Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Table of Contents
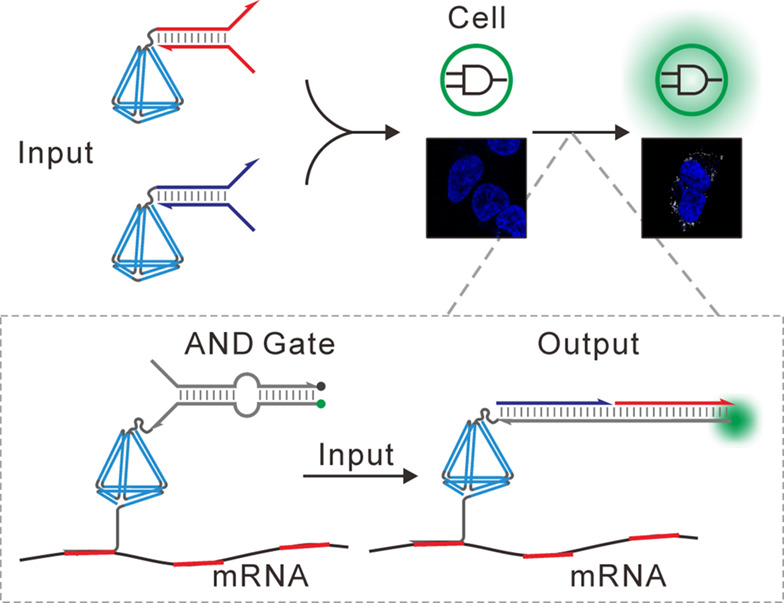
Intracellular Logic Computation with Framework Nucleic Acid-Based Circuits for mRNA Imaging†
- First Published: 02 December 2020
Overcome Debye Length Limitations for Biomolecule Sensing Based on Field Effective Transistors†
- First Published: 26 November 2020
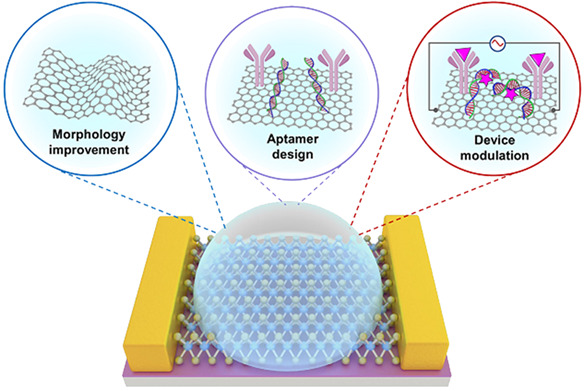
The performance of field effective transistor (FET) biosensors is limited to the charge screening in the solution, and previous reviews have not systematically elucidate this mechanism. In this review, we first expound the generation mechanism of this charge screening, then highlight recent advances to overcome this debye screening, including morphology improvements, aptamer design and device modulation. Finally, the challenges and perspectives involving overcoming charge screening are discussed. This review is beneficial to the development of label free, real-time and ultra-sensitivity FET biosensors.
