Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
UV Photodetection: Atomically Thin Oxyhalide Solar-Blind Photodetectors (Small 23/2020)
- First Published: 12 June 2020

In article number 2000228, Luying Li, Tianyou Zhai, and co-workers prepare large-size BiOCl flakes with thickness down to a monolayer via salt-assisted chemical vapor deposition. The 2D BiOCl photodetectors exhibit high responsivity throughout the solar-blind range at room and high temperatures. The success in fabrication of atomically thin BiOCl photodetectors opens opportunities for their potential applications in solar-blind UV photodetection.
Inside Front Cover
Radiation Therapy: Biomimetic Engineering of a Scavenger-Free Nitric Oxide-Generating/Delivering System to Enhance Radiation Therapy (Small 23/2020)
- First Published: 12 June 2020

In article number 2000655, Po-Liang Lai, Hsing-Wen Sung, and co-workers present a hollow microsphere system that may function as an incubator for the generation and delivery of NO in a scavenger-free environment. Upon leaving the incubator, the NO molecules may passively diffuse through their protected-surfactant layer gradually to the tumor site, performing long-lasting radiosensitization.
Inside Back Cover
Ionic Exchange: Ionic Exchange of Metal−Organic Frameworks for Constructing Unsaturated Copper Single-Atom Catalysts for Boosting Oxygen Reduction Reaction (Small 23/2020)
- First Published: 12 June 2020
In article number 2001384, Yi Wang, Yunteng Qu, Jinbo Bai, and co-workers develop an ionic exchange strategy to fabricate atomically dispersed CuNC material with unsaturated CuN3 centers. Oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) tests indicate that its half-wave potential and turnover frequency are significantly enhanced compared to that with CuN4 moieties. This suggests that decreasing N coordination number of the active center could greatly boost the ORR activity. This may inspire further design of efficient electrochemical catalysts.
Back Cover
Antibacterial Therapy: In Situ Fabrication of Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles/2D MOFs Hybrid as Nanozyme for Antibacterial Therapy (Small 23/2020)
- First Published: 12 June 2020

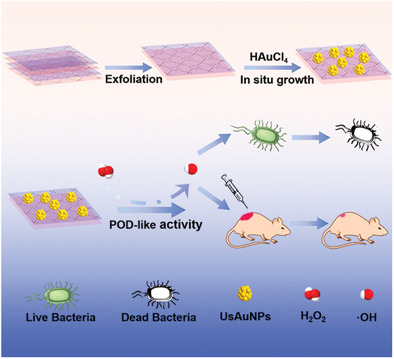
This work is inspired by oysters converting worthless sand into precious pearls. In article number 2000553, Chen Wang and co-workers present the “trash into treasure” process, which efficiently promotes antibacterial therapy and wound healing. The confinement effect of 2D Al-metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) maintains gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) as ultrasmall without gathering and makes them exhibit excellent peroxidase-like activity. The ultrasmall AuNPs/MOFs nanozymes representing oysters convert H2O2 symbolizing grains of sand into ·OH symbolizing valuable pearls.
Masthead
Correction
Layered Ca0.28MnO2·0.5H2O as a High Performance Cathode for Aqueous Zinc-Ion Battery
- First Published: 12 June 2020
Reviews
An Overview and Future Perspectives of Rechargeable Zinc Batteries
- First Published: 13 May 2020
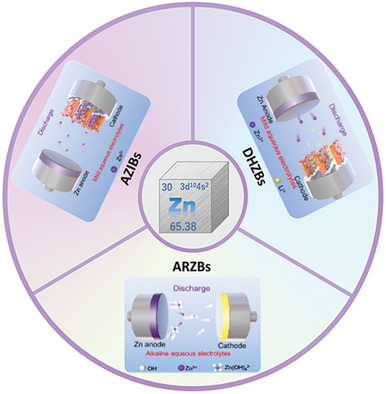
Herein, a systematic summary for the construction and mechanism of different aqueous zinc-based batteries is established. Details for three major zinc-based battery systems, including alkaline rechargeable Zn-based batteries, aqueous Zn ion batteries, and dual-ion hybrid Zn batteries are given. Combining the characteristics of zinc-based batteries with good use of concepts and ideas from other disciplines will surely pave the way for its commercialization.
