Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Top Downloaded Articles
Neurologic manifestations of nonhospitalized patients with COVID-19 in Wuhan, China
- First Published: 02 July 2020
Coronavirus in human diseases: Mechanisms and advances in clinical treatment
- First Published: 01 October 2020
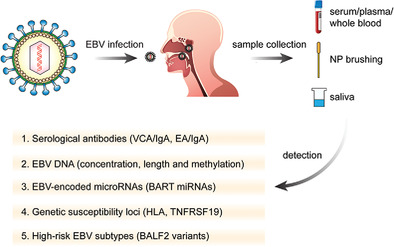
Current mechanisms of anti-CoV therapeutic strategies. The idea to disturb the normal life cycle of the virus provides significant insights into the clinical treatment strategies. All of SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2 encode structure proteins (like S protein), nonstructure proteins (eg, PLpro, 3CLpro, RdRp, and helicase), and accessory proteins that are essential for the viral life cycle and that are considered as important targets for the development of antiviral agents. Additionally, enhancement of INF response and several other cell signaling pathways are also regarded as potential anti-CoV strategies.
The challenges of the COVID-19 pandemic: Approaches for the elderly and those with Alzheimer's disease
- First Published: 09 April 2020
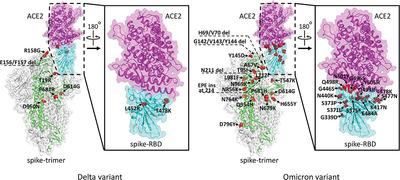
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Characteristics and prevention
- First Published: 13 December 2021
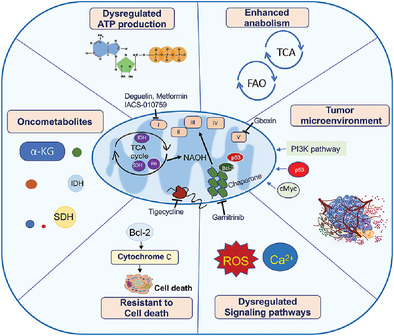
Metabolism in tumor microenvironment: Implications for cancer immunotherapy
- First Published: 03 June 2020
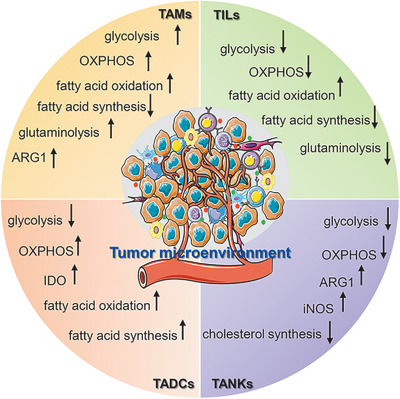
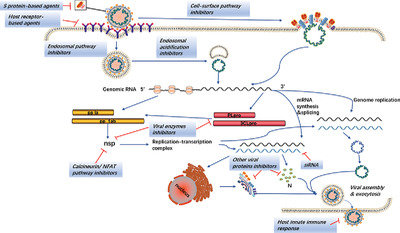
Metabolic reprogramming is the basis of tumor microenvironment, which consists of cellular and extracellular components. The cellular components are mainly composed of hematopoietic immune cells (For example, TAMs, tumor-associated macrophages; TILs, tumor-infiltrated lymphocytes; TADCs, tumor-associated dendritic cells; TANKs, tumor-associated natural killer cells) and resident stromal cells. The extracellular components are mainly composed of extracellular matrix and cell-secreted factors. The interaction between cancer cells and interstitial cells in the tumor microenvironment regulates tumorigenesis and progression.
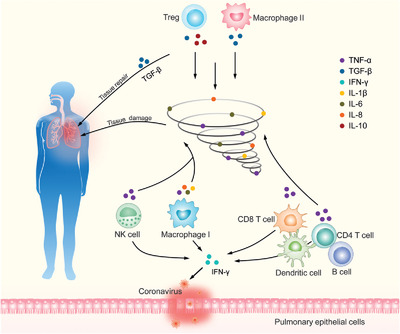
Regulatory T cells: A potential weapon to combat COVID-19?
