis and application of aminosiloxane-modified cationic waterborne polyurethane as fixing agent for nylon fabric
- First Published: 04 December 2021
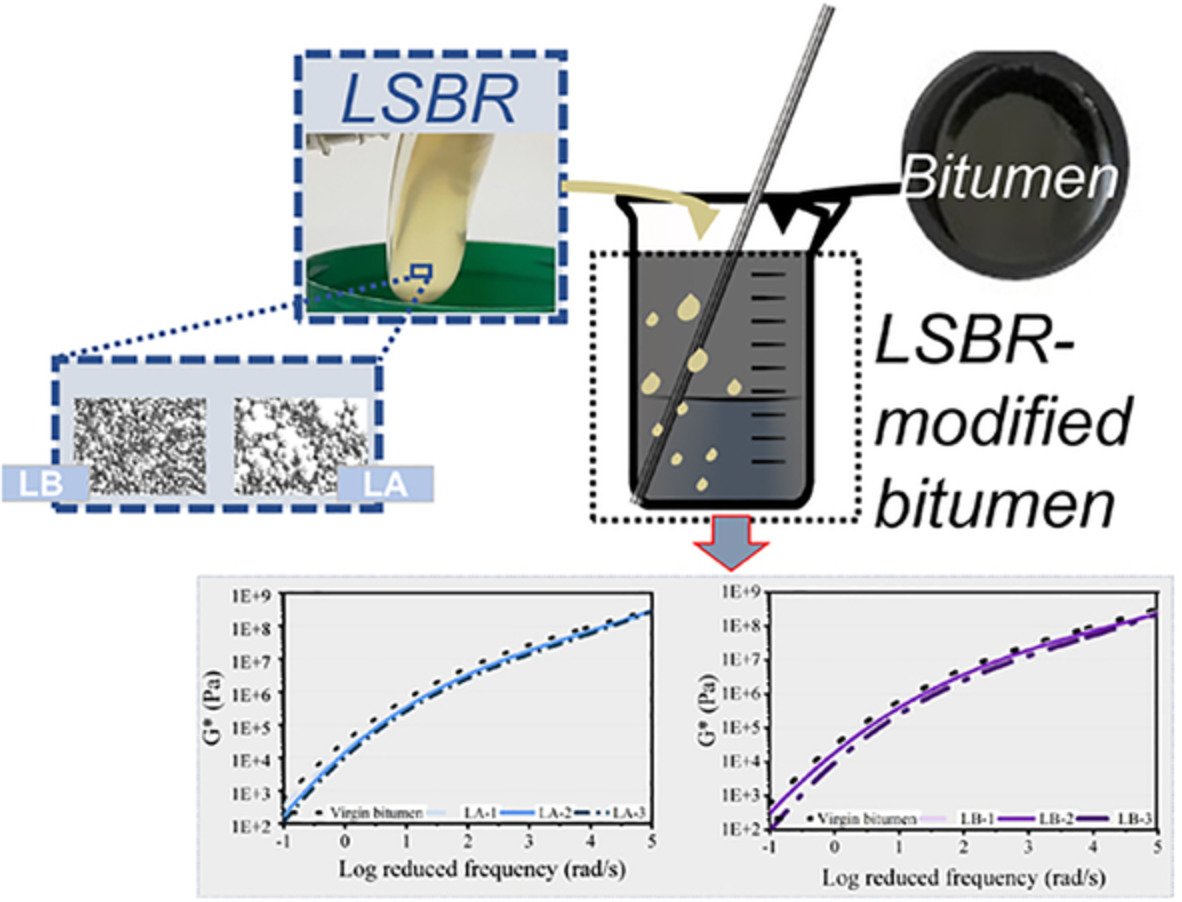
Evaluation of liquid rubber content and molecular weight on rheological properties of asphalt
- First Published: 03 December 2021
Photoactive graphene quantum dots/bacterial cellulose hydrogels: Structural, mechanical, and pro-oxidant study
- First Published: 02 December 2021
