Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Molecular-Cling-Effect of Fluoroethylene Carbonate Characterized via Ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene on SiOx/C Anode Materials – A New Perspective for Formerly Sub-Sufficient SEI Forming Additive Compounds (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Silicon Anodes
In article number 2302486, Martin Winter, Masoud Baghernejad, and co-workers investigate the complementary effect of fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) and ethoxy(pentafluoro) cyclotriphosphazene as additive compounds in an aprotic organic electrolyte in NCM523 II SiOx/C pouch cells. The authors discuss a novel property of FEC, here called molecular-cling-effect (MCE) and verified it with multiple analysis techniques. Also they thoroughly discuss the electrochemical impact of the additives on the cell performance and the relevant underlying reaction mechanisms.
Inside Front Cover
Optimizing Sieving Effect for CO2 Capture from Humid Air Using an Adaptive Ultramicroporous Framework (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Adaptive Ultramicroporous Frameworks
In article number 2302677, Qihui Chen, Maochun Hong, and co-workers develop an acid-base resistant ultramicroporous framework. It can sieve CO2 from humid air with the very high adsorption capacity/selectivity but the very low adsorption enthalpy. Here, the adsorbed-CO2-driven pore shrinkage can promote CO2 capture while the adsorbed-H2O-induced phase transitions in turn inhibit H2O adsorption.
Inside Back Cover
A Trojan-Horse-Like Biomimetic Nano-NK to Elicit an Immunostimulatory Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced GBM Chemo-Immunotherapy (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Biomimetic Nanoparticles
In article number 2301439, Rutong Yu, Xiuping Zhou, and co-workers construct a Trojan-horse-like nanoparticle system (R-NKm@NPs), which traverses across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and targets glioblastoma through the natural killer (NK) cell membrane decorated with cRGD. Notably, the R-NKm@NPs exhibit good antitumor ability by locally releasing temozolomide (TMZ) and IL-15, eliciting an immunostimulatory tumor microenvironment (TME) and chemo-immunotherapy response.
Back Cover
A Multidrug Delivery Microrobot for the Synergistic Treatment of Cancer (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Multidrug Delivery Microrobots
Dong Sun and co-workers fabricate the multidrug delivery microrobot by a step-by-step 3D printing method using different biodegradable materials. It includes three components: skeleton, head, and body. The skeleton can respond to magnetic fields for microrobot actuation and drug-targeted delivery. The drugs are separately stored in the head and body to enhance the synergistic efficacy of drugs. More details can be found in article number 2301889.
Masthead
Reviews
An Emerging Family of Piezocatalysts: 2D Piezoelectric Materials
- First Published: 29 June 2023
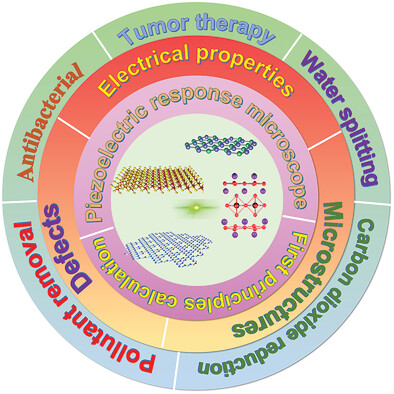
2D piezoelectric materials constitute a promising alternative for piezocatalysis due to their inherent advantages, such as high flexibility, large surface area, and abundant active sites. In this review, the state-of-the-art research progresses on 2D piezoelectric materials and their applications in piezocatalysis are summarized. The overall goal is to inspire and accelerate the practical deployment of 2D piezoelectric materials for piezocatalytic applications.
Stone–Wales Defect in Graphene
- First Published: 29 June 2023
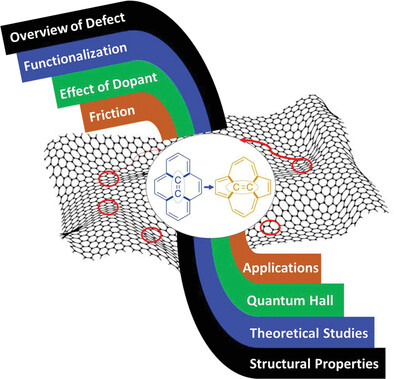
Defects in graphene may be attributed to intrinsic or extrinsic reasons, but they often deteriorate the uniqueness and confine their applications in devices. This article discusses Stone–Wales (SW) defect in graphene and its derivatives comprehensively. A particular emphasis is made on the experimental and theoretical aspect of the SW defect in graphene and its effect on different properties.
Chemical Modulation of Metal–Insulator Transition toward Multifunctional Applications in Vanadium Dioxide Nanostructures
- First Published: 02 July 2023
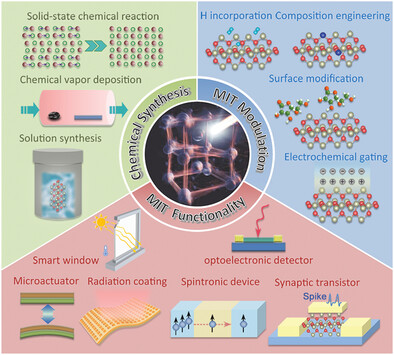
As a well-known metal–insulator transition (MIT) material, vanadium dioxide (VO2) is a model system to study electronic correlations and develop multifunctional applications in optics, thermotics, spintronics, and electronics. This review systematically introduces recent achievements concerning chemical strategies to synthesize VO2 nanostructures, modulate its MIT properties, and construct MIT-driven applications. The challenges and outlook on future development of this field are also provided.
Colloidal Polymer-Templated Formation of Inorganic Nanocrystals and their Emerging Applications
- First Published: 06 July 2023
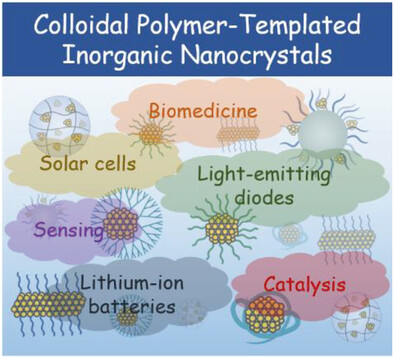
Recent works addressing the topic of colloidal polymer-templated formation of inorganic nanocrystals are summarized. Seven types of polymer colloids used for in situ synthesis of inorganic nanocrystals are reviewed. The emerging applications of these colloidal polymer-templated inorganic nanocrystals are discussed. Interdisciplinary efforts are required for advancing their rational design, synthesis, and applications.
Recent Advances and Perspectives on the Promising High-Voltage Cathode Material of Na3(VO)2(PO4)2F
- First Published: 05 July 2023
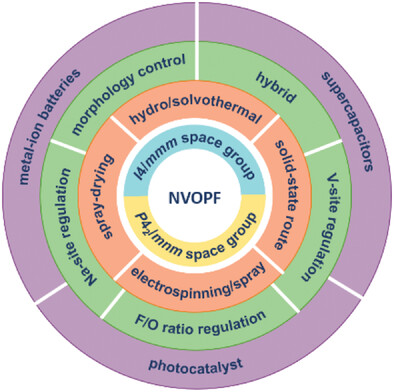
Na3(VO)2(PO4)2F (NVOPF) holds great promise for sodium-ion batteries to achieve high energy/power density. This work outlines the crystal structures, Na storage mechanisms, synthetic methods, rational design, and future perspectives of NVOPF and highlights its application for electrochemical energy storage. It is sincerely hoped that this review can inspire related researchers and promote the development of NVOPF-based cathode materials.
