Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
Cover Picture
Topological Phases of Chalcogenide Glasses Encoded in the Melt Dynamics (Phys. Status Solidi B 6/2018)
- First Published: 13 June 2018
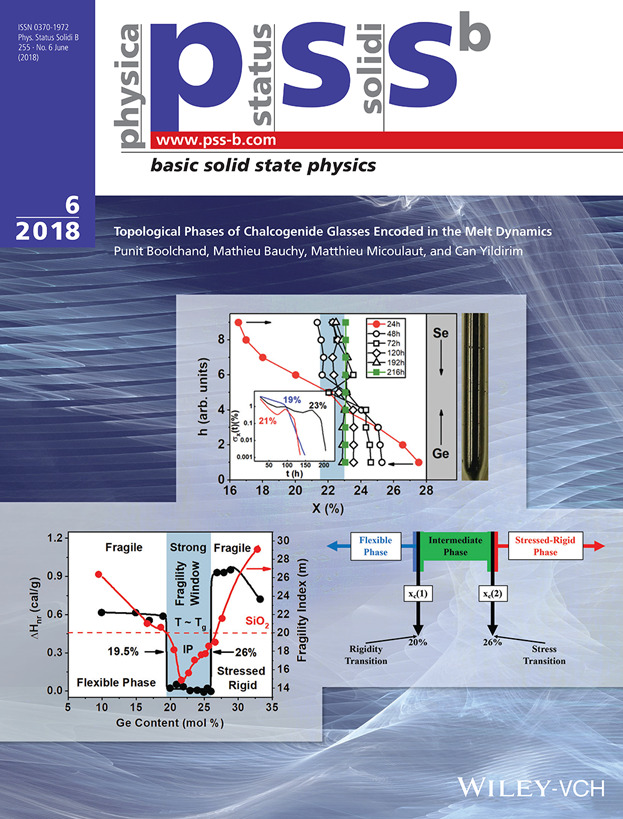
As a melt cools to form a glass, could it be that melt dynamics encode the glass topological phases? This question is addressed by Punit Boolchand and co-workers in article no. 1800027. Select Raman scattering and calorimetric experiments, on specially homogenized binary GexSe100–x and GexS100–x glasses show that, in each chalcogenide glass system, the melt fragility index (m) displays a minimum (m < 20) in the 20% < x < 26% compositional range – the fragility window. Enthalpy of relaxation (ΔHnr) at the glass transition temperature (Tg) in each glass system displays a square-well-like behavior with ΔHnr ~ 0, in the same 20% < x < 26% composition range – the reversibility window. The correlation between fragility and reversibility windows suggests that melt dynamics determine the glass topological phases, a feature that could be generic in glass science.
This article is part of the special section on “Amorphous and Nanostructured Chalcogenides”, comprising 5 articles in this issue of pss(b) and guest-edited by Mihai Popescu.
Masthead
Back Cover
Stability and Pressure Dependent Properties of Ternary Lithium Borides of Gold and Silver (Phys. Status Solidi B 6/2018)
- First Published: 13 June 2018

The lithium gold borides (LiAu3B) offer great prospect for the most efficient of potential battery systems and also as superconducting material. Aydin and Şimşek investigate these compounds by density functional first-principles calculations in article no. 1700666. The skeleton of the crystal structure consists of infinitely parallel Au3B blocks which are generated by stacking trigonal prisms, and they are located at the corners of two-dimensional pseudo honeycombs. The effect of lithium atoms to deviation of structural parameters is negligible. The pressure-dependent behavior is remarkable, insofar as Li is becoming more electropositive with the increasing pressure, and contrary, Au3B units are more electronegative. Dynamic stability of the compound diminishes at about 20 GPa pressure. The structure is unstable in fully absence of Li atoms and in existence of Ag3B blocks.
Original Papers
Amorphous and Nanostructured Chalcogenides
Formation of Nanoscale Structures on Chalcogenide Films
- First Published: 15 September 2017
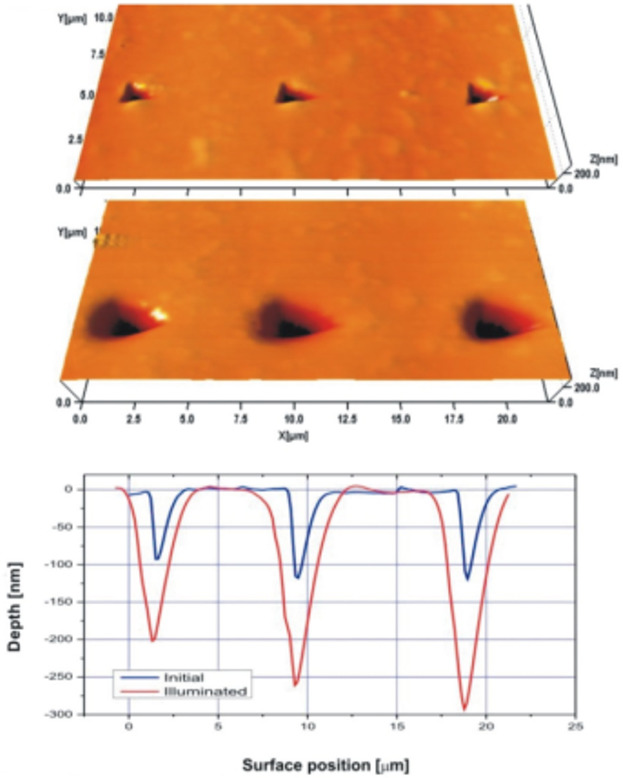
Thin films of chalcogenide vitreous semiconductors are characterized by a much higher resolving power than that of conventional optical focusing systems. The key interest is focused on the formation of elements with sizes significantly less than the values determined by the light diffraction limit. This process can be realized by using the nonlinear exposure characteristics of chalcogenide glass semiconductor films and a modification of their structure for the localization of exposing light to dimensions below the diffraction-limited area.
