Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
COMMENTARIES/PERSPECTIVES
Women in neuroscience special issue: Pandemic edition
- Pages: 5-6
- First Published: 13 September 2020
Women in neuroscience: Where are we in 2019?
- Pages: 9-12
- First Published: 08 April 2020
Gender inequality in academia: Problems and solutions for women faculty in STEM
- Pages: 13-23
- First Published: 25 October 2020
Lessons learned on my journey to a career as a minority woman in Neuroscience
- Pages: 24-25
- First Published: 26 February 2020
Women neuroscientists at Cohen Veterans Bioscience are charting new ground
- Pages: 26-28
- First Published: 13 March 2020
The Laboratory of the Biology of Addictive Diseases: Four Women in Neuroscience
- Pages: 29-36
- First Published: 08 July 2020
NEURODEVELOPMENT/EARLY LIFE
Molecular causes of sex-specific deficits in rodent models of neurodevelopmental disorders
- Pages: 37-56
- First Published: 23 December 2019
Long term effects of stress on hippocampal function: Emphasis on early life stress paradigms and potential involvement of neuropeptide Y
- Pages: 57-66
- First Published: 11 March 2020
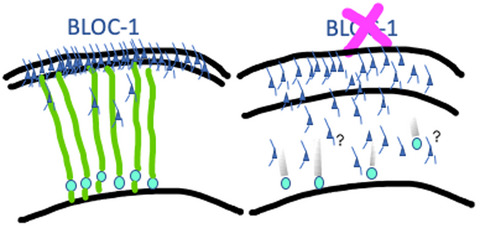
Sex-dimorphic effects of biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-1 deficiency on mouse perinatal brain development
- Pages: 67-89
- First Published: 20 May 2020
Chemogenetic manipulation of the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis counteracts social behavioral deficits induced by early life stress in C57BL/6J mice
- Pages: 90-109
- First Published: 01 June 2020
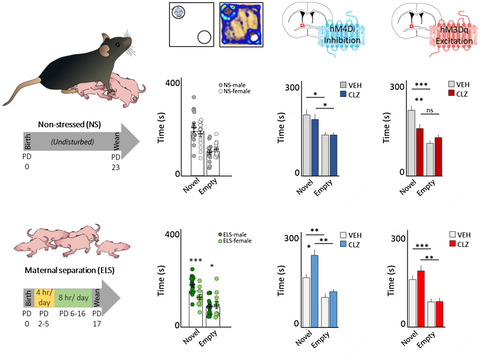
Early life stress (ELS) induces long-lasting social behavior deficits. We used chemogenetics to manipulate activity in the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis (BNST), which undergoes maturation during the early postnatal period. Altering BNST activity in adulthood produced divergent effects on social behavior that were dependent upon history of ELS.
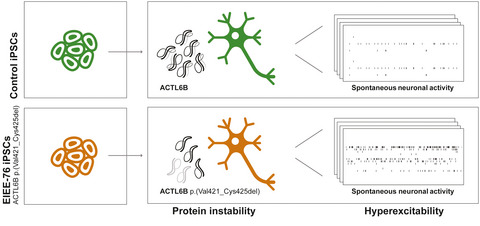
An epilepsy-associated ACTL6B variant captures neuronal hyperexcitability in a human induced pluripotent stem cell model
- Pages: 110-123
- First Published: 03 November 2020
NEURODEGENERATIVE DISEASES
The application of in vitro-derived human neurons in neurodegenerative disease modeling
- Pages: 124-140
- First Published: 13 March 2020
Targeting microglia L-type voltage-dependent calcium channels for the treatment of central nervous system disorders
- Pages: 141-162
- First Published: 29 January 2020
An update on cellular and molecular determinants of Parkinson's disease with emphasis on the role of the retromer complex
- Pages: 163-179
- First Published: 07 July 2020
DNA damage and repair in Parkinson's disease: Recent advances and new opportunities
- Pages: 180-189
- First Published: 12 February 2020
Cognitive function and its relationship with brain structure in myotonic dystrophy type 1
- Pages: 190-199
- First Published: 13 February 2020
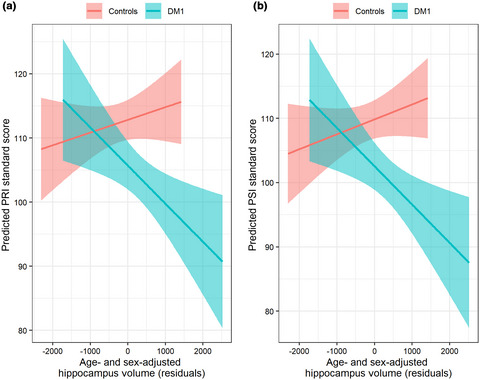
Myotonic dystrophy type 1 (DM1)-affected adults (blue) exhibit lower scores on measures of cognitive function than unaffected adults (pink). These differences are associated with enlarged hippocampal volume in DM1-affected individuals for Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale-IV index measures of perceptual reasoning (Panel a) and processing speed (Panel b).