Frontispiece
The Interplay of Growth Mechanism and Properties of ZnO Nanostructures for Different Applications (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023
ZnO Nanostructures
In article number 2302864, Breanna Clarke and Khashayar Ghandi provide a background on the structure, an analysis of the growth kinetics and mechanisms in-solution, and on substrates, and properties of ZnO nanostructures. ZnO nanostructures have applications in sensing, photocatalysis, functional textiles, and cosmetic industries, which are described in this article. The contradictions and gaps in the knowledge have been summarized, followed by suggestions for how to answer these gaps.
Reviews
The Interplay of Growth Mechanism and Properties of ZnO Nanostructures for Different Applications
- First Published: 04 July 2023
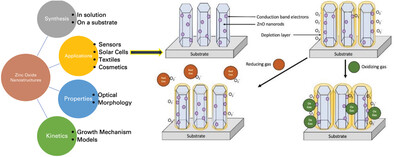
This review outlines the common synthetic methods that produce ZnO nanostructures for various applications such as sensors, solar cells, textiles, and cosmetics. In addition, the review investigates the growth mechanisms and the kinetic studies of ZnO nanostructure formation, while covering the contradictions and variations in results that arise.
Frontispiece
Continuous Covalent Organic Frameworks Membranes: From Preparation Strategies to Applications (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023
Continuous Covalent Organic Frameworks Membranes
Advanced covalent organic frameworks (COFs) membranes have received a lot of attention and a better trade-off between selectivity and permeability can be achieved due to the tunable pore size, high porosity, unique pore structure and the abundance of molecular/ion-specific functional groups on the framework. In article number 2303757, Li Gao, Xiaoming Yan, Gaohong He, and co-workers classify and summarize the preparation strategies of continuous COFs membranes and the applications in separation fields. Depending on the application environment and system, the applications are divided into three main chutes: gas phase, aqueous phase and charged environment.
Reviews
Continuous Covalent Organic Frameworks Membranes: From Preparation Strategies to Applications
- First Published: 28 June 2023
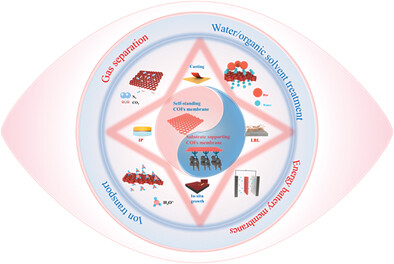
This work discusses the membrane forms of continuous covalent organic frameworks (COFs) membranes . Also, the preparation methods of them reported are classified and summarized, including layer-by-layer stacking, in situ growth, interfacial polymerization, and solvent casting. Besides, the applications in separation fields of them are also highlighted, including gas separation, water/organic solvent treatment, ion conduction, and energy battery membranes.
Frontispiece
Tri-Layered Bicomponent Microfilament Composite Fabric for Highly Efficient Cold Protection (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Highly Efficient Cold Protection
A tri-layered bicomponent microfilament composite fabric comprised of a hydrophobic layer of PET/PA@C6F13 bicomponent microfilament webs, an adhesive layer of LPET/PET fibrous web, and a fluffy-soft layer of PET/Cellulous fibrous web have been designed and also successfully been fabricated, promoting multiple advantages of waterproof breathable properties and high comfort performance that suitable for cold outdoor clothing applications. More details can be found in article number 2303820 by Heng Zhang and co-workers.
Research Articles
Tri-Layered Bicomponent Microfilament Composite Fabric for Highly Efficient Cold Protection
- First Published: 28 June 2023
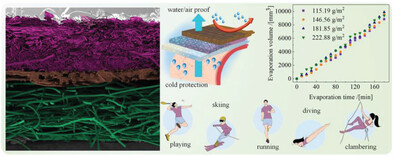
A tri-layered bicomponent microfilament composite fabric comprised of a hydrophobic layer of PET/PA@C6F13 bicomponent microfilament webs, an adhesive layer of LPET/PET fibrous web, and a fluffy-soft layer of PET/Cellulous fibrous web is designed and also successfully been fabricated, promoting multiple advantages of waterproof breathable properties and high comfort performance that suitable for cold outdoor clothing applications.
Frontispiece
Alleviation of Photoreceptor Degeneration Based on Fullerenols in rd1 Mice by Reversing Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Modulation of Mitochondrial DNA Transcription and Leakage (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023
Reversed Mitochondrial Dysfunction
Fullerenol nanoparticles are both stable and effective in protecting the degenerating retina. In article number 2205998, Yu Gong, Zhanjun Gu, Haiwei Xu, and co-workers propose the potential utility of fullerenols for safeguarding the mitochondrial genome to maintain electron transport chain function and simultaneously reversing the abnormal nuclear DNA expression patterns. The nanomaterials alleviate photoreceptor degeneration and are expected to serve as a viable means to treat retinitis pigmentosa.
Research Articles
Alleviation of Photoreceptor Degeneration Based on Fullerenols in rd1 Mice by Reversing Mitochondrial Dysfunction via Modulation of Mitochondrial DNA Transcription and Leakage
- First Published: 05 July 2023
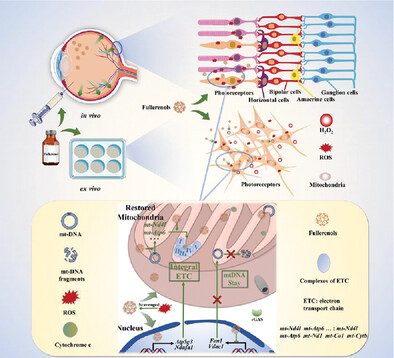
Fullerenols are both effective and stable in the degenerating retina. They exhibit better radical scavenging properties than glutathione and can prevent the loss of photoreceptors caused by oxidative stress. Through this process, fullerenols safeguard the mitochondrial genome to maintain electron transport chain function and reduce the transcription of genes encoding cGAS-STING pathway-related proteins to prevent secondary inflammation.
Frontispiece
A Biomimetic Peptide Functions as Specific Extracellular Matrix for Quiescence of Stem Cells against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
A biomimetic peptide (OAFF) binds to C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 (CXCR1) and forms fibrous networks on nucleus pulposus stem cells (NPSCs) for mimicking extracellular matrix formation, which induces NPSCs quiescence and ultimately overcomes obstacle in intradiscal injection therapy. More details can be found in article number 2300578 by Lei Wang, Bo Huang, and co-workers.
Research Articles
A Biomimetic Peptide Functions as Specific Extracellular Matrix for Quiescence of Stem Cells against Intervertebral Disc Degeneration
- First Published: 09 July 2023
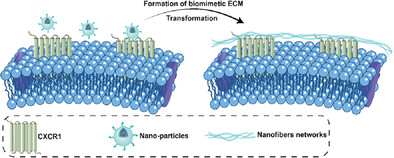
A biomimetic peptide functions as specific extracellular matrix (ECM) for quiescence of stem cells against intervertebral disc degeneration (IVDD). Nano-particles are able to bind to C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 1 (CXCR1) and transform into nanofibers networks on stem cells in the way of mimicking formation of ECM, which offers forcefully competitive inhibition with natural C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 8 (CXCL8) for inducing quiescence against IVDD.
Frontispiece
Photonic-Plasmonic Coupling Enhanced Fluorescence Enabling Digital-Resolution Ultrasensitive Protein Detection (Small 44/2023)
- First Published: 01 November 2023

Digital-Resolution Ultrasensitive Protein Detection
The synergistic coupling between a plasmonic nanostructure and a photonic crystal resonator enables a 52-fold improvement in the emission intensity of fluorescent dye molecules due to strong near-field enhancement, improved extraction efficiency, and an increased rate of spontaneous emission. This substantial boost in signal-to-noise ratio allows for the imaging and digital counting of human interleukin-6 with a 10 fg mL−1 limit of detection and a 7-log dynamic range. More details can be found in article number 2207239 by Srikanth Singamaneni, Brian T. Cunningham, and co-workers.
