Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
High glutamine increases stroke risk by inducing the endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition in moyamoya disease
- First Published: 15 April 2024
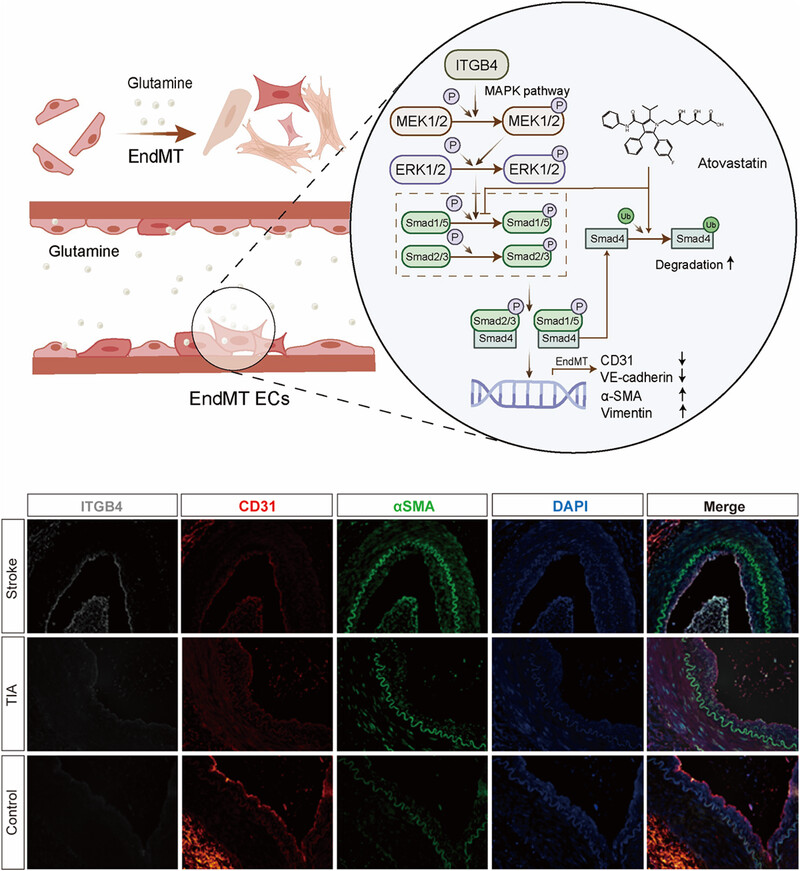
Glutamine levels were positively associated with a greater risk of stroke (OR = 1.599, p = 0.022). After treatment with glutamine, HBMECs exhibited enhanced proliferation, migration, and EndMT, all reversed by ITGB4 knockdown. In ITGB4-transfected HBMECs, the MAPK–ERK–TGF–β/BMP pathway was activated, with Smad4 knockdown reversing the EndMT. Furthermore, atorvastatin suppressed the EndMT by inhibiting Smad1/5 phosphorylation and promoting Smad4 ubiquitination in ITGB4-transfected HBMECs. Finally, ITGB4 upregulation was confirmed in the superficial temporal arteries of patients with MMD.
LETTER
Cardiomyogenic differentiation of an induced pluripotent stem cell line carrying PRKAG2 R302Q mutation
- First Published: 19 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Precise prediction of cerebrospinal fluid amyloid beta protein for early Alzheimer's disease detection using multimodal data
- First Published: 19 April 2024
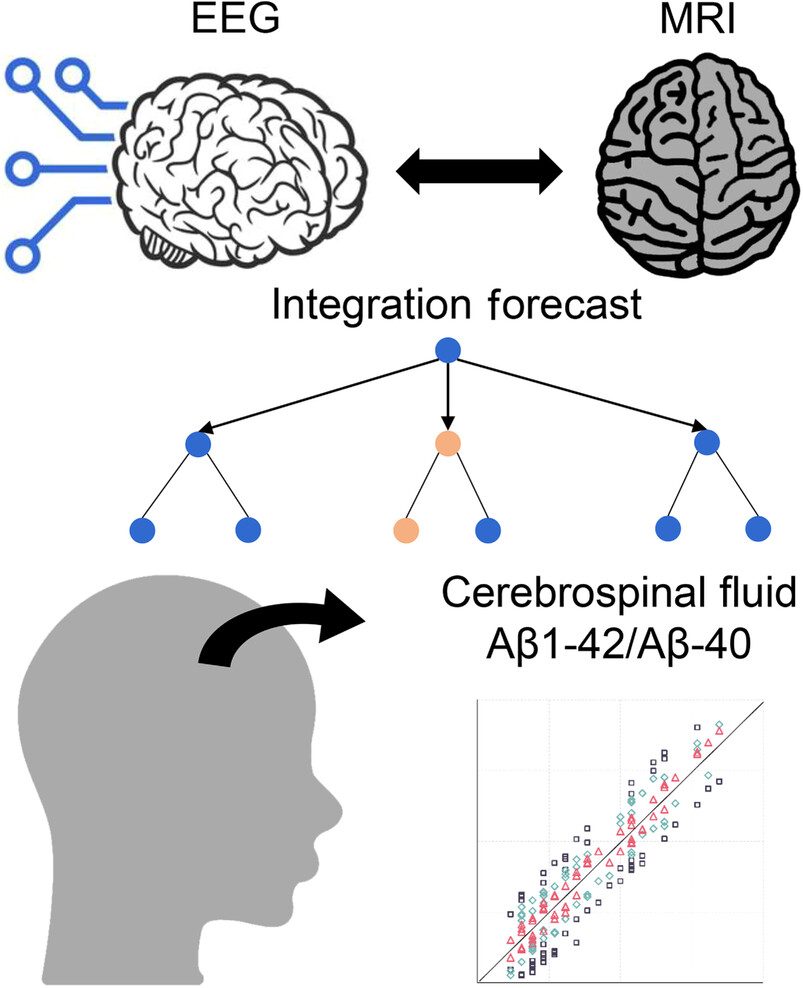
The diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease (AD) typically relies on costly and invasive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) markers, causing discomfort to patients. Sun et al. propose a cost-effective method for early detection that utilizes a random forest approach to accurately estimate the Aβ1-42/Aβ-40 content. The method is based on noninvasive techniques including EEG and MRI and was tested on a sample of 82 subjects, providing valuable diagnostic information.
