Journal list menu
Export Citations
Download PDFs
ISSUE INFORMATION
REVIEW
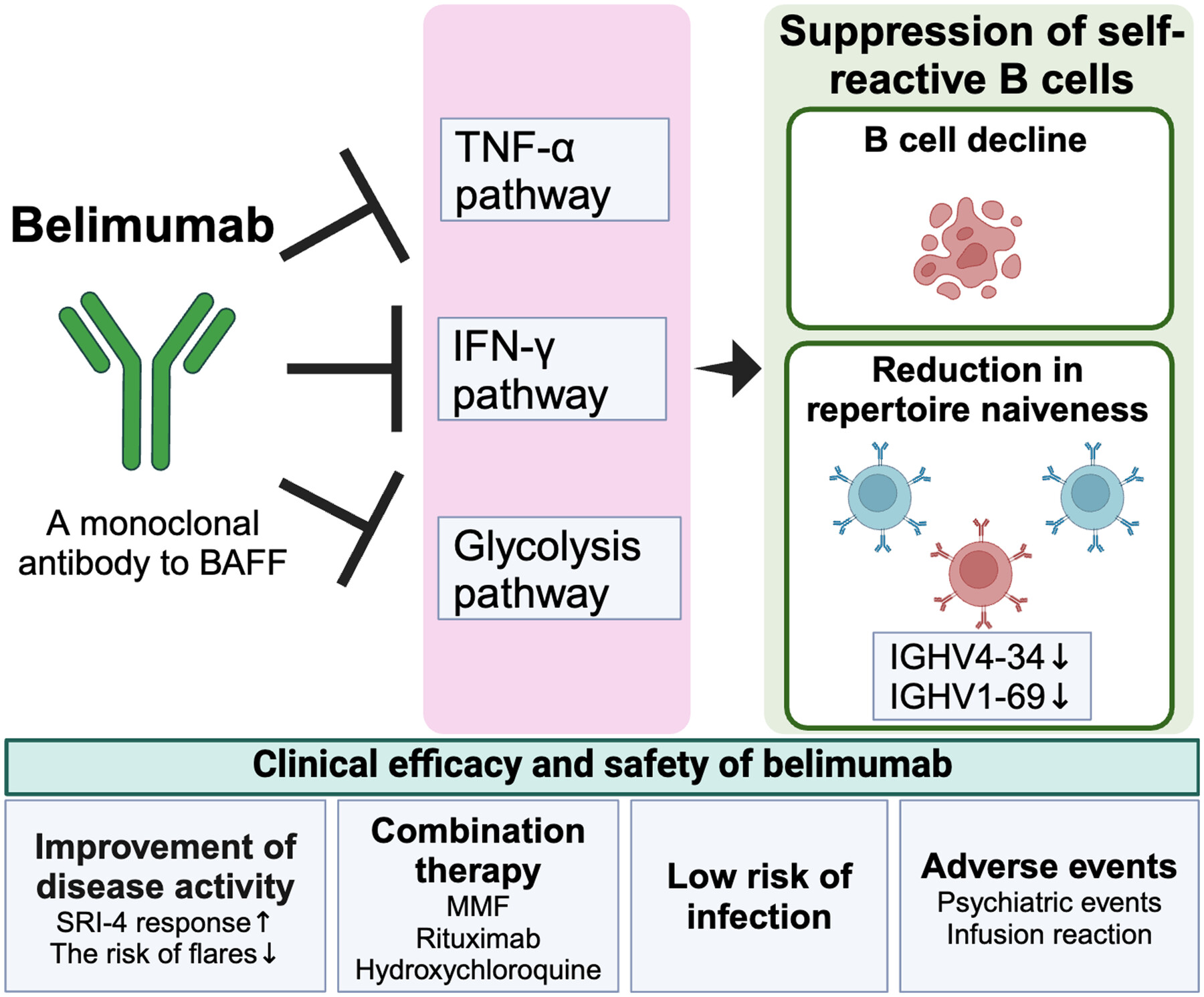
Treatment strategy for systemic lupus erythematosus using belimumab as indicated by multi-omics analysis
- Pages: 81-87
- First Published: 12 March 2025
Artificial intelligence in rheumatoid arthritis
- Pages: 88-100
- First Published: 27 February 2025
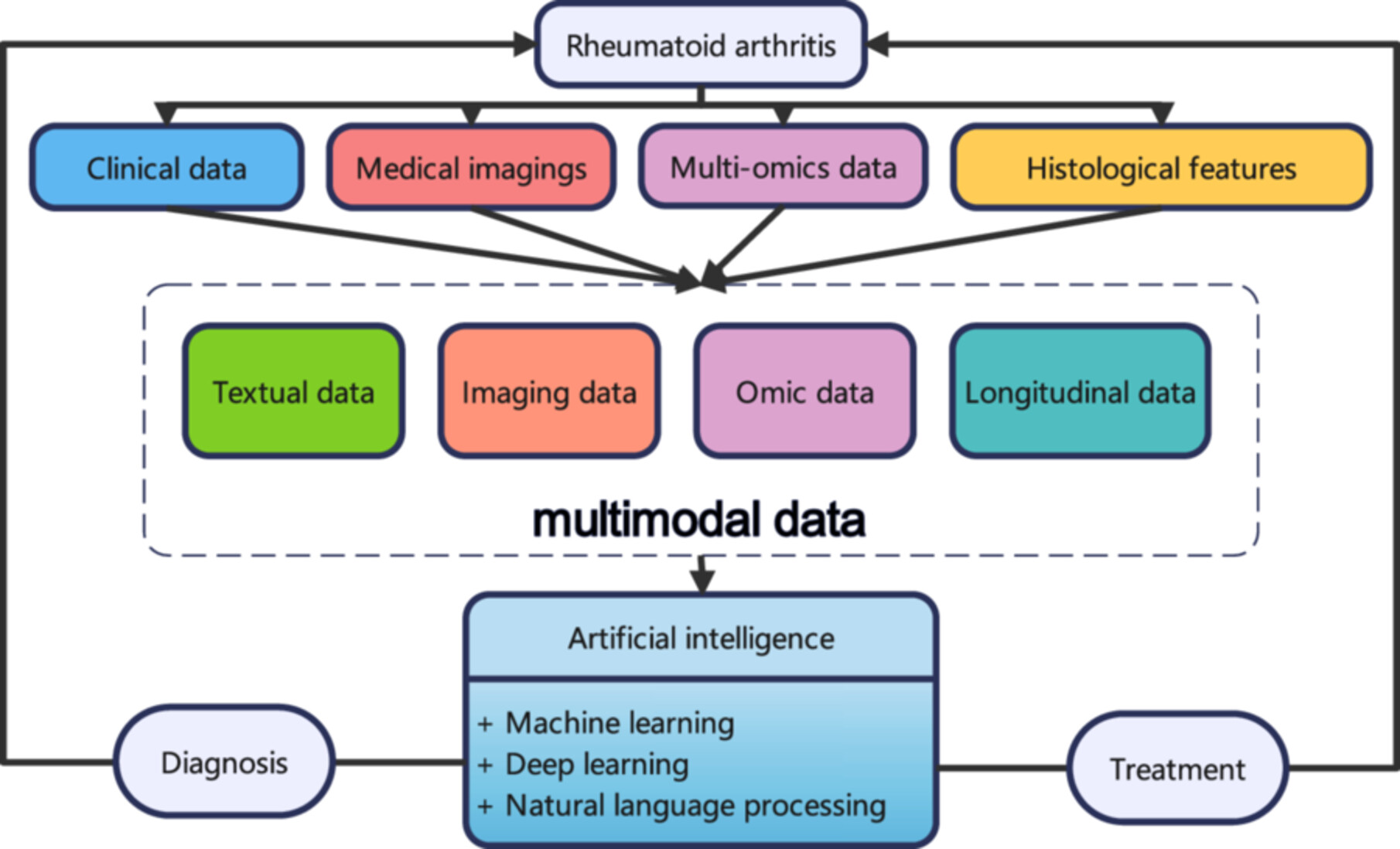
Advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) over the past 5 years have brought significant progress to the medical field, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA). AI integrates multimodal data, including clinical, imaging, omics, and longitudinal information, to enhance RA diagnosis and treatment. By leveraging techniques such as machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing, AI facilitates precise diagnostics and personalized therapeutic strategies, driving innovations in RA management.