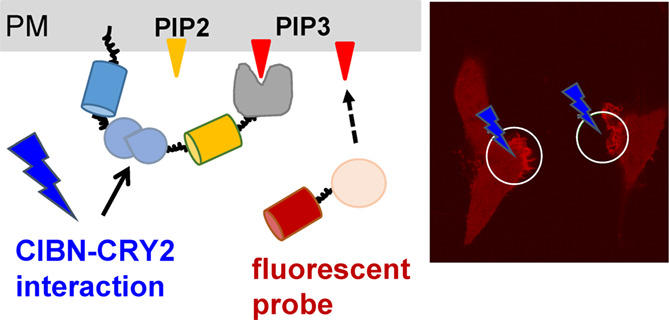
Optogenetic Control of Phosphatidylinositol (3,4,5)-Triphosphate Production by Light-Sensitive Cryptochrome Proteins on the Plasma Membrane
- First Published: 21 January 2021
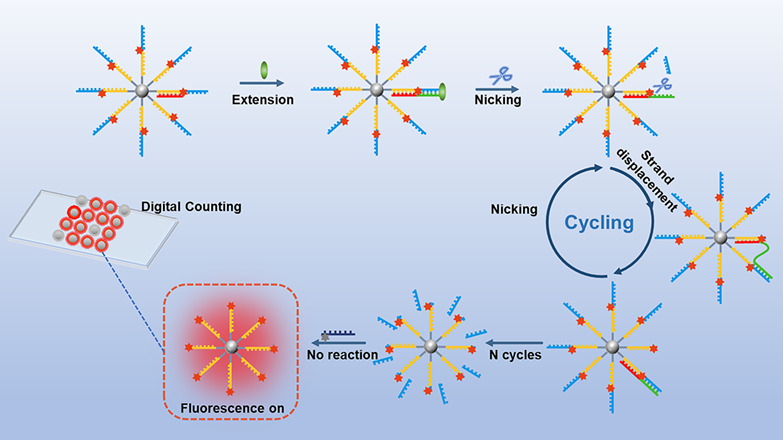
Target Extension-Activated DNA Walker on Nanoparticles for Digital Counting-Based Analysis of MicroRNA†
- First Published: 01 February 2021
Electrochemical Analysis for Multiscale Single Entities on the Confined Interface†
- First Published: 06 February 2021
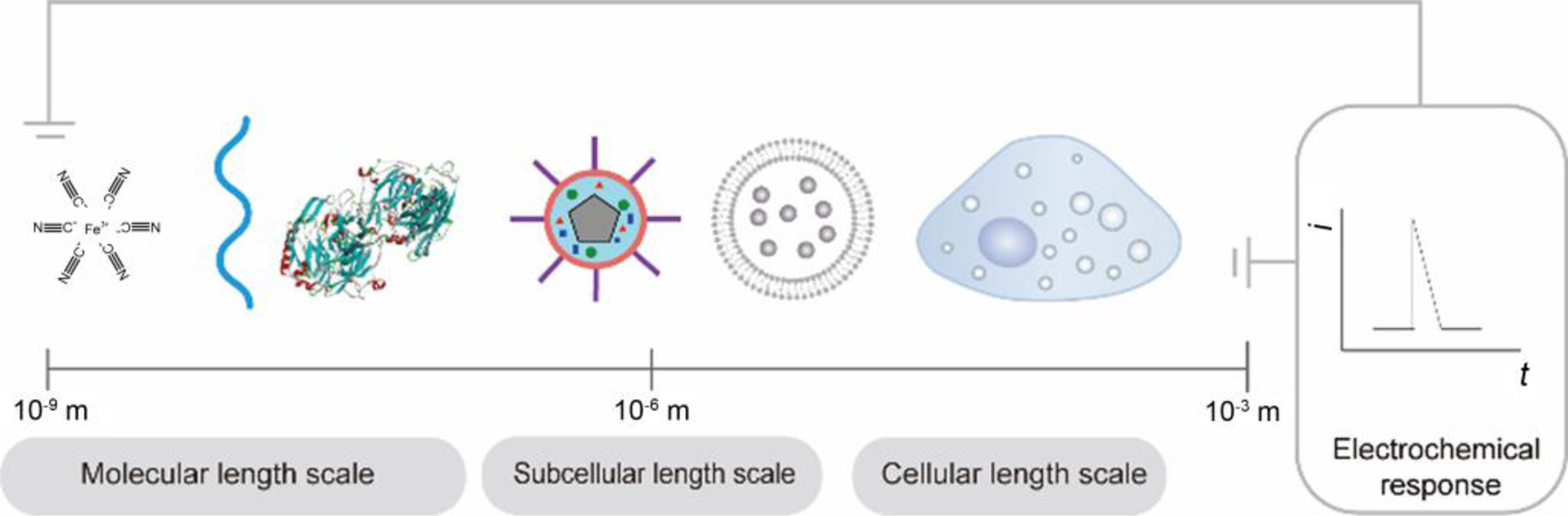
Single entities detection reveals heterogeneity and random processes hidden in ensemble measurements. Obtaining accurate single-entity information is challenging. The electrochemical analysis is at high spatial resolution and high temporal resolution to analyze single entities and measure the fast kinetics process. In this minireview, we will focus on the electrochemical strategies for single multiscale entities.
