Chinese Medical Association
Rheumatology & Autoimmunity journal publishes work spanning basic, clinical and translational medical advancements across the full spectrum of rheumatology and autoimmunity.
Journal Metrics
- 1.5CiteScore
- 1.3Journal Impact Factor
- 27%Acceptance rate
- 34 days Submission to first decision
You can enjoy the benefits of open access at no cost to you; our article publication charges are currently waived. And now we are indexed in multiple databases, such as ESCI, Scopus and DOAJ. Your work will be even more discoverable!
Featured Information
Articles
Systemic lupus erythematosus caused acquired hemophilia B without evidence of factor IX inhibitors
- 16 July 2025
Efficacy and safety of anifrolumab across organ domains of systemic lupus erythematosus: A systematic review and meta‐analysis
- 6 July 2025
Graphical Abstract
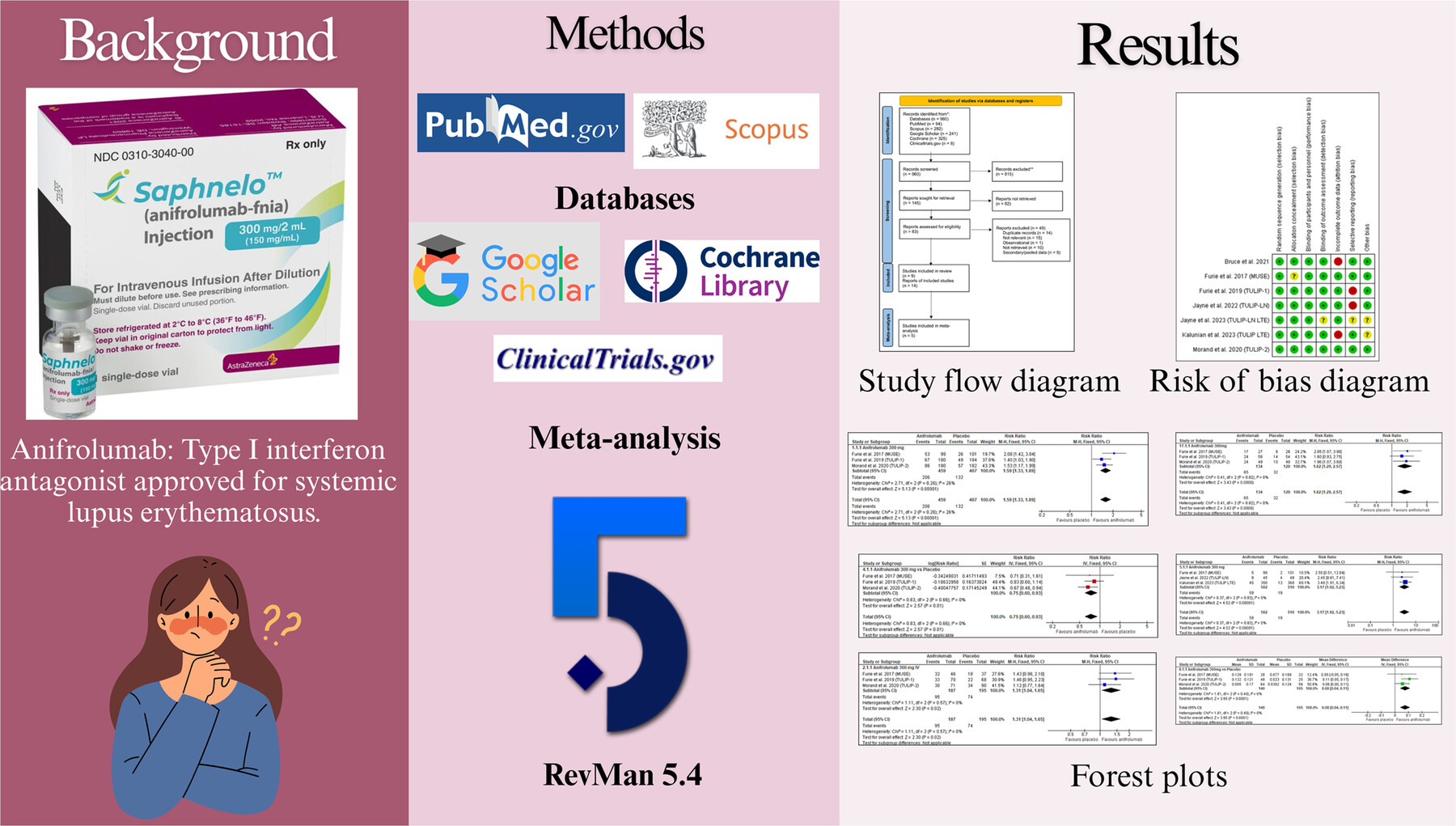
A systematic review and meta-analysis were conducted to review all clinical trial results of anifrolumab for treating systemic lupus erythematosus. Fourteen studies were included comprising 1322 patients and five studies were meta-analyzed. It was found that anifrolumab 300 mg IV led to clinical improvement across composite lupus scores, cutaneous disease, joint disease, and reduced flare rates. However, herpes zoster rates were increased. Early clinical trials on renal patients did not meet the primary endpoint but anifrolumab is under further investigation in lupus nephritis.