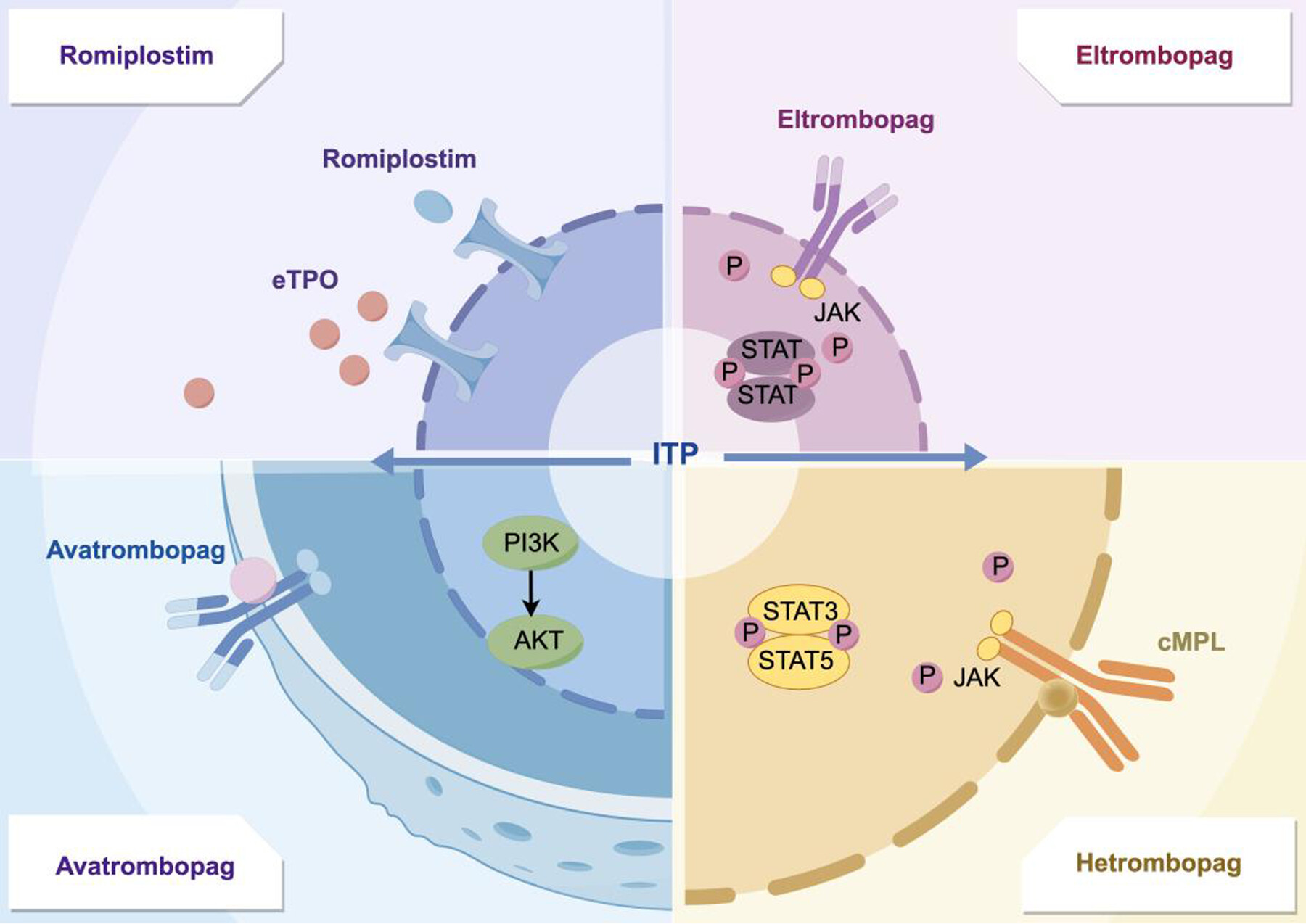
Hetrombopag: A promising thrombopoietin receptor agonist for the treatment of primary and secondary immune thrombocytopenia
- Pages: 101-115
- First Published: 27 February 2025
VIEWPOINT
NETosis: A bridge between cancer and autoimmunity
- Pages: 116-118
- First Published: 17 February 2025
META ANALYSIS
Effect of statins on psoriasis severity: A meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials
- Pages: 119-129
- First Published: 27 February 2025

This meta-analysis evaluated the impact of statins on psoriasis severity, analyzing data from 10 studies and meta-analyzing only eight studies (638 observations). While statins, especially topical forms, showed some efficacy in reducing Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores (standardized mean difference [SMD]: −0.82, 95% confidence intervals [CI]: −1.47 to −0.16), the overall effect was not statistically significant (SMD: −0.36, 95% CI: −0.72 to 0.00). No significant improvements were observed in quality of life (Dermatology Life Quality Index: SMD: 0.24, 95% CI: −0.09 to 0.57) or inflammation (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein: SMD: −0.12, 95% CI: −0.42 to 0.18). These findings suggest limited benefits of systemic statins for psoriasis severity.