A common genetic variant rs2821557 in KCNA3 is linked to the severity of multiple sclerosis
- Pages: 200-208
- First Published: 13 February 2020
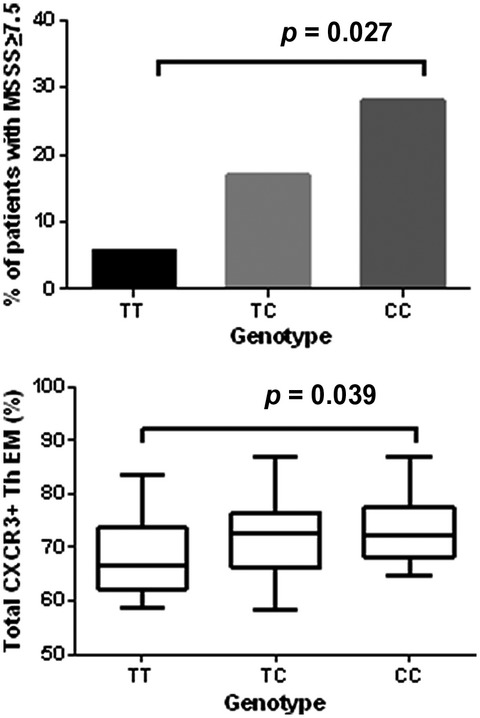
Case-series study involving 101 multiple sclerosis patients revealed a link between KCNA3 polymorphism rs2821557 and the rate of disease progression. Minor C allele carriers exhibited significantly higher incidence of the rapid disease course and higher counts of CXCR3+ TEM cells compared to TT genotype carriers.
Reduced social investigation and increased injurious behavior in transgenic 5xFAD mice
- Pages: 209-222
- First Published: 07 January 2020
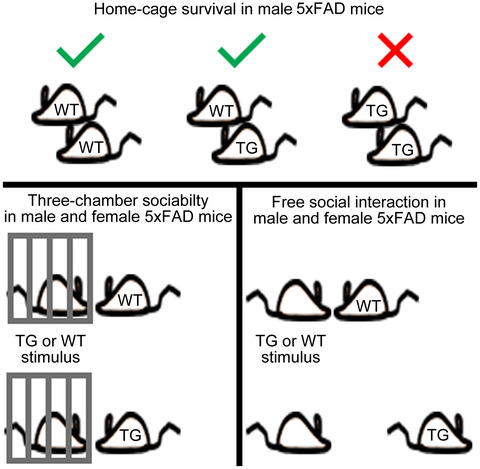
In 5xFAD mice, transgenic (TG) males cannot be reliably housed together due to home-cage aggression between 2 and 5 months of age, unlike wild-type (WT)-only and mixed-genotype cages. Six-month-old TG males and females also exhibit reduced investigation of free-roaming, but not restrained, conspecifics relative to WT controls.
Impaired intracellular trafficking of sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 contributes to the redox imbalance in Huntington’s disease
- Pages: 223-235
- First Published: 04 August 2020
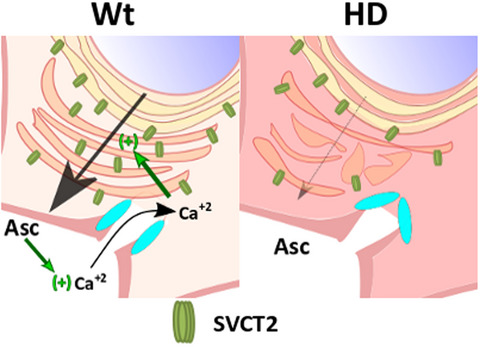
Extracellular ascorbic acid induces Ca2+ influx, stimulating sodium-dependent vitamin C transporter 2 (SVCT2) anterograde trafficking in wild-type cells. No ascorbic acid-induced cytosolic Ca2+ increase was observed in Huntington's disease (HD) cells. Thus, SVCT2 would fail to reach the cellular surface, affecting ascorbic acid uptake in HD cells.
