Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Study on the Transformation Process of Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Liquid-Based Cytology to Whole-Slide Image
- Pages: 106-114
- First Published: 08 January 2025
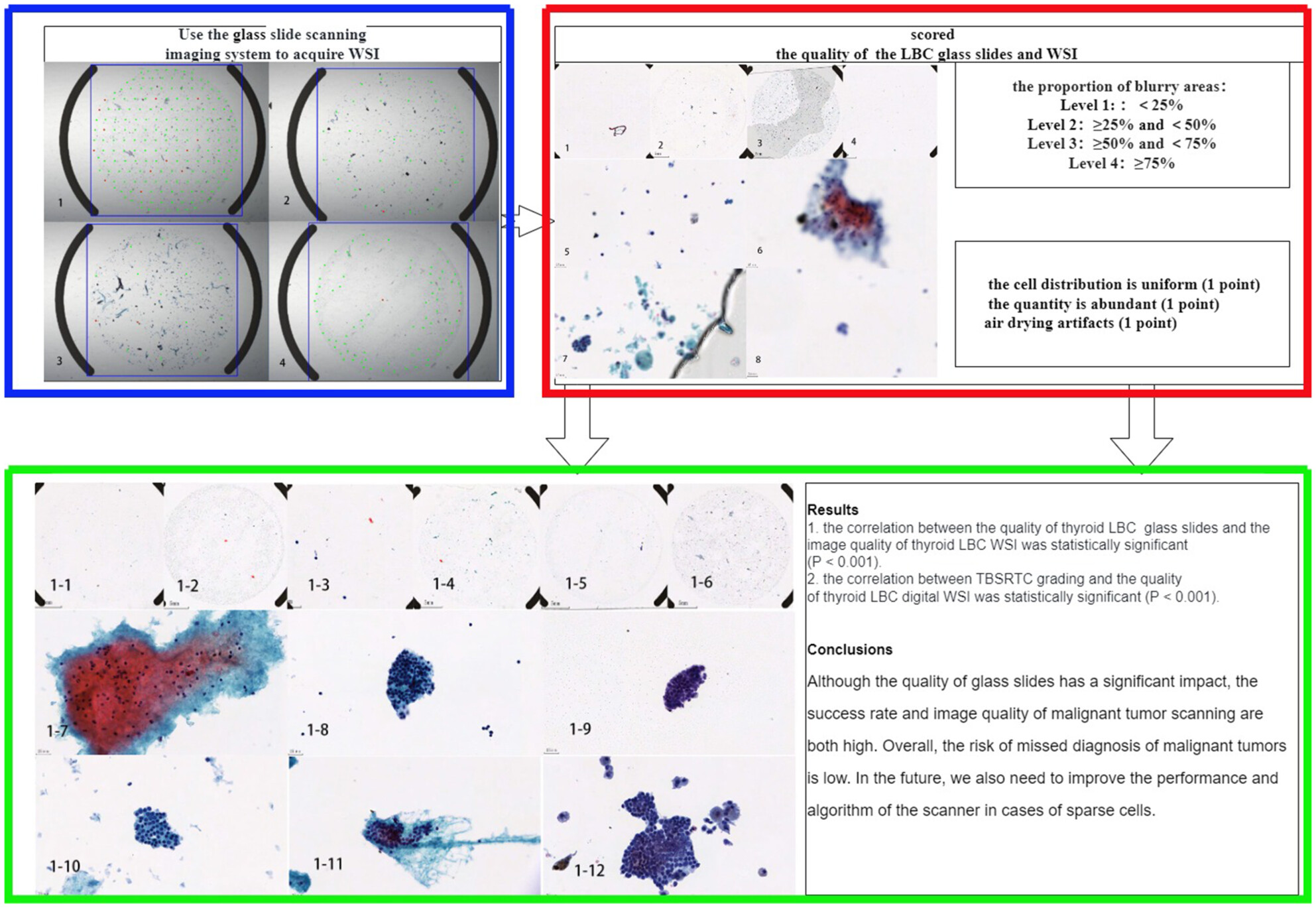
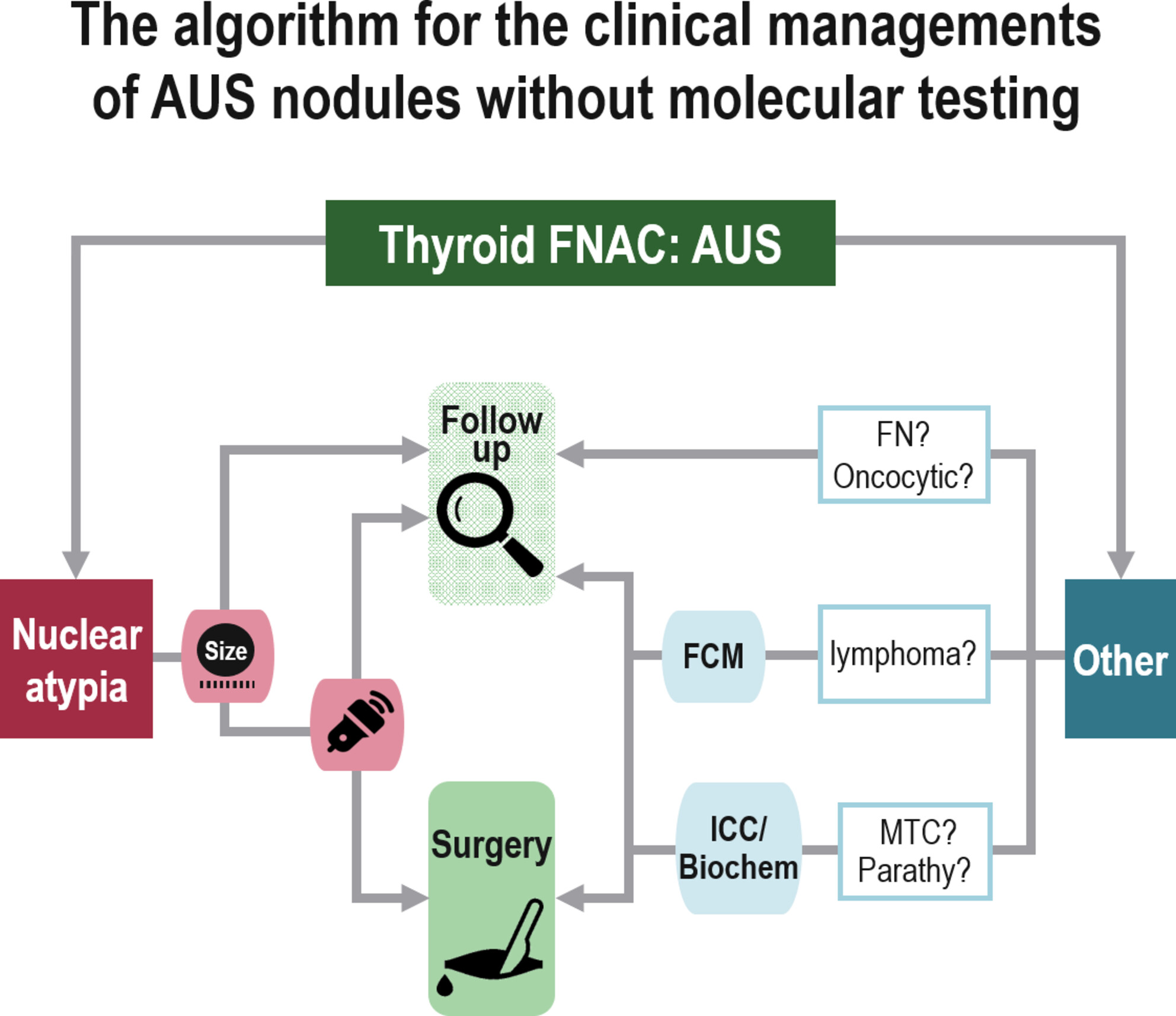
Proposal for Clinical Management of Nodules Diagnosed as Atypia of Undetermined Significance via Thyroid Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology in the Absence of Molecular Testing
- Pages: 115-122