Single Particle-Based Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy for Visual Detection of Copper Ions in Confined Space†
- First Published: 14 March 2021
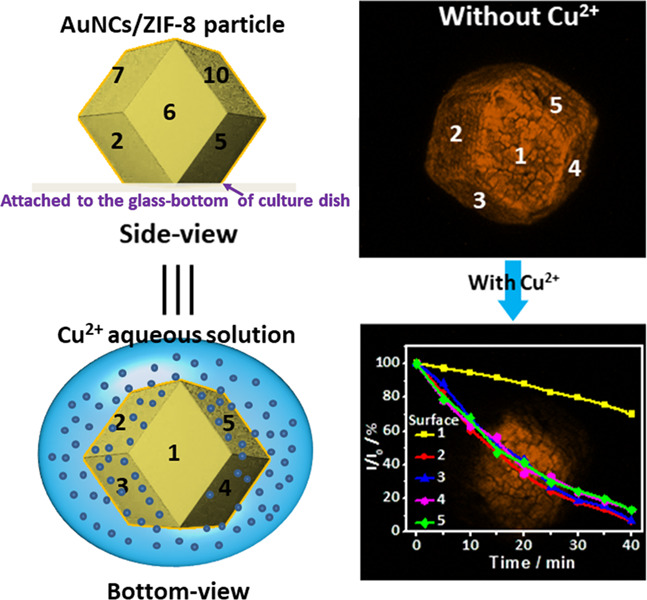
A single particle-based confocal laser scanning microscopy was developed for the visual detection of copper ions in confined space by using fluorescence microparticle, AuNCs/ZIF-8, which was synthesized by coating gold nanoclusters (AuNCs) onto the outer surface of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8). The synthesized AuNCs/ZIF-8 exhibits turn-off responses for Cu2+ via fluorescence quenching in the range of 2—15 μmol·L–1 with a detection limit of 0.9 μmol·L–1. Different distribution of AuNCs on the different surfaces of single ZIF-8 crystal and similar fluorescence quenching dynamics on the different surfaces of single AuNCs/ZIF-8 were obtained.
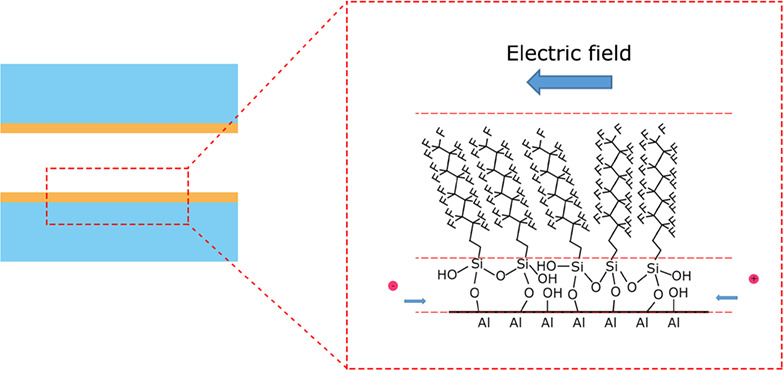
Electric Field Driven Surface Ion Transport in Hydrophobic Nanopores†
