DNA-Based Architectures for in situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nano-space†
Xiaoxue Hu
Shenzhen Research Institute, Nanjing University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518000 China
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorYide Huang
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao Yin
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorLizhi Dai
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ye Tian
Shenzhen Research Institute, Nanjing University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518000 China
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this authorXiaoxue Hu
Shenzhen Research Institute, Nanjing University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518000 China
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorYide Huang
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorHao Yin
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorLizhi Dai
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Ye Tian
Shenzhen Research Institute, Nanjing University, Shenzhen, Guangdong, 518000 China
College of Engineering and Applied Sciences, State Key Laboratory of Analytical Chemistry for Life Science, Chemistry and Biomedicine Innovation Center, Nanjing University, Nanjing, Jiangsu, 210093 China
E-mail: [email protected]Search for more papers by this author#These authors contributed equally to this work
†Dedicate to the Special Issue of In Situ Target Biomolecule Analysis in Confined Nanospace.
Abstract
In situ target biomolecule analysis is of great significance for real-time monitoring and regulation of endogenous biomarkers and elementary biomolecules in vivo. Gratifyingly, the rapid evolution of structural DNA nanotechnology during past decades has established an appealing toolbox for biological analysis and medical detection. The modulated self-assembly and underlying canonical Watson-Crick base-pairing rules provide possibilities for accurate controlling of the topologies and functions of obtained nanomaterials. The probes composed of diverse DNA nanostructures and DNA-nanoparticle complexes can create a confined space, which increases target accessibility and improves probe stability, sensitivity and specificity. In this minireview, we retrospect the research progress of in-situ biomolecular analysis based on DNA nanostructures for intracellular and in vivo biosensors in confined space. The characteristics of distinct DNA nanomaterials are first introduced, and then the fundamentals of biosensing process of designed DNA nanostructures are emphasized. Moreover, we elucidate our perspective over the challenges of this field and discuss the potential directions of this kind of application-oriented fabrication technique.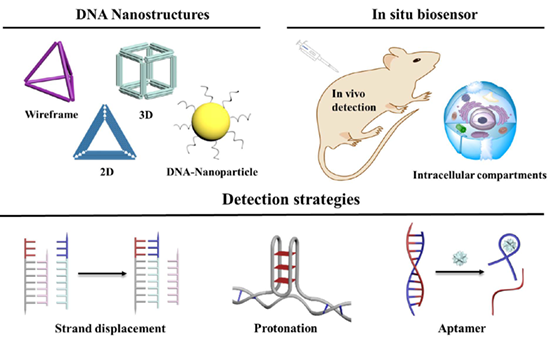
References
- 1 Cooper, G. M.; Hausman, R. E. The Cell: A Molecular Approach, Chapter 1, ASM Press, Washington DC/Sinauer Associates Inc., Sunderland MA, 2000.
- 2 Seeman, N. C. Nucleic acid junctions and lattices. J. Theor. Biol. 1982, 99, 237–247.
- 3 Kallenbach, N. R.; Ma, R. I.; Seeman, N. C. An immobile nucleic acid junction constructed from oligonucleotides. Nature 1983, 305, 829–831.
- 4 Kong, G.; Zhang, M.; Xiong, M.; Fu, X.; Ke, G.; Zhang, X.-B. DNA nanostructure-based fluorescent probes for cellular sensing. Anal. Methods 2020, 12, 1415–1429.
- 5 Li, L.; Xing, H.; Zhang, J.; Lu, Y. Functional DNA Molecules Enable Selective and Stimuli-Responsive Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2415–2426.
- 6 Yang, F.; Li, Q.; Wang, L.; Zhang, G. J.; Fan, C. Framework-Nucleic- Acid-Enabled Biosensor Development. ACS Sens. 2018, 3, 903–919.
- 7 He, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H.; Ribbe, A. E.; Mao, C. Self-assembly of hexagonal DNA two-dimensional (2D) arrays. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12202–12203.
- 8 Liedl, T.; Högberg, B.; Tytell, J.; Ingber, D. E.; Shih, W. M. Self-assembly of three-dimensional prestressed tensegrity structures from DNA. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 520–524.
- 9 Wei, B.; Dai, M.; Yin, P. Complex shapes self-assembled from single- stranded DNA tiles. Nature 2012, 485, 623–626.
- 10 Schmied, J. J.; Raab, M.; Forthmann, C.; Pibiri, E.; Wünsch, B.; Dammeyer, T.; Tinnefeld, P. DNA origami–based standards for quantitative fluorescence microscopy. Nat. Protoc. 2014, 9, 1367–1391.
