Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
FLUIDOT: A Modular Microfluidic Platform for Single-Cell Study and Retrieval, with Applications in Drug Tolerance Screening and Antibody Mining (Small Methods 3/2023)
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Front Cover
In article number 2201477, Lammertyn and co-workers developed FLUIDOT, a modular microfluidic platform in which microwells, optical tweezers, and an interchangeable cell-retrieval system are combined to enable in-depth screening and specific retrieval of single cells. They demonstrated the versatility of FLUIDOT by implementing applications in drug tolerance screening and antibody mining. The cover was designed by Jorik Waeterschoot.
Inside Front Cover
Stable and Ordered Body-Centered Cubic PdCu Phase for Highly Selective Hydrogenation (Small Methods 3/2023)
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Inside Front Cover
In article number 2201356, Pi, Bai, Xu, and co-workers show that body-centered cubic (bcc) PdCu can serve as selectivity controllers for selective hydrogenation of 3-nitrostyrene. Product selectivity can be precisely adjusted by changing the hydrogen source. H2 dissociates to form *H on bcc-PdCu, which preferentially reacts with CC to form 3-nitro-ethylbenzene with 93.8% selectivity. Bcc-PdCu catalyzes the reaction of NH3·BH3 and –NO2 to produce 3-amino-styrene with 94.5% selectivity.
Inside Back Cover
Low-Power, Multi-Transduction Nanosensor Array for Accurate Sensing of Flammable and Toxic Gases (Small Methods 3/2023)
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Inside Back Cover
In article number 2201352, Lee, Park, and co-workers demonstrated a low-power, multi-transduction nanosensor array by integrating nanostructured materials on bridge-type microheaters for accurate gas sensing. By using various responses of the nanosensor array based on chemiresistive and calorimetric mechanisms, it is possible to accurately identify flammable and toxic gases in real-time.
Back Cover
Controllable Synthesis of Carbon Yolk-Shell Microsphere and Application of Metal Compound–Carbon Yolk-Shell as Effective Anode Material for Alkali-Ion Batteries (Small Methods 3/2023)
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Back Cover
In article number 2201370, Cho, Kang, Park, and co-workers proposed a novel synthesis strategy for a nanostructured carbon yolk-shell microsphere that allows for the control of morphology and size of the yolk part for the first time. The prepared carbon yolk-shell microsphere was utilized as an effective reservoir for ultrafine metal compound nanocrystals. This rational synthesis strategy could be employed to further improve their application potential in various fields.
Masthead
Reviews
Electrocatalysis Mechanism and Structure–Activity Relationship of Atomically Dispersed Metal-Nitrogen-Carbon Catalysts for Electrocatalytic Reactions
- First Published: 15 January 2023

Atomically dispersed metal-nitrogen-carbon catalysts (M-N-C) have been widely used in the field of energy conversion. Electrocatalytic mechanism and structure–activity relationship play a vital role in the preparations and catalytic performance of M-N-C catalysts. In this review, the relative research methods are first introduced. Furthermore, clarifying the electrocatalytic mechanism and structure–activity relationship of M-N-C catalysts in different catalytic fields is in focus.
Noncrystalline Carbon Anodes for Advanced Sodium-Ion Storage
- First Published: 29 January 2023
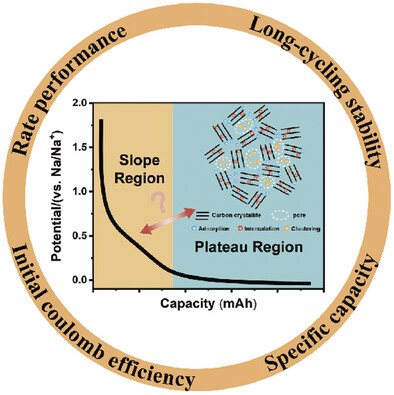
As an intensively studied anode material for sodium-ion batteries, noncrystalline carbon (NCC) has great potential and possibilities. Researchers have made in-depth studies of the sodium ions storage mechanisms in NCC these years. This article reviews the related literature and evaluates the relationship between sodium ion storage behaviors and carbon structure; and future prospects are also presented.