Mechanism of Musashi2 affecting radiosensitivity of lung cancer by modulating DNA damage repair
- First Published: 21 April 2024
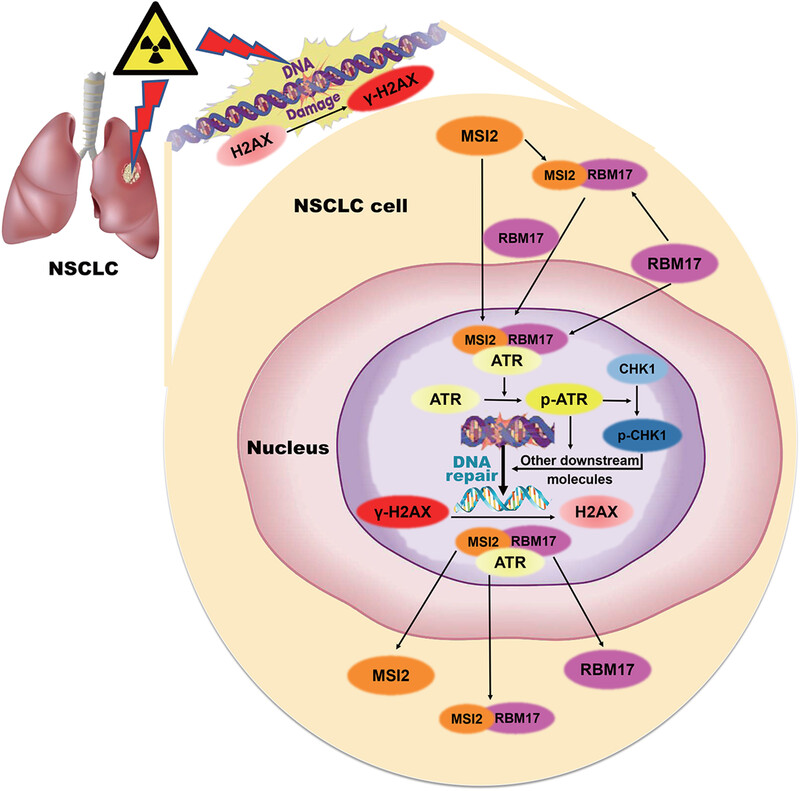
Scientific hypothesis: After radiation exposure, lung cancer cells undergo DNA damage, triggering RBM17 to sense signals. MSI2, assisted by RBM17, translocates into the nucleus, where it interacts with ATR and CHK1, activating downstream pathways. This activation enhances the DNA damage repair. Upon repair completion, MSI2 and RBM17 dissociate from ATR and exit the nucleus, returning to the initial state.
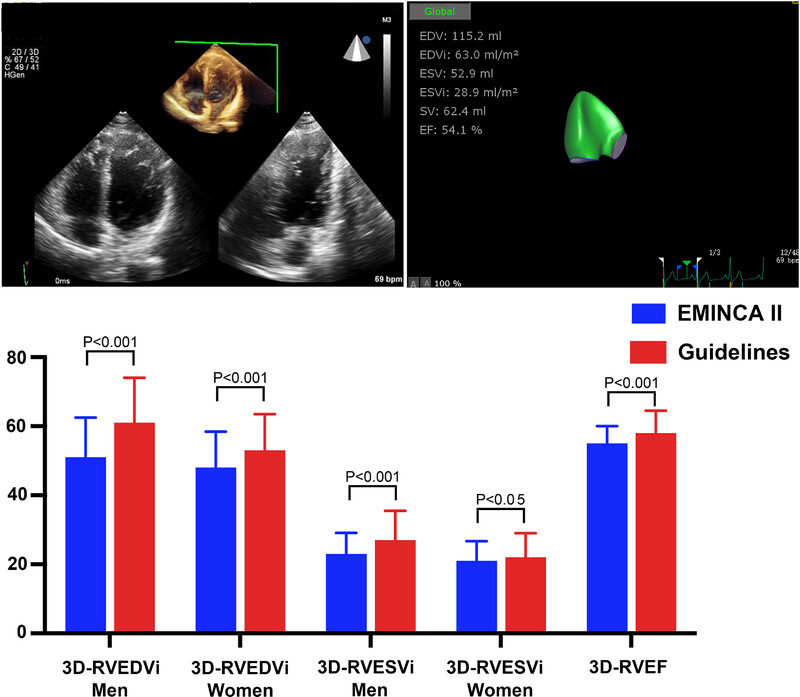
Right ventricular volume and function by three-dimensional echocardiography: results of the echocardiographic measurements in normal Chinese adults (EMINCA) II
- First Published: 21 April 2024
HIGHLIGHT
Deleting SUV39H1 in CAR-T cells epigenetically enhances the antitumor function