AGING
Functional brain connectivity changes across the human life span: From fetal development to old age
- Pages: 236-262
- First Published: 18 June 2020
The impact of aging on the subregions of the fusiform gyrus in healthy older adults
- Pages: 263-270
- First Published: 08 March 2020
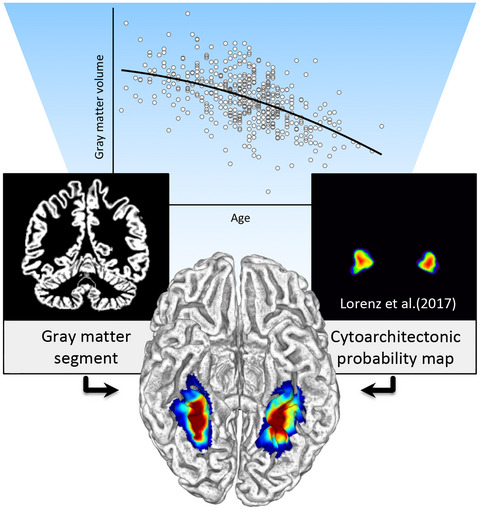
We investigated associations between age and regional gray matter in subregions of the fusiform gyrus. This was achieved by integrating imaging-based signal intensities with cytoarchitectonically defined tissue probabilities. Our analyses revealed significant negative correlations in all subregions but with differing trajectories.
REPRODUCTION
The role of maternal diet on offspring gut microbiota development: A review
- Pages: 284-293
- First Published: 28 February 2020
Circadian rhythms in the mouse reproductive axis during the estrous cycle and pregnancy
- Pages: 294-308
- First Published: 03 March 2020
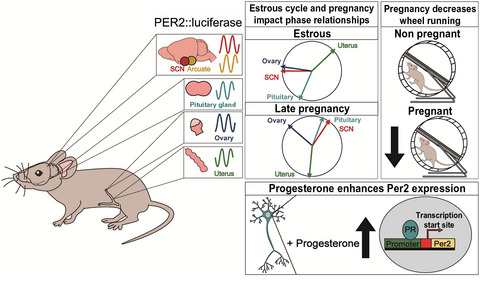
Functional circadian rhythms are essential for fertility and successful reproduction. PER2::Luciferase circadian reporter mice determined relationships between circadian rhythms during the estrous cycle and pregnancy and how these rhythms could be regulated by progesterone, a steroid important in reproductive function.
DEPRESSION/SUBSTANCE ABUSE
Sex/gender differences in brain function and structure in alcohol use: A narrative review of neuroimaging findings over the last 10 years
- Pages: 309-323
- First Published: 24 April 2020
Do corticosterone levels predict female depressive-like behavior in rodents?
- Pages: 324-331
- First Published: 08 July 2020
INTEGRATED CONNECTOME
Interactions with PDZ proteins diversify voltage-gated calcium channel signaling
- Pages: 332-348
- First Published: 01 June 2020
White matter disturbances in phenylketonuria: Possible underlying mechanisms
- Pages: 349-360
- First Published: 06 March 2020
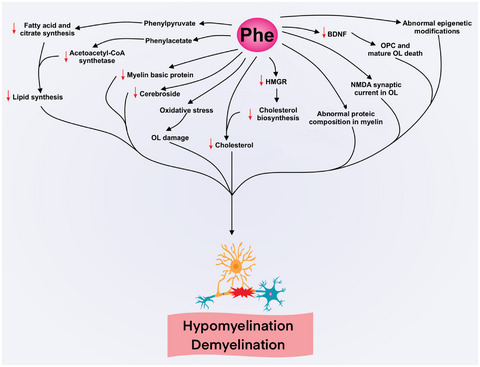
Alterations in lipid metabolism, impaired protein synthesis, epigenetic abnormal modifications, oxidative stress and lower brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels caused by phenylalanine accumulation may collaborate to hypomyelination/demyelination in phenylketonuria. HMGR: 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase; OL: oligodendrocytes; OPC: oligodendrocyte precursor cells.
