Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
COVID-19: A systematic review and update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment
- First Published: 17 February 2022
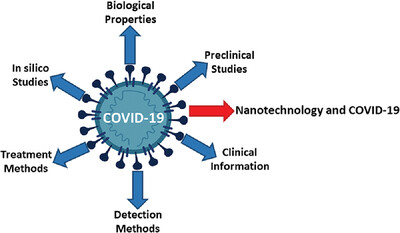
This review covers almost all topics related to SARS-CoV-2, including biological properties, pre-clinical studies, clinical information, diagnostic and treatment methods, and in silico studies, which is very useful for a quick understanding of the latest advances in this field. Also, in a separate section, the applications of nanotechnology in COVID-19 studies are examined.
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Immune escape and vaccine development
- First Published: 16 March 2022
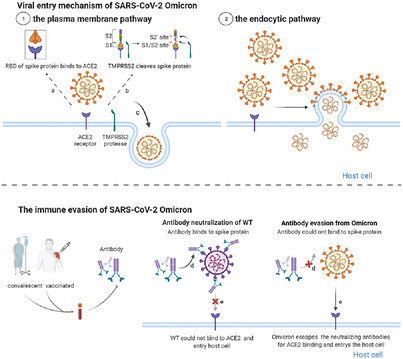
Omicron (B.1.1.529), the latest variant of concern, is partially resistant to the neutralizing activity of therapeutic antibodies and convalescent sera, which poses significant challenges for the clinical effectiveness of the current vaccines and therapeutic antibodies. We provide a comprehensive analysis and summary of the epidemiology and immune escape mechanisms of the Omicron variant. We also suggest some therapeutic strategies against the Omicron variant.
The SARS-CoV-2 main protease (Mpro): Structure, function, and emerging therapies for COVID-19
- First Published: 14 July 2022
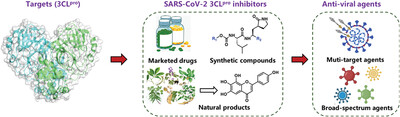
A comprehensive summary of recent advances in SARS-CoV-2 3CLpro inhibitors (including marketed drugs, peptidomimetic, and non-peptidomimetic synthetic compounds, as well as natural compounds and their derivatives), including the inhibitory activities, inhibitory mechanisms, and key structural features, provides new insights for designing and developing more efficacious 3CLpro inhibitors as broad-spectrum anti-coronavirus agents.
SARS-CoV-2 triggered oxidative stress and abnormal energy metabolism in gut microbiota
- First Published: 17 January 2022
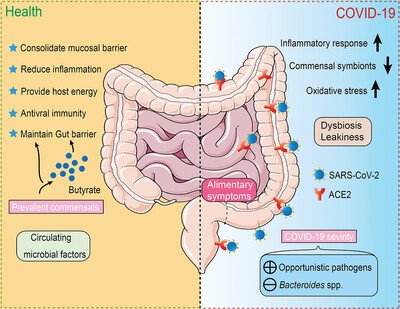
The gut microbiota of COVID-19 patients showed upregulation of oxidative stress and inflammation response, accompanied by depletion of symbiotic bacteria. The abundance of Bacteroides spp. is negatively correlated with disease severity, while the accumulation of opportunistic pathogens may exacerbate the progression of COVID-19. Healthy intestinal flora may enhance the organic defense against SARS-CoV-2 virus infection through butyrate metabolism.
mRNA vaccines in the prevention and treatment of diseases
- First Published: 25 August 2022
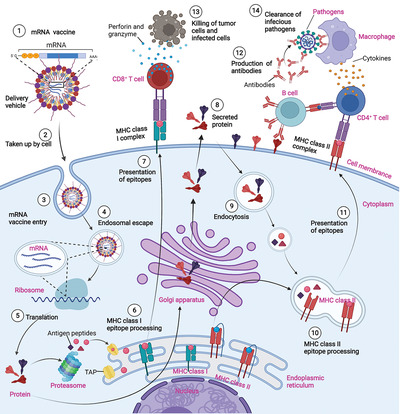
Mechanisms of mRNA vaccines for infectious diseases and cancers. mRNA molecules encoding tumor antigens are injected into body (either with or without delivery vehicles). The mRNA molecules are taken up and translated into protein antigens by antigen-presenting cells (APCs). After proteasomal processing of proteins, antigen peptides associate with MHC Class I molecule in the endoplasmic reticulum and are transferred to the APC surface, activating CD8+ T cells for a specific cellular immune response. Protein antigens, which are sorted for the endosome route, can activate CD4+ T cells via the MHC Class II presentation pathway. The secretory protein antigen or membrane antigen encoded by mRNA can stimulate B cells to produce neutralizing antibodies and activate phagocytes such as macrophages to secrete inflammatory cytokines, facilitating the clearance of circulating infectious pathogens and tumor cells.
