Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
EDITORIAL
Cytology Is No Longer ‘Just Cytology’: The Clear Message of the XII. Congress of Molecular Cytopathology in Naples
- Pages: 662-663
- First Published: 02 October 2024
The editorial summarises the key messages of the very successful XII. Congress of Molecular Cytopathology in Naples. The programme of this meeting covered many burning issues from all areas of cytology—from molecular testing to the role of liquid biopsy to the unification of terminology and its impact on patient management.
REVIEW
Liquid Biopsy Series
Exploring the potential of multiomics liquid biopsy testing in the clinical setting of lung cancer
- Pages: 664-670
- First Published: 01 June 2024
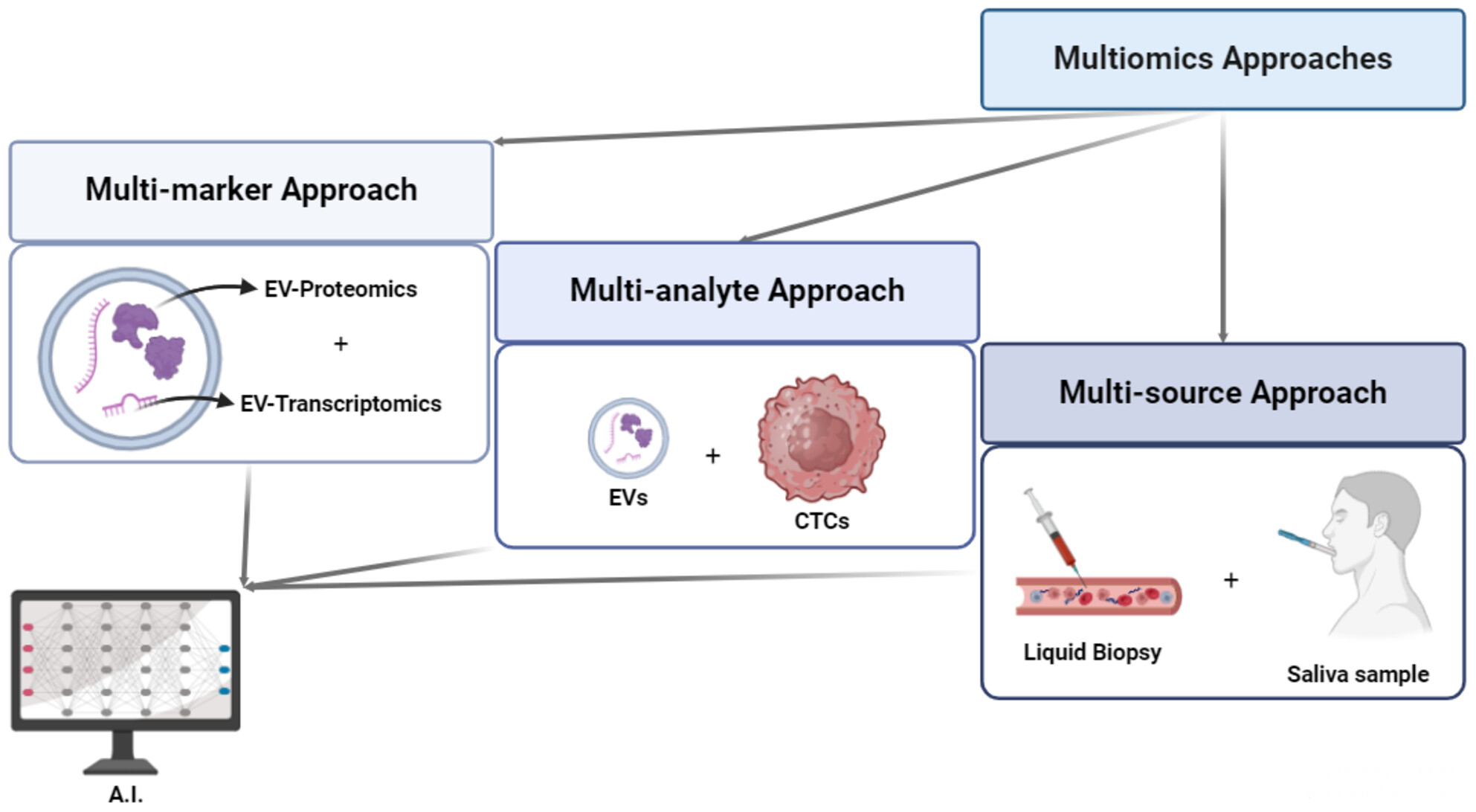
A flow diagram to visualize how multiomics approaches can be split into multi-marker, multi-analyte and multi-source approach; then, their link to AI, to decrypt and use in the clinical setting the messages hidden within them. The combined use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and multiomics could improve the diagnosis and prognosis of Lung Cancer (LC) via Liquid Biopsy (LB); through multi-marker, multi-analyte, and multi-source analysis, the way is paved for the achievement of these goals, once tested through appropriate large-scale multi-center studies.