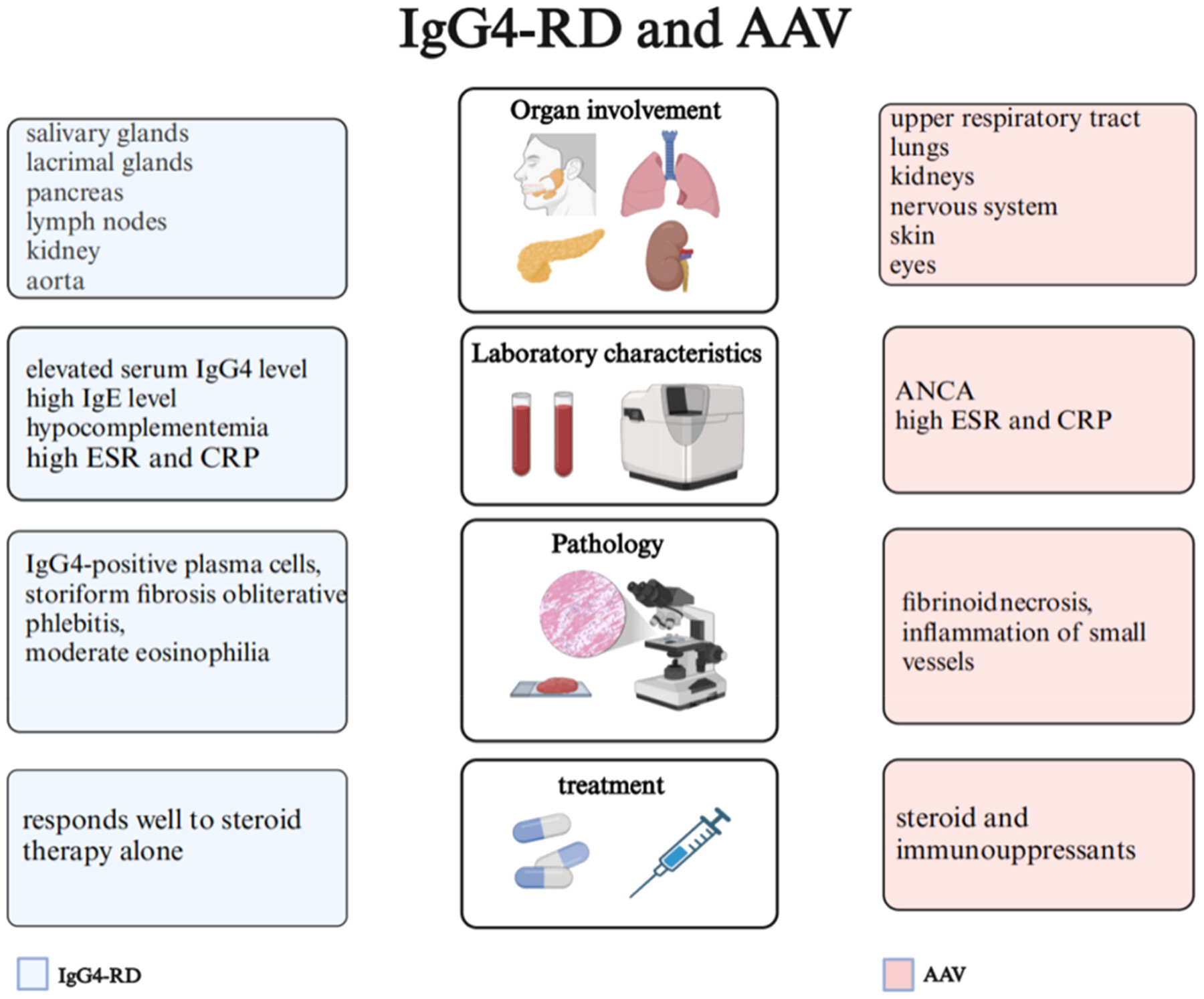
Clinical perspectives and comparisons between immunoglobulin G4‐related disease and antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody‐associated vasculitis
- 1 July 2025
Assessing gout risk associated with GLP‐1 therapy in obese patients with type 2 diabetes: A retrospective cohort study
- 1 July 2025
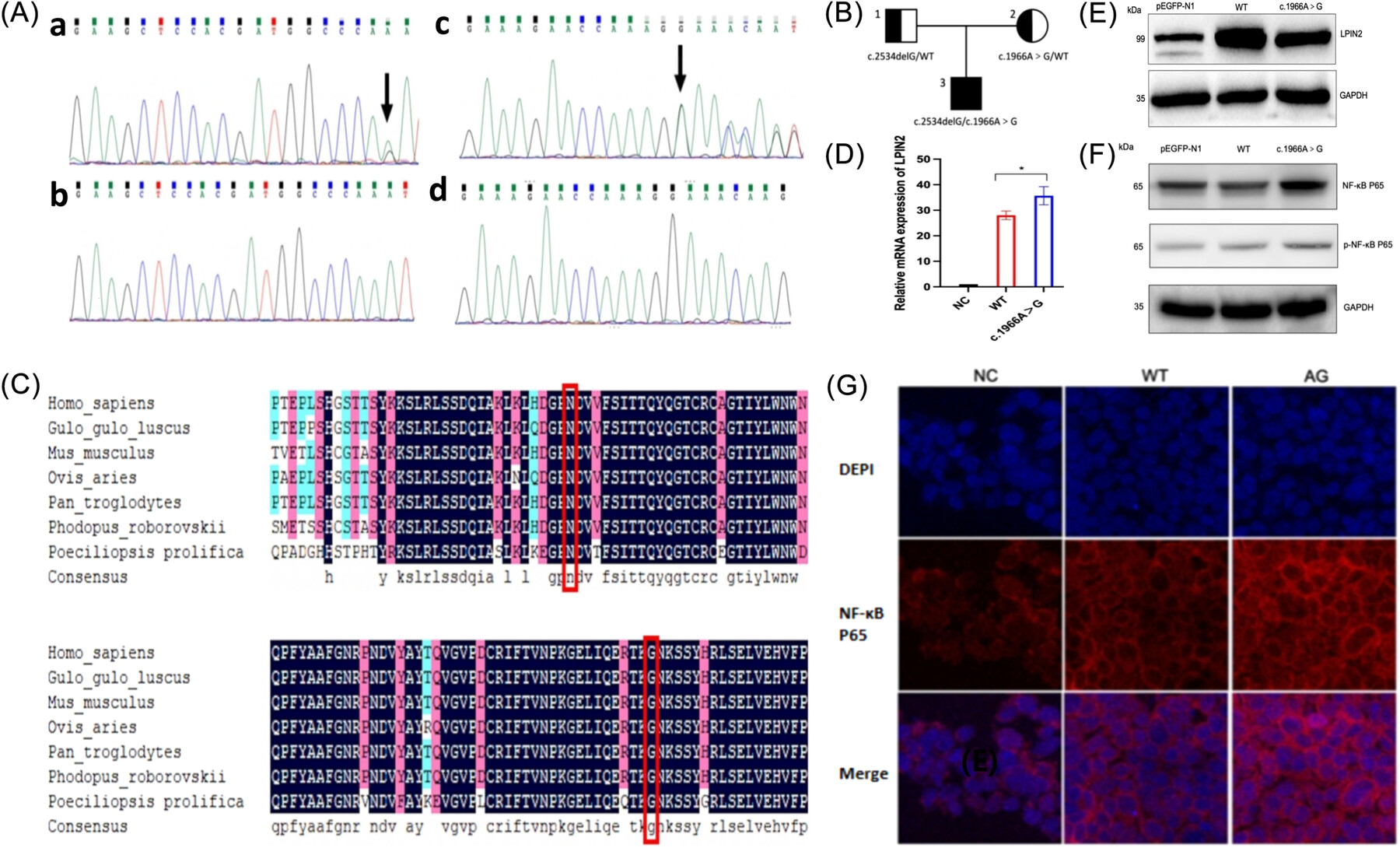
Novel LPIN2 mutations in Majeed syndrome induce NF-κB pathway activation
- 13 June 2025
Mitochondrial dynamics in autoimmune diseases
- 29 May 2025
Graphical Abstract
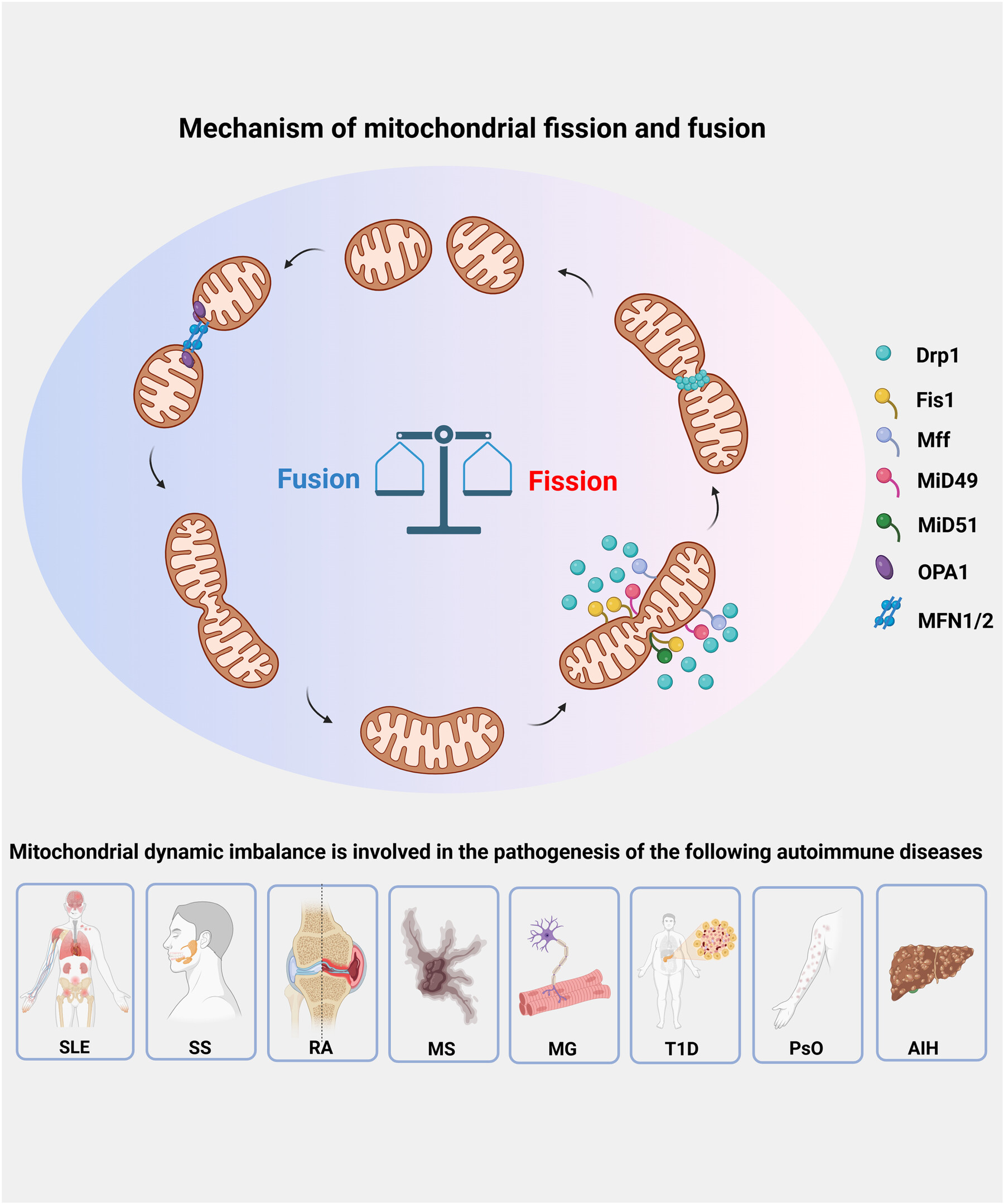
Roles of mitochondrial dynamic imbalance in autoimmune diseases. The imbalance of mitochondrial fusion and