Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Estimating three-dimensional motion of a creeping landslide from topographic data and associated land surface parameters
- First Published: 04 May 2025
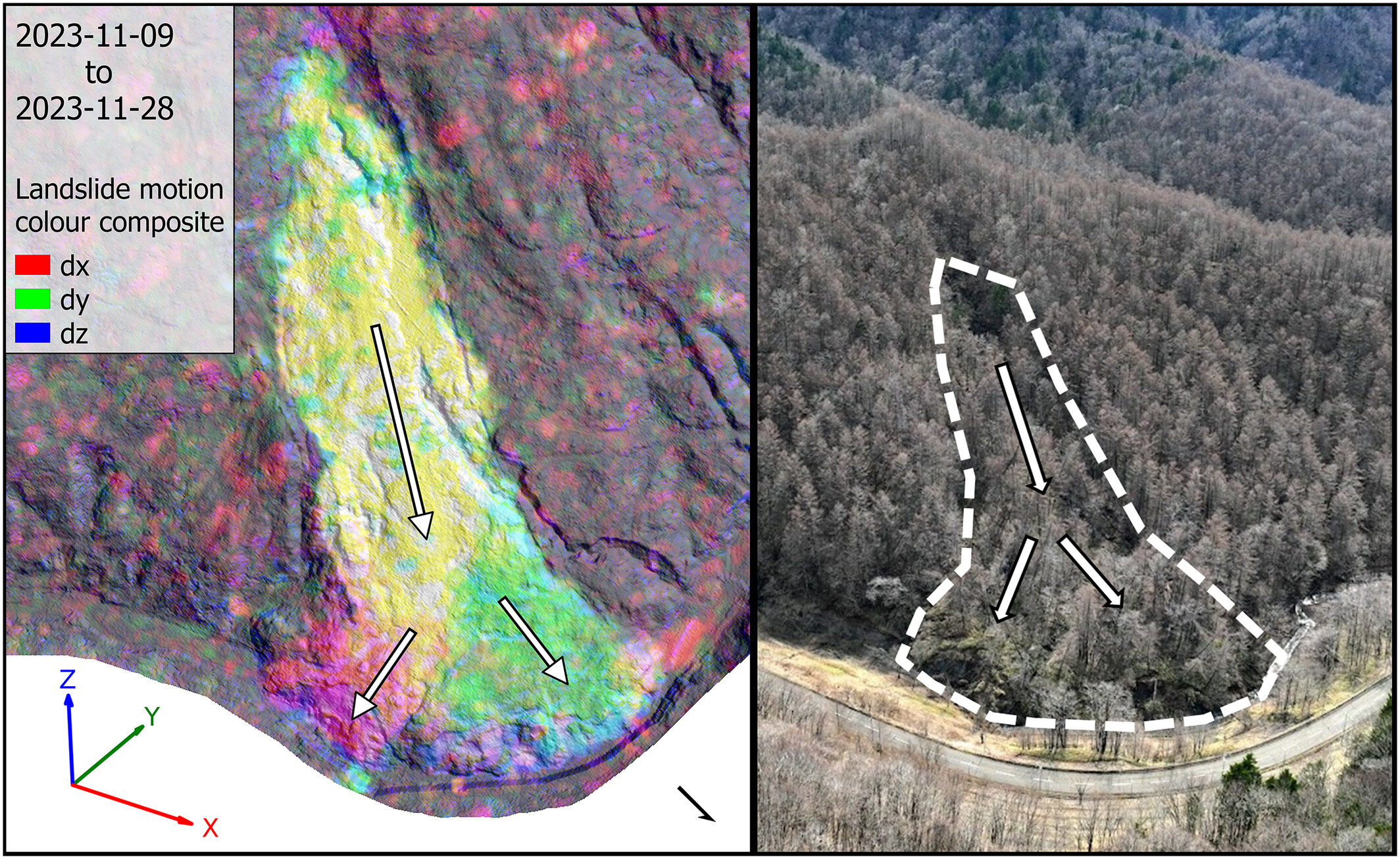

Displacement estimates were extracted from the optical flow analysis of digital elevation models to investigate a creeping landslide under dense vegetation. Displacement estimates achieved an average error below 1 m and derived surface properties provided simple and effective heuristics for landslide analysis.
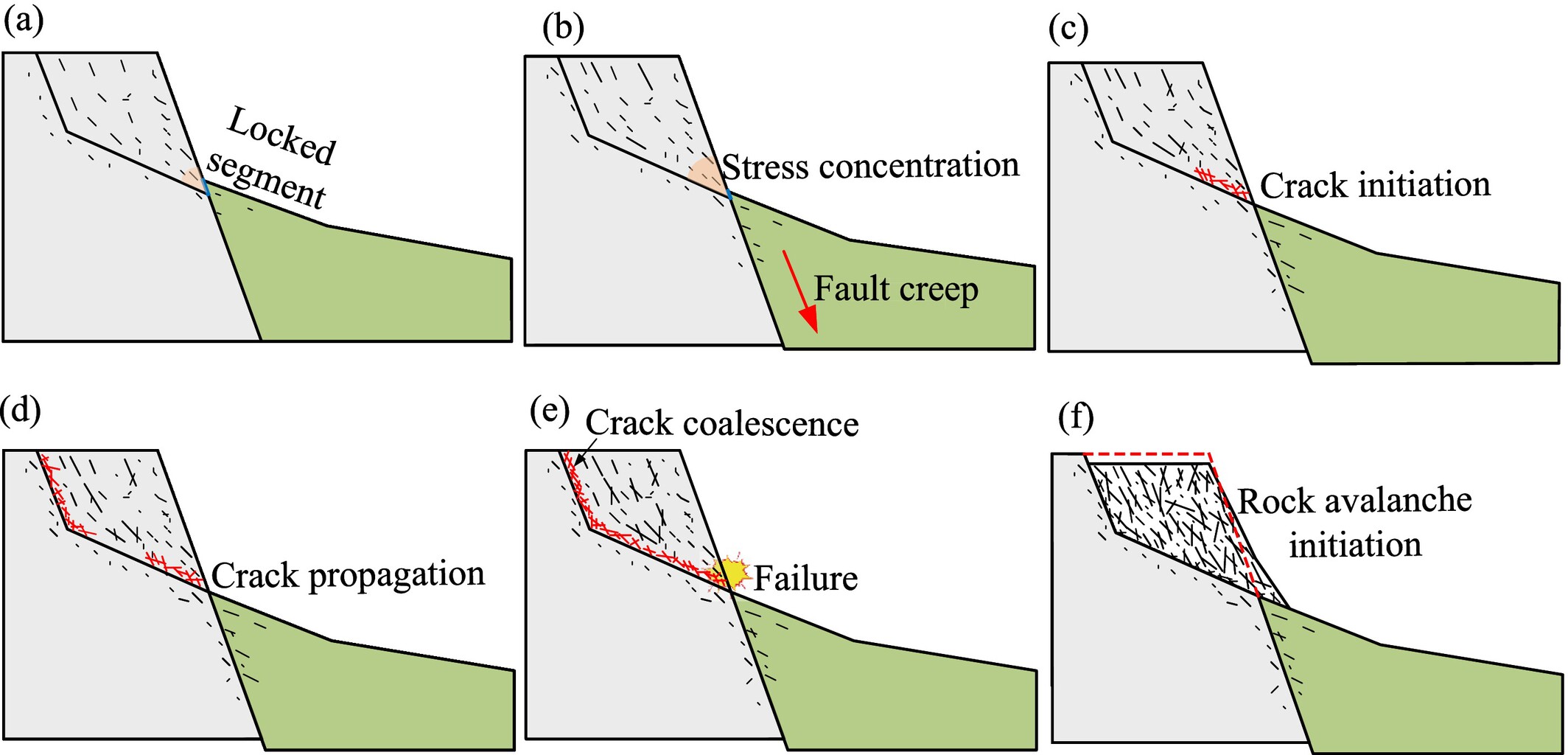
A possible initiation mechanism of Muztag rock avalanche induced by nearby fault creep
- First Published: 08 May 2025
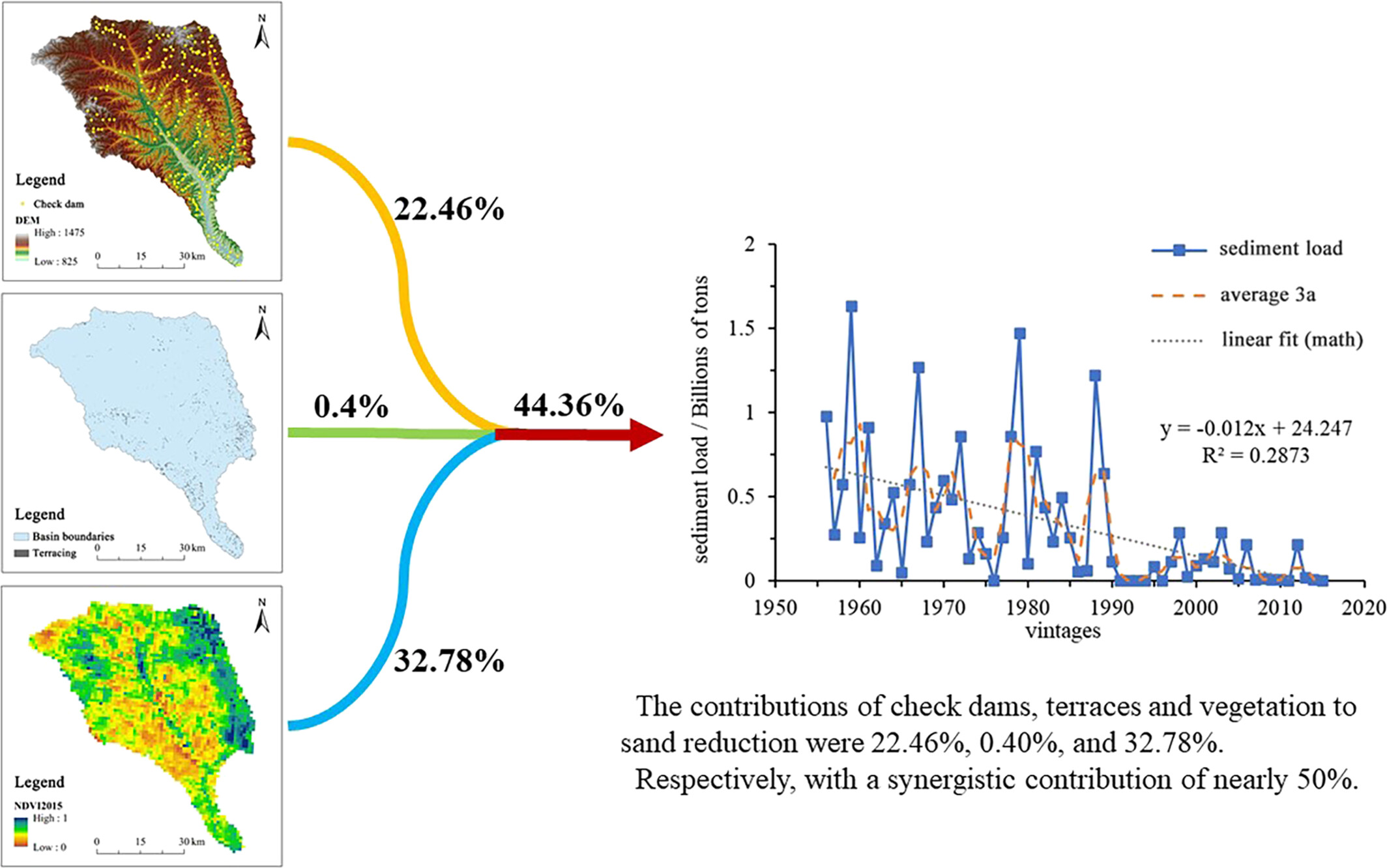
The synergistic effect of soil and water conservation measures on sediment supply reduction in a typical basin on the Loess Plateau, China
- First Published: 05 May 2025
Landslide monitoring from point cloud sequence using stereo feature matching
- First Published: 06 May 2025
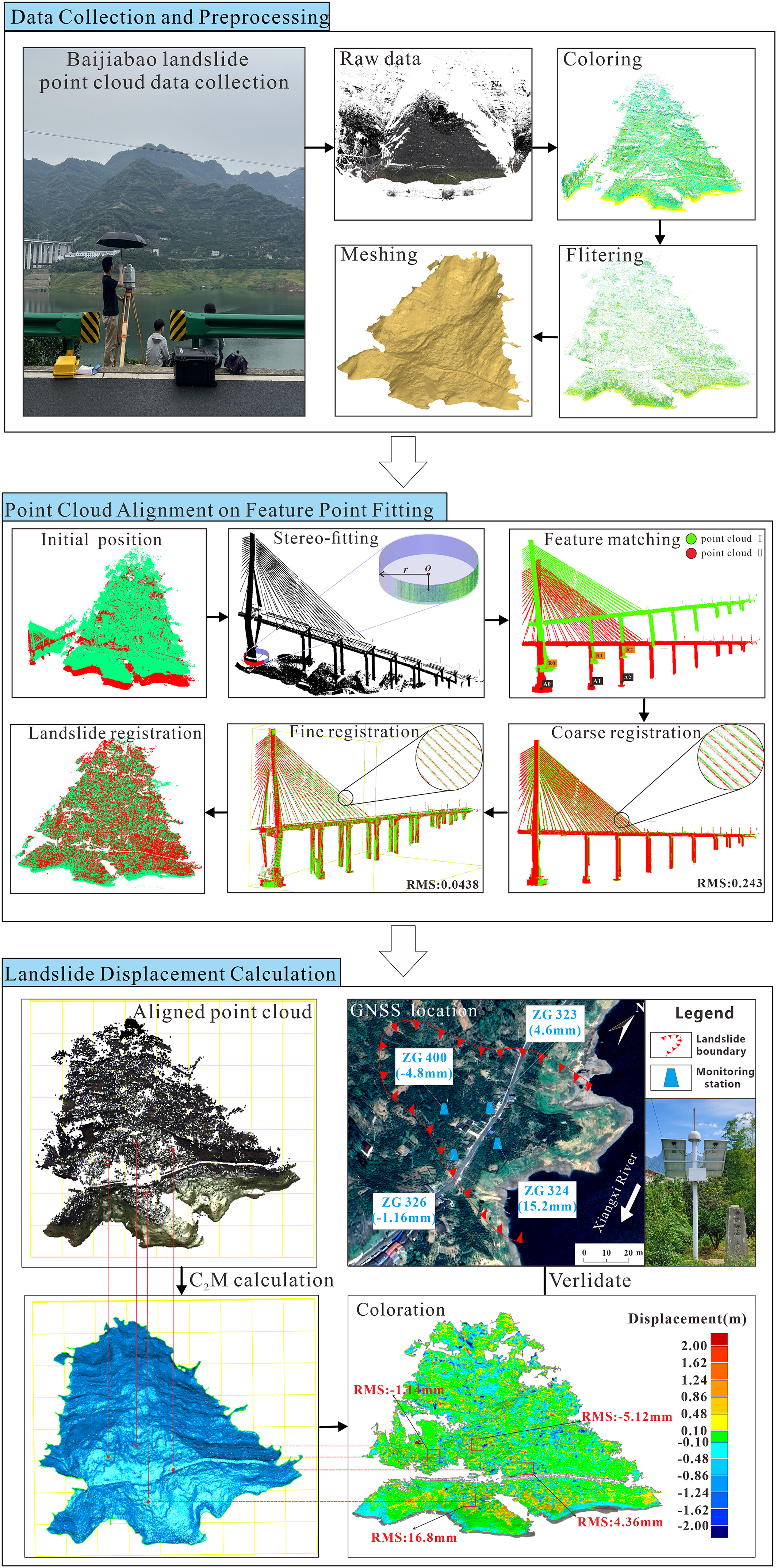
