Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Criteria for judging the immune markers of COVID-19 disease vaccines
- First Published: 31 December 2021
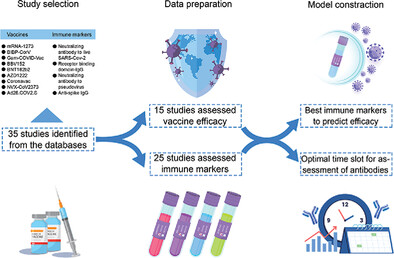
We evaluated different Abs and assessment times for coronavirus disease vaccines. We found anti-spike immunoglobulin G (IgG) may best estimate the vaccine efficacy and neutralizing Ab to live severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) also explained a fine relationship. The peak time of different Abs in messenger RNA virus was later than that in inactivated virus vaccines, and receptor-binding domain-IgG peaked earlier than Ab to live SARS-CoV-2.
Differential expression of inhibitory receptor NKG2A distinguishes disease-specific exhausted CD8+ T cells
- First Published: 10 January 2022
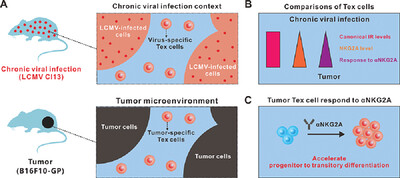
In the study, we profiled the inhibitory receptors (IRs) of exhausted CD8+ T (Tex) cells recognizing the same epitope but developed in distinct diseases. We found Tex cells derived from tumor show remarkably higher NKG2A expression than Tex cells derived from chronic viral infection. Blocking NKG2A augments the progenitor to transitory differentiation of tumor Tex cells, accompanied by reinforced effector function and increased proliferation.
Structural insights into the catalytic and inhibitory mechanisms of the flavin transferase FmnB in Listeria monocytogenes
- First Published: 10 January 2022
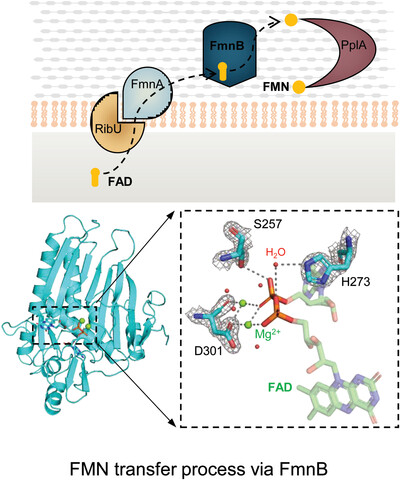
Flavin transferase FmnB is a key protein of the extracellular electron transfer pathway in Listeria monocytogenes, which can hydrolyze flavin adenine dinucleotide and transfer flavin mononucleotide. We analyzed the apo form of the enzyme and the complex structure of the binding substrate, as well as the complex structures of the binding three inhibitors, and identified key residues that affect enzyme activity.
SARS-CoV-2 triggered oxidative stress and abnormal energy metabolism in gut microbiota
- First Published: 17 January 2022
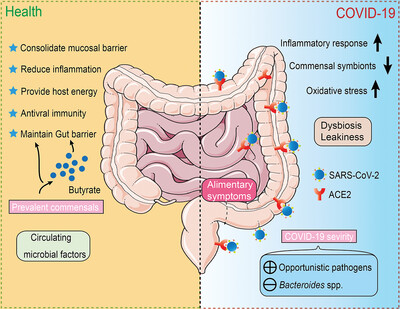
The gut microbiota of COVID-19 patients showed upregulation of oxidative stress and inflammation response, accompanied by depletion of symbiotic bacteria. The abundance of Bacteroides spp. is negatively correlated with disease severity, while the accumulation of opportunistic pathogens may exacerbate the progression of COVID-19. Healthy intestinal flora may enhance the organic defense against SARS-CoV-2 virus infection through butyrate metabolism.
REVIEWS
Recent advances and application of whole genome amplification in molecular diagnosis and medicine
- First Published: 03 February 2022
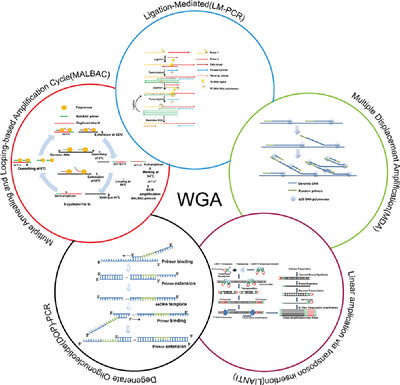
Whole genome amplification (WGA) is a technology for non-selective amplification of the whole genome sequence. This paper reviews WGA methods based on different principles, summarizes both amplification principle and amplification quality, and discusses the application prospects and challenges of WGA technology in molecular diagnosis and medicine.