- First Published: 21 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
NFKB2 mediates colorectal cancer cell immune escape and metastasis in a STAT2/PD-L1-dependent manner
- First Published: 24 April 2024
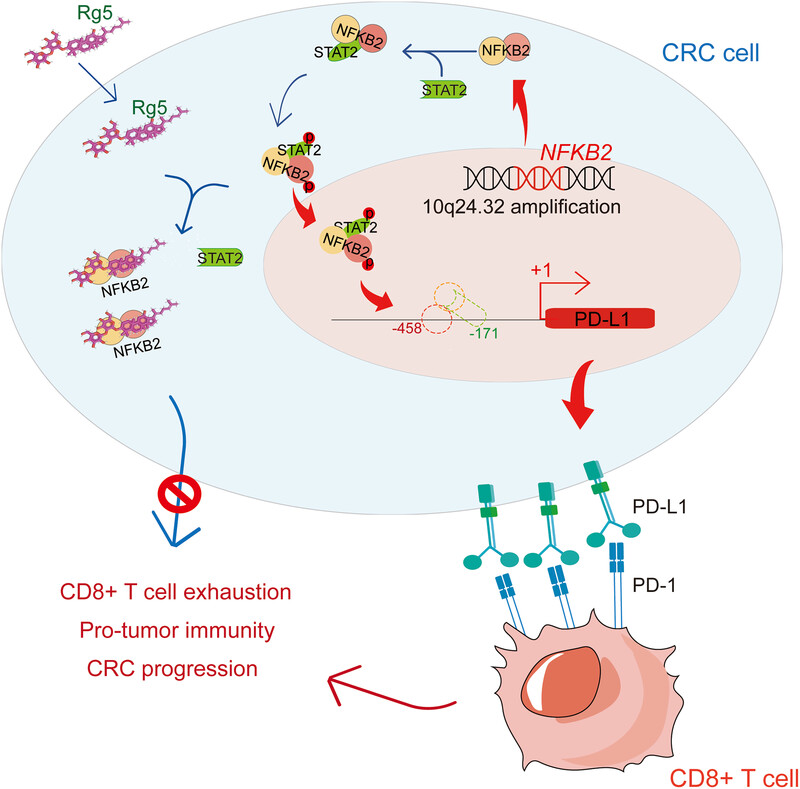
Amplification of 10q24.32 in CRC resulted in upregulation of NFKB2 protein levels, which directly interacts with STAT2, leading to STAT2 protein stabilization and phosphorylation, and consequently, further upregulating PD-L1. Rg5, a small-molecule inhibitor of NFKB2, could break the NFKB2-STAT2 interaction, with significant reduced PD-L1 expression and alleviated CD8+ T-cell exhaustion, leading to an enhanced sensitivity to PD-1 blockade-based immunotherapy.
REVIEWS
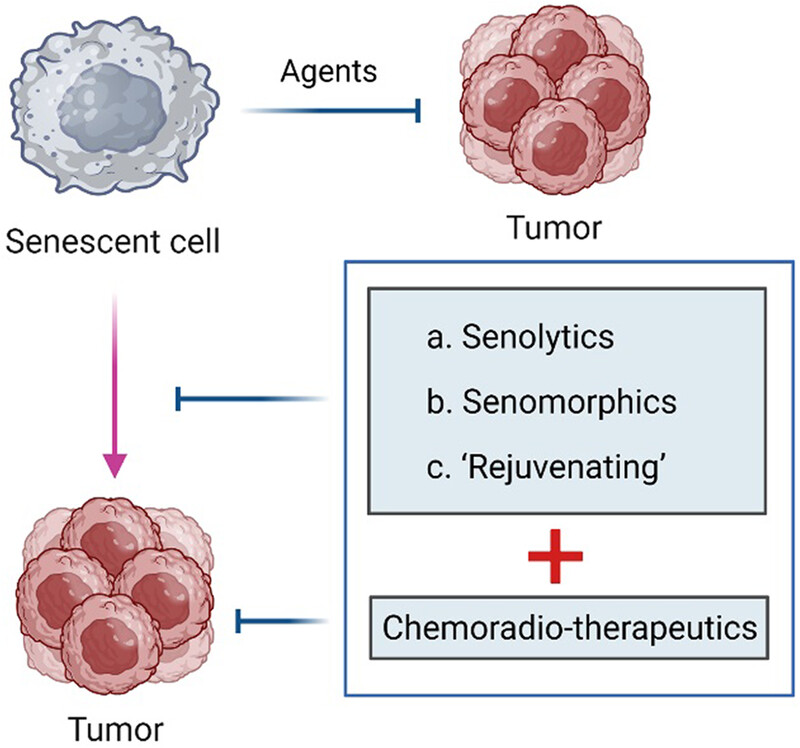
Cellular senescence in cancer: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic targets
- First Published: 24 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