Research Articles
FLUIDOT: A Modular Microfluidic Platform for Single-Cell Study and Retrieval, with Applications in Drug Tolerance Screening and Antibody Mining
- First Published: 15 January 2023
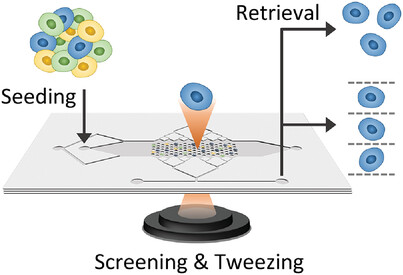
FLUIDOT is a versatile microfluidic platform in which microwells, optical tweezers, and an interchangeable cell-retrieval system are combined to enable in-depth screening, specific retrieval, and various downstream analyses of single cells. FLUIDOT enables phenotypic and genotypic analysis of diverse cell types, as demonstrated in a drug tolerance study on yeast cells and a mAb discovery trajectory from human B cells.
Stable and Ordered Body-Centered Cubic PdCu Phase for Highly Selective Hydrogenation
- First Published: 24 January 2023
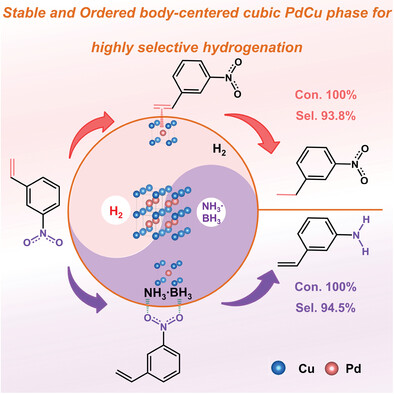
This study demonstrates that the ordered body-centered cubic phase of PdCu can serve as highly selective and active sites for 3-nitrostyrene hydrogenation to 3-nitro-ethylbenzene or 3-amino-styrene under mild conditions. Mechanism studies reveal the different selectivity is originated from the differences in surface (catalyst)-groups (reactants) interaction.
Low-Power, Multi-Transduction Nanosensor Array for Accurate Sensing of Flammable and Toxic Gases
- First Published: 24 January 2023
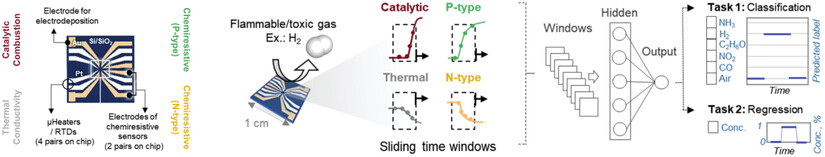
A low-power, multi-transduction nanosensor array is demonstrated by integrating nanostructured materials on bridge-type microheaters for accurate sensing of flammable and toxic gases. The nanosensor array operates based on chemiresistive and calorimetric mechanisms for enhanced selectivity. By applying transient responses of the nanosensor array to a convolutional neural network, it is possible to accurately identify flammable and toxic gases in real time.
Controllable Synthesis of Carbon Yolk-Shell Microsphere and Application of Metal Compound–Carbon Yolk-Shell as Effective Anode Material for Alkali-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 18 January 2023
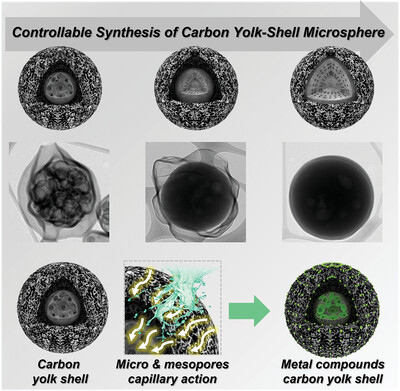
A novel synthetic strategy for nanostructured carbon yolk-shell microspheres that enables to control morphology and size of the carbon yolk in the microsphere is introduced. To the best of our knowledge, from hollow yolk-shell to dense core-shell structure with almost no empty space as a yolk gradually forms, a method to easily control the carbon nanostructure is proposed for the first time. The yolk-shell structured cobalt oxide-C, cobalt selenide-C showed good cycle performances and excellent rate capabilities for alkali-ion batteries.
Frontispiece
Theoretical Prediction of Thermoelectric Performance for Layered LaAgOX (X = S, Se) Materials in Consideration of the Four-Phonon and Multiple Carrier Scattering Processes (Small Methods 3/2023)
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Thermoelectric Performance
In article number 2201368, Tang and co-workers evaluated the thermoelectric performance of LaAgOX (X = S, Se) materials in consideration of four-phonon and multiple carrier scattering mechanisms. It is crucial for the rational design of state-of-the-art heteroanionic materials for thermoelectric applications.