Graphene and graphene oxide with anticancer applications: Challenges and future perspectives
- First Published: 09 February 2022
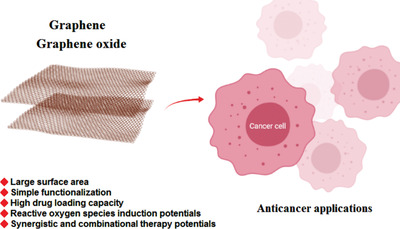
Important challenges, recent advancements, and future perspectives for deploying graphene- and graphene oxide-based nanosystems in cancer therapy are deliberated. Notably, large surface area, ease of functionalization, high drug loading capacity, and reactive oxygen species induction potentials have rendered these structures promising candidates for cancer therapy applications. The ease of functionalization bodes well for their utility in treating assorted types of cancers.
PERSPECTIVES
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: A next phase of the COVID-19 pandemic and a call to arms for system sciences and precision medicine
- First Published: 11 February 2022
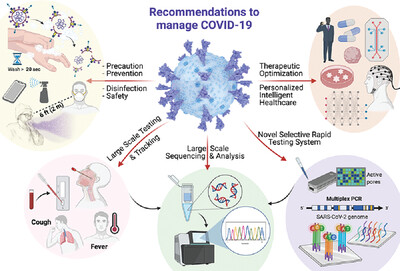
In this perspective, the authors first discussed the Omicron's origin, mutations, structure, pathogenesis, and its impact on human health while comparing it with the previous variant of concerns (VOCs). System science and precision medicine are introduced by employing Artificial Intelligence (AI), big data reservoirs, bioinformatic systems, advanced in vitro 3D models, and subtypes sciences to diagnose and eradicate the Omicron virus. Experts’ recommendations to successfully manage Omicron-SARS-CoV-2 variant are also provided.
REVIEWS
COVID-19: A systematic review and update on prevention, diagnosis, and treatment
- First Published: 17 February 2022
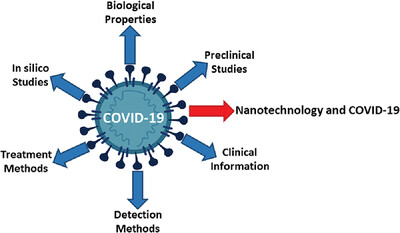
This review covers almost all topics related to SARS-CoV-2, including biological properties, pre-clinical studies, clinical information, diagnostic and treatment methods, and in silico studies, which is very useful for a quick understanding of the latest advances in this field. Also, in a separate section, the applications of nanotechnology in COVID-19 studies are examined.
ORIGINAL ARTICLES
Low hemoglobin is associated with worse outcomes via larger hematoma volume in intracerebral hemorrhage due to systemic disease
- First Published: 23 February 2022
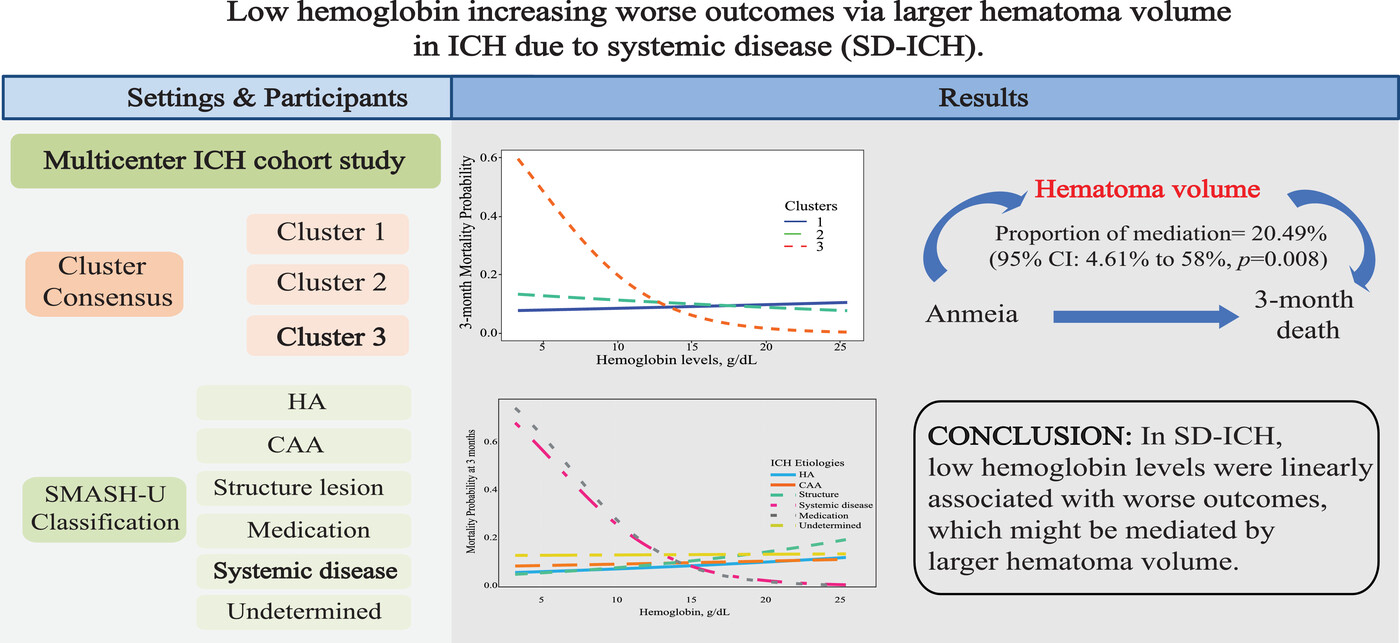
In this paper, we have analyzed 4643 ICH patients in a prospective multicenter cohort study. We employed both the unsupervised consensus cluster method and the SMASH-U etiologies scheme to classify the ICH patients. We found that, in both statistical and clinical classification system, low hemoglobin levels were linearly and consistently associated with 1-month survival (adjusted hazard ratio [HR] 7.93, 95% CI 2.20–28.60, p = 0.002) and 3-month death (aOR 0.75, 95% CI 0.60–0.92; p = 0.009) in patients of SD-ICH subtype. Moreover, the mediation analysis revealed that associations between lower hemoglobin with poor outcomes were partially mediated by baseline hematoma volume (p = 0.008).