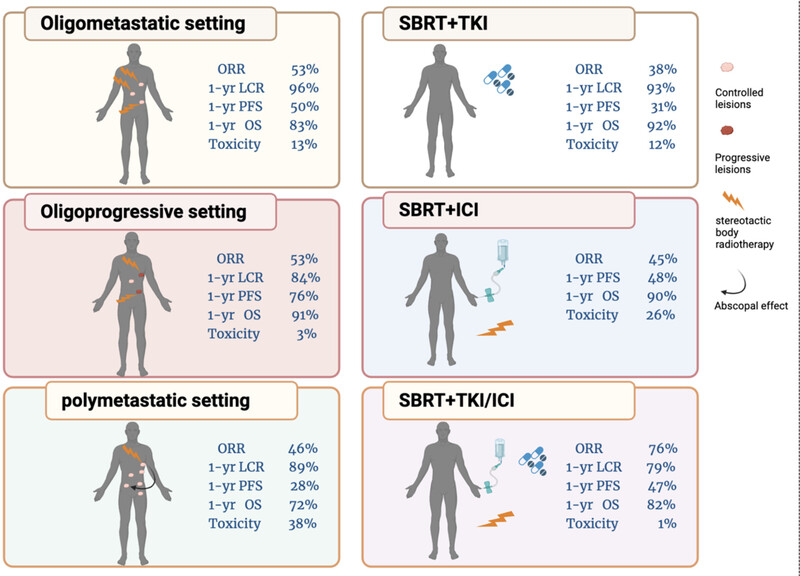
The efficacy and safety of stereotactic body radiotherapy combined with systematic therapy for metastatic renal cell carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- First Published: 24 April 2024
Mineral crude drug mirabilite (Mangxiao) inhibits the occurrence of colorectal cancer by regulating the Lactobacillus–bile acid–intestinal farnesoid X receptor axis based on multiomics integration analysis
- First Published: 25 April 2024
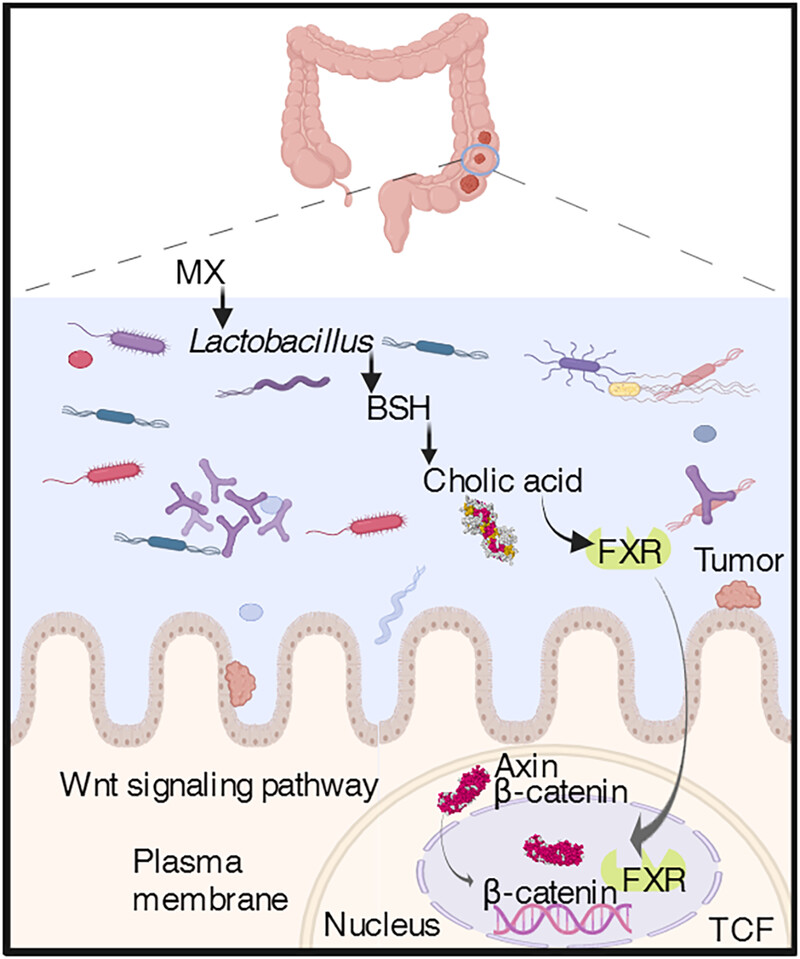
We found that Mangxiao (MX) was a unique mineral medicine that was effective in prevention and cure colorectal cancer. It was first time to find that MX could reshape the Lactobacillus–bile acid–FXR axis, thereby inhibiting the occurrence and development of CRC. The bacterial-targeted approach to control CRC provided a basis for the development of unique anticolorectal cancer drugs.