CASE REPORT
Liquid Biopsy Series
Transient ‘NeoBRAF wild type’ state in a patient with BRAFV600E mutant metastatic colorectal cancer
- Pages: 671-673
- First Published: 31 July 2024
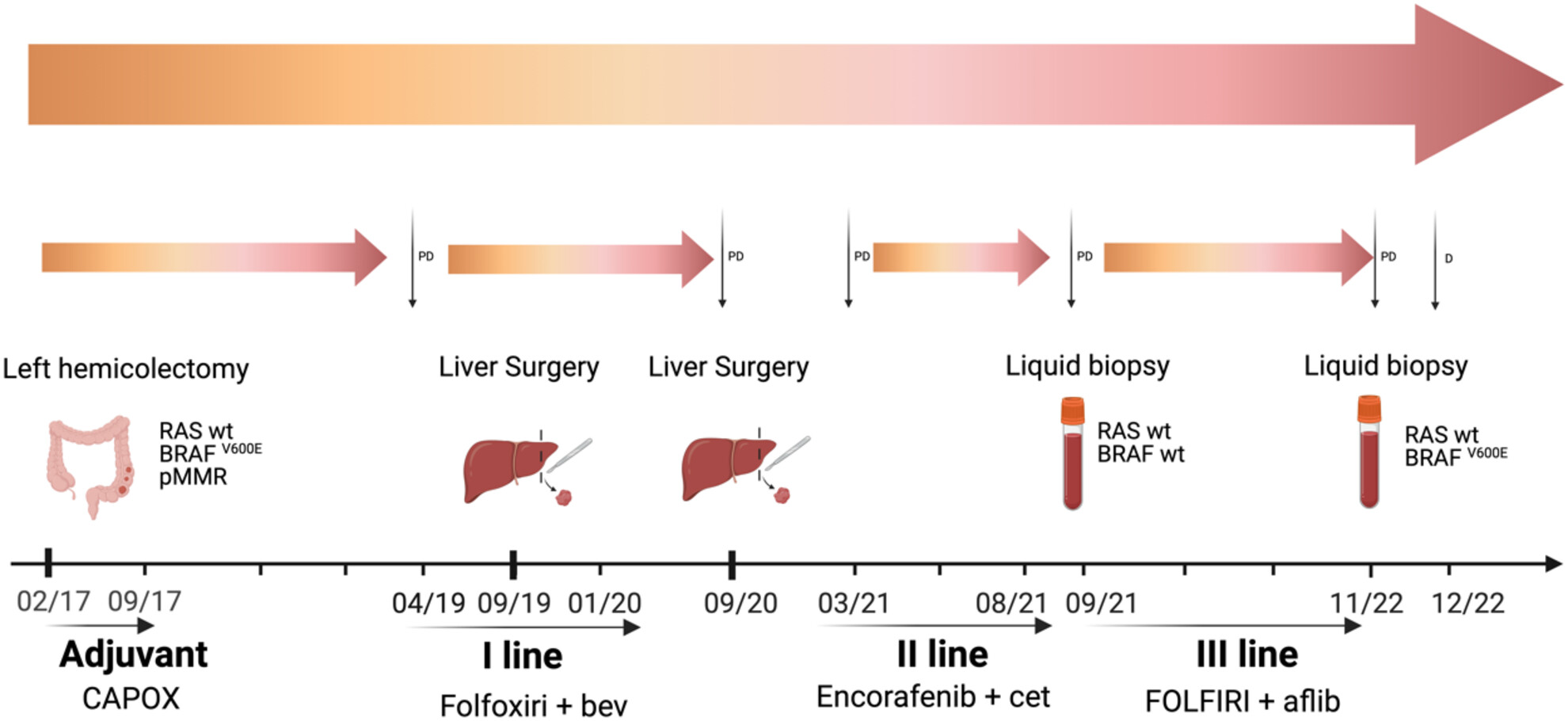
We report the case of a patient with a BRAFV600E mutant mCRC, with evidence of acquired ‘NeoBRAF wild-type’ (wt) state. The patient, longitudinally assessed by liquid biopsy, obtained a remarkable clinical outcome with a multimodal approach including surgery, systemic treatment and targeted therapy.
In patients with newly diagnosed RAS and BRAFV600E mutant mCRC, longitudinal assessment with liquid biopsy is not routinely used in clinical practice. We report the case of a patient with a BRAFV600E mutant mCRC, with evidence of acquired ‘neoBRAF wild-type’ (wt) state. The patient obtained a remarkable clinical outcome and has been longitudinally assessed by liquid biopsy.
REVIEW
Are we ready to bridge classification systems? A comprehensive review of different reporting systems in thyroid cytology
- Pages: 674-681
- First Published: 26 July 2024
The evaluation of thyroid lesions is common in the daily practice of cytology. While the majority of thyroid nodules are benign, in recent decades there has been increased detection of small and well-differentiated thyroid cancers. Combining ultrasound evaluation with fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is extremely useful in the management of thyroid nodules. Furthermore, the adoption of specific terminology, introduced by different thyroid reporting systems, has helped effectively communicate thyroid FNAC diagnoses in a clear and understandable way.
The paper is a brief evaluation of the different cytology terminology classification systems for thyroid nodules. The review aims to define the similarities and differences among these systems, especially in the field of indeterminate lesions.
Advances in diagnostic liquid-based cytology
- Pages: 682-694
- First Published: 04 June 2024
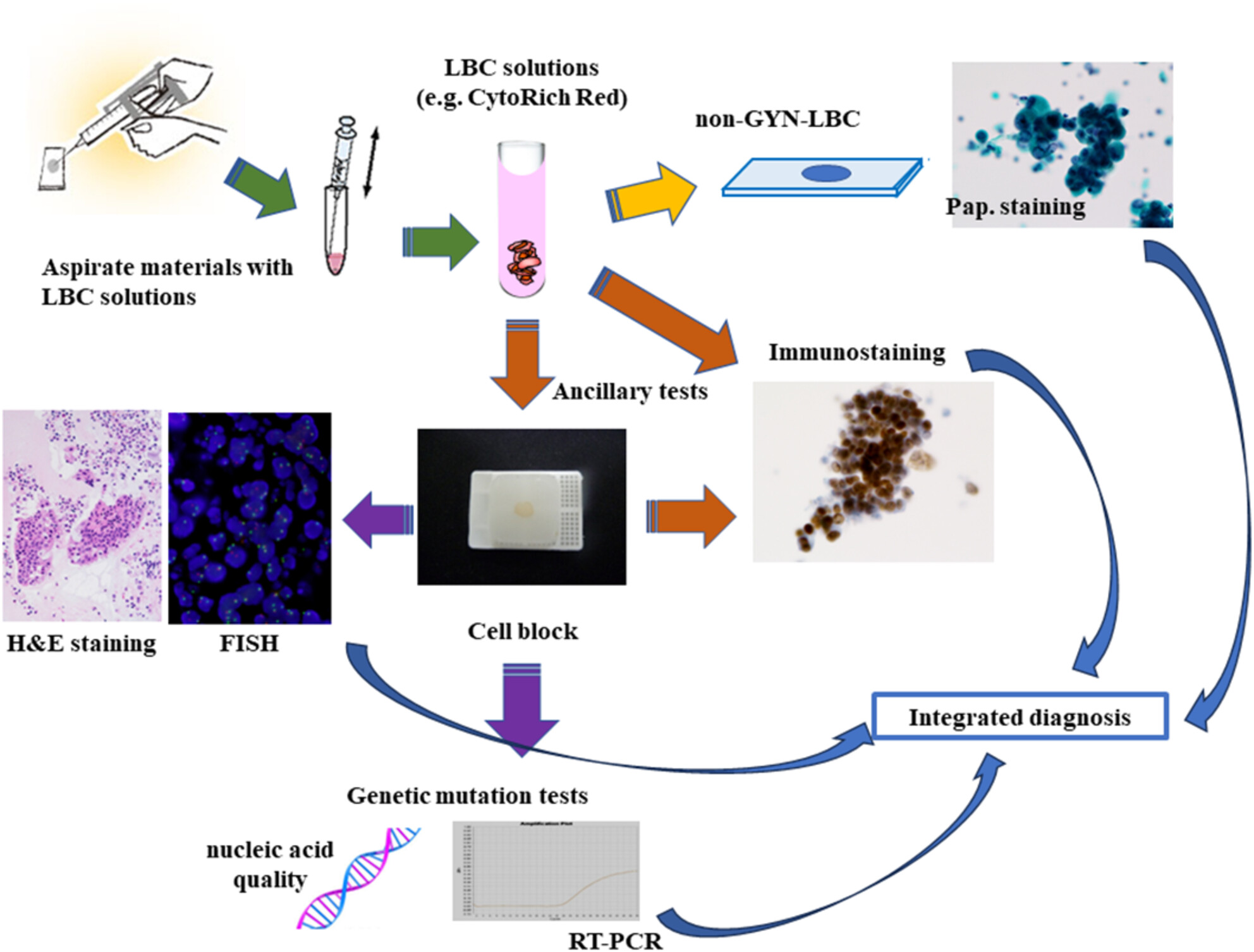
Cancer is a disease with highly diverse forms and characteristics. Diagnostic LBC is an essential tool for understanding this diversity of cancer.
