Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Cancer Immunotherapy: Platelet Membrane-Camouflaged Magnetic Nanoparticles for Ferroptosis-Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy (Small 22/2020)
- First Published: 04 June 2020

Malignant tumors pose a heavy threat to human health. In article number 2001704, Zhiqing Pang, Wuli Yang, and co-workers present a multifunctional nanoplatform integrating platelet membrane with dual ferroptosis inducers for high-performance ferroptosis-enhanced immunotherapy of tumors. The biomimetic nanoparticles can not only make tumor ablation by ferroptosis, but also further awaken and boost immune cells to join forces to fight tumors.
Inside Front Cover
Gold Nanorods: Light Tailoring of Internal Atomic Structure of Gold Nanorods (Small 22/2020)
- First Published: 04 June 2020

Gold nanorods (Au NRs) have attracted great attention owing to their significant role in catalysis, imaging, and photothermal therapy. The internal atomic structure control of metallic NRs has long been a challenge. In article number 2001101, Jianfeng Yan and co-workers demonstrate the concept of internal atomic structures tailored with light, and Au NRs with various internal atomic structure are fabricated.
Inside Back Cover
Ion-Selective Transport: Direct Fabrication of Freestanding and Patterned Nanoporous Junctions in a 3D Micro-Nanofluidic Device for Ion-Selective Transport (Small 22/2020)
- First Published: 04 June 2020

In article number 2000998, Dong Sung Kim and co-workers develop a direct fabrication process of a freestanding nanoporous junction in a microfluidic device through electrolyte-assisted electrospinning followed by impregnating a nanoporous material. The broad applicability of this novel fabrication is demonstrated as two different types of micro-nanofluidic devices performing reverse electrodialysis and ion concentration polarization based on the ion-selectivity.
Back Cover
Organ-On-A-Chip Systems: Human-on-Leaf-Chip: A Biomimetic Vascular System Integrated with Chamber-Specific Organs (Small 22/2020)
- First Published: 04 June 2020

In article number 2000546, Jiankang He, Xin Zhao, and co-workers report a human-on-leaf#x02010;chip system with biomimetic multiscale vasculature systems connecting vascularized organs, mimicking the complex in vivo architectures of the human cardiovascular system. The native organ-to-organ crosstalk is well recapitulated, implicating a strong potential for harnessing the leaf chip for circulatory-related studies such as metastasis.
Masthead
Reviews
Improving the Catalytic Activity of Carbon-Supported Single Atom Catalysts by Polynary Metal or Heteroatom Doping
- First Published: 04 May 2020
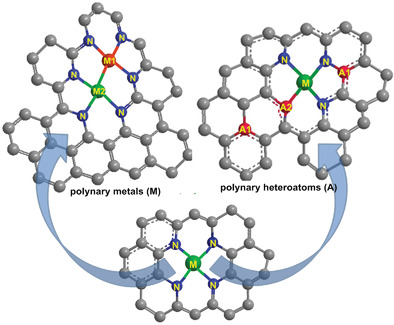
Carbon-supported single atoms catalysts (SACs) are the most widely researched electrocatalysts. Polynary metals and polynary heteroatoms doping strategies are the simple and effective ways to modulate the electronic structure of metal sites that play the leading role for catalyzing activity and product distribution. This Review provides a reference for the electronic structure modulation of other SACs.
Intracellular Labeling with Extrinsic Probes: Delivery Strategies and Applications
- First Published: 30 April 2020
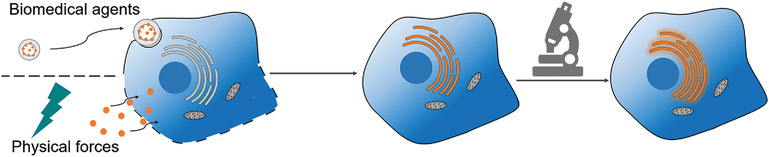
This Review provides a new horizon for intracellular delivery of extrinsic probes (cell-impermeable), including both biomedical and physical strategies. Borrowed from gene delivery methods, different biomedical agents are used in this case for intracellular delivery of probes mostly through endocytosis. Different physical forces are applied for direct intracellular delivery by cell-membrane disruption, inducing much higher efficiency than biomedical methods.