- First Published: 10 January 2025
Reporting Bone Cytopathology—A Proposal Based on a Single Tertiary Centre Experience
- Pages: 123-139
- First Published: 09 December 2024
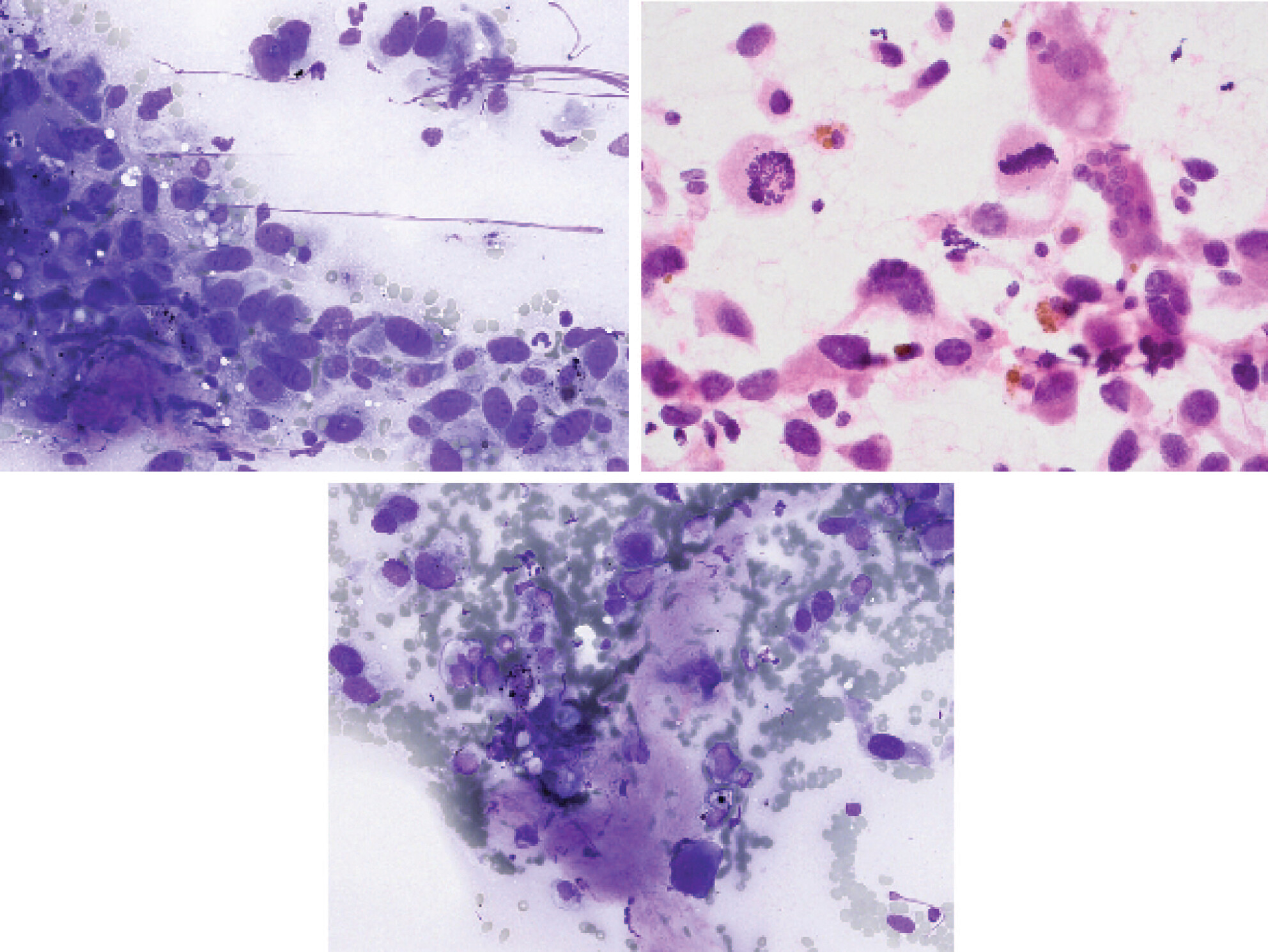
Fine-needle aspiration cytology is a reliable tool for diagnosing bone lesions, with high sensitivity, specificity and diagnostic accuracy across various tumour types. This study provides valuable insights for developing a standardised reporting system for bone cytopathology, aiming to improve diagnostic precision and patient management.