A methodology employing TLS technology developed to monitor Baijiabao landslide deformation, it improves point-cloud alignment using RANSAC-based stereo fitting method. Then we extract the displacement from the aligned point cloud by the C2M method and draw the displacement nephogram to determine the landslide displacement trend.
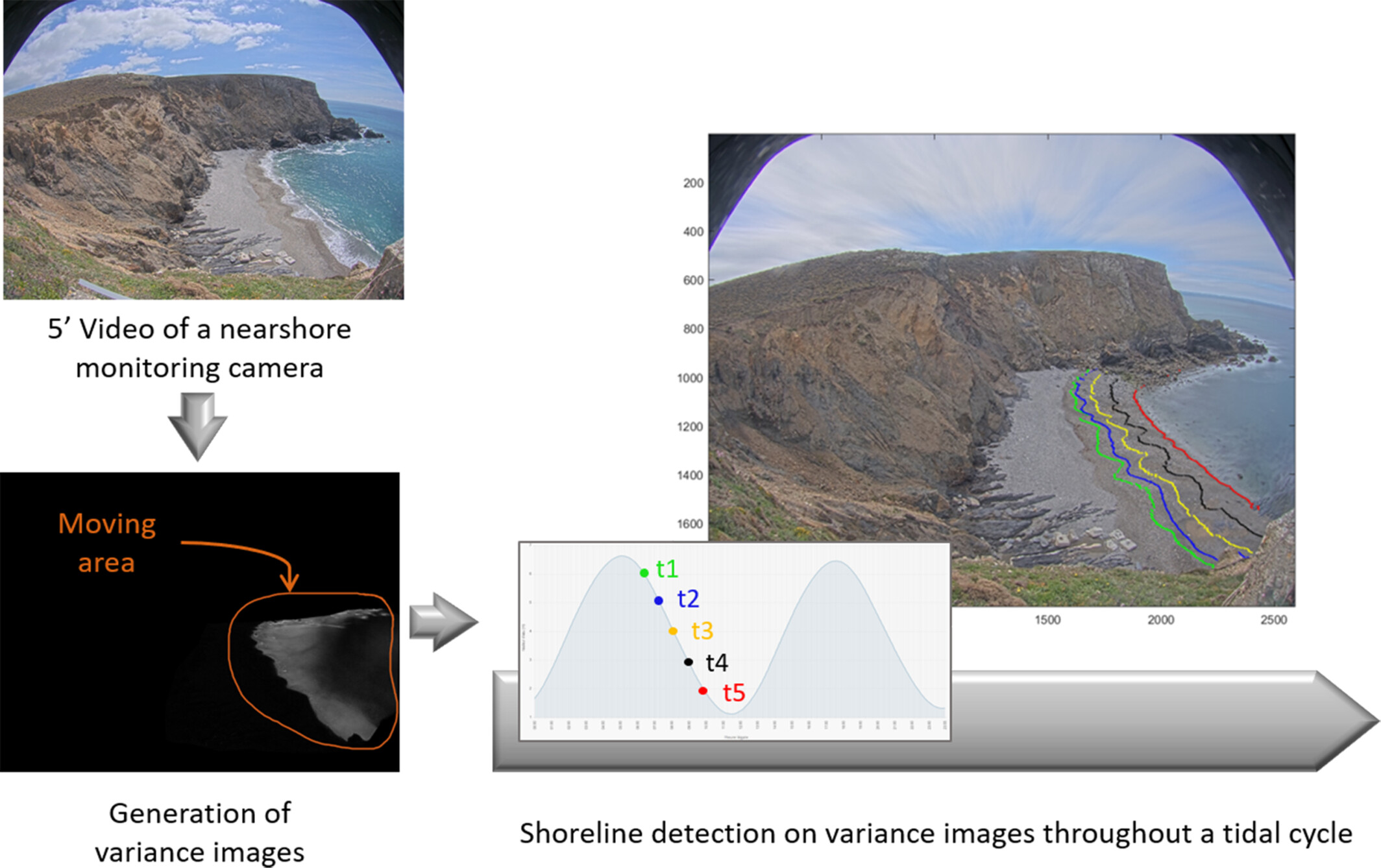
Variance-based shoreline extraction from nearshore video monitoring systems
- First Published: 10 May 2025
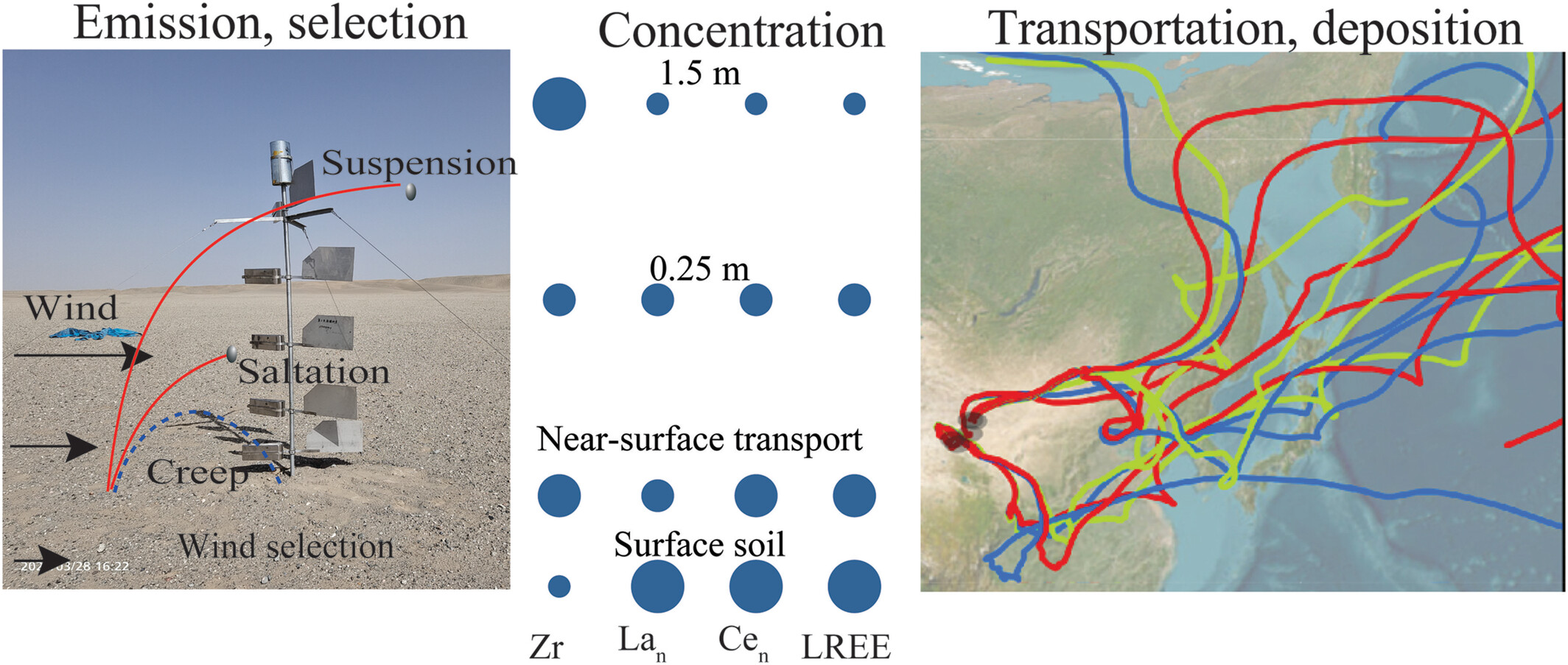
Geochemical differences between Gobi surface soil and transported dust: Implications for dust provenance identification in northern China's Gobi deserts
- First Published: 07 May 2025
Modelling the impact of trenches on soil erosion control using OpenLISEM on Mount Elgon, Uganda
- First Published: 09 May 2025
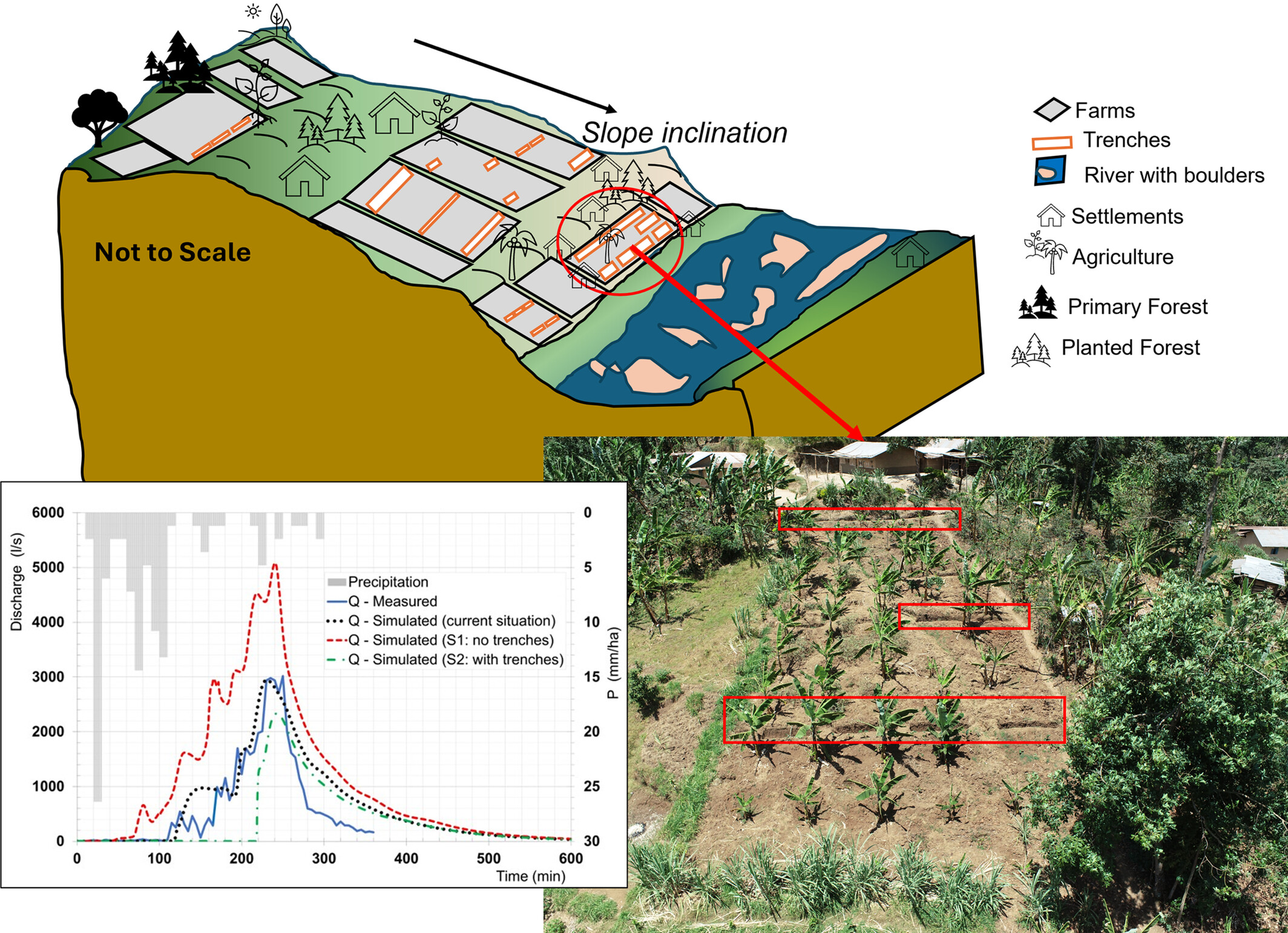
This study characterised trenches at field level and evaluated trench effectiveness in erosion control at sub-catchment level using OpenLISEM in the Mount Elgon region, Uganda. Field surveys reveal diverse trench dimensions (average length: 3 m, width: 0.7 m, depth: 0.5 m), mainly on contour lines in about 62% of the agricultural area. Simulations indicate wide-scale trench adoption would reduce runoff by 40.45% and soil loss by 33.81% compared to current conditions. Widespread trench use is recommended for sustainable land management.