Communications
Human-on-Leaf-Chip: A Biomimetic Vascular System Integrated with Chamber-Specific Organs
- First Published: 24 April 2020
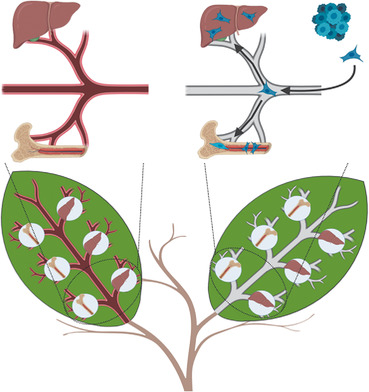
Organ-on-a-chip technology is slowly maturing as studies begin to focus on establishing a vascular network to maintain organ-to-organ crosstalk and biomimetic variables. To integrate multiple vascularized organs in one human-on-leaf-chip, chambers are edited in computer-aided design of the highly efficient leaf venation network for multiple organ cultures. In this proof-of-concept, liver and bone are co-cultured, which yields encouraging results.
Injectable and Crosslinkable PLGA-Based Microribbons as 3D Macroporous Stem Cell Niche
- First Published: 27 April 2020
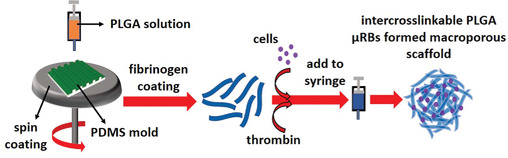
Poly(lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) has been widely used for fabricating 3D scaffolds. Previous methods for fabricating PLGA scaffolds do not support direct encapsulation and are not injectable. Here, a method to first fabricate PLGA into microribbon shape building blocks, which are injectable and can intercrosslink into 3D macroporous scaffolds while supporting homogeneous cell encapsulation and minimally invasive delivery, is reported.
Efficient Electrochemical Nitrogen Fixation over Isolated Pt Sites
- First Published: 27 April 2020
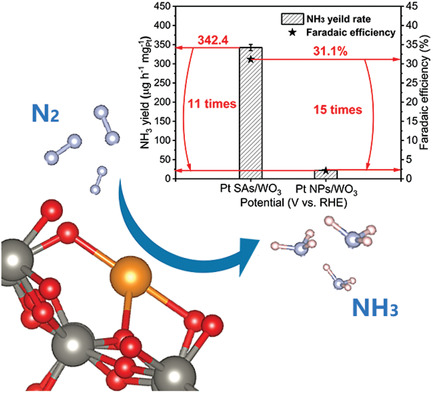
Isolated Pt atoms anchored on WO3 nanoplates exhibit highly active for ambient ammonia electrosynthesis, which is ascribed to facilitated chemisorption and activation of nitrogen and effective suppression for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER), immensely enhancing NH3 yield rate and Faradic efficiency. This groundbreaking research presents Pt-based nanocatalysts for electroreduction of nitrogen and provides an idea for the HER depression.
Multifunctional MoS2 Transistors with Electrolyte Gel Gating
- First Published: 30 April 2020
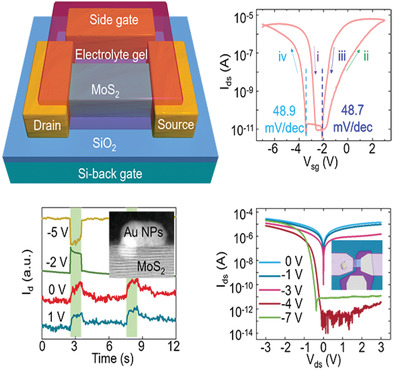
This work demonstrates MoS2 field effect transistors (FETs) with electrolyte gel gating, achieving flexible modulation of carrier concentration and type in MoS2. The MoS2 FETs exhibit high-performance negative photoconductive detection, because the deposited Au nanoparticles on the surface of MoS2 act as traps. Additionally, a MoS2 homogeneous p–n junction diode with a high rectification ratio is realized.
Thermal Shock Synthesis of Nanocatalyst by 3D-Printed Miniaturized Reactors
- First Published: 06 May 2020
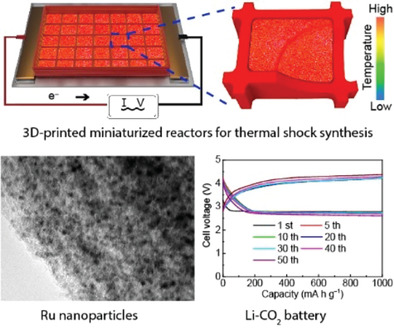
A 3D-printed, miniaturized reactor is constructed for variable heating up to 3000 K for microscale materials. To demonstrate the utility of the reactor, ultrafine Ru nanoparticles (2 nm) supported on a carbon substrate are prepared by transient heating (1500 K, 500 ms) and show good cycling stability as a cathode for Li-CO2 batteries.