HIGHLIGHTS
S-adenosyl methionine-AMP opens another skylight of CRISPR system: discovering novel second messenger for bacterial antiviral immunity
- First Published: 27 April 2024
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
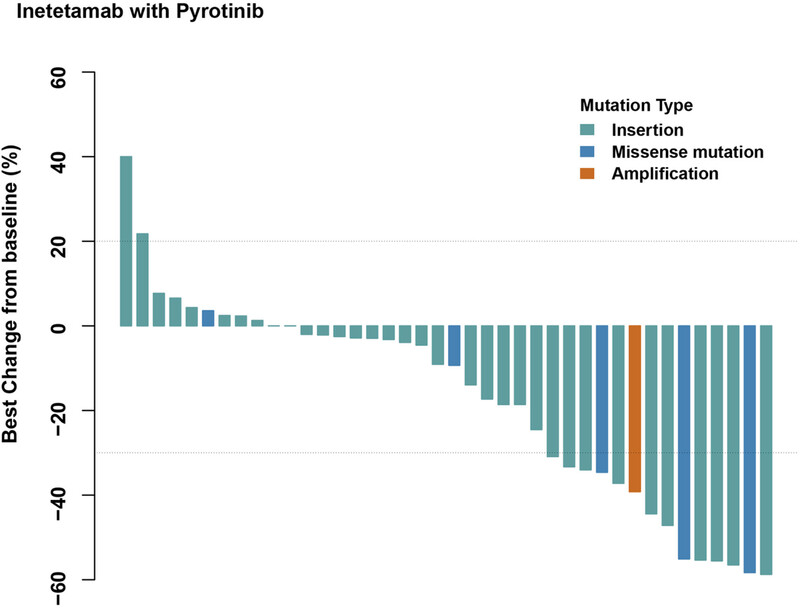
Phase 1b trial of anti-HER2 antibody inetetamab and pan-HER inhibitor pyrotinib in HER2-positive advanced lung cancer
- First Published: 29 April 2024
A chimeric adenovirus-vectored vaccine based on Beta spike and Delta RBD confers a broad-spectrum neutralization against Omicron-included SARS-CoV-2 variants
- First Published: 27 April 2024
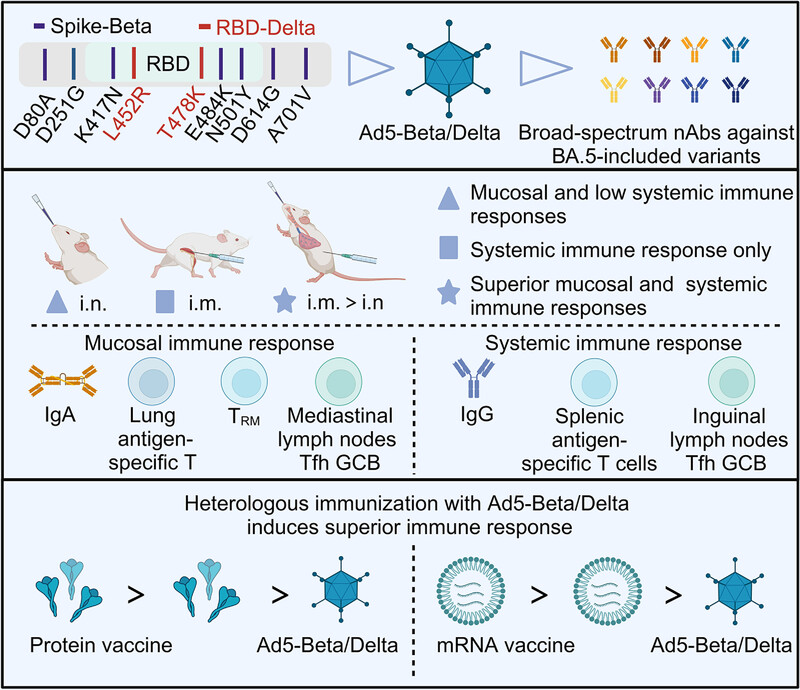
A chimeric adenovirus-vectored vaccine named Ad5-Beta/Delta was developed by introducing the RBD derived from the Delta variant (containing L452R and T478K) into the full-length spike protein of Beta variant. Immunization with Ad5-Beta/Delta induces broad-spectrum neutralizing activities against BA.5-included SARS-CoV-2 subvariants. Combination of intramuscular and intranasal delivery of Ad5-Beta/Delta induces superior systemic and mucosal immune responses. In addition, Ad5-Beta/Delta as a booster shot is able to elicit stronger protective immunity in heterologous vaccination after two injections of mRNA- and subunit protein-based vaccines.
REVIEWS
Toll-like receptors in health and disease
- First Published: 29 April 2024
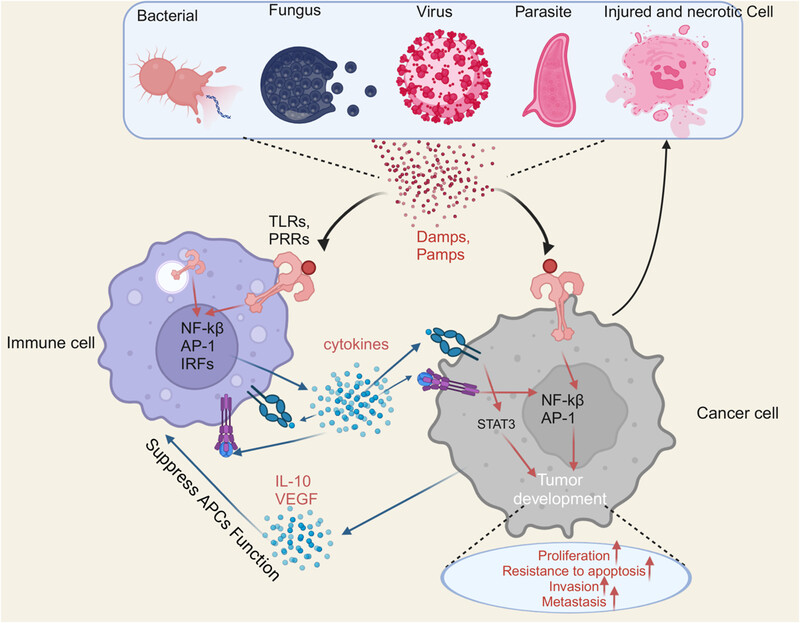
Interactions of TLRs with inflammation and tumor. TLRs are expressed on a variety of cells, including tumor cells and immune cells. TLRs signaling is involved in the carcinogenesis of the tumor microenvironment. TLRs expressed on immune cells and tumor cells are subjected to activation by pathogen-associated molecular patterns,damage-associated molecular patterns from microorganisms, viruses, parasites, injured and necrotic cancer cells. The release of cytokines and chemokines by these activated cells is an important part of the tumor microenvironment. Moreover, cytokine-activated infiltrating immune cells can subsequently induce additional cytokines that impair the function of antigen-presenting cells, leading to tumor immune tolerance.