Evaluation of Diagnostic Accuracy of the Paris System (TPS 2.0) in Urine Cytology Specimens: An Institutional Experience From a Large Cohort of a Tertiary Care Centre
- Pages: 140-149
- First Published: 19 November 2024
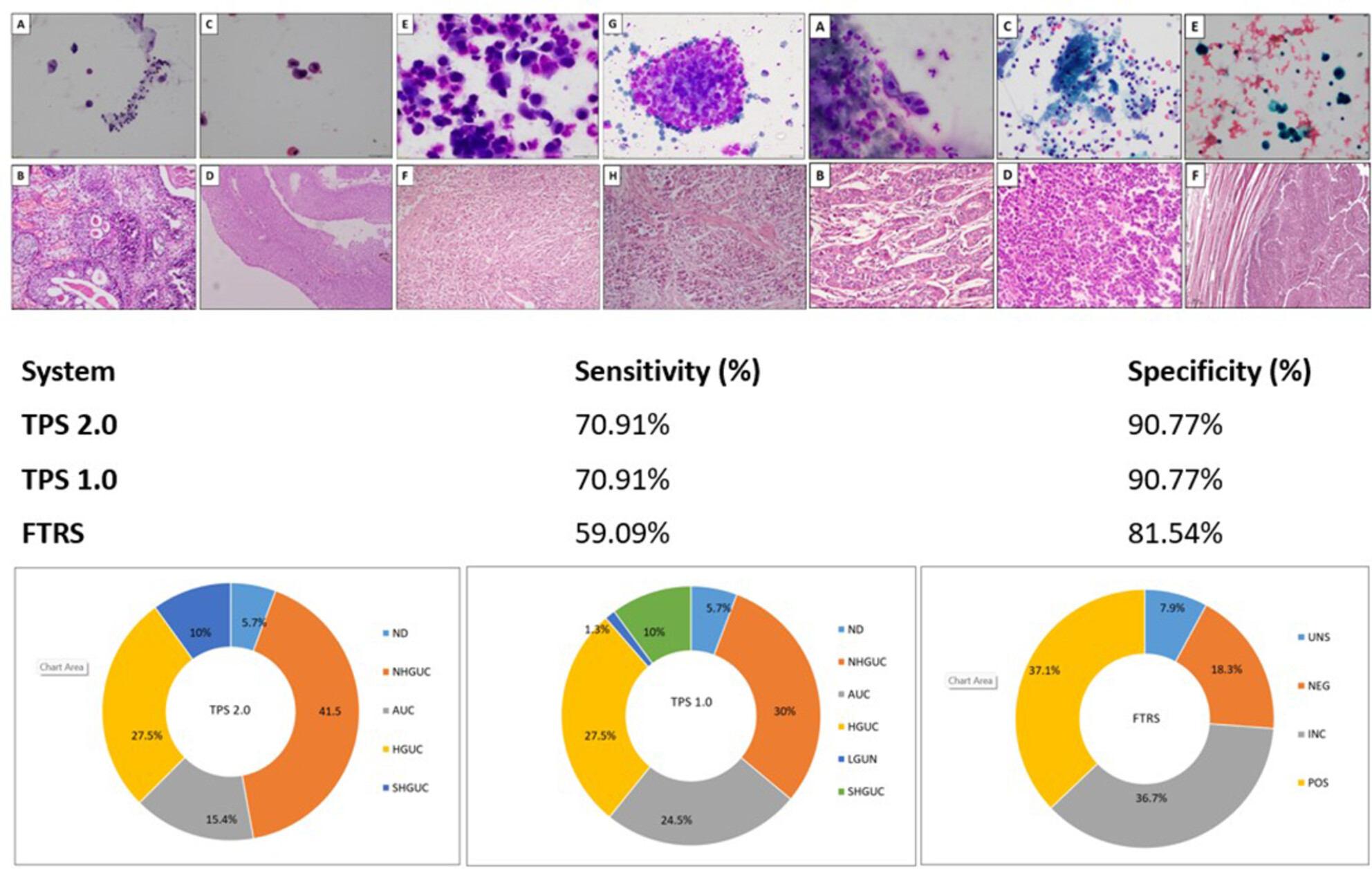
Urine cytology diagnostic performance using TPS 2.0, TPS 1.0 and FTRS for high-grade urothelial carcinoma (HGUC). Our study highlights that the Paris System (TPS) 2.0 significantly enhances the diagnostic accuracy and consistency of urine cytology in detecting high-grade urothelial carcinoma (HGUC), including upper tract urothelial carcinoma (UTUC). The integration of TPS 2.0 with emerging AI and molecular testing can further refine diagnostic precision and clinical management across urothelial neoplasms.
Detecting Cholangiocarcinoma in the Setting of Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Is Biliary Tract Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization Helpful?