Communications
Ionic Exchange of Metal−Organic Frameworks for Constructing Unsaturated Copper Single-Atom Catalysts for Boosting Oxygen Reduction Reaction
- First Published: 04 May 2020
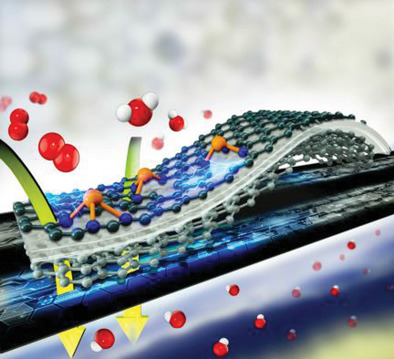
An ionic exchange strategy is developed to fabricate atomically dispersed CuNC material with unsaturated CuN centers (CuN3 moieties), which possesses a higher half-wave potential of 180 mV and the 10 times turnover frequency than that with CuN4 moieties in the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) test. Furthermore, the optimum CuN3 catalyst demonstrates a better performance in ORR and zinc–air batteries compared with commercial Pt/C.
Solid Electrolyte Interphase Evolution on Lithium Metal in Contact with Glyme-Based Electrolytes
- First Published: 11 May 2020
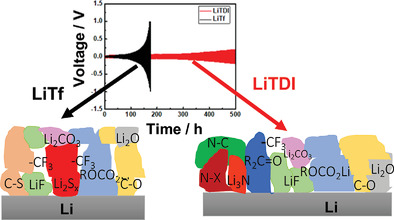
The performance of glyme-based electrolytes in symmetric lithium metal cells containing LiTDI salt is improved compared to LiTf salt as a consequence of chemical composition and morphology of the solid electrolyte interphase. The solid electrolyte interphase in the LiTDI case is more dense and contains additional species beneficial for ionic conduction and mechanical properties (e.g., Li3N).
A Dopant Replacement-Driven Molten Salt Method toward the Synthesis of Sub-5-nm-Sized Ultrathin Nanowires
- First Published: 07 May 2020
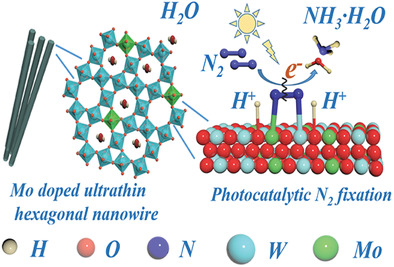
Hexagonal tungsten oxide with the morphology of ultrathin nanowires can be synthesized by molten-salt method, which is critically dependent on the substantial proportion of molybdenum (Mo) dopant. The ultrathin nanowires exhibit a high NH3-production rate of 370 µmol g−1 h−1 for photocatalytic nitrogen (N2) fixation, benefiting from the interplay between Mo-dopant and surface hydroxylation of the hexagonal structure.
Efficient Gene Therapy of Pancreatic Cancer via a Peptide Nucleic Acid (PNA)-Loaded Layered Double Hydroxides (LDH) Nanoplatform
- First Published: 13 May 2020
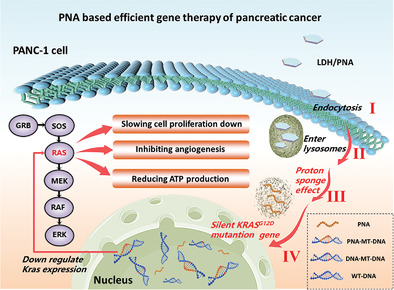
A peptide nucleic acid (PNA)-based gene therapy shows promise for safely inhibiting pancreatic cancer progression and metastasis via V-Ki-ras2 Kirsten ratsarcoma viral oncogene homolog mutation silencing. Treatments with layered double hydroxide loaded PNA demonstrate markedly inhibited growth of pancreatic cancer xenografts, and consequently, the 100% survival rate of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma xenografted mice for at least 60 days.