Research Articles
Theoretical Prediction of Thermoelectric Performance for Layered LaAgOX (X = S, Se) Materials in Consideration of the Four-Phonon and Multiple Carrier Scattering Processes
- First Published: 15 January 2023
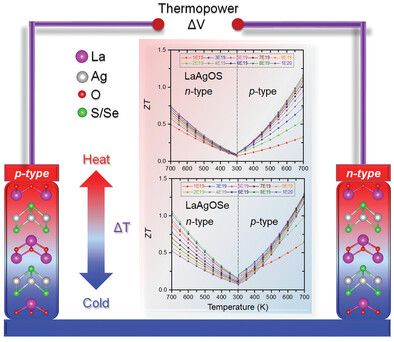
The crystal structure, electronic and phonon transport, and thermoelectric properties of layered LaAgOX (X = S, Se) are systematically analyzed using the first principles calculations. The optimal figure-of-merit ZTs of p-type LaAgOS and LaAgOSe are ≈1.16 and ≈1.29 at 700 K, which is comparable to most of the state-of-the-art thermoelectric materials.
Frontispiece
Highly Sensitive Detection of Complicated Mutations of Drug Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using a Simple, Accurate, Rapid, and Low-Cost Tailored-Design Competitive Wild-Type Blocking Assay (Small Methods 3/2023)
- First Published: 13 March 2023

Highly Sensitive Detection
In article number 2201322, Xu, Xu, Ying, and co-workers established a high-sensitive tailored-design competitive wild-type blocking assay for detecting as low as 1% complicated mutations of drug resistance in mycobacterium tuberculosis and its excellent sensitivity and specificity was validated on actual clinical samples. The simplicity, accuracy, rapidity, and low cost of the assay allow for great potential for clinical application, especially in high tuberculosis burden countries.
Research Articles
Highly Sensitive Detection of Complicated Mutations of Drug Resistance in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using a Simple, Accurate, Rapid, and Low-Cost Tailored-Design Competitive Wild-Type Blocking Assay
- First Published: 22 January 2023
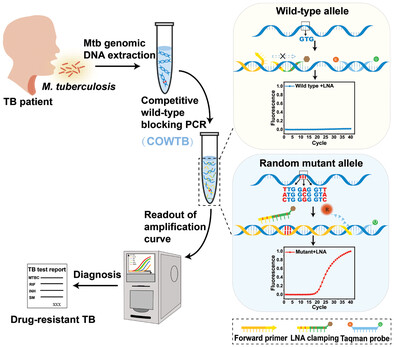
A tailored-design competitive wild-type blocking (COWTB) assay is established for highly sensitive detection of 1% or even 0.1% mutant ratio in drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis. The sensitivity of COWTB assay is 93.8% for rifampicin and 100% for isoniazid and streptomycin, and specificity is 100% each for the three antituberculosis drugs when evaluating 92 clinical samples on conventional polymerase chain reaction platform.
KOH-Enabled Axial-Oxygen Coordinated Ni Single-Atom Catalyst for Efficient Electrocatalytic CO2 Reduction
- First Published: 05 January 2023
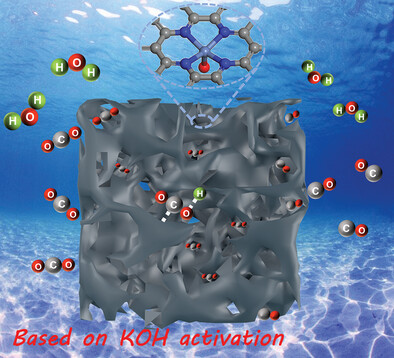
Based on multirole KOH activation strategy, hierarchically porous Ni single-atom catalysts with axial-oxygen coordination are constructed. Detailed mechanistic study reveals the role of axial-oxygen as an electronic modulator of Ni center, to facilitate the formation of *COOH intermediates and desorption of *CO.