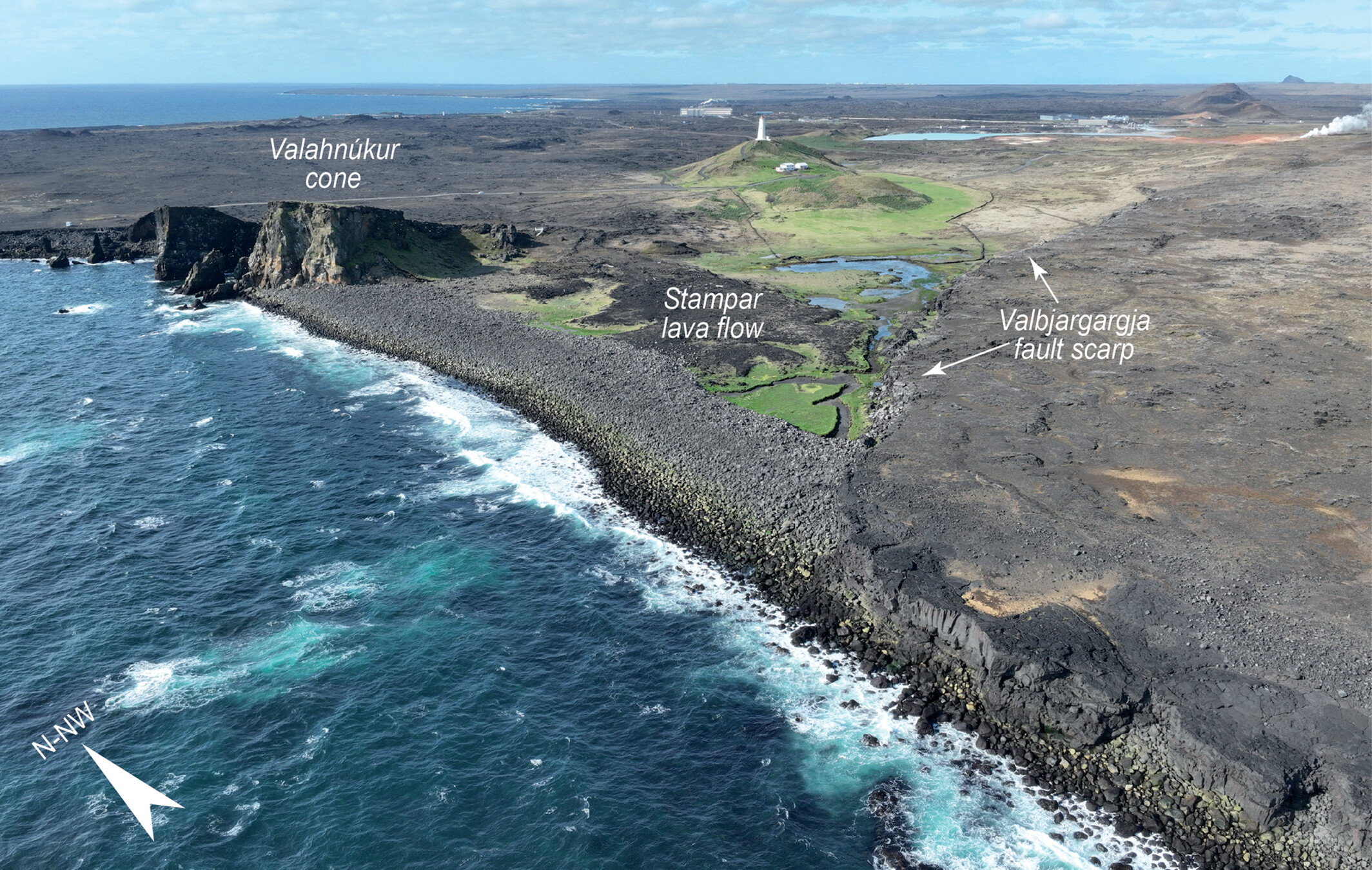
Multi-annual variability of storm events and morphological response in the SW Iceland: The Valahnúkamöl boulder barrier
- First Published: 08 May 2025
LETTER TO ESEX
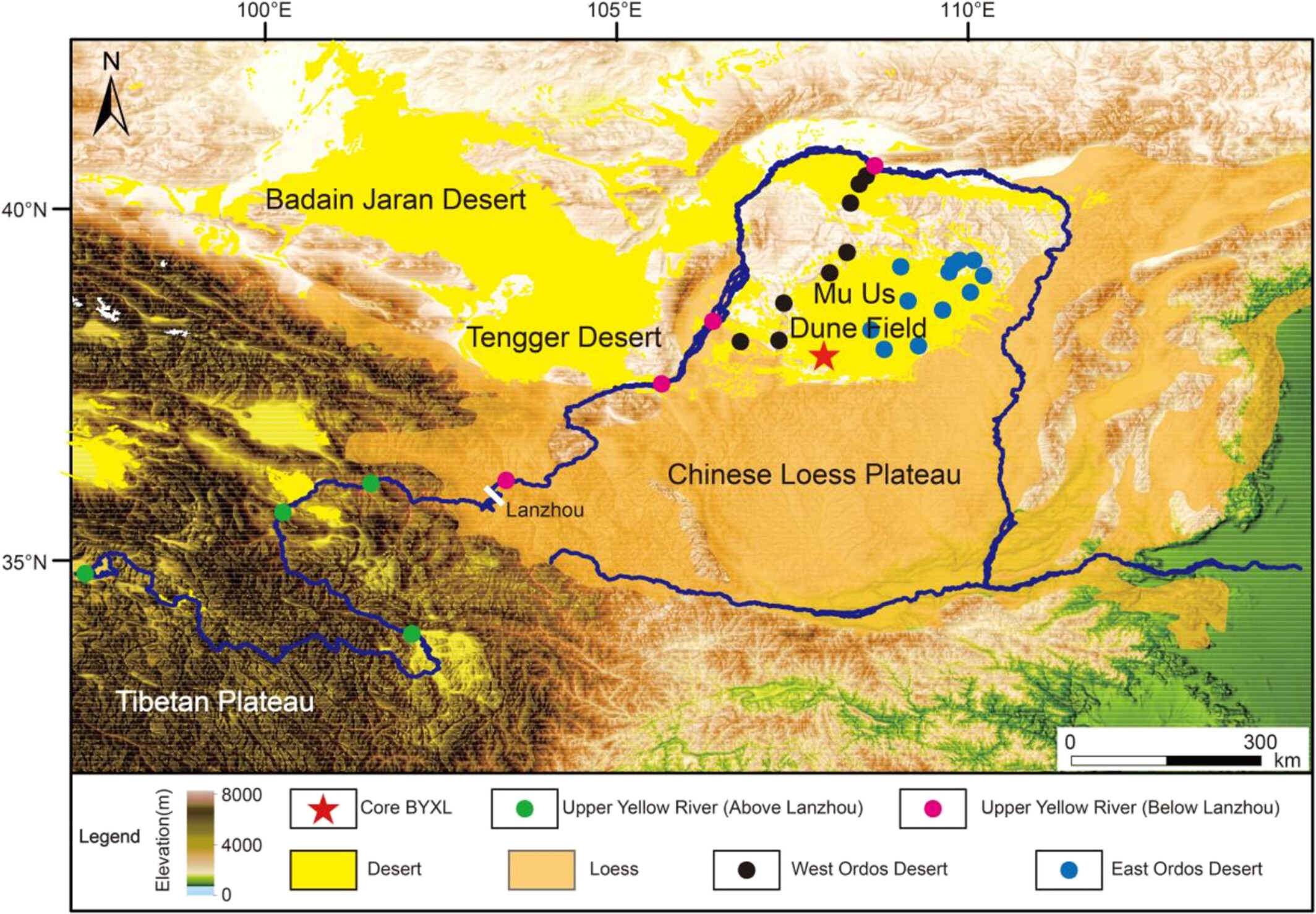
Drill core Uranium and Neodymium isotopic constraints on the provenance of the Mu Us dune field, northern China
- First Published: 10 May 2025
RESEARCH ARTICLE
Lagrangian simulation of bedload-sized particle trajectories at a 90° river confluence
- First Published: 12 May 2025
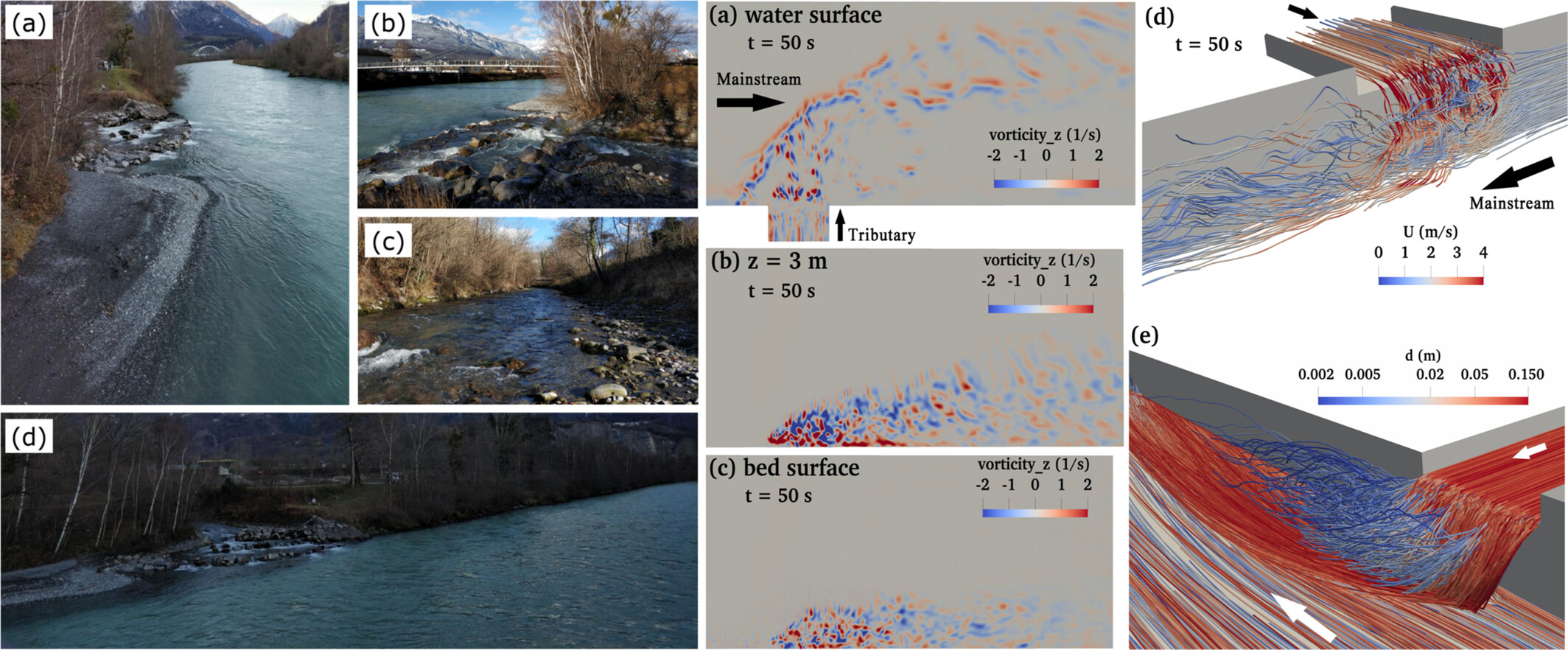
- Both time-variant flow structures and particle interactions impact particle trajectories
- Coarser particles and higher transport rates into the tributary penetrate more into the main channel
- Mainstream sediment moves underneath tributary sediment, explaining vertical sorting in tributary mouth bars
- Spatial density of particles decreases where bed shear is strongest, leading to scour hole formation
-
Left: view of the confluence of the Rhône and Avançon rivers
; right: flow structures and particle paths at the junction in Case 2.