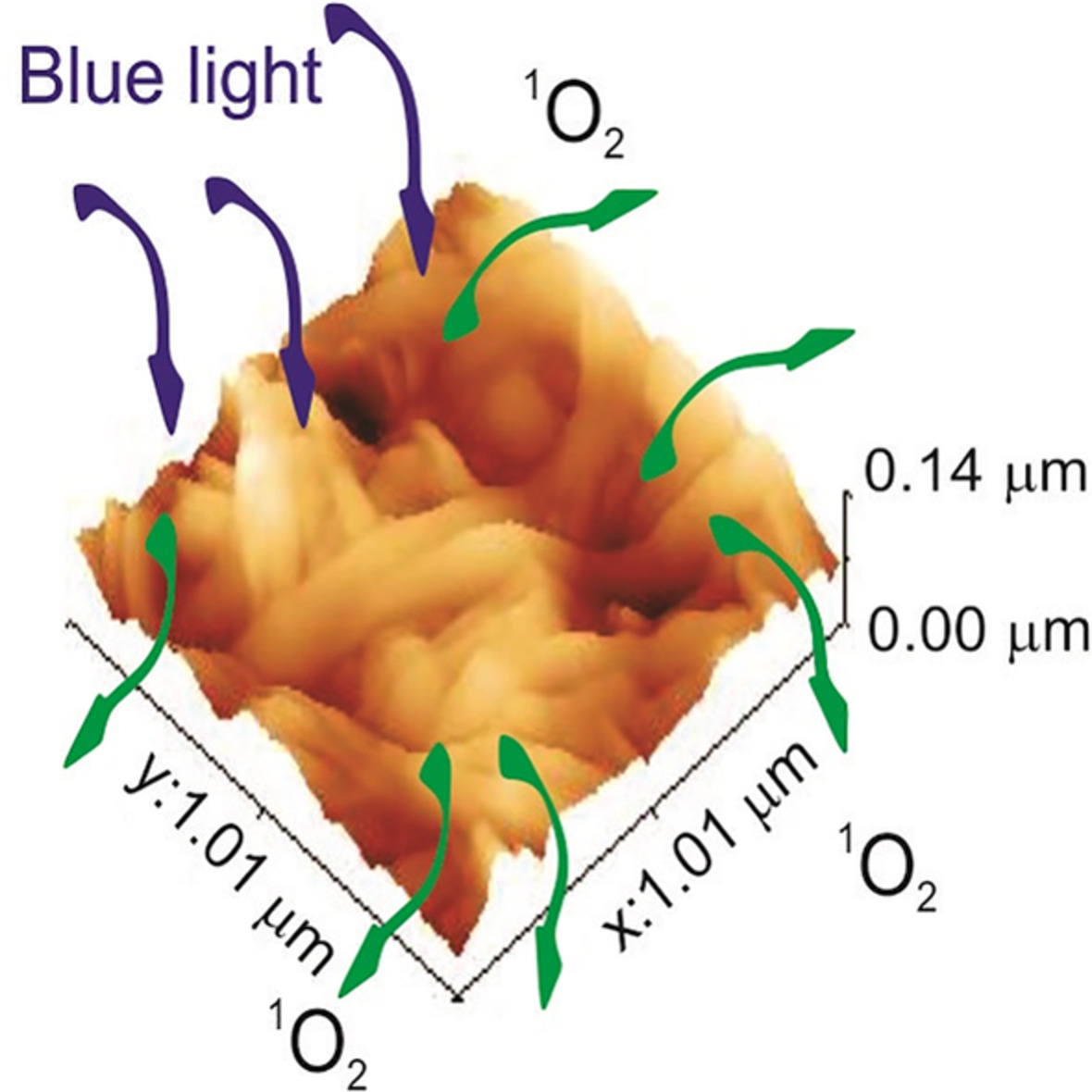
Photoactive GQDs-BC composite hydrogels are produced by immersing BC in GQDs acetone solution. Detailed structural, chemical and mechanical analyses show that photoactive GQDs are encapsulated into BC polymer matrix. Porosity test shows significant pore enlargement of GQDs-BC composite hydrogels. Composite hydrogels are highly potent oxygen radical generator and present advanced material for wound dressing application.