- First Published: 06 August 2020
Zeolite in tissue engineering: Opportunities and challenges
- First Published: 19 May 2020
A potent neutralizing nanobody against SARS-CoV-2 with inhaled delivery potential
- First Published: 04 March 2021
We reported nanobody (Nb) phage display libraries derived from four camels immunized with the SARS-CoV-2 spike receptor-binding domain (RBD), from which 381 Nbs were identified to recognize SARS-CoV-2-RBD including several mutants. Nb11-59 exhibited potent antiviral activity against authentic SARS-CoV-2 with 50% neutralizing dose (ND50) of 0.55 μg/ml, and it can be produced on large scale in Pichia pastoris with titers reached 20 g/L. Importantly, Nb11-59 showed a good stability and could be developed as an inhaled drug to treat COVID-19.
Lipid metabolism in cancer progression and therapeutic strategies
- First Published: 24 December 2020
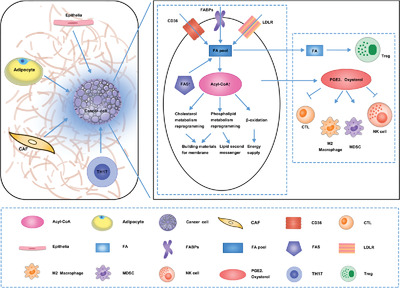
Lipid metabolic reprogramming-mediated crosstalk between cancer cells and tumor microenvironment contributes to cancer progression. Stromal cells, such as adipocyte, CAF, epithelia cells contribute to lipid metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. Cancer cells undergo lipid metabolism rewiring to generate building materials for membrane, lipid second messenger and energy supply. Cancer cells can also secret lipid metabolites to affect immune cell functions, creating a tumor-favoring immune microenvironment.
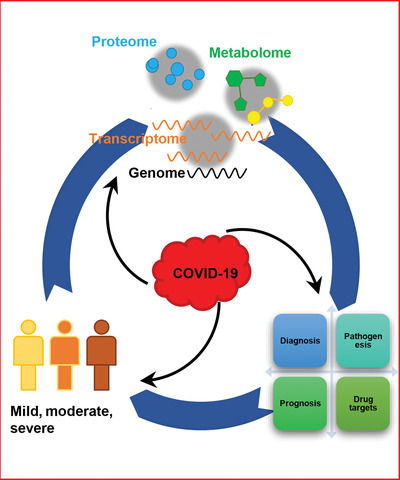
Application of omics technology to combat the COVID-19 pandemic
- First Published: 16 September 2021
Radiomics-based model for accurately distinguishing between severe acute respiratory syndrome associated coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) and influenza A infected pneumonia
- First Published: 13 August 2020
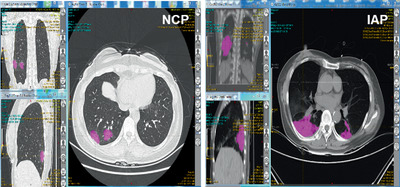
Clinicians have been faced with the challenge of differentiating between severe acute respiratory syndrome-associated coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infected pneumonia (NCP) and influenza A infected pneumonia (IAP). We developed a machine-learning algorithm based on radiomics to distinguish NCP fromIAP by texture analysis based on computed tomography (CT) imaging. Eight of 56 radiomic features extracted by LIFEx were selected to develop a radiomics score and subsequently constructed into a nomogram to predict NCP. The novel nomogram may efficiently distinguish between NCP and IAP patients.
Advances in pathogenesis and precision medicine for nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- First Published: 07 January 2021
Nasally inhaled therapeutics and vaccination for COVID-19: Developments and challenges
- First Published: 14 December 2021
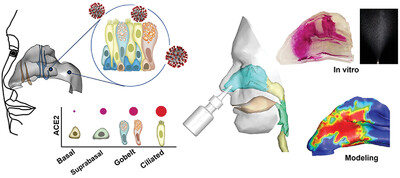
Nasal spray vaccines and therapeutics can be a potent alternative for COVID-19 management. The latest developments of nasal sprays either as repurposed or antiviral formulations were presented. Inherent challenges that hinder effective intranasal delivery were discussed in detail, which included nasal device issues and human nose physiological complexities. The need to develop an effective delivery system to target formulations at the ACE2-rich regions is particularly pressing in the context of emerging SARS-CoV-2 variants that evade current vaccines and develop resistance to existing therapies.




2688-2663.top-downloaded.cover.gif)