Inflammatory Cell-Inspired Cascade Nanozyme Induces Intracellular Radical Storm for Enhanced Anticancer Therapy
- First Published: 06 January 2023
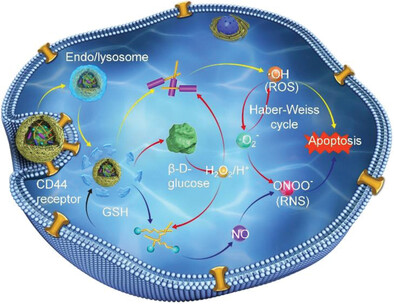
Glucose oxidase-templated nanozyme prepared via inverse microemulsion polymerization is designed to induce intracellular radical storm for enhanced anticancer therapy. Upon targeted internalization into tumor cells, the nanozyme triggers cascaded reactions including reduction-responsive nanozyme dissociation, GOx-catalyzed H2O2/H+ production, and arginine- and ferrocene-mediated reactive oxygen and nitrogen species generation, thus provoking pronounced anticancer efficacy.
Engineered Cell Membrane Vesicles Expressing CD40 Alleviate System Lupus Nephritis by Intervening B Cell Activation
- First Published: 05 January 2023
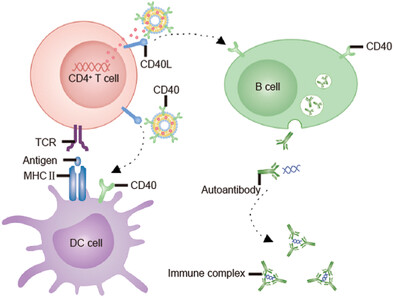
Genetically engineered cell membrane vesicles displaying CD40 can blunt B cells through disrupting the CD4+ T/B cell interaction. Thus, CD40 nanovesicles can restrain the generation of the germinal center structure and production of antibody from B cells. Moreover, immuno-suppressive drug encapsulated in the vesicles can achieve combined therapy. Overall, an engineered biomimetic vesicle is developed to alleviate lupus nephritis by bluntinvvg B cells.
Photochemically Etching BiVO4 to Construct Asymmetric Heterojunction of BiVO4/BiOx Showing Efficient Photoelectrochemical Water Splitting
- First Published: 05 January 2023
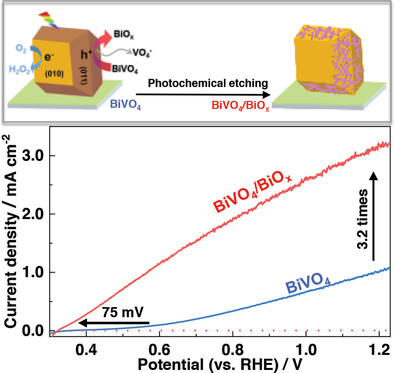
A photochemical etching process is developed to produce an asymmetric BiVO4/BiOx homologous heterojunction photoanode from a faceted BiVO4 crystal arrays, achieving an over three times enhancement on short-circuit photocurrent density and 75 mV enlargement on open-circuit voltage due to the formation of the strong p–n junction in its interface region, which promotes carrier separation and enlarges photovoltage.
Hydrogel Electrolyte with High Tolerance to a Wide Spectrum of pHs and Compressive Energy Storage Devices Based on It
- First Published: 06 January 2023
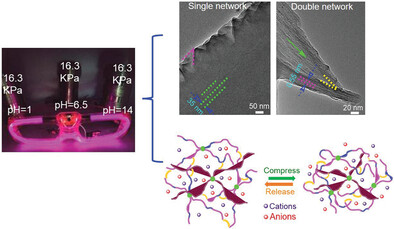
Dual crosslinking network hydrogel electrolyte comprising poly(sulfobetaine methacrylate) exhibits advantages of excellent mechanical capability in a wide spectrum of pHs. Superior compressible performance of the hydrogel electrolytes in the wide spectrum of pHs endows the various energy storage devices with excellent antideformation especially anticompressing performances in practical applications.
