Exploring the potential of multiomics liquid biopsy testing in the clinical setting of lung cancer
Andrea Gottardo
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorTancredi Didier Bazan Russo
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAlessandro Perez
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMarco Bono
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorEmilia Di Giovanni
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorEnrico Di Marco
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorRita Siino
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCarla Ferrante Bannera
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorClarissa Mujacic
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMaria Concetta Vitale
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorSilvia Contino
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiuliana Iannì
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiulia Busuito
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorFederica Iacono
A.R.N.A.S. Hospital Di Cristina, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorLorena Incorvaia
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiuseppe Badalamenti
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAntonio Galvano
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Antonio Russo
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Correspondence
Antonio Russo, Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), “P. Giaccone” University Hospital (A.O.U.P.) of Palermo, Via del Vespro 129, 90127 Palermo, Italy.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorViviana Bazan
Department of Biomedicine, Neuroscience and Advanced Diagnostic (Bi.N.D.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorValerio Gristina
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAndrea Gottardo
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorTancredi Didier Bazan Russo
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAlessandro Perez
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMarco Bono
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorEmilia Di Giovanni
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorEnrico Di Marco
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorRita Siino
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCarla Ferrante Bannera
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorClarissa Mujacic
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorMaria Concetta Vitale
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorSilvia Contino
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiuliana Iannì
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiulia Busuito
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorFederica Iacono
A.R.N.A.S. Hospital Di Cristina, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorLorena Incorvaia
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorGiuseppe Badalamenti
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAntonio Galvano
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorCorresponding Author
Antonio Russo
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Correspondence
Antonio Russo, Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), “P. Giaccone” University Hospital (A.O.U.P.) of Palermo, Via del Vespro 129, 90127 Palermo, Italy.
Email: [email protected]
Search for more papers by this authorViviana Bazan
Department of Biomedicine, Neuroscience and Advanced Diagnostic (Bi.N.D.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorValerio Gristina
Department of Precision Medicine in Medical, Surgical and Critical Care (Me.Pre.C.C.), University of Palermo, Palermo, Italy
Search for more papers by this authorAndrea Gottardo and Tancredi Didier Bazan Russo contributed equally to this work.
Viviana Bazan and Valerio Gristina Co-last authors.
Abstract
The transformative role of artificial intelligence (AI) and multiomics could enhance the diagnostic and prognostic capabilities of liquid biopsy (LB) for lung cancer (LC). Despite advances, the transition from tissue biopsies to more sophisticated, non-invasive methods like LB has been impeded by challenges such as the heterogeneity of biomarkers and the low concentration of tumour-related analytes. The advent of multiomics – enabled by deep learning algorithms – offers a solution by allowing the simultaneous analysis of various analytes across multiple biological fluids, presenting a paradigm shift in cancer diagnostics. Through multi-marker, multi-analyte and multi-source approaches, this review showcases how AI and multiomics are identifying clinically valuable biomarker combinations that correlate with patients' health statuses. However, the path towards clinical implementation is fraught with challenges, including study reproducibility and lack of methodological standardization, thus necessitating urgent solutions to solve these common issues.
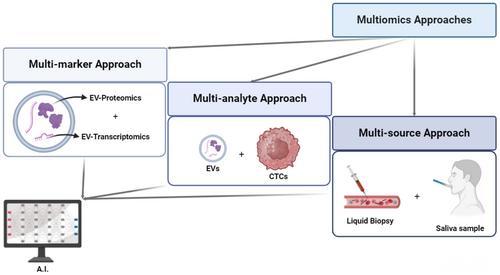
Graphical Abstract
A flow diagram to visualize how multiomics approaches can be split into multi-marker, multi-analyte and multi-source approach; then, their link to AI, to decrypt and use in the clinical setting the messages hidden within them. The combined use of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and multiomics could improve the diagnosis and prognosis of Lung Cancer (LC) via Liquid Biopsy (LB); through multi-marker, multi-analyte, and multi-source analysis, the way is paved for the achievement of these goals, once tested through appropriate large-scale multi-center studies.