- First Published: 11 February 2021
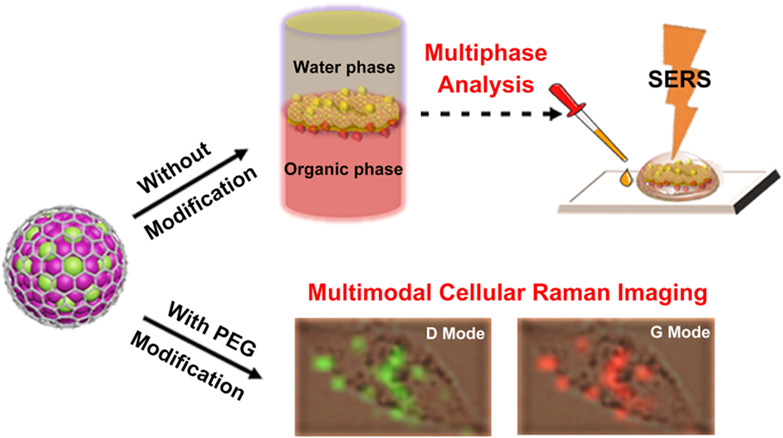
Versatile Graphene-Isolated AuAg-Nanocrystal for Multiphase Analysis and Multimodal Cellular Raman Imaging†
- First Published: 01 February 2021
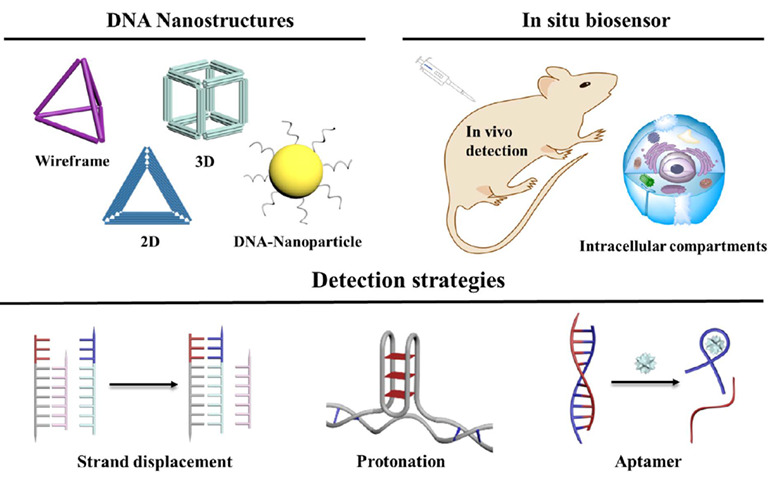
DNA-Based Architectures for in situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nano-space†
- First Published: 19 March 2021
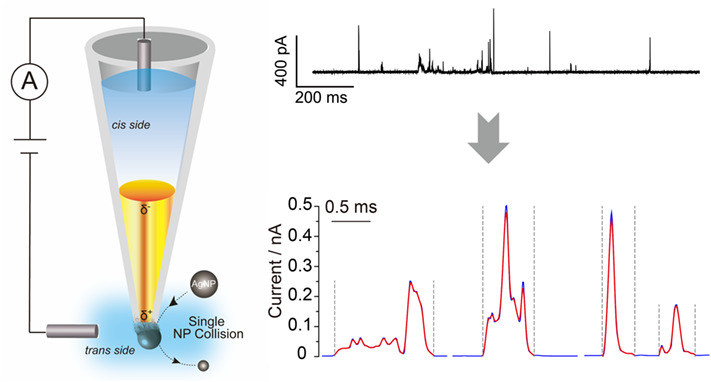
An Envelope Algorithm for Single Nanoparticle Collision Electrochemistry†
- First Published: 04 March 2021
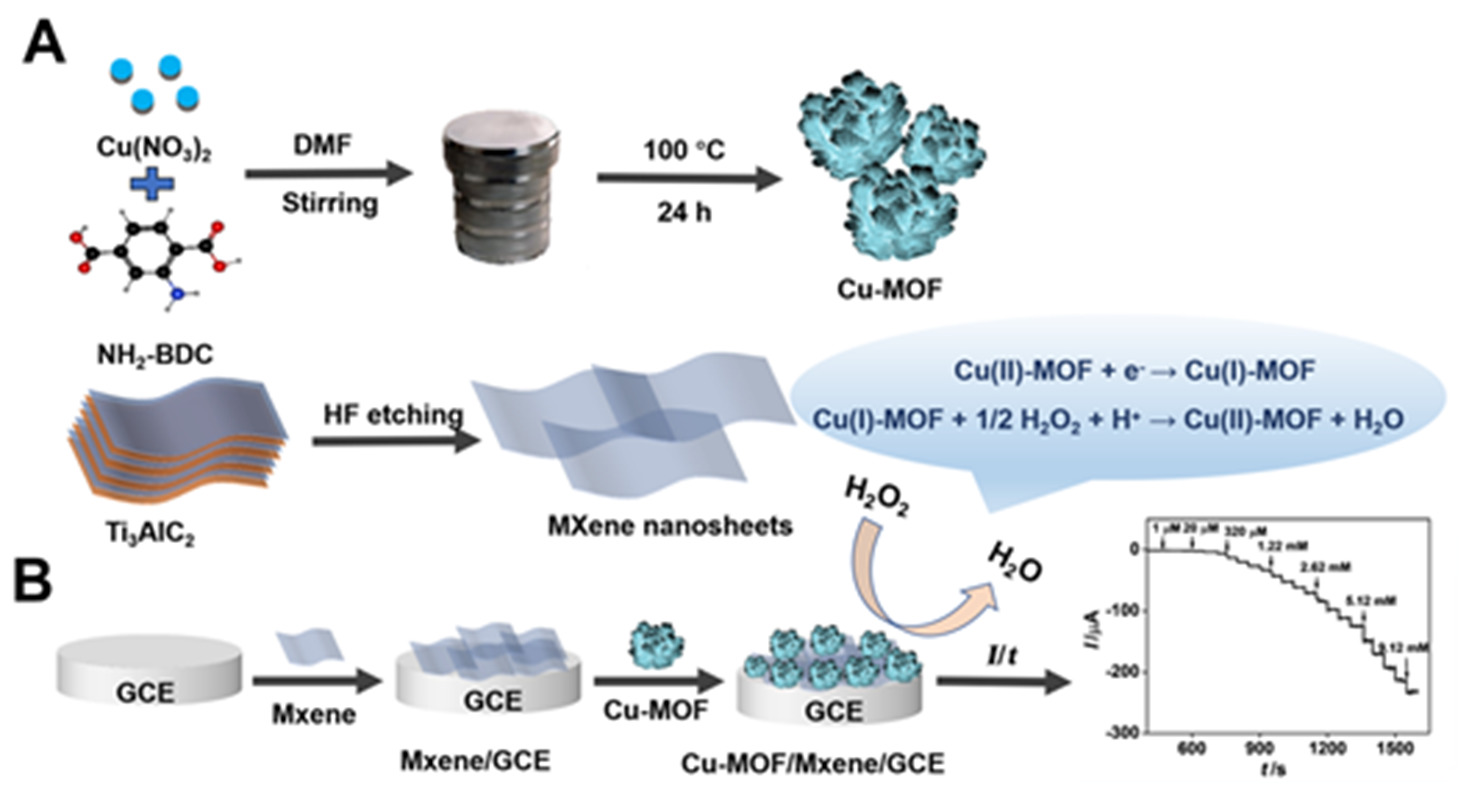
Enzyme-free Electrochemical Detection of Hydrogen Peroxide Based on the Three-Dimensional Flower-like Cu-based Metal Organic Frameworks and MXene Nanosheets†
- First Published: 18 April 2021
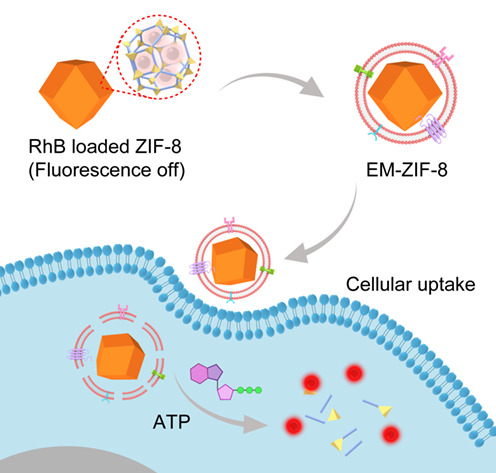
Exosome-Coated Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Nanoparticles for Intracellular Detection of ATP†
- First Published: 10 April 2021