Microtopography-scale research on the sediment connectivity of hillslopes based on optimised M&V depression-filling and a simulated annealing algorithm
- First Published: 14 May 2025

A simulated annealing mechanism was integrated into the M&V algorithm, thereby increasing the accuracy of the calculated IC values at the microtopographic scale. The IC value calculated via the M&V-SAA algorithm was significantly positively correlated with the sediment yield, whereas the IC values calculated via the other algorithms were not significantly correlated with the sediment yield.
Suspended transport of gravel in rivers: Empirical evidence from the 2022 flood in the Misa River (Eastern Apennines, Italy)
- First Published: 14 May 2025
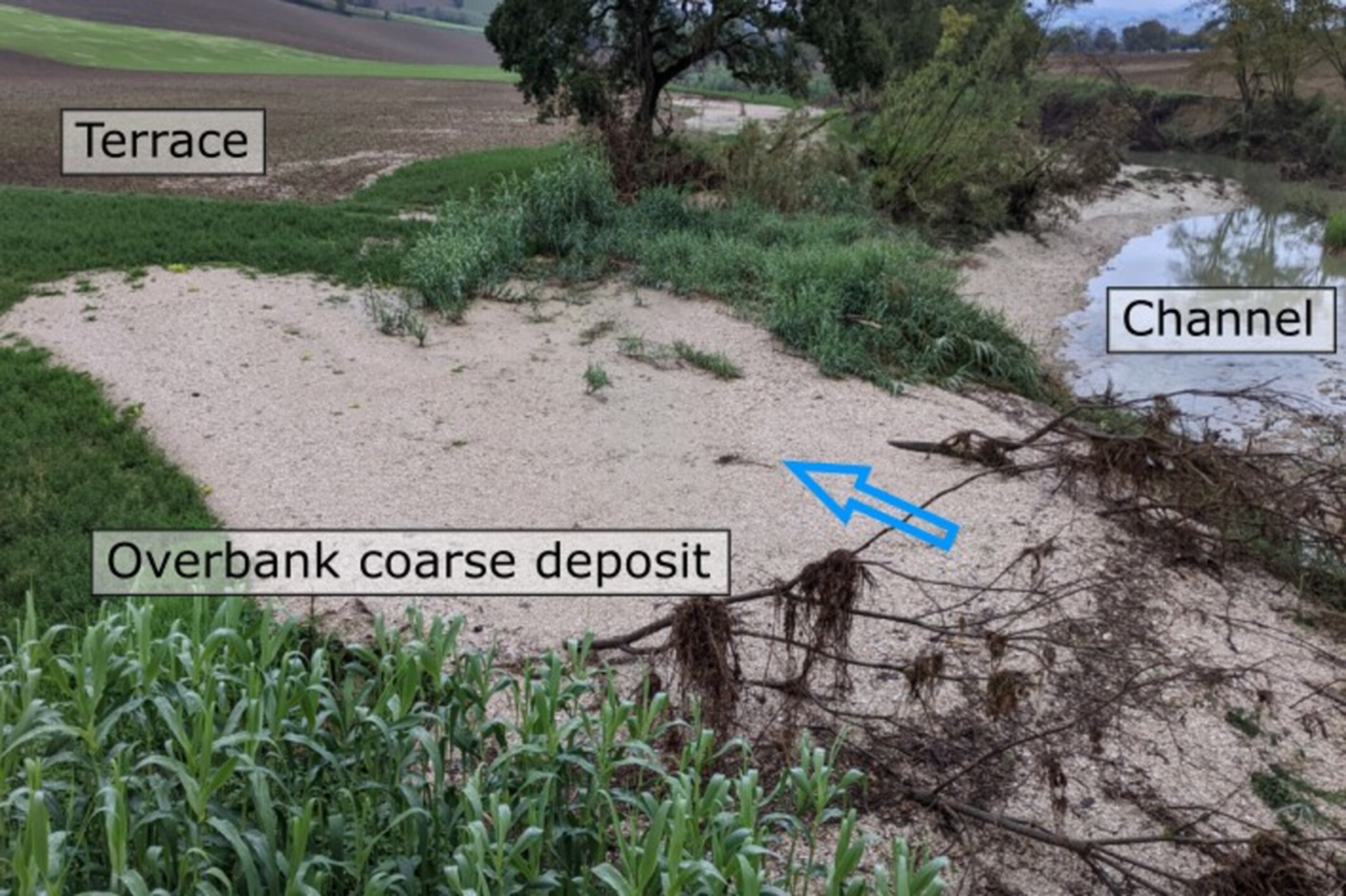

In September 2022, a high-magnitude flood in the Misa River (Italy) transported gravel in suspension, depositing it on superelevated terraces. This was driven by high water discharge, increased fluid density and an entrenched channel limiting widening. Our findings highlight how extreme floods can suspend gravel, refining flood hazard models and improving sediment transport predictions in gravel-bed rivers.