On the Influence of Surface Phenomena Upon Charge Transport in Te-Based Glassy Semiconductors
- First Published: 05 January 2018
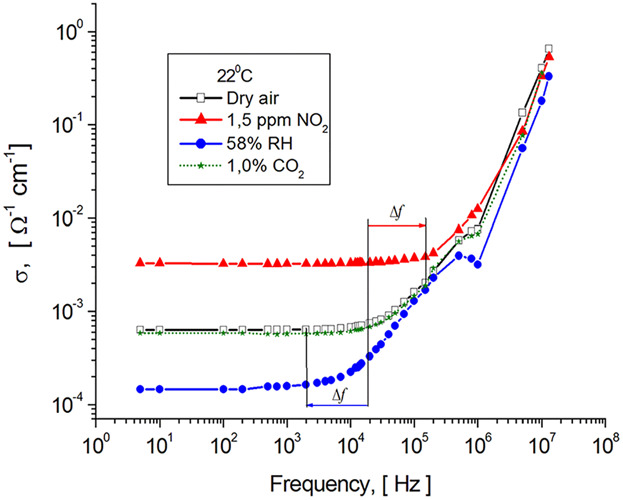
The ambient environment differently affects the AC spectra of conductivity of chalcogenide glassy semiconductors (ChGS): addition of both NO2 and water vapor strongly influences the shape of the conductivity spectrum, while the addition of CO2 practically does not affect it. Thus, the surface phenomena of ChGS caused by gas adsorption can lead to a modification of the charge transport mechanism. Apparently, this phenomenon is typical for disordered semiconductors and is due to both disturbing of the distribution of energetic states and variation of the mobility of free carriers in the region adjacent to surface.
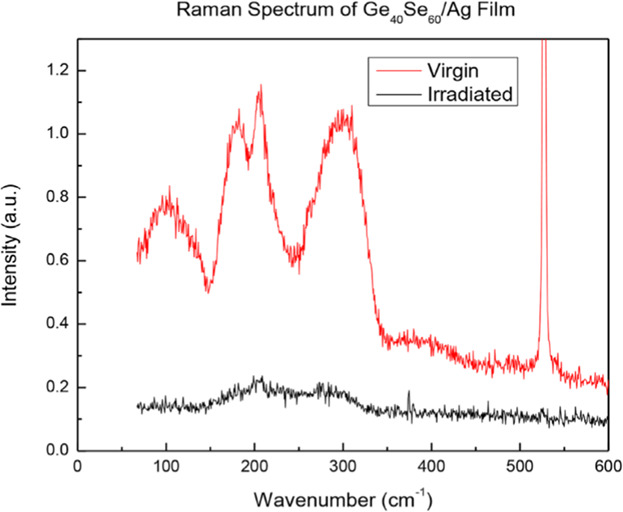
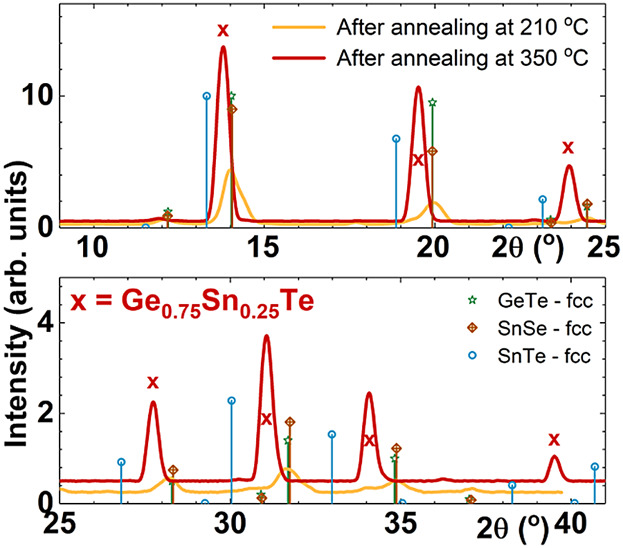
Thermal Stress Effect on the Structure and Properties of Single and Double Stacked Films of GeTe and SnSe
- First Published: 18 December 2017
Topological Phases of Chalcogenide Glasses Encoded in the Melt Dynamics
- First Published: 15 April 2018
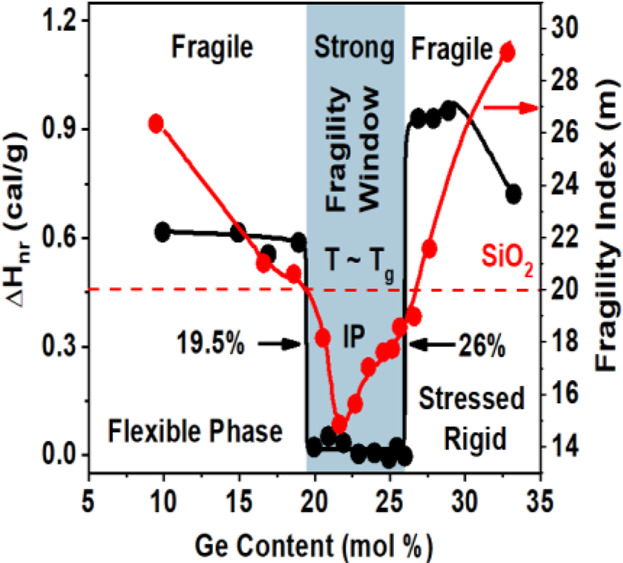
Since the inception of glass science, one has wondered whether the viscous slowdown of a melt could encode the nature of the resulting glass. Here, based on the characterization of homogeneous binary Ge–Se and Ge–S glasses and atomistic simulations, it is revealed that the dynamics of a melt unequivocally encodes the topological nature of the corresponding glass.