Research Articles
Photonic-Plasmonic Coupling Enhanced Fluorescence Enabling Digital-Resolution Ultrasensitive Protein Detection
- First Published: 27 April 2023
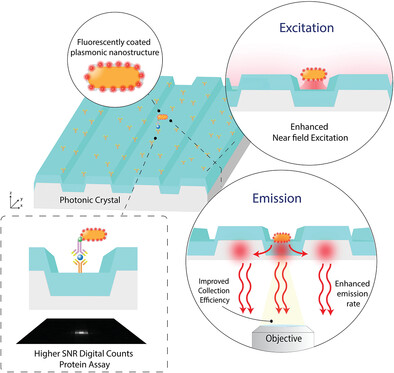
The synergistic coupling between a plasmonic nanostructure and a photonic crystal resonator enables a 52-fold improvement in the emission intensity of fluorophores due to strong near-field enhancement, improved extraction efficiency, and increased rate of spontaneous emission. The boosted signal to noise enables digital counting of human interleukin-6 with a 10 fg mL−1 limit of detection and a 7-log dynamic range.
Molecular-Cling-Effect of Fluoroethylene Carbonate Characterized via Ethoxy(pentafluoro)cyclotriphosphazene on SiOx/C Anode Materials – A New Perspective for Formerly Sub-Sufficient SEI Forming Additive Compounds
- First Published: 04 July 2023
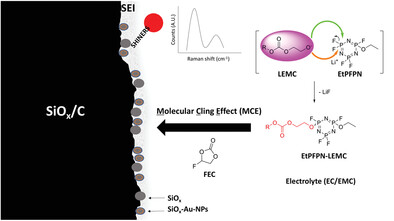
This work illustrates the reaction between lithium ethyl methyl carbonate (LEMC) and EtPFPN in the electrolyte upon (dis)charging. The reaction product EtPFPN-LEMC is not able to participate effectively in the solid-electrolyte interphase (SEI) formation, however, fluoroethylene carbonate (FEC) as an additional additive compound enables EtPFPN-LEMC to cling to the SEI and participate effectively in the SEI formation via the molecular-cling-effect (MCE).
Optimizing Sieving Effect for CO2 Capture from Humid Air Using an Adaptive Ultramicroporous Framework
- First Published: 25 June 2023
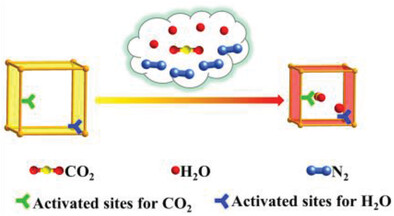
An adaptive ultramicroporous framework with multiple active sites is prepared; it can capture CO2 from humid air with the very high adsorption capacity/selectivity but a very low adsorption enthalpy. The polar ultramicropore is very suitable for CO2 sieving, and the additional adsorption sites for H2O and adsorbed-H2O-induced phase transition make H2O adsorption unable to prevent CO2 capture.
A Trojan-Horse-Like Biomimetic Nano-NK to Elicit an Immunostimulatory Tumor Microenvironment for Enhanced GBM Chemo-Immunotherapy
- First Published: 07 July 2023
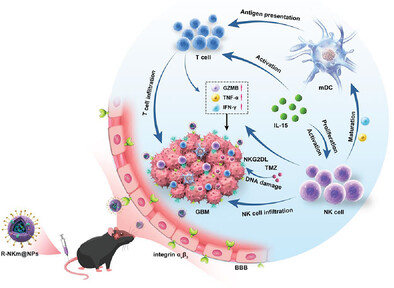
A Trojan-horse-like nanoparticle system is designed, which encapsulates biocompatible PLGA-coated temozolomide (TMZ) and IL-15 nanoparticles with cRGD peptide-decorated NK cell membrane (R-NKm@NPs). Mediated by the NK cell membrane cooperating with cRGD, the R-NKm@NPs traversed across the blood-brain barrier (BBB) and targeted glioblastoma (GBM). Notably, the R-NKm@NPs exhibit good antitumor ability by locally releasing TMZ and IL-15, eliciting an immunostimulatory tumor microenvironment (TME) and chemo-immunotherapy response.
A Multidrug Delivery Microrobot for the Synergistic Treatment of Cancer
- First Published: 09 July 2023
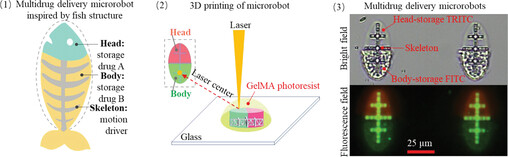
A multidrug delivery microrobot inspired by the fish structure with three components: skeleton, head, and body, is fabricated. The skeleton is made by poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate (PEGDA) photoresist embedding with Fe3O4 nanoparticles and can respond to magnetic fields for microrobot actuation and drug-targeted delivery. The drug storage structures, head, and body, made by biodegradable GelMA exhibit enzyme-responsive drug release.
Regulating Li-Ion Transport through Ultrathin Molecular Membrane to Enable High-Performance All-Solid-State–Battery
- First Published: 28 June 2023

An ultra-thin, sub-nanoporous polymeric membrane with thiol functional groups is employed in solid-state batteries with garnet-type electrolytes as an interlayer to solve some of the critical interfacial issues. The electronically insulating membrane regulates the flow of Li-ion across the interface and blocks any electronic leakage to suppress Li dendrites and offers excellent adhesion with the electrodes enabling high-performance solid-state batteries.
High-Throughput Computational Screening of All-MXene Metal–Semiconductor Junctions for Schottky-Barrier-Free Contacts with Weak Fermi-Level Pinning
- First Published: 28 June 2023
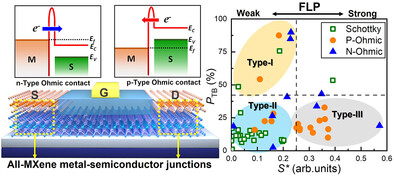
A new family of 2D metal–semiconductor junctions is developed by van der Waals integration of the metallic and semiconducting MXenes along the out-of-plane direction. By means of high-throughput first-principles calculations, a series of all-MXene metal–semiconductor junctions with weak Fermi-level pining and high carrier tunneling probability are screened, showing great potential for electronic and optoelectronic applications.
Amine–Aldehyde Condensation-Derived N-Doped Hard Carbon Microspheres for High-Capacity and Robust Sodium Storage
- First Published: 28 June 2023
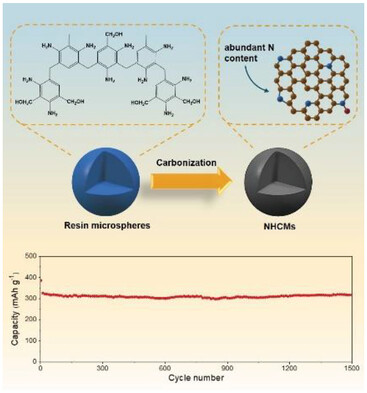
N-doped hard carbon microspheres (NHCMs) with abundant Na+ adsorption sites and adjustable interlayer distance are constructed via the amine–aldehyde condensation. The optimized NHCMs demonstrate a high reversible capacity, high initial Coulombic efficiency, ideal cyclability, and decent rate capability for sodium storage.