RNA modifications in pulmonary diseases
- First Published: 03 May 2024
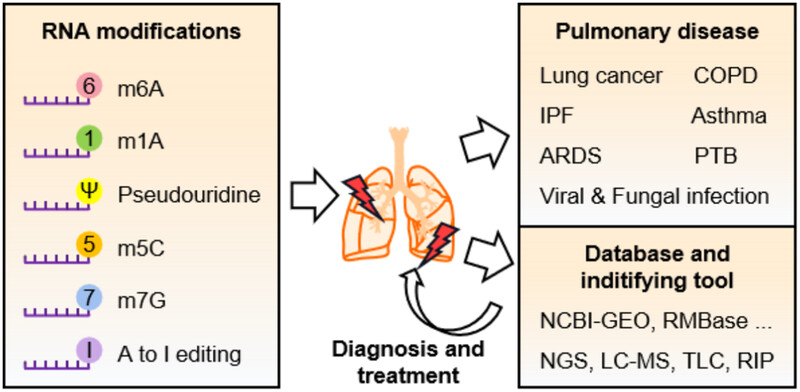
This review presents the crucial involvement of RNA epigenetic modifications (m6A, m1A, m5C, Ψ, m7G, and A-to-I editing) in pulmonary diseases, spanning chronic conditions to lung cancer. Focusing on their impact on disease regulation as promising biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Additionally, essential databases and tools are summarized, fostering insights for clinical research of pulmonary disease to improve diagnosis and treatment. m6A, N6-methylation of adenosine; m1A, N1-methylation of adenosine; m5C, 5-methylcytosine; Ψ, pseudouridine; m7G, 7-methylguanosine; A-to-I, adenosine to inosine; COPD, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; IPF, interstitial lung disease, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; ARDS, acute respiratory distress syndrome; PTB, pulmonary tuberculosis; RMBase, RNA Modification Base Database; NGS, next-generation sequencing; LC–MS, liquid chromatography mass spectrometer; TLC, thin layer chromatography; RIP, RNA immunoprecipitation.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
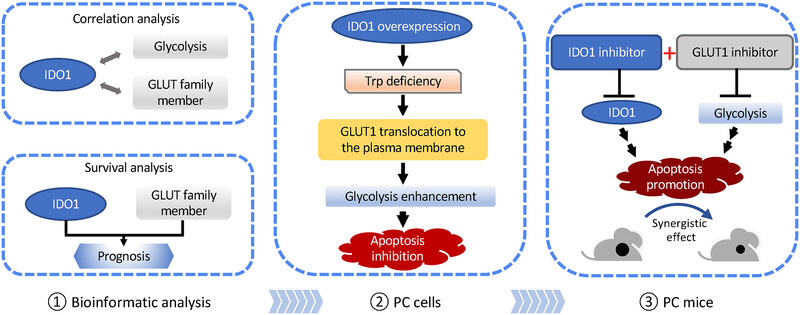
Tryptophan deficiency induced by indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1 results in glucose transporter 1-dependent promotion of aerobic glycolysis in pancreatic cancer
- First Published: 03 May 2024
HIGHLIGHT
KEYNOTE-811: Potential to revise first-line therapy for metastatic human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive gastric cancer