Perovskite-Like Ferrites
Evolution of Electronic Spectrum and Magnetic Properties of the High-Temperature Cubic Phase La1−xSrxFeO3−δ in Coherent Potential Approximation
- First Published: 05 January 2018
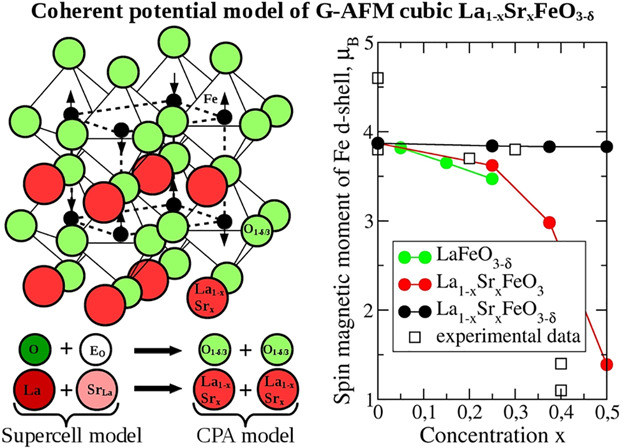
This article contains original results of calculations in the coherent potential approximation concerning the trends in the electronic spectrum and spin magnetic moments of iron in ionically compensated solid solutions La1−xSrxFeO3−δ (δ = x/2) with randomly distributed strontium acceptors and oxygen vacancies.
Electrodeposition
Effect of Bath pH on Interfacial Properties of Electrodeposited n-Cu2O Films
- First Published: 08 January 2018
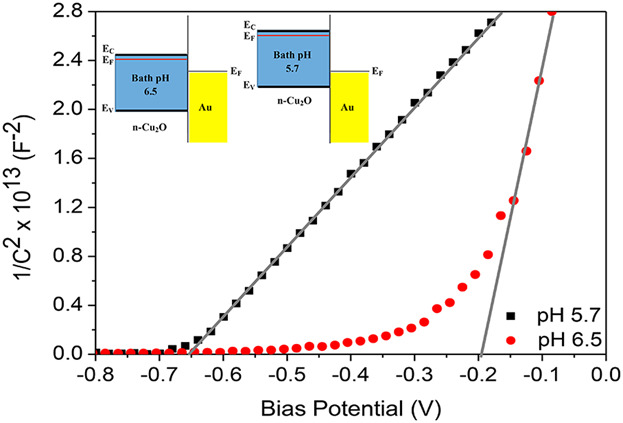
Kafi et al. carried out a systematic investigation of the interfacial properties of n-Cu2O/aqueous electrolyte junction, n-Cu2O/Au junction, and Cu2O p–n homojunction on electrodeposition bath pH. The authors observe that not only the flat-band potential of n-Cu2O/electrolyte junction but also the built-in potentials of n-Cu2O/Au and n-Cu2O/p-Cu2O junctions can be controlled with bath pH of Cu2O. Experimental evidence leads to the conclusion that bath pH modifies the relative band-edge position of electrodeposited n-Cu2O films at the interfaces.