This study aims to review the literature on diagnostic liquid-based cytology. Additionally, it provides an overview of the cytological applications of non-gynaecological liquid-based cytology.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Application of the international system for reporting serous fluid cytopathology on pleural effusion cytology with paired pleural biopsy: A new insight and novel approach on risk of malignancy
- Pages: 695-705
- First Published: 01 August 2024
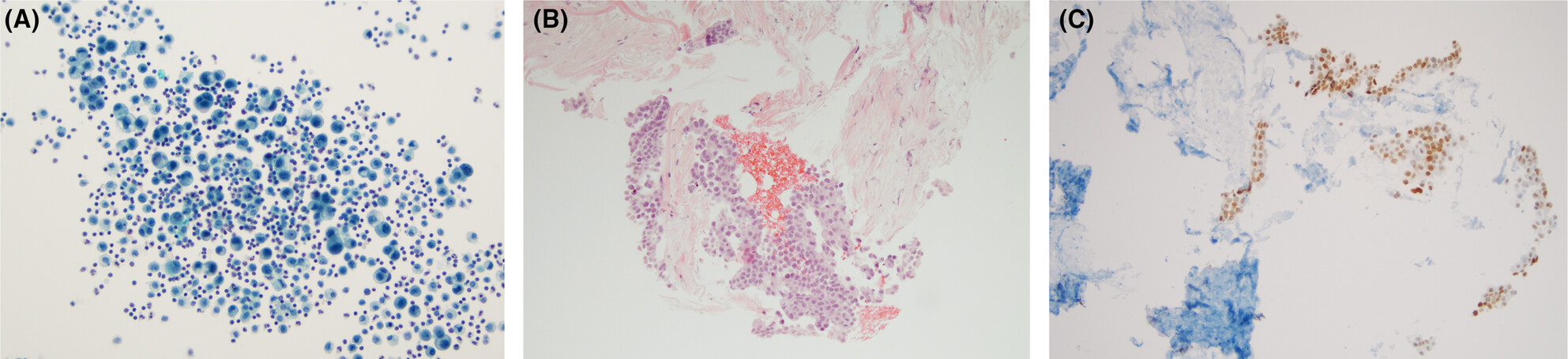
Pairing pleural fluids and pleural biopsies confirms a malignant pleural effusion is a reliable diagnosis and should be considered ‘gold standard’. However, a negative pleural effusion does not rule out pleural involvement with a malignant process since the malignant neoplasms are variable in shedding into the pleural cavity.
Comparison of the modified Masood's scoring index versus international academy of cytology Yokohama system in the categorization of breast fine needle aspirates
- Pages: 706-714
- First Published: 07 August 2024
The study compares the Modified Masood Scoring Index (MMSI) and the International Academy of Cytology (IAC) Yokohama System in categorizing breast fine needle aspirates, finding the Yokohama System to have higher diagnostic accuracy and better performance parameters, with a lower risk of false positives and negatives. Both systems are assessed against histopathological diagnoses, with the Yokohama System demonstrating superior sensitivity, specificity, and overall diagnostic accuracy in categorizing breast lesions.
The Bethesda System for Reporting Thyroid Cytopathology in the African American population: A tertiary centre experience
- Pages: 715-723
- First Published: 29 July 2024
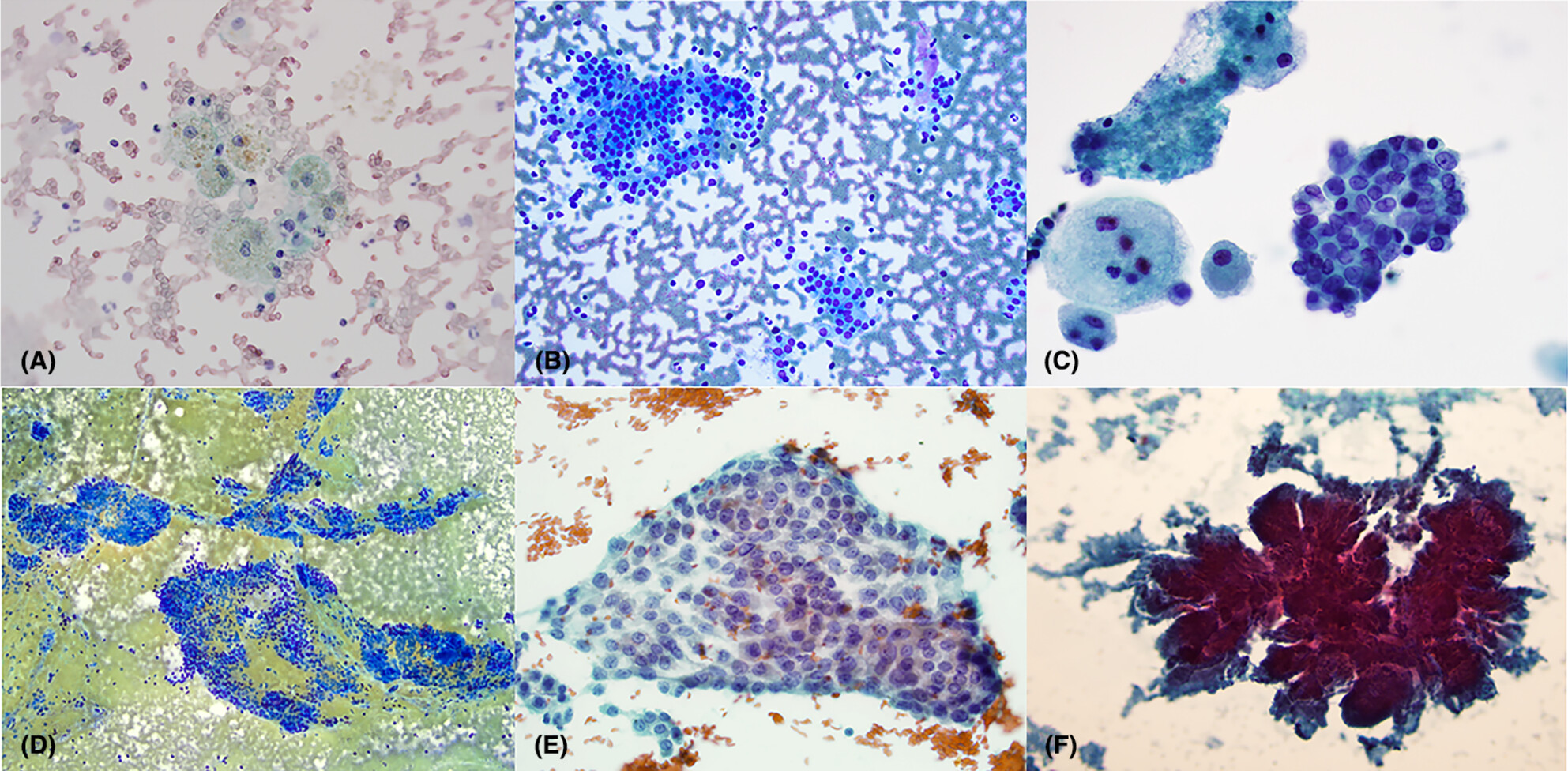
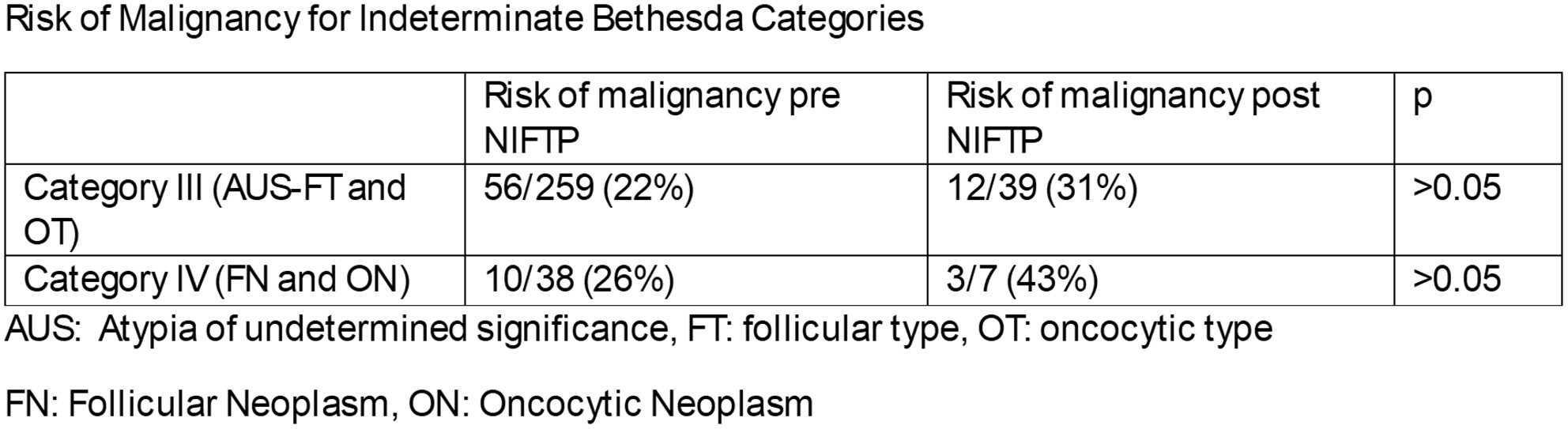
The thyroid nodules are more frequently seen in African American females than males while the risk of malignancy is higher in thyroid nodules in males. The risk of malignancy in Categories I, II and III is higher than those reported in the TBSRTC while being similar in Categories IV, V and VI.