- Pages: 150-155
- First Published: 04 October 2024
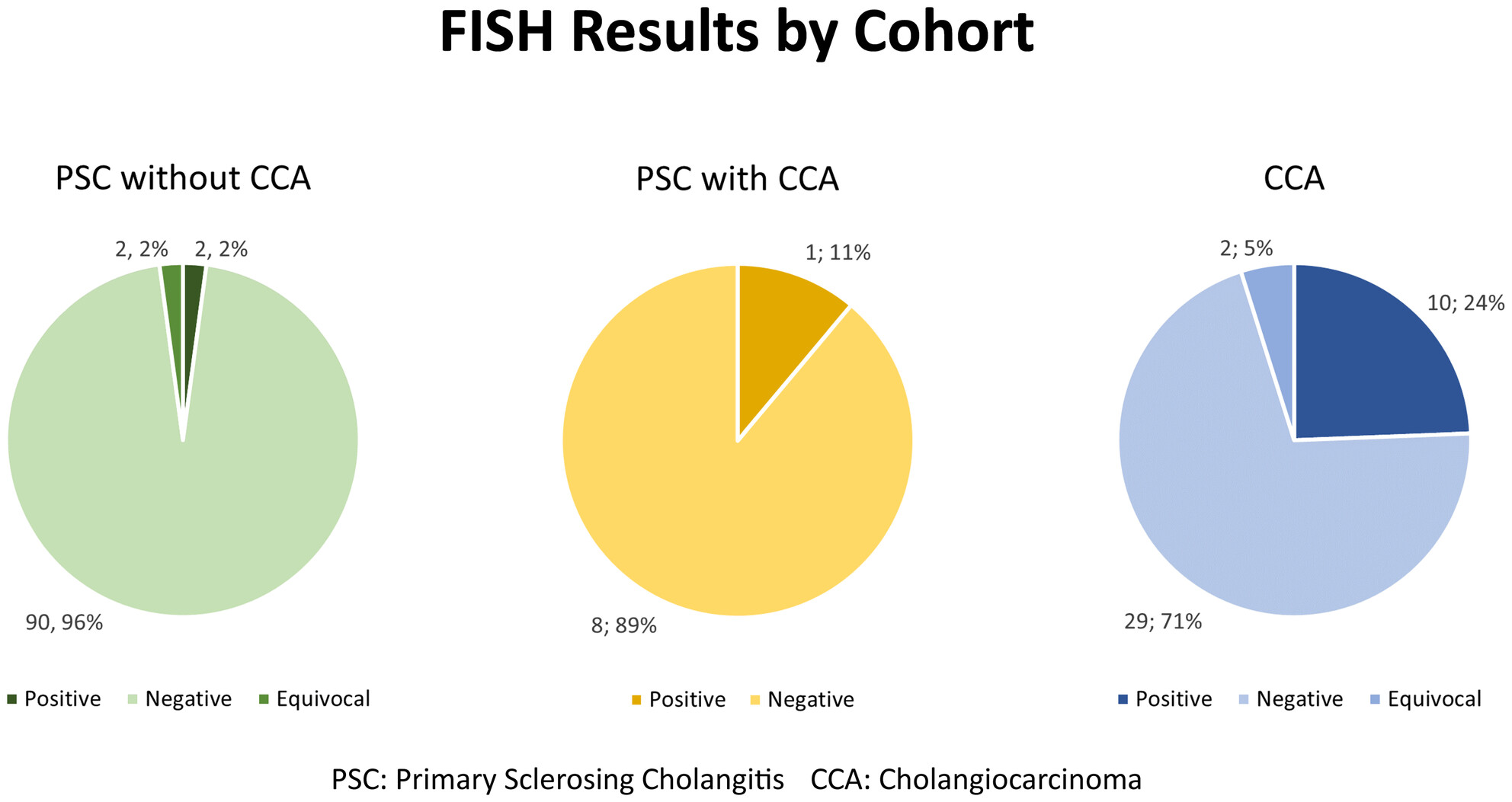
Biliary brushing cytology to detect cholangiocarcinoma is integral in the surveillance of patients with primary sclerosing cholangitis but has low sensitivity. FISH has been advocated to improve detection. This study showed low FISH positivity, which was also seen in the absence of cholangiocarcinoma.
Integration of AI-Assisted in Digital Cervical Cytology Training: A Comparative Study
- Pages: 156-164
- First Published: 08 December 2024
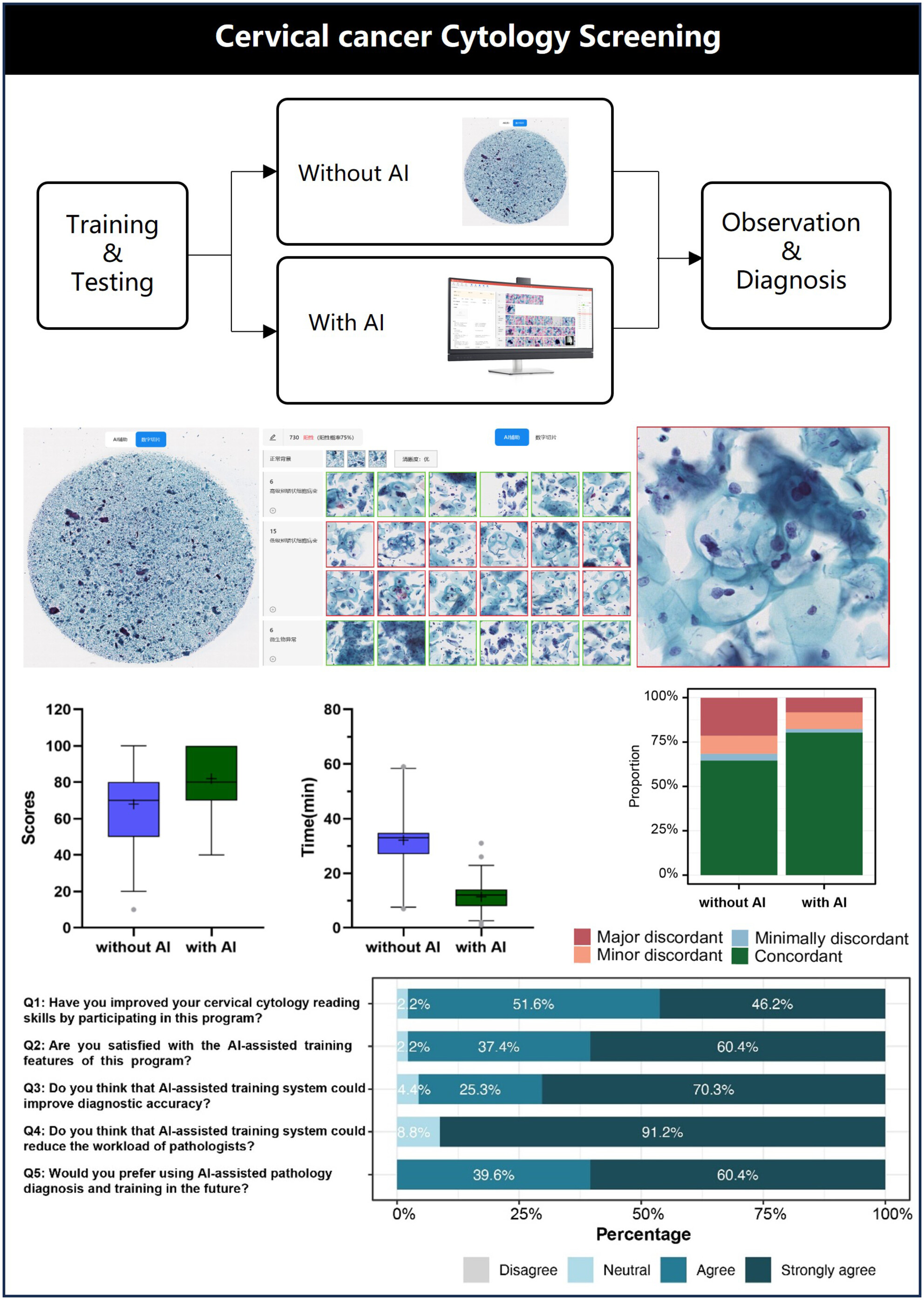
AI-assisted diagnosis can increase detection sensitivity and decrease subjectivity. This study innovatively integrated AI assistance and digital technology into cervical cytology training and demonstrated its positive impact on trainee performance and high acceptance among clinicians, suggesting its potential as a valuable adjunct to medical education.