- First Published: 07 May 2024
REVIEWS
Critical roles and clinical perspectives of RNA methylation in cancer
- First Published: 07 May 2024
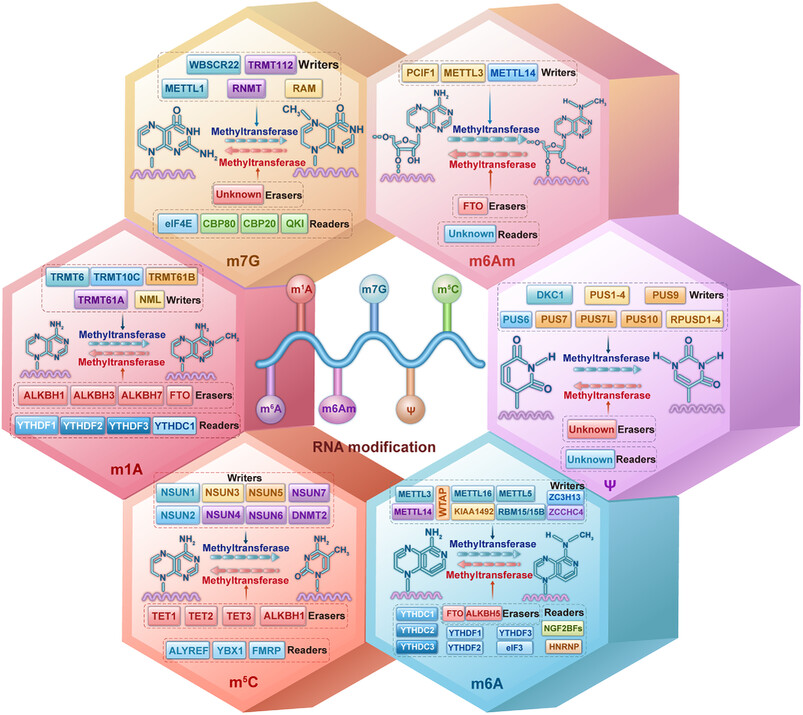
Overview of the mechanisms of m6A, m1A, m6Am, m7G, Ψ, and m5C regulation. RNA methylation is a dynamically reversible process that is modulated by methyltransferases (writers), demethylases (erasers), and recognition factors (readers). Under the regulation of these regulatory factors, RNA undergoes various RNA methylation modifications.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
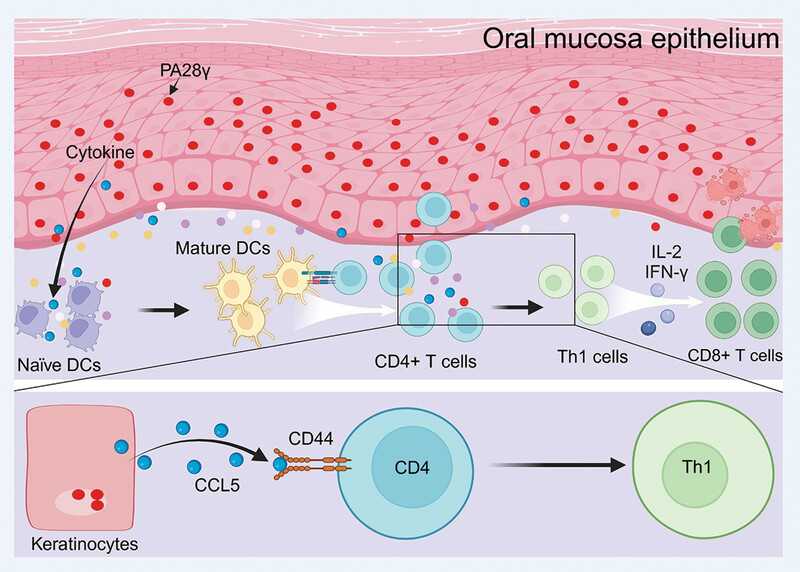
PA28γ induces dendritic cell maturation and activates T-cell immune responses in oral lichen planus
- First Published: 08 May 2024
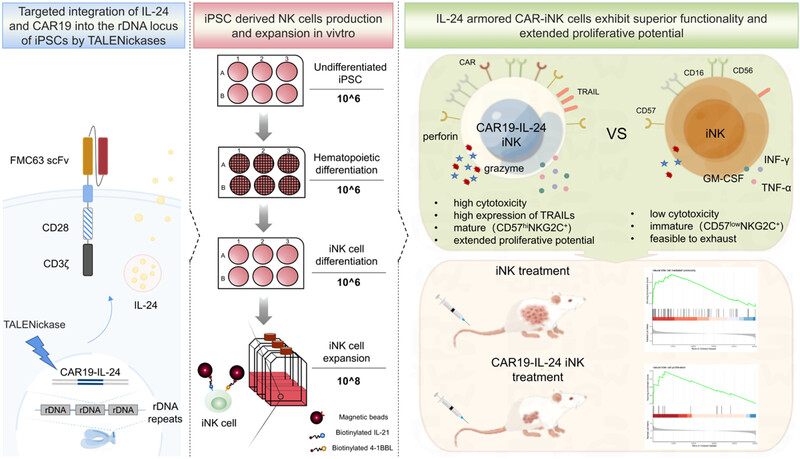
iPSC-derived NK cells with site-specific integration of CAR19 and IL24 at the multi-copy rDNA locus enhanced antitumor activity and proliferation
- First Published: 09 May 2024
Half-life extension of single-domain antibody–drug conjugates by albumin binding moiety enhances antitumor efficacy
- First Published: 09 May 2024
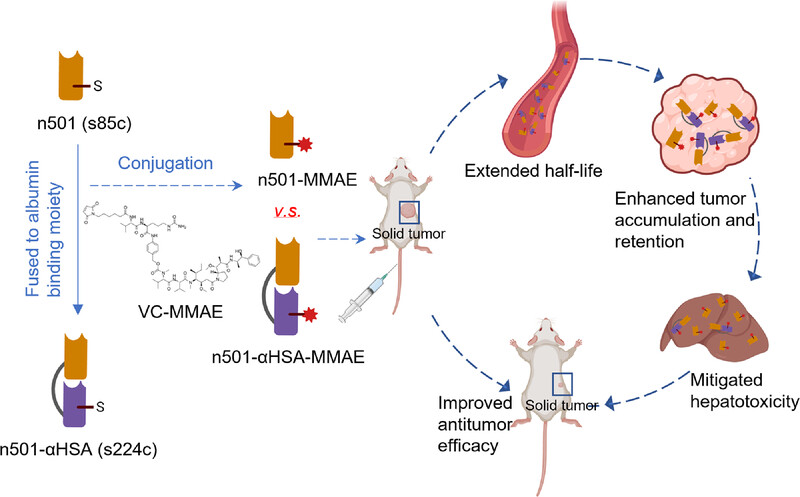
We innovatively fused an antihuman serum albumin nanobody to a single-domain antibody–drug conjugates targeting oncofetal antigen 5T4, conferring serum albumin binding, exhibiting a 10-fold extended half-life and enhanced tumor accumulation and retention in mice. Consequently, it demonstrated significantly improved antitumor efficacy in tumor xenografts despite less frequent dosing with mitigated hepatotoxicity.