Frontispiece
Water Treatment: High Virus Removal by Self-Organized Nanostructured 2D Liquid-Crystalline Smectic Membranes for Water Treatment (Small 23/2020)
- First Published: 12 June 2020

In article number 2001721, Takeshi Sakamoto, Hiroyuki Katayama, Takashi Kato, and co-workers achieve high virus removal for liquid-crystalline water treatment membranes. The liquid crystal forms 2D lamellar nanochannels allowing superior virus removal while maintaining efficient water flux. The removal efficiency is 99.999994%. Self-assembly of smectic liquid crystals and subsequent photopolymerization leads to the formation of nanostructured 2D materials.
Full Papers
High Virus Removal by Self-Organized Nanostructured 2D Liquid-Crystalline Smectic Membranes for Water Treatment
- First Published: 04 May 2020
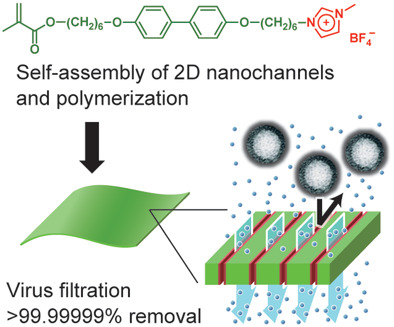
A 2D virus removal membrane for water treatment based on polymeric self-assembling liquid crystal is developed. The obtained polymer membrane shows excellent virus removal with 99.999994% efficiency. The liquid crystal forms 2D lamellar nanochannels allowing superior virus removal while maintaining improved permeation.
Atomically Thin Oxyhalide Solar-Blind Photodetectors
- First Published: 29 April 2020
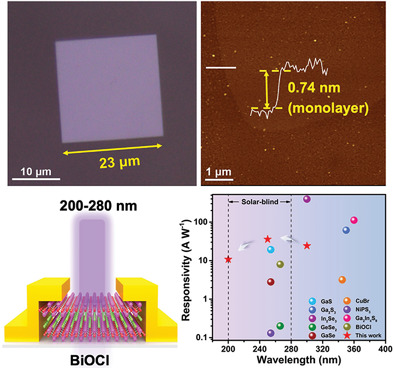
This work demonstrates the synthesis of large-size atomically thin BiOCl flakes via salt-assisted chemical vapor deposition. The BiOCl flake based solar-blind UV photodetectors exhibit a responsivity up to 35.7 A W−1 and detectivity of 2.2 × 1010 Jones at 250 nm, and also possess high responsivity across the solar-blind range.
Biomimetic Engineering of a Scavenger-Free Nitric Oxide-Generating/Delivering System to Enhance Radiation Therapy
- First Published: 04 May 2020
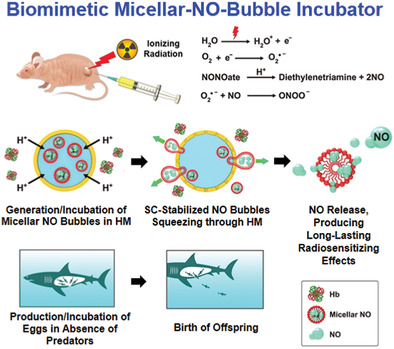
The as-proposed hollow microsphere system may function as an incubator for the generation and delivery of NO in a scavenger-free environment, analogous to the protection offered by ovoviviparous fish against predation before birth of their offspring. Upon leaving the incubator, the NO molecules may passively diffuse through their protected-surfactant layer gradually to the tumor site, performing long-lasting radiosensitization.
In Situ Fabrication of Ultrasmall Gold Nanoparticles/2D MOFs Hybrid as Nanozyme for Antibacterial Therapy
- First Published: 05 May 2020
Autonomous Biohybrid Urchin-Like Microperforator for Intracellular Payload Delivery
- First Published: 06 May 2020
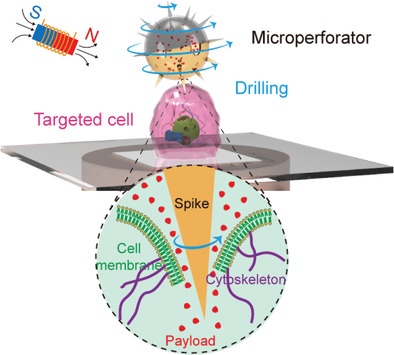
A magnetic urchin-like microswimmer based on sunflower pollen grain that can pierce the cancer cell membrane and actively deliver therapeutic drugs is reported. These dual-action microswimmers demonstrate good biocompatibility, high intelligence, precision in single-cell targeting, and sufficient drug loading, presenting a promising avenue for a variety of biomedical applications.