ORIGINAL ARTICLE
Immune cell alterations in a pristane-induced lupus model in C57BL/6J mice
- Pages: 130-139
- First Published: 21 January 2025
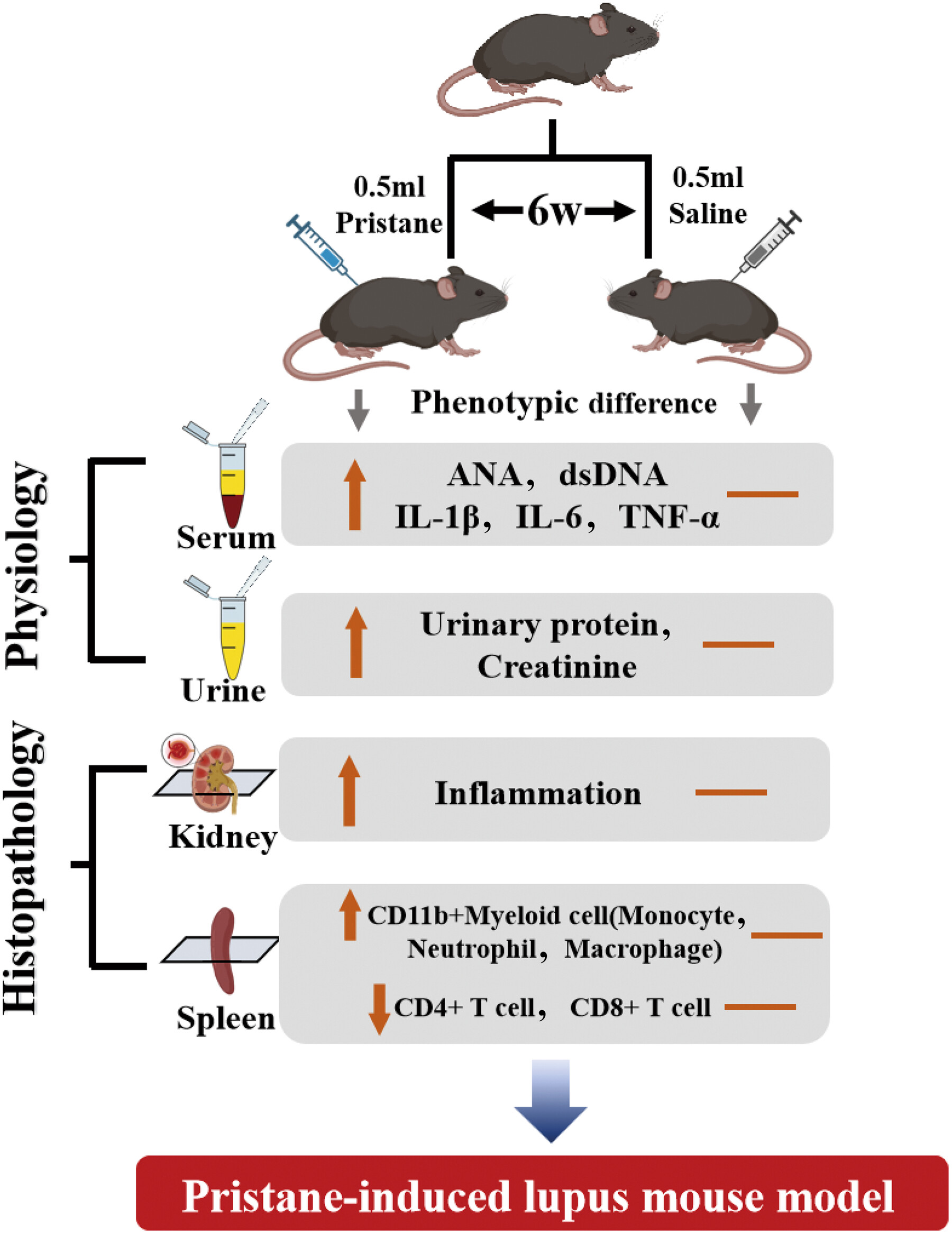
A pristane-induced systemic lupus erythematosus model was established in C57BL/6J mice. Mice were randomly assigned to a pristane group (0.5 mL pristane intraperitoneally) or a control group (0.5 mL saline intraperitoneally). Six months later, levels of antinuclear antibodies, serum inflammatory cytokines, urinary protein, renal injury, and immune cell changes were assessed.
