Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Comparison of antimicrobial properties of inorganic peroxide polymer composites
- First Published: 18 March 2024
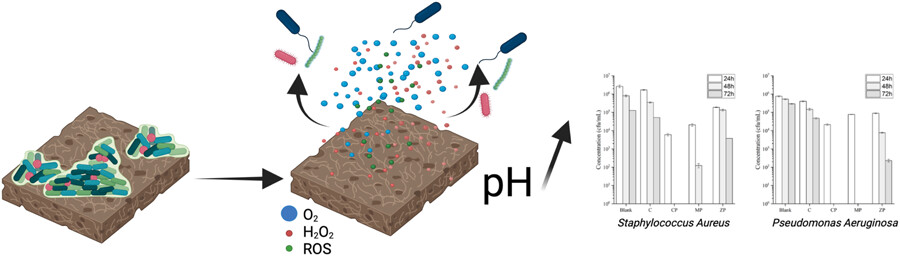
Inorganic peroxides are recognized as potential sustained release sources of hydrogen peroxide and oxygen when exposed to aqueous media. They were used extensively in the pre-antibiotic era to treat a variety of infections. Here we compare the release profiles of zinc, calcium, and magnesium peroxides and their antibacterial potential against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, as well as their toxicity toward mammalian cells.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Multiple biomaterials for immediate implant placement tissue repair: Current status and future perspectives
- First Published: 29 February 2024
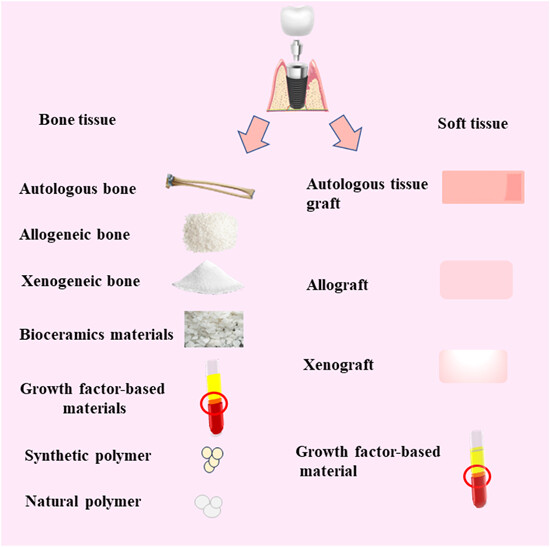
Immediate implant placement has been widely used to restore missing teeth. The inevitable loss of bone and soft tissue after extraction can affect the initial stability. Biomaterials are considered a promising option due to their good biocompatibility, biodegradability, and bioactive properties. Choosing the appropriate biomaterial can provide a better solution to the problem of immediate implant tissue deficiency.
HIGHLIGHT
Precise tumor treatment: pH-responsive nanoparticles for modulating and real-time monitoring tumor microenvironment
- First Published: 25 February 2024
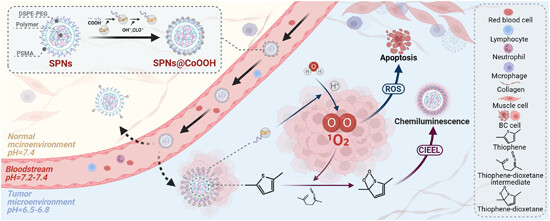
The tumor microenvironment (TME) presents a unique and complex milieu, characterized by spatial and temporal heterogeneity that significantly hinders cancer treatment strategies. Nanoparticles emerge as a versatile solution, potentially overcoming these challenges by enabling targeted therapy and real-time, concurrent assessment of therapeutic effectiveness under abnormal physiological and biochemical conditions. A recent study by Lu et al. introduces a significant innovation in the form of pH-responsive companion diagnostics (CDx) reagent, comprising core-satellite semiconducting polymer nanoparticles @ cobalt hydroxide oxide (SPNs@CoOOH). This novel structure demonstrates a specific affinity for TME targeting, while effectively combining chemiluminescence with reactive oxygen species (ROS)-mediated therapy. This synergy facilitates efficient tumor treatment alongside real-time monitoring, using only water as a resource in the body. As research in nanoparticle-based strategies progresses, the incorporation of pH-responsive systems heralds new possibilities for personalized and more effective cancer therapies.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Standardization of 3D printing parameters to control the size and shape of pores in Polylactic acid scaffolds
- First Published: 13 February 2024
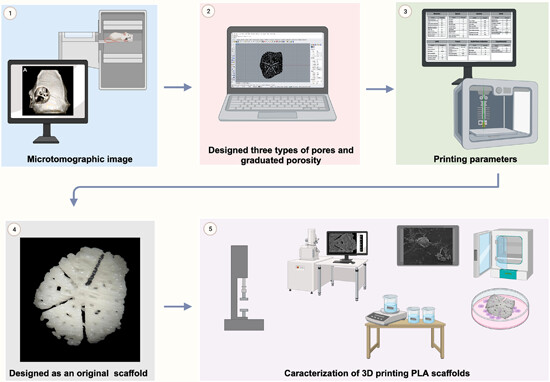
Design and characterization of a scaffold from an image with a critical size defect in Wistar-rat calvaria, modifying more than 50 printing parameters that allow printing different types of pores and graduated porosity, with anatomically exact adaptation to the defect using a printer three-dimensional commercial by fused deposition modeling technique.