‘Insufficient’/‘Inadequate’/‘Non-Diagnostic’ Category of the WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology, 2022: A Survey About Use in Practice
- Pages: 165-169
- First Published: 04 December 2024

There are different approaches to report inadequate samples for diagnosis in respiratory cytological samples. No clear criteria have been published for such cases. We carried out a survey among Spanish pathologists to assess the reproducibility on the practical use of these terms on cytopathological reports. Insufficient/Inadequate/Non-diagnostic category of the WHO Reporting System for Lung Cytopathology (2022) may cause discrepancies among cytopathologists and cytotechnologists. A survey was carried out to evaluate the reproducibility in the practical use of this category among Spanish pathologists in pulmonary FNACs samples.
CASE REPORT
Unveiling Diagnostic Clues of NTRK-Rearranged Spindle Cell Neoplasms in Fine-Needle Aspiration Specimens
- Pages: 170-174
- First Published: 13 December 2024
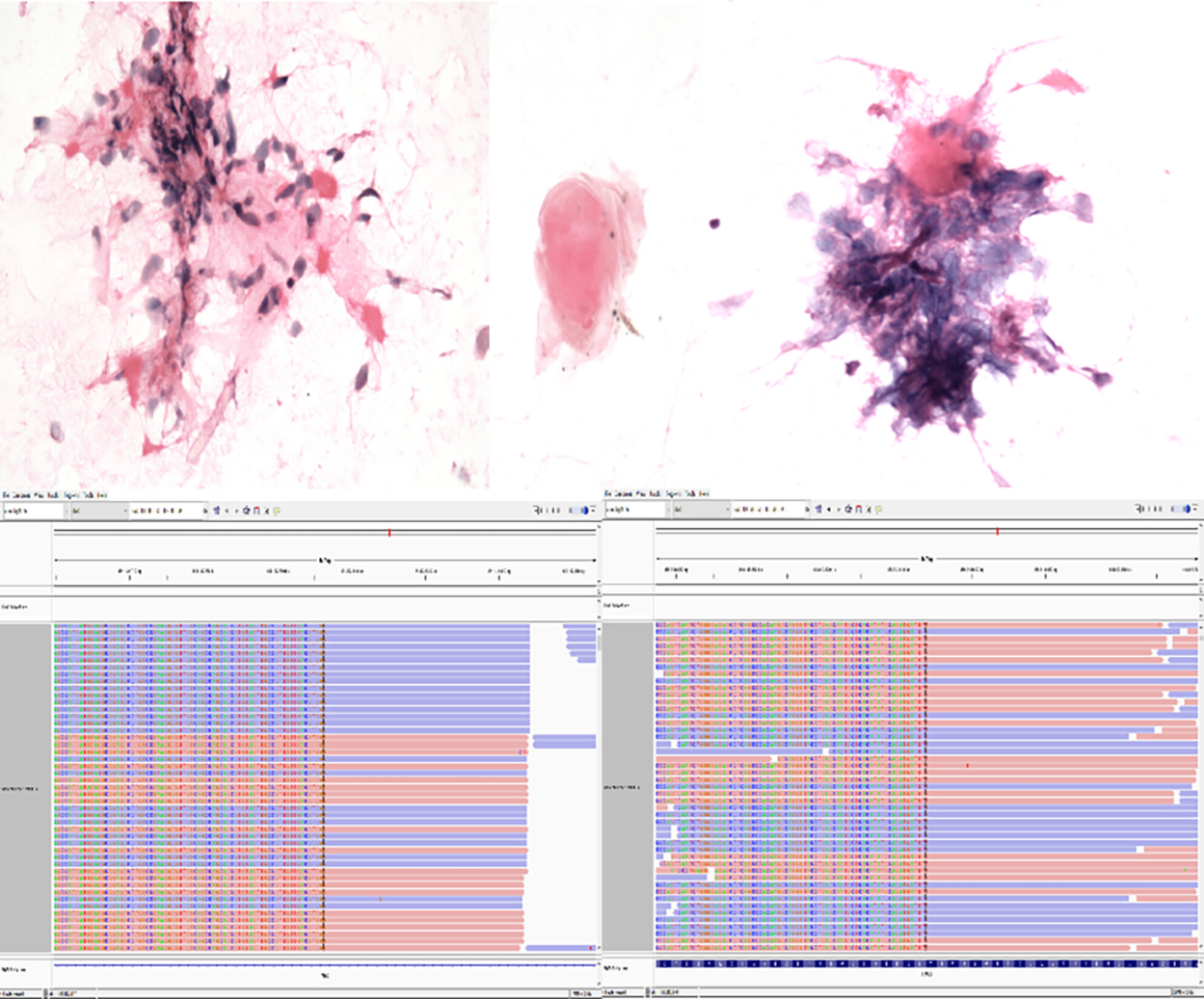
NTRK-rearranged spindle cell tumours are a new group of rare soft tissue tumours defined by molecular genetic characteristics, characterised by NTRK gene rearrangement. The diagnostic clues are a mixed pattern of sparse and densely aggregated arrangements of oval/spindle cells with red-stained unstructured substances in the background.
Cytological Features of Sialoblastoma: A Case Report With Summary of Prior Published Cases
- Pages: 175-179
- First Published: 24 December 2024
Cytological diagnosis of sialoblastoma can be challenging. This report describes describe the cytological findings of sialoblastoma in an infant along with its cytological differentials and a summary of prior published cases. Cellular smears composed of small round basaloid cells with occasional ductal formation were the main features.