fission is involved in the occurrence and development of autoimmune diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjogren's syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, multiple sclerosis, myasthenia gravis, type 1 diabetes, psoriasis, and autoimmune hepatitis.
Predictors of systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease progression: A retrospective study
- 20 May 2025
Graphical Abstract
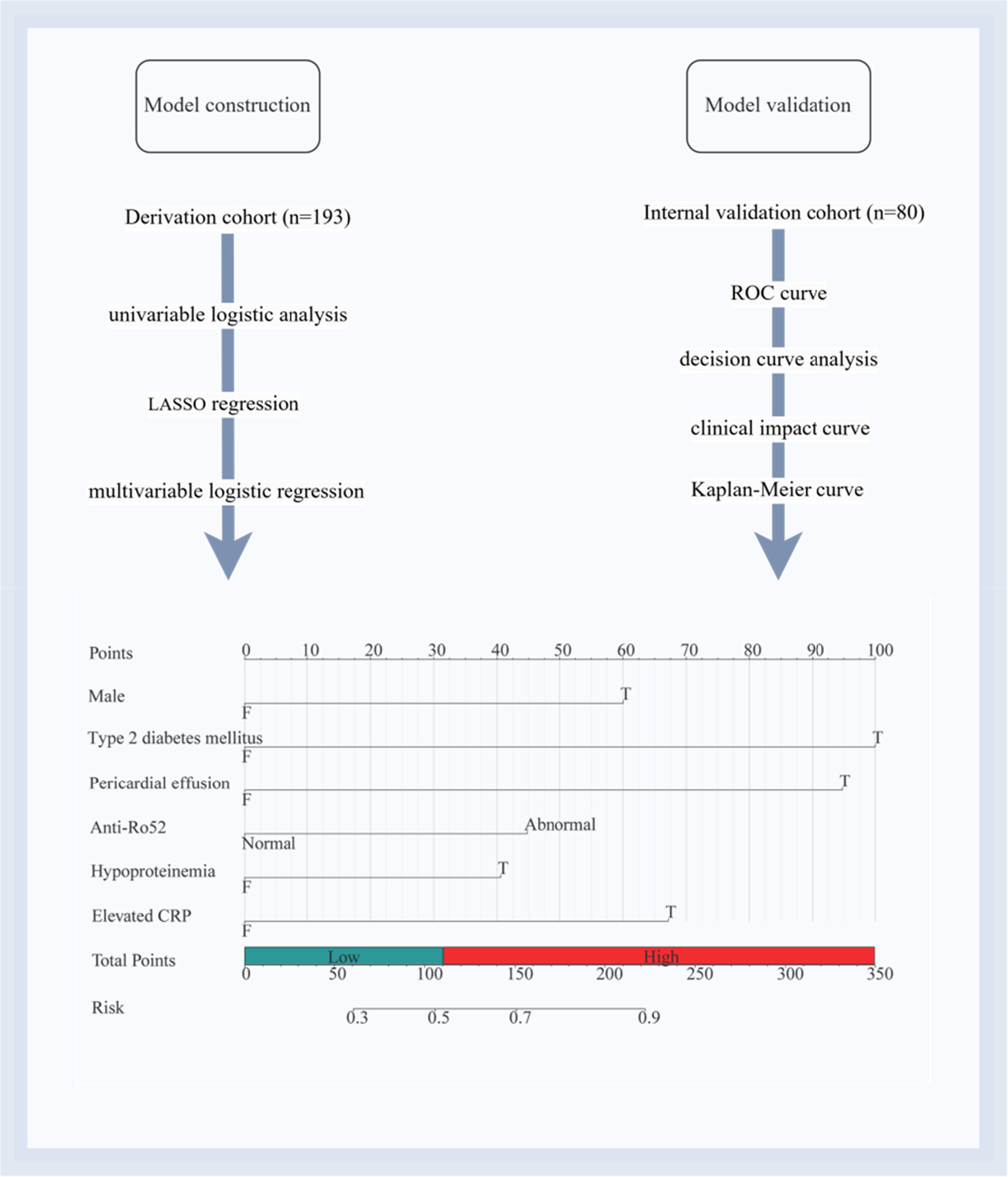
The final systemic sclerosis patients with interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) progression prediction model was composed of 6 significant risk factors: male, type 2 diabetes mellitus, pericardial effusion, anti-Ro52, hypoproteinemia, and elevated C-reactive protein. Our model demonstrated excellent prognostic utility.