Thyroid nodules are more frequently seen in African American (AA) females than AA males while the risk of malignancy is higher in thyroid nodules in males. In African Americans, the risk of malignancy in Categories I, II and III is higher than those reported in the TBSRTC while being similar in Categories IV, V and VI. The overall risk of thyroid malignancy in this AA patient population is higher (43.8%) than the previously reported overall risk of malignancy (36%) in the literature.
Cytomorphological characteristics of low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma in voided urine samples: Distinction from benign and high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma
- Pages: 724-732
- First Published: 11 July 2024
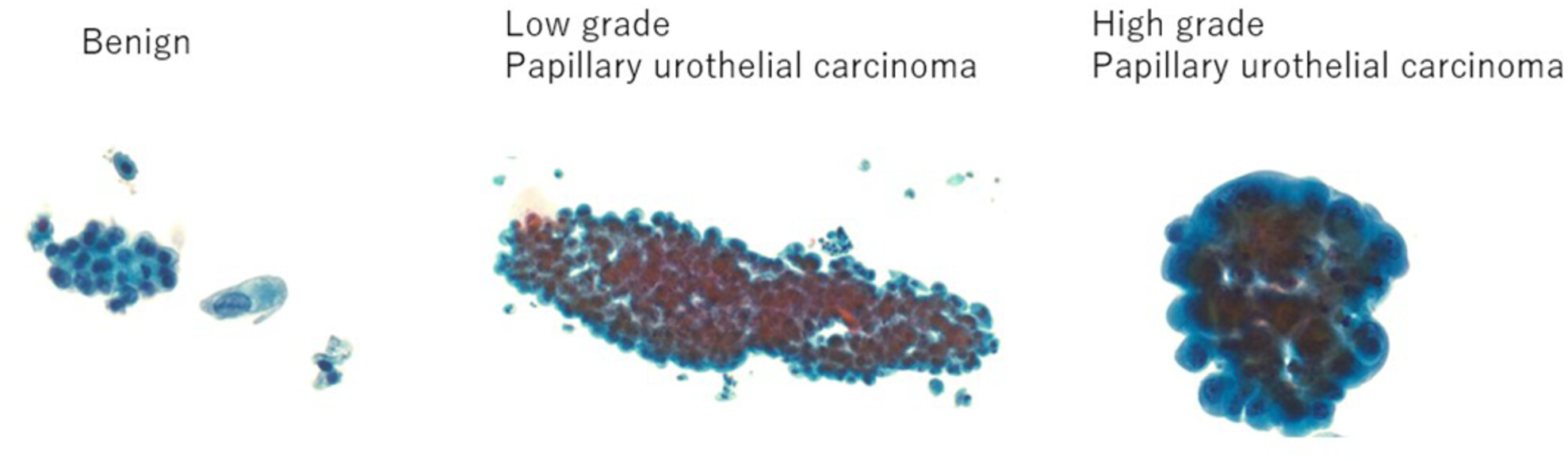
Several atypical cytomorphologic features such as nuclear enlargement, a higher nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, and small urothelial cell clusters in voided urine samples were statistically more prevalent in histologically confirmed low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma than in benign conditions. These atypical features were less pronounced compared with high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma.
Low-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma (LGPUC) diagnosis in urine cytology is challenging. Several atypical cytomorphologic features such as nuclear enlargement, a higher nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio, and small urothelial cell clusters in voided urine samples were statistically more prevalent in histologically confirmed LGPUC than in benign conditions. These atypical features were less pronounced compared to high-grade papillary urothelial carcinoma. Therefore, meticulous scrutiny of cytomorphology is necessary for an accurate LGPUC diagnosis.