Interleukin-33 increases the sensitivity of multiple myeloma cells to the proteasome inhibitor bortezomib through reactive oxygen species-mediated inhibition of nuclear factor kappa-B signal and stemness properties
- First Published: 09 May 2024
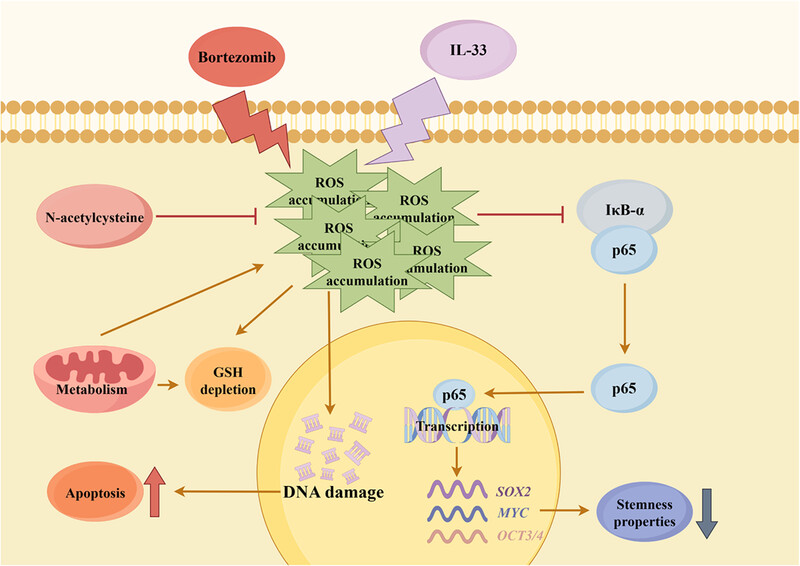
Bortezomib and IL-33 synergistically resulted in excessive accumulation of cellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) and depletion of glutathione (GSH), which in turn damaged DNA and ultimately triggered cell death. In addition, ROS overproduction hindered the nuclear translocation of NF-κB-p65, thereby decreasing the transcription levels of target stemness-related genes (SOX2, MYC, and OCT3/4). ROS elimination by N-acetylcysteine intervention can reverse the inhibition of nuclear factor kappa-B (NF-κB) activity and its transcriptional targets.
Associations of essential metals with the risk of aortic arch calcification: a cross-sectional study in a mid-aged and older population of Shenzhen, China
- First Published: 13 May 2024

This study aimed to evaluate the relationships between essential metal levels and aortic arch calcification (AoAC) risk in a mid-aged and older population of Shenzhen, China. The results showed that plasma levels of five essential metals were associated with AoAC and showed combined effect. Blood glucose played a significant role in mediating Mn exposure-associated AoAC risks.
Transcription factor EHF drives cholangiocarcinoma development through transcriptional activation of glioma-associated oncogene homolog 1 and chemokine CCL2
- First Published: 13 May 2024
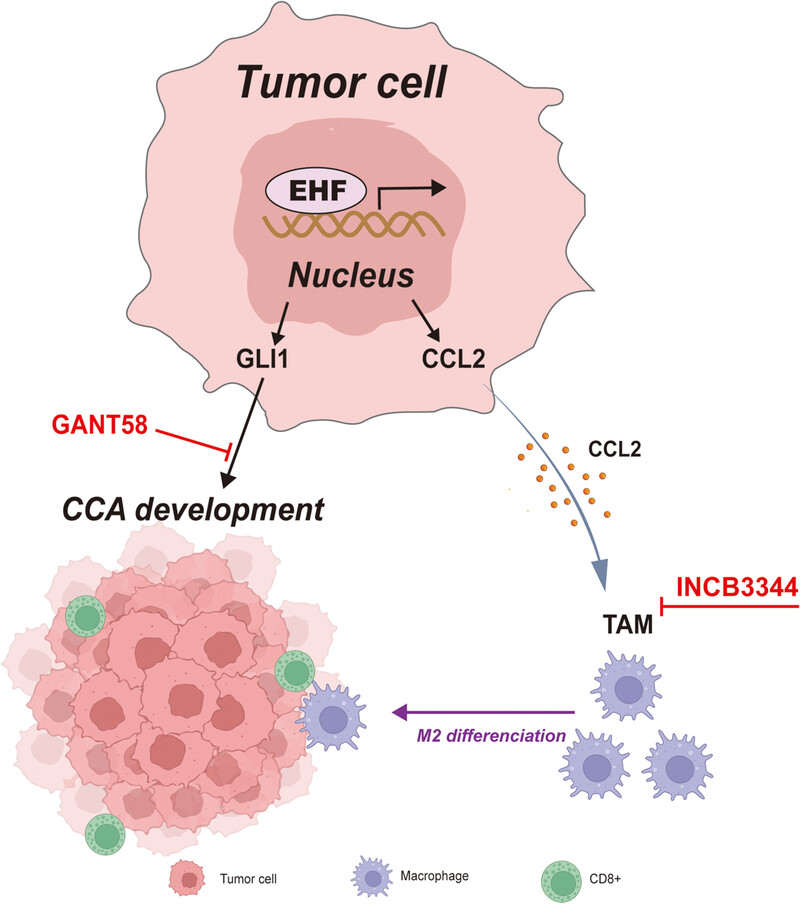
EHF plays a crucial role in promoting cholangiocarcinoma (CCA) by activating GLI1 transcription. Additionally, EHF proficiently recruits and activates tumor-associated macrophages via the CCL2/CCR2 axis, leading to tumor microenvironment remodeling. Furthermore, the strategic combination of GANT58 (a GLI1 inhibitor) and INCB3344 (a CCR2 inhibitor) significantly reduces EHF-driven CCA occurrence.
HIGHLIGHTS
Neoadjuvant immunotherapy: new horizon for lymph node preservation
- First Published: 13 May 2024