Association of OAS1 rs1051042 polymorphism with genetic susceptibility and clinical phenotypes to systemic lupus erythematosus in a Chinese population
- 15 May 2025
Graphical Abstract
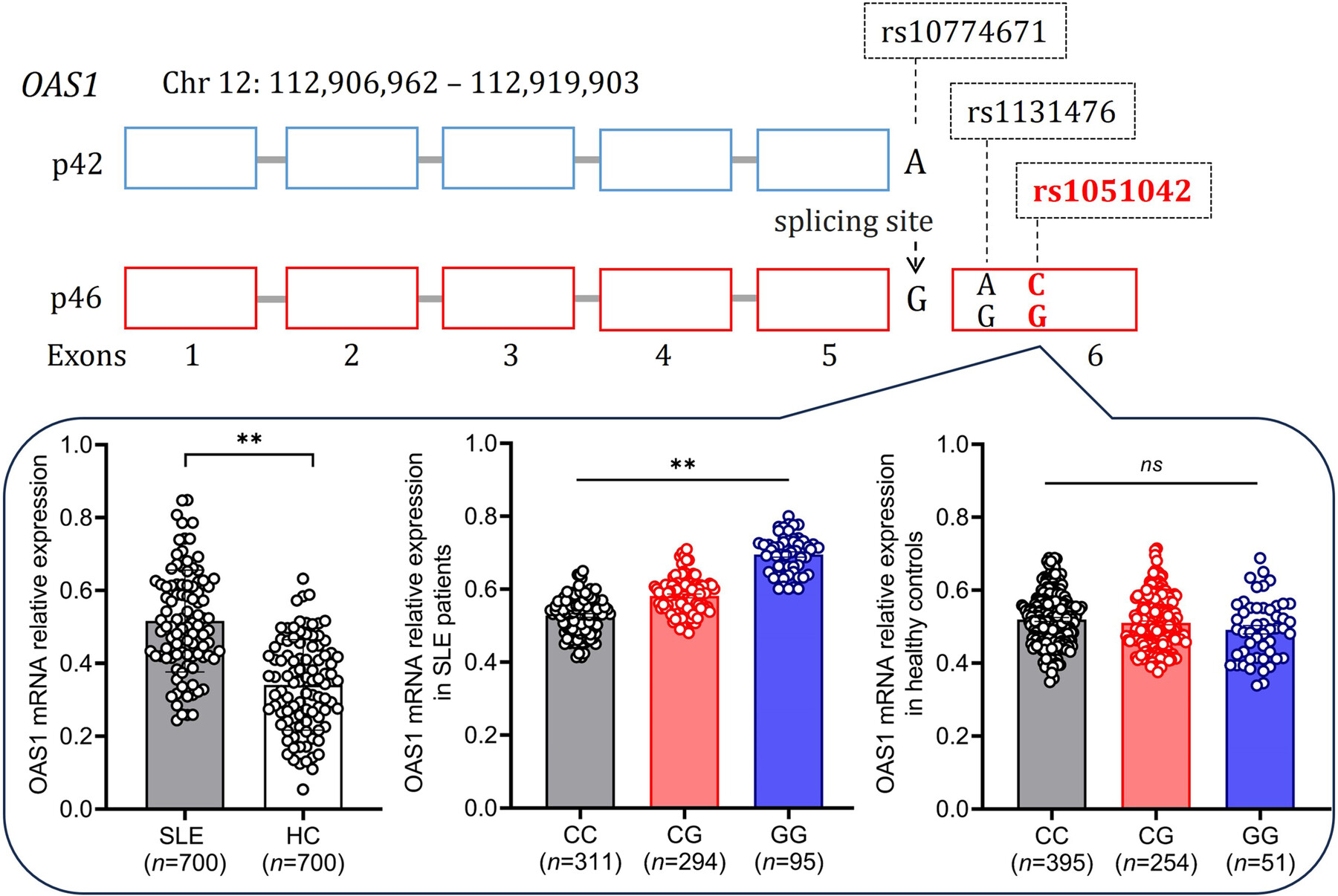
OAS1 is an interferon-induced gene that has been reported to be associated with the susceptibility of some infectious diseases, but there is little data on OAS1 single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) associated with Systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). In this study, we evaluated the association of OAS1 rs1051042 polymorphism with the genetic