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: A next phase of the COVID-19 pandemic and a call to arms for system sciences and precision medicine
- First Published: 11 February 2022
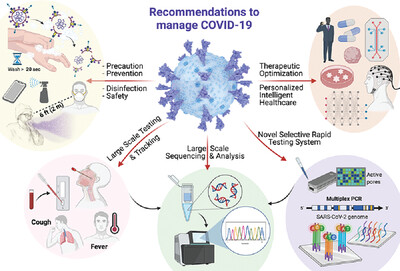
In this perspective, the authors first discussed the Omicron's origin, mutations, structure, pathogenesis, and its impact on human health while comparing it with the previous variant of concerns (VOCs). System science and precision medicine are introduced by employing Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data reservoirs, bioinformatic systems, advanced in vitro 3D models, and subtypes sciences to diagnose and eradicate the Omicron virus. Experts’ recommendations to successfully manage Omicron-SARS-CoV-2 variant are also provided.
Autophagy in health and disease: From molecular mechanisms to therapeutic target
- First Published: 10 July 2022
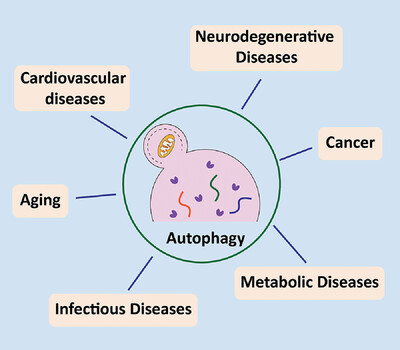
Macroautophagy/autophagy is an evolutionally conserved catabolic process induced under various stress conditions to maintain intracellular homeostasis. Dysregulation of autophagy is closely associated with various human diseases. This review will focus on the molecular mechanisms in control of autophagy, the implication of autophagy in various human diseases, and the development of pharmacological agents that target autophagy.
Graphene and graphene oxide with anticancer applications: Challenges and future perspectives
- First Published: 09 February 2022
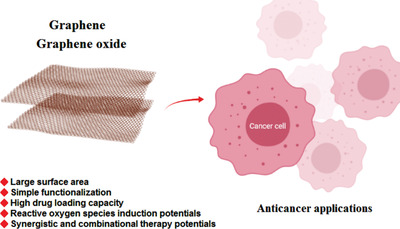
Important challenges, recent advancements, and future perspectives for deploying graphene- and graphene oxide-based nanosystems in cancer therapy are deliberated. Notably, large surface area, ease of functionalization, high drug loading capacity, and reactive oxygen species induction potentials have rendered these structures promising candidates for cancer therapy applications. The ease of functionalization bodes well for their utility in treating assorted types of cancers.
Redox signaling at the crossroads of human health and disease
- First Published: 31 March 2022
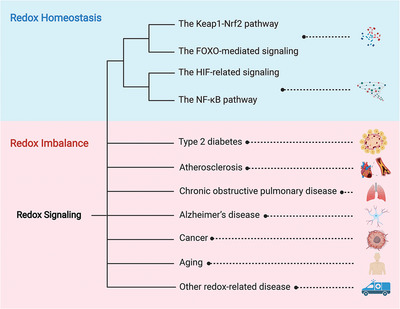
Redox homeostasis is essential for human health, supported by multiple functional signaling pathways including the Keap1-Nrf2, FOXO, HIF and NF-κB pathways. However, redox imbalance causes multiple serious diseases such as type 2 diabetes, atherosclerosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, Alzheimer's disease, cancer, and aging. Our review emphasizes the significance of redox manipulation in clinical therapeutics and points out the existing challenges involved in this field.