Elucidation of Active Sites on S, N Codoped Carbon Cubes Embedding Co–Fe Carbides toward Reversible Oxygen Conversion in High-Performance Zinc–Air Batteries
- First Published: 05 May 2020
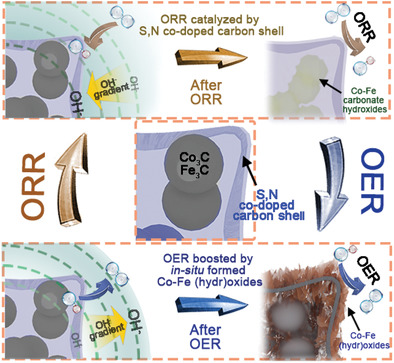
Co–Fe Prussian blue analogues are coated with methionine to fabricate S, N codoped carbon cubes embedding Co–Fe carbides, showing superb capacity in catalyzing reversible oxygen conversion. The activity origin and catalyst fate are well elucidated through elaborate control studies and postelectrolytic characterizations.
Sandwich Photothermal Membrane with Confined Hierarchical Carbon Cells Enabling High-Efficiency Solar Steam Generation
- First Published: 06 May 2020
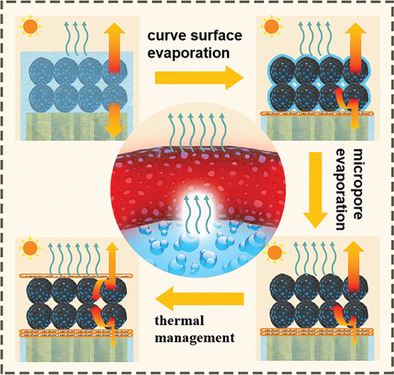
A sandwich photothermal membrane is prepared by confining the hierarchical porous carbon cells in two energy barriers to achieve a rapid water evaporation rate of 1.87 kg m−2 h−1 under 1 sun illumination. The significantly enhanced evaporation rate is mainly attributed to the inherently optimized micropore evaporation mode, and the synergistically regulated water transporting and thermal management performance.
Hierarchical Octahedra Constructed by Cu2S/MoS2⊂Carbon Framework with Enhanced Sodium Storage
- First Published: 06 May 2020
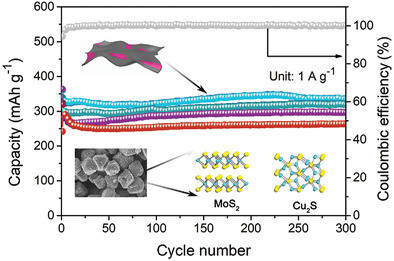
The first synthesis of novel hierarchical microoctahedra is realized by a self-template and subsequent vulcanization treatment, which are constructed by Cu2S/MoS2 heterojunction structural nanosheets immobilized on the 3D porous carbon framework (Cu2S/MoS2⊂PCF). Due to the distinctive structural and compositional features, these Cu2S/MoS2⊂PCF microoctahedra show excellent sodium-storage performance including high capacity, excellent rate capability, and superior cycling stability.
A Highly-Efficient Type I Photosensitizer with Robust Vascular-Disruption Activity for Hypoxic-and-Metastatic Tumor Specific Photodynamic Therapy
- First Published: 06 May 2020
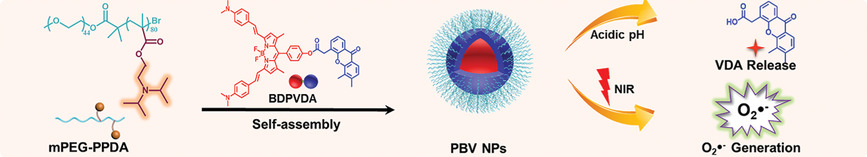
A type I photosensitizer (PBV NP) with excellent O2∙− photogeneration ability is devised. Triggered by acidic tumor microenvironment, vadimezan, a vascular disrupting agent, can be effectively released from PBV NPs, facilitating the shut-down of tumor vasculature. Harnessing the effective vadimezan release and O2∙− generation of PBV NPs, excellent hypoxic-tumor ablation is achieved without any metastasis occurrence during the whole life-span of mice .