Human CD141+ dendritic cells: A unique tolerogenic subset inducing immune tolerance in systemic lupus erythematosus patients
- Pages: 140-146
- First Published: 27 February 2025
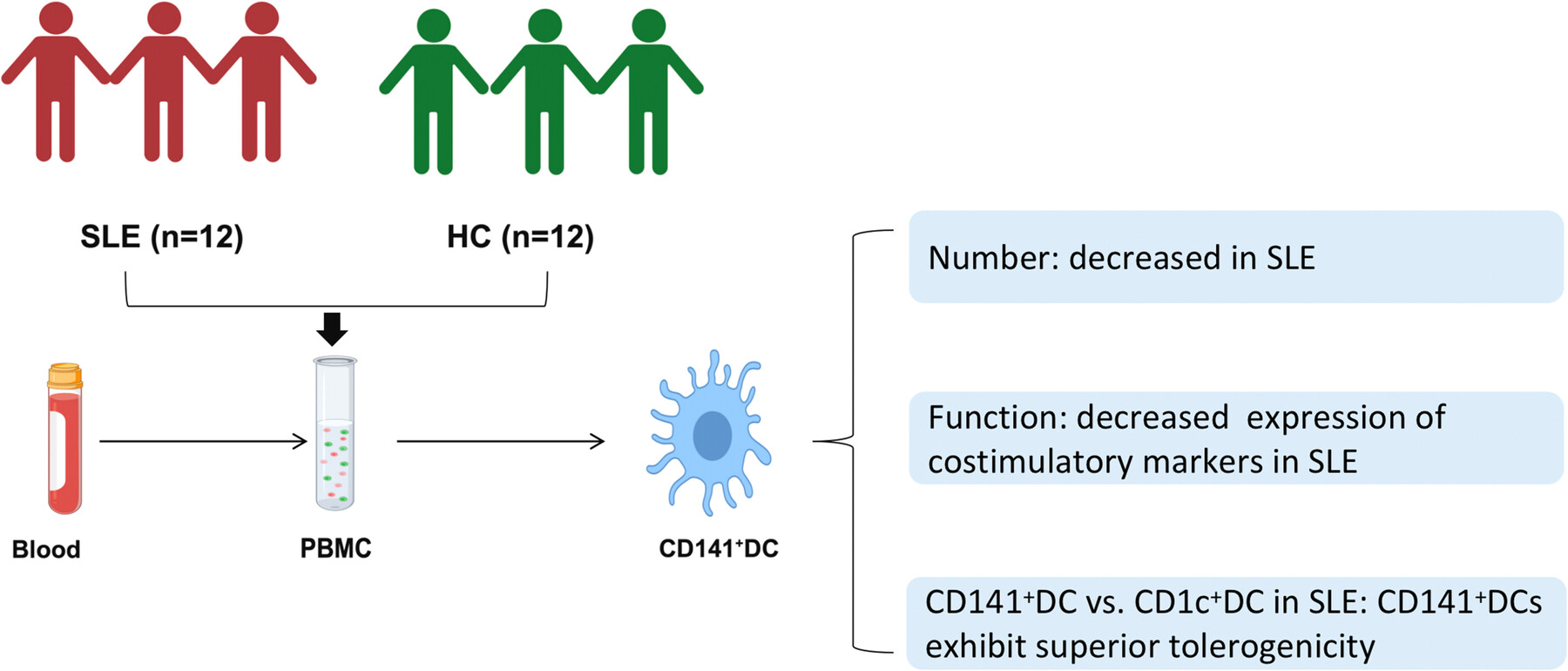
Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from 12 systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) patients and 12 healthy controls. The number and function of peripheral blood CD141+ dendritic cells (DCs) were compared between patients and controls. Moreover, the tolerogenic properties of CD141+ and CD1c+ DCs were compared in SLE patients.