CONFLICT OF INTEREST STATEMENT
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Open Research
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
REFERENCES
- 1Siegel RL, Giaquinto AN, Jemal A. Cancer statistics 2024. CA Cancer J Clin. 2024; 74(1): 12-49. doi:10.3322/caac.21820
- 2Best MG, Sol N, Kooi I, et al. RNA-Seq of tumor-educated platelets enables blood-based pan-cancer, multiclass, and molecular pathway cancer diagnostics. Cancer Cell. 2015; 28(5): P666-P676. doi:10.1016/j.ccell.2015.09.018
- 3Bracht JWP, Mayo-de-Las-Casas C, Berenguer J, Karachaliou N, Rosell R. The present and future of liquid biopsies in non-small cell lung cancer: combining four biosources for diagnosis, prognosis, prediction, and disease monitoring. Curr Oncol Rep. 2018; 20(9):70. doi:10.1007/s11912-018-0720-z
- 4https://islb.info/ (assessed on April 5, 2024).
- 5Pisapia P, Pepe F, Gristina V, et al. A narrative review on the implementation of liquid biopsy as a diagnostic tool in thoracic tumors during the COVID-19 pandemic. Mediastinum. 2021; 5:27. doi:10.21037/med-21-9
- 6Santini D, Botticelli A, Galvano A, et al. Network approach in liquidomics landscape. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023; 42(1): 193. doi:10.1186/s13046-023-02743-9
- 7Gristina V, la Mantia M, Peri M, et al. Navigating the liquid biopsy minimal residual disease (MRD) in non-small cell lung cancer: Making the invisible visible. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2023; 182: 103899. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2022.103899
- 8Gottardo A, Gristina V, Perez A, et al. Roles of tumor-educated platelets (TEPs) in the biology of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A systematic review. “Re-discovering the neglected biosources of the liquid biopsy family”. J Liquid Biopsy. 2024; 3:100136. doi:10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100136
10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100136 Google Scholar
- 9Gristina V, Barraco N, la Mantia M, et al. Clinical potential of circulating cell-free DNA (cfDNA) for longitudinally monitoring clinical outcomes in the first-line setting of non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A real-world prospective study. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14(23):6013. doi:10.3390/cancers14236013
- 10Ma W, Tang W, Kwok JSL, et al. A review on trends in development and translation of omics signatures in cancer. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2024; 23(December): 954-971. doi:10.1016/j.csbj.2024.01.024
- 11Kulkarni M, Kar R, Ghosh S, et al. Clinical impact of multi-omics profiling of extracellular vesicles in cancer liquid biopsy. J Liquid Biopsy. 2024; 3: 100138. doi:10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100138
10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100138 Google Scholar
- 12Boukovala M, Westphalen CB, Probst V. Liquid biopsy into the clinics: Current evidence and future perspectives. J Liquid Biopsy. 2024; 4:100146. doi:10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100146
10.1016/j.jlb.2024.100146 Google Scholar
- 13Freitas C, Sousa C, Machado F, et al. The role of liquid biopsy in early diagnosis of lung cancer. Front Oncol. 2021; 11:634316. doi:10.3389/fonc.2021.634316
- 14Wu Z, Yang Z, Dai Y, Zhu Q, Chen LA. Update on liquid biopsy in clinical management of non-small cell lung cancer. OncoTargets ther. 2019; 12: 5097-5109. doi:10.2147/OTT.S203070
- 15Gristina V, Malapelle U. Dissecting the nuances of cancer epigenomics in liquid biopsy. Epigenomics. 2024; 16(2): 79-83. doi:10.2217/epi-2023-0326
- 16Cammarata G, Barraco N, Giusti I, Gristina V, Dolo V, Taverna S. Extracellular vesicles-ceRNAs as ovarian cancer biomarkers: looking into circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Code. Cancers (Basel). 2022; 14(14): 3404. doi:10.3390/cancers14143404
- 17Purcell E, Owen S, Prantzalos E, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutations carried in extracellular vesicle-derived cargo mirror disease status in metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021; 9:724389. doi:10.3389/fcell.2021.724389