Harpagide Inhibits Microglial Activation and Protects Dopaminergic Neurons as Revealed by Nanoelectrode Amperometry†
- First Published: 15 April 2021
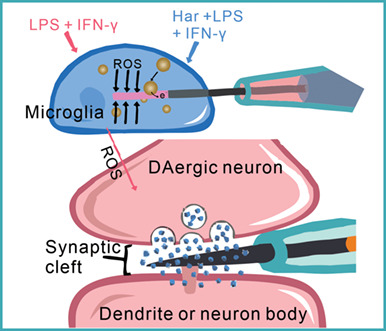
In this work, nanoelectrode amperometry was used to investigate how natural product harpagide inhibits microglia activation and protects DAergic neurons. Intracellular monitoring with single platinized SiC@C NWEs showed that harpagide can efficiently decrease intracellular ROS concentration in microglia suffering activation by inflammatory factors LPS and IFN-γ; Intra-synapse monitoring using CFNEs indicated that harpagide can effectively protect DAergic neuron exocytosis function from microglial inflammation. The results indicate that harpagide inhibits microglia from activation, reduces inflammation-mediated neural injury and maintains dopamine exocytosis function. These conclusions establish that harpagide possesses promising avenues for preventive or therapeutic interventions against PD and other NDDs.
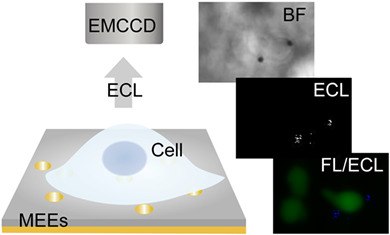
