Accuracy of ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration cytology in evaluation of thyroid nodules using different ultrasonographic and cytological features
Abstract
Background
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a reliable method for preoperative evaluation of thyroid nodules particularly if ultrasound-guided (USG-FNAC). The main purpose of this study is to evaluate the efficacy of USG-FNAC and its accuracy.
Methods
We retrospectively studied 212 thyroidectomy cases with preoperative ultrasonography and FNAC data during the period 2015–2022 using TI-RADS for final ultrasound diagnosis and Bethesda system for cytological diagnosis.
Results
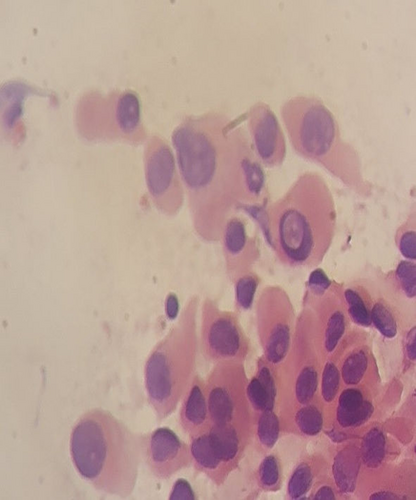
The studied cases were 200 females and 12 males. Thyroid cancer was more prevalent under 20 years old (78.5%). Papillary thyroid carcinoma comprises 84% of all cancer cases. Significant ultrasound features (p-value <0.05) favour malignancy were hypoechogenicity (66%), mixed echogenicity (84%), irregular border (61%), microcalcification (68%) and rim halo (63.6%). Malignancy was found in 21% of TI-RADS-2, 65% of TI-RADS-4 and 100% of TI-RADS-5. There is a significant difference between different categories of Bethesda system. All cases in Cat-VI were malignant (100%). Malignancy was also found in 81% of Cat-V, 20% of Cat-IV, 33% of Cat-III, 16% of Cat-II and 43% of Cat-I. Cytological features consistent with malignancy were as follows: grooving (94%), nuclear irregularities (89%), nuclear pseudoinclusion (89%) and little colloid (82%). In our study, USG-FNAC sensitivity was 83%, specificity 85%, PPV 85%, NPV 83% and accuracy 84%.
Conclusion
Ultrasound features in favour of malignancy in thyroid nodules are hypoechoic or complex echogenicity, irregular border, punctuate calcification and presence of rim halo. Cytological features in favour of malignancy are grooving, nuclear irregularities, nuclear pseudoinclusion and little or absent colloid.
Graphical Abstract
Fine-needle aspiration cytology is a sensitive method in preoperative diagnosis of thyroid nodules particularly malignant nodules. It is also specific to typing malignancy. In particular papillary thyroid carcinoma nuclear features are obvious in cytology. These features are nuclear grooving, nuclear irregularity, moulding, overlapping and pseudonuclear inclusion.
This research is a combined cytology and radiology effort for evaluation of Bethesda and TRADS systems using different cytological and sonographic features. The findings raise the question ‘Should these systems be used separately or scored together?’
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data sets generated during the current study will be available upon reasonable request.