REVIEW ARTICLE
Management of peripheral nerve injuries using natural based biomaterials and their derivatives: Advances and prospective
- First Published: 03 February 2024
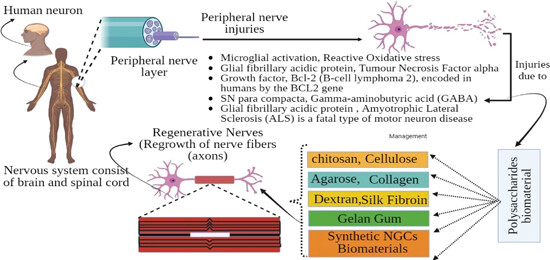
The nervous system comprises peripheral nerves and peripheral neurons, which consist of neurons and nerve fibers. These neurons can be damaged by various factors such as glial fibrillary protein, microglial activation, tumor necrosis, growth factor, Bcl-2, Sn paracompact, gamma-aminobutyric, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and other factors. However, these factors can be mitigated by utilizing polysaccharides, a natural biomaterial, which stimulates the growth and regeneration of nerve fibers.
PERSPECTIVE
Spatiotemporal omics of life energy: Towards medicine of frequencies and terahertz drugs
- First Published: 23 January 2024
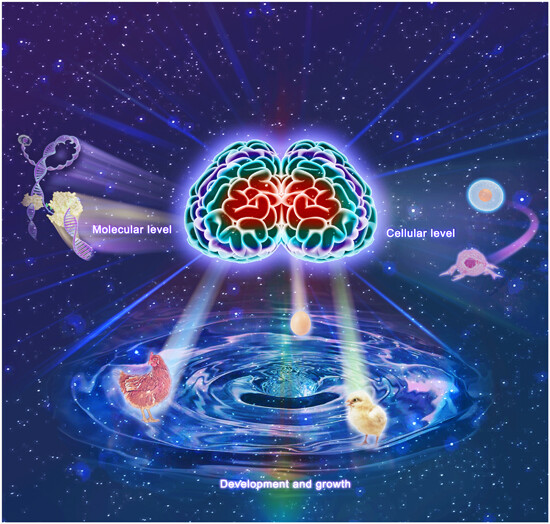
Intricate life processes are governed by precise combinations of spatiotemporal frequencies. Life activities span molecular events such as the replication of genetic substances, cellular transformations such as between cancer cells and stem cells, and organismal development from fertilized eggs to adults. Water orchestrates all life reactions through resonant coupling. The brain harmonizes matter, energy, and information for life. Spatiotemporal omics of vibrational frequencies emerges as crucial for unraveling the mystery of life.
REVIEW ARTICLES
Nanotechnology-based CRISPR/Cas9 delivery system for genome editing in cancer treatment
- First Published: 14 January 2024
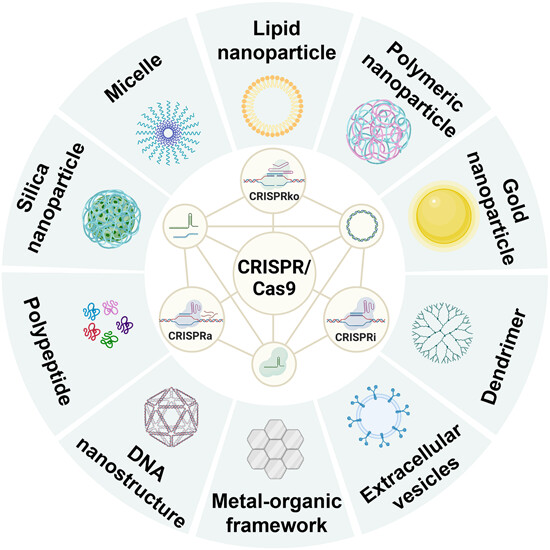
Schematic of the clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats (CRISPR)/CRISPR associated protein 9 (Cas9) system and its nanotechnology delivery methods. The CRISPR/Cas9 system can be delivered in the forms of DNA, mRNA/sgRNA, or ribonucleoprotein (RNP). The gene editing tools based on CRISPR/Cas9 include CRISPR knockout (CRISPR KO), CRISPR interference (CRISPRi) and CRISPR activation (CRISPRa). Lipid nanoparticles, polymers, inorganic compounds, polypeptide, dendrimers, and extracellular vesicles are the most often employed substances for CRISPR/Cas9 system delivery. Created with Biorender.com.
LETTER
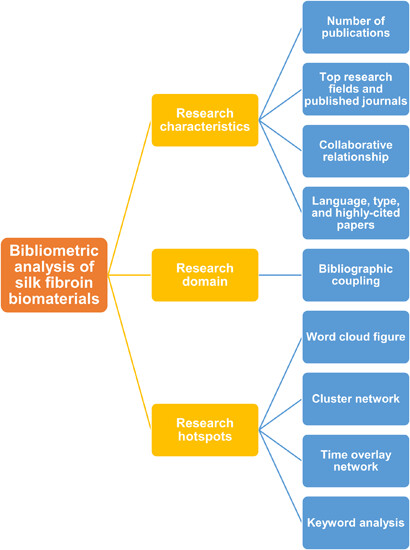
Research progress of silk fibroin biomaterials: A bibliometric analysis from 2012 to 2022
- First Published: 06 January 2024