Structure Design for Ultrahigh Power Density Proton Exchange Membrane Fuel Cell
- First Published: 06 January 2023
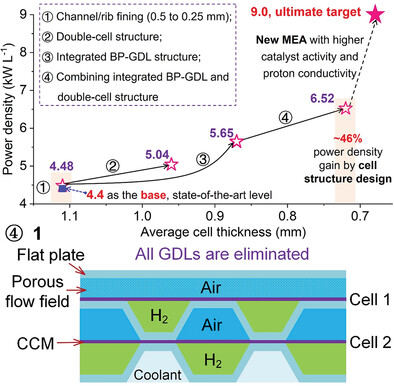
The cell structure combining fine channel/rib, gas diffusion layer elimination and double-cell structure is believed to increase the power density of proton exchange membrane fuel cell from 4.4 to 6.52 kW L−1 with the existing membrane electrode assembly (MEA), showing nearly equal importance with the new MEA development in achieving the next-generation fuel cell of ultrahigh power density.
To Molecularly Block Hydrogen Evolution Sites of Molybdenum Disulfide toward Improved Catalytic Performance for Electrochemical Nitrogen Reduction
- First Published: 06 January 2023

2H-molybdenum disulfide (2H-MoS2) is extensively applied for electrochemical nitrogen reduction, but the catalytic efficiency is limited by the competing hydrogen evolution. This work shows that the hydrogen evolution sites of 2H-MoS2 can be molecularly blocked by cobalt phthalocyanine through potential axial coordination. The strategy is efficient to improve the nitrogen reduction activity of 2H-MoS2.
Diagnosis of Unruptured Intracranial Aneurysm by High-Performance Serum Metabolic Fingerprints
- First Published: 12 January 2023

Nanoparticle enhanced laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry is applied to obtain high-performance unruptured intracranial aneurysm (UIA)-specific serum metabolic fingerprints. Diagnostic performance with an area-under-the-curve (AUC) of 0.842 is achieved by machine learning. The screened metabolic-biomarker-panel showed satisfactory diagnosis (AUC of 0.812) and effective growth risk assessment (p<0.05) of UIAs. This work will contribute to diagnostics and biomarker screening of UIAs.
