Exosome-Coated Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework Nanoparticles for Intracellular Detection of ATP†
Wenxing Lv
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
‡W. L. and Z. H. contributed equally.
† Dedicate to the Special Issue of In Situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nanospace.
Search for more papers by this authorZiwei Han
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
‡W. L. and Z. H. contributed equally.
† Dedicate to the Special Issue of In Situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nanospace.
Search for more papers by this authorYike Li
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanjuan Huang
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiashu Sun
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoquan Lu
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Key Laboratory of Bioelectrochemistry and Environmental Analysis of Gansu Province, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou, Gansu, 730070 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chao Liu
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorWenxing Lv
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
‡W. L. and Z. H. contributed equally.
† Dedicate to the Special Issue of In Situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nanospace.
Search for more papers by this authorZiwei Han
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
‡W. L. and Z. H. contributed equally.
† Dedicate to the Special Issue of In Situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nanospace.
Search for more papers by this authorYike Li
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorYanjuan Huang
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorJiashu Sun
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Xiaoquan Lu
Tianjin Key Laboratory of Molecular Optoelectronic Sciences, Department of Chemistry, School of Science, Tianjin University, Tianjin, 300072 China
Key Laboratory of Bioelectrochemistry and Environmental Analysis of Gansu Province, College of Chemistry and Chemical Engineering, Northwest Normal University, Lanzhou, Gansu, 730070 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Chao Liu
Beijing Engineering Research Center for BioNanotechnology, CAS Key Laboratory of Standardization and Measurement for Nanotechnology, CAS Center for Excellence in Nanoscience, National Center for Nanoscience and Technology, Beijing, 100190 China
School of Future Technology, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, 100049 China
E-mail: [email protected]; [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorMain observation and conclusion
The intracellular delivery of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) encapsulated with functional biomolecules represents a promising avenue in the field of biomedicine and biosensing. To improve the cellular uptake efficiency of MOFs, here we report the fabrication of cancer cell-derived exosome membrane (EM)-coated zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (EM-ZIF-8) nanoparticles by using a microfluidic sonication device. EM-ZIF-8 nanoparticles loaded with FITC-labeled bovine serum albumin (BSA) can be taken up by cancer cells and evade phagocytosis more efficiently than their counterparts (ZIF-8 nanoparticles). Moreover, we use EM-ZIF-8 loaded with Rhodamine B (RhB) for in situ imaging of cellular adenosine triphosphate (ATP). The shield effect of ZIF-8 suppresses the fluorescence of RhB, and the presence of ATP disrupts the ZIF-8 structure based on the competitive coordination between ATP and Zn2+, leading to the restoration of RhB fluorescence. This method allows accurate detection of the fluctuation of ATP in A549 cells induced by Ca2+ or 2-DDG treatment. The devised biomimetic EM-ZIF-8 nanoparticles thus provide an efficient platform for intracellular drug delivery and ATP sensing.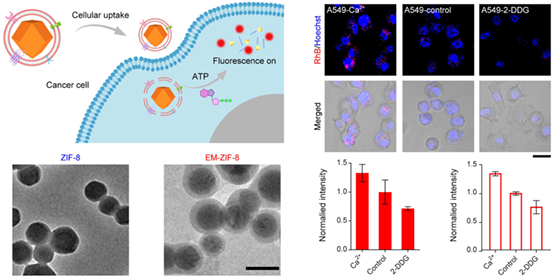
Supporting Information
| Filename | Description |
|---|---|
| cjoc202100162-sup-0001-Supinfo.pdfPDF document, 628.4 KB |
Appendix S1: Supporting Information |
Please note: The publisher is not responsible for the content or functionality of any supporting information supplied by the authors. Any queries (other than missing content) should be directed to the corresponding author for the article.
References
- 1 Horcajada, P.; Chalati, T.; Serre, C.; Gillet, B.; Sebrie, C.; Baati, T.; Eubank, J. F.; Heurtaux, D.; Clayette, P.; Kreuz, C.; Chang, J.-S.; Hwang, Y. K.; Marsaud, V.; Bories, P.-N.; Cynober, L.; Gil, S.; Férey, G.; Couvreur, P.; Gref, R. Porous metal–organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 172–178.