Magnetic Hysteresis
Hysteresis Behavior of the Magnetodielectric Effect in Mn–Zn Ferrite
- First Published: 05 January 2018
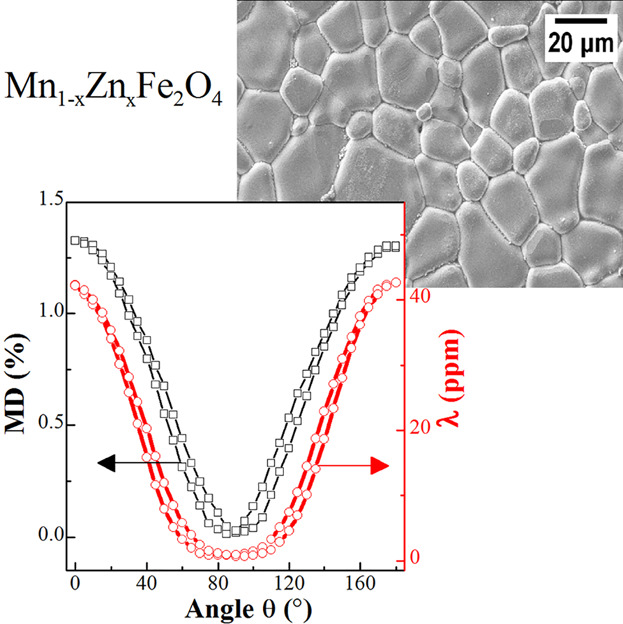
The authors have investigated the hysteresis behavior of the magnetodielectric effect for Mn–Zn ferrite with different Zn doping. Both magnetodielectric and magnetostriction curves show similar hysteresis behavior. The hysteresis behavior of the magnetodielectric effect is restricted by the magnitude of magnetoresistance ratios. It is demonstrated that the hysteresis behavior of the magnetodielectric effect results from the combination of magnetoresistance and magnetostriction effects.
Microwave Absorbers
Enhanced Microwave Absorption Properties of FeNi Nanocrystals Decorating Reduced Graphene Oxide
- First Published: 02 January 2018
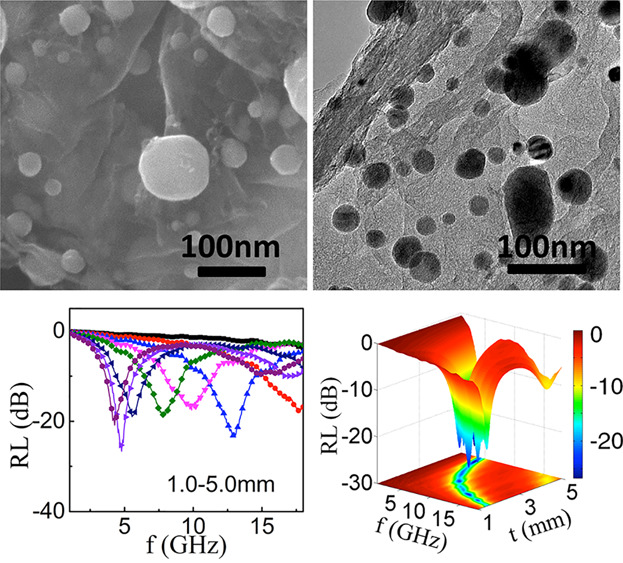
The SEM and TEM images of FeNi@rGO show that FeNi nanocrystals with size of 10–100 nm are uniformly anchored on the reduced graphene oxide (rGO) without any agglomeration. Generally, a reflection loss (RL) exceeding −10 dB can be obtained in the frequency range from 3.60 GHz to 18.00 GHz, with thickness from 1.27 to 5.00 mm for the FeNi@rGO composite.
Trilayer Junctions
Zero Bias Conductance in d-Wave Superconductor/Ferromagnet/d-Wave Superconductor Trilayers
- First Published: 06 February 2018
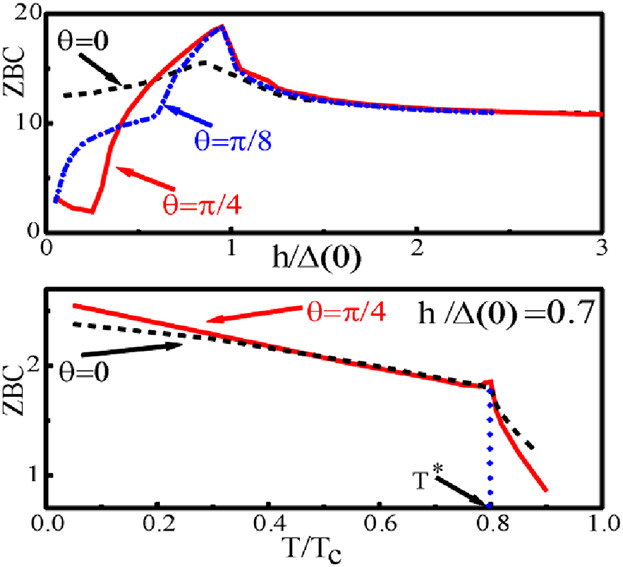
The influence of exchange field h in the barrier, temperature T, and misorientation of d-wave superconducting electrodes on zero bias conductance (ZBC) in d-wave superconductor/ferromagnet/d-wave superconductor (DFD) junctions is presented. In the small fields domain, the ZBC could be enhanced by increasing the exchange field (up to h ≈ Δ), while the temperature dependence of ZBC may show a kink at T = T* from which it is possible to determine the value of h, since h = Δ(T*).