Transparent Oil–Water Separating Spiky SiO2 Nanoparticle Supramolecular Polymer Superhydrophobic Coatings
- First Published: 22 January 2023
Exceptional Hydrogen Diffusion Rate over Ru Nanoparticle-Doped Polar MgO(111) Surface
- First Published: 22 January 2023
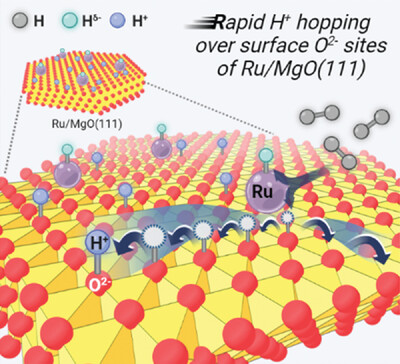
Hydrogen mobility on oxide-based materials is critical for fuel cells and related catalytic systems. Herein, highly diffusive hydrogen over the Ru-supported MgO(111) surface via a proton hopping mechanism is discovered by using in-situ quasielastic neutron scattering. This is attributed to the strong electrostatic field of terminal oxygen anions in the polar MgO(111), which allows for less-localized covalency for the proton migration.
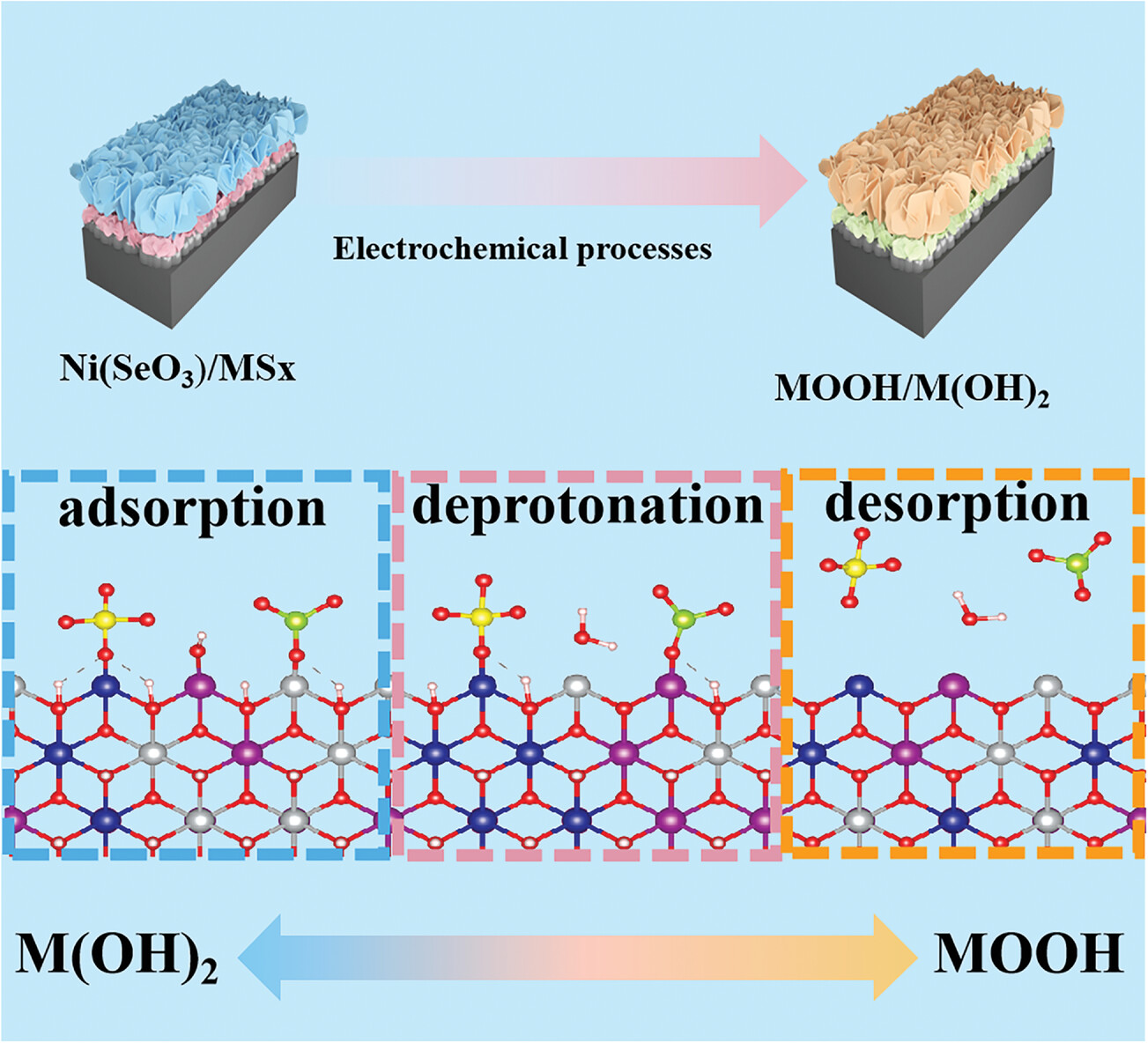
Achieving Ultrahigh Energy-Density Aqueous Supercapacitors via a Novel Acidic Radical Adsorption Capacity-Activation Mechanism in Ni(SeO3)/Metal Sulfide Heterostructure
- First Published: 18 January 2023
Reexamining the Post-Treatment Effects on Perovskite Solar Cells: Passivation and Chloride Redistribution
- First Published: 11 January 2023
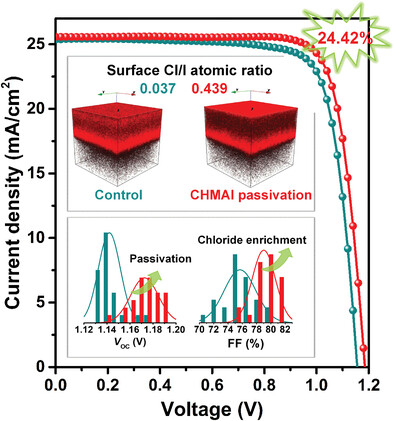
This work demonstrates an universal chloride redistribution and passivation induced by post-treatment. The chloride enrichment on the surface can improve charge transport and the passivation can reduce the recombination. When cyclohexylmethylammonium iodide (CHMAI) post-treated perovskite film, the Cl/I ratio on surface increased from 0.037 to 0.439, which leveraged their roles in charge transport/recombination. Finally, CHMAI perovskite solar cells deliver a champion power conversion efficiency of 24.42%.