- 2 Kreno, L. E.; Leong, K.; Farha, O. K.; Allendorf, M.; Van Duyne, R. P.; Hupp, J. T. Metal–Organic Framework Materials as Chemical Sensors. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1105–1125.
- 3 Lee, J.; Farha, O. K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K. A.; Nguyen, S. T.; Hupp, J. T. Metal–organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459.
- 4 Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276–279.
- 5 Lou, X. D.; Huang, Y.; Yang, X.; Zhu, H.; Heng, L. P.; Xia, F. External Stimuli Responsive Liquid-Infused Surfaces Switching between Slippery and Nonslippery States: Fabrications and Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1901130.
- 6 Chen, J. J.; Gao, H. J.; Li, Z. H.; Li, Y. X.; Yuan, Q. Ferriporphyrin-inspired MOFs as an artificial metalloenzyme for highly sensitive detection of H2O2 and glucose. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 1398–1401.
- 7 Park, K. S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A. P.; Choi, J. Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F. J.; Chae, H. K.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2006, 103, 10186–10191.
- 8 Phan, A.; Doonan, C. J.; Uribe-Romo, F. J.; Knobler, C. B.; O'Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O. M. Synthesis, Structure, and Carbon Dioxide Capture Properties of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks. Acc. Chem. Res. 2010, 43, 58–67.
- 9 Alsaiari, S. K.; Patil, S.; Alyami, M.; Alamoudi, K. O.; Aleisa, F. A.; Merzaban, J. S.; Li, M.; Khashab, N. M. Endosomal Escape and Delivery of CRISPR/Cas9 Genome Editing Machinery Enabled by Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 143–146.
- 10 Kaneti, Y. V.; Dutta, S.; Hossain, M. S. A.; Shiddiky, M. J. A.; Tung, K.-L.; Shieh, F.-K.; Tsung, C.-K.; Wu, K. C. W.; Yamauchi, Y. Strategies for Improving the Functionality of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks: Tailoring Nanoarchitectures for Functional Applications. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700213.
- 11 Ren, H.; Zhang, L. Y.; An, J. P.; Wang, T. T.; Li, L.; Si, X. Y.; He, L.; Wu, X. T.; Wang, C. G.; Su, Z. M. Polyacrylic acid@zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 nanoparticles with ultrahigh drug loading capability for pH-sensitive drug release. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 1000–1002.
- 12 Pan, Y.; Zhan, S. S.; Xia, F. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-based biosensor for detection of HIV-1 DNA. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 546, 5–9.
- 13 Yi, J. T.; Chen, T. T.; Huo, J.; Chu, X. Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 for Ratiometric Fluorescence Imaging of MicroRNA in Living Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12351–12359.
- 14 Chen, J. M.; Guo, L. H.; Chen, L. F.; Qiu, B.; Hong, G. L.; Lin, Z. Y. Sensing of Hydrogen Sulfide Gas in the Raman-Silent Region Based on Gold Nano-Bipyramids (Au NBPs) Encapsulated by Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8. ACS Sens. 2020, 5, 3964–3970.
- 15 Zhang, W.; Wang, C.; Peng, M. H.; Ren, G. Y.; Li, K.; Lin, Y. Q. ATP-responsive laccase@ZIF-90 as a signal amplification platform to achieve indirect highly sensitive online detection of ATP in rat brain. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 6436–6439.
- 16 Wang, K.; Qian, M. P.; Qi, H. L.; Gao, Q.; Zhang, C. X. Multifunctional zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 for real-time monitoring ATP fluctuation in mitochondria during photodynamic therapy. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 15663–15669.
- 17 Chen, P.; He, M.; Chen, B.; Hu, B. Size- and dose-dependent cytotoxicity of ZIF-8 based on single cell analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 205, 111110.
- 18 Li, S. X.; Wang, K. K.; Shi, Y. J.; Cui, Y. N.; Chen, B. L.; He, B.; Dai, W. B.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X. Q.; Zhong, C. L.; Wu, H. N.; Yang, Q. Y.; Zhang, Q. Novel Biological Functions of ZIF-NP as a Delivery Vehicle: High Pulmonary Accumulation, Favorable Biocompatibility, and Improved Therapeutic Outcome. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2715–2727.