Myoepithelial-Rich Pleomorphic Adenoma With Novel PLAG1 Inversion on Chromosome 8, and LRP1B, PBRM1 and TCF3 Mutations
- Pages: 180-186
- First Published: 16 November 2024
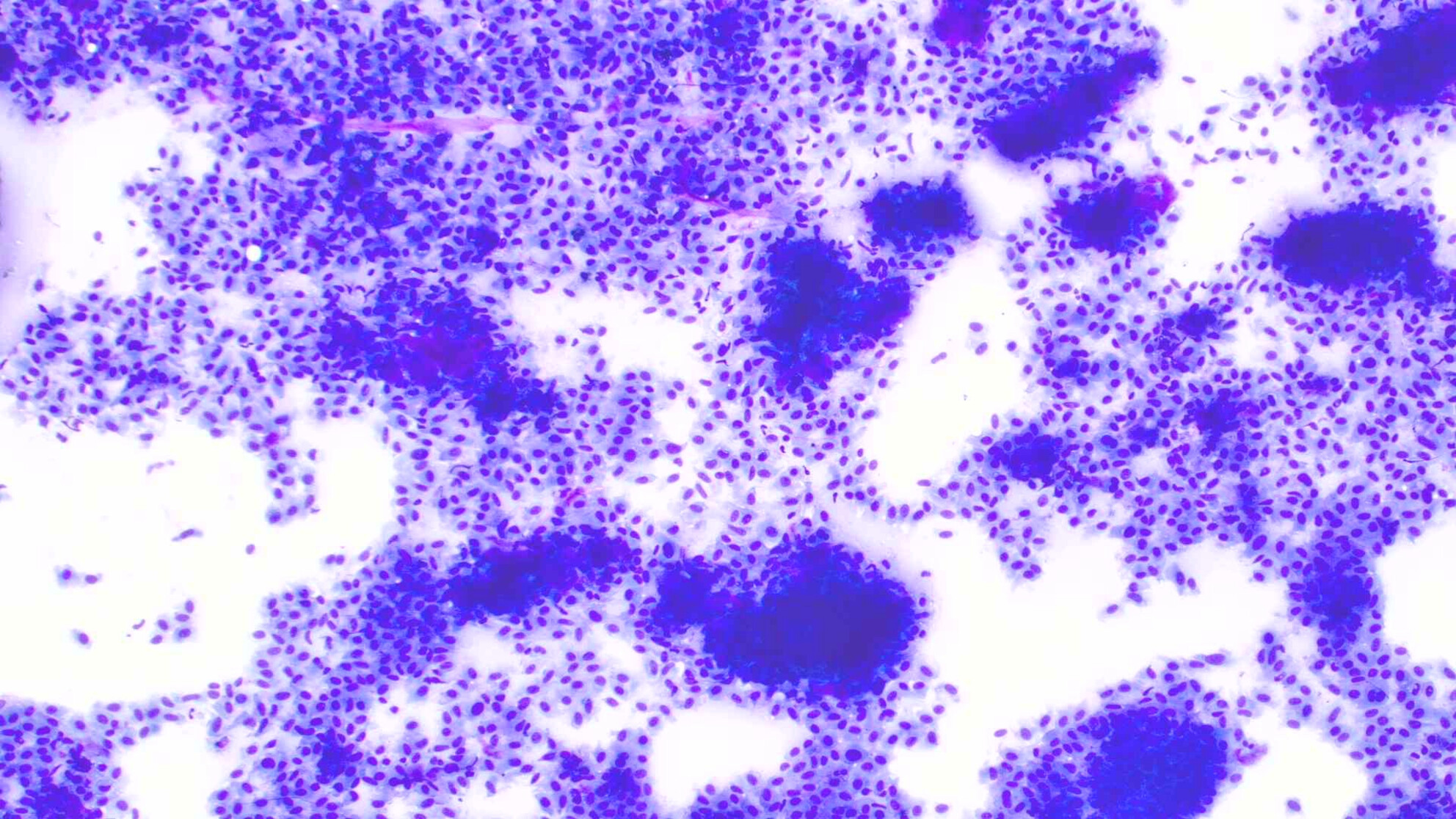
Representative images of a fine-needle aspiration showing a myoepithelial-rich pleomorphic adenoma with a novel PLAG1 inversion of chromosome 8 and LRP1B, PBRM1 and TCF3 mutations.
The diagnosis of pleomorphic adenoma may be challenging due to the predominance of one of the three components. We present the case of a 64-year-old male with a remote history of a submandibular gland excision and recent regrowth of his mass in the surgical bed, which was consistent with a myoepithelial-rich pleomorphic adenoma with a novel inversion of the chromosome 8 and LRP1B, PBRM1, and TCF3 mutations. The cytomorphologic and immunophenotypic pitfalls of this tumor and the differential diagnoses are reviewed in this article.
Plasmablastic Lymphoma in the Submandibular Region Diagnosed by FNAC: A Case Report and Literature Review
- Pages: 187-196
- First Published: 03 November 2024
FNAC is effective in the diagnosis of plasmablastic lymphoma. Immunophenotypic profile and morphological features are crucial for accurate diagnosis and cell block is an excellent tool for IHC. The literature review confirms the importance of FNAC as a diagnostic tool for PBL.
The authors present a literature review of FNAC-diagnosed plasmablastic lymphoma (PBL) cases and present a case of PBL in an HIV patient diagnosed by FNAC. Immunophenotypic profile and morphological features are crucial for accurate diagnosis and cell block is an excellent tool for IHC. The current study highlights the efficacy of FNAC in diagnosing PBL.
Fine Needle Aspiration of CD20-Negative Diffuse Large B Cell Lymphoma Presenting as an Anterior Neck Mass
- Pages: 197-200
- First Published: 22 October 2024
Aggressive lymphoma of the neck presenting with life-threatening airway compromise requires quick diagnosis, which can be rendered with fine needle aspiration cytology. In atypical cases, using multiple B cell markers can be helpful to avoid misdiagnosis.
ENIGMA PORTAL
Lymphocytic-rich effusion
- Pages: 201-203
- First Published: 10 October 2024
Cytopathology plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and management of lymphocytic effusions, which are fluid collections rich in lymphocytes often associated with conditions like infections, malignancies, and autoimmune diseases. By examining the cytological features of the cells present in the effusion, cytopathologists can help distinguish between benign and malignant processes, identify specific infectious agents, and provide insights into underlying disease mechanisms. This information is vital for guiding treatment decisions and monitoring disease progression, making cytopathology an essential tool in the clinical evaluation of lymphocytic effusions.