- 18D'Ambrosi S, Giannoukakos S, Antunes-Ferreira M, et al. Combinatorial blood platelets-derived circRNA and mRNA signature for early-stage lung cancer detection. Int J Mol Sci. 2023; 24(5): 4881. doi:10.3390/ijms24054881
- 19de Wit S, Rossi E, Weber S, et al. Single tube liquid biopsy for advanced non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Cancer. 2019; 144(12): 3127-3137. doi:10.1002/ijc.32056
- 20Moon SM, Kim JH, Kim SK, et al. Clinical utility of combined circulating tumor cell and circulating tumor DNA assays for diagnosis of primary lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 2020; 40(6): 3435-3444. doi:10.21873/anticanres.14329
- 21Xie J, Hu B, Gong Y, et al. A comparative study on ctDNA and tumor DNA mutations in lung cancer and benign cases with a high number of CTCs and CTECs. J Transl Med. 2023; 21(1): 873. doi:10.1186/s12967-023-04746-8
- 22Liu HE, Vuppalapaty M, Wilkerson C, et al. Detection of EGFR mutations in cfDNA and CTCs, and comparison to tumor tissue in non-small-cell-lung-cancer (NSCLC) patients. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:572895. doi:10.3389/fonc.2020.572895
- 23Mondelo-Macía P, García-González J, León-Mateos L, et al. Clinical potential of circulating free DNA and circulating tumour cells in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer treated with pembrolizumab. Mol Oncol. 2021; 15(11): 2923-2940. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.13094
- 24Kapeleris J, Müller Bark J, Ranjit S, et al. Prognostic value of integrating circulating tumour cells and cell-free DNA in non-small cell lung cancer. Heliyon. 2022; 8(7):e09971. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e09971
- 25Markou AN, Londra D, Stergiopoulou D, et al. Preoperative mutational analysis of circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and plasma-cfDNA provides complementary information for early prediction of relapse: A pilot study in early-stage non-small cell lung cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2023; 15(6): 1877. doi:10.3390/cancers15061877
- 26Taylor C, Chacko S, Davey M, et al. Peptide-affinity precipitation of extracellular vesicles and cell-free DNA improves sequencing performance for the detection of pathogenic mutations in lung cancer patient plasma. Int J Mol Sci. 2020; 21(23): 9083. doi:10.3390/ijms21239083
- 27Eslami-S Z, Cortés-Hernández LE, Sinoquet L, et al. Circulating tumour cells and PD-L1-positive small extracellular vesicles: the liquid biopsy combination for prognostic information in patients with metastatic non-small cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer. 2024; 130(1): 63-72. doi:10.1038/s41416-023-02491-9
- 28Wang N, Yao C, Luo C, et al. Integrated plasma and exosome long noncoding RNA profiling is promising for diagnosing non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2023; 61(12): 2216-2228. doi:10.1515/cclm-2023-0291
- 29Ye M, Tong L, Zheng X, et al. A classifier for improving early lung cancer diagnosis incorporating artificial intelligence and liquid biopsy. Front Oncol. 2022; 12:853801. doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.853801
- 30Xing L, Su J, Guarnera MA, et al. Sputum microRNA biomarkers for identifying lung cancer in indeterminate solitary pulmonary nodules. Clin Cancer Res. 2015; 21(2): 484-489. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-1873
- 31Thunnissen FBJM. Sputum examination for early detection of lung cancer. J Clin Pathol. 2003; 56(11): 805-810. doi:10.1136/jcp.56.11.805
- 32Xing L, Todd NW, Yu L, Fang H, Jiang F. Early detection of squamous cell lung cancer in sputum by a panel of microRNA markers. Mod Pathol. 2010; 23(8): 1157-1164. doi:10.1038/modpathol.2010.111
- 33Shen J, Liao J, Guarnera MA, et al. Analysis of MicroRNAs in sputum to improve computed tomography for lung cancer diagnosis. J Thorac Oncol. 2014; 9(1): 33-40. doi:10.1097/JTO.0000000000000025
- 34Liao J, Shen J, Leng Q, Qin M, Zhan M, Jiang F. MicroRNA-based biomarkers for diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Thorac Cancer. 2020; 11(3): 762-768. doi:10.1111/1759-7714.13337
- 35Baburaj G, Damerla RR, Udupa KS, et al. Liquid biopsy approaches for pleural effusion in lung cancer patients. Mol Biol Rep. 2020; 47(10): 8179-8187. doi:10.1007/s11033-020-05869-7