Perovskite Cobaltites
Magnetic Relaxation Phenomena above the Freezing Temperature in the Single Layered Cobaltite La0.75Sr1.25CoO4
- First Published: 06 February 2018
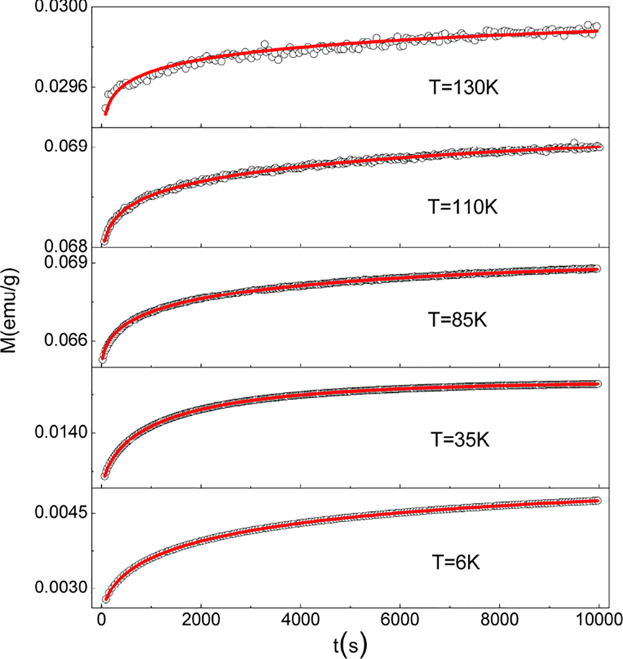
This work introduces the magnetic relaxation properties of La0.75Sr1.25CoO4. Not only below but also above the freezing temperature Tf, all magnetization measurements as a function of time display a cooperative relaxation. Above Tf, the ZFC (zero-field-cooled) relaxation follows the stretched exponential form while the FC (field-cooled) relaxation rate can be well described by a power law. These magnetic relaxation phenomena can be attributed to the local interactions between ferromagnetic clusters.
Porous Silicon
EPR Study of Porous Si:C and SiO2:C Layers
- First Published: 05 January 2018
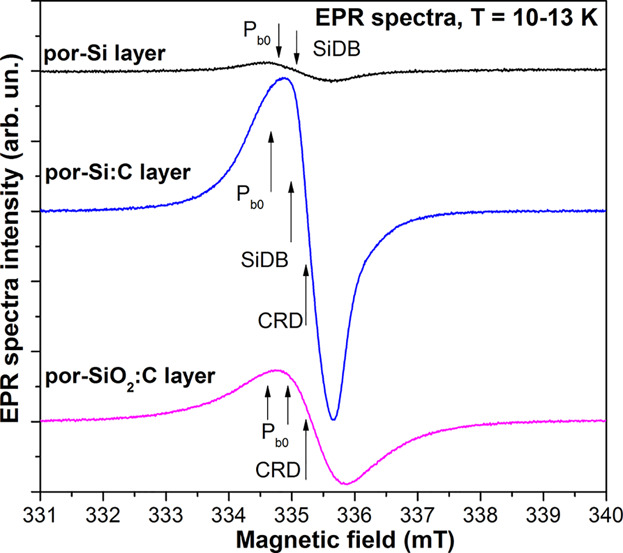
Three electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) signals, due to the Pb0 defect at the Si/SiO2 interface, silicon dangling bonds (SiDB), and carbon-related defect (CRD), respectively, were observed in carbonized porous silicon (por-Si:C). The oxidation of por-Si:C gives rise to the formation of carbon clusters and the decrease of CRD spin concentration thanks to the formation of COH carboxylic groups.
SnO2 Thin Films
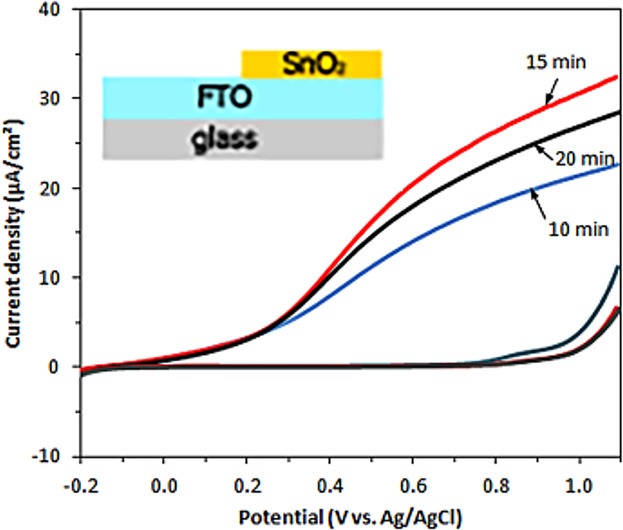
Effect of Film Thickness on Photoelectrochemical Performance of SnO2 Prepared via AACVD
- First Published: 02 February 2018
Defect Chalcopyrites
Effects of Biaxial Strains and High Pressure on the Structural, Electronic, and Vibrational Properties of DC-HgM2Te4 (M = Al, In)
- First Published: 15 January 2018
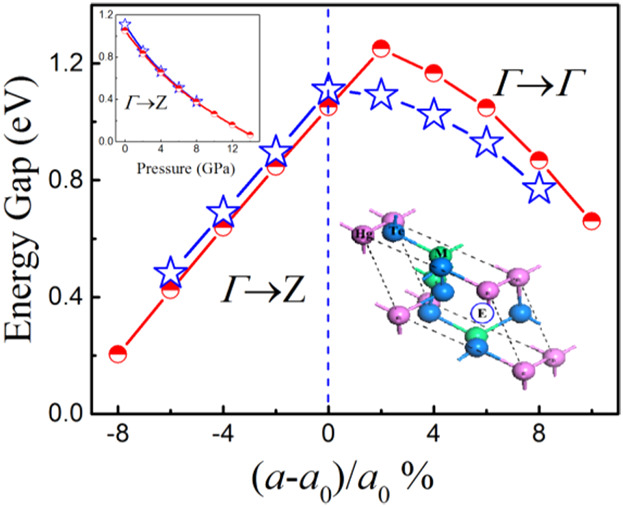
Biaxial strains and high pressure have a crucial effect on tailoring the physical properties of defect chalcopyrites such as DC-HgAl2Te4 and DC-HgIn2Te4. Different external forces play different roles in adjusting the Eg values of the defect chalcopyrites in this work. Regulating the tensile biaxial strain can make an indirect-to-direct band gap transition.
BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
Structure and Electrical Conductivity of Irradiated BaTiO3 Nanoparticles
- First Published: 06 February 2018
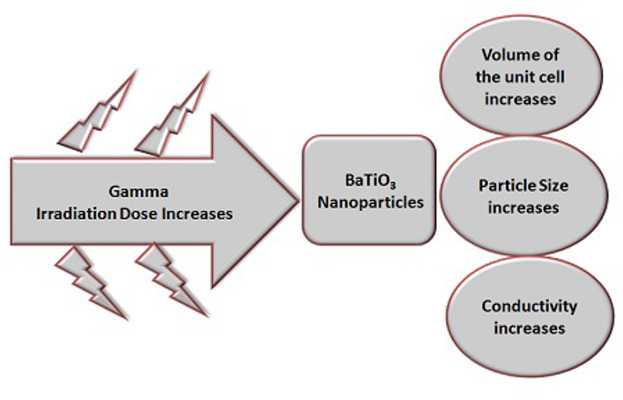
BaTiO3 nanoparticles, synthesized through hydrothermal method, were subjected to gamma radiation at room temperature with different dosages of 0, 50, 100, 150, 200, and 250 kGy. The properties of BaTiO3 are investigated via X-ray diffraction, Raman spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and impedance analyzer to clarify the changes of the crystal phase, the structure, size, dielectric property and conductivity. It is evident that there will be increase in volume of the unit cell, particle size and electrical conductivity.
Magnetic Nanoparticles
La1−xSrxMnO3 Nanoparticles for Magnetic Hyperthermia
- First Published: 31 January 2018
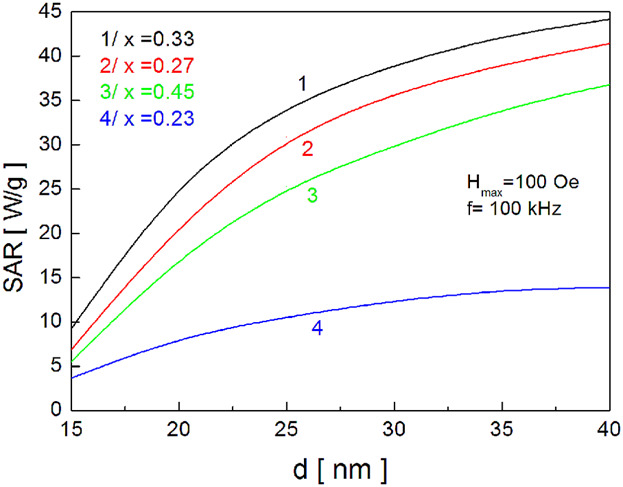
Apostolov et al. investigate LSMO nanoparticles with different Sr-dopant concentrations, sizes up to 30 nm and phase transition temperature TC = 315 K. The numerical results for the dependence of TC, saturation magnetization Ms and coercivity HC on the nanoparticles sizes and the Sr doping concentration are explained on a microscopic level. The authors calculate the specific absorption rate (SAR) which characterizes the efficiency of the absorption energy when magnetic hyperthermia is applied as a therapeutic method for the treatment of tumors.
Charge Trapping
Excellent Charge-Storage Properties of Polystyrene/SFXs Electret Films by Repeated Contact with an AFM Probe
- First Published: 14 February 2018

The charge-storage properties of PS/SFXs films are studied by the single and repeated-contact modes with atomic force microscopy probe. The results show that the contact duration and the number of contacts can improve the properties of the trapped charges in samples. The repeated-contact mode is promising for stability of trapped charges in PS/SFXs. The possible physical mechanisms are discussed.