Interface-Strengthened Polymer Nanocomposites with Reduced Dielectric Relaxation Exhibit High Energy Density at Elevated Temperatures Utilizing a Facile Dual Crosslinked Network
- First Published: 06 May 2020
Dual crosslinked network achieved by a well-controlled, step-by-step crosslinking strategy, leading to an ultrastable dielectric polymer nanocomposite, exhibits a significantly enhanced high-temperature dielectric stability, owing to the strengthened interfaces and reduced molecular chains relaxation. More notably, the high-temperature energy storage properties under the high fields and high-temperature have significantly enhanced.
Frontispiece
Zinc Oxide: From Precursor Chemistry to Gas Sensors: Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition Process Engineering for Zinc Oxide Layers from a Nonpyrophoric Zinc Precursor for Gas Barrier and Sensor Applications (Small 22/2020)
- First Published: 04 June 2020
In article number 1907506, Anjana Devi and co-workers introduce a new, nonpyrophoric zinc precursor for plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition (PEALD) of zinc oxide (ZnO). Here, oxygen plasma is used to react with adsorbed zinc precursor on chemiresistor structures to form highly pure ZnO which is used effectively as a selective gas sensing layer for NO2 in a functional gas sensor device.
Full Papers
From Precursor Chemistry to Gas Sensors: Plasma-Enhanced Atomic Layer Deposition Process Engineering for Zinc Oxide Layers from a Nonpyrophoric Zinc Precursor for Gas Barrier and Sensor Applications
- First Published: 28 April 2020
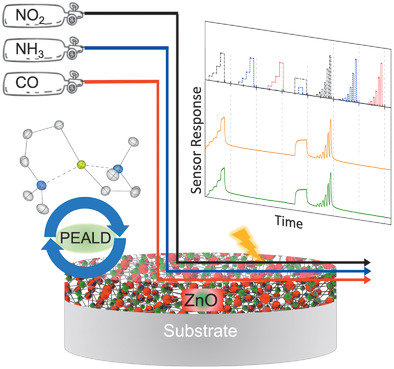
The application of an exciting nonpyrophoric zinc precursor as an alternative for diethyl zinc in a plasma enhanced atomic layer deposition process yielding zinc oxide thin films which can be effectively used as gas barrier as well as semiconducting gas sensing layers for selective NO2 detection is presented.
Platelet Membrane-Camouflaged Magnetic Nanoparticles for Ferroptosis-Enhanced Cancer Immunotherapy
- First Published: 27 April 2020
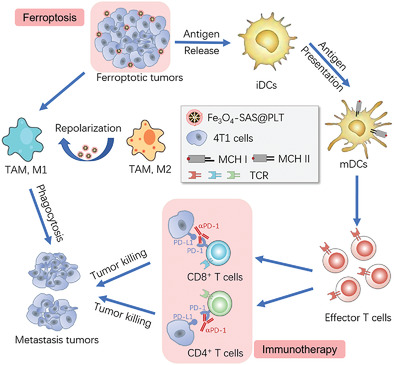
A new strategy for reinforcing systemic antitumor immunity by using a biomimetic magnetic nanoparticle (Fe3O4-SAS@PLT) to trigger ferroptosis is proposed, for enhancing the therapeutic effect of programmed cell death 1 immune checkpoint blockade therapy. Fe3O4-SAS@PLT can repolarize tumor-assoicated macrophages and continuously eliminate metastatic tumors by enhancing tumor-related immune response, providing a valuable way of clinically applicable synergistic immunotherapy in cancer.
Light Tailoring of Internal Atomic Structure of Gold Nanorods
- First Published: 24 April 2020
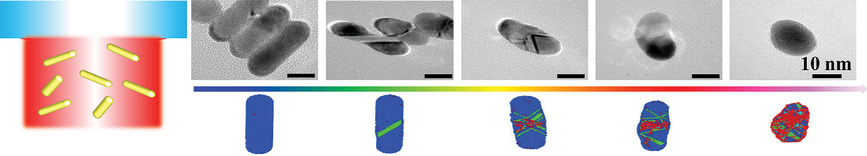
Gold nanorods (Au NRs) have attracted great attention owing to their significant role in catalysis, imaging, and photothermal therapy. The internal atomic structure control of metallic NRs has long been a challenge. Here, the concept of internal atomic structure tailored with light is demonstrated and Au NRs with various internal atomic structure are fabricated.