- 11 Schmied, J. J.; Gietl, A.; Holzmeister, P.; Forthmann, C.; Steinhauer, C.; Dammeyer, T.; Tinnefeld, P. Fluorescence and super-resolution standards based on DNA origami. Nat. Methods. 2012, 9, 1133–1134.
- 12 Rothemund, P. W. K. Folding DNA to create nanoscale shapes and patterns. Nature 2006, 440, 297–302.
- 13 Goodman, R. P.; Berry, R. M.; Turberfield, A. J. The single-step synthesis of a DNA tetrahedron. Chem. Commun. 2004, 1372–1373.
- 14 Han, D.; Pal, S.; Nangreave, J.; Deng, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. DNA origami with complex curvatures in three-dimensional space. Science 2011, 332, 342–346.
- 15 Zhao, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. Organizing DNA Origami Tiles into Larger Structures Using Preformed Scaffold Frames. Nano. Lett. 2011, 11, 2997–3002.
- 16 Tian, Y.; Lhermitte, J. R.; Bai, L.; Vo, T.; Xin, H. L.; Li, H.; Li, R.; Fukuto, M.; Yager, K. G.; Kahn, J. S. Ordered three-dimensional nanomaterials using DNA-prescribed and valence-controlled material voxels. Nat. Mater. 2020, 19, 789–796.
- 17 Hong, F.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Y.; Yan, H. DNA Origami: Scaffolds for Creating Higher Order Structures. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12584−12640.
- 18 Walsh, A. S.; Yin, H.; Erben, C. M.; Wood, M. J.; Turberfield, A. J. DNA cage delivery to mammalian cells. ACS Nano. 2011, 5, 5427–5432.
- 19 Liang, L.; Li, J.; Li, Q.; Huang, Q.; Shi, J.; Yan, H.; Fan, C. Single-particle tracking and modulation of cell entry pathways of a tetrahedral DNA nanostructure in live cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 7745–7750.
- 20 Li, J.; Pei, H.; Zhu, B.; Liang, L.; Wei, M.; He, Y.; Chen, N.; Li, D.; Huang, Q.; Fan, C. Self-Assembled Multivalent DNA Nanostructures for Noninvasive Intracellular Delivery of Immunostimulatory CpG Oligonucleotides. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8783–8789.
- 21 Tay, C. Y.; Yuan, L.; Leong, D. T. Nature-Inspired DNA Nanosensor for Real-Time in Situ Detection of mRNA in Living Cells. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5609–5617.
- 22 Zhou, W.; Li, D.; Xiong, C.; Yuan, R.; Xiang, Y. Multicolor-Encoded Reconfigurable DNA Nanostructures Enable Multiplexed Sensing of Intracellular MicroRNAs in Living Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 13303–13308.
- 23 He, L.; Lu, D.; Liang, H.; Xie, S.; Zhang, X.; Liu, Q.; Yuan, Q.; Tan, W. mRNA-Initiated, Three-Dimensional DNA Amplifier Able to Function inside Living Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018, 140, 258–263.
- 24 Peng, P.; Du, Y.; Zheng, J.; Wang, H.; Li, T. Reconfigurable Bioinspired Framework Nucleic Acid Nanoplatform Dynamically Manipulated in Living Cells for Subcellular Imaging. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2019, 58, 1648–1653.
- 25 Zheng, X.; Peng, R.; Jiang, X.; Wang, Y.; Xu, S.; Ke, G.; Fu, T.; Liu, Q.; Huan, S.; Zhang, X. Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer-Based DNA Nanoprism with a Split Aptamer for Adenosine Triphosphate Sensing in Living Cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 10941–10947.
- 26 Liu, L.; Rong, Q.; Ke, G.; Zhang, M.; Li, J.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, M.; Zhang, X. B. Efficient and Reliable MicroRNA Imaging in Living Cells via a FRET-Based Localized Hairpin-DNA Cascade Amplifier. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3675–3680.
- 27 Zhou, Y. J.; Wan, Y. H.; Nie, C. P.; Zhang, J.; Chen, T. T.; Chu, X. Molecular Switching of a Self-Assembled 3D DNA Nanomachine for Spatiotemporal pH Mapping in Living Cells. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 10366–10370.
- 28 Winter, J.; Jung, S.; Keller, S.; Gregory, R. I.; Diederichs, S. Many roads to maturity: microRNA biogenesis pathways and their regulation. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2009, 11, 228–234.