Quantifying streambank erosion: A comparison of physical surveys, aerial imagery and UAS LiDAR surveys
- First Published: 14 May 2025
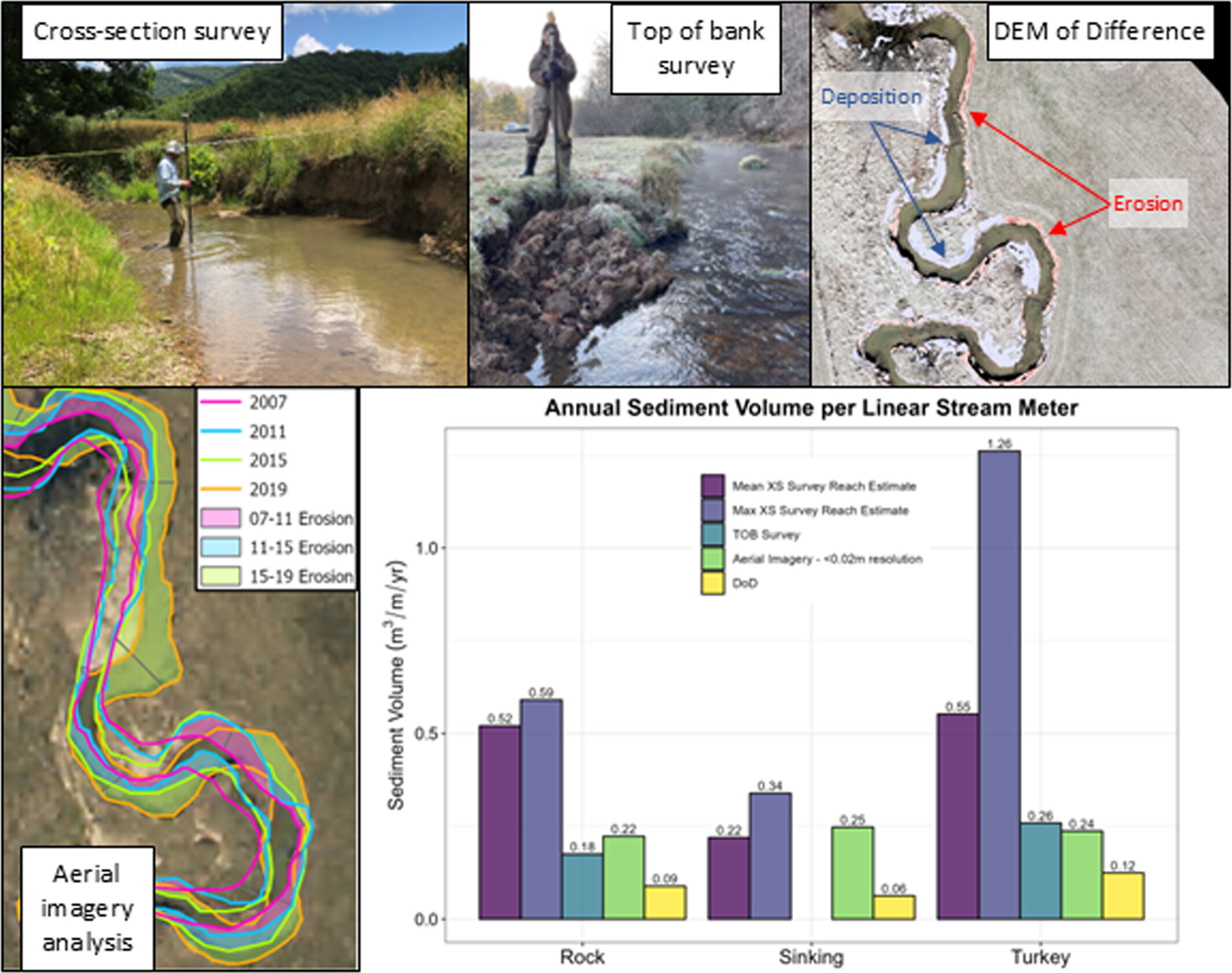
Four methods were used to quantify short-term (1–2 years) reach-wide streambank erosion rates along three low-order streams in western Virginia: (1) bank height and cross-section (XS) surveys, (2) bank height and top of bank (TOB) surveys, (3) bank height survey and aerial imagery analysis and (4) DEM of Difference (DoD) using UAS LiDAR with channel Geomorphic Change Detection (GCD) software. Results show physical surveys are best for quantifying short-term erosion rates for small, low-order streams in this region.
Links between pore system evolution, lake genesis and limnological characteristics: Evidence from basin morphology, specific conductivity and lake level variability on San Salvador Island, Bahamas
- First Published: 14 May 2025
The hydro-geomorphic effects of wooden leaky barriers in a steep headwater stream
- First Published: 15 May 2025
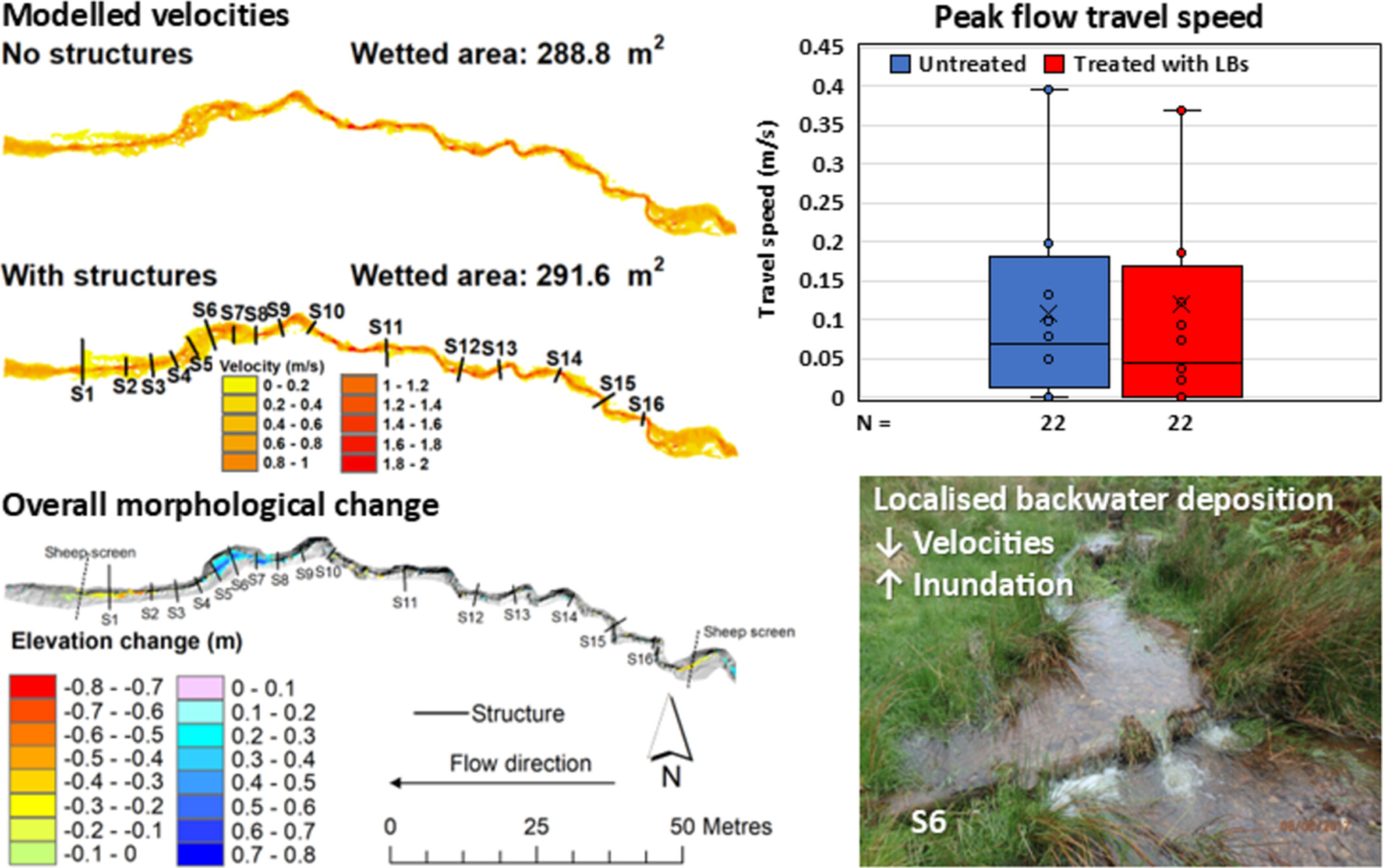
The hydro-geomorphic effects of 16 in-stream wooden leaky barriers (LBs) were monitored over three years. The effects on velocities, inundation extent and celerity were limited. Localised backwater deposition initiated by LBs reduced velocities and increased inundation. A reach-wide net deposition response of 3.49 ± 0.36 m3 was observed.
The impact of outer-bar alongshore variability on inner-bar rip dynamics
- First Published: 21 May 2025
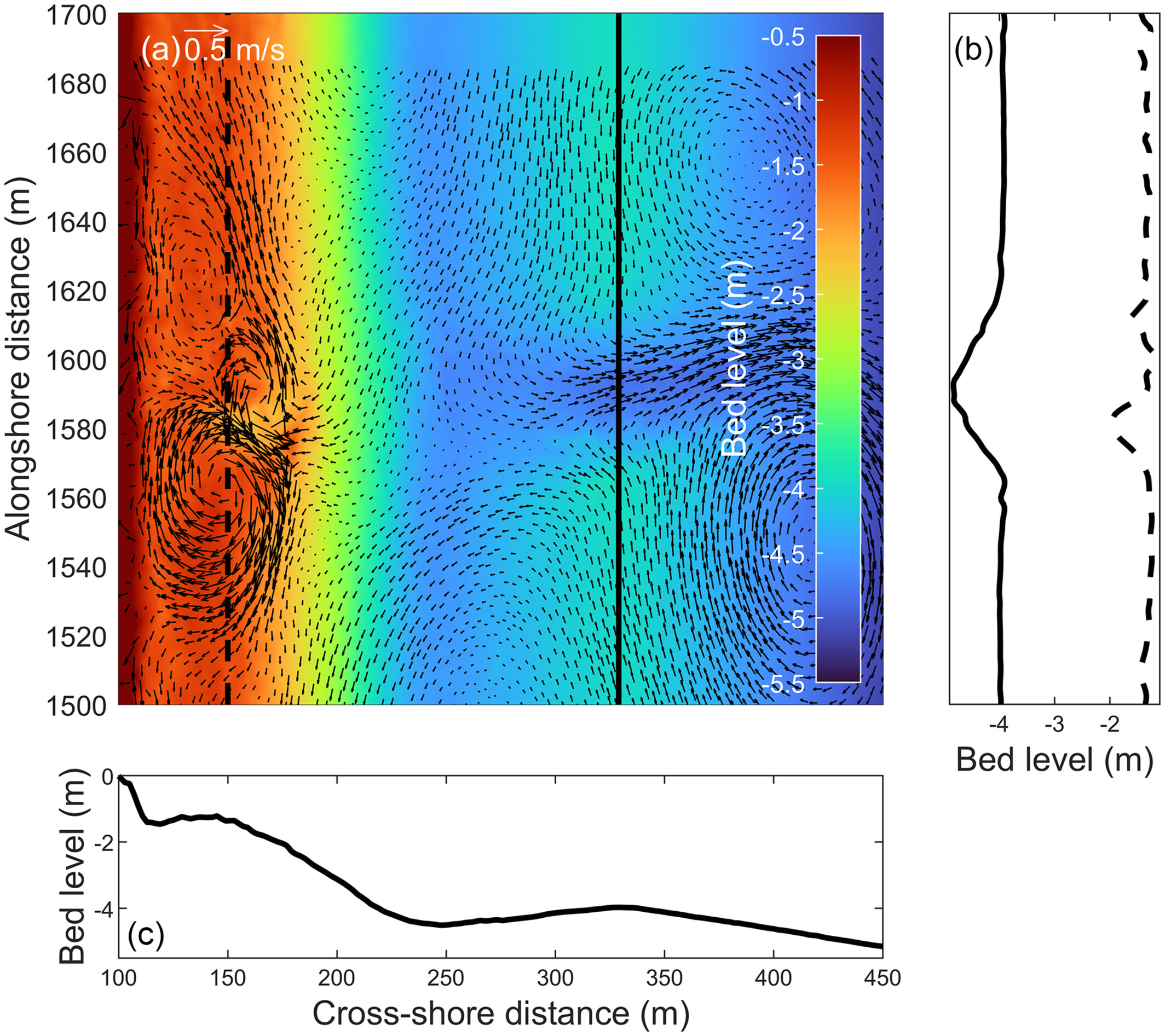
Single, moderate-scale perturbations in outer-bar elevation are shown to generate rip channels across an inner bar. The coupling between the inner- and outer-bar channel positions depends on the outer-bar perturbation depth and transverse slope. The inner-bar rip may de-coupled or re-coupled from the outer bar as channels evolve.