- 19 Ruyra, À.; Yazdi, A.; Espín, J.; Carné-Sánchez, A.; Roher, N.; Lorenzo, J.; Imaz, I.; Maspoch, D. Synthesis, Culture Medium Stability, and In Vitro and In Vivo Zebrafish Embryo Toxicity of Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 2508–2518.
- 20 Batrakova, E. V.; Kim, M. S. Using exosomes, naturally-equipped nanocarriers, for drug delivery. J. Controlled Release 2015, 219, 396–405.
- 21 Sun, D. M.; Zhuang, X. Y.; Xiang, X. Y.; Liu, Y. L.; Zhang, S. Y.; Liu, C. R.; Barnes, S.; Grizzle, W.; Miller, D.; Zhang, H. G. A Novel Nanoparticle Drug Delivery System: The Anti-inflammatory Activity of Curcumin Is Enhanced When Encapsulated in Exosomes. Mol. Ther. 2010, 18, 1606–1614.
- 22 van den Boorn, J. G.; Schlee, M.; Coch, C.; Hartmann, G. SiRNA delivery with exosome nanoparticles. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 325–326.
- 23 Zhang, H. X.; Wang, Z. H.; Zhang, Q. X.; Wang, F.; Liu, Y. Ti3C2 MXenes nanosheets catalyzed highly efficient electrogenerated chemiluminescence biosensor for the detection of exosomes. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2019, 124–125, 184–190.
- 24 Zhang, Q. X.; Wang, F.; Zhang, H. X.; Zhang, Y. Y.; Liu, M. L.; Liu, Y. Universal Ti3C2 MXenes Based Self-Standard Ratiometric Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer Platform for Highly Sensitive Detection of Exosomes. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 12737–12744.
- 25 Li, Y. K.; Deng, J. Q.; Han, Z. W.; Liu, C.; Tian, F.; Xu, R.; Han, D.; Zhang, S. H.; Sun, J. S. Molecular Identification of Tumor-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Using Thermophoresis-Mediated DNA Computation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 1290–1295.
- 26 Dai, Y.; Somoza, R. A.; Wang, L.; Welter, J. F.; Li, Y.; Caplan, A. I.; Liu, C. C. Exploring the Trans-Cleavage Activity of CRISPR-Cas12a (cpf1) for the Development of a Universal Electrochemical Biosensor. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 17399–17405.
- 27 Lu, M.; Huang, Y. Y. Bioinspired exosome-like therapeutics and delivery nanoplatforms. Biomaterials 2020, 242, 119925.
- 28 Yong, T. Y.; Zhang, X. Q.; Bie, N. N.; Zhang, H. B.; Zhang, X. T.; Li, F. Y.; Hakeem, A.; Hu, J.; Gan, L.; Santos, H. A.; Yang, X. L. Tumor exosome-based nanoparticles are efficient drug carriers for chemotherapy. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3838.
- 29 Wang, Y. Q.; Hu, X. X.; Zhang, L. L.; Zhu, C. L.; Wang, J.; Li, Y. X.; Wang, Y. L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y. F.; Yuan, Q. Bioinspired extracellular vesicles embedded with black phosphorus for molecular recognition- guided biomineralization. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2829.
- 30 Cheng, G.; Li, W. Q.; Ha, L.; Han, X. H.; Hao, S. J.; Wan, Y.; Wang, Z. G.; Dong, F. P.; Zou, X.; Mao, Y. W.; Zheng, S. Y. Self-Assembly of Extracellular Vesicle-like Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles for Protection and Intracellular Delivery of Biofunctional Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 7282–7291.
- 31 Han, Z. W.; Lv, W. X.; Li, Y. K.; Chang, J. Q.; Zhang, W.; Liu, C.; Sun, J. S. Improving Tumor Targeting of Exosomal Membrane-Coated Polymeric Nanoparticles by Conjugation with Aptamers. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2020, 3, 2666–2673.
- 32 Chang, J. Q.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Y. K.; Han, Z. W.; Tian, F.; Liu, C.; Feng, Q.; Wang, Y. G.; Sun, J. S.; Zhang, L. Multilayer Ratiometric Fluorescent Nanomachines for Imaging mRNA in Live Cells. Small Methods 2020, 5, 2001047.