Mg Compensating Design in the Melting-Sintering Method For High-Performance Mg3(Bi, Sb)2 Thermoelectric Devices
- First Published: 28 June 2023
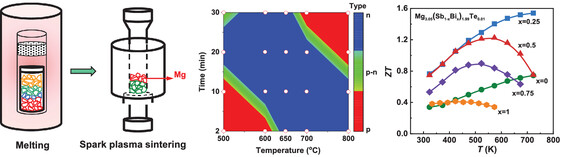
An Mg compensating strategy is proposed to realize high-performance n-type Mg3(Bi, Sb)2 thermoelectric alloys by the melting-sintering approach, reaching peak ZT≈1.55 at 723 K, and average ZT ≈1.25 within 323–723 K. This strategy can also be used to obtain n-type Mg3(Bi, Sb)2/Fe legs by a one-step sintering process, displaying low interfacial contact resistivity, and improved thermal stability.
Synthesis and Broadband Photodetection of a P-Type 1D Van der Waals Semiconductor HfSnS3
- First Published: 28 June 2023
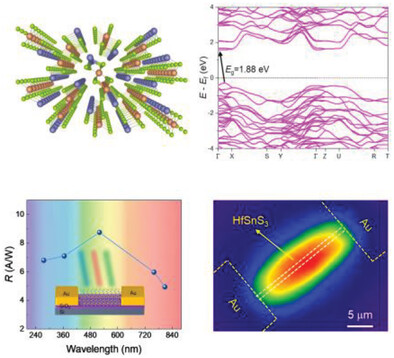
1D van der Waals p-type semiconductor (indirect bandgap, ≈1.67 eV) ternary HfSnS3 with high quality is synthesized via a facile one-step chemical vapor transport method. High-performance photodetector based on HfSnS3 nanowires, which ascribed to the photoconductive effect, exhibits a broadband response with the spectrum from UV (275 nm) to near-infrared (808 nm).
Construction of Dual-Channel Water Transport in Mesoporous Silica Low Humidity Sensors to Achieve High Sensitivity
- First Published: 27 June 2023
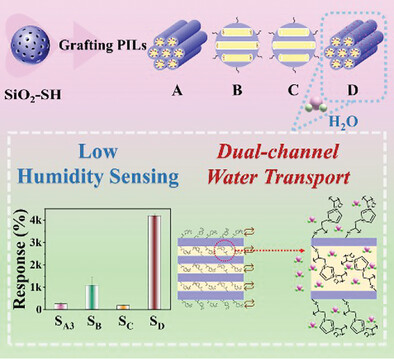
The specific positions of mesoporous silica are selectively functionalized through thiol-ene click reaction to enhance the water molecules adsorption capacity. A novel construction strategy of dual-channel water transport is proposed to improve the sensitivity of humidity sensors, providing a promising method for designing low humidity sensing materials.
Engineering Interfacial Built-in Electric Field in Polymetallic Phosphide Heterostructures for Superior Supercapacitors and Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution
- First Published: 28 June 2023
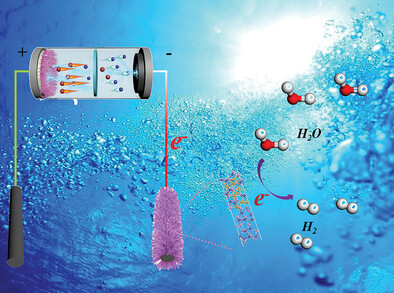
The patterned rod-like CoP@NiCoP core-shell heterostructure is designed and constructed to generates a built-in electric field by the interfacial interaction within the heterojunction between the two components. This core-shell heterostructure adjusts the interfacial charge state, create more active sites, and suppresses the volume expansion during charging and discharging, therefore accelerating the charge transfer and improving the electrochemical and electrocatalytical performance.
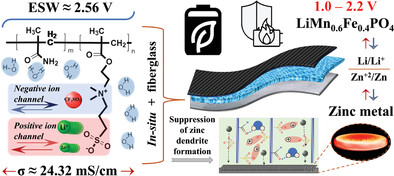
Exploiting High-Voltage Stability of Dual-Ion Aqueous Electrolyte Reinforced by Incorporation of Fiberglass into Zwitterionic Hydrogel Electrolyte
- First Published: 28 June 2023
Regulating Zinc Storage Behaviors of Tunnel Structure Cathodes Via Tungsten Induction
- First Published: 28 June 2023
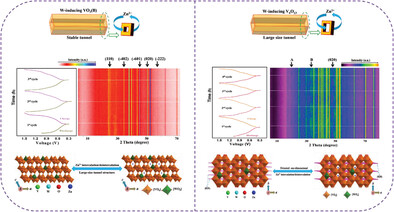
A chemical tungsten induction strategy to regulate zinc storage behaviors of tunnel B-phase vanadium dioxide (VO2(B)) and vanadium oxide (V6O13) cathodes is demonstrated. Operando/non-operando analyses corroborate that tungsten induced VO2(B) can achieve zinc storage without obvious lattice change and tungsten induced V6O13 can realize the oriented zinc storage with high electrochemical performance.
Unveiling Interfacial Effects for Efficient and Stable Hydrogen Evolution Reaction on Ruthenium Nanoparticles-Embedded Pentlandite Composites
- First Published: 29 June 2023
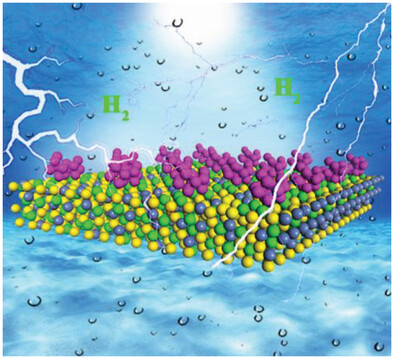
The interaction between Fe5Ni4S8 and Ru nanoparticles can adjust the d-band center of Ru nanoparticles, as well as balance both the hydrolytic dissociation energy and hydrogen binding energy. The as-prepared Ru/Fe5Ni4S8 electrocatalyst possesses improved cycle stability and efficient hydrogen evolution reaction activity at high currents and under pH-universal conditions.
Porous Mo3P/Mo Nanorods as Efficient Mott-Schottky Cathode Catalysts for Low Polarization Li-CO2 Battery
- First Published: 29 June 2023
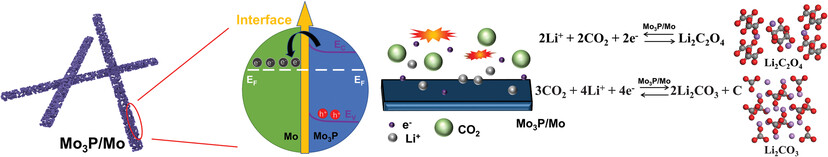
Porous Mo3P/Mo nanorods as Mott-Schottky heterojunctions catalysts are fabricated and utilized as cathodes for Li-CO2 batteries. Mott-Schottky heterojunctions formed by the contact between Mo and Mo3P drive the recombination of electron distribution inside the material, accelerate the transfer of electrons, and stabilize Li2C2O4 during the discharge process and boost electrochemical performances.
Electrochemical Etching Switches Electrocatalytic Oxygen Evolution Pathway of IrOx/Y2O3 from Adsorbate Evolution Mechanism to Lattice-Oxygen-Mediated Mechanism
- First Published: 29 June 2023
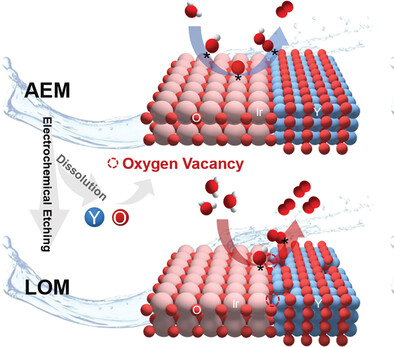
Pre-electrochemical etching treatment on IrOx/Y2O3 hybrid nanotube electrocatalysts enables their high performance for oxygen evolution by switching the adsorbate evolution pathway into lattice oxygen mediated (LOM) one in alkaline electrolyte. Extensive mechanism studies reveal that the abundant oxygen vacancy induced by the pre-electrochemical etching triggered the LOM-dominant pathway of IrOx.