Morphogenesis of high mountains entirely covered by granitoid boulders and blocks in the northeastern part of Australia
- First Published: 21 May 2025
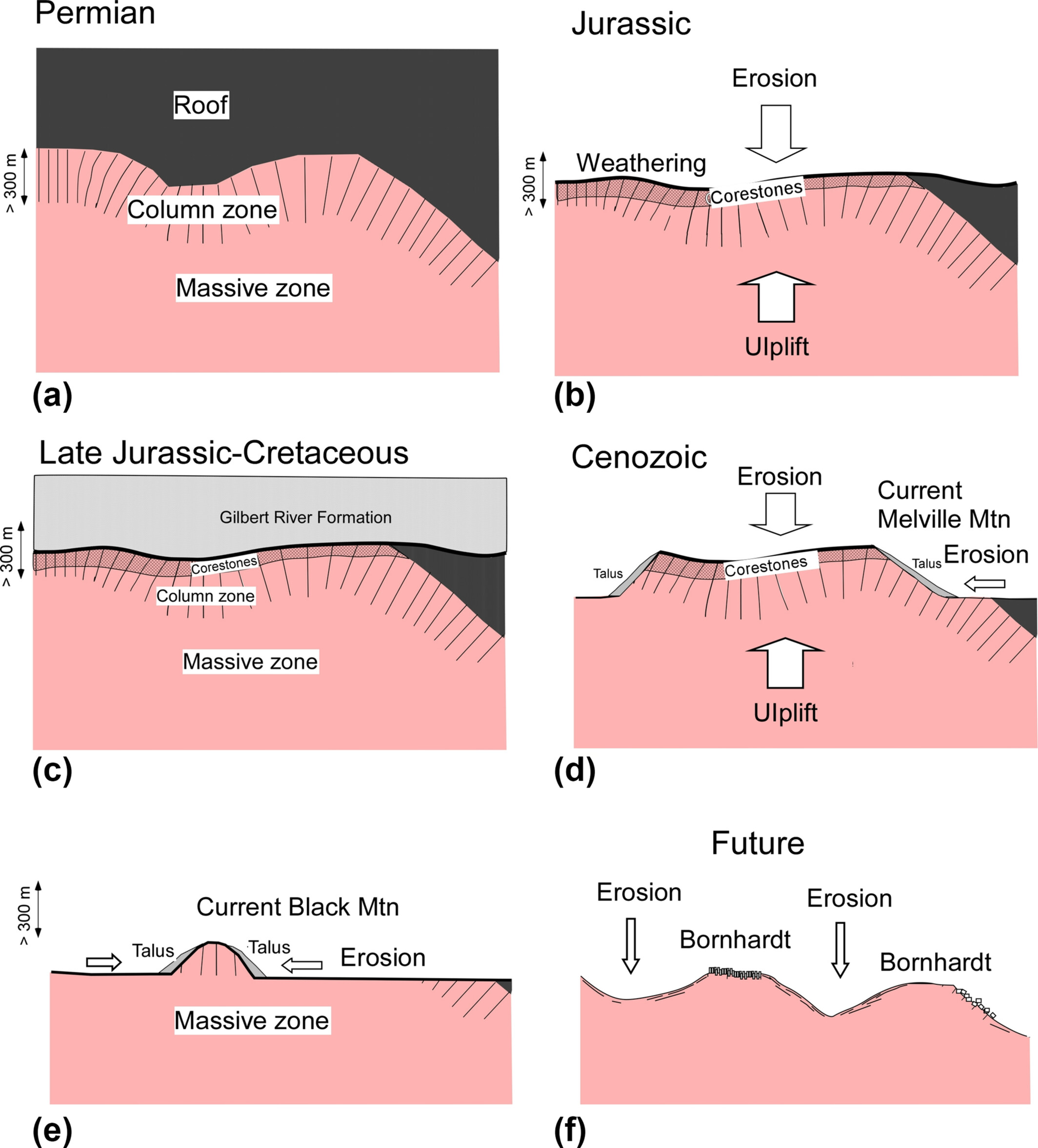
Melville and Black Mountains, northeast Australia, are 300 to 500 m high and entirely covered by granitoid boulders and blocks, which derived from rock columns made during the granitoid emplacement. Subsurface weathering in Jurassic, subsequent uplift and exhumation of the corestones and farther erosion made these mountains.
Quaternary non-karst caves in tills: A pilot study
- First Published: 23 May 2025
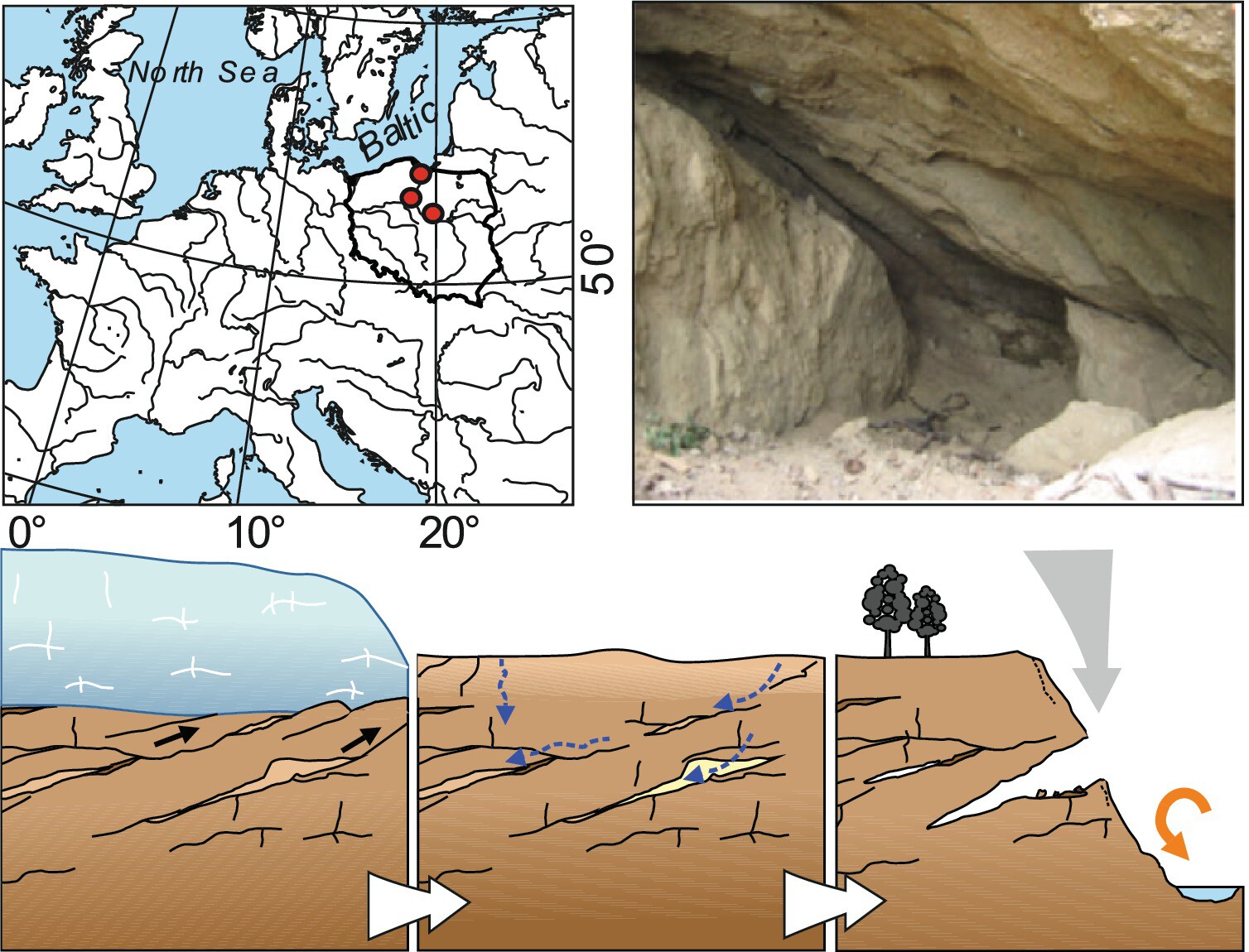
Quaternary caves are young forms subjected to constant evolution. They are developed in Quaternary unlithified glacial tills, associated with the presence of glacitectonic disturbances. Caves are situated in the northern part of the Polish Lowlands, located on steep slopes of river valleys and a seashore cliff.
CASE STUDY
A karst rather than periglacial origin for small enclosed depressions of the Landes Triangle, southwest France
- First Published: 25 May 2025
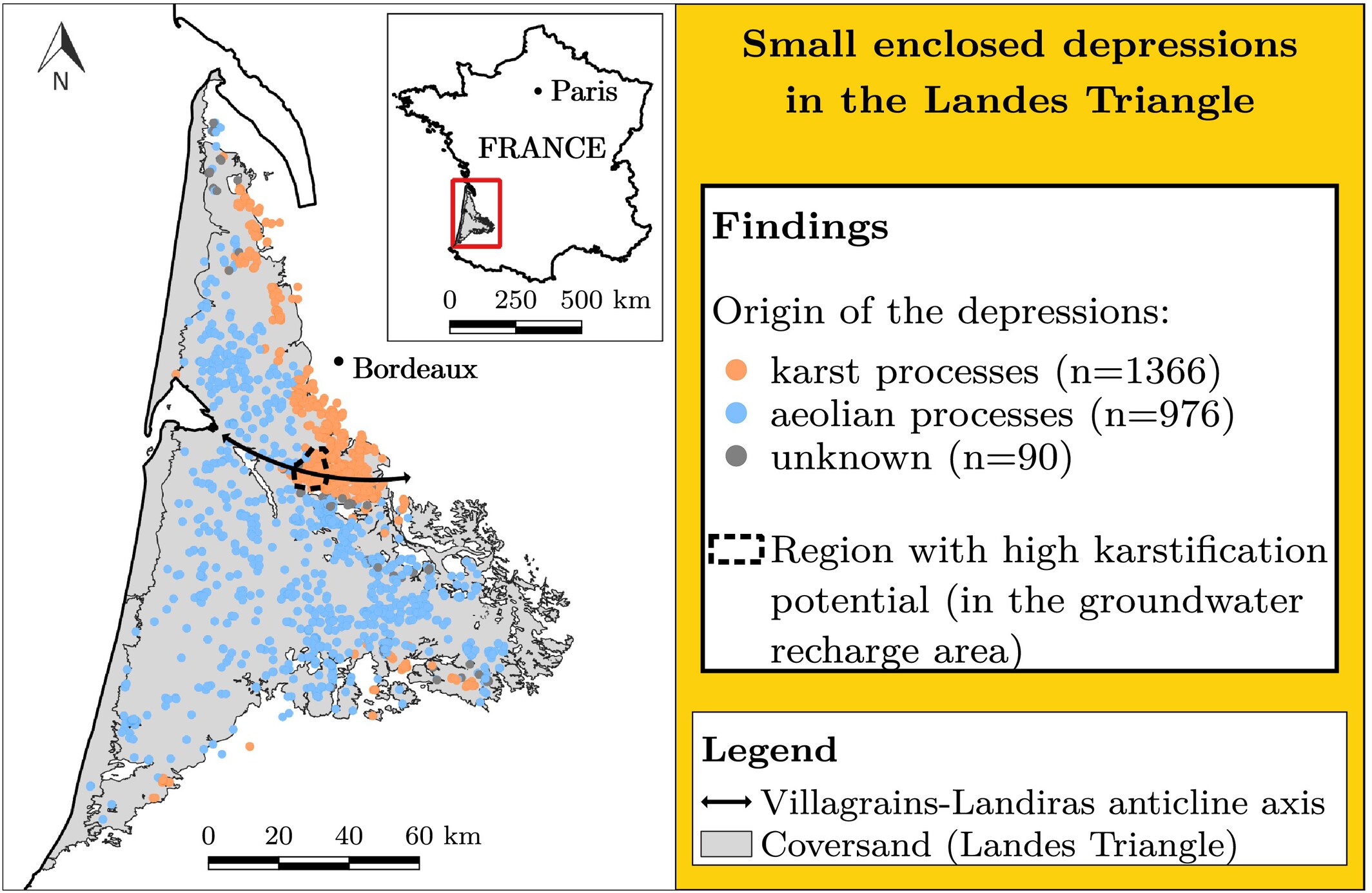
The Landes Triangle is dotted with 2,400 + shallow depressions of unknown origin, that fall into two distinct groups in terms of morphology, distribution and geology. In the central and western parts of the region, the depressions are likely of aeolian origin, while a crypto-karst origin is favoured elsewhere.