Direct Fabrication of Freestanding and Patterned Nanoporous Junctions in a 3D Micro-Nanofluidic Device for Ion-Selective Transport
- First Published: 29 April 2020
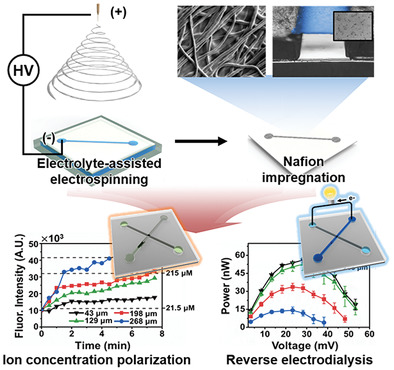
A freestanding nanoporous junction is directly fabricated, patterned, and integrated in a microfluidic device through electrolyte-assisted electrospinning followed by impregnating a nanoporous material. The broad applicability of this fabrication is demonstrated as two different types of micro-nanofluidic devices performing reverse electrodialysis and ion concentration polarization based on the ion-selectivity of the nanoporous junction.
Black Phosphorus Quantum Dots Cause Nephrotoxicity in Organoids, Mice, and Human Cells
- First Published: 27 April 2020
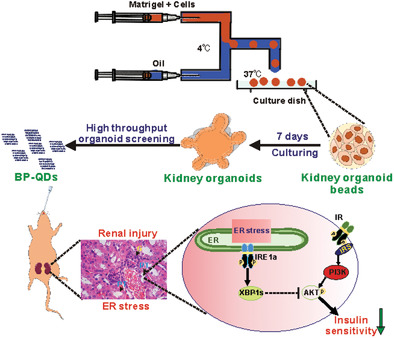
This study establishes a high-throughput screening platform based on organoids that is used to evaluate the nephrotoxicity of quantum dots (QDs). Black phosphorus (BP)-QDs have toxic effects on the kidney, as shown by screening on the organoids. The nephrotoxicity of BP-QDs is validated in mice and human renal tubular epithelial cells. Endoplasmic reticulum stress IRE1α signaling is proven to mediate renal toxicity and insulin insensitivity caused by BP-QDs.
Active Particle Based Selective Transport and Release of Cell Organelles and Mechanical Probing of a Single Nucleus
- First Published: 04 May 2020
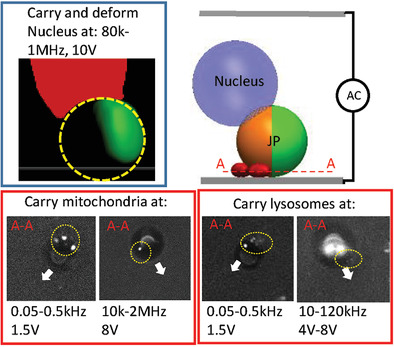
It is demonstrated that self-propelling metallo-dielectric Janus particles, under an externally applied electric field, can trap and transport deformable cell organelles in a selective and releasable manner. Moreover, electro-deformation of the trapped nucleus can act as a promising label-free biomechanical marker. Hence, the Janus particle constitutes an ex vivo platform for manipulation and mechanical probing of subcellular components.
Designing Internal Hierarchical Porous Networks in Polymer Monoliths that Exhibit Rapid Removal and Photocatalytic Degradation of Aromatic Pollutants
- First Published: 29 April 2020
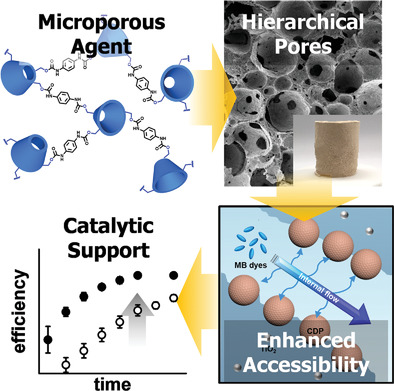
Hierarchical porous polymer monoliths are prepared based on Pickering high internal phase emulsion that is stabilized by microporous, cyclodextrin-based polymer agents. The materials are designed to contain hierarchical porosity that comprise macro-channels and small pores, and capable of exhibiting enhanced sorption and photocatalytic activity for the removal of aromatic pollutants.