STAT3 pathway in cancers: Past, present, and future
- First Published: 23 March 2022
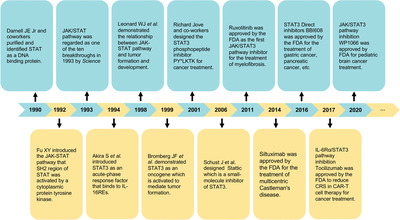
Since the discovery of the signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) in 1994, the STAT3 pathway has been proven to play a pivotal role in cancer initiation, progression, and metastasis. This review summarizes the mechanisms of the STAT3 pathway regulation and the relationship between the STAT3 pathway and cancer hallmarks. The emerging development of the STAT3 pathway inhibitors, novel drug delivery systems, and perspective on the overall utility of the STAT3 pathway are also introduced.
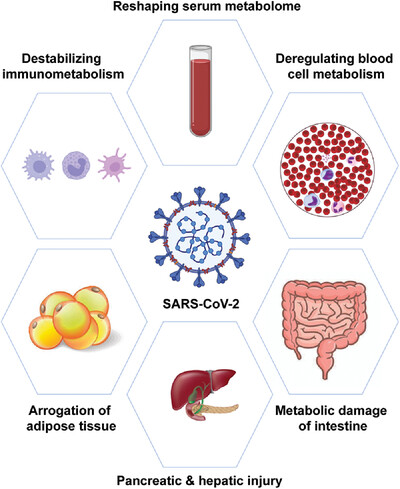
COVID-19 metabolism: Mechanisms and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 09 August 2022
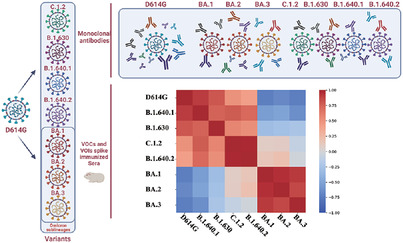
Antigenicity comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron sublineages with other variants contained multiple mutations in RBD
- First Published: 09 April 2022
Inflammatory pathways in COVID-19: Mechanism and therapeutic interventions
- First Published: 01 August 2022
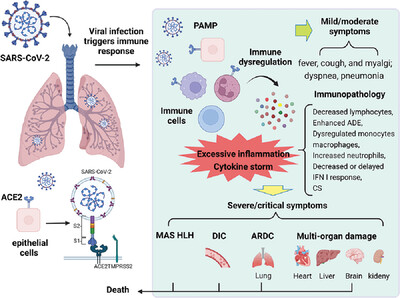
The 2019 coronavirus disease (COVID-19) pandemic has become a global crisis, with SARS-CoV-2 infection inducing excessive inflammation and cytokine storm. Cytokine storm leads to acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) and multi-organ failure, which are important causes of COVID-19 progression and death. Therefore, elucidating the inflammatory pathways of COVID-19 is crucial for the therapeutic strategy of COVID-19.
Cryo-EM structure of G-protein-coupled receptor GPR17 in complex with inhibitory G protein
- First Published: 10 September 2022
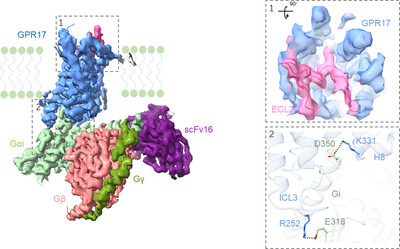
GPR17 is a class A orphan G protein-coupled receptor. The 3.02 Å resolution structure elucidates the activated GPR17 in complex with the Gαi, Gβ, Gγ, and scFv16 in the ligand-free state. The ECL2 of GPR17 occupies the orthosteric binding pocket to promote its self-activation. Meanwhile, the residues D350 and E318 of Gαi form two salt bridges with K3318.49 and R252 of GPR17, respectively, which play a prominent role in the assembly of complex.
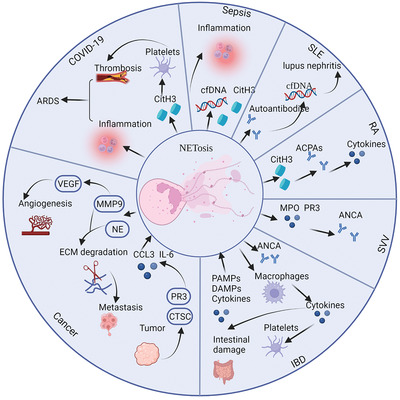
Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic target of NETosis in diseases
- First Published: 19 August 2022