Confined Electrochemiluminescence at Microtube Electrode Ensembles for Local Sensing of Single Cells†
- First Published: 16 June 2021
Deep Learning-Assisted Visualized Fluorometric Sensor Array for Biogenic Amines Detection
- First Published: 10 November 2021
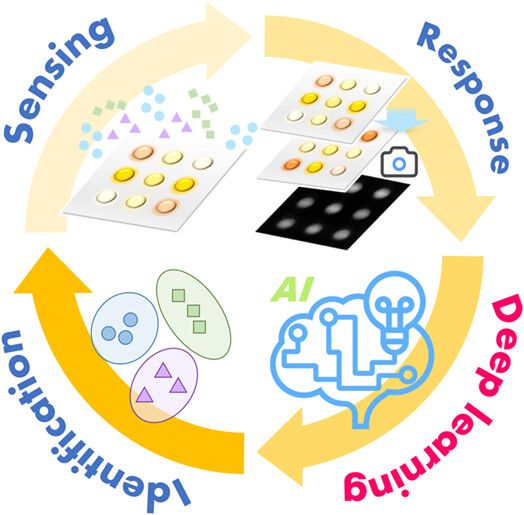
An effective deep learning-assisted visualized fluorometric array-based sensing method for biogenic amines (BAs) detection was developed. 9 typical machine learning algorithms were investigated for qualitative and quantitative analysis of seven BAs. The DL algorithm of convolutional neural network (CNN) approaches 99.29% prediction accuracy in wide volume fraction range (200—2500 cm3/m3). This method also provides a new way for meat freshness monitoring, which contributes the practical significance for the large-sample detection of food quality monitoring and disease diagnosis. The further development of the sensor array can facilitate the detection of a wider variety of analytes.