The Brownian and Flow-Driven Rotational Dynamics of a Multicomponent DNA Origami-Based Rotor
- First Published: 03 May 2020
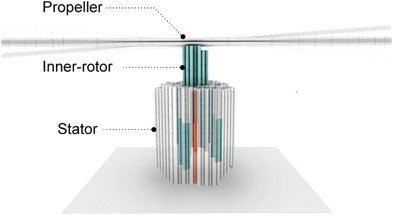
A multicomponent DNA origami-based rotor is created and characterized using negative stain and cryo electron microscopy. The nanodevice is immobilized on a microfluidic chamber and its Brownian and flow-driven rotational behavior is analyzed in real time by single-molecule fluorescence microscopy. The rotor randomly switches among three different rotational states. Its mobility increases under moderate flow rates.
Role of Redox-Inactive Transition-Metals in the Behavior of Cation-Disordered Rocksalt Cathodes
- First Published: 04 May 2020
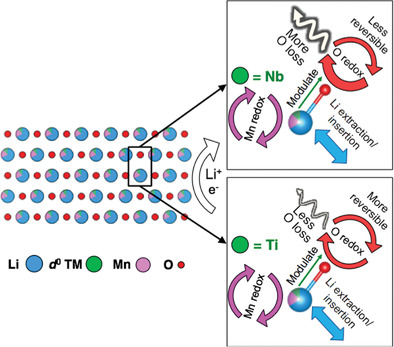
The role of d0 transition-metal (TM) cations in the redox chemistry of model Li-rich cation-disordered rocksalt cathodes is investigated. Although electrochemically inactive, d0 TM is found to serve as a modulator for the reversible and irreversible oxygen redox processes. This results in significant differences in chemical, structural, and cycling stabilities of the cathode materials.
Time-Resolved Fluorescence Anisotropy of a Molecular Rotor Resolves Microscopic Viscosity Parameters in Complex Environments
- First Published: 04 May 2020
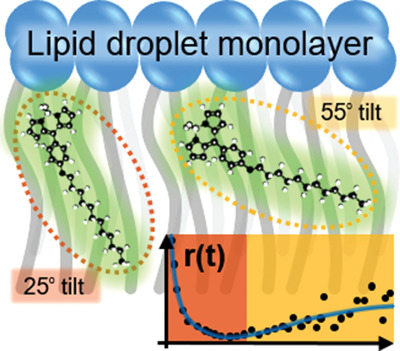
Fluorescent molecular rotors (FMRs, viscosity-dependent fluorescence lifetime probes) are combined with time-resolved fluorescence anisotropy imaging for novel multiplex viscosity imaging in model and live cell lipid droplets. All-atom molecular dynamics simulations identify two FMR tilt states which are connected to extracted viscosity parameters, namely FMR lifetime and rotational correlation time.
Rethinking the Characterization of Nanoscale Field-Effect Transistors: A Universal Approach
- First Published: 06 May 2020
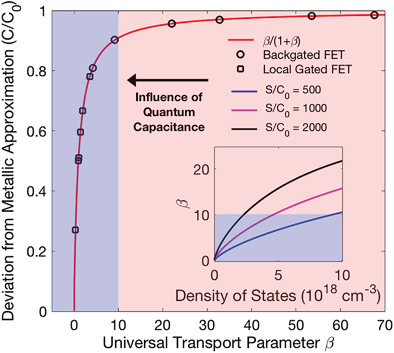
The influence of quantum capacitance on deviation from the metallic capacitance model (C/C0) for experimental data from literature as a function of a universal parameter β is presented. This introduces a quantum capacitance-limited transport regime (shaded blue), where the metallic approximation is invalid (shaded red). Inset: β dependence on density of states for different capacitive couplings (surface area to capacitance S/C0).