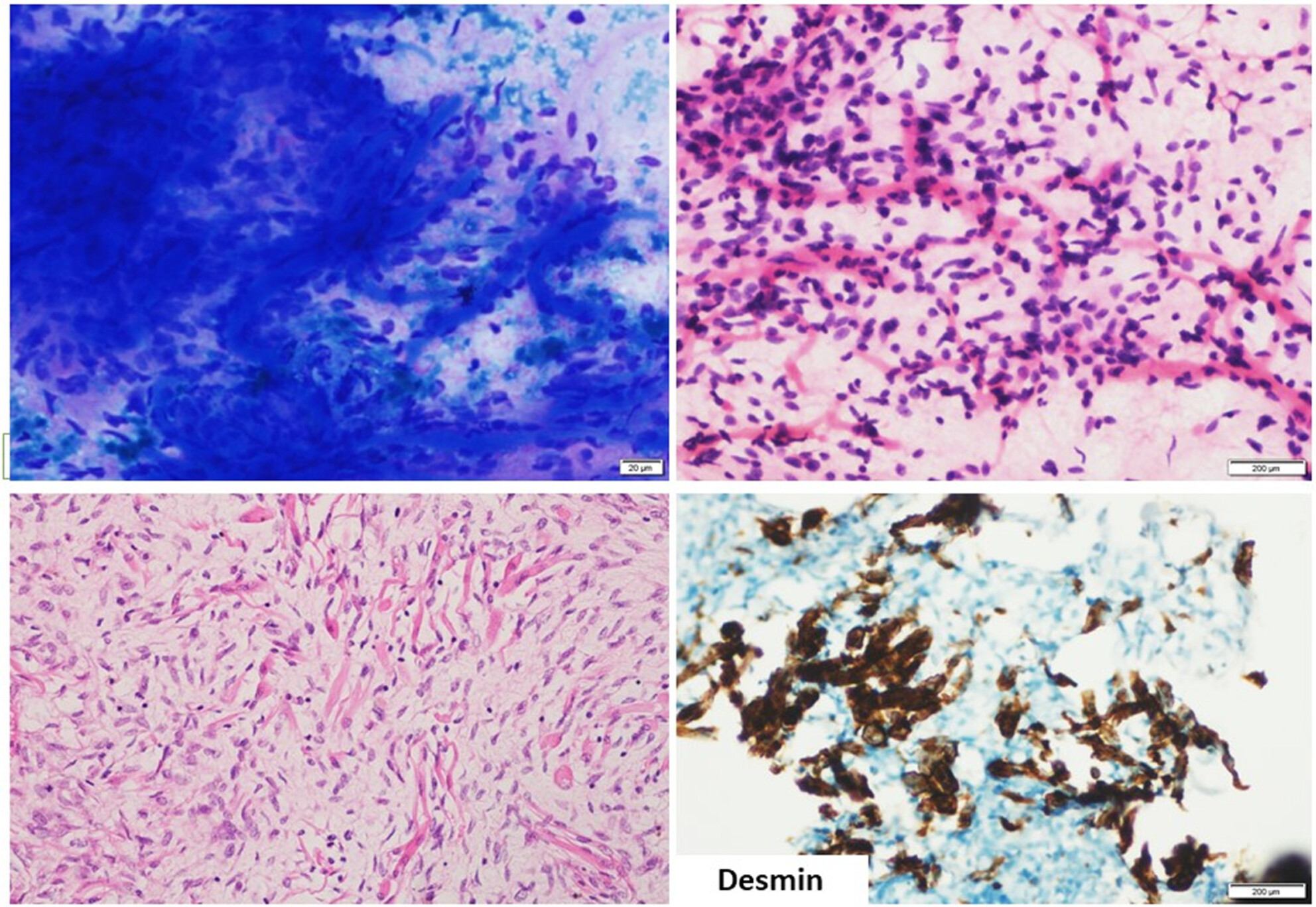
Cytology of an Axillary Mass: A Rare Case
- Pages: 204-207
- First Published: 17 December 2024
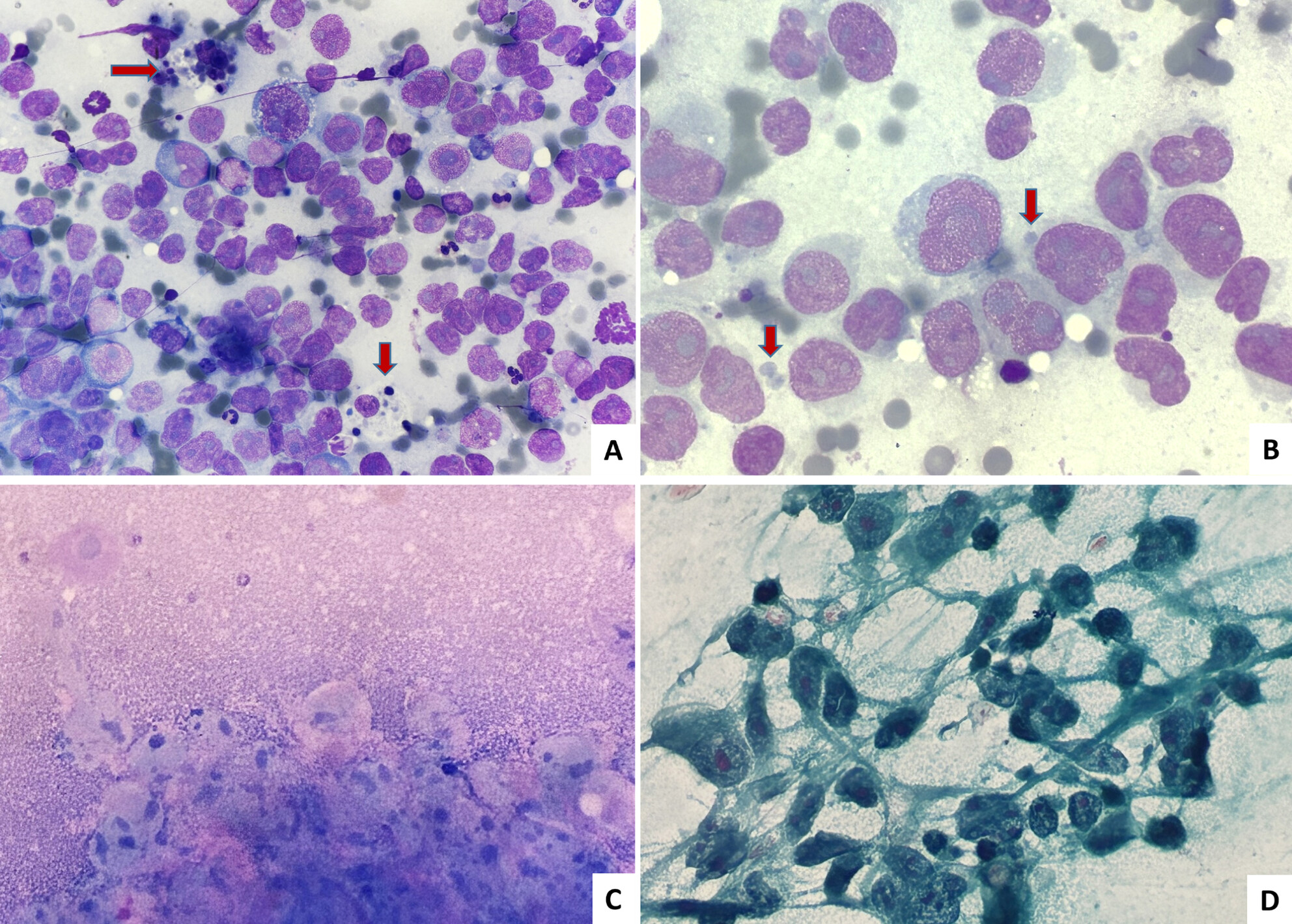
This is an interesting case of rhabdomyosarcoma, presenting at an unusual site and diagnosed on FNAC. The smears depict the typical malignant small round cell morphology and tigroid background. It illustrates the role of cell block and immunohistochemistry as important ancillary adjuncts to morphology.