susceptibility and clinical phenotypes of SLE. Our results revealed patients with CG and GG genotypes were more susceptible to SLE. The genotype CG, GG, and allele G were associated with increased genetic susceptibility of SLE. OAS1 rs1051042 polymorphism was associated with clinical manifestations of SLE including malar rash, lupus nephritis, and anti-dsDNA antibodies. The expression levels of OAS1 were more significantly increased in genotype GG than in genotype CC and CG. Our results indicate polymorphism of OAS1 rs1051042 was associated with the genetic susceptibility and specific clinical phenotypes of SLE in the Chinese population.
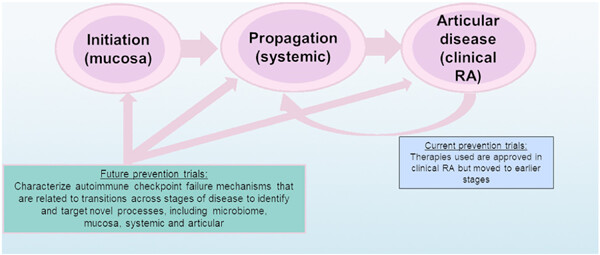
Mechanism‐driven strategies for prevention of rheumatoid arthritis
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 109-119
- 15 June 2022
Graphical Abstract
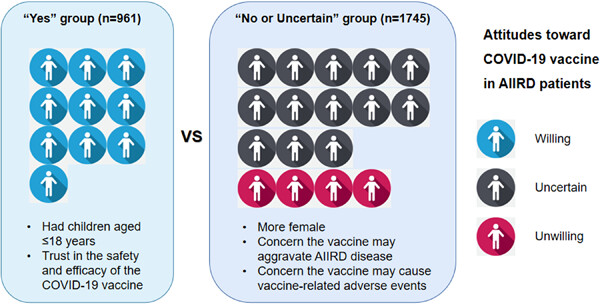
The COVID‐19 vaccine: Attitudes and vaccination in patients with autoimmune inflammatory rheumatic diseases
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 82-91
- 15 February 2022
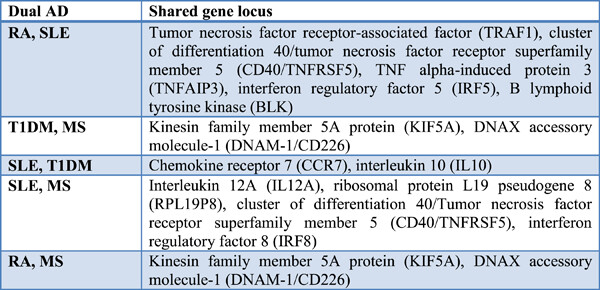
Dual autoimmune diseases: Rheumatoid arthritis with systemic lupus erythematosus and Type 1 diabetes mellitus with multiple sclerosis
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 120-128
- 20 April 2022
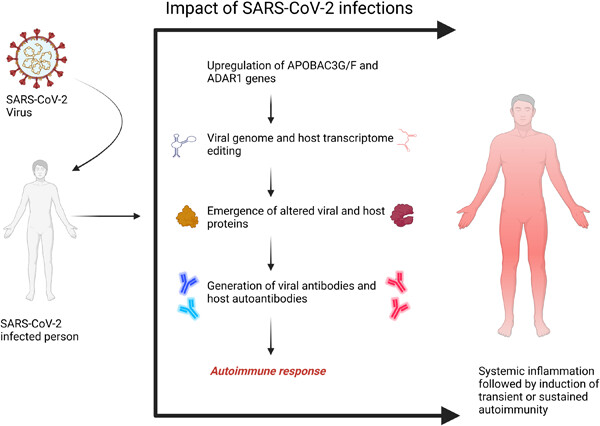
Molecular insights into onset of autoimmunity in SARS‐CoV‐2 infected patients