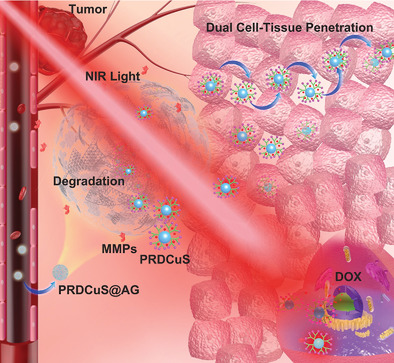
Biodegradable Nanocomposite with Dual Cell-Tissue Penetration for Deep Tumor Chemo-Phototherapy
- First Published: 06 May 2020
Electron-Deficient and Quinoid Central Unit Engineering for Unfused Ring-Based A1–D–A2–D–A1-Type Acceptor Enables High Performance Nonfullerene Polymer Solar Cells with High Voc and PCE Simultaneously
- First Published: 06 May 2020
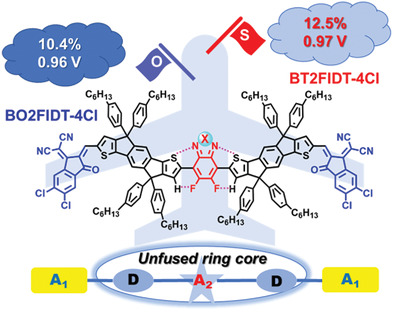
An effective intramolecular locking strategy is designed by introducing the central electron-deficient quinoid to unfused ring A1–D–A2–D–A1-type nonfullerene small molecule acceptors (NF-SMAs). The polymer solar cells (PSCs) based on BT2FIDT-4Cl with difluorobenzothiadiazole central unit show a power conversion efficiency (PCE) of 12.5% with Voc of near 1 V. This is the best result for nonfused ring NF-SMAs with electron-deficient A2 unit in binary PSCs.
Thermoplasmonic-Triggered Release of Loads from DNA-Modified Hydrogel Microcapsules Functionalized with Au Nanoparticles or Au Nanorods
- First Published: 06 May 2020
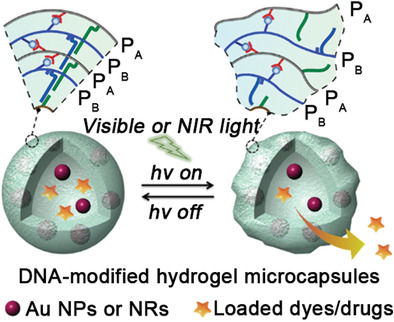
DNA-modified hydrogel microcapsules, cross-linked by glucosamine–boronate ester bridges and duplex nucleic acids and functionalized with Au nanoparticles or Au nanorods, are developed. The microcapsules present switchable ON/OFF thermoplasmonic drug release. The selective triggering release of drugs and selective cytotoxicity toward cancer cells are demonstrated.
Oxygen-Deficient Ferric Oxide as an Electrochemical Cathode Catalyst for High-Energy Lithium–Sulfur Batteries
- First Published: 05 May 2020
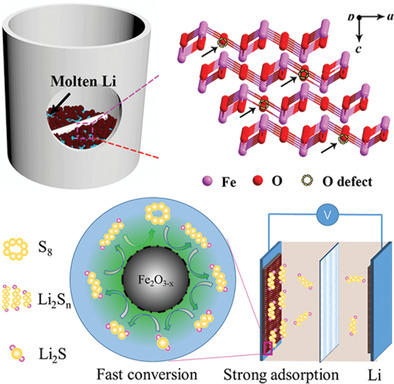
Oxygen-deficient ferric oxide (Fe2O3−x), prepared by lithiothermic reduction, is proposed as a low-cost and effective cathodic catalyst. The batteries with Fe2O3−x deliver a high capacity of 512 mAh g−1 over 500 cycles at 4 C. In addition, a high-loading porous cathode is prepared by freeze-drying and a high areal capacity of 12.24 mAh cm−2 is achieved.
Novel 3D Nanoporous Zn–Cu Alloy as Long-Life Anode toward High-Voltage Double Electrolyte Aqueous Zinc-Ion Batteries
- First Published: 06 May 2020
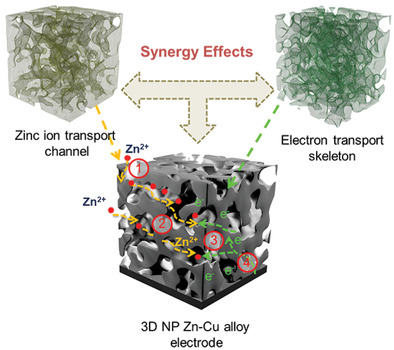
Unique electron/ion transports paths can simultaneously minimize the four primary resistances to improve the electrochemical stability of Zn anode. Besides, the fabricated Zn–Br2 battery with maximum areal specific capacity of ≈1.56 mAh cm−2 is close to the level of commercial Li-ion batteries. The design concept provides a general strategy for next-generation batteries with high reversibility.