Oncocytic/Hürthle cell lesions have the same implied risk of neoplasm/malignancy as their follicular counterparts
- Pages: 733-737
- First Published: 16 July 2024
Accuracy of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in evaluation of thyroid nodules using different ultrasonographic and cytological features
- Pages: 738-748
- First Published: 13 July 2024
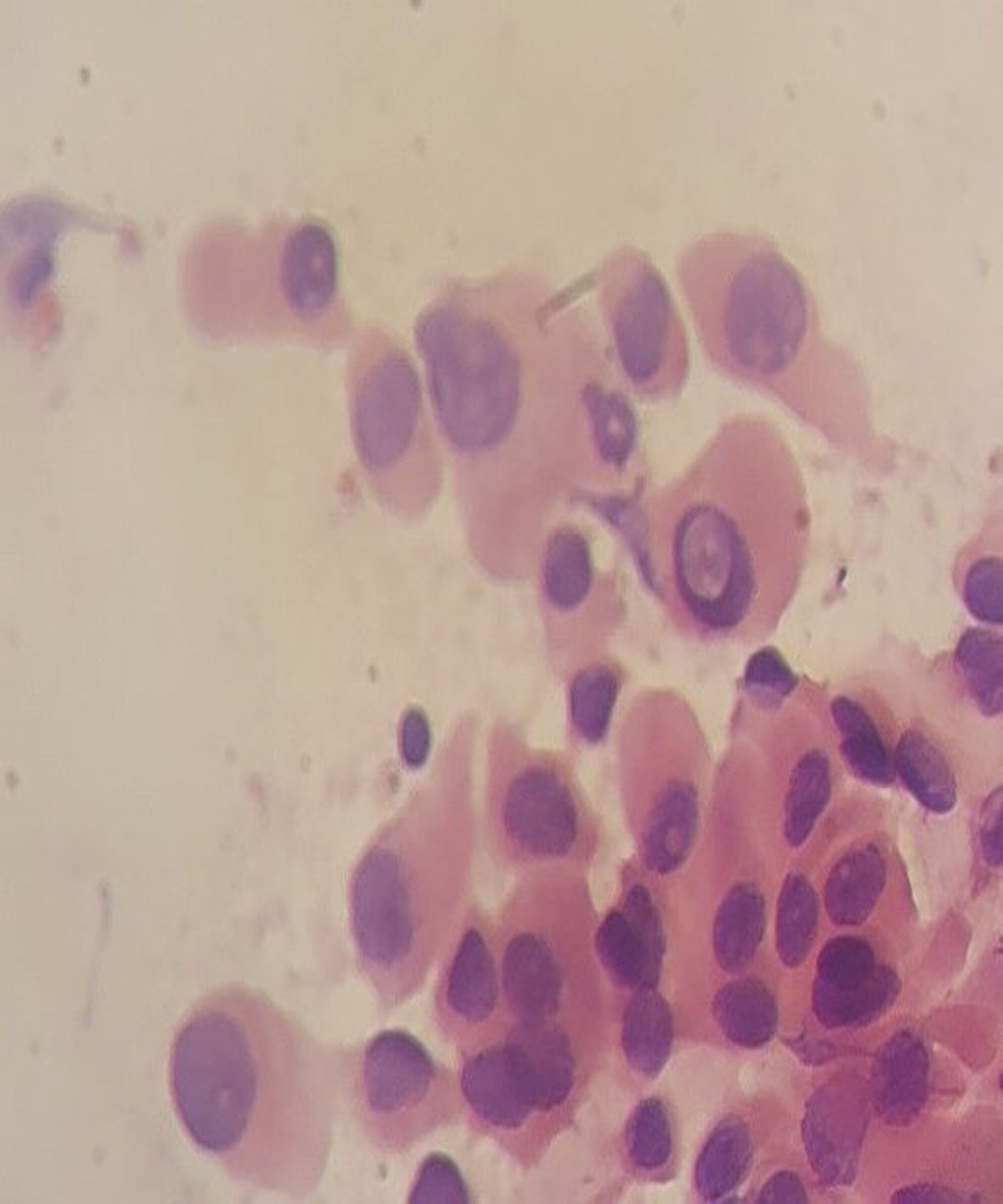
Fine-needle aspiration cytology is a sensitive method in preoperative diagnosis of thyroid nodules particularly malignant nodules. It is also specific to typing malignancy. In particular papillary thyroid carcinoma nuclear features are obvious in cytology. These features are nuclear grooving, nuclear irregularity, moulding, overlapping and pseudonuclear inclusion.
This research is a combined cytology and radiology effort for evaluation of Bethesda and TRADS systems using different cytological and sonographic features. The findings raise the question ‘Should these systems be used separately or scored together?’
Evaluation and application of American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System for improved malignancy detection in paediatric thyroid nodules
- Pages: 749-756
- First Published: 30 June 2024
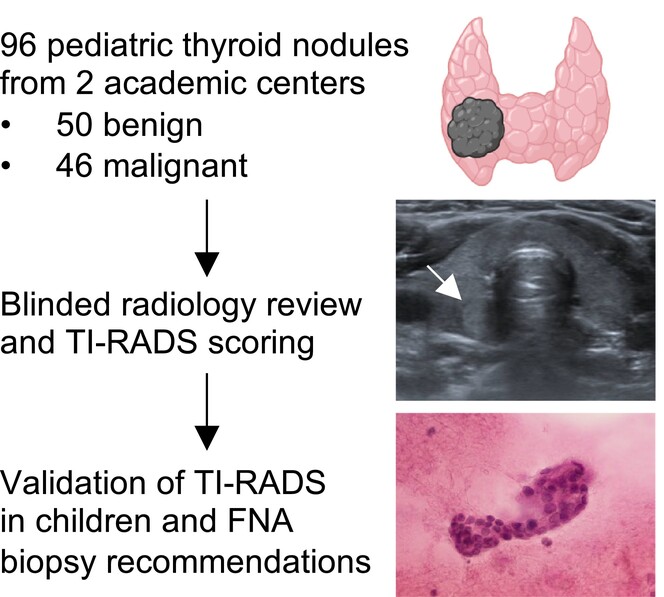
Blinded radiologist review of paediatric thyroid ultrasounds confirms that the American College of Radiology Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TI-RADS, originally designed for adults) is able to risk-stratify paediatric thyroid nodules. However, TI-RADS requires additional modifications to determine the optimal cutoff for fine needle aspiration biopsy—some of which are proposed in this work—in order to reduce the missed malignancy rate in children.
Does HPV-18 co-infection increase the risk of cervical pathology in individuals with HPV-16?