Carbon-Shielded Selenium-Rich Trimetallic Selenides as Advanced Electrode Material for Durable Li-Ion Batteries and Supercapacitors
- First Published: 15 January 2023
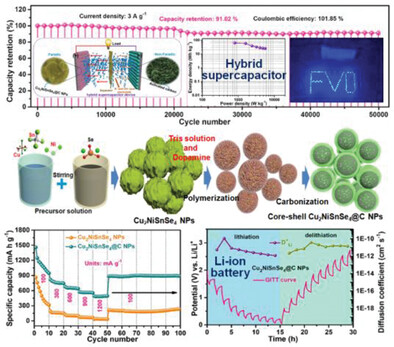
The core-shell Cu2NiSnSe4@C nanoparticles (NPs) are synthesized and used as an electrode material for Li-ion batteries (LIBs) and hybrid supercapacitors. In LIBs, it exhibits high reversible cycling capacity with good rate capability. The core-shell Cu2NiSnSe4@C NPs are also employed as a battery-type electrode for a hybrid supercapacitor. The fabricated hybrid supercapacitor shows excellent energy and power densities.
Efficient Charge Transfer and Effective Active Sites in Lead-Free Halide Double Perovskite S-Scheme Heterojunctions for Photocatalytic H2 Evolution
- First Published: 15 January 2023
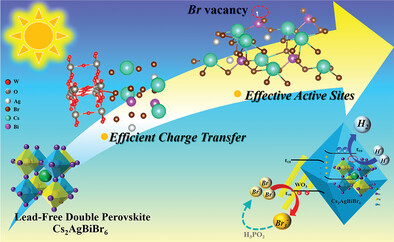
A rod-on-octahedron S-scheme heterojunction by VBr-Cs2AgBiBr6 and WO3 is rationally constructed. Enriched Br vacancies on Cs2AgBiBr6 (022) surfaces are introduced by atom thermal vibration during solvothermal process, which are the effective active sites for hydrogen evolution. The as-prepared S-scheme heterojunction exhibits a superior photocatalytic performance over the other perovskite-based catalysts, emerging a new strategy in the applications of perovskite-based photocatalysts.
Porous Graphene Produced by Carbothermal Shock for Green Electromagnetic Interference Shielding in Both Microwave and Terahertz Bands
- First Published: 15 January 2023

Porous graphene with different degrees of defect is efficiently prepared from low value sucrose by adjusting the discharge conditions of carbothermal shock. The as prepared graphene exhibits competitive shielding performance in both microwave and terahertz bands. In particular, the absorption-dominated shielding performance can be achieved at a filler loading of only 5 wt% in the THz band.
In Situ Quantification of Strain-Induced Piezoelectric Potential of Dynamically Bending ZnO Microwires
- First Published: 22 January 2023
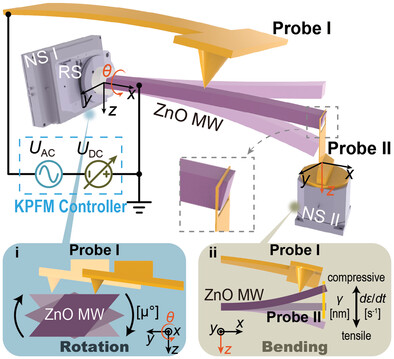
This paper proposes a Kelvin probe force microscopy technique based on a dual-probe atomic force microscope. It can not only characterizes the surface potentials of different crystal faces of microwires in a natural state through controllable axial rotation, but also directly in situ detect the piezoelectric potentials of dynamically bending microwires, which promotes the development of piezoelectric device technology.
Super-Bright Green Perovskite Light-Emitting Diodes Using Ionic Liquid Additives
- First Published: 15 January 2023
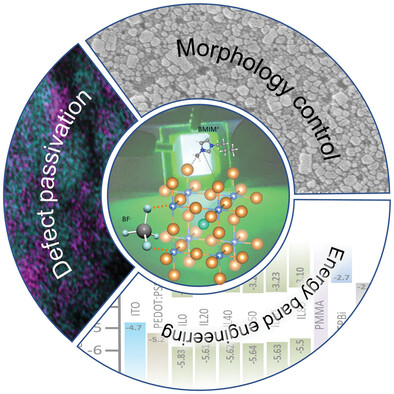
This article demonstrates the huge potential of ionic liquids as a novel and stand-alone additive for high performance perovskite light-emitting diodes. Ionic liquid has multirole effects on the perovskite layer including morphology control, band energy modification, defect passivation, and reduction of ion migration, which result in an impressive luminance of 3.28 × 105 cd m−2 with 13.75% external quantum efficiency.