Wide-Potential-Window Bimetallic Hydrated Eutectic Electrolytes with High-Temperature Resistance for Zinc-Ion Hybrid Capacitors
- First Published: 29 June 2023
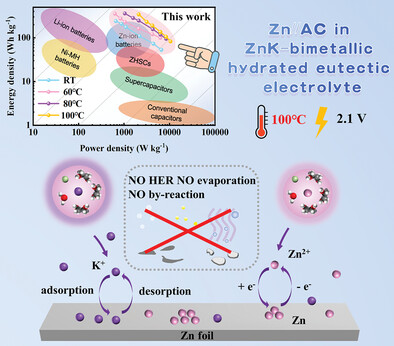
A novel bimetallic hydrated eutectic electrolyte (ZnK–HEE) is designed, and its solvation shell is studied by molecular dynamics simulations and density functional theory calculations. This work provides an effective strategy for the development of innovative electrolyte systems for high-performance Zincion hybrid capacitors with high-temperature resistance and wide potential window.
Confinement Effects on the Structure of Entropy-Induced Supercrystals
- First Published: 29 June 2023
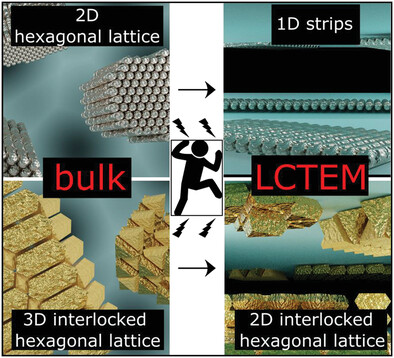
Gold triangles (AuNTs) and silver nanorods (AgNRs) are assembled by depletion-induced self-assembly. Structural analysis shows that the AuNTs and AgNRs form 3D and 2D hexagonal lattices in bulk, respectively. The colloidal crystals are also imaged by in situ Liquid-Cell Transmission Electron Microscopy. Under confinement, the affinity of the nanoparticles for the liquid cell windows leads to SCs with a lower dimensionality than their bulk counterparts.
Amino-Functionalized Interfacial Layer Enables an Ultra-Uniform Amorphous Solid Electrolyte Interphase for High-Performance Aqueous Zinc-Based Batteries
- First Published: 29 June 2023
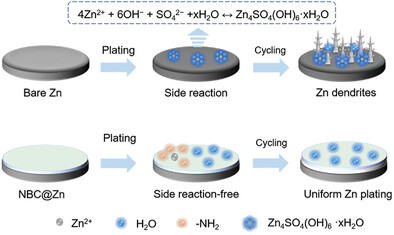
An amino-grafted bacterial cellulose (NBC) film is prepared as artificial solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) for the Zn metal anodes, which can significantly reduce zinc nucleation overpotential and lead to the dendrite-free deposition of Zn metal along the (002) crystal plane more easily without any external stimulus.
Amplified Ferroptosis and Apoptosis Facilitated by Differentiation Therapy Efficiently Suppress the Progression of Osteosarcoma
- First Published: 02 July 2023
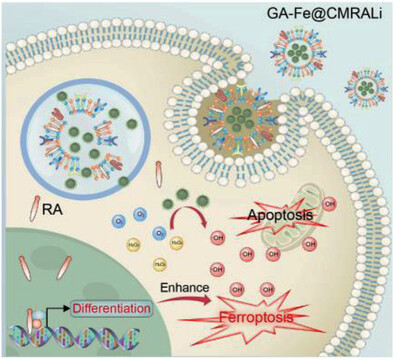
Here, a cancer-cell-membrane-camouflaged biocompatible platform (GA-Fe@CMRALi liposome) is constructed to inhibit osteosarcoma efficiently by combining distinct differentiation and ferroptosis therapies through magnified reactive oxygen species-triggered ferroptosis and apoptosis with homologous target capability to tumor sites. The combinational approach exhibits favorable therapeutic efficacy against osteosarcoma in vitro and in vivo. Notably, mRNA sequencing is utilized to disclose the potential mechanisms.
A Halogen-Bonded Organic Framework (XOF) Emissive Cocrystal for Acid Vapor and Explosive Sensing, and Iodine Capture
- First Published: 02 July 2023
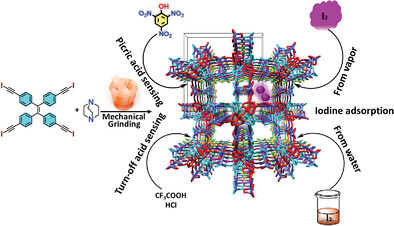
A 3D halogen-bonded organic framework (XOF) is made with mechanical grinding through cocrystal engineering. The 10-fold interpenetrated diamondoid framework has 5 Å zig-zag permanent pores. The emissive XOF exhibits turn-off sensing with acid vapors and picric acid. The XOF reversibly captures iodine from gas phase, organic solvent and in aqueous phase; even under acidic and mildly basic pH.
Highly Enhancing CO2 Photoreduction by Metallization of an Imidazole-linked Robust Covalent Organic Framework
- First Published: 30 June 2023

Metallizing an imidazole-linked robust photosensitive covalent organic framework (PyPor-COF), effective photocatalysts for CO2 conversion are constructed. Co-PyPor-COF achieves a CO production rate highly up to 9645 µmol g−1 h−1 with a selectivity of 96.7%, while Ni-PyPor-COF can further tandem catalyze CO to CH4. It demonstrates that effective photocatalysts for CO2 conversion can be obtained by metallization of photoactive COFs.
Two Birds One Stone: Graphene Assisted Reaction Kinetics and Ionic Conductivity in Phthalocyanine-Based Covalent Organic Framework Anodes for Lithium-ion Batteries
- First Published: 30 June 2023
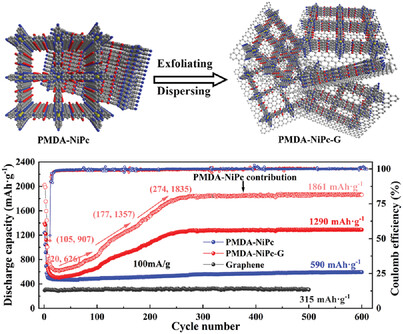
Layer-less and small-volume phthalocyanine based covalent organic frameworks (PMDA-NiPc-G) with carbonyl and graphene networks w ere in situ synthesized. The high electron conduction and Li+ diffusion coefficient of PMDA-NiPc-G contribute to the redox reaction at the active site through the strong contact and charge transfer between PMDA-NiPc and graphene, which achieves superior electrochemical energy storage behaviors in Li-ion batteries.
All-Graphene Quantum Dot-Derived Battery: Regulating Redox Activity Through Localized Subdomains
- First Published: 02 July 2023
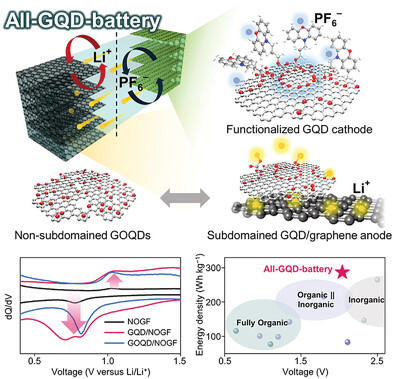
An all-graphene quantum dot (GQD)-derived battery is proposed as a novel platform for sustainable energy storage. Previously unobservable redox behaviors of functional groups in subdomained GQDs are explored to understand the effect of spatially controlled redox sites on electrochemical activity and reversibility. This study also provides a promising method to expedite the practical use of naturally abundant organic redoxophores.