- Pages: 757-760
- First Published: 11 July 2024
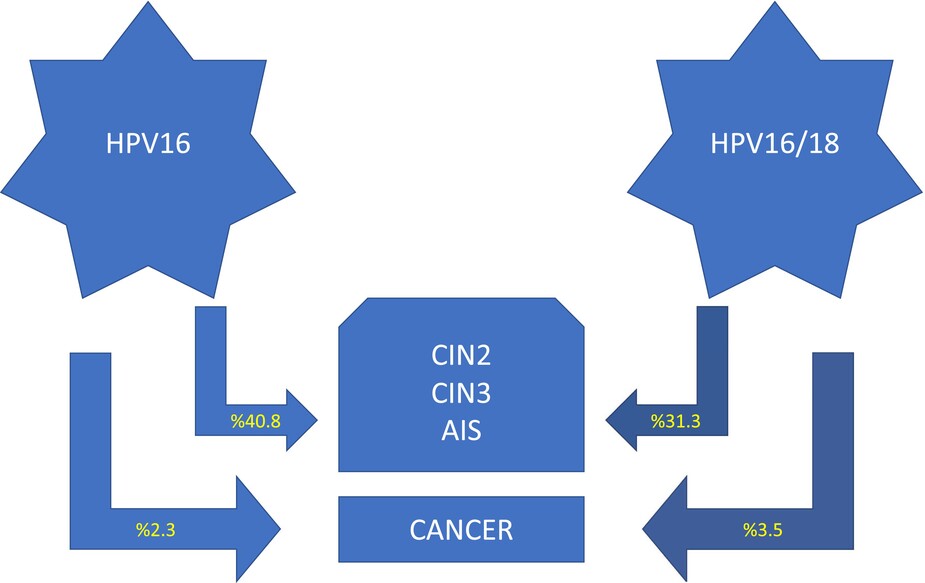
In this study, 40.9% and 31.8% of patients in HPV16 and HPV16/18 groups, respectively, had CIN2+ lesions. 2.2% and 3.0% of patients in HPV16 and HPV16/18 groups, respectively, had cancer.
Gokkaya et al. reported 40.9% for CIN2+ lesions and 2.2% for cancer in HPV16-positive patients. The ratios were 31.8% and 3.0%, respectively, in HPV16/18-positive patients.
Practical issues related to immunocytochemistry on cytological smears: Tips and recommendations
- Pages: 761-769
- First Published: 16 July 2024
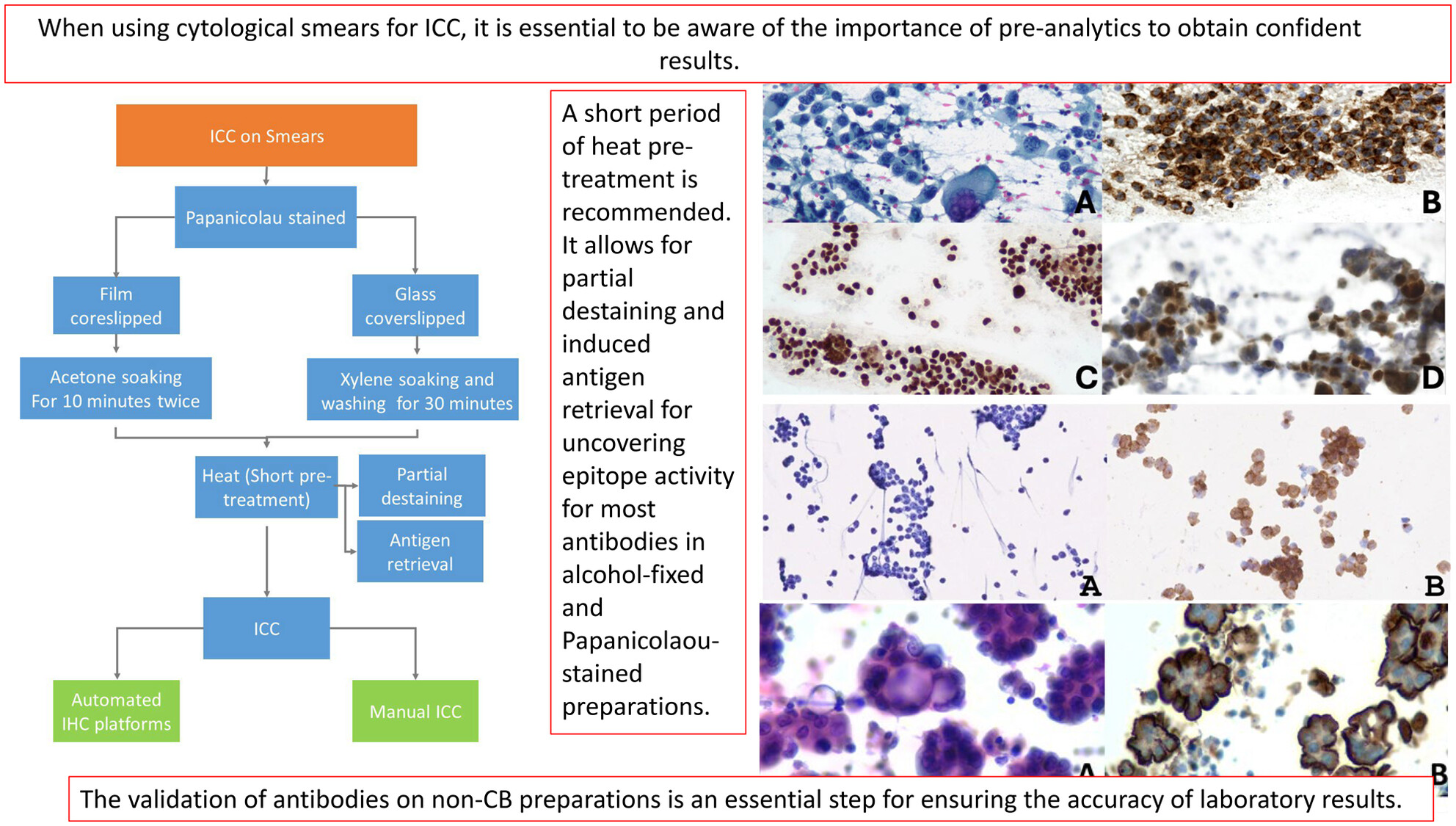
When using cytological smears for Immunocytochemistry (ICC), it is essential to be aware of the importance of pre-analytics to obtain confident results. The validation of antibodies on non-CB preparations is an essential step for ensuring the accuracy of laboratory results.
ICC is an essential ancillary technique that can be performed on cytological smears and its success relies on accurate specimen collection, handling, appropriate triage and processing. Detailing preparation, fixation and protocols for nuclear and cytoplasmic antibodies represents the focus of this review.