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 198-202
- 27 October 2022
Inflammasomes and their roles in autoimmune diseases
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 197-217
- 15 December 2024
Graphical Abstract
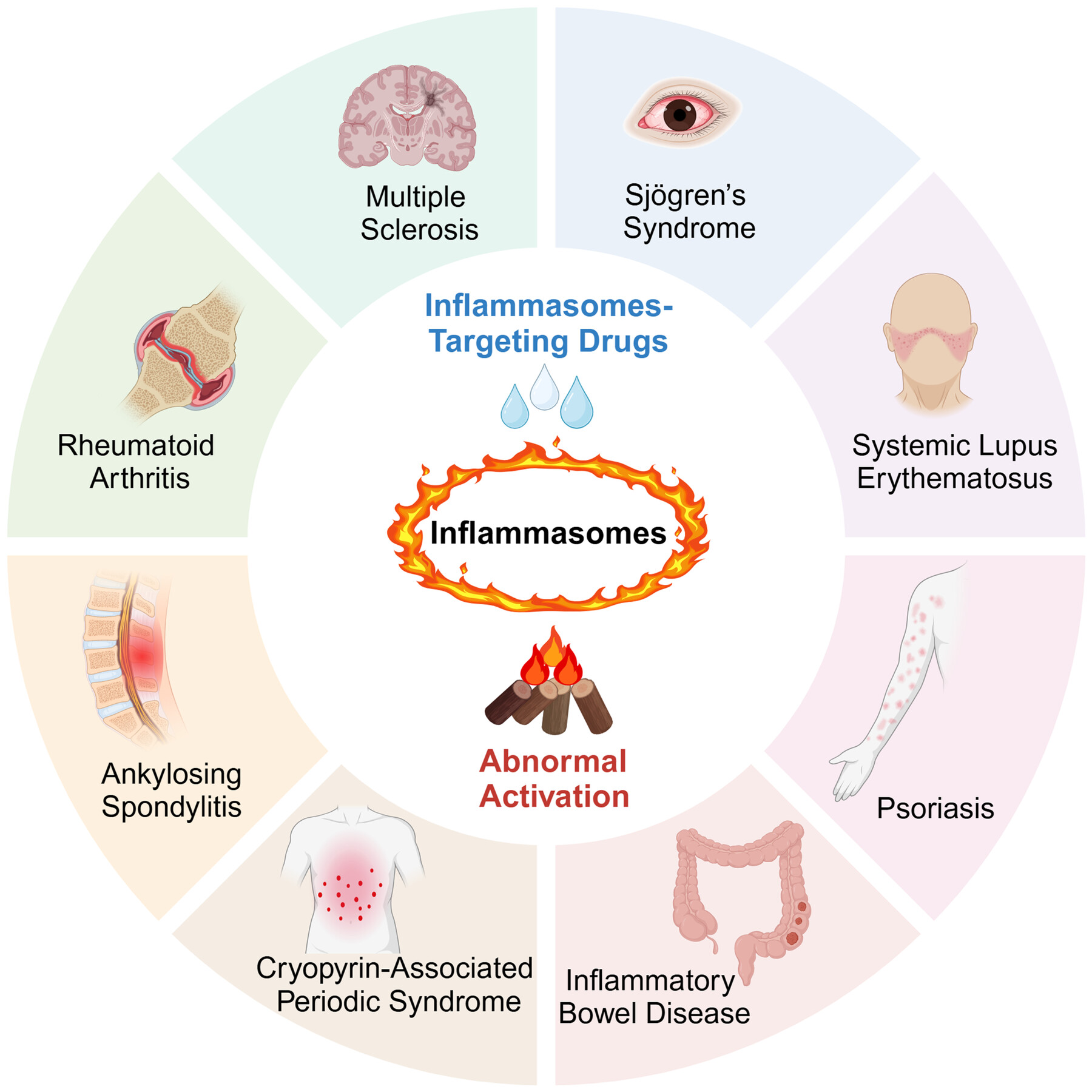
This review offers an introduction to the immunological functions of inflammasomes and elucidates their pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, inflammatory bowel disease, cryopyrin-associated periodic syndrome, psoriasis, Sjögren's syndrome, and ankylosing spondylitis. Additionally, this review highlights the importance of developing drugs targeting inflammasomes as promising therapeutic avenues.