Strong, Tough, and Anti-Swelling Supramolecular Conductive Hydrogels for Amphibious Motion Sensors
- First Published: 02 July 2023
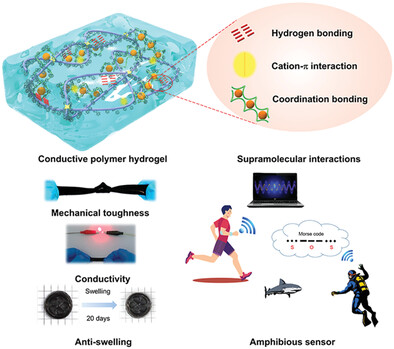
A method is proposed to prepare high-performance conductive polymer hydrogels by introducing multiple supramolecular interactions between polymer networks. The obtained supramolecular hydrogels with highly tough, conductive, and anti-swelling properties have been successfully applied to amphibious sensors.
Multiple Bio-Actives Loaded Gellan Gum Microfibers from Microfluidics for Wound Healing
- First Published: 01 July 2023
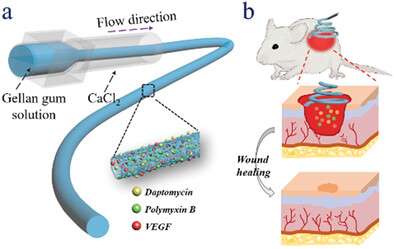
Here, multiple bio-actives loaded gellan gum microfibers are prepared for wound healing through microfluidic spinning technology. The bioactive microfibers are endowed with controllable and uniform morphology, sustained drug release, and effective antibacterial activity, together with accelerated angiogenesis effects. Based on the above properties, the practical value in wound healing of these bioactive microfibers is revealed via animal experiments.
Electrochemical Investigation of Calcium Substituted Monoclinic Li3V2(PO4)3 Negative Electrode Materials for Sodium- and Potassium-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 02 July 2023
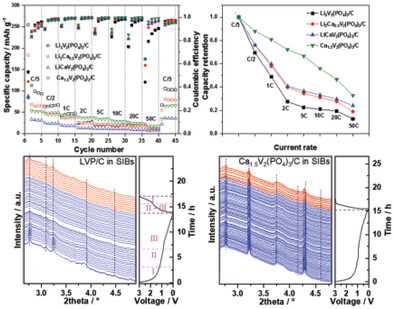
This work demonstrates that the Li3V2(PO4)3 (LVP) and Ca-substituted materials are promising as high-performance negative electrodes for Na/K-ion batteries (SIBs/PIBs) and insertion of different monovalent cations can strongly influence the redox reaction and structure evolution of the host materials. In operando synchrotron diffraction and in operando X-ray absorption spectroscopy unveil that the Ca-substitution of LVP makes a notable change in the reaction mechanism in SIBs.
Novel PdPtCu Nanozymes for Reprogramming Tumor Microenvironment to Boost Immunotherapy Through Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Blocking IDO-Mediated Immune Escape
- First Published: 02 July 2023
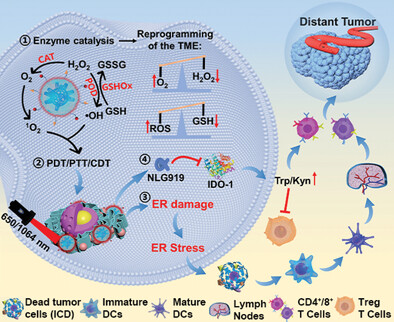
A novel PdPtCu nanozyme with multienzymic activities is synthesized, which not only reshapes the tumor microenvironment (TME) through enzyme catalysis, but also boosts immunotherapy through endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and blocking indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase-mediated immune escape. The strategy realizes ER-targeted enzyme catalysis/photodynamic therapy/photothermal therapy/chemodynamic therapy/immunotherapy synergistic therapy and reverses the immunosuppressive TME.
Guest-Stimulated Nonplanar Porphyrins in Flexible Metal−Organic Frameworks
- First Published: 02 July 2023
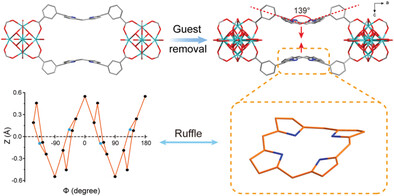
A series of flexible Zr-porphyrin metal−organic frameworks (MOFs) are prepared to exhibit a guest-stimulated breathing behavior. The structure of Zr-porphyrin MOF suffers from porphyrin distortion to form a ruffled geometry due to the crystal packing forces under the desorption of guest molecules. The MOF with nonplanar Co-porphyrin exhibits enhanced performance in the catalysis of CO2/propylene oxide coupling reaction.
3D Printable Gelatin Methacryloyl (GelMA)-Dextran Aqueous Two-Phase System with Tunable Pores Structure and Size Enables Physiological Behavior of Embedded Cells In Vitro
- First Published: 04 July 2023
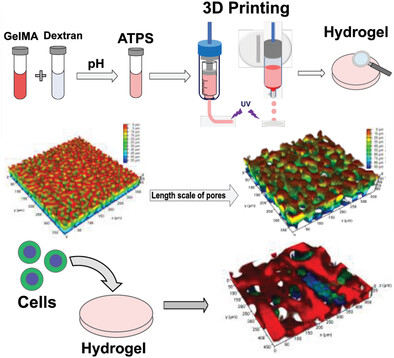
Porous hydrogels from gelatin methacryloyl-dextran aqueous two-phase system (ATPS) are developed. By fine-tuning the pH and dextran concentration, hydrogels with regular disconnected pores and bicontinuous interconnected pores are fabricated by casting and 3D printing. Bicontinuous solution and physical gels are respectively printed by inkjet and microextrusion, resulting in hydrogels with tailorable length scale of pores, suitable for sustaining cell distribution.
Impermeable Graphene Skin Increases the Heating Efficiency and Stability of an MXene Heating Element
- First Published: 04 July 2023
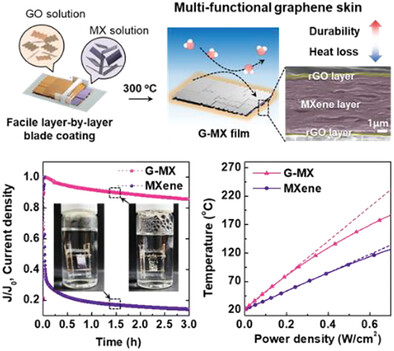
An impermeable graphene skin strategy applied on MXene enhances the durability and almost doubles the heating efficiency of MXene heating units. This skin layer features the hydrophobic sp2 carbon structure on the surface and the tight and tortuous pathway inside the layer, which impede the permeation of water molecules and regulate the heat loss from the film surface.
Novel Semiconductive Ternary Hybrid Heterostructures for Artificial Optoelectronic Synapses
- First Published: 04 July 2023
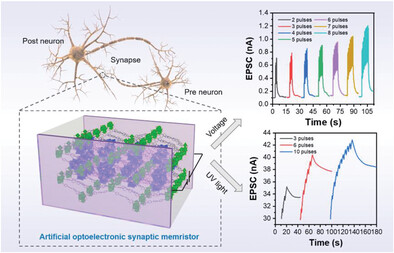
A facile and effective strategy to build semiconductive ternary D-D’-A hybrid heterostructures via introducing electroactive Keggin-type POMs into photochromic metalloviologen-based D-A framework. This hybrid can readily achieve dual-modulated synaptic plasticity when used in an artificial optoelectronic synapse, which create a great opportunity to provide expected functionalities for synaptic biomimicry and neuromorphic computation.