Cervical cancer screening efficacy using SurePath, ThinPrep and conventional cytology: A large data set analysis from the Japan Cancer Society
- Pages: 770-775
- First Published: 08 August 2024
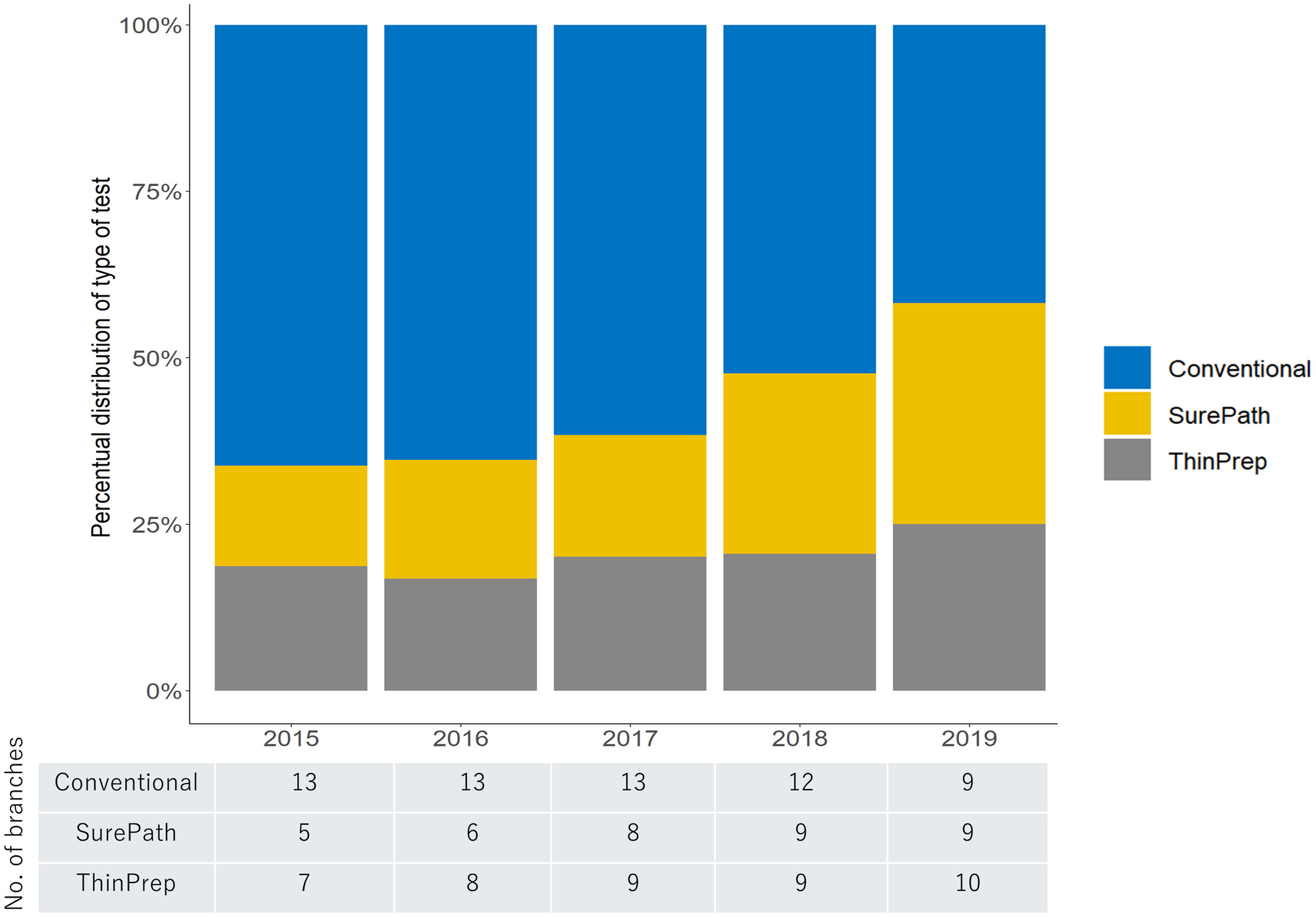
This study represents real-world data of population-based cervical cancer screening in Japan. Liquid-based cytology, particularly SurePath, is useful for detecting CIN2 or higher in population-based cervical cancer screening in Japan. Further widespread use of liquid-based cytology would lead to efficient detection of cervical precancerous lesions.
CASE REPORT
A case report of primary central nervous system lymphoma with immune deficiency/disorder setting diagnosed by cerebrospinal fluid cytology
- Pages: 776-779
- First Published: 09 August 2024
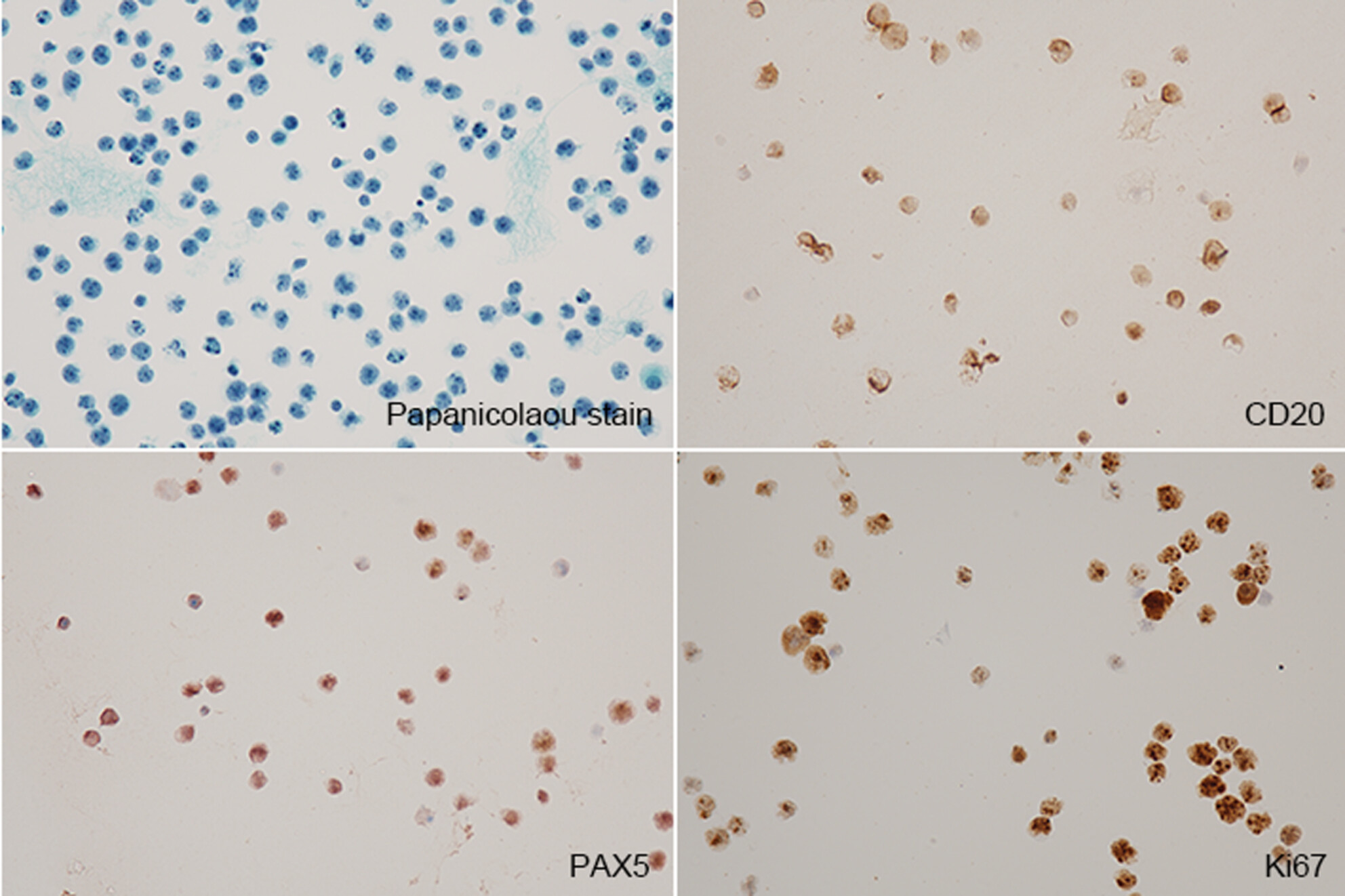
Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) cytology of primary central nervous system lymphoma arising in the immune deficiency/dysregulation setting (IDD-PCNSL) has not been described. This study presented a case of IDD-PCNSL-DLBCL, a GCB phenotype who was successfully diagnosed by CSF cytology in conjunction with ICC, ISH, FCM and clinical information.