ATP Suppression by pH-Activated Mitochondria-Targeted Delivery of Nitric Oxide Nanoplatform for Drug Resistance Reversal and Metastasis Inhibition
- First Published: 06 May 2020
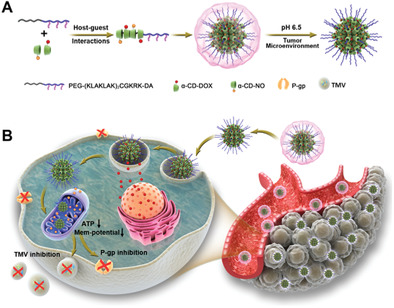
An acid-activated mitochondria-targeted drug nanoplatform is developed for precise subcellular delivery of nitric oxide to induce mitochondria dysfunction through facilitating mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and downregulating adenosine triphosphate (ATP) level. Such an energy suppressing strategy proves crucial in inhibiting P-glycoprotein-related bioactivities and tumor-derived microvesicles formation, showing great potential to overcome drug resistance and cancer metastasis.
Freestanding 1T-MnxMo1–xS2–ySey and MoFe2S4–zSez Ultrathin Nanosheet-Structured Electrodes for Highly Efficient Flexible Solid-State Asymmetric Supercapacitors
- First Published: 06 May 2020
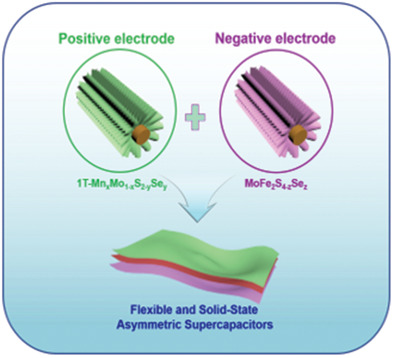
A single-step fabrication of 1T-MnxMo1−xS2−ySey and MoFe2S4−zSez nanosheet arrays based high-performance flexible and solid-state asymmetric supercapacitor (FS-ASC) is reported. FS-ASC shows high energy density and power density compared to contemporary reported transition-metal dichalcogenides based supercapacitor due to increase in surface area, enrichment of 1T phase, and expansion in the interlayer spacing following co-doping and intercalation of metal and nonmetals .
DNA-Driven Two-Layer Core–Satellite Gold Nanostructures for Ultrasensitive MicroRNA Detection in Living Cells
- First Published: 06 May 2020
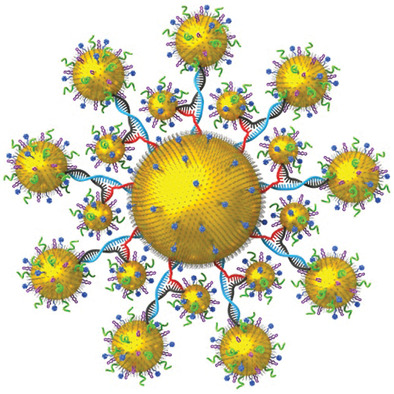
DNA-driven two-layer core–satellite assembly is fabricated to detect the microRNA (miRNA) in living cells. With the circular dichroism and surface-enhanced Raman scattering signals, the ultrasensitive detection of miRNA in living cells is successfully achieved. The developed fabrication strategy opens up an avenue for ultrasensitive, highly accurate, and reliable diagnoses of clinical diseases.
Hydrogen Terminated Germanene for a Robust Self-Powered Flexible Photoelectrochemical Photodetector
- First Published: 10 May 2020
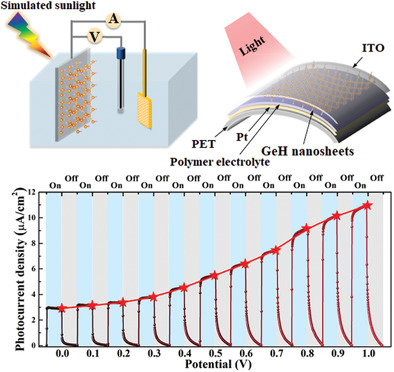
A flexible, controllable, and robust photoelectrochemical (PEC)-type photodetector based on hydrogen-terminated germanene is demonstrated that exhibits a high photocurrent density of 2.9 µA cm−2 with zero bias potential, excellent responsivity as well as short response time. This efficient strategy suggests a path to promising high-performance, self-powered, flexible photodetectors, and it also paves the way to a practical application of germanene.