Standardized Figures of Merit for Proper Benchmarking of Photocatalytic Inactivation of Bacteria Using Thin Films Based on TiO2 Nanostructures
- First Published: 04 July 2023
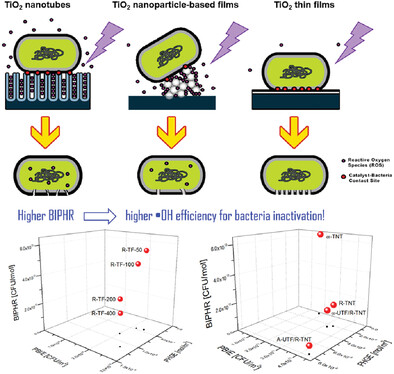
Studies of photocatalysts for bacterial inactivation in wastewater have increased, but standardized methods to analyze their photocatalytic antibacterial activity are lacking. This work proposes three figures of merit to evaluate the photocatalytic activity of TiO2-based coatings for bacteria inactivation, enabling a comprehensive comparison of films prepared under diverse conditions. These parameters have potential applications in the design of fixed-bed reactors.
Deterministic Magnetization Reversal in Synthetic Antiferromagnets using Natural Light
- First Published: 04 July 2023
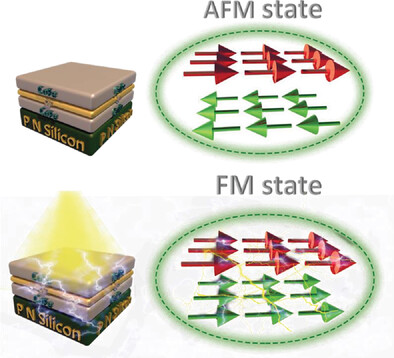
A nearly 180° deterministic magnetization switching between antiferromagnetic (AFM) and ferromagnetic (FM) state is accomplished by visible light control of interfacial exchange interaction. The magnetic optical Kerr measurements first reveal sunlight control of the magnetic domain switching. This work may pave the way toward fast, compact, and energy-efficient solar-driven magnetic random-access memories.
Ultralight, Heat-Insulated, and Tough PVA Hydrogel Hybridized with SiO2@cellulose Nanoclaws Aerogel via the Synergy of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Interfacial Interactions
- First Published: 04 July 2023
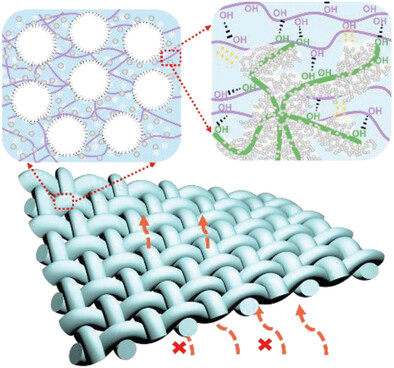
Combining hydrogel and aerogel with cellulose nanoclaws (CNCWs) as the interfacial reinforcement, the lightweight and strong toughening of porous hydrogel with excellent thermal insulation and motion sensing properties is achieved by combining hydrogen bonding interactions and hydrophobic interactions. This strategy provides a new idea for the toughening and functionalization of porous hydrogels.
Unravel the Tangle: Atomistic Insight into Ultrahigh Curcumin-Loaded Polymer Micelles
- First Published: 04 July 2023
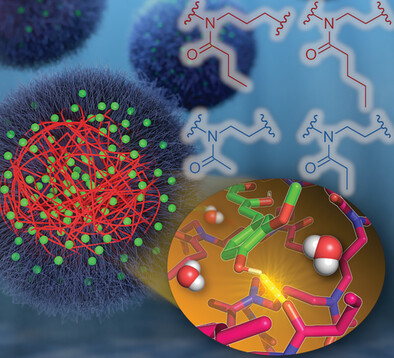
All-atom molecular dynamics simulations are able to reveal the underlying structure–property relationships of previously experimentally characterized, drug-loaded amphiphilic triblock copolymer micelles. In line with the experimental differences in maximum loading capacities and previous hypotheses, altering the structure of monomers of the inner hydrophobic micelle core or the outer hydrophilic shell effects both drug–polymer interactions and corona hydration.
AFM-Based Poroelastic@Membrane Analysis of Cells and its Opportunities for Translational Medicine
- First Published: 04 July 2023
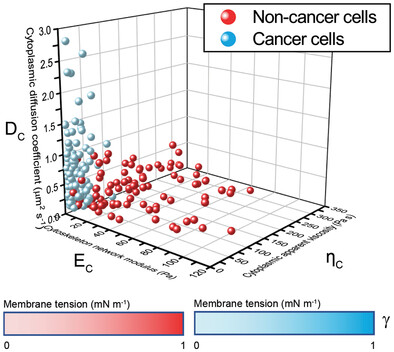
This paper presents a method to characterize the mechanical properties of cells based on poroelastic@membrane model. The method can intuitively show the mechanical differences between non-cancer cells and cancer cells and is expected to be applied to the diagnosis of urothelial carcinoma with a non-invasive method in clinic.
The Structural and Electronic Engineering of Molybdenum Disulfide Nanosheets as Carbon-Free Sulfur Hosts for Boosting Energy Density and Cycling Life of Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 04 July 2023
Vanadium-doped molybdenum disulfide nanosheets are used as carbon-free sulfur host materials in LiS batteries. Vanadium doping remarkably improves the electronic conductivity, polysulfides adsorption capability, and electrochemical catalytic effect, while the sandwich structure of sulfur composites increases the space utilization during cycle, which promise high mass capacity, areal capacity, volumetric capacity, and cycling stability.
Fluorine Passivation Inhibits “Particle Talking” Behaviors under Thermal and Electrical Conditions of Pure Blue Mixed Halide Perovskite Nanocrystals
- First Published: 04 July 2023
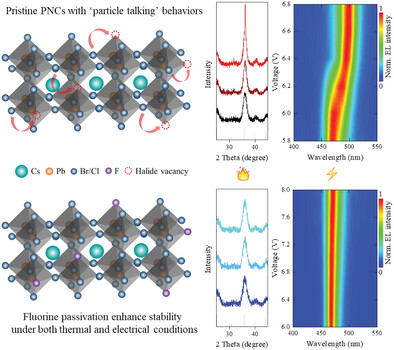
Efficient mixed halide CsPb(Br/Cl)3 nanocrystals with thermal and electric stability are demonstrated by fluorine passivation on halide vacancies. The strong bonding of Pb–F and the formation of fluorine-rich shell enhance the crystal stability and inhibit “particle talking” behaviors that fluorine-treated perovskite nanocrystals exhibit superior resistance of thermal quenching and uniform pure blue electroluminescence emission.
Atomic Engineering Modulates Oxygen Reduction of Hollow Carbon Matrix Confined Single Metal-Nitrogen Sites for Zinc-Air Batteries
- First Published: 07 July 2023

Various hollow carbon matrix confined single metal-nitrogen sites are obtained by a synergetic etching-defense strategy with the aid of tannic acid. The function of metal center and coordination circumstance, as well as spatial confinement of the three-dimensional carbon support in tuning electronic feature is addressed to modulate the oxygen reduction reaction activity for zinc-air batteries.