RESEARCH ARTICLE
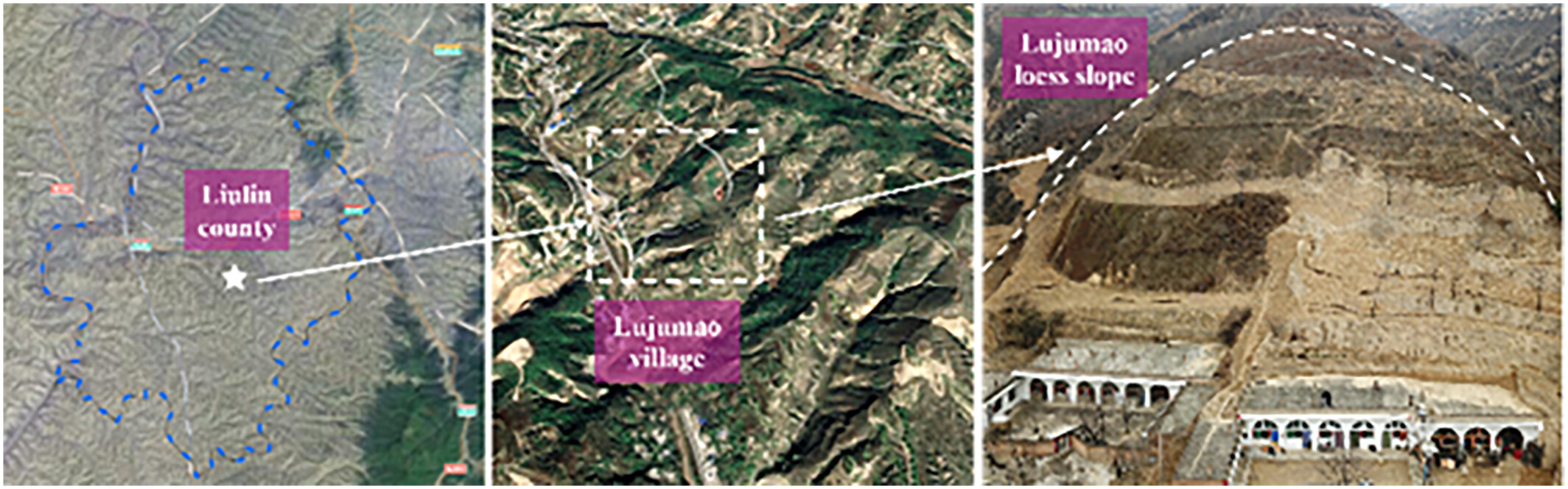
Instability mechanism and control measures of loess slope induced by heavy rainfall
- First Published: 25 May 2025
Drainage divides migration of the Heihe River in the Qilian Mountains, northeastern Tibet: Insights for the drainage reorganization in an orogenic belt
- First Published: 23 May 2025
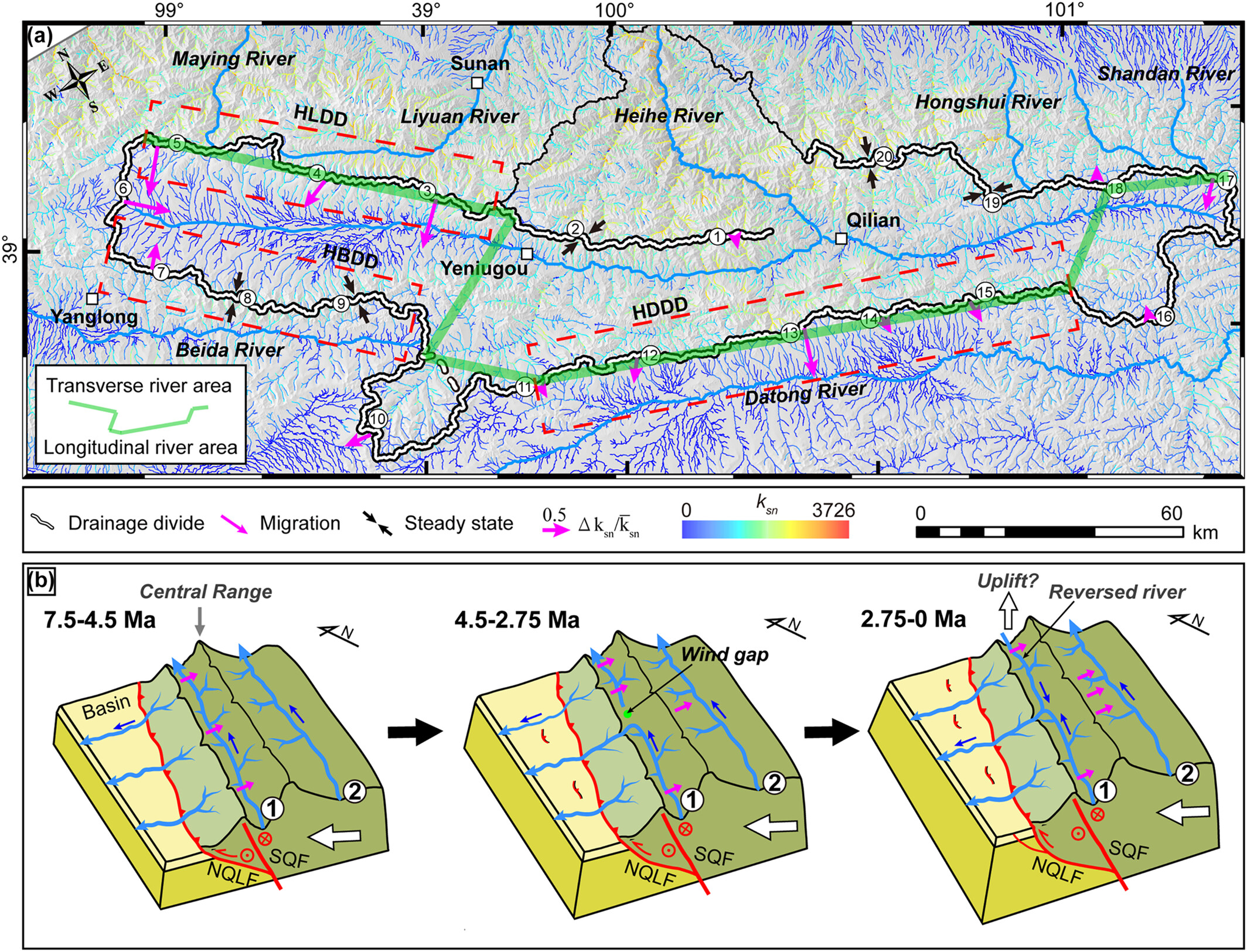
- This study evaluates the stability of drainage divides in the Heihe River Basin using the χ-plot and Gilbert metric methods, revealing an ongoing dynamic evolution characterized by both expansion and contraction.
- The findings highlight that regional tectonic evolution is the primary driver of drainage reorganization, with climate, lithology and local fault activity playing minor roles.
- The Heihe River's progressive transformation into a fully transverse system exemplifies the competitive dynamics between transverse and longitudinal rivers.
Holocene landslides in the Fraser Canyon Corridor and implications for ‘ecohazard’ assessment
- First Published: 25 May 2025
Detection of paraglacial sediment supply using detrital 10Be in postglacial landscapes of southwest British Columbia
- First Published: 27 May 2025
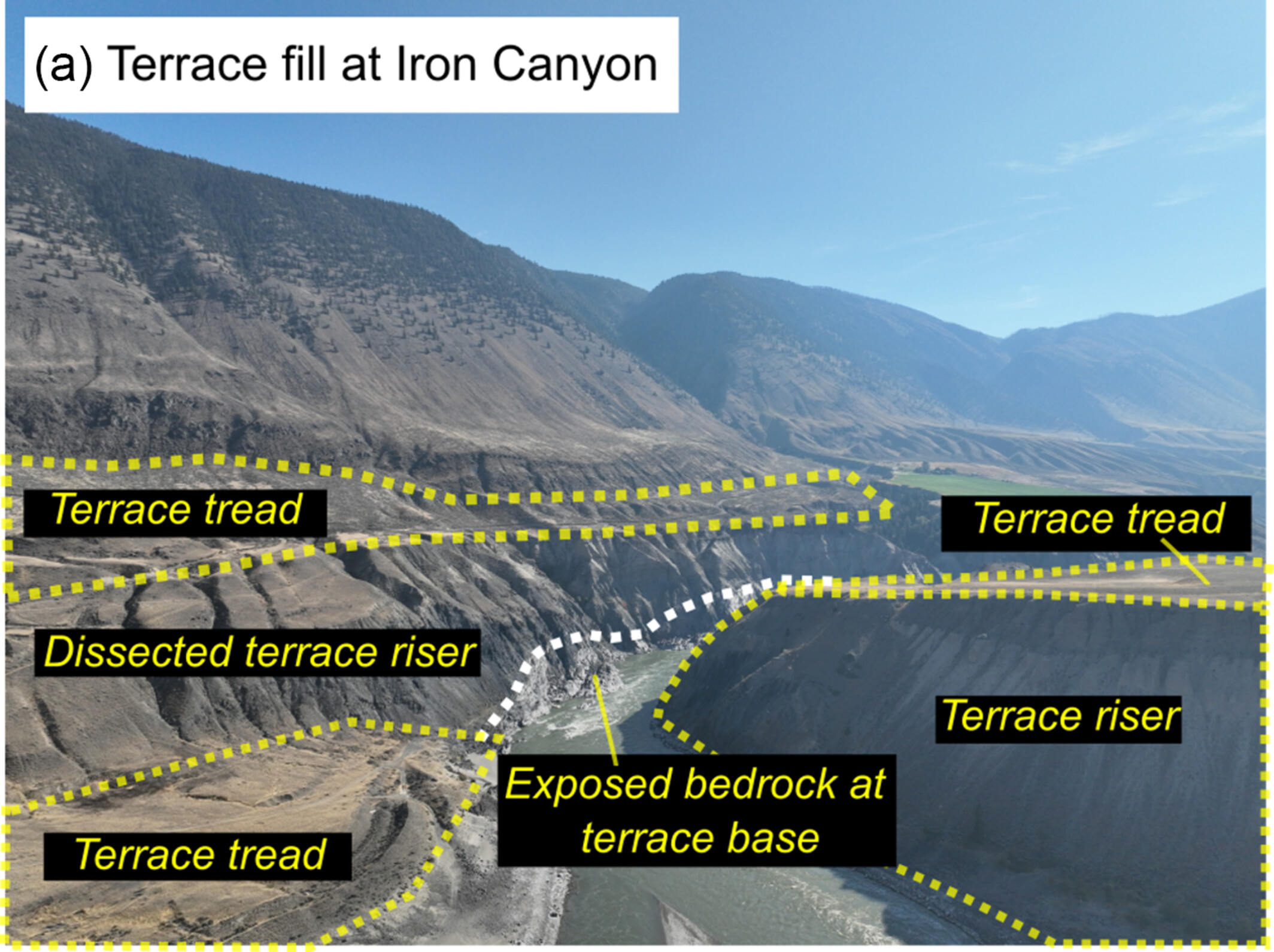
We use 10Be concentrations in paraglacial terrace fills and modern fluvial sediments to demonstrate the extent to which legacies of past glaciation still dominate landscape denudation in the Fraser River basin, Canada. Despite widespread paraglacial terrace fills, we find surprisingly limited contributions of paraglacial sediment to modern fluvial sediment loads.