Photo-assisted shape memory lignin/cellulose acetate composites for information encryption
- First Published: 02 December 2021
A study on the flame retardant modification of bisphenol A benzoxazine
- First Published: 10 December 2021
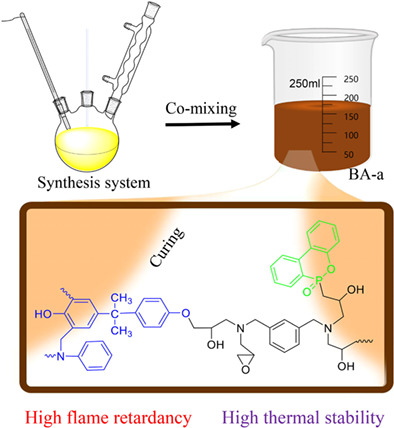
In this study, a P-N synergistic flame retardant AG601-DOPO (A-D) was synthesized by the reaction of an epoxy resin (AG601) with 9,10-dihydro-9-oxo-10-phosphophenanthrene-10-oxide (DOPO). A-D was then mixed with BA-a in different ratios, heated, melted, poured and cured to obtain samples. These samples were tested and characterized. The results showed that the modified BA-a had high flame retardant properties and high thermal stability, while maintaining high glass transition temperature and excellent mechanical properties.