Measuring image distortions arising from age-related macular degeneration: An Iterative Amsler Grid (IAG)
- First Published: 04 March 2022
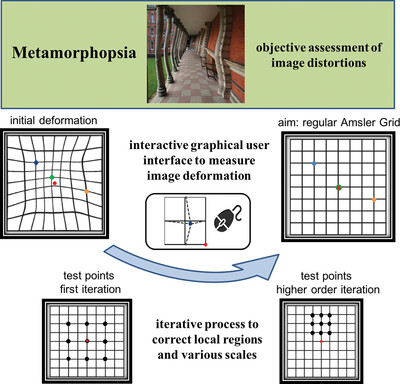
We developed an objective method, where using an interactive graphical user interface, participants dragged the intersection point of a cross-like grid element to the center of the reference square (with different size for different iterations), with the goal to correct deviations from the ideal Amsler Grid. In healthy participants, we verified it to generate quantitative measures of image deformations as experienced in AMD patients. This has the potential to inform future clinical application to assess AMD and guiding interventions, going beyond subjective patient reports.
Tyrosine phosphatase SHP2 exacerbates psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via ERK5-dependent NETosis
- First Published: 04 March 2022
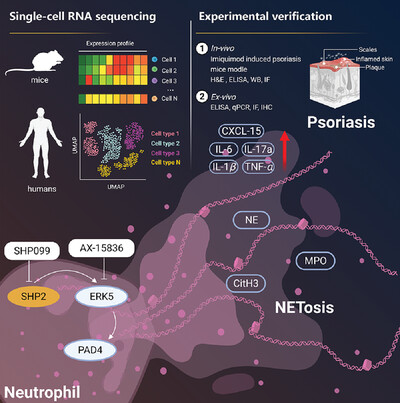
Single-cell RNA sequencing and experimental verification were combined to announce that SHP2 aggravates psoriasis-like skin inflammation in mice via ERK5-dependent NETosis. During this process, inflammatory cytokines: TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17a, and CXCL-15 were infiltrated in skin and contributed to psoriasis. Our study provides evidence for the role of SHP2 in NETosis and psoriasis. SHP2 may be a potential therapeutic target for the treatment of psoriasis.
REVIEWS
Trained immunity: A Yin-Yang balance
- First Published: 06 March 2022
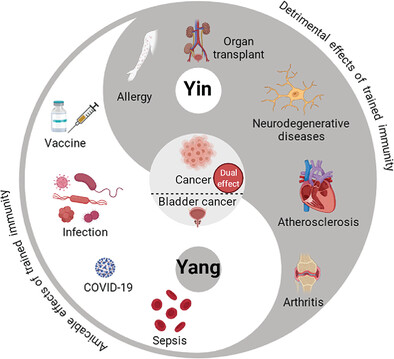
Trained immunity, a de facto innate immune memory, is defined as a long-term functional reprogramming of cells of the innate immune system. The dual effect of trained immunity is consistent with the Yin-Yang theory in traditional Chinese philosophy. The Yin-Yang aspects of trained immunity provide an opportunity to treat inflammatory, infectious, and autoimmune diseases by optimizing innate immune memory.
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Epidemic waves caused by SARS-CoV-2 omicron (B.1.1.529) and pessimistic forecasts of the COVID-19 pandemic duration
- First Published: 09 March 2022
REVIEWS
SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant: Immune escape and vaccine development
- First Published: 16 March 2022
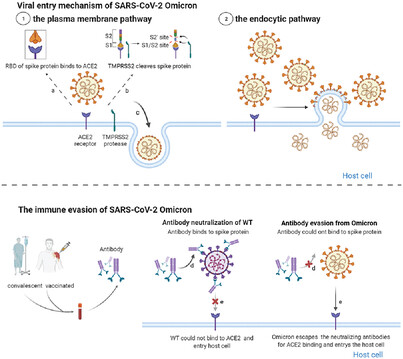
Omicron (B.1.1.529), the latest variant of concern, is partially resistant to the neutralizing activity of therapeutic antibodies and convalescent sera, which poses significant challenges for the clinical effectiveness of the current vaccines and therapeutic antibodies. We provide a comprehensive analysis and summary of the epidemiology and immune escape mechanisms of the Omicron variant. We also suggest some therapeutic strategies against the Omicron variant.