- 36Wu S-G, Gow CH, Yu CJ, et al. Frequent epidermal growth factor receptor gene mutations in malignant pleural effusion of lung adenocarcinoma. Eur Respir J. 2008; 32(4): 924-930. doi:10.1183/09031936.00167407
- 37Morgensztern D, Waqar S, Subramanian J, Trinkaus K, Govindan R. prognostic impact of malignant pleural effusion at presentation in patients with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 2012; 7(10): 1485-1489. doi:10.1097/JTO.0b013e318267223a
- 38Shin S, Kim J, Kim Y, Cho SM, Lee KA. Assessment of real-time PCR method for detection of EGFR mutation using both supernatant and cell pellet of malignant pleural effusion samples from non-small-cell lung cancer patients. Clin Chem Lab Med. 2017; 55(12): 1962-1969. doi:10.1515/cclm-2016-0851
- 39Tong L, Ding N, Tong X, et al. Tumor-derived DNA from pleural effusion supernatant as a promising alternative to tumor tissue in genomic profiling of advanced lung cancer. Theranostics. 2019; 9(19): 5532-5541. doi:10.7150/thno.34070
- 40Kimura H, Fujiwara Y, Sone T, et al. EGFR mutation status in tumour-derived DNA from pleural effusion fluid is a practical basis for predicting the response to gefitinib. Br J Cancer. 2006; 95(10): 1390-1395. doi:10.1038/sj.bjc.6603428
- 41Kawahara A, Fukumitsu C, Taira T, et al. Epidermal growth factor receptor mutation status in cell-free DNA supernatant of bronchial washings and brushings. Cancer Cytopathol. 2015; 123(10): 620-628. doi:10.1002/cncy.21583
- 42Lee JS, Hur JY, Kim IA, et al. Liquid biopsy using the supernatant of a pleural effusion for EGFR genotyping in pulmonary adenocarcinoma patients: A comparison between cell-free DNA and extracellular vesicle-derived DNA. BMC Cancer. 2018; 18(1):1236. doi:10.1186/s12885-018-5138-3
- 43Hummelink K, Muller M, Linders TC, et al. Cell-free DNA in the supernatant of pleural effusion can be used to detect driver and resistance mutations, and can guide tyrosine kinase inhibitor treatment decisions. ERJ Open Res. 2019; 5(1):00016–2019. doi:10.1183/23120541.00016-2019
- 44Villatoro S, Mayo-de-Las-Casas C, Jordana-Ariza N, et al. Prospective detection of mutations in cerebrospinal fluid, pleural effusion, and ascites of advanced cancer patients to guide treatment decisions. Mol Oncol. 2019; 13(12): 2633-2645. doi:10.1002/1878-0261.12574
- 45Darooei R, Sanadgol G, Gh-Nataj A, et al. Discriminating tuberculous pleural effusion from malignant pleural effusion based on routine pleural fluid biomarkers, using mathematical methods. Tanaffos. 2017; 16(2): 157-165.
- 46Kim Y, Shin S, Lee KA. Exosome-based detection of EGFR T790M in plasma and pleural fluid of prospectively enrolled non-small cell lung cancer patients after first-line tyrosine kinase inhibitor therapy. Cancer Cell Int. 2021; 21(1):50. doi:10.1186/s12935-021-01761-x
- 47Tsakonas G, Tadigotla V, Chakrabortty SK, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid as a liquid biopsy for molecular characterization of brain metastasis in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. Lung Cancer. 2023; 182: 107292. doi:10.1016/j.lungcan.2023.107292
- 48Incorvaia L, Russo A, Cinieri S. The molecular tumor board: a tool for the governance of precision oncology in the real world. Tumori. 2022; 108(4): 288-290. doi:10.1177/03008916211062266
- 49Gristina V, Pisapia P, Barraco N, et al. The significance of tissue-agnostic biomarkers in solid tumors: the more the merrier? Expert Rev Mol Diagn. 2023; 23(10): 851-861. doi:10.1080/14737159.2023.2245752
- 50Galvano A, Castiglia M, Rizzo S, et al. Moving the target on the optimal adjuvant strategy for resected pancreatic cancers: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Cancers (Basel). 2020; 12(3):534. doi:10.3390/cancers12030534
- 51Pisapia P, Costa JL, Pepe F, et al. Next generation sequencing for liquid biopsy based testing in non-small cell lung cancer in 2021. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2021; 161: 103311. doi:10.1016/j.critrevonc.2021.103311
- 52Galvano A, Castellana L, Gristina V, et al. The diagnostic accuracy of PIK3CA mutations by circulating tumor DNA in breast cancer: an individual patient data meta-analysis. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 2022; 14:17588359221110162. doi:10.1177/17588359221110162