- 29 Fu, X.; Ke, G.; Peng, F.; Hu, X.; Li, J.; Shi, Y.; Kong, G.; Zhang, X. B.; Tan, W. Size-selective molecular recognition based on a confined DNA molecular sieve using cavity-tunable framework nucleic acids. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1518.
- 30 Winfree, E.; Liu, F.; Wenzler, L. A.; Seeman, N. C. Design and self-assembly of two-dimensional DNA crystals. Nature 1998, 394, 539–544.
- 31 Douglas, S. M.; Dietz, H.; Liedl, T.; Högberg, B.; Graf, F.; Shih, W. M. Self-assembly of DNA into nanoscale three-dimensional shapes. Nature 2009, 459, 414–418.
- 32 Meng, H.-M.; Zhang, X.; Lv, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, N.-N.; Fu, T.; Fan, H.; Liang, H.; Qiu, L.; Zhu, G. DNA dendrimer: an efficient nanocarrier of functional nucleic acids for intracellular molecular sensing. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 6171–6181.
- 33 Chen, G.; Liu, D.; He, C.; Gannett, T. R.; Lin, W.; Weizmann, Y. Enzymatic synthesis of periodic DNA nanoribbons for intracellular pH sensing and gene silencing. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 3844–3851.
- 34 Hu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Yan, J.; Wen, N.; Xiong, H.; Cai, S.; He, Q.; Peng, D.; Liu, Z.; Liu, Y. Dynamic DNA Assemblies in Biomedical Applications. Adv. Sci. 2020, 7, 2000557.
- 35 Liu, L.; Dou, C. X.; Liu, J. W.; Wang, X. N.; Ying, Z. M.; Jiang, J. H. Cell Surface-Anchored DNA Nanomachine for Dynamically Tunable Sensing and Imaging of Extracellular pH. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 11198–11202.
- 36 Zeng, S.; Liu, D.; Li, C.; Yu, F.; Fan, L.; Lei, C.; Huang, Y.; Nie, Z.; Yao, S., Cell-Surface-Anchored Ratiometric DNA Tweezer for Real-Time Monitoring of Extracellular and Apoplastic pH. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13459–13466.
- 37 Di, Z.; Zhao, J.; Chu, H.; Xue, W.; Zhao, Y.; Li, L. An Acidic-Microenvironment-Driven DNA Nanomachine Enables Specific ATP Imaging in the Extracellular Milieu of Tumor. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1901885.
- 38 Peng, H.; Li, X.; Zhang, H.; Le, X.C. A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14378.
- 39 Martin-Gracia, B.; Martin-Barreiro, A.; Cuestas-Ayllon, C.; Grazu, V.; Line, A.; Llorente, A.; de la Fuente, J. M.; Moros, M. Nanoparticle- based biosensors for detection of extracellular vesicles in liquid biopsies. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 6710–6738.
- 40 Cutler, J. I.; Auyeung, E.; Mirkin, C. A. Spherical nucleic acids. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 1376–1391.
- 41 Li, F.; Pei, H.; Wang, L.; Lu, J.; Gao, J.; Jiang, B.; Zhao, X.; Fan, C. Nanomaterial-based fluorescent DNA analysis: A comparative study of the quenching effects of graphene oxide, carbon nanotubes, and gold nanoparticles. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 4140–4148.
- 42 Wang, C. C.; Wu, S. M.; Li, H. W.; Chang, H. T. Biomedical Applications of DNA-Conjugated Gold Nanoparticles. ChemBioChem 2016, 17, 1052–1062.
- 43 Wu, Q.; Liu, Z.; Su, L.; Han, G.; Liu, R.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, C.; Zhang, Z. Sticky-flares for in situ monitoring of human telomerase RNA in living cells. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 9386–9392.
- 44 Zhan, R.; Guo, W.; Gao, X.; Liu, X.; Xu, K.; Tang, B. Reconstruction of nano-flares based on Au–Se bonds for high-fidelity detection of RNA in living cells. Chem. Commun. 2020, 56, 5178–5181.
- 45 Yang, X.-J.; Zhang, K.; Zhang, T.-T.; Xu, J.-J.; Chen, H.-Y. Reliable forster resonance energy transfer probe based on structure-switching DNA for ratiometric sensing of telomerase in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 4216–4222.
- 46 Zhang, K.; Fan, Z.; Huang, Y.; Xie, M.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. A well-designed Gold nanoparticle based fluorescence probe for assay Argonaute2 and Let-7a interaction in living cells. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 312, 128000.