BRIEF REPORT
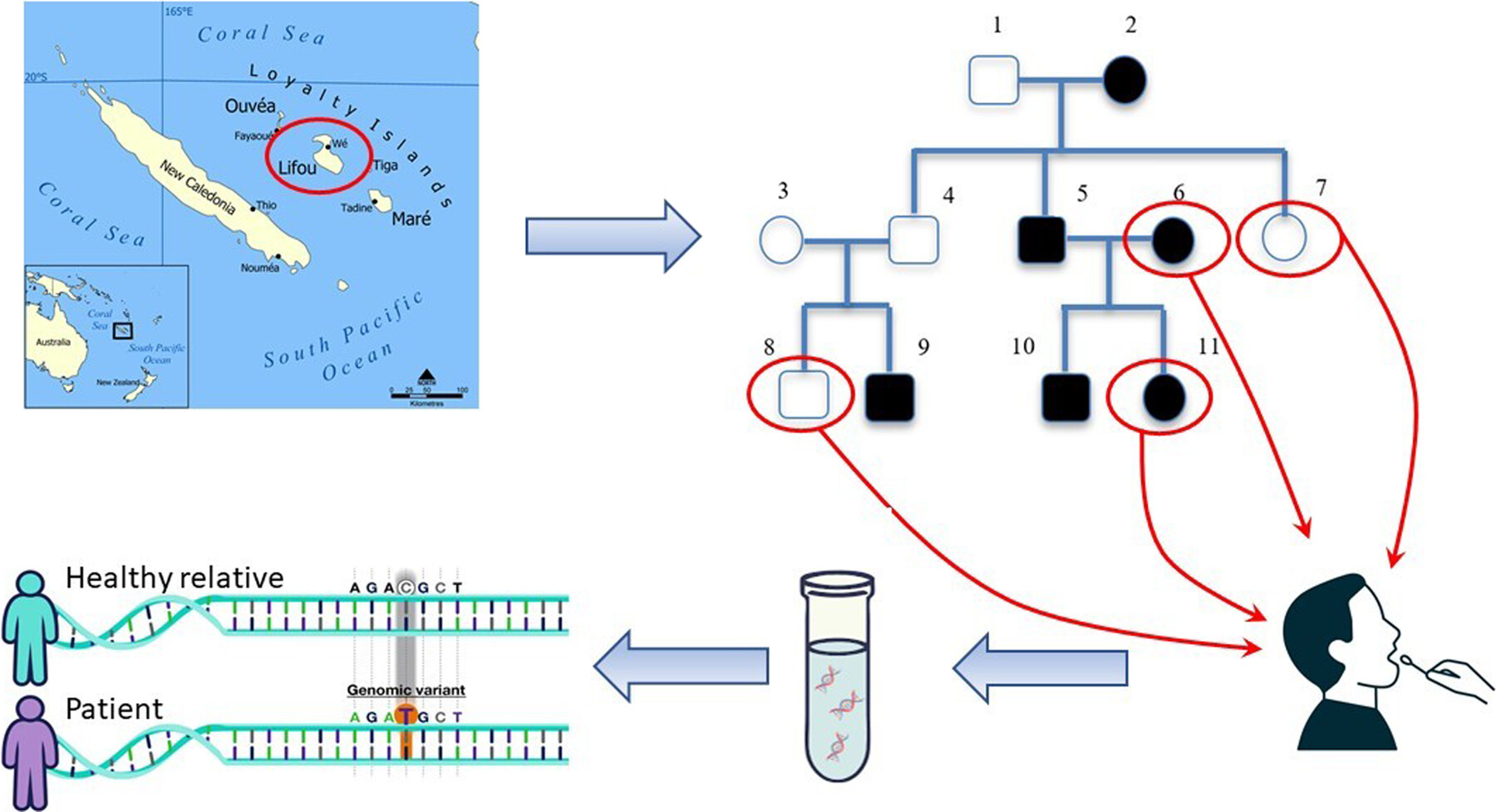
Whole-exome sequencing in families from Lifou Island (New Caledonia) reveals candidate variants involved in gout pathogenesis
- Pages: 147-151
- First Published: 10 April 2025
LETTER TO THE EDITOR
Successful treatment with upadacitinib for Sjögren's syndrome complicated by atopic dermatitis
- Pages: 152-154
- First Published: 03 December 2024
Misleading ulcers: A rare case of lymphomatoid papulosis initially diagnosed as acquired reactive perforating collagenosis
- Pages: 155-156
- First Published: 27 February 2025
Assessment of factors influencing outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Omicron subvariants BA.5.2/BF.7 infection in rheumatoid arthritis patients
- Pages: 157-159
- First Published: 10 April 2025