Cytology of Bilateral Lymph Nodal Masses in a Young Adult
- Pages: 208-210
- First Published: 06 December 2024
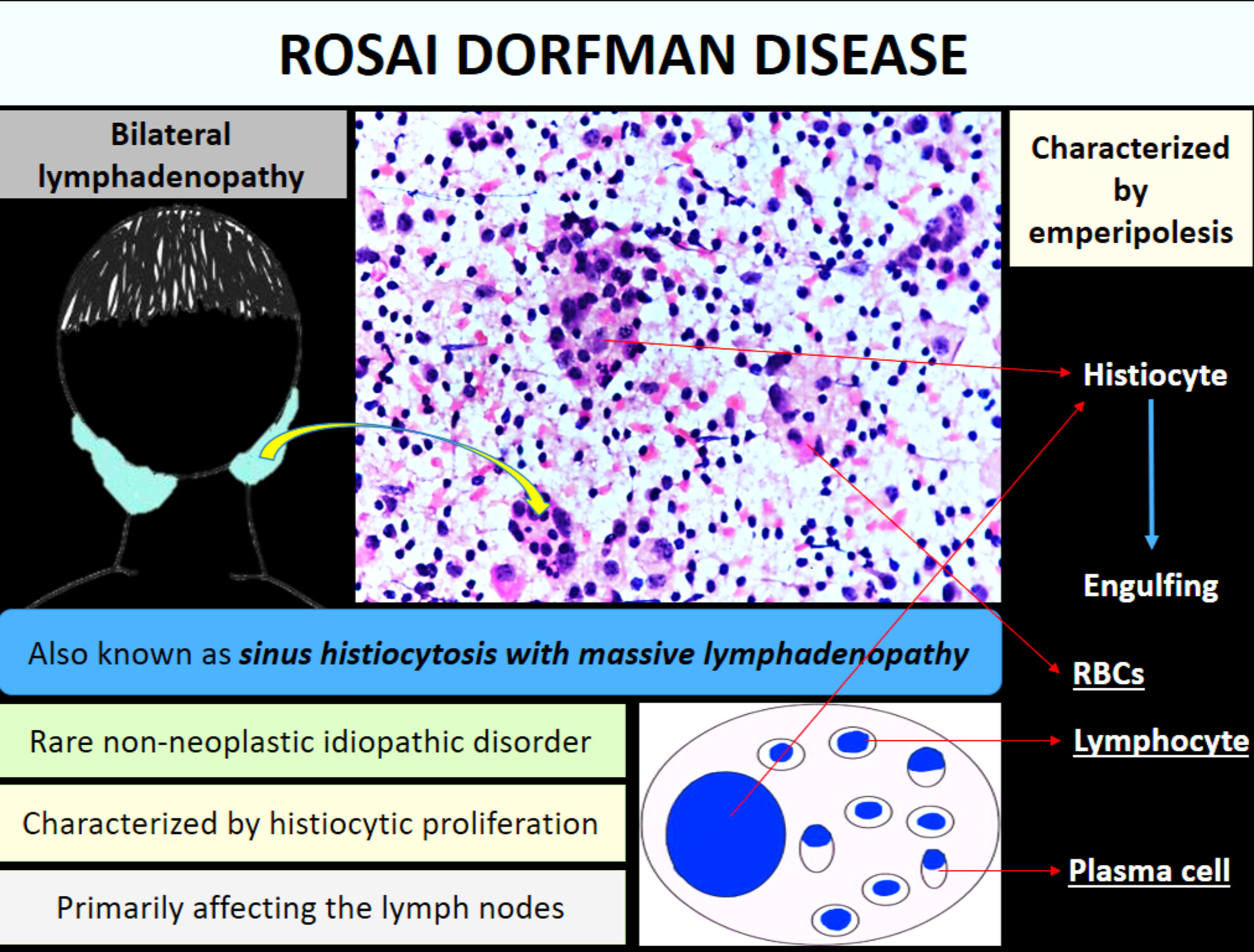
Rosai Dorfman Destombes disease, also known as sinus histiocytosis with massive lymphadenopathy, is a rare non-neoplastic idiopathic disorder characterised by histiocytic proliferation with evidence of emperipolesis. They present with a varied spectrum of clinical manifestations and cytomorphological features, posing diagnostic challenges and therapeutic dilemmas.
Rare case of stromal predominant Wilm's tumour with rhabdomyoblastic differentiation in FNAC smears
- Pages: 211-215
- First Published: 26 September 2024