- 47 Zhang, J.; Cui, Y.-X.; Feng, X.-N.; Cheng, M.; Tang, A.-N.; Kong, D.-M. pH-controlled intracellular in situ reversible assembly of a photothermal agent for smart chemo-photothermal synergetic therapy and ATP imaging. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 39624–39632.
- 48 Qin, X.; Yuan, C.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y. A fluorescein–gold nanoparticles probe based on inner filter effect and aggregation for sensing of biothiols. J. Photopolym. Photobiol., B 2020, 210, 111986.
- 49 Bruchez, M.; Moronne, M.; Gin, P.; Weiss, S.; Alivisatos, A. P. Semiconductor nanocrystals as fluorescent biological labels. Science 1998, 281, 2013–2016.
- 50 Chan, W. C.; Nie, S. Quantum dot bioconjugates for ultrasensitive nonisotopic detection. Science 1998, 281, 2016–2018.
- 51 Hu, S. H.; Chen, Y. W.; Hung, W. T.; Chen, I. W.; Chen, S. Y. Quantum- dot-tagged reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites for bright fluorescence bioimaging and photothermal therapy monitored in situ. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 1748–1754.
- 52 Yuan, R.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, L.; Cheng, W.; Tu, Z.; Ding, S. Target- triggered DNA nanoassembly on quantum dots and DNAzyme-modulated double quenching for ultrasensitive microRNA biosensing. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2017, 92, 342–348.
- 53 Ma, Y.; Mao, G.; Wu, G.; Fan, J.; He, Z.; Huang, W. A novel nano-beacon based on DNA functionalized QDs for intracellular telomerase activity monitoring. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2020, 304, 127385.
- 54 Sun, J.; Liu, F.; Yu, W.; Jiang, Q.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.; Wang, F.; Liu, X. Highly sensitive glutathione assay and intracellular imaging with functionalized semiconductor quantum dots. Nanoscale 2019, 11, 5014–5020.
- 55 Rabie, H.; Zhang, Y.; Pasquale, N.; Lagos, M. J.; Batson, P. E.; Lee, K. B. NIR Biosensing of Neurotransmitters in Stem Cell-Derived Neural Interface Using Advanced Core-Shell Upconversion Nanoparticles. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1806991.
- 56 Gao, R.; Hao, C.; Xu, L.; Xu, C.; Kuang, H. Spiny nanorod and upconversion nanoparticle satellite assemblies for ultrasensitive detection of messenger RNA in living cells. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 5414–5421.
- 57 Yang, L.; Zhang, K.; Bi, S.; Zhu, J.-J. Dual-acceptor-based upconversion luminescence nanosensor with enhanced quenching efficiency for in situ imaging and quantification of microRNA in living cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 38459–38466.
- 58 Meng, L.; Zheng, X.; Zheng, Z.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, L.; Zhou, P.; Xin, G.-Z.; Li, P.; Li, H.-J. A sensitive upconverting nanoprobe based on signal amplification technology for real-time in situ monitoring of drug-induced liver injury. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 15325–15335.
- 59 Xiao, M.; Lai, W.; Man, T.; Chang, B.; Li, L.; Chandrasekaran, A. R.; Pei, H. Rationally engineered nucleic acid architectures for biosensing applications. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 11631–11717.
- 60 Anastassacos, F. M.; Zhao, Z.; Zeng, Y.; Shih, W. M. Glutaraldehyde cross-linking of oligolysines coating DNA origami greatly reduces susceptibility to nuclease degradation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142, 3311–3315.
- 61 Cassinelli, V.; Oberleitner, B.; Sobotta, J.; Nickels, P.; Grossi, G.; Kempter, S.; Frischmuth, T.; Liedl, T.; Manetto, A. One-Step Formation of “Chain-Armor”-Stabilized DNA Nanostructures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7795–7798.
- 62 Shin, S.; Jung, Y.; Uhm, H.; Song, M.; Son, S.; Goo, J.; Jeong, C.; Song, J.-J.; Kim, V. N.; Hohng, S. Quantification of purified endogenous miRNAs with high sensitivity and specificity. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 6033.
- 63 Li, B.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, T.; Yang, B.; Huang, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, B. Construction of Dual-Color Probes with Target-Triggered Signal Amplification for In Situ Single-Molecule Imaging of MicroRNA. ACS Nano 2020, 14, 8116–8125.