Constructing Pure Phase Tungsten-Based Bimetallic Carbide Nanosheet as an Efficient Bifunctional Electrocatalyst for Overall Water Splitting
- First Published: 07 May 2020
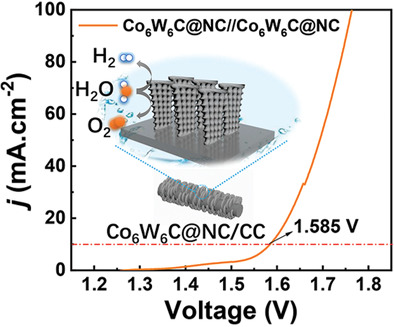
Vertically aligned porous cobalt tungsten carbide nanosheet embedded in N-doped carbon matrix is constructed via a facile metal–organic frameworks derived method and exhibits excellent hydrogen evolution reaction and oxygen evolution reaction catalytic activity in alkaline solution. The two-electrode water splitting device requires a low cell voltage of 1.585 V at 10 mA cm−2 with a great stability.
Nanoscale Correlations between Metal–Insulator Transition and Resistive Switching Effect in Metallic Perovskite Oxides
- First Published: 10 May 2020
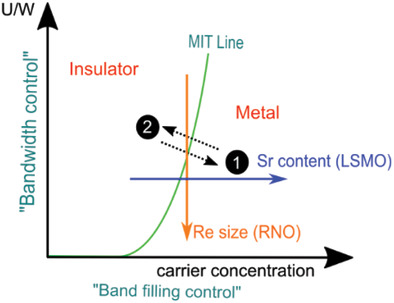
This work originally addresses the role of chemical substitution in tuning the metal–insulator transition (MIT) and the associated changes in the intrinsic resistive switching (RS) parameters in two strongly correlated systems, lanthanum strontium manganites (band-filling-controlled MIT) and rare-earth nickelates (bandwidth-controlled MIT) through scanning probe microscopy. These findings can help to optimize RS devices based on metallic complex oxides.
Resource-Efficient Low-Temperature Synthesis of Microcrystalline Pb2B5O9X (X = Cl, Br) for Surfaces Studies by Optical Second Harmonic Generation
- First Published: 13 May 2020

A resource-efficient ionic-liquid-assisted, low-temperature synthesis route of high-quality Pb2B5O9X (X = Cl, Br) borate-halide microcrystallites is reported herein. Due to their finite size and large specific surface area, they exhibit excellent second harmonic conversion efficiencies. This is highly useful for surface studies, such as monitoring chemical reactions with picosecond time resolution, when investigating in situ (photo-) catalysis, and for biological sensing.
A Humidity-Induced Nontemplating Route toward Hierarchical Porous Carbon Fiber Hybrid for Efficient Bifunctional Oxygen Catalysis
- First Published: 13 May 2020
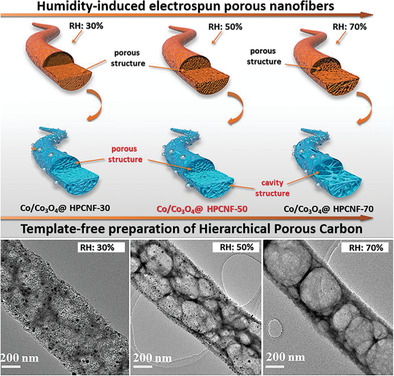
A new humidity-induced nontemplating strategy for the general synthesis of hierarchical carbon hybrid nanofibers with abundant mesopores and interconnected cavities is developed. Benefiting from the unique topology, the resulted hybrid catalyst exhibits excellent bifunctional electrocatalytic activities toward oxygen reduction/evolution reactions. Zinc–air battery based on this catalyst shows high power density and long cycle life.