Defect-Mediated Growth of Crystallographic Shear Plane
- First Published: 07 July 2023
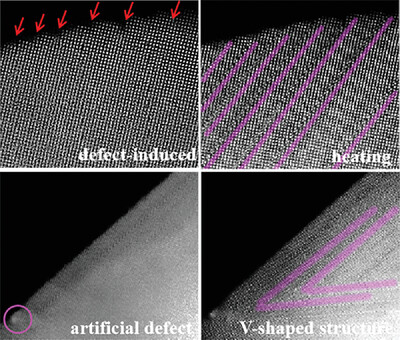
Crystallographic shear plane is a special plane defect, which is composed of blocks comprising edge-sharing octahedrons and 3D open tunnels. Herein, the experiments and theoretical calculations prove that edge step defects can provide nucleation sites for crystallographic shear planes. Moreover, artificial defects can also induce its growth and regulate direction.
Si/Organic Integrated Narrowband Near-Infrared Photodetector
- First Published: 10 July 2023
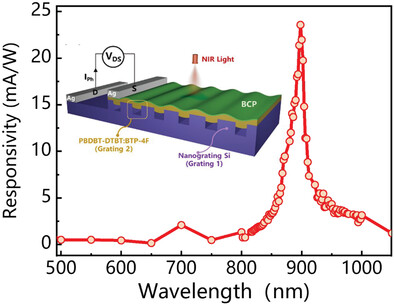
The narrow band Si-based photodetector is obtained the full-width-at-half-maximum of only 26 nm at 895 nm for the first time by constructing the Si nanograting/organic heterojunction. The response peak can be successfully tailored from 895 to 977 nm by consistently reducing the thicknesses of the organic film, indicating facile tunability for NIR detection.
Calcifying Coccolithophore: An Evolutionary Advantage Against Extracellular Oxidative Damage
- First Published: 11 July 2023
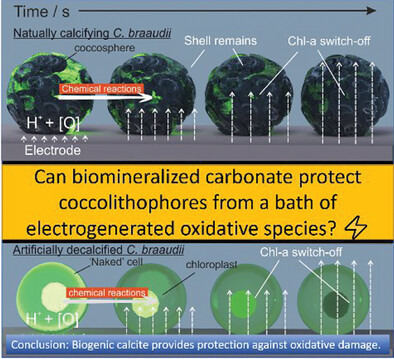
Fluoroelectrochemical experiments reveal the presence of a CaCO3 shell of a naturally calcifying coccolithophore, Coccolithus braarudii, offers protection against extracellular oxidants as measured by the time required for the switch-off in their chlorophyll signal, compared to the deshelled equivalents, suggesting the shift toward calcification in some haptophytes offers advantages in respect of survival in the surface of radical-rich waters.
Selective Proteolysis of Activated Transcriptional Factor by NIR-Responsive Palindromic DNA Thalidomide Conjugate Inhibits the Canonical Smad Pathway
- First Published: 07 July 2023
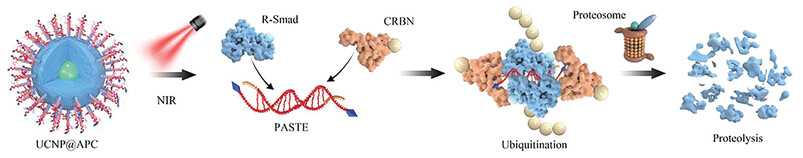
The canonical TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway plays a central role in fibrogenesis. Abnormal activation of R-Smad is reported to be tightly associated with the pathogenesis of fibrosis. Here, an NIR-responsive palindromic DNA thalidomide conjugate (PASTE) has been developed for the selective proteolysis of activated phosphorylated R-Smad, which leads to the inhibition of the canonical Smad pathway.
Metal Ion-induced Gelation of High-concentration Graphite-like Crystalline Nanosheet Aqueous Suspensions
- First Published: 07 July 2023

Graphite-like crystalline nanosheets (GCN) achieve high-concentration, high-stability aqueous suspensions of up to 200 mg mL−1 without using any additives. Moreover, concentrated GCNs aqueous suspension is spontaneously transformed into a gel at room temperature by adding a low-concentration Na+, Cu2+, or Fe3+, which is a metastable state between the common solution and coagulation. Heat treatment of GCN gels produces porous metal/carbon materials.
Identifying And Unveiling the Role of Multivalent Metal States for Bidirectional UOR and HER Over Ni, Mo-Trithiocyanuric Based Coordination Polymer
- First Published: 07 July 2023
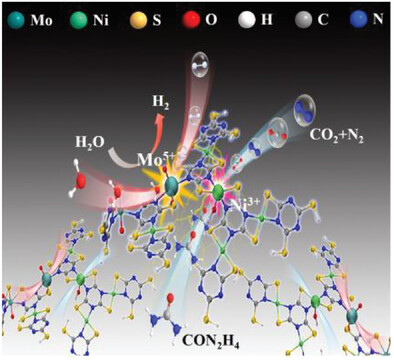
An “adsorption energy-oriented” design strategy is proposed to synthesize a self-supported bimetallic Mo-Ni-C3N3S3 coordination polymer (Mo-NT@NF) with strong metal–ligand interactions and different H2O/urea adsorption energies. Energy-efficient overall-urea electrolysis for green H2 production can be achieved through a bidirectional UOR/HER reaction pathway triggered by N, S-anchored Ni3+/Mo5+ sites.
Hierarchical NiCo@NiOOH@CoMoO4 Core–Shell Heterostructure on Carbon Cloth for High-Performance Asymmetric Supercapacitors
- First Published: 15 September 2023
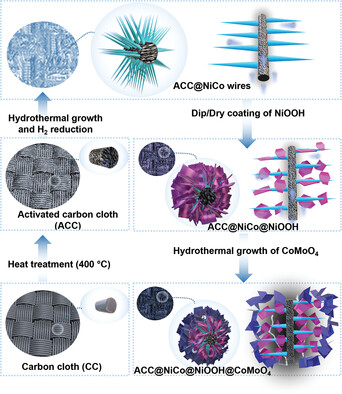
The introduction of a functional scaffold for supercapacitors via simple and exclusive hydrothermal deposition of NiCo nanoneedles is presented, followed by a coating of NiOOH nanoflakes core–shell and uniform hydrothermal deposition of CoMoO4 nanosheets. The structured core–shell heterostructure ACC@NiCo@NiOOH@CoMoO4 electrode results in exceptional specific areal capacitance of 2920 mF cm-2 and exceptional cycling stability for 10 000 charge-discharge cycles.
Experimental Revelation of Surface and Bulk Lattices in Faceted Cu2O Crystals
- First Published: 28 June 2023
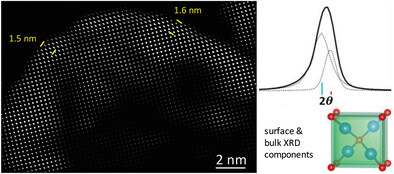
High-resolution X-ray diffraction patterns reveal bulk and surface layer components for polyhedral Cu2O crystals, while transmission electron microscopy analysis provides first visual evidence of the surface layer contributing to their various facet-dependent properties. The surface layer can affect Raman spectra and tune the crystal bandgap.
Biased Symmetry Breaking in the Formation of Intercalated Layered Double Hydroxides: toward Control of Homochiral Supramolecular Assembly
- First Published: 27 June 2023

The planar achiral molecules achieve biased symmetry breaking by the formation of 2D intercalated layered double hydroxide (LDH, host–guest nanomaterials) in vortex motion, and the chiral bias of the homochiral supramolecular assembly (HSA) can be predicted in advance by controlling the vortex direction.