Self-repairing oil-impregnated gel coatings based on reversible physical cross-linking for anti-fouling and anti-corrosion
- First Published: 08 December 2021
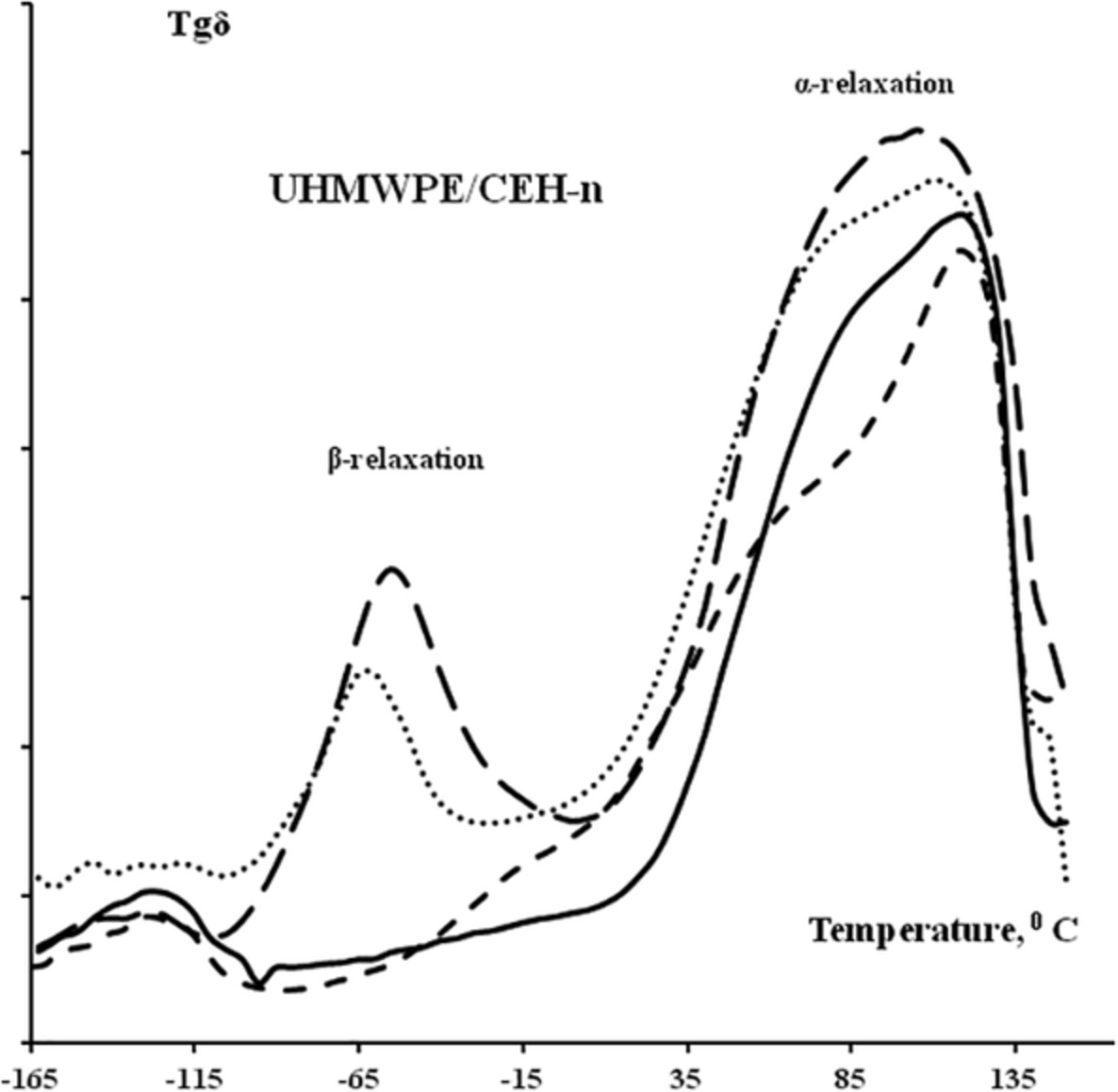
In-reactor blends based on ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene: Effect of microstructure of modifying fraction on the morphology and viscoelastic behavior of blends
- First Published: 04 December 2021
Effect of UV light polymerization time on the properties of plastic crystal composite polyacrylate polymer electrolyte for all solid-state lithium-ion batteries
- First Published: 09 December 2021
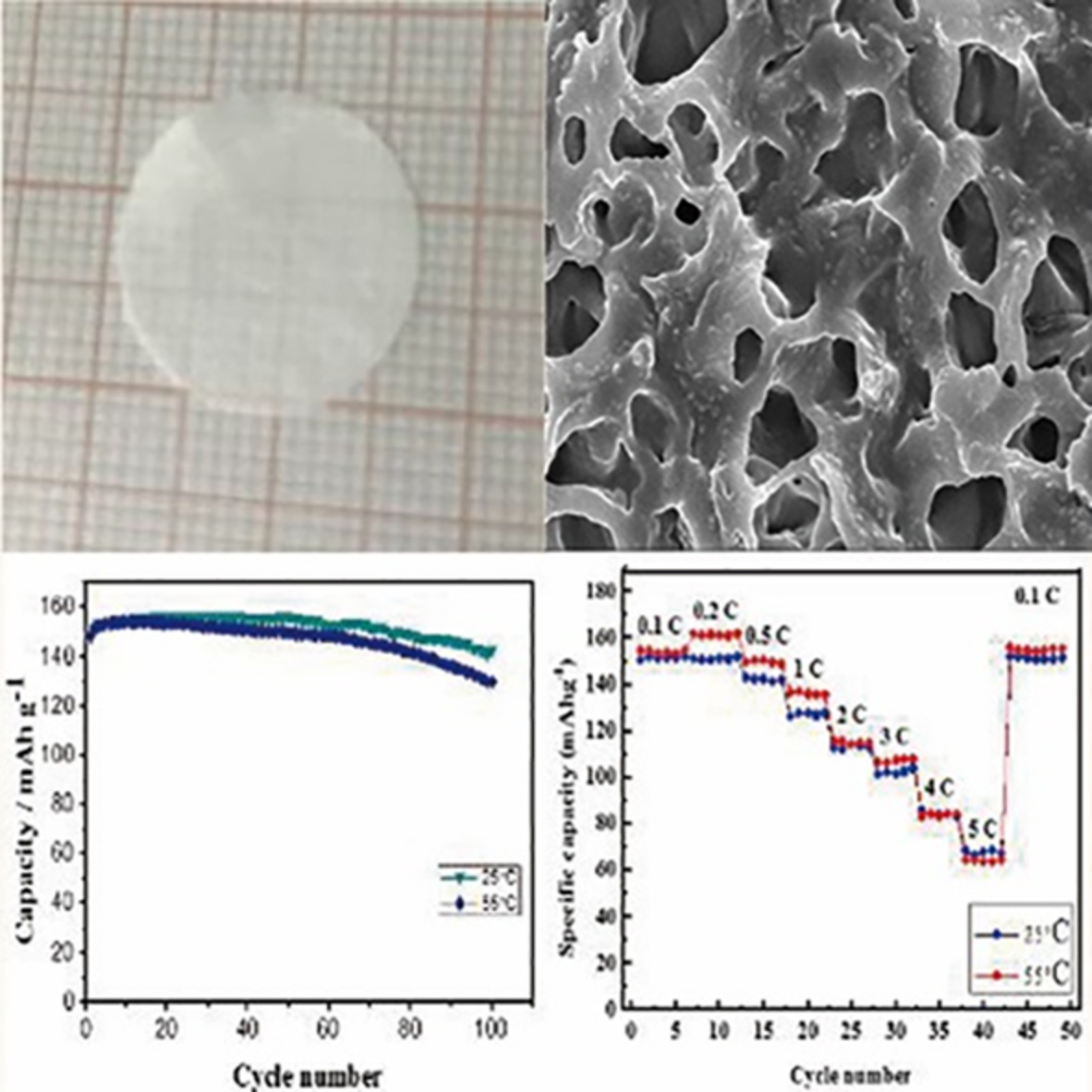