- 33 Li, Y. K.; Liu, C.; Bai, X.; Tian, F.; Hu, G. Q.; Sun, J. S. Enantiomorphic Microvortex-Enabled Supramolecular Sensing of Racemic Amino Acids by Using Achiral Building Blocks. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2020, 59, 3486–3490.
- 34 El Andaloussi, S.; Mäger, I.; Breakefield, X. O.; Wood, M. J. A. Extracellular vesicles: biology and emerging therapeutic opportunities. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2013, 12, 347–357.
- 35 Kamerkar, S.; LeBleu, V. S.; Sugimoto, H.; Yang, S.; Ruivo, C. F.; Melo, S. A.; Lee, J. J.; Kalluri, R. Exosomes facilitate therapeutic targeting of oncogenic KRAS in pancreatic cancer. Nature 2017, 546, 498–503.
- 36 Majeti, R.; Chao, M. P.; Alizadeh, A. A.; Pang, W. W.; Jaiswal, S.; Gibbs, K. D., Jr.; van Rooijen, N.; Weissman, I. L. CD47 Is an Adverse Prognostic Factor and Therapeutic Antibody Target on Human Acute Myeloid Leukemia Stem Cells. Cell 2009, 138, 286–299.
- 37 Kim, H.-N.; Ponte, F.; Nookaew, I.; Ucer Ozgurel, S.; Marques-Carvalho, A.; Iyer, S.; Warren, A.; Aykin-Burns, N.; Krager, K.; Sardao, V. A.; Han, L.; de Cabo, R.; Zhao, H.; Jilka, R. L.; Manolagas, S. C.; Almeida, M. Estrogens decrease osteoclast number by attenuating mitochondria oxidative phosphorylation and ATP production in early osteoclast precursors. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11933.
- 38 Zhao, T. V.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Xia, S.; Shi, P.; Li, L.; Chen, Z.; Yin, C.; Eriguchi, M.; Chen, Y.; Bernstein, E. A.; Giani, J. F.; Bernstein, K. E.; Shen, X. Z. ATP release drives heightened immune responses associated with hypertension. Sci. Immunol. 2019, 4, eaau6426.
- 39 Edsall, J. T.; Felsenfeld, G.; Goodman, D. S.; Gurd, F. R. N. The Association of Imidazole with the Ions of Zinc and Cupric Copper. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1954, 76, 3054–3061.
- 40 Deng, J. J.; Wang, K.; Wang, M.; Yu, P.; Mao, L. Q. Mitochondria Targeted Nanoscale Zeolitic Imidazole Framework-90 for ATP Imaging in Live Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2017, 139, 5877–5882.
- 41 Li, P.-H.; Lin, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-T.; Ciou, W.-R.; Chan, P.-H.; Luo, L. Y.; Hsu, H.-Y.; Diau, E. W.-G.; Chen, Y.-C. Using Gold Nanoclusters As Selective Luminescent Probes for Phosphate-Containing Metabolites. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 5484–5488.
- 42 Halestrap, A. P.; Pasdois, P. The role of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore in heart disease. Biochim. Biophys. Acta, Bioenerg. 2009, 1787, 1402–1415.
- 43 Ralser, M.; Wamelink, M. M.; Struys, E. A.; Joppich, C.; Krobitsch, S.; Jakobs, C.; Lehrach, H. A catabolic block does not sufficiently explain how 2-deoxy-D-glucose inhibits cell growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008, 105, 17807–17811.
- 44 Wang, R.; Zhao, X.; Chen, X.; Qiu, X.; Qing, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, L.; Hu, X.; He, Z.; Zhong, D.; Wang, Y.; Luo, Y. Rolling Circular Amplification (RCA)-Assisted CRISPR/Cas9 Cleavage (RACE) for Highly Specific Detection of Multiple Extracellular Vesicle MicroRNAs. Anal. Chem. 2020, 92, 2176–2185.
- 45 Illes, B.; Hirschle, P.; Barnert, S.; Cauda, V.; Wuttke, S.; Engelke, H. Exosome-Coated Metal–Organic Framework Nanoparticles: An Efficient Drug Delivery Platform. Chem. Mater. 2017, 29, 8042–8046.