Characterization of post-event kinematics of Baige landslide using multi-source remotely-sensed imagery
- First Published: 08 May 2025
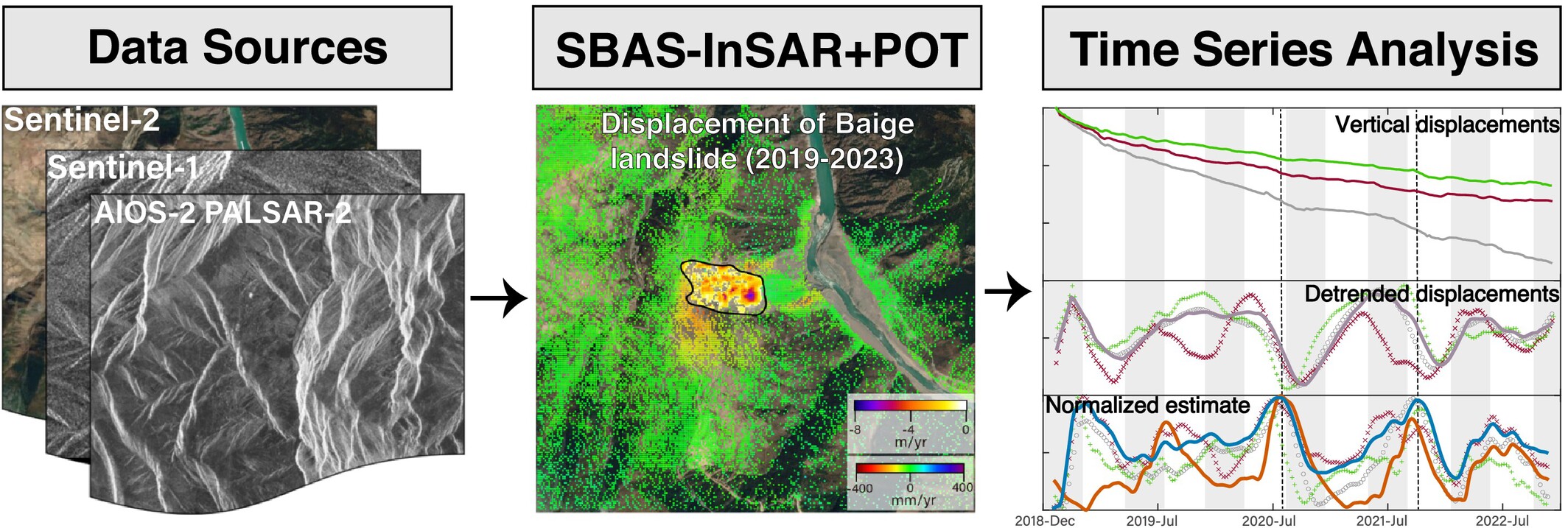
This study integrates multi-source remote sensing to reveal the post-2018 kinematics of the Baige landslide, identifying significant displacements in the residual unstable and head scarp areas. Seasonal displacement patterns are correlated with rainfall, and a hydraulic diffusivity of 4.95 × 10−5 m2/s and an unstable mass thickness of ~65 m highlight ongoing instability risks.
Relationship between the fractal dimension of soil aggregates and erosion in degraded lands in the Qinling–Ba mountainous area of China
- First Published: 27 May 2025
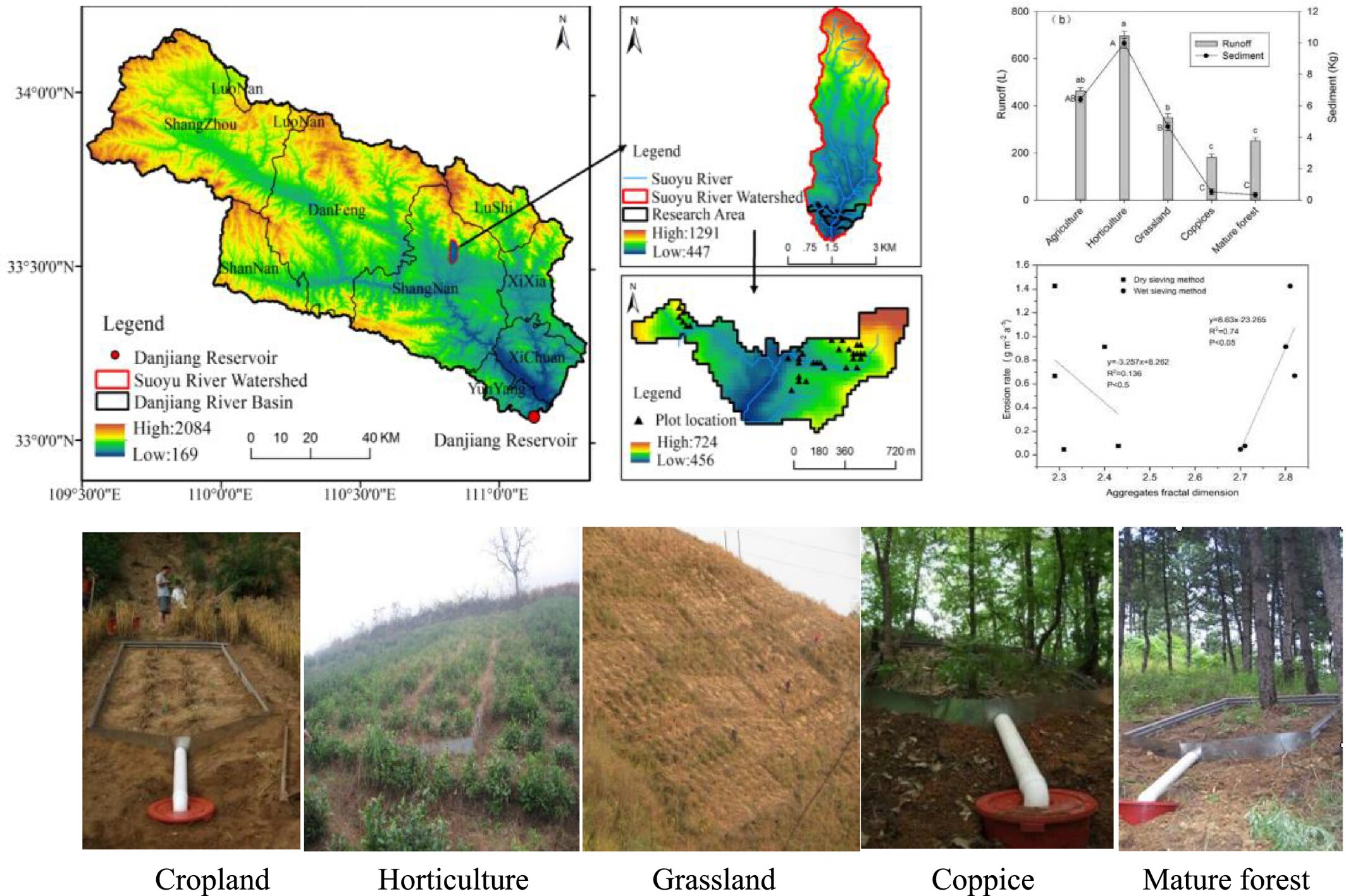
- Water stable aggregate content decreased with increasing of land degradation
- Erosion is positively and linearly related with stable aggregate fractal dimension
- Erosion rates are negatively related with aggregates stability
- Aggregate fractal dimension can serve as parameter for monitoring soil degradation
Mineralogical characterisation of aeolian sands using multispectral satellite datasets: Implications for dune field evolution, Wahiba Dune Field, Oman
- First Published: 27 May 2025
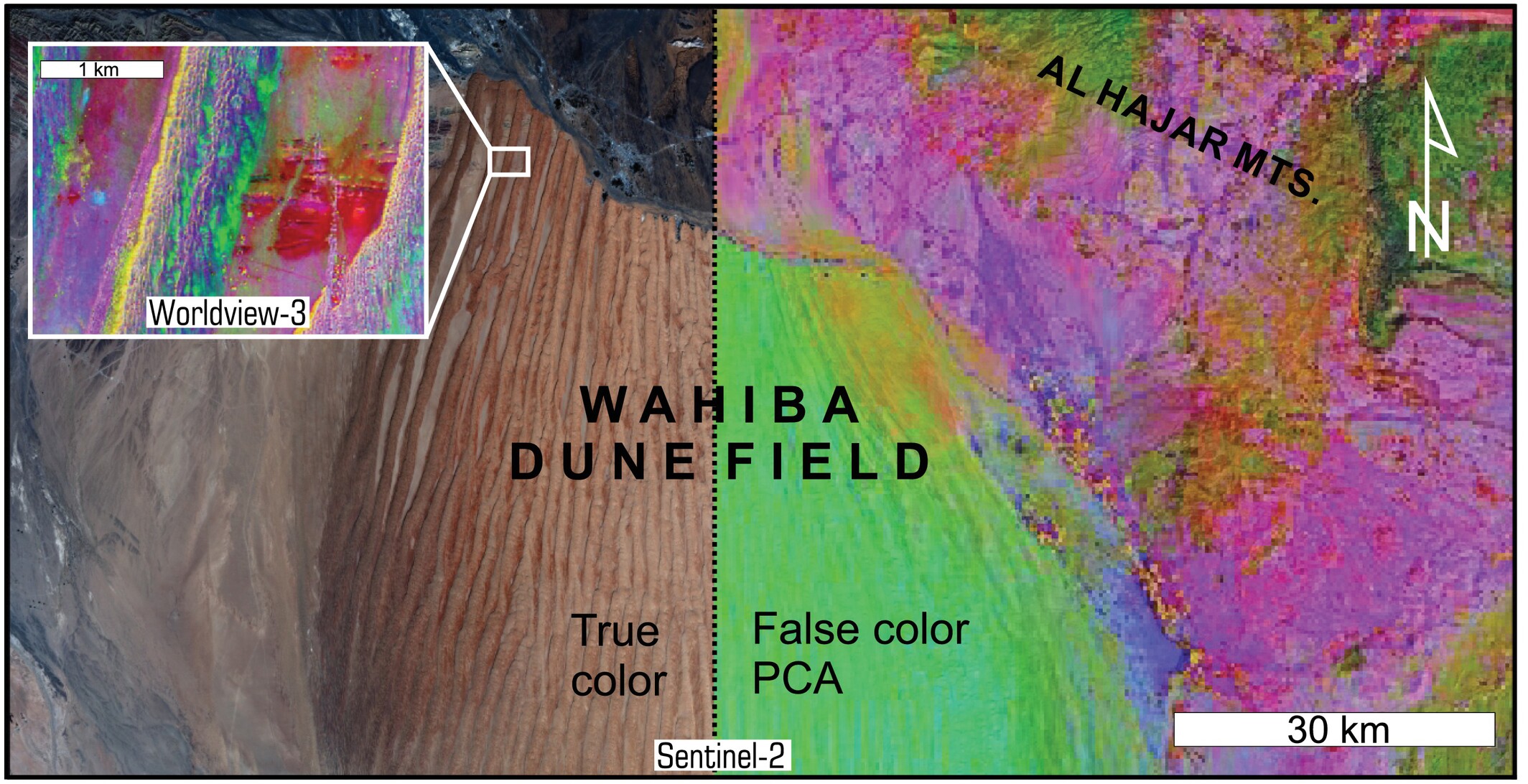
This study develops a remote sensing methodology that integrates high-resolution satellite imagery with field validation to map the Wahiba Dune Field of Oman. Findings reveal the sensitivity of contemporary geomorphic surfaces to local sediment dynamics and highlight the value of multi-scale analysis in interpreting dune field evolution.