To solve the issues of low ionic conductivity, poor interfacial stability, and weak mechanical strength in the current polymer electrolytes, herein, the UV curing method is proposed to in-situ polymerize the plastic crystal composite solid polymer electrolyte (S-PCCE). At the same time, the influence of UV irradiation time on the performance of electrolyte was discussed in detail.
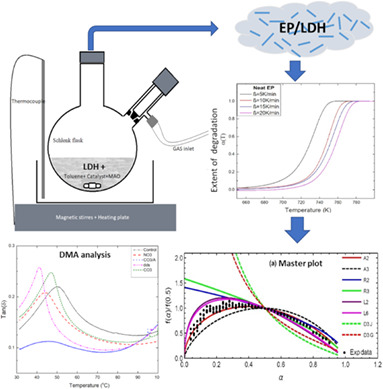
Degradation kinetics and thermomechanical properties of in-situ polymerized layered double hydroxides-ethylene-propylene copolymer
- First Published: 09 December 2021
Preparation of an oxyalkylated lignin-g-polylactic acid copolymer to improve the compatibility of an organosolv lignin in blended poly(lactic acid) films
- First Published: 04 December 2021
Environment-tolerant conductive and superhydrophobic poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) fabric prepared via γ-ray activation and reduced graphene oxide/nano SiO2 modification
- First Published: 06 December 2021
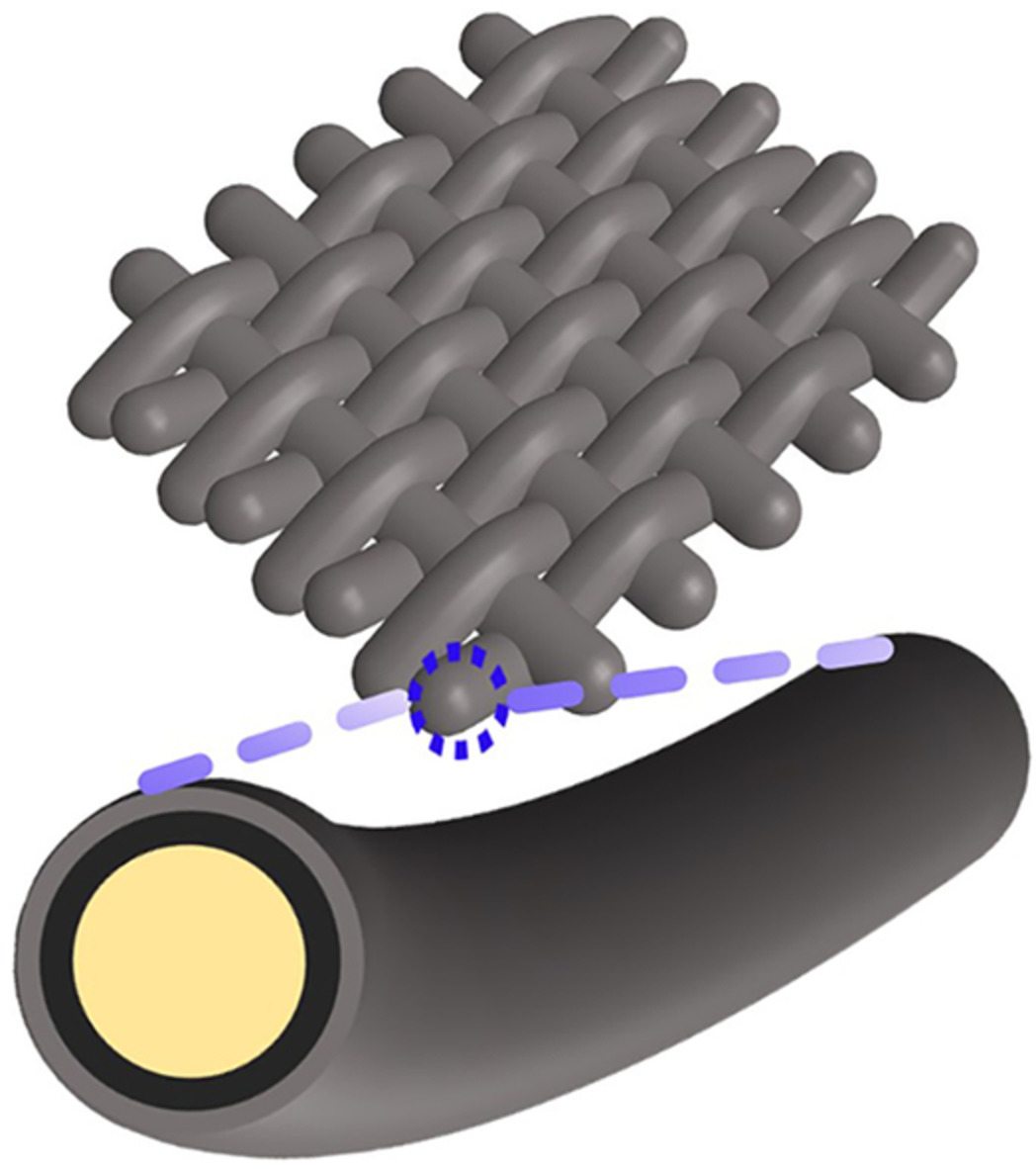
Poly(m-phenylene isophthalamide) (PMIA) fabric with integrated conductive and superhydrophobic abilities via a simple method including γ-ray irradiation and dip-coating was fabricated. The surface roughness of PMIA was enhanced and the content of the oxygen element was increased after γ-ray irradiation, benefiting greatly the decorating of graphene oxide and silica nanoparticles. The conductivity and superhydrophobic ability were realized by the reduction of graphene oxide and microscale aggregation of silica nanoparticles.