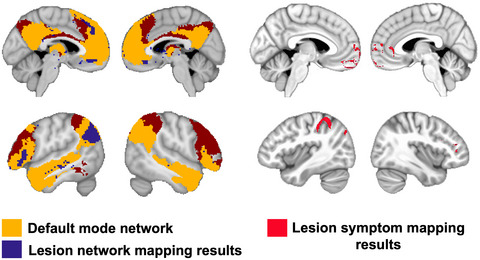
Lesion network mapping demonstrates that mind-wandering is associated with the default mode network
- Pages: 361-373
- First Published: 28 June 2020
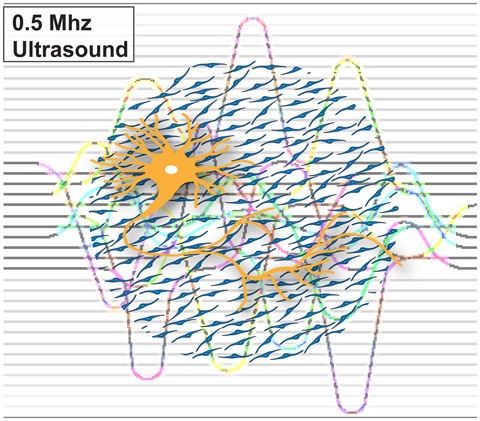
The effects of low intensity focused ultrasonic stimulation on dorsal root ganglion neurons and Schwann cells in vitro
- Pages: 374-391
- First Published: 02 August 2020
Reelin activates the small GTPase TC10 and VAMP7 to promote neurite outgrowth and regeneration of dorsal root ganglia (DRG) neurons
- Pages: 392-406
- First Published: 11 July 2020
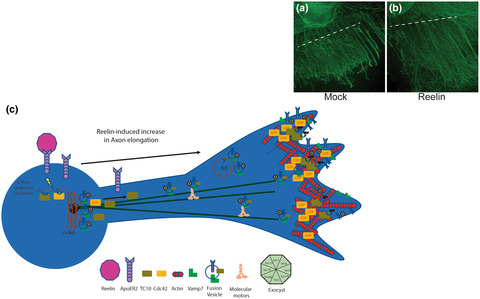
Axonal growth is a relevant process for development and regeneration. After peripheral nervous system (PNS) injury, Reelin levels increase, and mice devoid of Reelin show an impairment in nerve regeneration. Here we show, for the first time, that Reelin increases the regenerative outcome of dorsal root ganglia axons after axotomy (a mock, b Reelin treated). (c) After binding to its receptor, Apolipoprotein E-receptor 2, Reelin activates the Rho GTPases Cdc42 that regulates actin dynamics, and TC10, required for membrane addition by interacting with the exocyst complex. TC10 recruits to membrane vesicles that potentially could come from Golgi and/or recycling endosomes. TC10 vesicles also contain ApoER2 and the v-SNARE protein VAMP7. Reelin increases the fusion of vesicles, containing VAMP7, at the growth cone. Therefore, Reelin signaling could have a therapeutic role in PNS lesions, improving axonal outgrowth.
Lithium influences whole-organism metabolic rate in Drosophila subobscura
- Pages: 407-418
- First Published: 29 July 2020
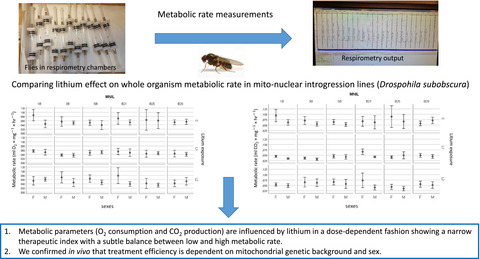
Metabolic parameters (O2 consmption and CO2 production) are influenced by lithium in dose-dependent fashion showing a narrow therapeutic index with a subtle balance between low and high metabolic rate. We confirmed in vivo that treatment efficiency is dependent on mitochondrial genetic background and sex.