Co-Doped Anatase
Electronic Structure and Optical Absorption Spectra of C–Cr Co-Doped Anatase TiO2 Based on First Principles
- First Published: 19 January 2018
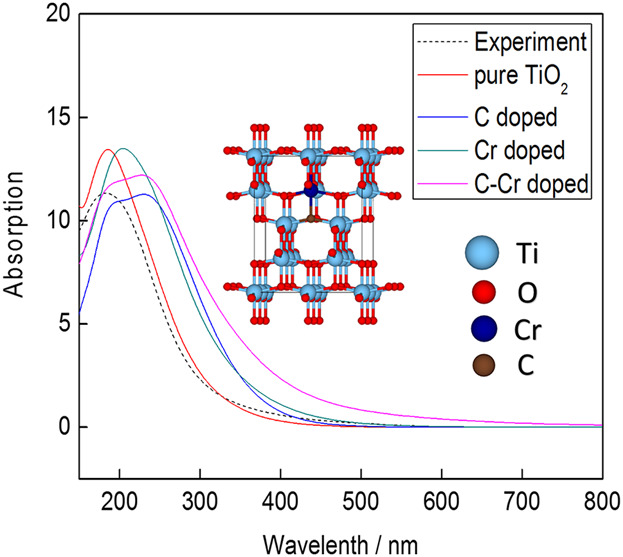
The electronic and optical properties of C/Cr doped TiO2 are compared via theoretical calculation by GGA + U method, based on density functional theory. The visible light absorption of anatase TiO2 is effectively enhanced by C–Cr co-doping. The synergistic effect of C and Cr on the electronic structure is responsible for improvement of photocatalytic performance.
Anatase Thin Films
The Effect of Strain and Grain Size on Phonon and Electron Confinements in TiO2 Thin Films
- First Published: 20 February 2018
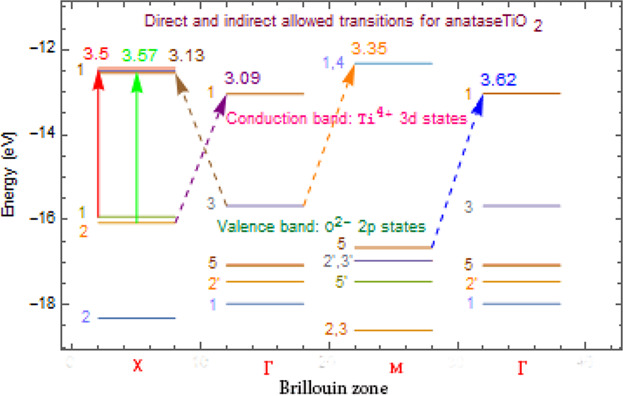
Anatase TiO2 thin films are investigated by absorption spectroscopy and Raman scattering. Absorption spectroscopy shows that band gap energy increases with decreasing grain size. An absorption model is used to determine the grain size, size distribution, and allowed transition energies. Two direct transitions and four indirect ones are observed. Raman spectroscopy shows that the phonon frequency, accompanied with the indirect transition, is blueshifted as grain size decreases.
Porous Silicon
Long-Range Interaction Between NO2 Molecules, Impurity Boron Atoms and Si Atoms with Dangling Bonds in Porous Silicon
- First Published: 07 February 2018
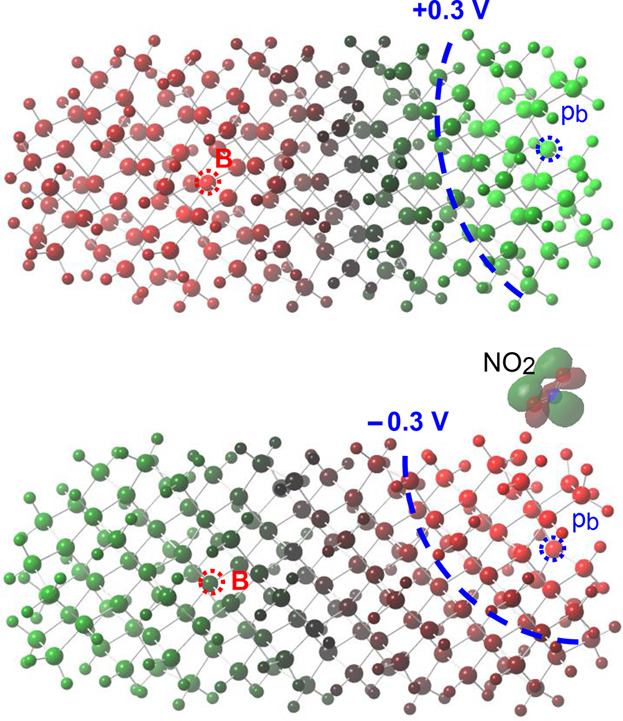
DFT calculations show that surface dangling bonds of Si atoms (pb-centers) can passivate impurity B atoms in porous silicon at large distances up to 25 Å. In this case, around the positively charged pb-center an area of increased potential appears and a Coulomb blockade (CB) of free holes arises. The NO2 molecule adsorbed on the OH group near the pb-center creates an acceptor level. After an electron capture by this level, СB is removed.