Cerebrospinal fluid cytology in a case of epithelioid glioblastoma
- Pages: 780-785
- First Published: 13 August 2024
ENIGMA PORTAL
Pericardial effusion: Unusual immunohistochemical expression
- Pages: 786-788
- First Published: 31 July 2024
Endometrial Gastric-type Carcinoma is a rare disease, especially in cytology. A 65-year-old woman was admitted to the hospital due to intermittent chest tightness with dyspnoea. The chest CT showed a soft tissue shadow of the left lung with bronchial occlusion and pericardial effusion. What was her diagnosis?
The diagnostic conundrum of hyper eosinophilia—Sheer tenacity of a parasite
- Pages: 789-791
- First Published: 28 August 2024
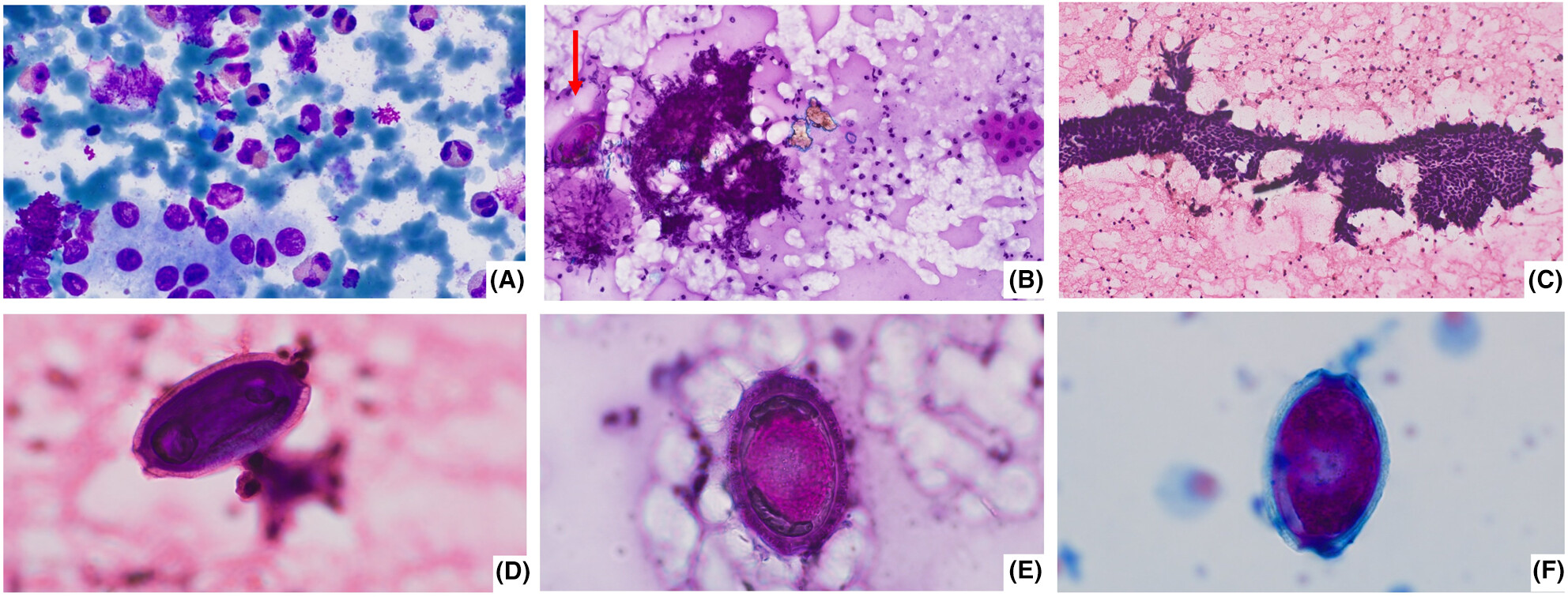
We present an interesting and rare case of Capillaria hepatica infection in a 2-year-old boy, who presented with fever, rash, hepatomegaly and peripheral eosinophilia. FNAC of hepatic lesion showed parasitic eggs and PCR from the aspirate confirmed the diagnosis. We describe the cytomorphological features and provide educational multiple-choice questions related to the topic.
CORRESPONDENCE
Commentary on ‘Development and validation of a minimally invasive protocol for assessing oxidative stress markers in exfoliated oral cells’
- Pages: 792-793
- First Published: 02 August 2024
The assessment of reactive oxygen species (ROS) offers immense prospects for the diagnosis of chronic diseases. A protocol to assess redox imbalance in exfoliated cells can prove beneficial in our understanding of the role of ROS in the diagnosis of these diseases. Further studies on the development of such protocols are needed.
Metastatic pleomorphic undifferentiated uterine sarcoma detected in pleural effusion
- Pages: 794-799
- First Published: 15 August 2024
Undifferentiated uterine sarcoma is an extremely rare cytologically challenging finding in pleural effusions undistinguished from the more common causes of malignant effusions. Cellblock is a valuable diagnostic tool when combined with certain diagnostic clues, relevant immunoprofile and knowledge of the patient's history.