High Resolution Electrochemical Imaging for Sulfur Vacancies on 2D Molybdenum Disulfide
- First Published: 22 January 2023

With optimized electrodes and newly designed thermal drift calibration software, it is possible to visualize and locate the nanoscale active sites formed by S vacancies on inert MoS2 basal plane by high-resolution scanning electrochemistry microscopy. Moreover, the related hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) kinetics and the stability in different environments are quantitatively analyzed though this strategy.
Reducing Carbonaceous Salts for Facile Fabrication of Monolayer Graphene
- First Published: 26 January 2023
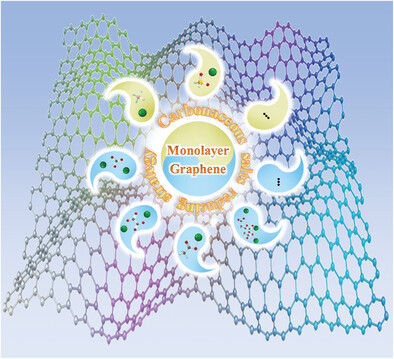
A brand new method to directly convert carbonaceous salts into gram-scale, contamination-free, micron-sized, and high-quality freestanding graphene via a simple one-step redox reaction of green-chemistry synthesis is proposed, in which the redox couple can be a combination of a variety of input reductants and oxidants that are low cost and easily accessible.
Reduced VOC Deficit of Mixed Lead–Tin Perovskite Solar Cells via Strain-Releasing and Synergistic Passivation Additives
- First Published: 30 January 2023
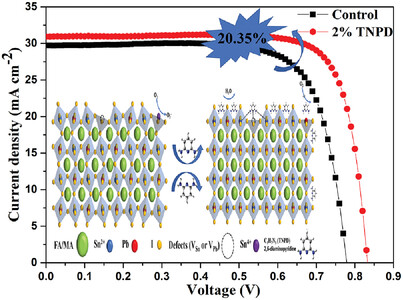
The additive 2,6-diaminopyridine (TNPD) not only effectively induces crystal growth and ultimately passivates the resulting perovskite films via bidentate anchoring, but also releases the micro-strain generated during the film growth. TNPD-involved devices attain the best power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 20.35% (the control PCE =17.28%).
Fascinating Electrocatalysts with Dispersed Di-Metals in MN3-M′N4 Moiety as Two Active Sites Separately for N2 and CO2 Reduction Reactions and Jointly for CN Coupling and Urea Production
- First Published: 31 January 2023
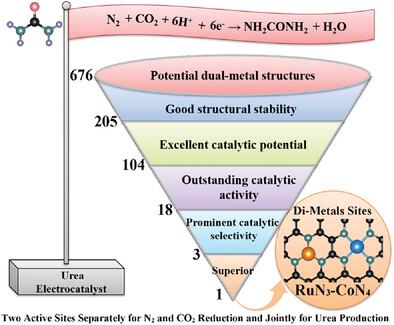
Three possible reaction pathways for urea production, a five-step high-throughput screening method for excellent catalytic activity and a five-aspect high-throughput screening strategy for outstanding catalytic selectivity are proposed based on MN3-M′N4 moiety. Finally, RuN3-CoN4 with strong foundation for experimental preparation is identified as the eminent urea electrocatalyst rooted from dispersed di-metals as two active sites.
Multilayered Helical Spherical Triboelectric Nanogenerator with Charge Shuttling for Water Wave Energy Harvesting
- First Published: 29 January 2023
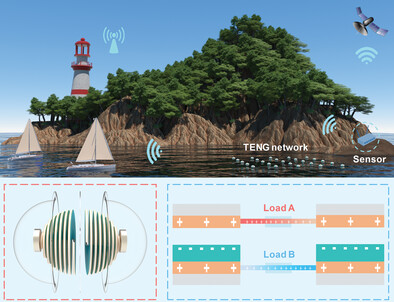
A spherical triboelectric nanogenerator (TENG) with two spring-like multilayered helical units (MH-TENG) is designed to harvest water wave energy based on the charge shuttling mechanism. The MH-TENG is applied to power a water quality detector, a Bluetooth thermo-hygrometer, and a self-powered intelligent wireless alarm system, demonstrating application prospects of TENGs toward large-scale island internet of things.