Ternary Lithium Borides
Stability and Pressure Dependent Properties of Ternary Lithium Borides of Gold and Silver
- First Published: 14 April 2018
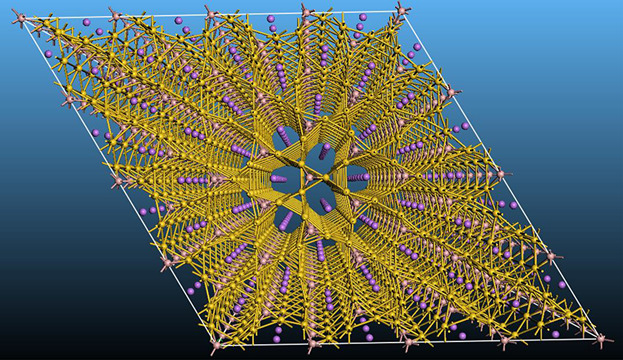
The structural, electronic, and mechanical properties, and dynamic stabilities of LiAu3B and LiAg3B ternary borides, and those of related LixAu9B3 (x = 0, 1, 2) sub-structures have been investigated. The calculations show that LiAu3B is thermodynamically, mechanically, and dynamically stable at the ambient conditions. The effects of the Li-concentration on the physical properties of the structures are discussed.
Lanthanide Sesquioxides
Ab Initio Study on Structure, Elastic, and Mechanical Properties of Lanthanide Sesquioxides
- First Published: 14 February 2018

The lanthanide sesquioxides (Ln2O3) are widely used in many applications such as catalysis, neutron absorbers in nuclear reactors, lasers, biomedical applications, optical displays, solid oxide fuel cells, etc. Density functional theory is used to study the structural and mechanical properties of the oxides. The knowledge about structural and mechanical properties of these oxides has significant impact on selecting suitable materials for novel applications.
Silicon Nitride
Effects of Hydrostatic Pressure and Biaxial Strains on the Elastic and Electronic Properties of β-Si3N4
- First Published: 12 February 2018
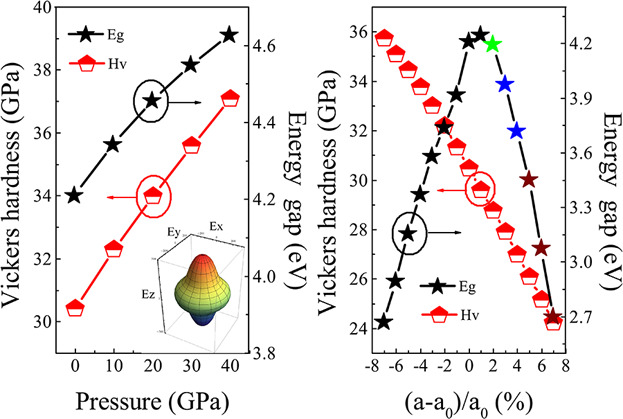
Hydrostatic pressure and biaxial strains have a significant effect on the electronic and elastic properties of hexagonal β-Si3N4. Hardness and anisotropy enhancement as well as band gap tuning can be observed by using strain engineering. β-Si3N4 undergoes an indirect to direct band-gap transition at ϵxx = 5%, while β-Si3N4 is always an indirect band-gap semiconductor under pressure and compressive strains.
Transition Metal Perovskites
Valence State of Pb in Transition Metal Perovskites PbTMO3 (TM = Ti, Ni) Determined From X-Ray Absorption Near-Edge Spectroscopy
- First Published: 07 February 2018
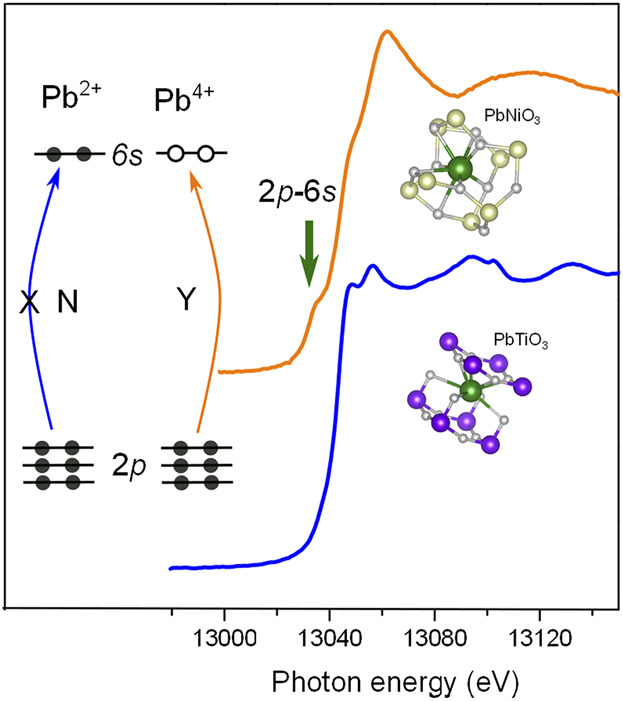
The pre-edge peak from dipole allowed 2p–6s transition is a sensitive finger-print of the Pb valence state in solid state materials. Such a pre-edge feature is observed in PbNiO3, from which the valence of Pb is determined to be Pb4+ with two 6 s holes, and no such 2p–6s related excitation is observed in PbTiO3, indicating the formation of Pb2+ with fully occupied 6s2 state in this material.