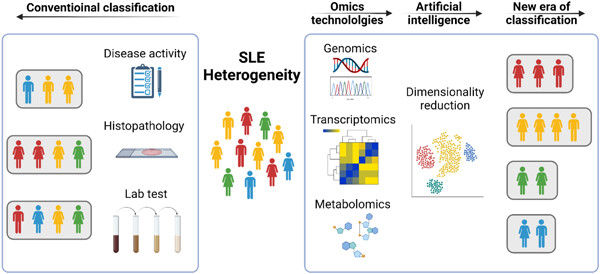
Understand SLE heterogeneity in the era of omics, big data, and artificial intelligence
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 40-51
- 11 October 2021
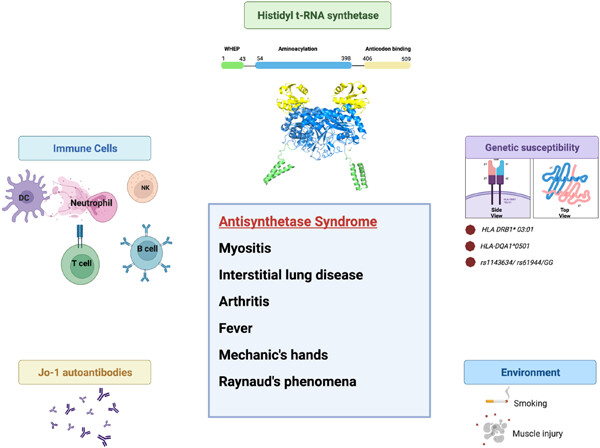
Anti‐Jo1 autoantibodies, from clinic to the bench
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 57-68
- 31 March 2022
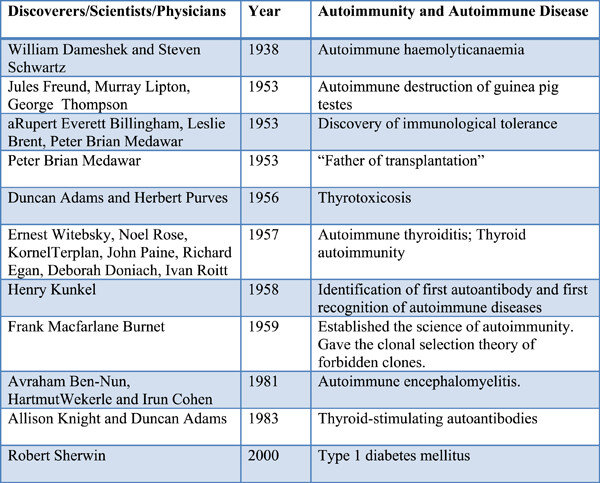
Origins and history of autoimmunity—A brief review
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 9-14
- 21 September 2022
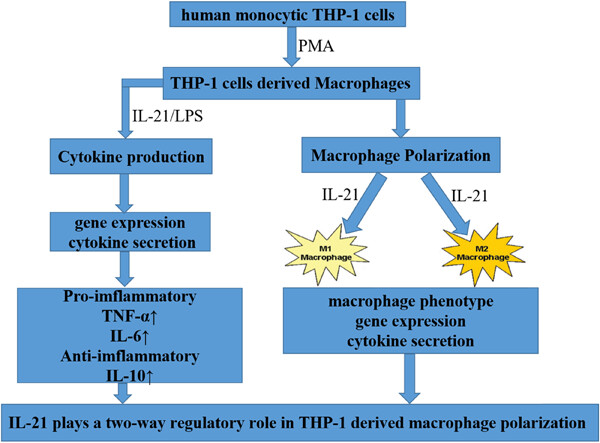
IL‐21 regulates macrophage activation in human monocytic THP‐1‐derived macrophages
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 18-29
- 11 August 2021
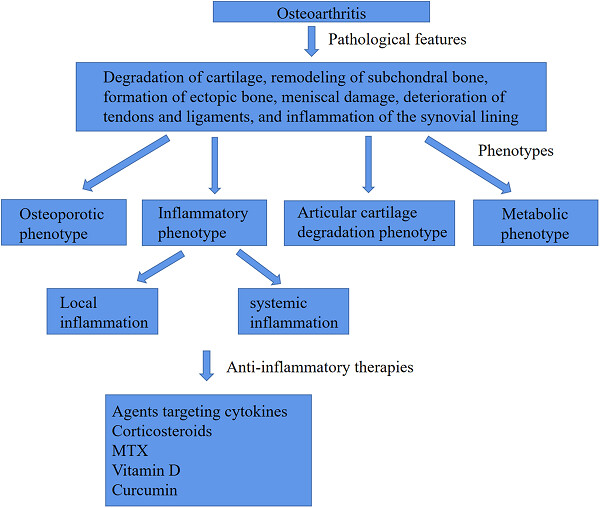
Inflammatory phenotype of osteoarthritis and its potential therapies
- Rheumatology & Autoimmunity
- 92-100
- 20 December 2021